From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
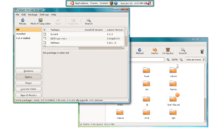
Xming displaying Synaptic and Nautilus |
|
| Original author(s) | Alexander Gottwald (2004–2005)[1] |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Alexander Gottwald (?–2005)[2][3] Colin Harrison(2005 — present)[4] |
| Initial release | November 9, 2004; 18 years ago |
| Stable release |
7.7.0.38, proprietary |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows XP/Server 2003/Vista/Server 2008/7/Server 2012/8.x/10 |
| Type | Display server |
| License | Proprietary software[5] |
| Website | www |
Xming is an X11 display server for Microsoft Windows operating systems, including Windows XP and later.[6][7][8]
Features[edit]
Xming provides the X Window System display server, a set of traditional sample X applications and tools, as well as a set of fonts. It features support of several languages and has Mesa 3D, OpenGL, and GLX 3D graphics extensions[6] capabilities.
The Xming X server is based on Cygwin/X,[9] the X.Org Server. It is cross-compiled on Linux with the MinGW compiler suite and the Pthreads-Win32 multi-threading library. Xming runs natively on Windows and does not need any third-party emulation software.
Xming may be used with implementations of Secure Shell (SSH) to securely forward X11 sessions from other computers.[7] It supports PuTTY and ssh.exe, and comes with a version of PuTTY’s plink.exe. The Xming project also offers a portable version of PuTTY. When SSH forwarding is not used, the local file Xn.hosts must be updated with host name or IP address of the remote machine where the GUI application is started.
The software has been recommended by authors of books on free software when a free X server is needed,[10][11] and described as simple[12] and easier to install though less configurable than other popular free choices like Cygwin/X.[13]
Transition to proprietary license[edit]
Since May 2007, payment must be made to download new releases.[14] Purchasing a license will allow the user access to new downloads for one year; however, MIT-licensed releases (referred to by the author as «public domain» releases) can still be downloaded with no payment on SourceForge.[15]
See also[edit]
- Cygwin/X
Notes[edit]
- ^ «Alexander Gottwald — mingw only xserver». sourceware.org.
- ^ «Alexander Gottwald — New Cygwin/X and Xming maintainer wanted». sourceware.org.
- ^ «Xming — Freedesktop.org». 5 December 2004. Archived from the original on 2004-12-05.
- ^ Free as a Bird — Linux GUI with Xming, A Prisoner of Windows LG #129 ( August 2006), Linux Gazette — Xming is a port of the X.org X11 server to the Windows environment, currently maintained by Colin Harrison who took over from Alexander Gottwald.
- ^ «Xming’s Terms and Conditions». Xming. Retrieved October 13, 2009.
- ^ a b Joe ‘Zonker’ Brockmeier (2007-08-08). «Use Linux over Windows with Xming». Linux.com. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ^ a b David Mair (2006-11-22). «Xming — A X Server for Windows». Novell. Archived from the original on 2009-05-30. Retrieved 2009-06-09.
- ^ Harrison, Colin. «Xming X Server for Windows — Official Website». wayback.archive-it.org. Archived from the original on 2012-10-10. Retrieved 2017-03-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Harrison, Colin. «Xming X Server for Windows — Code». www.straightrunning.com.
- ^ Van Vugt 2009:273
- ^ Garrido 2007:366
- ^ Iskander 2007:41
- ^ Peckar 2008:182
- ^ Harrison, Colin. «Xming X Server for Windows — Official Website». www.straightrunning.com.
- ^ «Xming X Server for Windows». SourceForge.
References[edit]
- Iskander, Magued (2007). Innovations in E-learning, Instruction Technology, Assessment, and Engineering Education. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-6261-2.
- Van Vugt, Sander (2009). Beginning the Linux Command Line. Apress. ISBN 978-1-4302-1889-0.
- Garrido, José M; Richard Schlesinger (2007). Principles of modern operating systems. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7637-3574-6.
