Товарищи, добрый день. Так как у меня появились несколько идей для написания будущих статей, я решил немного подготовить сайт. В будущем, нам скорее всего понадобится инструмент PowerShell, который уже сейчас превосходит по возможностям стандартную командную строку, но все равно развивается параллельно ей. Подробнее лучше прочитать на википедии, а у нас практические знания, поэтому переходим к инструкции. И снова у нас несколько способов:
- Через меню «Пуск»
- Через командную строку
- Через проводник
- Заменой командной строки в контекстном меню «Пуск» (только современные операционные системы)
Самый популярный способ у нас будет первым, для Windows 10: открываем меню «Пуск» → «Все программы» → ищем каталог «Windows PowerShell» и выбираем файл нужной разрядности. На 32 битных системах будет только 32 битный исполняющий файл.
Если необходим PowerShell с правами администратора, то кликаем правой клавишей мыши по файлу, выбираем «Дополнительно» и жмем «Запуск от имени администратора».
Для Windows 8.x и старше: Открываем меню «Пуск» → открываем раздел «Все программы» → листаем до раздела служебные и открываем Windows PowerShell этот сриншот сделан на 32 битной системе и здесь уже видно, что файл будет только один.
Запуск от имени администратора по тому же сценарию, правой клавишей по файлу и выбираем «Запустить от имени администратора»
2. Запуск PowerShell через командную строку
Да, для любителей нестандартных путей, тоже способ есть)) Много способов запуска командной строки описаны здесь. Здесь же я опишу способ, который подходит для современных операционных систем. Нажимаем правой клавишей мыши по углу пуск или жмем Win+X, а в открывшемся меню выбираем подходящую командную строку. Если вам необходим PowerShell с правами администратора, то выбираем и командную строку с правами администратора.
В открывшееся окно вводим powershell и жмём Enter. После этого командная строка будет работать полностью как Windows PowerShell.
3. Запуск Windows PowerShell через окно проводника Windows.
Открываем проводник и переходим в одну из папок:
a) 64bit PowerShell если стоит 64 битная система или 32bit PowerShell, если стоит 32 битная система
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0
b) 32bit PowerShell на 64 битных системах находится в папке:
C:\Windows\syswow64\Windowspowershell\v1.0
Можно просто вставить ссылку в адресную строку.
Если вам нужен PowerShell с обычными правами, просто запускаем выделенный файл. Если же с правами администратора, жмём правой клавишей мыши и выбираем «Запуск от имени администратора».
4. Замена командной строки на PowerShell в контекстном меню «Пуск».
