Время на прочтение
4 мин
Количество просмотров 340K
Сразу оговорюсь, «преодолевал» в названии отражает только тот факт, что теперь моя XP видит всю память, установленную на системной плате. Не я придумал способ, я просто им воспользовался и теперь хочу поделиться.
Вопрос о четырёх гигабайтах памяти в Windows XP (здесь, и далее 32 бит) поднимался на просторах Интернет неоднократно. И так же неоднократно делался вывод, что более четырёх увидеть в принципе невозможно, а так как оборудование тоже требует адресного пространства, то и того меньше. Обычно 3.25 Гб, или около того. Очень подробно и убедительно история вопроса освещена здесь: Четыре гигабайта памяти — недостижимая цель?
Меня этот вопрос тоже волновал. Хотя, казалось бы, можно поставить 64 битную систему, или даже Windows Server (как известно он даже в 32-битной версии видит всю память), но я хотел пользоваться Windows XP. Два раза за последние 3 года я переходил на Windows 7, в первый раз на 64-битную, второй раз на 32-х битную, но в итоге оба раза вернулся назад на XP, которая живёт у меня без переустановки с 2007 года.
Последний раз я отказался от семёрки в пользу старушки буквально две недели назад. Притом, надо отметить, что семёрка была хоть и 32-х битная, но в ней была разблокирована возможность видеть всю доступную память. Способ разблокировки доступен в Интернет. И теперь мне с новой силой захотелось решить этот вопрос и в XP.
Поиски привели на этот сайт: Patch Vista’s Kernel to Address more than 4 GB of Memory
Статья посвящена разблокировке Windows Vista, зато в комментариях, пара человек описывает аналогичный способ для Windows XP. Я решил последовать их советам и опробовать эту методику на практике.
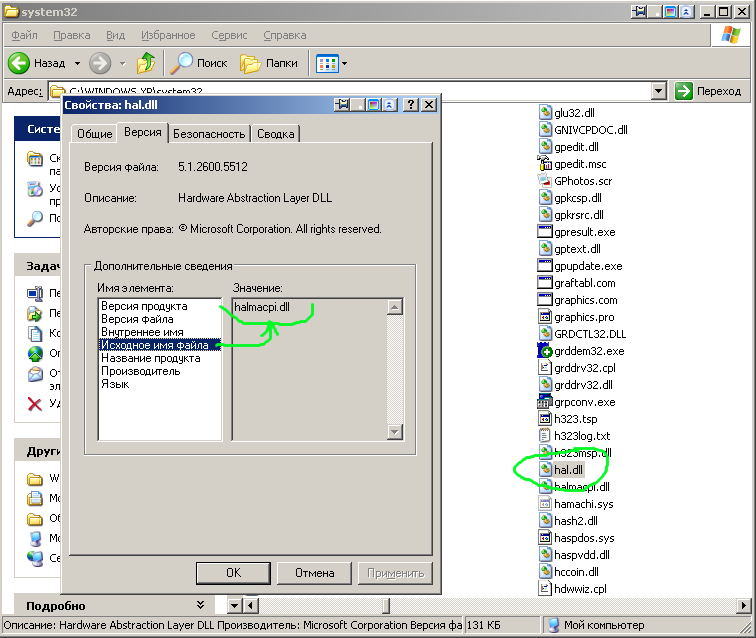
Для начала нужен дистрибутив Windows XP SP1. Возможно, подойдёт и просто первый сервиспак, не знаю, у меня его нет. В общем-то, там нужен только один файл. А именно файл библиотеки Hardware Abstraction Layer. Начиная со второго сервиспака эта библиотека работает с PAE «фиктивно», т.е. даже если режим расширенной трансляции адресов включён – он ничего не делает и не выходит за пределы четырёх гигабайт. А вот библиотека от первого сервиспака работает полноценно и может адресоваться ко всей доступной памяти, аналогично тому, как работает с памятью 32-битный Windows Server. В установленной Windows XP данный файл называется hal.dll, но в дистрибутиве имеется несколько HAL-файлов, и только один из них инсталлируется в систему под именем hal.dll в процессе установки. Необходимо было узнать, какой из файлов нужно использовать на моём конкретном оборудовании. Делается это просто, надо вызвать Свойства в контекстном меню проводника на файле hal.dll в установленной Windows. Файл находится в папке %systemroot%\system32, и вот что я увидел:
В дистрибутиве Windows XP SP1 в папке I386, я взял файл HALMACPI.DL_. Это архив, в котором находится один файл, искомый мной halmacpi.dll. Я его извлёк WinRAR’ом, но можно обойтись и командной строкой:
expand HALMACPI.DL_ HALMACPI.DLL
Полученный файл надо поместить в папку %systemroot%\system32, что я и сделал. Хочу ещё раз обратить внимание, что если кто-то захочет повторить мои шаги, файл надо брать с именем, указанном в свойстве «Исходное имя файла» в свойствах hal.dll из установленной Windows XP.
Второе, что необходимо сделать, это получить пропатченную версию ядра Windows. Как известно, существует 4-ре версии ядра:
- ntoskrnl.exe — однопроцессорное ядро Windows.
- ntkrnlmp.exe— многопроцессорное ядро Windows.
- ntkrnlpa.exe — однопроцессорное ядро Windows с более чем 3 ГБ оперативной памяти.
- ntkrpamp.exe — многопроцессорное ядро Windows с более чем 3 ГБ оперативной памяти.
В той инструкции, которую я использовал, говорилось про ядро ntkrnlpa.exe и в моей инсталляции Windows стоит именно оно. Что делать, если попадётся другое ядро – я, честно говоря, не знаю.
Первым делом, я сделал копию ядра, назвал его krnl16.exe, в принципе название неважно. Далее HEX-редактором (я использовал DOS-Navigator, по старой памяти) надо найти последовательность
- BB 00 00 10 00 33 FF 6A 07 8B F0 и заменить её на
- BB 00 00 40 00 33 FF 6A 07 8B F0
Здесь 1000h = 4096 Мб, заменяем на 4000h = 16384 Мб. Т.е. поднимаем ограничение до 16Гб. В принципе, можно вписать и большее число. Пропатченный файл также должен располагаться в system32.
Теперь осталось отредактировать boot.ini. Нужно скопировать имеющуюся строчку и дописать пару параметров. У меня была строка:
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS.XP=«Microsoft Windows XP Professional RU» /FASTDETECT /USEPMTIMER /NOSERIALMICE /NOEXECUTE=OPTIN
Я добавил в неё /KERNEL=KRNL16.EXE /HAL=HALMACPI.DLL /PAE и в результате получилось:
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS.XP=«Microsoft Windows XP Professional RU 16Gb» /FASTDETECT /USEPMTIMER /NOSERIALMICE /NOEXECUTE=OPTIN /KERNEL=KRNL16.EXE /HAL=HALMACPI.DLL /PAE
Теперь есть возможность загружаться как в стандартный Windows с присущим ему ограничением на память, так и в пропатченный, так как я не заменял ни одного системного файла, а только добавил два, которые включаются в работу с помощью вышеописанных параметров boot.ini
Ребут!
И… BSOD.
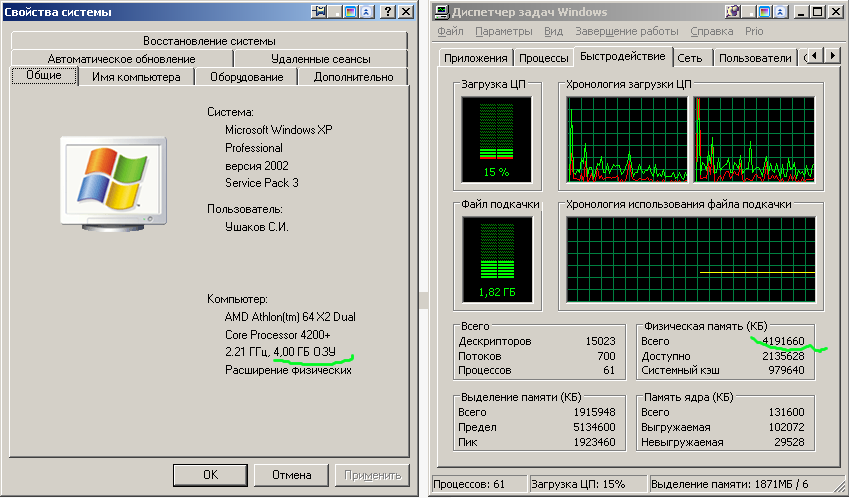
В принципе, такое может быть. Как следует из обзора истории проблемы на ixbt причиной, по которой Microsoft отключила адресацию верхней памяти, было существование кривых драйверов под различное оборудование, кривизна которых, впрочем, проявлялась только в полноценном режиме PAE. Вполне вероятно, у меня сбоит один из них, за 6 лет в системе накопилось много всего, но какой? Пробую запуститься в безопасном режиме, и УРА! Вот они, мои гигабайты:
Но как определить сбойный модуль? Погуглив, я нашёл для этого методику, которая заключается в анализе малого дампа памяти, создаваемого Windows при BSOD. Анализ производится программой Blue Screen View, но вот все найденные мной способы включения режима записи дампа к успеху не привели: дамп не создавался, поэтому пришлось использовать научный метод тыка. Для начала я деинсталлировал то ненужное, что нашлось в системе. А именно драйвер защиты Guardant и драйвера ATI от старой видеокарты.
Ребут.
Результат превзошёл мои ожидания. Честно говоря, я не ожидал, что метод тыка даст такие результаты, и попробовал его просто, чтобы сделать хоть что-нибудь. Который из драйверов вызывал проблему, я точно не знаю, но думаю, что, скорее всего Guardant.
Но главное: цель достигнута, и теперь я подумываю о расширении памяти до 8-ми Гб.
- Примечание 1. Поскольку в методике используется dll из первого сервиспака, есть вероятность, что в ней имеются какие-либо уязвимости, закрытые последующими сервиспаками. Я не изучал этот вопрос.
- Примечание 2. Некоторые драйверы в пропатченой Windows XP могут вызывать BSOD. Впрочем, их крайне мало в природе.
- Примечание 3. В первоисточнике ценных знаний сообщают, что на некоторых системах имеются проблемы с USB при использовании данной методики. У меня пока проблем нет. По крайней мере, клавиатуры, мышки и флешки работают в штатном режиме.
Привет, друзья. У нас на сайте в категории публикаций о компьютерном железе есть статья «Как узнать, сколько оперативной памяти поддерживает компьютер или ноутбук». Это небольшой мануал, в нём показывается, как на официальных сайтах материнских плат, процессоров и ноутбуков, а также с помощью программы AIDA64 узнать максимально возможный объём оперативной памяти. Тот граничный объём, который мы при желании сможем установить на наше компьютерное устройство в соответствии с заложенным в него по этой части потенциалом. Но, друзья, многие ли из вас знают, что и Windows, причём даже в 64-битной версии, также имеет максимальный объём поддержки оперативной памяти? Давайте посмотрим, какой потенциал в этом плане есть у операционной системы от Microsoft.
Сколько оперативной памяти поддерживает Windows
Если не все из вас, то как минимум большинство, прекрасно знают, что 32-битная Windows видит максимум 4 Гб оперативной памяти компьютера. Если на нём установлен больший объём, 32-битная система не будет его видеть. Если у компьютера больше 4 Гб памяти, нужно использовать только 64-битную Windows. Это, безусловно, так, но только для большей части выпусков Windows. У старых версий операционной системы есть 32-битные редакции, которые поддерживают меньший, нежели 4 Гб, объём оперативной памяти. Что же касается 64-битных систем, то и у них есть свой лимит поддержки. Со времён Windows XP этот лимит увеличился в разы, тем не менее даже для Windows 10 он существует. Ну а теперь давайте конкретно разберём, какие выпуски системы сколько оперативной памяти поддерживают.