- Peckar, Mike (2008). Fognet’s Field Guide to OpenView Network Node Manager — Revised. Lulu.com. ISBN 978-0-9785627-2-4.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- Xming on SourceForge
- WebCache of Original project homesite at the Wayback Machine (archived October 2, 2007)
Xming is the leading X Window System Server for Microsoft Windows 8/7/Vista/XP (+ server 2012/2008/2003). It is fully featured, small and fast, simple to install and because it is standalone native Microsoft Windows, easily made portable (not needing a machine-specific installation).
License
BSD License, Public Domain, MIT License, zlib/libpng License
Quant offers a wide range of solutions for retail. Within one integrated software system, it allows you to efficiently combine the management of retail space, shelf labels and marketing materials with task management, reporting and automatic replenishment.
Additional Project Details
Operating Systems
Windows
Intended Audience
Advanced End Users, System Administrators, Developers, End Users/Desktop
User Interface
X Window System (X11), OpenGL, Project is a window manager, Project is a remote control application
Programming Language
C++, C
Related Categories
C++ Terminal Emulators ,
C++ Window Managers ,
C++ Distributed Computing Software,
C Terminal Emulators ,
C Window Managers ,
C Distributed Computing Software
Xming is the leading X Window System Server for Microsoft Windows®.
It is fully featured, lean, fast, simple to install and because it is standalone native Windows, easily made portable (not needing a machine-specific installation or access to the Windows registry).
Xming is totally secure when used with SSH and optionally includes an enhanced Plink SSH client and a portable PuTTY replacement package. Xming installers include executable code, and libraries, only built by me, Colin Harrison (Project Xming’s chief developer) + this website is free of adverts, pop-ups and usage tracking of any kind, including cookies, and is hosted on machines only administered by me.
Mesa with
GLX, or
Microsoft WGL, provide interactive
OpenGL® 2D and 3D network transparent graphics rendering.
High performance Windows AIGLX is available for graphics cards that support hardware-accelerated OpenGL.
PuTTY is Project Xming’s preferred and integrated X terminal emulator for Microsoft Windows: superseding any requirement for a cumbersome POSIX API compatibility layer and simulated directory mount points.
Xming is cross-compiled on Linux for Microsoft Windows, using MinGW-w64, mostly from canonical
X.Org source code with my patches applied. It is kept current and secure with frequent updates from
X.Org,
XCB,
XKB,
FreeType,
PThreads4W,
Mesa,
PuTTY and xorg group issues in
freedesktop gitlab.
Screenshots
 Xming -multiwindow mode on Windows 7 with five clients including a remote ParaView. |
 and an xlogo X client on another. |
 XDMCP on one X server used to access a remote Raspberry Pi and a few clients on another. |
Releases
| Website Releases | Version | State/Notes | Released | MD5 signatures | Size MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xming Xming-x64 |
7.7.0.95 | Website Release | 2 Oct 2023 | MD5 signatures | 6.71 7.08 |
| Xming-portablePuTTY Xming-portablePuTTY-x64 |
7.7.0.69 | Website Release | 2 Aug 2021 | MD5 signatures | 2.95 3.05 |
| See Donations for how to obtain a Donor Password. |
| Public Domain Releases | Version | State/Notes | Released | MD5 signature | Size MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xming-fonts | 7.7.0.10 | Public Domain | 9 Aug 2016 | ed1a0ab53688615bfec88ab399ae5470 | 31.1 |
| Xming Xming-mesa |
6.9.0.31 | Public Domain | 4 May 2007 | 4cd12b9bec0ae19b95584650bbaf534a e580debbf6110cfc4d8fcd20beb541c1 |
2.10 2.50 |
| Website Snapshots | Version | State/Notes | Snapshot | MD5 signature | Size MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snapshot Xming Snapshot Xming-x64 |
7.7.0.96 | Work in progress | 3 Oct 2023 17:51 | Not yet released | 6.71 7.08 |
| See Donations for how to obtain a Donor Password. |
Windows installers
Xming installers make it child’s play to quickly install project components, interactively, with a few mouse clicks.
They also install/uninstall, silently, using command line parameters.
Installers are for all Microsoft Windows editions no older than Windows 7 sp1 or Windows Server 2008 R2 sp1, but not ARM-based machines.
