Windows Event Log is a built-in feature of the Microsoft Windows operating system that records and stores various system, security, and application events that occur on a computer.
These events can include errors, warnings, and information messages. Using this event log, administrators can troubleshoot problems, monitor system health, and track user activity.
The Windows Event Log is organized into three main categories:
System, Application, and Security.
The Application log contains events related to applications and services, whereas the System log includes events associated with system components and drivers. Logon sessions, unsuccessful login attempts, and other security-related incidents are documented in the Security log.
This windows event log entries include detailed information such as the date and time the event occurred, the source of the event, and any relevant error codes.
Windows Event Log Importance
The role of event log monitoring is crucial for system and network engineers because it enables them to stay informed about any problems, illegal activity, network breakdowns, and other key issues that might be arising inside a computer.
It provides complete details about each event, including its origin, username, sensitivity level, and other information. This information can be very helpful in identifying and resolving structural failures, as well as in forecasting upcoming challenges based on data patterns.
Network administrators can effectively discover and handle issues before they become serious by keeping an eye on event logs. This might possibly save a lot of time and effort when investigating and fixing the issue. This can help to guarantee that systems continue to be safe, dependable, and performing at their best.
How to Access Windows Event Log?
#1. Using GUI
Step 1 – Open the Start menu and search for “Event Viewer”.
Step 2 – Click on the Event Viewer application to open it.
Step 3 – In the leftmost panel, you will see a list of event logs. Choose the Windows Logs option and then click the desired log to view.
Step 4 – In the middle panel, you can see a list of events for the selected log. You can use the filter options at the right-hand side of the screen to narrow down the events you are interested in.
Step 5 – To view the details of an event, double-click on it. This will open the Event Properties dialog box, which contains detailed information about the event ID, source, severity level, date and time, user name, computer name, and description.
Step 6 – You can use the menu options and toolbar at the top of the screen to perform various actions such as saving and clearing logs, creating custom views, and filtering events.
#2. Using Command Prompt
You can access the Windows Event Log using the Command Prompt or PowerShell by using the “wevtutil” command. Here are some examples.
- To display all events in the System log
wevtutil qe System- To display the events in the Application log
wevtutil qe ApplicationThe output may look like this.
- To display all events in the Security log
wevtutil qe Security- To display events from a specific source in the System log.
wevtutil qe System /f:text /c:1 /rd:true /q:"*[System[Provider[@Name='source_name']]]" Here you need to replace “source_name” with the name of the event source you want to view.
- To export events from a log to a file
wevtutil epl System C:\Logs\SystemLog.evtx
Replace “System” with the name of the log you want to export, and “C:\Logs\SystemLog.evtx” with the path and filename where you want to save the exported log.
#3. Using Run
You can also access the Windows Event Log using the Run dialog box in Windows. Here’s how:
Step 1 – Press the “Windows key + R” on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
Step 2 – Type “eventvwr.msc” in the Run dialog box and press Enter.
Step 3 – The Event Viewer utility will open and display the main console window.
Step 4 – In the left-hand side console window, you can expand the “Windows Logs” folder to see the System, Application, Security, Setup, and other logs.
Step 5 – Click on the log you want to view its contents in the right panel. You can filter and sort the events as well as create custom views & save them for future use.
When to use these Event Logs?
Generally, You can use the Windows Event Log whenever you need to monitor, troubleshoot, or audit events on a Windows system. Here are some specific situations where you might use it.
Monitoring system health
The Windows Event Log can provide valuable information about system errors, warnings, and performance issues which allows you to proactively monitor and maintain the health of your system.
Troubleshooting problems
When you encounter a problem on a Windows system, the Event Log can provide an indication of the cause and help you diagnose the issue. By analyzing event logs, you can easily identify the root cause of a problem and take steps to resolve it.
Auditing and tracking user activity
The Security log in the Event Log can be used to track user logins, logoff, failed logon attempts, and other security-related events, which can help you identify potential security threats and take appropriate action.
Compliance reporting
Many regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR require organizations to maintain event logs and provide regular reports. The Windows Event Log can be used to meet these compliance requirements.
How to Read these Event Logs?
It can be a little difficult to read the Windows Event Log at first, but with enough practice and familiarity, it gets simpler to understand the data it provides. Here are some general steps to follow when reading the Windows Event Log.