Windows 10
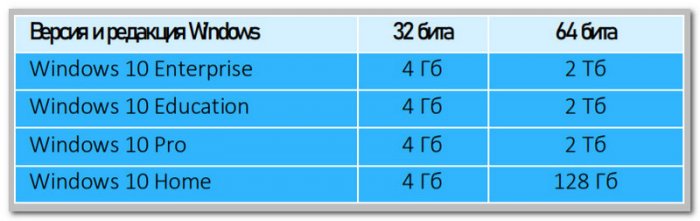
32-битные редакции Windows 10 поддерживают стандартный максимум оперативной памяти 4 Гб. 64-битные редакции Pro, Enterprise и Education – максимум 2 Тб. Редакция Home ограничена 128 Гб.
Windows 8.1
Все 32-битные редакции Windows 8.1 ограничены видимостью 4 Гб памяти. 64-битные редакции Pro и Enterprise видят максимум 512 Гб. А базовая редакция Core (это аналог Home) – максимум 128 Гб.
Windows 7
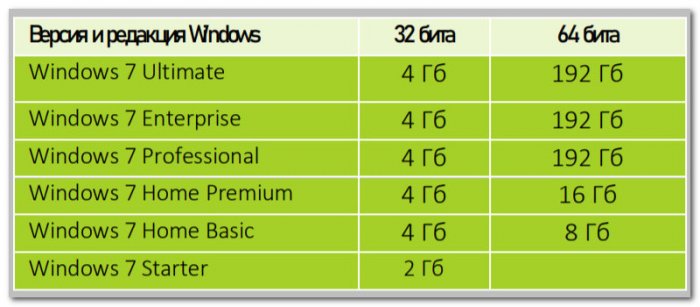
64-битные редакции Ultimate, Enterprise, Professional поддерживают 192 Гб оперативной памяти. Но, внимание тех, друзья, кто хочет увеличить объём памяти на устройствах с лицензионными младшими 64-битными редакциями Windows 7: Home Premium видит максимум 16 Гб, а Home Basic – максимум 8 Гб. У Windows 7 есть ещё базовая редакция Starter, она поставляется только 32-битной, предназначена специально для маломощных компьютеров и поддерживает только 2 Гб оперативной памяти. Остальные 32-битные редакции Windows 7 видят стандартный граничный объём 4 Гб.
Windows Vista
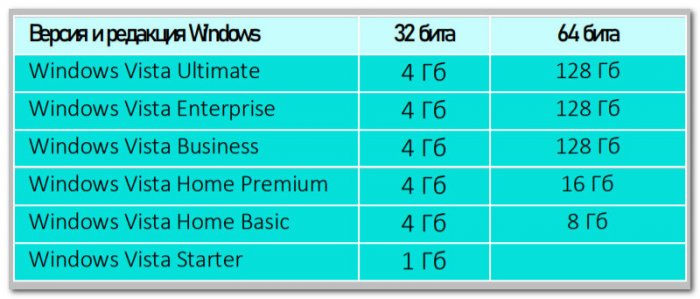
32-битные редакции Windows Vista ограничиваются стандартом 4 Гб. Но, как и у Windows 7, у Vista есть базовая только 32-битная редакция Starter, и она видит только 1 Гб оперативной памяти. 64-битные редакции Home Basic и Home Premium видят, соответственно, максимум 8 Гб и 16 Гб. 64-битные редакции Business, Enterprise, Ultimate поддерживают максимум 128 Гб.
Windows XP
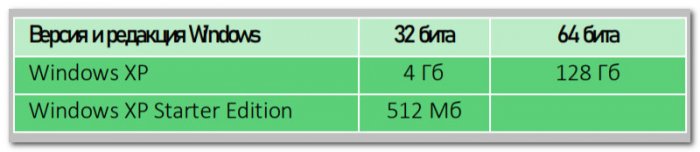
Windows XP 32-битная видит максимум 4 Гб, 64-битная – максимум 128 Гб. У XP также есть базовая только 32-битная редакция Starter Edition, и она может видеть максимум 512 Мб оперативной памяти.
Особенности поддержки 32-битной Windows 4 Гб оперативной памяти
Друзья, 4 Гб — это номинальный показатель поддержки оперативной памяти 32-битными Windows. На деле 32-битная Windows может не видеть все 4 Гб и ограничиваться 3 Гб с лишним. Чтобы она видела все 4 Гб, нужно кое-что проделать в операционной системе. Что, смотрим в статье сайта «Как заставить 32-битную Windows использовать более 3 Гб оперативной памяти».
Не все знают, что операционные системы Windows от компании Microsoft поддерживают только определенный объем оперативной памяти. Поэтому если вы используете, к примеру, Windows XP 32 bit, то даже при наличии 16 Гб оперативной памяти система будет поддерживать не более 4 Гб из них, а на деле еще меньше. Связано это с внутренними архитектурными ограничениями.
Сегодня я расскажу о том, сколько памяти поддерживает эта операционная система в различных ее поколениях.
- Windows XP x86 (32 bit): 4 гб
- Windows XP x64 (64 bit): 128 Гб
Windows 7
- Windows 7 Starter x86 (32 bit): 2 Гб
- Windows 7 Home Basic x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 7 Home Premium x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 7 Professional x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 7 Enterprise x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 7 Ultimate x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 7 Home Basic x64 (64 bit): 8 Гб
- Windows 7 Home Premium x64 (64 bit): 16 Гб
- Windows 7 Professional x64 (64 bit): 192 Гб
- Windows 7 Enterprise x64 (64 bit): 192 Гб
- Windows 7 Ultimate x64 (64 bit): 192 Гб
Windows 8
- Windows 8 x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 8 Professional x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 8 Enterprise x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 8 x64 (64 bit): 128 Гб
- Windows 8 Professional x64 (64 bit): 512 Гб
- Windows 8 Enterprise x64 (64 bit): 512 Гб
Windows 10
- Windows 10 Home x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 10 Home x64 (64 bit): 128 Гб
- Windows 10 Pro x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб
- Windows 10 Pro x64 (64 bit): 512 Гб
Как видите, 64-битная редакция поддерживает практически невероятный объем оперативной памяти, которого с лихвой хватит для домашнего пользования. А вот в случае с 32-битной версией нужно быть внимательным: зачастую система не поддерживает даже указанные 4 Гб, оставляя пользователю от 2,8 Гб до 3,5 Гб памяти.
Виртуальное адресное пространство пользовательского режима для каждого 64-разрядного процесса
Не применяются
С изображением _ Набор _ с _ _ учетом больших адресов файлов (по умолчанию):
x64: Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 или более поздней версии: 128 тб
x64: Windows 8 и Windows Server 2012 или более ранняя 8 тб
Системы на базе Intel Itanium: 7 ТБ
384 гб или предельное число системных фиксаций, в зависимости от того, какое значение меньше Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2: 15,5 тб или предельное число системных фиксаций, в зависимости от
Windows server 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 и Windows Vista: 128 гб или предельное число системных фиксаций, в зависимости от того, что меньше
Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP: До 128 ГБ в зависимости от конфигурации и ОЗУ.
озу или 128 гб, в зависимости от того, какой размер меньше (адресное пространство ограничено 2 x RAM) Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2: озу или 16 тб, в зависимости от того, какое значение меньше (адресное пространство ограничено 2 x RAM).
Windows server 2008 R2, Windows 7 и Windows server 2008: 75% от озу до максимум 128 гб
Windows Vista: 40% озу не более 128 гб.
Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP: До 128 ГБ в зависимости от конфигурации и ОЗУ.
всегда 1 тб независимо от объема физической памяти Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2: 16 тб.
Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP: До 1 ТБ в зависимости от конфигурации и ОЗУ.
ограничения физической памяти: Windows 11
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения физической памяти для Windows 11.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 | Ограничение на ARM64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Корпоративная | 4 Гб | 6 TБ | 6 TБ |
| Windows 10 для образовательных учреждений | 4 Гб | 2 ТБ | 2 ТБ |
| Windows 10 Pro для рабочих станций | 4 Гб | 6 TБ | 6 TБ |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 Гб | 2 ТБ | 2 ТБ |
| Windows 10 Домашняя | 4 Гб | 128 ГБ | 128 ГБ |
Ограничения физической памяти: Windows 10
В следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows 10.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Корпоративная | 4 Гб | 6 TБ |
| Windows 10 для образовательных учреждений | 4 Гб | 2 ТБ |
| Windows 10 Pro для рабочих станций | 4 Гб | 6 TБ |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 Гб | 2 ТБ |
| Windows 10 Домашняя | 4 Гб | 128 ГБ |
Ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2016
В следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2016.
| Версия | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2016 Datacenter | 24 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard | 24 ТБ |
Ограничения физической памяти: Windows 8
В следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows 8.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 8 Корпоративная | 4 Гб | 512 ГБ |
| Windows 8 Профессиональная | 4 Гб | 512 ГБ |
| Windows 8 | 4 Гб | 128 ГБ |
Ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2012
В следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2012. Windows Server 2012 доступен только в выпусках X64.
| Версия | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | 4 TБ |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard | 4 TБ |
| Windows Server 2012 Essentials | 64 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2012 Foundation | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard | 4 TБ |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 | 4 TБ |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows 7
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения физической памяти для Windows 7.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 Максимальная | 4 Гб | 192 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Корпоративная | 4 Гб | 192 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Профессиональная | 4 Гб | 192 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Домашняя расширенная | 4 Гб | 16 Гб |
| Windows 7 Домашняя базовая | 4 Гб | 8 Гб |
| Windows 7 Начальная | 2 Гб | Н/Д |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2008 R2
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2008 R2. Windows Сервер 2008 R2 доступен только в 64-разрядных выпусках.
| Версия | Ограничение в x64 | Ограничение на IA64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter | 2 ТБ | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise | 2 ТБ | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 для систем на базе Itanium | 2 ТБ | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | 8 Гб | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | 32 ГБ | |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | 128 ГБ | |
| Windows Web Server 2008 R2 | 32 ГБ |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2008
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2008. ограничения, превышающие 4 гб для 32-разрядных Windows предполагают, что PAE включен.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 | Ограничение на IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 Datacenter | 64 ГБ | 1 TБ | |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise | 64 ГБ | 1 TБ | |
| Windows Server 2008 HPC Edition | 128 ГБ | ||
| Windows Server 2008 Standard | 4 Гб | 32 ГБ | |
| Windows Server 2008 для систем на базе процессоров Itanium | 2 ТБ | ||
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 | 4 Гб | 32 ГБ | |
| Windows Web Server 2008 | 4 Гб | 32 ГБ |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Vista
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Vista.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Vista Ultimate | 4 Гб | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Enterprise | 4 Гб | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Business | 4 Гб | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | 4 Гб | 16 Гб |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | 4 Гб | 8 Гб |
| Windows Vista Starter | 1 ГБ |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Home Server
Windows Home Server доступен только в 32-разрядном выпуске. Ограничение физической памяти — 4 ГБ.