Safety note: make sure you put an installer in an empty directory (or in one containing only other Project Xming installer files) before running it to avoid the possibility of a rogue file ‘hijack’. It is also wise to check the MD5 signatures of installers (I list a range of better checksums, than md5sum, for the installers in the download directory).
Xming
Optional extras are the Plink for Xming SSH client, XLaunch wizard, Tools and clients and GLX test clients. At least 24.8MB of free disk space is required. The x64 version is specific for 64-bit Windows x64. Note: use 32-bit Xming on Itanium/ia64.
Don’t install anywhere other than the default directory unless you really know what you are doing and install using right-click ‘Run as administrator’ if necessary.
OpenGL support is now provided by all Xming installers (Xming used to have separate builds and installers; with and without Mesa).
If you intend to use PuTTY: make sure you pick the correct Plink SSH client for use with Xming-portablePuTTY or original PuTTY i.e. there are two different Plink(s) in an Xming installer.
The Xming executable has an absolute minimum of fonts; the so-called built-ins.
X clients usually need extra fonts to supplement these…
Xming-fonts
This additional installer provides standard core X fonts (which are usually required) and optional extended Bitstream Vera replacement fonts from DejaVue. At least 19.8MB of free disk space is required (for the default selection of fonts). Note: one Xming-fonts installer is common for both 32-bit and 64-bit Xming.
You should install Xming-fonts in the same directory you installed Xming.
For an x64 (native 64-bit) installation on 64-bit Windows (x64) this defaults to…
C:\Program Files\Xming (also the default install directory on 32-bit Windows)
and for a native 32-bit WoW64 installation on 64-bit Windows (x64 or ia64) defaults to…
C:\Program Files (x86)\Xming
If you have installed both 32 and 64-bit Xming, on 64-bit Windows, you will need Xming-fonts in both the directories above i.e. sub-directory ‘fonts’ and contents.
I separated these fonts from Xming installers, above, since they have a high installed footprint, don’t change very often and modern X applications use client-side fonts instead via fontconfig. Xming-fonts are however needed by traditional X applications e.g. emacs.
Since these standard X Window fonts tend to be ugly, you could use better TrueType fonts from your Microsoft system like this.
Instead of installing Xming-fonts, to provide core X fonts, you could use an X font server on your network.
Xming-portablePuTTY
This optional installer provides a fully portable replacement for PuTTY. At least 6.4MB of free disk space is required. You should not install portablePuTTY in the same directory you installed Xming: it is completely autonomous. The x64 version is specific for 64-bit Windows x64.
Don’t install anywhere other than the default directory unless you really know what you are doing and install using right-click ‘Run as administrator’ if necessary.
Xming-portablePuTTY works without requiring access to the Windows registry. The portable Plink executable incorporates the changes for the Plink for Xming SSH client.
Using Xming
Note this website convention: Window = X Window Windows = Microsoft Windows®
What can you use Xming for?
All the normal X Window Server functions and some you might not have thought of
- Extend the magic of X11
Network Transparency to the ubiquitous Microsoft Desktop.
- Enable your Windows and Linux/Unix machines to integrate as a heterogeneous Private/Personal Cloud by using Xming and PuTTY. Be clear, not cloudy, about where your data is and who may access, or indeed, exploit it!
- Use your Microsoft computer as a thin client terminal to remote Linux/Unix machines
.
- Headless a Linux/Unix machine by removing its keyboard, mouse, monitor and maybe even its graphics card. Execute commands via PuTTY terminals, and display via Xming, over your network.
- Window’s drivers are often faster and more capable than Linux drivers for hardware-accelerated OpenGL enabled graphics cards. Xming can exploit the capabilities of an OpenGL enabled device, on a Windows machine, by use of its -wgl option in all modes including XDMCP (e.g. -query).
- You can display remote X clients directly on the Windows Desktop without running a remote Display Manager and so free up the resources used by that DM.
- Remote control your
Raspberry Pi from Windows. Here is an example XLaunch file to display Midori for Raspbian jessie using Plink.