Вот во втором способе, мы использовали контекстное меню «Пуска» и там по-умолчанию добавлена командная строка. Это можно исправить. Скажем для системных администраторов, все чаще нужен PowerShell, вместо командной строки и вместе с добавлением контекстного меню, Microsoft добавили возможность замены командной строки на Windows PowerShell. Для этого, необходимо кликнуть правой клавишей мыши по пустому месту на «Панели задач». И выбрать её «Свойства».
На вкладке «Навигация» ставим галочку на «Заменить командную строку оболочкой Windows PowerShell…» и жмём ОК.
Теперь в контекстном меню можно сразу же запускать Windows PowerShell.
Вроде всё. Надеюсь эта статья оказалась вам полезной, нажмите одну из кнопок ниже, чтобы рассказать о ней друзьям. Также подпишитесь на обновления сайта, введя свой e-mail в поле справа или подписавшись на группу во Вконтакте и канал YouTube.
Спасибо за внимание
Материал сайта geekteam.pro
Использование некоторых команд и командлетов требует повышенных прав. Примерами действий, требующих прав администратора, являются управление службами (установка, запуск, остановка, удаление) и управление пакетами (добавление и удаление провайдеров пакетов, установка и удаление пакетов).
Связанная статья: Как проверить, запущен ли скрипт PowerShell или терминал PowerShell от имени администратора
К примеру, следующий командлет с попыткой добавить нового провайдера пакетов:
Install-PackageProvider chocolatey
Вызовет следующую ошибку:
Install-PackageProvider: Administrator rights are required to install packages in ''. Log on to the computer with an account that has Administrator rights, and then try again, or install in 'C:\Users\MiAl\AppData\Local\PackageManagement\ProviderAssemblies' by adding "-Scope CurrentUser" to your command. You can also try running the Windows PowerShell session with elevated rights (Run as Administrator).
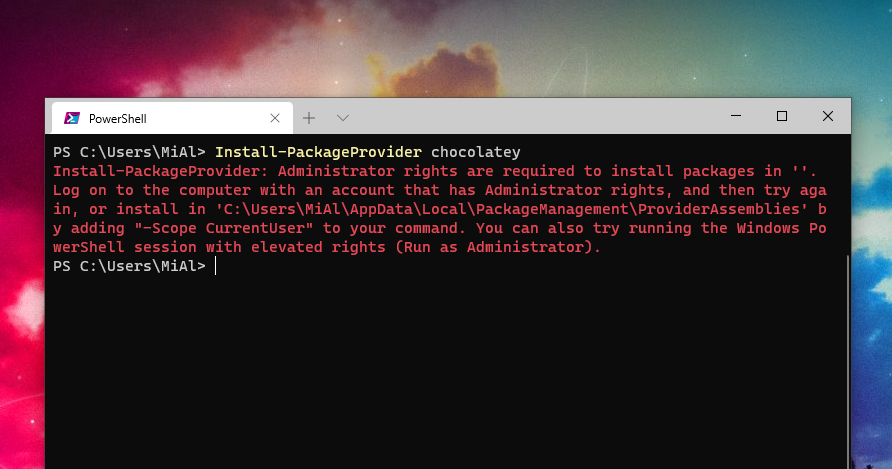
Чтобы исправить эту ошибку, нужно запустить PowerShell с правами администратора.
Как запустить PowerShell с правами администратора в Windows
Рассмотрим несколько способов.
1. Запуск PowerShell с правами администратора через Меню продвинутого пользователя
Нажмите Win+x и в открывшемся меню выберите пункт «Windows PowerShell (администратор)»:
Если у вас в ОС установлено две версии PowerShell (предустановленная с Windows версия PowerShell 5, а также установленная вручную версия PowerShell 7), то таким образом откроется PowerShell 5.
2. Запуск PowerShell с правами администратора из меню Пуск
Чтобы от имени администратора открыть PowerShell 7 нажмите меню Пуск и введите в поиск «PowerShell», выберите пункт «Run as Administrator»:

3. Как запустить Windows Terminal с правами администратора в Windows
По умолчанию в Windows Terminal используется оболочка PowerShell, поэтому если запустить Terminal с правами администратора, то в нём Terminal также будет с повышенными правами.
Напомним, что терминал не входит в стандартный набор программ Windows 10 и его нужно устанавливать из Microsoft Store. В Windows 11 данная программа установлена по умолчанию.
Перейдите в меню пуск и начните писать «Terminal»:

Если вы не видите пункт «Запуск от имени администратора», то нажмите стрелочку, чтобы развернуть весь список:
Кликните на пункте «Запуск от имени администратора».
4. Как запустить PowerShell с правами администратора в командной строке
Если у вас уже открыта консоль PowerShell с правами обычного пользователя, то прямо из неё вы можете запустить новый процесс PowerShell с повышенными правами:
Start-Process PowerShell -Verb RunAs
Эта команда запустит версию PowerShell 5 или PowerShell 6 — в зависимости от того, что у вас установлено в системе по умолчанию. Чтобы запустить последнюю версию, которую вы установили вручную, то есть PowerShell 7, выполните команду:
Start-Process pwsh -Verb RunAs

Как запустить PowerShell с правами администратора в Linux
Для запуска PowerShell с повышенными правами в Linux выполните команду с sudo:
sudo pwsh
Связанные статьи:
- Ошибка 0x800702e4 при запуске `C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7-preview\pwsh.exe’ (РЕШЕНО) (100%)
- Ошибка в PowerShell «New-Item: Access to the path ‘…’ is denied» (РЕШЕНО) (100%)
- Как проверить, запущен ли скрипт PowerShell или терминал PowerShell от имени администратора? (РЕШЕНО) (85.7%)
- Как установить PowerShell в Linux (50%)
- Как получить справку по командам PowerShell (50%)
- Устранение неполадок: групповая политика (GPO) не применяется (RANDOM — 14.3%)
Some commands or tasks require elevation, meaning they must run in the context of an administrator. Such is true with PowerShell scripts, too. Running PowerShell scripts as an administrator means the PowerShell session must be elevated.
There are several ways to run PowerShell scripts as an administrator interactively and non-interactively—which is suitable for automation. We’ll cover them in this article, so stick around and enjoy.
Ways to Run PowerShell as Administrator (Interactive)
Running PowerShell scripts as an administrator requires an elevated PowerShell session. In most cases, doing so interactively is sufficient for users to run one-off or seldom-used scripts.
Here are the ways to interactively start PowerShell as an administrator so you can run your scripts and commands in God mode.
Note. These methods will trigger the UAC prompt to appear.
Windows Power User Menu
The Power User Menu is the quickest way to start PowerShell as an administrator.
Press Win+X on the keyboard or right-click the Start button to pull up the Power User Menu and click Windows PowerShell (Admin).
Note that on a Windows 11 computer, the Windows PowerShell (Admin) is replaced with Terminal (Admin) by default.
Run as Administrator Context Menu
The context menu (right-click pop-up menu) of executable files and their shortcuts include the Run as administrator context menu. This means you can right-click and select Run as administrator whenever you see the Windows PowerShell or PowerShell icon. Here are some examples:
Create a PowerShell Shortcut with Run as Administrator Enabled
You can also create a shortcut to run PowerShell as administrator.
- Right-click anywhere on the desktop and click New → Shortcut.
- Type powershell.exe (Windows PowerShell) or pwsh.exe (PowerShell 7+) and click Next.
- Type the shortcut name and click Finish.
- Right-click the new shortcut and click Properties.
- Click Advanced on the Properties window. Check the “Run as administrator” box and click OK → OK.
Every time you launch PowerShell using the new shortcut, it will run as administrator.
Start PowerShell as Administrator from CMD
Another way to run PowerShell as administrator is by invoking it from the command line or as a CMD script.
From the CMD prompt, run one of the following commands to run Windows PowerShell or PowerShell Core:
REM Run Windows PowerShell as Admin
PowerShell -Command "& {Start-Process powershell -Verb RunAs}"REM Run PowerShell Core as Admin
Pwsh -Command "& {Start-Process Pwsh -Verb RunAs}"
You can also create a CMD script using these commands. Open Notepad, paste one of the previous commands, and save it as a CMD file.