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2003 R2
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2003 R2. ограничения свыше 4 гб для 32-разрядных Windows предполагают, что PAE включен.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Сервер 2003 R2 Datacenter Edition | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
1 TБ |
| Windows сервер 2003 R2 выпуск Enterprise | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
1 TБ |
| Windows сервер 2003 R2 выпуск Standard | 4 Гб | 32 ГБ |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2003 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2003 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2). ограничения свыше 4 гб для 32-разрядных Windows предполагают, что PAE включен.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 | Ограничение на IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Сервер 2003 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2), Datacenter Edition | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
1 TБ | 2 ТБ |
| Windows сервер 2003 с пакетом обновления 2 (sp2), выпуск Enterprise | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
1 TБ | 2 ТБ |
| Windows сервер 2003 с пакетом обновления 2 (sp2), выпуск Standard | 4 Гб | 32 ГБ |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2003 с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1)
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2003 с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1). ограничения свыше 4 гб для 32-разрядных Windows предполагают, что PAE включен.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 | Ограничение на IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Сервер 2003 с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1), Datacenter Edition | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
1 ТБ | 1 ТБ |
| Windows сервер 2003 с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1), выпуск Enterprise | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
1 ТБ | 1 ТБ |
| Windows сервер 2003 с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1), выпуск Standard | 4 Гб | 32 ГБ |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Server 2003
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Server 2003. ограничения свыше 4 гб для 32-разрядных Windows предполагают, что PAE включен.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение на IA64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
512 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
512 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition | 4 Гб | |
| Windows Сервер 2003, Web Edition | 2 Гб | |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | 4 Гб | |
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | 32 ГБ | |
| Windows служба хранилища Server 2003 выпуск Enterprise | 8 Гб | |
| Windows Storage Server 2003 | 4 Гб |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows XP
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows XP.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 | Ограничение на IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP | 4 Гб | 128 ГБ | 128 ГБ (не поддерживается) |
| Windows XP Starter Edition | 512 Мб | Н/Д | Н/Д |
ограничения физической памяти: Windows Embedded
в следующей таблице указаны ограничения на физическую память для Windows Embedded.
| Версия | Ограничение на x86 | Ограничение в x64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Embedded | 4 Гб | |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | 4 Гб | |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | 4 Гб | 192 ГБ |
Влияние графических карт и других устройств на ограничения памяти
устройства должны сопоставлять память ниже 4 гб для совместимости с Windows выпусками, не поддерживающими PAE. Таким образом, если в системе имеется 4 ГБ ОЗУ, некоторые из них отключены или повторно сопоставлены с BIOS 4 ГБ. при повторном отображении памяти память X64 Windows может использовать эту память. клиентские версии Windows X86 не поддерживают физическую память свыше 4 гб, поэтому они не могут получить доступ к этим переназначенным регионам. любой выпуск X64 Windows или X86 Server может.
Версии клиента x86 с включенным PAE имеют доступное 37-разрядное (128 ГБ) физическое адресное пространство. Ограничением, которое накладывает эти версии, является максимально допустимый физический электронный адрес, а не размер пространства операций ввода-вывода. Это означает, что драйверы, поддерживающие PAE, могут фактически использовать физическое пространство свыше 4 ГБ при необходимости. Например, драйверы могут сопоставлять «потерянные» области памяти, расположенные выше 4 ГБ, и предоставлять эту память как электронный диск.
Источник
Как я преодолевал предел 4Гб на Windows XP 32бит
Сразу оговорюсь, «преодолевал» в названии отражает только тот факт, что теперь моя XP видит всю память, установленную на системной плате. Не я придумал способ, я просто им воспользовался и теперь хочу поделиться.
Вопрос о четырёх гигабайтах памяти в Windows XP (здесь, и далее 32 бит) поднимался на просторах Интернет неоднократно. И так же неоднократно делался вывод, что более четырёх увидеть в принципе невозможно, а так как оборудование тоже требует адресного пространства, то и того меньше. Обычно 3.25 Гб, или около того. Очень подробно и убедительно история вопроса освещена здесь: Четыре гигабайта памяти — недостижимая цель?
Меня этот вопрос тоже волновал. Хотя, казалось бы, можно поставить 64 битную систему, или даже Windows Server (как известно он даже в 32-битной версии видит всю память), но я хотел пользоваться Windows XP. Два раза за последние 3 года я переходил на Windows 7, в первый раз на 64-битную, второй раз на 32-х битную, но в итоге оба раза вернулся назад на XP, которая живёт у меня без переустановки с 2007 года.
Последний раз я отказался от семёрки в пользу старушки буквально две недели назад. Притом, надо отметить, что семёрка была хоть и 32-х битная, но в ней была разблокирована возможность видеть всю доступную память. Способ разблокировки доступен в Интернет. И теперь мне с новой силой захотелось решить этот вопрос и в XP.
Поиски привели на этот сайт: Patch Vista’s Kernel to Address more than 4 GB of Memory
Статья посвящена разблокировке Windows Vista, зато в комментариях, пара человек описывает аналогичный способ для Windows XP. Я решил последовать их советам и опробовать эту методику на практике.
Для начала нужен дистрибутив Windows XP SP1. Возможно, подойдёт и просто первый сервиспак, не знаю, у меня его нет. В общем-то, там нужен только один файл. А именно файл библиотеки Hardware Abstraction Layer. Начиная со второго сервиспака эта библиотека работает с PAE «фиктивно», т.е. даже если режим расширенной трансляции адресов включён – он ничего не делает и не выходит за пределы четырёх гигабайт. А вот библиотека от первого сервиспака работает полноценно и может адресоваться ко всей доступной памяти, аналогично тому, как работает с памятью 32-битный Windows Server. В установленной Windows XP данный файл называется hal.dll, но в дистрибутиве имеется несколько HAL-файлов, и только один из них инсталлируется в систему под именем hal.dll в процессе установки. Необходимо было узнать, какой из файлов нужно использовать на моём конкретном оборудовании. Делается это просто, надо вызвать Свойства в контекстном меню проводника на файле hal.dll в установленной Windows. Файл находится в папке %systemroot%system32, и вот что я увидел:
В дистрибутиве Windows XP SP1 в папке I386, я взял файл HALMACPI.DL_. Это архив, в котором находится один файл, искомый мной halmacpi.dll. Я его извлёк WinRAR’ом, но можно обойтись и командной строкой:
expand HALMACPI.DL_ HALMACPI.DLL
Полученный файл надо поместить в папку %systemroot%system32, что я и сделал. Хочу ещё раз обратить внимание, что если кто-то захочет повторить мои шаги, файл надо брать с именем, указанном в свойстве «Исходное имя файла» в свойствах hal.dll из установленной Windows XP.
Теперь осталось отредактировать boot.ini. Нужно скопировать имеющуюся строчку и дописать пару параметров. У меня была строка:
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)WINDOWS.XP=«Microsoft Windows XP Professional RU» /FASTDETECT /USEPMTIMER /NOSERIALMICE /NOEXECUTE=OPTIN
Я добавил в неё /KERNEL=KRNL16.EXE /HAL=HALMACPI.DLL /PAE и в результате получилось:
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)WINDOWS.XP=«Microsoft Windows XP Professional RU 16Gb» /FASTDETECT /USEPMTIMER /NOSERIALMICE /NOEXECUTE=OPTIN /KERNEL=KRNL16.EXE /HAL=HALMACPI.DLL /PAE
Теперь есть возможность загружаться как в стандартный Windows с присущим ему ограничением на память, так и в пропатченный, так как я не заменял ни одного системного файла, а только добавил два, которые включаются в работу с помощью вышеописанных параметров boot.ini
Ребут!
И… BSOD.
В принципе, такое может быть. Как следует из обзора истории проблемы на ixbt причиной, по которой Microsoft отключила адресацию верхней памяти, было существование кривых драйверов под различное оборудование, кривизна которых, впрочем, проявлялась только в полноценном режиме PAE. Вполне вероятно, у меня сбоит один из них, за 6 лет в системе накопилось много всего, но какой? Пробую запуститься в безопасном режиме, и УРА! Вот они, мои гигабайты:
Но как определить сбойный модуль? Погуглив, я нашёл для этого методику, которая заключается в анализе малого дампа памяти, создаваемого Windows при BSOD. Анализ производится программой Blue Screen View, но вот все найденные мной способы включения режима записи дампа к успеху не привели: дамп не создавался, поэтому пришлось использовать научный метод тыка. Для начала я деинсталлировал то ненужное, что нашлось в системе. А именно драйвер защиты Guardant и драйвера ATI от старой видеокарты.
Ребут.
Результат превзошёл мои ожидания. Честно говоря, я не ожидал, что метод тыка даст такие результаты, и попробовал его просто, чтобы сделать хоть что-нибудь. Который из драйверов вызывал проблему, я точно не знаю, но думаю, что, скорее всего Guardant.
Но главное: цель достигнута, и теперь я подумываю о расширении памяти до 8-ми Гб.
Источник
Максимальные объемы памяти для ОС Windows
↑ следующая новость | предыдущая новость ↓
Максимальные объемы памяти и адресного пространства зависят от платформы, операционной системы, а также от значения параметра IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE в структуре LOADED_IMAGE и настроек 4GT (4-gigabyte tuning), если они используются. Параметр IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE может принимать значения «set» (установка) или «cleared» (сброс) – в зависимости от выбранной опции /LARGEADDRESSAWARE. 4GT (или технология настройки памяти для приложений, или переключатель /3GB switch) – это технология (применяемая только в 32-битных системах), с помощью которой можно изменять объем виртуального адресного пространства, доступного для пользовательских приложений. Применение этой технологии позволяет уменьшить общий объем системного виртуального адресного пространства и за счет этого максимизировать ресурс системы.
Физические ограничения на объем памяти для 32-битных платформ также зависят от поддержки технологии Physical Address Extension (PAE), которая позволяет 32-битным версиям Windows использовать более 4 ГБ физической памяти.
Максимальные объемы памяти и адресного пространства
В таблице ниже приведены значения максимальных объемов памяти и адресного пространства для поддерживаемых версий Windows. Если не оговорено иное, указанные значения распространяются на все поддерживаемые версии.
| Тип памяти | Версии Windows x32 | Версии Windows x64 | |
| Виртуальное адресное пространство пользовательских приложений для каждого 32-битного процесса |
2 ГБ.
До 3 ГБ при использовании IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE и 4GT |
2 ГБ при значении IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE «cleared» (используется по умолчанию).
От 1 до 2 ГБ при использовании 4GT |
8 ТБ.
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – 128 ТБ |
| Выгружаемый стек (Paged pool) | 384 ГБ или назначенный лимит системы, который в любом случае меньше.
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – 15,5 ТБ или назначенный лимит системы, который в любом случае меньше. Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 и Windows Vista – лимитируется объемом доступного виртуального адресного пространства для системных приложений. Начиная с Windows Vista с пакетом Service Pack 1 (SP1), объем выгружаемого стека также может лимитироваться значением ключа реестра PagedPoolLimit. Windows Home Server и Windows Server 2003 – 530 МБ. Windows XP – 490 МБ |
384 ГБ или назначенный лимит системы, который в любом случае меньше.
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – 15,5 ТБ или назначенный лимит системы, который в любом случае меньше. Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 и Windows Vista – 128 ГБ или назначенный лимит системы, который в любом случае меньше. Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP – до 128 ГБ в зависимости от конфигурации и RAM. |
|
| Невыгружаемый стек (Nonpaged pool) | 75% RAM или 2 ГБ (заведомо меньше).