#1. Open the Event log
The first step is to open the event log. You can access it by using any of the above-mentioned methods.
#2. Navigate to the appropriate log
There are several logs in the Event Viewer, including the Application, System, Security, and Setup logs. Each log contains different types of events. Select the log that contains the events you want to view.
#3. Filter event
You can filter events by severity level, event source, date range, and other criteria. This can help you narrow down the events you are interested in.
#4. View event details
Examine each event carefully to view its details, including the event ID, source, severity level, date & time, user name, computer name, and description. This information can help you identify the cause of the event and take appropriate action.
#5. Use event properties
Many events have additional properties that provide more information about the event.
For example, a security event might have properties such as logon type, logon process, and authentication package. These properties can help you understand the context of the event and its significance.
#5. Analyze patterns
Always try to look for patterns in the events to identify recurring issues or trends. For example, if you see a series of disk errors, it could indicate a problem with the disk hardware or configuration.
Windows Event Severity Levels
The Windows Event Log uses severity levels to categorize events based on their importance or impact on the system. There are five severity levels in the Windows Event Log, listed below from highest to lowest severity:
- Critical: This severity level is reserved for events that indicate a critical system or application failure that requires immediate attention. Examples include system crashes, major hardware failures, and critical application errors.
- Error: It is used for events that indicate a serious problem that requires attention but not necessarily immediate action. Some common examples are application crashes, network connectivity failures, and disk errors.
- Warning: It indicates a potential issue that system administrators should keep an eye on, including low disk space warnings and security policy violations.
- Verbose: It is used for events that provide detailed information about system or application activity, typically for troubleshooting or debugging purposes.
- Information: It shows that everything went smoothly. Almost all logs include information events.
These severity levels allow administrators & system analysts to quickly identify critical issues that require attention and prioritize their response accordingly.
Conclusion ✍️
I hope you found this article helpful in learning about the windows event log and its importance. You may also be interested in learning about the various ways to recover deleted data in Windows 11.
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать грубую лексику.
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать разговорную лексику.
В то же время журнал событий Windows регистрирует сообщение.
Записывает сообщение о состояние в журнал событий Windows.
Если между контрольными точками происходит ошибка, записывает сообщение об изменении состояния в журнал событий Windows.
Writes a status message to the Windows event log when an error occurs between milestones.
Определяет, какие ошибки ASP записываются в журнал событий Windows.
Если выполнение сценария не завершается в течение указанного промежутка времени, ASP останавливает сценарий и записывает событие в журнал событий Windows.
If the script does not finish running by the end of the timeout period, ASP stops the script and writes an event to the Windows event log.
Решение.Проверьте журнал событий Windows, чтобы определить причину неудачной попытки изменить пароль в системе UNIX.
Solution:Check the Windows event log to determine why the attempt to change the password on the UNIX system failed.
Сведения о папке, используемой Configuration Manager 2007 для занесения данных в журнал событий Windows.
Provides information about the folder used by Configuration Manager 2007 to report to the Windows Event Log. Status Message Tasks
Если балансировка сетевой нагрузки обнаружит несогласованное правило на узлах кластера, сообщение об этом будет записано в журнал событий Windows. Ознакомьтесь с журналом событий, чтобы определить проблемный узел и правило, которое вызывает ошибку.
If NLB detects an inconsistent rule among the hosts in the cluster, it records a message in the Windows event log. Consult the event log to determine the host in question and which rule is responsible for the issue.
Также можно использовать средство командной строки «Журнал событий Windows» для предоставления учетной записи доступа к отдельным журналам.
Alternatively, you can use the Windows Event Log command-line utility to grant an account access to individual logs.
Администраторы могут следить за работой приложения и состоянием антивирусной защиты при помощи подробных HTML-отчетов или просматривая журнал событий Windows.
The system administrator can control the operation of the application and the antivirus protection status using descriptive HTML reports or by viewing the Windows event log.
Чтобы проверить сведения об ошибках и предупреждениях, можно также просмотреть журнал событий Windows. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Установка балансировки сетевой нагрузки.
You can also view the Windows event logs to check for errors and warnings. For more information see Installing Network Load Balancing.