You can then run PowerShell as administrator by double-clicking on the CMD file.
Start a PowerShell Instance in Task Manager
The Task Manager is a high-privilege process that requires elevation. This means that when opening the Task Manager, the UAC prompt appears.
But once you’re in Task Manager, you can run PowerShell as administrator from it, and it will no longer trigger the UAC prompt.
- On the Task Manager window, click Run new task.
- Enter powershell.exe for Windows PowerShell or pwsh.exe for PowerShell Core.
- Check the “Create this task with administrative privileges” box and click OK.
Ways to Run PowerShell as Administrator (Non-Interactive)
What if you must run a PowerShell script unattended with administrative privileges? Like, in an automation scenario, when a script must run without user intervention and the UAC prompt must be bypassed?
In this example, I’m using a script called “RunMeAsAdmin.ps1” with the following code. This script outputs a message indicating whether it is run as administrator.
if (([System.Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal] [System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()).IsInRole([System.Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole]::Administrator)){
"Run as admin - SUCCESSFUL"
}
else {
"Run as admin - FAILED"
} Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
As a Task with the Highest Privileges Enabled in Task Scheduler,
The out-of-the-box solution to run PowerShell scripts with non-interactive administrative rights is adding a Task Scheduler entry. The scheduled task can be configured to run with the highest privileges without triggering the UAC prompt.
Related post. Run PowerShell Script with Task Scheduler.
- Open the Task Scheduler and click “Create a task.”
- Under the General tab, configure the following:
- The name is RunMeAsAdmin.
- Select Run only when user is logged on.
- Check Run with highest privileges.
- Configure for your operating system version (eg. Windows 10 or Windows Server 2022).
- Switch to the Actions tab and click New.
- In the New Action window:
- Type powershell.exe for Windows PowerShell or pwsh.exe for PowerShell Core in the “Program/script” box.
- Type -file “path_to_script” inside the “Add arguments” box where path_to_script is the full path of your script.
- Click OK to close the New Action window.
Optionally, you can add a scheduled trigger if needed. But we’ll skip this step for this example.
- Click OK to save the new task.
- Once the task is created, select it from the list and click Run in the Actions pane.
- Or you can trigger it from PowerShell by running the below command:
Start-ScheduledTask -TaskName <task name>
As you can see below, the task is triggered in a non-administrator PowerShell session, and the script runs in an Administrator session.
Related. List, Add, Edit, and Delete Scheduled Tasks with PowerShell.
Run PowerShell Scripts in an Automation Server (CI/CD)
A better solution to run PowerShell scripts with administrator privileges is through automation servers or CI/CD solutions. One example is Jenkins with the PowerShell plugin.
This article does not cover the Jenkins installation and configuration. For more information, refer to How to Install Jenkins with Let’s Encrypt SSL Certificate on Windows.
Suppose you have Jenkins. You can create a new Freestyle project. In this example, I’ll name it Run Me As Admin.
Add a PowerShell step under Build Steps, paste the script, and click Save.
Once the project is created, you will see it on the dashboard. Click the Build Now button to trigger the build (run the PowerShell script.)
After the build, click the build number under the Build History and select Console Output.
Review the console output; you should see a similar result to the one below.
Conclusion
Running PowerShell scripts as an administrator is optional, but knowing it is possible when necessary is good. The methods we explored in this tutorial produced the same results but exhibited different behaviors or user experiences, especially in systems where UAC is turned on.
Solutions to running PowerShell scripts as an administrator that bypasses the UAC prompt are also available. For automation purposes or without user intervention, you can use the built-in Task Scheduler to run PowerShell script with elevated privileges.
Third-party automation servers are also excellent for running PowerShell scripts as an administrator, such as Jenkins, which we briefly demonstrated.