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – объем RAM или 16 ТБ (заведомо меньше); объем адресного пространства лимитирован двойным объемом RAM. Windows Vista – лимитируется только объемами виртуального адресного пространства для системных приложений и физической памяти. Начиная с Windows Vista с пакетом SP1, объем невыгружаемого стека также может лимитироваться значением ключа реестра NonPagedPoolLimit. Windows Home Server, Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP – 256 МБ; при использовании 4GT – 128 МБ. |
Объем RAM или 128 ГБ (заведомо меньше); объем адресного пространства лимитирован двойным объемом RAM.
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – объем RAM или 16 ТБ (заведомо меньше); объем адресного пространства лимитирован двойным объемом RAM. Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 – 75% RAM (не более 128 ГБ). Windows Vista – 40% RAM (не более 128 ГБ). Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP – до 128 ГБ в зависимости от конфигурации и RAM. |
|
| Виртуальное адресное пространство системного кэша (физически ограничено только физической памятью) | Лимитируется доступным объемом виртуального адресного пространства для системных приложений или значением ключа реестра SystemCacheLimit.
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – 16 ТБ. Windows Vista – лимитируется только доступным объемом виртуального адресного пространства для системных приложений. Начиная с Windows Vista с пакетом SP1, объем виртуального адресного пространства системного кэша может также лимитироваться значением ключа реестра SystemCacheLimit. Windows Home Server, Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP – 860 МБ при установке значения «set» ключа реестра LargeSystemCache и без использования 4GT; до 448 МБ – при использовании 4GT. |
1 TB независимо от объема физической RAM.
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – 16 ТБ. Windows Server 2003 и Windows XP – до 1 ТБ в зависимости от конфигурации и RAM. |
Максимальные объемы оперативной памяти для версий ОС Windows
| Операционная система | Максимальный объем памяти |
| Windows 10 Enterprise x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 10 Enterprise x64 | 2 ТБ |
| Windows 10 Education x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 10 Education x64 | 2 ТБ |
| Windows 10 Pro x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 10 Pro x64 | 2 ТБ |
| Windows 10 Home x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 10 Home x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2016 Datacenter | 24 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard | 24 ТБ |
| Windows 8.1 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 8.1 x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows 8.1 Pro x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 8.1 Pro x64 | 512 ГБ |
| Windows 8.1 Enterprise x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 8.1 Enterprise x64 | 512 ГБ |
| Windows 8 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 8 x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows 8 Professional x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 8 Professional x64 | 512 ГБ |
| Windows 8 Enterprise x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 8 Enterprise x64 | 512 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials x64 | 64 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard x64 | 4 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter x64 | 4 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2012 Foundation x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2012 Essentials x64 | 64 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard x64 | 4 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2012 Datacenter x64 | 4 ТБ |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard x64 | 4 ТБ |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 x64 | 4 ТБ |
| Windows 7 Starter x32 | 2 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Home Basic x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Home Basic x64 | 8 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Home Premium x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Home Premium x64 | 16 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Professional x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Professional x64 | 192 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Enterprise x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Enterprise x64 | 192 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Ultimate x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows 7 Ultimate x64 | 192 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation x64 | 8 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise x64 | 2 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter x64 | 2 ТБ |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Web Server 2008 R2 x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems | 2 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2008 Foundation x64 | 8 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 Standard x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 Standard x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise x32 | 64 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2008 Datacenter x32 | 64 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 Datacenter x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2008 HPC Edition x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems | 2 ТБ |
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Web Server 2008 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Web Server 2008 x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Starter x32 | 1 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Home Basic x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Home Basic x64 | 8 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Home Premium x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Home Premium x64 | 16 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Business x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Business x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Enterprise x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Enterprise x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Ultimate x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Vista Ultimate x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows Home Server x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Web Edition x32 | 2 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Standard Edition x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Standard Edition x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Enterprise Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Enterprise Edition x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Datacenter Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Datacenter Edition x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Datacenter Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Datacenter Edition x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Datacenter Edition IA64 | 2 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Enterprise Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Enterprise Edition x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Enterprise Edition IA64 | 2 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Standard Edition x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Standard Edition x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Datacenter Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Datacenter Edition x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Datacenter Edition IA64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Enterprise Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Enterprise Edition x64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Enterprise Edition IA64 | 1 ТБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Standard Edition x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Standard Edition x64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition IA64 | 512 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition x32 | 64 ГБ (16 ГБ с 4GT) |
| Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition IA64 | 512 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Server 2003, Web Edition x32 | 2 ГБ |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 IA64 | 32 ГБ |
| Windows Storage Server 2003, Enterprise Edition x32 | 8 ГБ |
| Windows Storage Server 2003 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows XP x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows XP x64 | 128 ГБ |
| Windows XP Starter Edition x32 | 512 МБ |
| Windows XP Home Edition | 4 ГБ |
| Windows XP Professional Edition | 4 ГБ |
| Windows XP Professional x64 Edition | 128 ГБ |
| Windows XP Embedded x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 x32 | 4 ГБ |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 x64 | 192 ГБ |
Примечание – для 32-битных версий Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Windows Server 2003 лимит памяти свыше 4 ГБ предполагает использование PAE.
Влияние ограничений памяти на использование видеокарт и других устройств
Для обеспечения совместимости устройств с версиями Windows, не оснащенными PAE, используемая память устройств не должна превышать 4 ГБ. То есть, если система имеет 4 ГБ RAM, избыточная память некоторых устройств или не будет использоваться, или будет переформатирована BIOS’ом. С переформатированной памятью устройств могут работать 64-битные версии Windows. 32-битные пользовательские версии Windows не поддерживают физическую память свыше 4 ГБ, поэтому они не могут обращаться к переформатированным разделам, в отличие от 32-битных серверных версий или любых 64-битных версий.
Источник
Вам также понравится
Adblock
detector
Прошло несколько лет с тех пор, как была написана статья «Четыре гигабайта памяти — недостижимая цель?», а вопросов, почему Windows не видит все четыре гигабайта, меньше не стало. К числу вопрошающих добавились и обладатели 64-разрядных систем, которых эта проблема, казалось бы, не должна была коснуться. И стало ясно, что пора писать новую статью на эту же тему. Как и раньше, речь пойдет только об операционных системах Windows, причем в основном клиентских, то есть Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 и грядущей Windows 8. В некоторых случаях намеренно будут использоваться несколько упрощенные описания тех или иных аспектов. Это даст возможность сосредоточиться на предмете данной статьи, не вдаваясь в излишние подробности, в частности, внутреннего устройства процессоров и наборов микросхем (чипсетов) для системных плат. Рекомендуем предварительно прочитать указанную выше статью, так как не всё, сказанное в ней, будет повторено здесь.
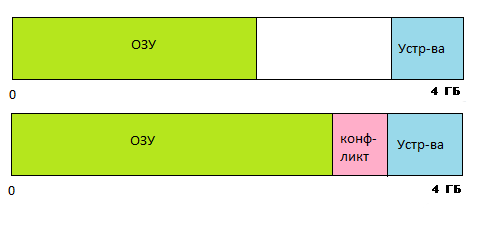
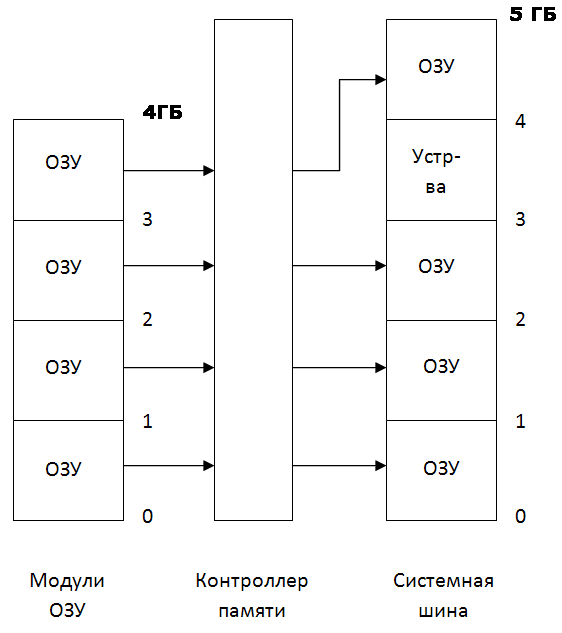
Хотя теоретически 32-разрядной системе доступны (без дополнительных ухищрений) до 4 ГБ физической памяти, 32-разрядные клиентские версии Windows не могут использовать весь этот объем из-за того, что часть адресов используется устройствами компьютера. Ту часть ОЗУ, адреса которой совпадают с адресами устройств, необходимо отключать, чтобы избежать конфликта между ОЗУ и памятью соответствующего устройства — например, видеоадаптера.
Рис. 1. Если оперативная память в адресах, используемых устройствами, не отключена, возникает конфликт
Оперативная память заполняет адреса, начиная с нулевого, а устройствам, как правило, отводятся адреса в четвертом гигабайте. Пока размер ОЗУ не превышает двух-трех гигабайт, конфликты не возникают. Как только верхняя граница установленной памяти входит в ту зону, где находятся адреса устройств, возникает проблема: по одному и тому же адресу находятся и ячейка оперативной памяти, и ячейка памяти устройства (того же видеоадаптера). В этом случае запись данных в память приведет к искажению изображения на мониторе и наоборот: изменение изображения — к искажению содержания памяти, то есть программного кода или данных (скажем, текста в документе). Чтобы конфликты не возникали, операционной системе приходится отказываться от использования той части ОЗУ, которая перекрывается с адресами устройств.
В середине девяностых годов прошлого века для расширения доступного объема ОЗУ была разработана технология PAE (Physical Address Extension), увеличивающая число линий адреса с 32 до 36 — тем самым максимальный объем ОЗУ вырастал с 4 до 64 ГБ. Эта технология первоначально предназначалась для серверов, однако позже появилась и в клиентской Windows XP. Некоторые особенности реализации этой технологии в современных контроллерах памяти дают возможность не только использовать PAE по ее прямому назначению, но и «перекидывать» память в другие адреса. Таким образом, часть памяти, которая ради предотвращения конфликтов не используется, может быть перемещена в старшие адреса, например в пятый гигабайт — и снова стать доступной системе.
В обсуждении первой статьи было высказано замечание, что некорректно отождествлять наличие в контроллере памяти системной платы поддержки PAE — и способность платы переадресовывать память; что это вполне могут быть вещи, друг с другом не связанные. Однако практика показывает, что в «железе» для настольных систем это понятия взаимозаменяемые. К примеру, Intel в документации к своему набору микросхем G35 ни слова не говорит о возможности (реально существующей) переадресации памяти, зато подчеркивает поддержку РАЕ. А не поддерживающий PAE набор i945 не имеет и переадресации памяти. С процессорами AMD64 и последними моделями процессоров Intel дело обстоит еще проще: в них контроллер памяти встроен в процессор, и поддержка PAE (и ОЗУ размером более 4 ГБ) автоматически подразумевает поддержку переадресации.
Рис. 2. Переадресация
Рисунок достаточно условный, переадресация совсем не обязательно выполняется блоками именно по одному гигабайту, дискретность может быть другой и определяется контроллером памяти (который, напомним, является либо частью оборудования системной платы, либо частью процессора). В программе BIOS Setup компьютера обычно бывает настройка, разрешающая или запрещающая переадресацию. Она может иметь различные наименования — например, Memory remap, Memory hole, 64-bit OS и тому подобное. Ее название лучше всего выяснить в руководстве к системной плате. Необходимо отметить, что если используется 32-разрядная система, то на некоторых системных платах, преимущественно достаточно старых, переадресацию необходимо отключать — в противном случае объем доступного системе ОЗУ может уменьшиться.