- Extend server-side X fonts to include any TrueType fonts on your Windows machine. These high quality fonts can be accessed, in situ, and added to the X server font list.
- Use Xming with portablePuTTY as a pocket X server by copying both to a USB flash drive etc. Once made portable; no installed software or access to the Windows registry is needed.
- Old slow redundant Windows machines can be easily re-cycled into slick Linux machines and then accessed with Xming from your latest Windows computer. You will then get the best of both worlds, each with its own separate system architecture, security and philosophy. Xming elegantly and efficiently provides input control and graphical display for software that is running on the remote system.
- Use SSH and X-Forwarding in -multiwindow mode, instead of
VNC, to reclaim precious resources (including desktop space) and facilitate cut-and-paste between windows.
- You can run Xming on multiple monitors in many ways, e.g. if you have two monitors on a Windows machine, you could put the full remote Linux/Unix session on the second monitor using
>Xming -query <IP address of remote host> -nodecoration -screen 0 @2 -clipboard -wgl
Xinerama could be used to create one large virtual display, e.g. with two monitors
>Xming -query <IP address of remote host> -nodecoration -screen 0 @1 -screen 1 @2 +xinerama -clipboard
Manuals
This documentation is constantly being updated and may be incorrect for old versions. Don’t be put off, there needs to be a lot of it to cover the many uses for the X protocol, but for most users Xming installs quickly and can be started, by the XLaunch wizard, in just a few seconds.
Xming Manual.
This doesn’t contain any X server commands. You can view all the applicable X server commands for Xming with -help or run this XLaunch file. These online X.Org Manual pages also give more detail on
generic X server and X client options.
Note: not all general options are logical for Windows or honoured by Xming.
Manuals are also available for XLaunch, Xmingrc, portablePuTTY, PuTTY, Xmon, the Run utility and command line use of Xming’s install and uninstall programs. All Tools and clients also have Xming manuals.
I also have a Recipe for setting up a headless Raspberry Pi and remote controlling it with PuTTY and Xming.
Getting started
Use XLaunch -find if all you want is to login to a remote machine and interact with its Display Manager via Microsoft Windows (using XDMCP).
This is an elegant way to use an xserver but XDMCP mode is not very secure. It is safer to work via X-Forwarding and the SSH protocol, e.g. using PuTTY, on shared networks. Getting started with PuTTY X-Forwarding is described below and in more detail here.
A good tip: get PuTTY working first with Pageant, and use Saved Sessions, before using Xming/Xmingrc/XLaunch. Those Saved Sessions should only use the SSH-2 protocol, ‘Enable X11 forwarding’ and for the following example set ‘X display location’ to ‘localhost:0’.
To simply start Xming in -multiwindow mode from Command Prompt (the Windows cmd console)
>"C:\Program Files\Xming\Xming.exe" -multiwindow -clipboard If you now need a Command Prompt: run it from Xming's notification area icon menu. Many useful variables will then be inherited e.g. %CD% and %DISPLAY%
This gives you a multiwindow/multimonitors X server on display-number 0 (the default), with an integrated Windows window manager. Note…
- You cannot run two X servers with the same display-number; use the :display-number option if you want multiple instances.
- On recent Windows versions: in order to easily use Xming’s notification area icon(s) you should set ‘Show icon and notifications’, for the Xming X server icon.
You could now run, for example, firefox on a remote machine like this (Xming will ‘serve’ control and display locally)…
- just type ‘firefox’ on a PuTTY terminal connected to a remote machine
- or from a Command Prompt use PuTTY’s Plink tool one of two ways…
>plink -ssh -2 -X <user@remote-host> firefox either, with user@remote-host >plink -load <session-name> firefox or, with a PuTTY Saved Session name.
XLaunch makes using Xming with PuTTY’s Plink and generic Windows ssh clients easy…
The XLaunch wizard
XLaunch is a wizard for simplifying the startup of an Xming X server. Its re-usable XML configuration files also act as mini-session managers. One X client can be selected for concurrent display from a local or remote machine. When remote, the X client is accessed securely via PuTTY or
SSH.