Cyril Kardashevsky
I enjoy technology and developing websites. Since 2012 I’m running a few of my own websites, and share useful content on gadgets, PC administration and website promotion.
В этой базовой инструкции подробно описано 7 способов запустить PowerShell от имени администратора, в Windows.
Запуск PowerShell с правами администратора, частая необходимость при получении доступа или изменении параметров системы.
Содержание
Запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, с помощью:
- Меню Пуск
- Меню Быстрые ссылки
- Меню Файл
- Меню Поиск
- Командная строка
- PowerShell (с правами пользователя)
- Меню Выполнить
Article in other languages:
?? — How to Run PowerShell as Administrator
?? — Cómo ejecutar PowerShell como administrador
?? — Comment exécuter PowerShell en tant qu’administrateur
?? — So führen Sie PowerShell als Administrator aus
?? — Hoe te PowerShell uitvoeren als administrator
Меню Пуск
Первый способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, используя кнопку Пуск.
- Нажмите кнопку Пуск;
- В списке программ нажмите Windows PowerShell;
- Щелкните по Windows PowerShell правой клавишей мыши, выберите Дополнительно и Запуск от имени администратора.
Меню Быстрые ссылки
Второй способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, используя меню Быстрые ссылки.
- Щёлкните по кнопке Пуск правой клавишей мыши (или нажмите сочетание Windows+X);
- Нажмите Windows PowerShell (администратор).
Меню Файл
Третий способ запустить PowerShell от имени администратора — это используя меню Файл при выделении файла или папки в проводнике Windows.
- Выделите файл или папку в окне Проводника Windows;
- Щелкните по меню Файл, наведите курсор на треугольник расширенного выбора в пункте Windows PowerShell;
- Выберите Запустить Windows PowerShell от имени администратора.
Меню Поиск
Четвертый способ запуска PowerShell с правами администратора — это используя Поиск Windows из начального меню.
- Щелкните по строке Поиск на панели задач (или нажмите сочетание Windows+S);
- Введите текст PowerShell;
- Щелкните по треугольнику расширенные результаты в пункте Windows PowerShell и нажмите Запуск от имени администратора.
Пятый способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, с помощью командной строки.
Запустите командную строку и выполните команду:
powershell "start-process powershell -verb runas"Запуск PowerShell от имени администратора с помощью PowerShell (с правами пользователя)
Шестой способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, с помощью консоли PowerShell запущенной с правами пользователя.
Запустите консоль PowerShell и выполните команду:
start-process powershell –verb runasМеню Выполнить
Седьмой способ — используйте меню Выполнить, для запуска Windows PowerShell с правами администратора.
Откройте меню Выполнить.
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Windows+R (или щелкните по кнопке Пуск правой клавишей мыши, выберите Выполнить);
- Введите команду powershell;
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
? В этой статье обсуждалось как запустить PowerShell с правами администратора, для запуска программ или изменения параметров системы требующих повышенных прав. Я надеюсь, вы смогли запустить консоль PowerShell с повышенными правами выбранным способом. Однако, если вы столкнулись с каким-то проблемами при запуске PowerShell, не стесняйтесь написать в комментариях. Я постараюсь помочь.
Whether you’re just starting out with PowerShell or you already know how to run commands, there are times when you must use PowerShell to ‘run as administrator’ Why? Because sometimes, any activity you do inside of PowerShell will require elevated privileges.
In this tutorial, you’re going to learn just about every way possible to run PowerShell as administrator from the perspective of an end-user, a command-line junkie, or an IT admin!
This tutorial has many sections each showcasing how to run PowerShell as administrator. Feel free to click on whichever method you prefer in the Table of Contents.
Prerequisites
This article will be a hands-on tutorial. If you’d like to follow along, please be sure you have:
- A Windows 10 PC – Although Windows 10 was used as an example for this article, most of the methods provided will work with Windows 7+.
- An account with administrator privileges. If you don’t already have one, learn how to create one here.
- PowerShell – Most of these methods will work with Windows PowerShell 5.1 or PowerShell 7.
Running PowerShell as Administrator with a Right-Click
One of the simplest ways to run PowerShell as administrator is with a right-click. There are a few different areas where you can right click on PowerShell and run it. Let’s run through them.
Using the Search Bar
The Search Bar is practically one of the easiest ways to run most of the programs installed on your computer. It’s also an easy way to run any program as administrator, including PowerShell.
To run PowerShell, specifically, as administrator from the search bar:
- Click on the search box at the taskbar and type powershell. This action will bring up the PowerShell edition of your preference.
- Look for Windows PowerShell or just PowerShell, if using PowerShell Core, from the search result.
- Right-click on the menu item and select Run as administrator.
You can see these steps demonstrated in the screenshot below.