По умолчанию в Windows XP режим РАЕ был отключен, поскольку реальной надобности в нем не было (напомним, что в 2001 году типичный объем памяти настольного компьютера составлял 128—256 МБ). Тем не менее, если его включить, то ХР могла бы использовать все четыре гигабайта памяти — при условии, конечно, что системная плата поддерживала бы РАЕ. Но, повторим, реальной надобности включать этот режим в те годы не было. При желании читатель может для пробы установить на современный компьютер Windows XP или Windows XP SP1 (делать это для работы, конечно, не стоит), включить режим PAE и своими глазами убедиться, что системе доступны четыре гигабайта ОЗУ.
В 2003 году «Майкрософт» начала разрабатывать второй пакет исправлений для Windows XP (вышедший в 2004 году), поскольку столкнулась с необходимостью существенно снизить число уязвимостей в компонентах ОС. Одним из путей было использование предотвращения выполнения данных (Data Execution Prevention, DEP) — набора программных и аппаратных технологий, позволяющих выполнять дополнительные проверки содержимого памяти и в ряде случаев предотвращать запуск вредоносного кода. Эти проверки выполняются как на программном уровне, так и на аппаратном (при наличии соответствующего процессора). AMD назвала эту функцию процессора «защита страниц от выполнения» (no-execute page-protection, NX), а Intel использовала термин «запрет на выполнение» (Execute Disable bit, XD).
Однако использование такой аппаратной защиты требует перевода процессора в режим PAE, поэтому Windows XP SP2 при обнаружении подходящего процессора стала включать этот режим по умолчанию. И вот тут «Майкрософт» столкнулась с довольно серьезной проблемой: оказалось, что не все драйверы могут работать в режиме PAE. Попробуем пояснить эту особенность, не слишком углубляясь в устройство процессоров и механизмы адресации.
В Windows используется так называемая плоская модель памяти. Тридцать два разряда адреса обеспечивают обращение к пространству размером четыре гигабайта. Таким образом, каждой ячейке ОЗУ или ячейке памяти другого устройства соответствует определенный адрес, и никаких двусмысленностей тут быть не может. Включенный режим PAE дает возможность использовать 36 разрядов адреса и увеличить количество ячеек памяти в 16 раз. Но ведь система команд процессора остается той же самой и может адресовать только 4 миллиарда (двоичных) байтов! И вот, чтобы обеспечить возможность доступа к любому из 64 миллиардов байтов, указав только 32 разряда адреса, в процессоре включается дополнительный этап трансляции адресов (те, кого интересуют подробности, могут обратиться к специальной литературе — например, книге Руссиновича и Соломона «Внутреннее устройство Windows»). В результате 32-разрядный адрес в программе может указывать на любой из байтов в 36-разрядном пространстве.
Прикладных программ эта особенность никак не касается, они работают в своих собственных виртуальных адресах. А вот драйверам, которые должны обращаться к реальным адресам конкретных устройств, приходится решать дополнительные задачи. Ведь сформированный этим драйвером 32-разрядный адрес может после дополнительного этапа трансляции оказаться совсем другим, и выданная драйвером команда может, например, вместо вывода значка на экран изменить значение в одной из ячеек таблицы Excel. А если окажутся запорченными какие-либо системные данные, то тут и до аварийного завершения работы с выводом синего экрана рукой подать. Поэтому для успешной работы в режиме PAE драйверы должны быть написаны с учетом особенностей этого режима.
Однако поскольку исторически сложилось так, что до того времени в клиентских компьютерах PAE не использовался, некоторые компании не считали нужным поддерживать этот режим в написанных ими драйверах. Ведь оборудование, которое они выпускали (звуковые платы, к примеру), не предназначалось для серверов, и драйверы не имели серверной версии — так зачем без необходимости эти драйверы усложнять? Тем более, что для тестирования работы в режиме PAE раньше требовалось устанавливать серверную ОС и использовать серверное оборудование (системные платы для настольных компьютеров лишь относительно недавно стали поддерживать PAE). Так что разработчикам драйверов проще и выгоднее было просто забыть про этот PAE и обеспечить работоспособность на обычных клиентских компьютерах с обычными персональными, а не серверными ОС.
И вот с такими драйверами и возникли проблемы в XP SP2. Хотя количество фирм, драйверы которых переставали работать или даже вызывали крах системы, оказалось невелико, количество выпущенных этими фирмами устройств исчислялось миллионами. Соответственно, и количество пользователей, которые могли бы после установки SP2 получить неприятный сюрприз, оказывалось весьма значительным. В результате многие пользователи и сами отказались бы устанавливать этот пакет, и разнесли бы о нем дурную славу, что повлияло бы и на других пользователей. Они, хоть и без каких-либо веских причин, тоже отказались бы его устанавливать.
А необходимость повышения безопасности ХР компания «Майкрософт» ощущала очень остро. Впрочем, рассуждения на тему, почему мы увидели Windows XP SP2 и не увидели чего-то наподобие Windows XP Second Edition, выходят за рамки данной статьи.
Главное, что нас интересует, это то, что для обеспечения совместимости с плохо написанными драйверами функциональность PAE в SP2 для Windows XP была обрезана. И хотя сам этот режим существует и, более того, на компьютерах с современными процессорами включается по умолчанию, никакого расширения адресного пространства он не дает, просто передавая на выход те же адреса, которые были поданы на вход. Фактически система ведет себя как обычная 32-разрядная без PAE.
То же самое поведение было унаследовано Windows Vista, а затем перешло к Windows 7 и будущей Windows 8. Конечно, 32-разрядным. Причина, по которой это поведение не изменилось, осталась той же самой: обеспечение совместимости. Тем более что необходимость выгадывать доли гигабайта отпала: те, кому нужны большие объемы памяти, могут использовать 64-разрядные версии ОС.
Иногда можно услышать вопрос: если именно этот обрезанный режим PAE мешает системе видеть все четыре гигабайта — так, может, отключить его вовсе, чтобы не мешал, и, вуаля, системе станут доступны 4 ГБ? Увы, не станут: для этого требуется как раз наличие PAE, притом полноценного. Другой не так уж редко задаваемый вопрос звучит так: если устройства действительно мешают системе использовать всю память и резервируют ее часть под свои нужды, то почему же они ничего не резервировали, когда в компьютере стояло два гигабайта ОЗУ?
Вернемся к первому рисунку и рассмотрим ситуацию подробнее. Прежде всего отметим, что нужно четко различать два понятия: размер адресного пространства и объем ОЗУ. Смешение их воедино препятствует пониманию сути вопроса. Адресное пространство — это набор всех существующих (к которым может обратиться процессор и другие устройства) адресов. Для процессоров семейства i386 это 4 гигабайта в обычном режиме и 64 ГБ с использованием PAE. У 64-разрядных систем размер адресного пространства составляет 2 ТБ.
Размер адресного пространства никак не зависит от объема ОЗУ. Даже если вытащить из компьютера всю оперативную память, размер адресного пространства не изменится ни на йоту.
Адресное пространство может быть реальным, в котором работает сама операционная система, и виртуальным, которое ОС создает для работающих в ней программ. Но особенности использования памяти в Windows будут описаны в другой статье. Здесь же отметим только, что к реальному адресному пространству программы доступа не имеют — по реальным адресам могут обращаться только сама операционная система и драйверы.
Рассмотрим, как же в компьютере используется адресное пространство. Сразу подчеркнем, что его распределение выполняется оборудованием компьютера («железом») и операционная система в общем случае не может на это повлиять. Есть только один способ: изменить настройки оборудования с помощью технологии Plug&Play. О ней много говорили в середине 90-х годов прошлого века, но теперь она воспринимается как что-то само собой разумеющееся, и всё увеличивается число людей, которые о ней даже не слышали.
С помощью этой технологии можно изменять в определенных, заданных изготовителем, пределах адреса памяти и номера портов, используемых устройством. Это, в свою очередь, дает возможность избежать конфликтов между устройствами, которые могли бы произойти, если бы в компьютере оказалось два устройства, настроенных на использование одних и тех же адресов.
Базовая программа в системной плате, часто обобщенно называемая BIOS (хотя на самом деле BIOS (базовой системой ввода-вывода) она не является) при включении компьютера опрашивает устройства. Она определяет, какие диапазоны адресов каждое устройство может использовать, потом старается распределить память так, чтобы ни одно устройство не мешало другому, а затем сообщает устройствам свое решение. Устройства настраивают свои параметры согласно этим указаниям, и можно начинать загрузку ОС.
Раз уж об этом зашла речь, заметим, что в ряде системных плат есть настройка под названием «P&P OS». Если эта настройка выключена (No), то системная плата выполняет распределение адресов для всех устройств. Если включена (Yes), то распределение памяти выполняется только для устройств, необходимых для загрузки, а настройкой остальных устройств будет заниматься операционная система. В случае Windows XP и более новых ОС этого семейства данную настройку рекомендуется включать, поскольку в большинстве случаев Windows выполнит требуемую настройку по крайней мере не хуже, чем BIOS.
Поскольку при таком самоконфигурировании распределяются адреса памяти, не имеет никакого значения, сколько ОЗУ установлено в компьютере — процесс все равно будет протекать одинаково.
Когда в компьютер вставлено некоторое количество ОЗУ, то адресное пространство для него выделяется снизу вверх, начиная с нулевого адреса и дальше в сторону увеличения адресов. Адреса устройств, наоборот, выделяются в верхней области (в четвертом гигабайте) в сторону уменьшения адресов, но не обязательно смежными блоками — чаще, наоборот, несмежными. Как только зоны адресов, выделяемых для ОЗУ (с одной стороны) и для устройств (с другой стороны), соприкоснутся, становится возможным конфликт адресов, и объем используемого ОЗУ приходится ограничивать.
Поскольку изменение адреса при настройке устройств выполняется с некоторым шагом, определяемым характеристиками устройства, заданными изготовителем, то сплошной участок адресов для устройств получить невозможно — между адресами отдельных устройств появляются неиспользуемые промежутки. Теоретически эти промежутки можно было бы использовать для обращения к оперативной памяти, но это усложнило бы работу диспетчера памяти операционной системы. По этой и по другим причинам Windows использует ОЗУ до первого адреса памяти, занятого устройством. ОЗУ, находящееся от этого адреса и выше, останется неиспользуемым. Если, конечно, контроллер памяти не организует переадресацию.
Иногда задают вопрос: а можно ли повлиять на распределение адресов, чтобы сдвинуть все устройства в адресном пространстве как можно выше и сделать как можно больше памяти доступной системе. В общем случае без вмешательства в конструкцию или микропрограммы самих устройств это сделать невозможно. Если же руки все-таки чешутся, а времени не жалко, можно попробовать следующий метод: в BIOS Setup включить настройку «PnP OS» (она может или вовсе отсутствовать или называться по-другому), чтобы адреса для большинства устройств распределяла Windows, а затем переустанавливать драйверы, используя отредактированные файлы inf с удаленными областями памяти, которые, на ваш взгляд, расположены слишком низко.
В интернете можно найти разные советы, которые, якобы, должны дать системе возможность использовать все четыре гигабайта, основанные на принудительном включении PAE. Как легко понять из изложенного, никакого выигрыша это дать не может, поскольку не имеет значения, включен ли PAE автоматически или принудительно — работает этот режим в обоих случаях одинаково.