Remote login using XDMCP is also provided as well as a host finder and chooser via the -find command and XPing button…
 |
 |
Also use XLaunch to just simply start the X server and then run several X clients later by hand, or from Xmingrc menu entries.
Example .xlaunch configuration files for a remote xterm via PuTTY and a remote login via XDMCP.
Using the wizard to get a remote wireshark via PuTTY in -multiwindow mode…
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
You can select the windowing mode, the way sessions are started and save the configuration for later reuse. An XLaunch configuration file can be just clicked to rerun saved settings without having to go through the wizard pages. Also automatic validation of configuration files against the XLaunch XML Schema Definition is selectable when starting the wizard. Additionally, automatic display-number (i.e. X server) allocation is provided.
Help is available for each XLaunch page via the ‘Help’ button, or F1, and from these links…
Display settings Session type Start program XDMCP settings Additional parameters Finish configuration Host Finder
Xmingrc and the X icon menu
You can configure the X toolbar icon menu (i.e. the right-click menu on Xming’s notification area icon), Windows icons, styles and system menus (i.e. the right-click menu on a Window’s title bar) using an Xmingrc file. Additionally, on the icon menu, a Host Finder is provided for listing, choosing and then accessing any responding XDMCP hosts on your network, as well as a log file viewer.
It is also possible to not hide the root window (Note: you may lose control of your desktop it you don’t ‘Hide Root Window’) and disable the ‘X11 PRIMARY Selection’ (the highlighted text copying mechanism with X clients).
I use this Xmingrc file to open X Window clients (singly or combined in session files), PuTTY and Command Prompt terminals, and to control access to the X server.
Remote Linux/Unix (and local Windows) programs can be run from Xmingrc menu items. Use of Plink is recommended when starting remote programs.
Xmingrc is a structured text file, so to avoid errors, study the installed default Xmingrc file (plus my Xmingrc file: see screenshots below).


Tools and clients
Many X.Org tools and clients have been ported to Microsoft Windows console (Windows CUI) applications and built modular using MinGW-w64…
| appres | atobm | bitmap | bmtoa | cxpm | editres | ico | listres |
| mkfontscale | oclock | setxkbmap | sxpm | twm | viewres | xauth | xcalc |
| xclipboard | xclock | xcutsel | xdpyinfo | xev | xeyes | xfontsel | xhost |
| xkbcomp | xkill | xlogo | xlsatoms | xlsclients | xlsfonts | xmessage | xmodmap |
| Xmon | xprop | xrandr | xrdb | xset | xsetroot | xwininfo |
Use the links in the table above to view Xming manuals for each entry.
Note: xkbcomp is built without a Windows console (Windows GUI), and always installed, as it is used by Xming during X server startup. Also Xmon is sourced here not from X.Org.
These additional tools are also supplied in Xming installers…
Examples, from Command Prompt
>xsetroot -cursor_name left_ptr -fg white -bg black -solid SteelBlue >setxkbmap de -model pc105 >xkbcomp -a :0 %TEMP%/desc.xkb Output the keyboard source, including comments. >xkill -frame Use in -multiwindow mode to select a client to close. >xroot -geometry 50x50+500+50 -color SteelBlue Useful with -rootless and some window managers.
An example of the interactive X protocol monitor, Xmon, being used on Windows 7
>xmonui | xmond Xmonui graphics front-end piped to an xmond console providing trace,
for display 1 clients, while an X server is running display 0.
Using PuTTY with Xming is highly recommended as it provides SSH for Windows (typically used to log into remote Linux/Unix machines and execute commands) and Plink is especially useful…
Plink for Xming SSH client
Plink is a command line connection tool, similar to Linux/Unix ssh, that is used for automating secure remote operations from XLaunch and Xmingrc.
The Xming Plink SSH client is made with MinGW-w64 from patched
PuTTY code.