Результатов: 11. Точных совпадений: 11. Затраченное время: 30 мс
Содержание:
- 1 Где находится журнал событий Windows
- 2 Как открыть журнал
- 3 Как использовать содержимое журнала
- 4 Очистка, удаление и отключение журнала
Даже когда пользователь ПК не совершает никаких действий, операционная система продолжает считывать и записывать множество данных. Наиболее важные события отслеживаются и автоматически записываются в особый лог, который в Windows называется Журналом событий. Но для чего нужен такой мониторинг? Ни для кого не является секретом, что в работе операционной системы и установленных программ могут возникать сбои. Чтобы администраторы могли находить причины таких ошибок, система должна их регистрировать, что собственно она и делает.
Итак, основным предназначением Журнала событий в Windows 7/10 является сбор данных, которые могут пригодиться при устранении неисправностей в работе системы, программного обеспечения и оборудования. Впрочем, заносятся в него не только ошибки, но также и предупреждения, и вполне удачные операции, например, установка новой программы или подключение к сети.
Физически Журнал событий представляет собой набор файлов в формате EVTX, хранящихся в системной папке %SystemRoot%/System32/Winevt/Logs.
Хотя эти файлы содержат текстовые данные, открыть их Блокнотом или другим текстовым редактором не получится, поскольку они имеют бинарный формат. Тогда как посмотреть Журнал событий в Windows 7/10, спросите вы? Очень просто, для этого в системе предусмотрена специальная штатная утилита eventvwr.
Как открыть журнал
Запустить утилиту можно из классической Панели управления, перейдя по цепочке Администрирование – Просмотр событий или выполнив в окошке Run (Win+R) команду eventvwr.msc.
В левой колонке окна утилиты можно видеть отсортированные по разделам журналы, в средней отображается список событий выбранной категории, в правой – список доступных действий с выбранным журналом, внизу располагается панель подробных сведений о конкретной записи. Всего разделов четыре: настраиваемые события, журналы Windows, журналы приложений и служб, а также подписки.
Наибольший интерес представляет раздел «Журналы Windows», именно с ним чаще всего приходится работать, выясняя причины неполадок в работе системы и программ. Журнал системных событий включает три основных и две дополнительных категории. Основные это «Система», «Приложения» и «Безопасность», дополнительные – «Установка» и «Перенаправленные события».
Категория «Система» содержит события, сгенерированные системными компонентами – драйверами и модулями Windows.
Ветка «Приложения» включает записи, созданные различными программами. Эти данные могут пригодиться как системным администраторам и разработчикам программного обеспечения, так и обычным пользователям, желающим установить причину отказа той или иной программы.
Третья категория событий «Безопасность» содержит сведения, связанные с безопасностью системы. К ним относятся входы пользователей в аккаунты, управление учётными записями, изменение разрешений и прав доступа к файлам и папкам, запуск и остановка процессов и так далее.
Так как число событий может исчисляться тысячами и даже десятками тысяч, в eventvwr предусмотрена возможность поиска и фильтрации событий по свойствам – важности, времени, источнику, имени компьютера и пользователя, коду и так далее. Допустим, вы хотите получить список системных ошибок. Выберите слева Журналы Windows – Система, справа нажмите «Фильтр текущего журнала» и отметьте в открывшемся окне галочкой уровень события – пункты «Ошибка» и «Критическое». Нажмите «OK» и утилита тут же отфильтрует записи.
Чтобы просмотреть конкретную запись, кликните по ней дважды – сведения откроются в окошке «Свойства событий».
Как использовать содержимое журнала
Хорошо, теперь мы в курсе, где находится журнал событий и как его открыть, осталось узнать, как его можно использовать. Сразу нужно сказать, что в силу своей специфичности содержащиеся в нем сведения мало что могут поведать обычному пользователю. О чем говорит, к примеру, ошибка «Регистрация сервера {BF6C1E47-86EC-4194-9CE5-13C15DCB2001} DCOM не выполнена за отведенное время ожидания»? Не обладающему соответствующими знаниями юзеру будет непросто определить причину неполадки, с другой стороны, что мешает поискать ответ в Интернете?
Так, описание приведенной выше ошибки имеется на сайте Microsoft и указывает оно на проблемы со SkyDrive, кстати, не представляющие совершенно никакой угрозы. Если вы не пользуетесь этим сервисом, ошибку можно игнорировать или отключить ее источник в «Планировщике заданий». А еще описание ошибки можно отправить разработчику, предварительно сохранив его в файл XML, CSV или TХT.