Может возникнуть также вопрос: а что будет, если установить видеоадаптер с четырьмя гигабайтами памяти. Ведь тогда получается, что система останется совсем без ОЗУ и работать не сможет. На самом деле ничего страшного не произойдет: видеоадаптеры уже довольно давно используют участок адресного пространства размером 256 МБ, и доступ ко всему объему памяти видеоускорителя осуществляется через окно такого размера. Так что больше 256 мегабайт видеоадаптер не отнимет. Возможно, в каких-то моделях размер этого окна увеличен вдвое или даже вчетверо, но автору в руки они пока не попадали.
64 разряда
Итак, с 32-разрядными системами мы разобрались. Теперь перейдем к 64-разрядным.
Вот уж тут-то, казалось бы, никаких подводных камней быть не должно. Система может использовать куда больше четырех гигабайт, так что, на первый взгляд, достаточно воткнуть в системную плату память и установить систему. Но оказывается, не все так просто. Прежде всего, отметим, что специального оборудования, предназначенного только для 64-разрядных систем, найти не удастся (мы говорим об обычных ПК). Любая системная плата, сетевая плата, видеоадаптер и пр., работающие в 64-разрядной системе, должны с одинаковым успехом работать в 32-разрядной.
А это означает, что адреса устройств должны оставаться в пределах первых четырех гигабайт. И значит, все ограничения, накладываемые на объем памяти, доступный 32-разрядной системе, оказываются применимыми и к 64-разрядной — конечно, в том случае, если системная плата не поддерживает переадресацию или если эта переадресация отключена в настройках.
Не поддерживают переадресацию системные платы на наборах микросхем Intel до 945 включительно. Новыми их, конечно, не назовешь, но компьютеры на их базе еще существуют и используются. Так вот, на таких платах и 64-разрядная, и 32-разрядная системы смогут увидеть одинаковое количество памяти, и оно будет меньше 4 ГБ. Почему меньше — описано выше.
С 64-разрядными процессорами AMD дело обстоит проще: у них контроллер памяти уже довольно давно встроен в процессор, и переадресация отсутствует только в устаревших моделях. Все процессоры для 939-контактного гнезда и более новые поддерживают больше 4 ГБ и, соответственно, умеют выполнять переадресацию памяти. То же самое относится к процессорам Intel семейств Core i3, i5, i7.
Впрочем, и тут может быть загвоздка: если на системной плате не выполнена разводка дополнительных адресных линий, то не будет и возможности обратиться к переадресованной памяти. А некоторые младшие модели системных плат для удешевления выпускают именно такими, так что необходимо смотреть описание конкретной системной платы.
И здесь нас поджидает сюрприз, подобный тому, с которым мы сталкиваемся в 32-разрядной системе: использование адресного пространства для работы устройств может ограничить объем памяти, доступный Windows.
Например, если системная плата поддерживает до 8 ГБ ОЗУ (скажем, использующая набор микросхем G35), и установить все эти 8 ГБ, то использоваться будут только ≈7—7,25 ГБ. Причина заключается в следующем: на такой системной плате разведены 33 линии адреса, что, с точки зрения изготовителя, вполне логично — зачем усложнять конструкцию, если больше 8 ГБ плата все равно не поддерживает? Поэтому даже если контроллер памяти сможет перекинуть неиспользуемый участок ОЗУ в девятый гигабайт, обратиться к нему все равно будет невозможно. Для этого потребуется 34-разрядный адрес, который физически нельзя сформировать на 33-разрядной системной шине. Точно так же на платах, поддерживающих 16 ГБ, Windows сможет использовать ≈15—15,25 ГБ и так далее.
С переадресацией связан еще один малоизвестный нюанс. Ограничение размера памяти, выполняемое в программе msconfig (или соответствующими настройками конфигурации загрузки) относится не к собственно величине памяти, а к верхней границе адресов используемой памяти.
Рис. 3. Эта настройка ограничивает верхнюю границу адресов, а не размер памяти
То есть если задать эту величину равной 4096 МБ, то память, расположенная выше этой границы (переадресованная в пятый гигабайт, например), использоваться не будет, и фактически объем памяти будет ограничен примерно тремя гигабайтами. Эту особенность в некоторых случаях удается использовать для диагностики того, работает переадресация или нет. Например, автору встретился случай, когда на ноутбуке Windows использовала 3,75 ГБ из четырех, и было неясно: то ли не работает переадресация, то ли память используется на какие-то нужды. Установка флажка и ограничение размера памяти четырьмя гигабайтами привели к тому, что стали использоваться только 3,25 ГБ. Из этого можно сделать вывод, что переадресация работала, а четверть гигабайта, следовательно, использовалась для видеоадаптера или каких-то других целей.
Ну и напоследок стоит сказать о том, что даже при работающей переадресации и 64-разрядной системе несколько десятков или даже сотен мегабайт памяти все равно могут оказаться зарезервированными для оборудования. Причины такого резервирования лучше всего выяснить у изготовителя системной платы, но чаще всего можно предположить, что она используется для встроенных видеоадаптера или контроллера RAID.
Автор статьи является MS MVP — Windows Expert-IT Pro
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows XP running the Luna visual style, showing the start menu, taskbar, and My Computer window |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
August 24, 2001; 22 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
October 25, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| Final release | Service Pack 3 (5.1.2600.5512) / April 21, 2008; 15 years ago[3] |
| Marketing target | Consumer and Business |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, and Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland |
|
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by |
|
| Succeeded by | Windows Vista (2007) |
| Official website | Windows XP (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Excludes Itanium and some embedded editions: Mainstream support ended on April 14, 2009.[4] Extended support ended on April 8, 2014.[4] Exceptions exist until at most April 9, 2019, |
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft’s Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and business users and Windows Me for home users, and is available for any devices running Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows Me that meet the new Windows XP system requirements.
Development of Windows XP began in the late 1990s under the codename «Neptune», built on the Windows NT kernel and explicitly intended for mainstream consumer use. An updated version of Windows 2000 was also initially planned for the business market. However, in January 2000, both projects were scrapped in favor of a single OS codenamed «Whistler», which would serve as a single platform for both consumer and business markets. As a result, Windows XP is the first consumer edition of Windows not based on the Windows 95 kernel or MS-DOS. Windows XP removed support for PC-98, i486 and SGI Visual Workstation 320 and 540 and will only run on 32-bit x86 CPUs and devices that use BIOS firmware.
Upon its release, Windows XP received critical acclaim, noting increased performance and stability (especially compared to Windows Me), a more intuitive user interface, improved hardware support, and expanded multimedia capabilities. Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 were succeeded by Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, released in 2007 and 2008, respectively. However, some criticisms of Windows XP were its security issues at launch, and many people believed their anti-piracy schemes had gone too far.
Mainstream support for Windows XP ended on April 14, 2009, and extended support ended on April 8, 2014. Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, based on Windows XP Professional, received security updates until April 2019. After that, unofficial methods were made available to apply the updates to other editions of Windows XP. Microsoft discouraged this practice, citing compatibility issues.[5] However, over eight years from the end of life date (September 2022), the majority of PCs in some countries (such as Armenia) still appeared to be running on Windows XP.[6] As of September 2022, globally, just 0.39% of Windows PCs[7] and 0.1% of all devices across all platforms continued to run Windows XP.
Development
In the late 1990s, initial development of what would become Windows XP was focused on two individual products: «Odyssey», which was reportedly intended to succeed the future Windows 2000 and «Neptune», which was reportedly a consumer-oriented operating system using the Windows NT architecture, succeeding the MS-DOS-based Windows 98.[8]
However, the projects proved to be too ambitious. In January 2000, shortly prior to the official release of Windows 2000, technology writer Paul Thurrott reported that Microsoft had shelved both Neptune and Odyssey in favor of a new product codenamed «Whistler», named after Whistler, British Columbia, as many Microsoft employees skied at the Whistler-Blackcomb ski resort.[9] The goal of Whistler was to unify both the consumer and business-oriented Windows lines under a single, Windows NT platform. Thurrott stated that Neptune had become «a black hole when all the features that were cut from Windows Me were simply re-tagged as Neptune features. And since Neptune and Odyssey would be based on the same code-base anyway, it made sense to combine them into a single project».[10]
At PDC on July 13, 2000, Microsoft announced that Whistler would be released during the second half of 2001, and also unveiled the first preview build, 2250, which featured an early implementation of Windows XP’s visual styles system and interface changes to Windows Explorer and the Control Panel.[11]
Microsoft released the first public beta build of Whistler, build 2296, on October 31, 2000. Subsequent builds gradually introduced features that users of the release version of Windows XP would recognize, such as Internet Explorer 6.0, the Microsoft Product Activation system and the Bliss desktop background.[12]
Whistler was officially unveiled during a media event on February 5, 2001, under the name Windows XP, where XP stands for «eXPerience».[13]
Release
In June 2001, Microsoft indicated that it was planning to spend at least US$1 billion on marketing and promoting Windows XP, in conjunction with Intel and other PC makers.[14] The theme of the campaign, «Yes You Can», was designed to emphasize the platform’s overall capabilities. Microsoft had originally planned to use the slogan «Prepare to Fly», but it was replaced because of sensitivity issues in the wake of the September 11 attacks.[15]
On August 24, 2001, Windows XP build 2600 was released to manufacturing (RTM). During a ceremonial media event at Microsoft Redmond Campus, copies of the RTM build were given to representatives of several major PC manufacturers in briefcases, who then flew off on decorated helicopters. While PC manufacturers would be able to release devices running XP beginning on September 24, 2001, XP was expected to reach general, retail availability on October 25, 2001. On the same day, Microsoft also announced the final retail pricing of XP’s two main editions, «Home» (as a replacement for Windows Me for home computing) and «Professional» (as a replacement for Windows 2000 for high-end users).[16]
New and updated features
User interface
While retaining some similarities to previous versions, Windows XP’s interface was overhauled with a new visual appearance, with an increased use of alpha compositing effects, drop shadows, and «visual styles», which completely changed the appearance of the operating system. The number of effects enabled are determined by the operating system based on the computer’s processing power, and can be enabled or disabled on a case-by-case basis. XP also added ClearType, a new subpixel rendering system designed to improve the appearance of fonts on liquid-crystal displays.[17] A new set of system icons was also introduced.[18] The default wallpaper, Bliss, is a photo of a landscape in the Napa Valley outside Napa, California, with rolling green hills and a blue sky with stratocumulus and cirrus clouds.[19]
The Start menu received its first major overhaul in XP, switching to a two-column layout with the ability to list, pin, and display frequently used applications, recently opened documents, and the traditional cascading «All Programs» menu. The taskbar can now group windows opened by a single application into one taskbar button, with a popup menu listing the individual windows. The notification area also hides «inactive» icons by default. A «common tasks» list was added, and Windows Explorer’s sidebar was updated to use a new task-based design with lists of common actions; the tasks displayed are contextually relevant to the type of content in a folder (e.g. a folder with music displays offers to play all the files in the folder, or burn them to a CD).[20]
The «task grouping» feature introduced in Windows XP showing both grouped and individual items
Fast user switching allows additional users to log into a Windows XP machine without existing users having to close their programs and log out. Although only one user at the time can use the console (i.e., monitor, keyboard, and mouse), previous users can resume their session once they regain control of the console.[21] Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also introduced new features to Windows XP post-release, including the Windows Security Center, Bluetooth support, the executable space protection, Windows Firewall, and support for SDHC cards that are larger than 4 GB and smaller than 32 GB.[22][23][24][25]
Infrastructure
Windows XP uses prefetching to improve startup and application launch times.[26] It also became possible to revert the installation of an updated device driver, should the updated driver produce undesirable results.[27]