These modifications substitute Windows prompts for many console ones because XLaunch and Xming are built console free (GUI) and so stdout/stderr messages are hidden when Plink is spawned from them. Use as a replacement for Plink in ‘standard’ PuTTY (i.e. installers or binaries downloaded from Simon Tatham’s website). Note: Xming-portablePuTTY’s Plink incorporates the same changes but is not compatible with ‘standard’ PuTTY (there is a choice of two different Plink(s) in an Xming installer).
An example using Plink in a .js file to display a remote xterm.
The Run utility
The Run utility is an autonomous tool used to start Windows applications with a hidden attached console command window. This is the Manual for run.
Its 32-bit binary, 64-bit binary and source code are supplied separately from Project Xming; and licensed GPLv2.
Here is an example Desktop Shortcut using run and Plink to display a remote konsole.
Donations
I greatly appreciate contributions towards improving Xming’s development and hosting resources. Plus, if you found Xming useful, a little thanks gives me the motivation to make it even better.
Without updating equipment my Xming development can’t continue or advance, hence this hardware funding initiative…
If the button is faultily not setting £10 (GBP), email me and I’ll setup a PayPal money request instead or just send £10 to my PayPal account.
Note: you don’t need a PayPal account to use the donation button and can pay with a credit/debit card.
By donating a minimum of £10 (GBP) you will get a Donor Password, sent by email, enabling download access to Xming Website Releases and Development Snapshots, for one year, and permission to use Xming Website Releases as a private individual.
If you can’t donate money for legal reasons just send £10 to my PayPal account or email me for alternatives. My email address and PayPal account are the same: colin@xming.myzen.co.uk
See Terms and Conditions for license purchasing.
Xming Website Builds include…
I have actively contributed to the X.Org Foundation’s open source implementation of the X Window System for many years. Other projects also benefit from Xming developments. These are freely available for their use when correctly cited in accordance with 
Support
I get so much email that I literally do not have time to answer it all. I regret this, but there’s nothing I can do about it. So if you can possibly avoid sending mail to me, I recommend you do so. In particular, support requests are probably better sent to newsgroups, or passed to a local expert if possible. Reports will ALWAYS be ignored by me if your complete Xming log file is not attached, if the report lacks detail and clarity and if you compare Xming with an X server not built directly from X.Org code. If a Plink problem I need the Plink command line used or a copy of your config.xlaunch file and if an Xmingrc problem I need a copy of your Xmingrc file! Tell me, upfront, if you are using virtual machine interfaces between Windows and Linux/Unix installed on the same machine, or starting Xming over RDP. Failing to follow instructions, or answer questions, will quickly lose any interest in your problem. I do however appreciate well formulated reports and suggestions; but read this website’s documentation first before asking a question…I don’t reply if the answer is already here.
Most issues, outside the scope of the Manuals, can be resolved by consulting the Trouble with Xming? documentation and Terms and Conditions…
Terms and Conditions
This URL links to the Project Xming’s Ts&Cs including details on copyright, licensing, donations and purchases with many clarifications.
Ts&Cs may change from time to time. It remains your responsibility to check them whenever you access this website or download, install and use any Project Xming software.
Table of contents
- Screenshots
-
Releases
- Links and release status
-
Windows installers
- Xming
- Xming-fonts
- Xming-portablePuTTY
-
Using Xming
- What can you use Xming for?
- Manuals
- Getting started
- The XLaunch wizard
- Xmingrc and the X icon menu
- Tools and clients
- Plink for Xming SSH client
- The Run utility
- Donations
- Support
- Terms and Conditions
The Xming website, documentation and images are licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.0 UK: England & Wales License.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft product screen shots: «Used with permission from Microsoft.»
Copyright © 2005-2023 Colin Harrison All Rights Reserved
Xming — это свободный и открытый X-сервер для операционной системы Windows. Он позволяет пользователям Windows устанавливать соединение с серверами Linux и запускать графические приложения с удаленных машин. Xming является полностью совместимым с оригинальным X-сервером X.Org и предлагает широкий спектр функций и возможностей.
Установка и настройка Xming довольно просты и занимают минимум времени. После установки пакета Xming, пользователь должен настроить соединение между Windows и удаленным сервером Linux. Для этого необходимо указать IP-адрес и номер порта удаленного сервера. В случае успешного соединения, пользователь сможет запускать и работать с графическими приложениями, используя Xming.