Также пользователи могут связывать отслеживаемые события с задачами в «Планировщике заданий». Для этого необходимо кликнуть ПКМ по записи, выбрать «Привязать задачу к событию» и создать с помощью запустившегося мастера нужное задание. В следующий раз, когда произойдет такое событие, система сама запустит выполнение задания.
Очистка, удаление и отключение журнала
На жестком диске файлы журнала занимают сравнительно немного места, тем не менее, у пользователя может возникнуть необходимость их очистить. Сделать это можно разными способами: с помощью оснастки eventvwr, командной строки и PowerShell. Для выборочной очистки вполне подойдет ручной способ. Нужно зайти в журнал событий, кликнуть ПКМ по очищаемому журналу в левой колонке и выбрать в меню опцию «Очистить журнал».
Если вы хотите полностью удалить все записи журнала, удобнее будет воспользоваться запущенной от имени администратора командной строкой. Команда очистки выглядит следующим образом:
for /F “tokens=*” %1 in (‘wevtutil.exe el’) DO wevtutil.exe cl “%1”
Вместо командной строки для быстрой и полной очистки журнала также можно воспользоваться консолью PowerShell. Откройте ее с повышенными правами и выполните в ней такую команду:
wevtutil el | Foreach-Object {wevtutil cl “$_”}
При очистке через PowerShell в журнале могут остаться несколько записей. Это не беда, в крайнем случае события можно удалить вручную.
Итак, мы знаем, как открыть журнал событий, знаем, как его использовать и очищать, в завершение давайте посмотрим, как его полностью отключить, хотя делать это без особой нужды не рекомендуется, так как вместе с журналом событий отключатся некоторые, возможно нужные вам службы.
Командой services.msc откройте оснастку «Службы», справа найдите «Журнал событий Windows», кликните по нему дважды, в открывшемся окошке свойств тип запуска выберите «Отключено», а затем нажмите кнопку «Остановить».
Изменения вступят в силу после перезагрузки компьютера. Вот и все, больше системные и программные события регистрироваться не будут.
By
- Kinza Yasar,
-
Alexander S. Gillis,
Technical Writer and Editor
What is the Windows event log?
The Windows event log is a detailed and chronological record of system, security and application notifications stored by the Windows operating system that network administrators use to diagnose system problems and predict future issues.
The operating system (OS) and applications use these event logs to record important hardware and software actions the administrator can use to troubleshoot issues with the OS. The Windows OS tracks specific events in its log files, such as application installations, security management, system setup operations on initial startup, and problems or errors.
Microsoft first offered the Windows event log the release of Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It has been included in all subsequent versions of Windows.
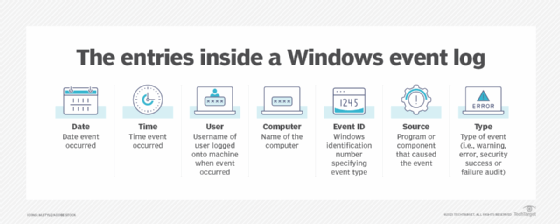
The elements of a Windows event log
Each event in a log entry contains the following information:
- Level. Severity of event, including information, critical, warning, error, verbose.
- Date. Date an event occurred.
- Time. Time an event occurred.
- Source. Program or component that caused the event.
- Event ID. A Windows identification number that specifies the event type.
- Task category. Recorded event log type.
- User. Username of the user logged onto the machine when the event occurred.
- Computer. Name of the computer.
Here are some examples of how log entries are displayed.
| Level | Date | Time | Source | Event ID | Task Category |
| Information | 5/16/2018 | 8:41:15 AM | Service Control Manager | 7036 | None |
| Warning | 5/11/2018 | 10:29:47 AM | Kernel-Event Tracing | 1 | Logging |
| Error | 5/16/2018 | 8:41:15 AM | Service Control Manager | 7001 | None |
| Critical | 5/11/2018 | 8:55:02 AM | Kernel-Power | 41 | (63) |
Information stored in Windows event logs
The Windows operating system records events in five areas — application, security, setup, system and forwarded events:
- Application events. These relate to incidents with the software installed on the local computer. If an application crashes, then the Windows event log will create an application log entry about the issue containing the application name and information on why it crashed.
- Security events. These store information based on the Windows system’s audit policies. Typical events logs stored include login attempts and resource access. For example the Windows security log stores a record when the computer attempts to verify account credentials when a user tries to log on to a machine.