A copy protection system known as Windows Product Activation was introduced with Windows XP and its server counterpart, Windows Server 2003. All Windows licenses must be tied to a unique ID generated using information from the computer hardware, transmitted either via the internet or a telephone hotline. If Windows is not activated within 30 days of installation, the OS will cease to function until it is activated. Windows also periodically verifies the hardware to check for changes. If significant hardware changes are detected, the activation is voided, and Windows must be re-activated.[28]
Networking and internet functionality
Windows XP was originally bundled with Internet Explorer 6, Outlook Express 6, Windows Messenger, and MSN Explorer. New networking features were also added, including Internet Connection Firewall, Internet Connection Sharing integration with UPnP, NAT traversal APIs, Quality of Service features, IPv6 and Teredo tunneling, Background Intelligent Transfer Service, extended fax features, network bridging, peer to peer networking, support for most DSL modems, IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) connections with auto configuration and roaming, TAPI 3.1, and networking over FireWire.[29] Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop were also added, which allow users to connect to a computer running Windows XP from across a network or the Internet and access their applications, files, printers, and devices or request help.[30] Improvements were also made to IntelliMirror features such as Offline Files, Roaming user profiles and Folder redirection.[31]
Backwards compatibility
To enable running software that targets or locks out specific versions of Windows, «Compatibility mode» was added. The feature allows pretending a selected earlier version of Windows to software, starting at Windows 95.[32]
While this ability was first introduced in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2, it had to be activated through the «register server» and was only available to administrator users, whereas Windows XP has it activated out of the box and also grants it to regular users.[33]
Other features
- Improved application compatibility and shims compared to Windows 2000.[34]
- DirectX 8.1, upgradeable to DirectX 9.0c.[35]
- A number of new features in Windows Explorer including task panes, thumbnails, and the option to view photos as a slideshow.[36]
- Improved imaging features such as Windows Picture and Fax Viewer.[37]
- Faster start-up, (because of improved Prefetch functions) logon, logoff, hibernation, and application launch sequences.[26]
- Numerous improvements to increase the system reliability such as improved System Restore,[38] Automated System Recovery,[39] and driver reliability improvements through Device Driver Rollback.[40]
- Hardware support improvements such as FireWire 800,[41] and improvements to multi-monitor support under the name «DualView».[42]
- Fast user switching.[43]
- The ClearType font rendering mechanism, which is designed to improve text readability on liquid-crystal display (LCD) and similar monitors, especially laptops.[17]
- Side-by-side assemblies[44] and registration-free COM.[45]
- General improvements to international support such as more locales, languages and scripts, MUI support in Terminal Services, improved Input Method Editors, and National Language Support.[46]
Removed features
Some of the programs and features that were part of the previous versions of Windows did not make it to Windows XP. Various MS-DOS commands available in its Windows 9x predecessor were removed,[47] as were the POSIX and OS/2 subsystems.[48]
In networking, NetBEUI, NWLink and NetDDE were deprecated and not installed by default.[49] Plug-and-play–incompatible communication devices (like modems and network interface cards) were no longer supported.[50]
Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also removed features from Windows XP, including support for TCP half-open connections[51] and the address bar on the taskbar.[52]
Editions
Windows XP was released in two major editions on launch: Home Edition and Professional Edition. Both editions were made available at retail as pre-loaded software on new computers and as boxed copies. Boxed copies were sold as «Upgrade» or «Full» licenses; the «Upgrade» versions were slightly cheaper, but require an existing version of Windows to install. The «Full» version can be installed on systems without an operating system or existing version of Windows.[14] The two editions of XP were aimed at different markets: Home Edition is explicitly intended for consumer use and disables or removes certain advanced and enterprise-oriented features present on Professional, such as the ability to join a Windows domain, Internet Information Services, and Multilingual User Interface. Windows 98 or Me can be upgraded to either edition, but Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 can only be upgraded to Professional.[53] Windows’ software license agreement for pre-loaded licenses allows the software to be «returned» to the OEM for a refund if the user does not wish to use it.[54] Despite the refusal of some manufacturers to honor the entitlement, it has been enforced by courts in some countries.[55]
Two specialized variants of XP were introduced in 2002 for certain types of hardware, exclusively through OEM channels as pre-loaded software. Windows XP Media Center Edition was initially designed for high-end home theater PCs with TV tuners (marketed under the term «Media Center PC»), offering expanded multimedia functionality, an electronic program guide, and digital video recorder (DVR) support through the Windows Media Center application.[56] Microsoft also unveiled Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, which contains additional pen input features, and is optimized for mobile devices meeting its Tablet PC specifications.[57] Two different 64-bit editions of XP were made available. The first, Windows XP 64-Bit Edition, was intended for IA-64 (Itanium) systems; as IA-64 usage declined on workstations in favor of AMD’s x86-64 architecture, the Itanium edition was discontinued in January 2005.[58] A new 64-bit edition supporting the x86-64 architecture, called Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, was released in April of the same year.[59]
Microsoft also targeted emerging markets with the 2004 introduction of Windows XP Starter Edition, a special variant of Home Edition intended for low-cost PCs. The OS is primarily aimed at first-time computer owners, containing heavy localization (including wallpapers and screen savers incorporating images of local landmarks), and a «My Support» area which contains video tutorials on basic computing tasks. It also removes certain «complex» features, and does not allow users to run more than three applications at a time. After a pilot program in India and Thailand, Starter was released in other emerging markets throughout 2005.[60] In 2006, Microsoft also unveiled the FlexGo initiative, which would also target emerging markets with subsidized PCs on a pre-paid, subscription basis.[61]
As a result of unfair competition lawsuits in Europe and South Korea, which both alleged that Microsoft had improperly leveraged its status in the PC market to favor its own bundled software, Microsoft was ordered to release special editions of XP in these markets that excluded certain applications. In March 2004, after the European Commission fined Microsoft €497 million (US$603 million), Microsoft was ordered to release «N» editions of XP that excluded Windows Media Player, encouraging users to pick and download their own media player software.[62] As it was sold at the same price as the edition with Windows Media Player included, certain OEMs (such as Dell, who offered it for a short period, along with Hewlett-Packard, Lenovo and Fujitsu Siemens) chose not to offer it. Consumer interest was minuscule, with roughly 1,500 units shipped to OEMs, and no reported sales to consumers.[63] In December 2005, the Korean Fair Trade Commission ordered Microsoft to make available editions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 that do not contain Windows Media Player or Windows Messenger.[64] The «K» and «KN» editions of Windows XP were released in August 2006, and are only available in English and Korean, and also contain links to third-party instant messenger and media player software.[65]
Service packs
A service pack is a cumulative update package that is a superset of all updates, and even service packs, that have been released before it.[66] Three service packs have been released for Windows XP. Service Pack 3 is slightly different, in that it needs at least Service Pack 1 to have been installed, in order to update a live OS.[67] However, Service Pack 3 can still be embedded into a Windows installation disc; SP1 is not reported as a prerequisite for doing so.[68]
The unique boot screens from the RTM to Service Pack 1 versions of Windows XP that identified the edition of Windows XP currently running, including a green progress bar for Home Edition and a blue progress bar for Professional, Embedded, Tablet PC Edition, and Media Center Edition were removed in Service Pack 2 of Windows XP and was replaced with a generic «Windows XP» boot screen with a blue progress bar.
Service Pack 1
Service Pack 1 (SP1) for Windows XP was released on September 9, 2002. It contained over 300 minor, post-RTM bug fixes, along with all security patches released since the original release of XP. SP1 also added USB 2.0 support, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine, .NET Framework support, and support for technologies used by the then-upcoming Media Center and Tablet PC editions of XP.[69] The most significant change on SP1 was the addition of Set Program Access and Defaults, a settings page which allows programs to be set as default for certain types of activities (such as media players or web browsers) and for access to bundled, Microsoft programs (such as Internet Explorer or Windows Media Player) to be disabled. This feature was added to comply with the settlement of United States v. Microsoft Corp., which required Microsoft to offer the ability for OEMs to bundle third-party competitors to software it bundles with Windows (such as Internet Explorer and Windows Media Player), and give them the same level of prominence as those normally bundled with the OS.[70]
On February 3, 2003, Microsoft released Service Pack 1a (SP1a). It was the same as SP1, except the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine was excluded.[71]
Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Windows XP Home edition and Professional edition was released on August 25, 2004.[72] Headline features included WPA encryption compatibility for Wi-Fi and usability improvements to the Wi-Fi networking user interface,[73] partial Bluetooth support,[74] and various improvements to security systems.
Headed by former computer hacker Window Snyder,[75][76] the service pack’s security improvements (codenamed «Springboard»,[77] as these features were intended to underpin additional changes in Longhorn) included a major revision to the included firewall (renamed Windows Firewall, and now enabled by default), and an update to Data Execution Prevention, which gained hardware support in the NX bit that can stop some forms of buffer overflow attacks. Raw socket support is removed (which supposedly limits the damage done by zombie machines) and the Windows Messenger service (which had been abused to cause pop-up advertisements to be displayed as system messages without a web browser or any additional software) became disabled by default. Additionally, security-related improvements were made to e-mail and web browsing. Service Pack 2 also added Security Center, an interface that provides a general overview of the system’s security status, including the state of the firewall and automatic updates. Third-party firewall and antivirus software can also be monitored from Security Center.[78]
In August 2006, Microsoft released updated installation media for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 SP2 (SP2b), in order to incorporate a patch requiring ActiveX controls in Internet Explorer to be manually activated before a user may interact with them. This was done so that the browser would not violate a patent owned by Eolas.[79] Microsoft has since licensed the patent, and released a patch reverting the change in April 2008.[80] In September 2007, another minor revision known as SP2c was released for XP Professional, extending the number of available product keys for the operating system to «support the continued availability of Windows XP Professional through the scheduled system builder channel end-of-life (EOL) date of January 31, 2009.»[81]
Windows XP Service Pack 2 was later included in Windows Embedded for Point of Service and Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.
Service Pack 3
The third and final Service Pack, SP3, was released through different channels between April[3] and June 2008,[82] about a year after the release of Windows Vista, and about a year before the release of Windows 7. Service Pack 3 was not available for Windows XP x64 Edition, which was based on the Windows Server 2003 kernel and, as a result, used its service packs[83] rather than the ones for the other editions.[84]
It began being automatically pushed out to Automatic Updates users on July 10, 2008.[85] A feature set overview which detailed new features available separately as stand-alone updates to Windows XP, as well as backported features from Windows Vista, was posted by Microsoft.[86] A total of 1,174 fixes are included in SP3.[87] Service Pack 3 could be installed on systems with Internet Explorer up to and including version 8; Internet Explorer 7 was not included as part of SP3.[88] It also did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released one year after XP SP3.