Xming также предлагает дополнительные возможности, такие как поддержка возможности переадресации X11, возможность работы в режиме многих окон и графический настройщик автонастройки Xlaunch, который помогает пользователям настроить сервер Xming без необходимости вводить команды вручную.
Использование Xming значительно упрощает процесс работы с графическими приложениями на Windows, позволяя пользователю работать с удаленными машинами и запускать приложения, которые обычно доступны только на Linux-серверах. Xming является надежным и удобным инструментом для разработчиков, системных администраторов и всех, кто нуждается в доступе к графическим приложениям в среде Windows.
Содержание
- Что такое Xming и зачем он нужен?
- Xming: основные функции и преимущества
- Почему Xming необходим для пользователей Windows?
- Как подключить Xming к Windows?
- Шаги установки Xming на компьютер
С помощью Xming можно легко настроить соединение с удаленным сервером, запустить графические приложения и отображать их окна на компьютере с Windows. Благодаря Xming, пользователи могут взаимодействовать с графическими интерфейсами программ, работающих на удаленных серверах, а также использовать функции оконных менеджеров и системных средств Linux или Unix. Это делает Xming очень удобным инструментом для разработчиков, системных администраторов и пользователей, которым нужно работать с приложениями, предназначенными для других операционных систем.
Настраивать Xming несложно. После установки, пользователю нужно указать адрес удаленного сервера и учетные данные для соединения. А затем просто запускать нужные приложения и работать с ними, как будто они были установлены непосредственно на компьютере с Windows.
Таким образом, Xming позволяет использовать графические приложения из других операционных систем на компьютере с Windows, что облегчает работу с различными типами программ и повышает гибкость и удобство использования операционной системы Windows.
Xming: основные функции и преимущества
Главные функции Xming включают:
1. Поддержка X-протокола: Xming полностью совместим с X Window System, что позволяет запускать любые графические приложения на удаленном сервере и получать доступ к ним через протокол X.
2. Быстрая и стабильная работа: Xming обладает высокой производительностью и стабильностью, что обеспечивает плавное отображение графических приложений и минимальное количество сбоев.
3. Простота настройки: Xming имеет интуитивно понятный и легко настраиваемый интерфейс. Он предлагает широкий спектр опций и параметров, которые позволяют настроить X-сервер под ваши индивидуальные потребности.
4. Поддержка мультимониторных систем: Xming позволяет использовать несколько мониторов для отображения графических приложений, что увеличивает рабочее пространство и повышает эффективность работы.
5. Легкость установки и использования: Xming поставляется в виде установщика, который обеспечивает простую и быструю установку. После установки Xming автоматически запускается и готов к использованию.
6. Большое сообщество: Xming имеет активное сообщество пользователей, которые предлагают поддержку, советы и решения проблем. Вы всегда можете обратиться к сообществу за помощью или поделиться своим опытом.
В целом, Xming — это мощный и удобный инструмент для запуска графических приложений на удаленном сервере и отображения их на вашем компьютере. Он обладает множеством функций и преимуществ, что делает его идеальным выбором для разработчиков, администраторов и любых пользователей, работающих с графическими приложениями.
Почему Xming необходим для пользователей Windows?
Вот где Xming входит в игру: он является X-сервером для Windows, который позволяет исполнять приложения, разработанные для X Window System, на компьютерах с ОС Windows. Xming предоставляет полностью функциональную среду X Window System внутри Windows и позволяет пользователю использовать графический интерфейс множества приложений, включая терминалы, редакторы, графические редакторы и другие инструменты.
Одной из основных причин использования Xming является доступ к готовым инструментам и приложениям в Linux и Unix, которые могут быть необходимы для работы или развлечения пользователей. Также Xming позволяет пользователям обмениваться рабочим столом между системами, виртуальными машинами или с удаленной машиной через сеть. Это особенно полезно для разработчиков программного обеспечения, которые могут разрабатывать и отлаживать приложения на разных системах без необходимости переключения компьютеров.