- Setup events. These include enterprise-focused events relating to the control of domains, such as the location of logs after a disk configuration. This log will also keep track of occurrences involving Active Directory on domain controllers.
- System events. These relate to incidents on Windows-specific systems, such as the status of device drivers.
- Forwarded events. These arrive from other machines on the same network when an administrator wants to use a computer that gathers multiple logs.
Using the Event Viewer
In Windows, the event logs are stored in the C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\ folder. They are created for each system access, operating system blip, security modification, hardware malfunction and driver issue.
The role of the Event Viewer tool is to scan through those text log files and gather and present them in an intuitive user interface (UI), similar to how a database reporting tool would.
The following steps can be taken to check the events logs through the Event Viewer:
- Press the Windows key + R on the keyboard to open the Run window.
- Enter eventvwr in the Run dialog box and press OK.
- Expand the Windows Logs menu in the Event Viewer window.
- Notice the different types of event logs found under the Windows Logs menu, including application logs, security logs, setup logs, system logs and forwarded events.
- Click on one of the event logs to search for and view the recorded events under it.
Windows events severity levels
Windows categorizes every event with a severity level. The levels in order of severity are information, verbose, warning, error and critical.
- Information. Most logs consist of information-based events. Logs with this entry usually mean the event occurred without incident or issue. An example of a system-based information event is Event 42, Kernel-Power, which indicates the system is entering sleep mode.
- Verbose. These events represent progress or success messages for a specific event.
- Warning. Warning level events are based on particular events, such as a lack of storage space. Warning messages can bring attention to potential issues that might not require immediate action. Event 51, Disk is an example of a system-based warning related to a paging error on the machine’s drive.
- Error. An error level indicates a device may have failed to load or operate expectedly. Event 5719, NETLOGON is an example of a system error when a computer cannot configure a secure session with a domain controller. The error level’s severity is low and doesn’t require instant troubleshooting.
- Critical. Critical level events indicate the most severe problems. Event ID 41, Kernel-Power is an example of a critical system event when a machine reboots without a clean shutdown.
Other tools to view Windows event logs
Microsoft also provides the wevtutil command-line utility in the System32 folder that retrieves event logs; runs queries; and exports, archives and clears logs.
A few popular third-party utilities that also work with Windows event logs include the following:
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager (SEM). This tool provide a centralized log collection, real-time event correlation and remediation, file integrity monitoring and threat detection through an intuitive dashboard and user interface. It also automatically collects logs from servers, applications and network devices.
- Site24X7. This powerful Windows event log management tool from ManageEngine can identify anomalies in Windows event logs, logs from custom programs and logs from services. It can also send immediate notifications when errors arise.
- Sumo Logic log management and log analytics. This log management software offers real-time analytics, custom dashboards, and machine learning for both cloud-based and on-prem applications.
- Datadog. Datadog’s cloud monitoring tool with log management capabilities offers dashboards, alarms, search and filtering in addition to log management features.
Using PowerShell to query events
Microsoft builds Windows event logs in Extensible Markup Language (XML) format with an EVTX extension. XML provides more granular information and a consistent format for structured data.
Administrators can build complicated XML queries with the Get-WinEvent PowerShell cmdlet to add or exclude events from a query.
Logs provide insightful information about a system’s internal operations. Discover and investigate the function of Windows log monitoring in the enterprise.
This was last updated in March 2023
Continue Reading About Windows event log
- Query event logs with PowerShell to find malicious activity
- The 3 pillars of observability: Logs, metrics and traces
- Top 12 application performance monitoring tools
- 5 distributed tracing tools to ease application monitoring
- The definitive guide to enterprise IT monitoring
Dig Deeper on IT operations and infrastructure management
-
log analytics
By: Alexander Gillis
-
Build a PowerShell logging function for troubleshooting
By: Adam Bertram
-
The role of Windows log monitoring in the enterprise
By: Brien Posey
-
The 3 pillars of observability: Logs, metrics and traces
By: Chris Tozzi
Операционная система Windows, системные службы и приложения записывают события и ошибки в системные журналы, чтобы в дальнейшем у системного администратора была возможность проверки операционной системы и диагностики проблем.