If you pin a program to the start menu or taskbar, you can also right-click on the menu item there as well. With this method, Windows 10 creates a shortcut for PowerShell that is more accessible to you at the start menu or the taskbar.
To run PowerShell as administrator on a pinned item:
- Find the PowerShell icon in the search box again.
- Right-click on the PowerShell icon and select Pin to Start or Pin to Taskbar.

- Click on the Start button
- Look for Windows PowerShell (or PowerShell Core) on the right side of the Start Menu.
- Right-click on the menu item and choose Run as administrator.

Running PowerShell as Administrator Using File Explorer
Are you in Windows’ File Explorer, you can fire up PowerShell as administrator there too!
- Open up File Explorer by using Win Key + E shortcut keys or by simply clicking the icon at the taskbar as you can see on the screenshot below.
2. Once in File Explorer, click on File → Open Windows PowerShell → Open Windows PowerShell as administrator as shown below.

Using the PowerShell Executable
Whether you’re using a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system, you can run PowerShell as administrator from its respective location.
- In File Explorer, navigate to one of the folders below.
- For 32-bit OS: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0
- For 64-bit OS: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0
- Find the powershell.exe file.
- Right-click on powershel.exe and select Run as Adminstrator.

Creating a Shortcut for PowerShell on the Desktop
If you’d like an easy way to invoke PowerShell, you can also create a Windows shortcut for it.
- Once you’ve got the Create Shortcut process started, provide the path to the PowerShell executable. For Windows PowerShell, that path is:
- For 32-bit OS: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
- For 64-bit OS: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe

2. Provide the shortcut a handy name (PowerShell Admin for example).

3. Find the shortcut you just created and right-click on it and choose Properties as shown below.

4. Click on Shortcut tab and then on the Advanced button and the Advanced Properties window will pop-up.

5. In the Advanced Properties window, select the Run as administrator checkbox and click OK.

6. Back to the Shortcut Properties, click OK to apply the changes and you’re all set.
Another way to easily access PowerShell is via the Win-X menu as shown in the following screenshot. This menu was never given an official name but was widely referred to as Win-X (or power user menu) as the shortcut to access it is Win Key + X.
Once the menu is up, simply click on Windows PowerShell (Admin) and you’re off to th races.

Using the Run Command Window
The Run Command Window is a powerful tool that lets you run programs without searching for them using the SearchBar, Start Menu or File Explorer. To run PowerShell as administrator via the Run command window:
- Press Win Key + R. A a small window will pop up as shown in the screenshot below.
- Type in powershell and press Ctrl+Shift+Enter or press and hold Ctrl+Shift.
- Click OK to make PowerShell run as administrator.

You’re now running PowerShell as administrator.
Using Task Manager
Task Manager is a tool that lets you monitor or end a process of the programs and services that are currently running on your computer. You can also use it to execute a task such as running PowerShell as administrator manually.
To run PowerShell as administrator via the task manager:
- Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc keys on your keyboard or as you see in the screenshot below
You can alternatively right-click on the Task Bar and select Task Manager to bring up Task Manager.

2. Once Task Manager opens, go up to File and click on Run new task as shown below.

3. You should then see a window pop up that looks similar to the Run window described earlier.
4. Type in powershell ensuring you also check the Create this task with administrative privileges checkbox and click OK to make PowerShell run as administrator.
Running PowerShell as Administrator with the Command Line
If you regularly find yourself on the command line, don’t fret, you can run PowerShell as administrator there too!
If you already have cmd. exe open running as adminstrator using the same techniques described in this article, you can simply run start powershell and it will be running as adminstrator.
If you’re running a command prompt not as administrator yet, that’s not a problem. Invoke the Start-Process cmdlet with PowerShell from cmd. exe using the -Verb runas parameter.
powershell Start-Process powershell -Verb runAsIf you’re already in a PowerShell window, you can run Start-Process powershell -Verb runas directly to open a new PowerShell instance running as administrator
Creating a Batch File to Run PowerShell as Administrator
So you now know how to invoke PowerShell as administrator from a command prompt. If you already know how to do that, you can create a batch file to automate it!
Open up your favorite text editor, paste in the following line and save the file as PowerShell as admin.bat anywhere you’d like.
Powershell.exe -Command "& {Start-Process Powershell.exe -Verb RunAs}"Run the batch file and you’ll notice up comes a PowerShell window running as administrator!
Creating a Scheduled Task to Run PowerShell as Administrator
Task Scheduler is a built-in app on Windows 10 that lets you virtually run automated tasks. Hence, you can also use it to create a task that runs PowerShell as administrator each time you logon to your computer, for example.
Start up the Create Taskbox and specify the file to run as one of the below:
- For 32-bit OS: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
- For 64-bit OS: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
In the Create Task windows, provide the values to all of the menu items shown below ensuring the Run with highest privileges checkbox is checked.

Now when the scheduled task is invoked, it will execute PowerShell as administrator!
Further Reading
- PowerShell Objects, Properties and Methods
- How to Set Up and Manage Scheduled Tasks with PowerShell


























 Optionally, you can add a scheduled trigger if needed. But we’ll skip this step for this example.
Optionally, you can add a scheduled trigger if needed. But we’ll skip this step for this example.