Кроме того, Xming обеспечивает полностью настраиваемую среду, которая поддерживает настройку различных параметров, таких как шрифты, цветовая схема, разрешение экрана и другие опции, позволяя полностью адаптировать X Window System к нуждам пользователей Windows.
Безусловно, Xming является незаменимым инструментом для пользователей Windows, которые нуждаются в доступе к приложениям, разработанным для X Window System, или желают работать с Linux или Unix-системами на своем компьютере с ОС Windows.
Как подключить Xming к Windows?
Для подключения Xming к операционной системе Windows вам потребуется выполнить следующие шаги:
| Шаг 1: | Скачайте установщик Xming с официального сайта проекта. |
| Шаг 2: | Запустите установочный файл и следуйте инструкциям мастера установки. |
| Шаг 3: | Настройте параметры Xming согласно вашим потребностям. Укажите, какие опции и варианты инсталлировать, чтобы получить необходимую функциональность. |
| Шаг 4: | После завершения установки запустите Xming с помощью ярлыка на рабочем столе или из меню «Пуск». |
| Шаг 5: | Проверьте работоспособность Xming, запустив приложение, которое использует графический интерфейс (например, xterm или xclock). |
| Шаг 6: | Если необходимо, настройте дополнительные параметры Xming, такие как автоматический запуск при старте Windows или настройка сетевых параметров. |
Теперь ваш Xming готов к использованию и может быть подключен к удаленному серверу X. Приложения с графическим интерфейсом, запущенные на удаленном сервере, будут отображаться на вашем компьютере под управлением Windows с помощью Xming.
Шаги установки Xming на компьютер
Для установки Xming на компьютер следуйте следующим шагам:
1. Перейдите на официальный веб-сайт Xming и загрузите последнюю версию программы для операционной системы Windows.
2. Запустите загруженный файл установки Xming.
3. В процессе установки выберите язык, в который будет переведен интерфейс программы.
4. Прочитайте и принимайте условия лицензионного соглашения, чтобы продолжить установку.
5. Выберите папку, в которую будет установлен Xming, либо оставьте значение по умолчанию.
6. Выберите, какие компоненты Xming вы хотите установить. Рекомендуется оставить все настройки по умолчанию.
7. Если у вас отсутствует Microsoft Visual C++ 2015 Redistributable, установите его, следуя инструкциям на экране.
8. Нажмите кнопку «Установить» и дождитесь завершения процесса установки.
9. После завершения установки вы можете запустить Xming и настроить его параметры согласно вашим потребностям.
Оказывается, что для Windows имеется замечательный X сервер, позволяющий прямо в Windows запускать и использовать Linux программы
Конечно, для новичков это кажется довольно сложно и дико, но на самом деле всё просто, запуская Xming на Windows вы открываете через сеть доступ к оконной системе вашей Windows, и любая, имеющая право и техническую возможность, программа сможет рисовать на рабочем столе Windows свои окна
Имеются 2 вопроса, какие приложения имеют возможность и как получить права
1. практически любое графическое приложение Linux может отображать себя на удалённые дисплеи, исключения наверно составляют mc, htop, mocp, но их можно запустить внутри xterm, gnome-terminal
2. Xming не ограничивает по IP адреса программы для подключения, но вынуждает использовать cookie для идентификации, за эту настройку отвечает программа putty (ssh клиент)
И так для установки и запуска необходимо скачать putty (ssh клиент) и набор компонентов Xming в первую очередь нужно взять Xming Xming-fonts, установка проста и тривиальна, а вот настройка рутинна и скучна, смотрите ролик
Вот, с помощью таких не хитрых операций, в течении минуты можно получить настроенные Linux приложения и даже в противной Windows можно будет поработать, конечне если не тошнит от её шрифтов
ps: в настройке putty — connection — SSH — X11 — X display location нужно указывать сетевое имя или реальный ip адрес Windows компьютера с запущеным Xming
pss: можно так же держать несколько X серверов используя число DISPLAY в настройка копии X сервера
psss: на 1 X сервер можно отображать приложения с разных хостов и от разных пользователей