Получить доступ к этим записям можно через встроенное приложение Просмотр событий (Event Viewer). Есть несколько вариантов запуска данного приложения:
- через меню Пуск – Средства администрирования Windows – >Просмотр событий (Start – Windows Administrative Tools – Event Viewer);
- в командной строке или в окне Выполнить набрать eventvwr.msc:
В Диспетчере серверов в разделе Средства выбрать Просмотр событий (Server Manager – Tools – Event Viewer):
Описание интерфейса программы
Окно программы состоит из следующих компонентов:
- Панель навигации позволяет выбрать конкретный журнал, записи которого необходимо просмотреть;
- Список событий, содержащийся в выбранном журнале. В колонках выведена базовая информация о событии. Их можно отсортировать по датам, типам, категориям событий и т.д.;
- Детальная информация о выбранном во второй панели событии. Также детальную информацию можно открыть в отдельном окне, если кликнуть по нужному событию два раза;
- Панель быстрых действий, которые можно совершить с данным журналом или событием. Действия также доступны в контекстном меню (клик правой кнопкой мыши по журналу или событию).
Для удобства просмотра и управления системные журналы разбиты по категориям:
- Приложения (Application) – как и гласит название, содержит события и ошибки приложений;
- Безопасность (Security) – если в операционной системе включена и настроена функция аудита, журнал будет содержать записи, связанные с отслеживанием соответствующих событий (например, авторизация пользователя или попытки неудачного входа в операционную систему);
- Система (System) – здесь регистрируются события операционной системы и системных сервисов;
- Установка (Setup) – события, связанные с инсталляцией обновлений Windows, дополнительных приложений.
В разделе Журналы приложений и служб (Applications and Services Logs) можно найти более детальную информацию о событиях отдельных служб и приложений, зарегистрированных в операционной системе, что бывает полезно при диагностике проблем в работе отдельных сервисов.
Сами события также разделяются на типы:
- Сведения (Information) — информируют о штатной работе приложений.
- Предупреждение (Warning) — событие, свидетельствующее о возможных проблемах в будущем (например, заканчивается свободное место на диске – приложения могут продолжать работу в штатном режиме, но когда место закончится совсем, работа будет невозможна).
- Ошибка (Error) — проблема, ведущая к деградации приложения или службы, потерям данных.
- Критическое (Critical) — значительная проблема, ведущая к неработоспособности приложения или службы.
- Аудит успеха (Success audit) — событие журнала Безопасность (Security), обозначающее успешно осуществленное действие, для которого включено отслеживание (например, успешный вход в систему).
- Аудит отказа (Failure audit) — событие журнала Безопасность (Security) обозначающее безуспешную попытку осуществить действие, для которого включено отслеживание (например, ошибка входа в систему).
Работа с журналами
Службы и приложения могут генерировать огромное количество самых разнообразных событий. Для простоты доступа к нужным записям журнала можно использовать функцию фильтрации журнала:
Правый клик по журналу – Фильтр текущего журнала… (>Filter Current Log…), либо выбрать данную функцию в панели быстрых действий. Открывшееся окно позволяет настроить фильтр и отобразить только те события, которые необходимы в данный момент:
Можно задать временной период, уровни события, выбрать журналы и конкретные источники событий. Если известны коды событий, которые нужно включить или исключить из фильтра, их также можно указать.
Когда необходимость в фильтрации событий отпадет, ее можно отключить действием Очистить фильтр (Clear Filter):
Приложение Просмотр событий (Event Viewer) позволяет также настроить дополнительные свойства журналов. Доступ к настройкам можно получить через панель быстрых действий, либо через контекстное меню журнала – правый клик по журналу – Свойства (Properties):
В открывшемся окне настроек можно увидеть путь, по которому сохраняется файл журнала, текущий размер, а также можно задать максимальный размер файла:
В нижней части окна можно выбрать вариант действия при достижении журналом максимального значения:
- Переписывать события при необходимости (Overwrite events as needed) – новое событие будет записываться поверх самого старого события в журнале, таким образом будут доступны события только за определенный диапазон времени.
- Архивировать журнал при заполнении (Overwrite the log when full) – заполненный журнал будет сохранен, последующие события будут записываться в новый файл журнала. При необходимости доступа к старым событиям, архивный файл можно будет открыть в приложении Просмотр событий (Event Viewer).
- Не переписывать события (Do not overwrite events) – при заполнении журнала выдается системное сообщение о необходимости очистить журнал, старые события не перезаписываются.
Аverage rating : 4.5
Оценок: 4
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
700
300