Service Pack 3 included security enhancements over and above those of SP2, including APIs allowing developers to enable Data Execution Prevention for their code, independent of system-wide compatibility enforcement settings,[89] the Security Support Provider Interface,[90] improvements to WPA2 security,[91] and an updated version of the Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider Module that is FIPS 140-2 certified.[92]
In incorporating all previously released updates not included in SP2, Service Pack 3 included many other key features. Windows Imaging Component allowed camera vendors to integrate their own proprietary image codecs with the operating system’s features, such as thumbnails and slideshows.[93] In enterprise features, Remote Desktop Protocol 6.1 included support for ClearType and 32-bit color depth over RDP,[94] while improvements made to Windows Management Instrumentation in Windows Vista to reduce the possibility of corruption of the WMI repository were backported to XP SP3.[95]
In addition, SP3 contains updates to the operating system components of Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE) and Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, and security updates for .NET Framework version 1.0, which is included in these editions. However, it does not include update rollups for the Windows Media Center application in Windows XP MCE 2005.[96] SP3 also omits security updates for Windows Media Player 10, although the player is included in Windows XP MCE 2005.[96] The Address Bar DeskBand on the Taskbar is no longer included because of antitrust violation concerns.[97]
Unofficial SP3 ZIP download packages were released on a now-defunct website called The Hotfix from 2005 to 2007.[98][99] The owner of the website, Ethan C. Allen, was a former Microsoft employee in Software Quality Assurance and would comb through the Microsoft Knowledge Base articles daily and download new hotfixes Microsoft would put online within the articles. The articles would have a «kbwinxppresp3fix» and/or «kbwinxpsp3fix» tag, thus allowing Allen to easily find and determine which fixes were planned for the official SP3 release to come. Microsoft publicly stated at the time that the SP3 pack was unofficial and advised users to not install it.[100][101] Allen also released a Vista SP1 package in 2007, for which Allen received a cease-and-desist email from Microsoft.[102]
Windows XP Service Pack 3 was later included in Windows Embedded Standard 2009 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009.
System requirements
System requirements for Windows XP are as follows:
| Minimum | Recommended | |
|---|---|---|
| Home/Professional Edition[A] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 64 MB[E][F] | 128 MB |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) or over | 1024 x 768 or over |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| Professional x64 Edition[J] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 256 MB | |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) or over | 1024 x 768 or over |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| 64-Bit Edition[K] | ||
| CPU | Itanium 733 MHz | Itanium 800 MHz |
| Memory | 1 GB | |
| Free space | 6 GB | |
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) or over | 1024 x 768 or over |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse |
Notes
- ^ «System requirements for Windows XP operating systems». April 28, 2005. Archived from the original on August 6, 2011. Retrieved March 12, 2007.
- ^ Even though this is Microsoft’s stated minimum processor speed for Windows XP, it is possible to install and run the operating system on early IA-32 processors such as a P5 Pentium without MMX instructions. Windows XP is not compatible with processors older than Pentium (such as 486) or the Cyrix 6×86 because it requires the
CMPXCHG8Binstruction. - ^ «Windows XP Minimal Requirement Test». Winhistory.de. September 9, 2011. Archived from the original on December 21, 2011. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows XP: Required firmware and partition mapping scheme of hard disk drive». Support.microsoft.com. June 26, 2013. Archived from the original on April 27, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ A Microsoft TechNet paper from Summer 2001 (before Windows XP’s actual release), states that: «A computer with 64 MB of RAM will have sufficient resources to run Windows XP and a few applications with moderate memory requirements.» (Emphasis added.) These were said to be office productivity applications, e-mail programs, and web browsers (of the time). With such a configuration, user interface enhancements and fast user switching are turned off by default. For comparable workloads, 64 MB of RAM was then regarded as providing an equal or better user experience on Windows XP with similar settings than it would with Windows Me on the same hardware. In a later section of the paper, superior performance over Windows Me was noted with 128 MB of RAM or more, and with computers that exceed the minimum hardware requirements.
- ^ Sechrest, Stuart; Fortin, Michael (June 1, 2001). «Windows XP Performance». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on July 27, 2010. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ «Hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 1». Microsoft. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ «The hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 2». Microsoft. April 18, 2005. Archived from the original on November 24, 2010. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ^ «Windows XP – End of Support, Migration Guide, Download – TechNet». technet.microsoft.com. 2007. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Professional x64 Edition SP2 VL EN (MSDN-TechNet)». Programmer Stuffs. March 23, 2011. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows XP 64-Bit Edition». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 15, 2001. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
Physical memory limits
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows XP can support varies depending on the product edition and the processor architecture. All 32-bit editions of XP support up to 4 GB, except the Windows XP Starter edition, which supports up to 512 MB of RAM.[103] 64-bit editions support up to 128 GB.[104]
Processor limits
Windows XP Professional supports up to two physical processors;[105]
Windows XP Home Edition supports only one.[106]
However, XP supports a greater number of logical processors:
32-bit editions support up to 32 logical processors,[107] and 64-bit editions support up to 64 logical processors.[108]
Upgradeability
Several Windows XP components are upgradable to the latest versions, which include new versions introduced in later versions of Windows, and other major Microsoft applications are available. These latest versions for Windows XP include:
- ActiveSync 4.5
- DirectX 9.0c (June 7, 2010, Redistributable)
- Internet Explorer 8 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (Internet Explorer 6 SP1 and Outlook Express 6 SP1 on Windows XP before SP2.)
- Windows Media Format Runtime and Windows Media Player 11 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (and Windows Media Player 10 on Windows XP original release.)
- Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and 2007
- .NET Framework up to and including version 4.0 (4.5 and higher versions are not supported.)
- Visual Studio 2005 on Windows XP versions below SP2, Visual Studio 2008 on Windows XP SP2 and Visual Studio 2010 on Windows XP SP3
- Windows Script Host 5.7
- Windows Installer 4.5
- Microsoft NetMeeting 3.02
- Office 2010 was the last version of Microsoft Office to be compatible with Windows XP.
- The Windows Services for UNIX subsystem can be installed to allow certain Unix-based applications to run on the operating system.
Support lifecycle
| Expiration date | |
|---|---|
| Mainstream support | April 14, 2009[4] |
| Extended support | April 8, 2014[4] The official exceptions ended in April 2019. |
| Applicable XP editions: | |
| Home Edition, Professional Edition, Professional x64 Edition, Professional for Embedded Systems, Media Center Editions (all), Starter Edition, Tablet PC Edition and Tablet PC Edition 2005,[4] as well as Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.[109] | |
| Exceptions | |
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition (Itanium edition, including Version 2003) | Unsupported as of June 30, 2005[110] |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mainstream support ended on January 11, 2011[4] Extended support ended on January 12, 2016[4] |
| Windows Embedded for Point of Service | Mainstream support ended on April 12, 2011[111] Extended support ended on April 12, 2016[111] |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | Mainstream support ended on January 14, 2014 Extended support ended on January 8, 2019[112] |
| Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 | Mainstream support ended on April 8, 2014 Extended support ended on April 9, 2019[113] |
Support for the original release of Windows XP (without a service pack) ended on August 30, 2005.[4] Both Windows XP Service Pack 1 and 1a were retired on October 10, 2006,[4] and both Windows 2000 and Windows XP SP2 reached their end of support on July 13, 2010, about 24 months after the launch of Windows XP Service Pack 3.[4] The company stopped general licensing of Windows XP to OEMs and terminated retail sales of the operating system on June 30, 2008, 17 months after the release of Windows Vista.[114] However, an exception was announced on April 3, 2008, for OEMs producing what it defined as «ultra low-cost personal computers», particularly netbooks, until one year after the availability of Windows 7 on October 22, 2009. Analysts felt that the move was primarily intended to compete against Linux-based netbooks, although Microsoft’s Kevin Hutz stated that the decision was due to apparent market demand for low-end computers with Windows.[115]
Variants of Windows XP for embedded systems have different support policies: Windows XP Embedded SP3 and Windows Embedded for Point of Service SP3 were supported until January and April 2016, respectively. Windows Embedded Standard 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded Standard 7, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded POSReady 7, were supported until January and April 2019, respectively.[116] These updates, while intended for the embedded editions, could also be downloaded on standard Windows XP with a registry hack, which enabled unofficial patches until April 2019. However, Microsoft advised Windows XP users against installing these fixes, citing incompatibility issues.[5][117]
End of support
On April 14, 2009, Windows XP exited mainstream support and entered the extended support phase; Microsoft continued to provide security updates every month for Windows XP, however, free technical support, warranty claims, and design changes were no longer being offered. Extended support ended on April 8, 2014, over 12 years after the release of Windows XP; normally Microsoft products have a support life cycle of only 10 years.[118] Beyond the final security updates released on April 8, no more security patches or support information are provided for XP free-of-charge; «critical patches» will still be created, and made available only to customers subscribing to a paid «Custom Support» plan.[119] As it is a Windows component, all versions of Internet Explorer for Windows XP also became unsupported.[120]
In January 2014, it was estimated that more than 95% of the 3 million automated teller machines in the world were still running Windows XP (which largely replaced IBM’s OS/2 as the predominant operating system on ATMs); ATMs have an average lifecycle of between seven and ten years, but some have had lifecycles as long as 15. Plans were being made by several ATM vendors and their customers to migrate to Windows 7-based systems over the course of 2014, while vendors have also considered the possibility of using Linux-based platforms in the future to give them more flexibility for support lifecycles, and the ATM Industry Association (ATMIA) has since endorsed Windows 10 as a further replacement.[121] However, ATMs typically run the embedded variant of Windows XP, which was supported through January 2016.[122] As of May 2017, around 60% of the 220,000 ATMs in India still run Windows XP.[123]
Furthermore, at least 49% of all computers in China still ran XP at the beginning of 2014. These holdouts were influenced by several factors; prices of genuine copies of later versions of Windows in the country are high, while Ni Guangnan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences warned that Windows 8 could allegedly expose users to surveillance by the United States government,[124] and the Chinese government banned the purchase of Windows 8 products for government use in May 2014 in protest of Microsoft’s inability to provide «guaranteed» support.[125] The government also had concerns that the impending end of support could affect their anti-piracy initiatives with Microsoft, as users would simply pirate newer versions rather than purchasing them legally. As such, government officials formally requested that Microsoft extend the support period for XP for these reasons. While Microsoft did not comply with their requests, a number of major Chinese software developers, such as Lenovo, Kingsoft and Tencent, will provide free support and resources for Chinese users migrating from XP.[126] Several governments, in particular those of the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, elected to negotiate «Custom Support» plans with Microsoft for their continued, internal use of Windows XP; the British government’s deal lasted for a year, and also covered support for Office 2003 (which reached end-of-life the same day) and cost £5.5 million.[127]
On March 8, 2014, Microsoft deployed an update for XP that, on the 8th of each month, displays a pop-up notification to remind users about the end of support; however, these notifications may be disabled by the user.[128] Microsoft also partnered with Laplink to provide a special «express» version of its PCmover software to help users migrate files and settings from XP to a computer with a newer version of Windows.[129]
Despite the approaching end of support, there were still notable holdouts that had not migrated past XP; many users elected to remain on XP because of the poor reception of Windows Vista, sales of newer PCs with newer versions of Windows declined because of the Great Recession and the effects of Vista, and deployments of new versions of Windows in enterprise environments require a large amount of planning, which includes testing applications for compatibility (especially those that are dependent on Internet Explorer 6, which is not compatible with newer versions of Windows).[130] Major security software vendors (including Microsoft itself) planned to continue offering support and definitions for Windows XP past the end of support to varying extents, along with the developers of Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera web browsers;[120] despite these measures, critics similarly argued that users should eventually migrate from XP to a supported platform.[131] The United States’ Computer Emergency Readiness Team released an alert in March 2014 advising users of the impending end of support, and informing them that using XP after April 8 may prevent them from meeting US government information security requirements.[132]
Microsoft continued to provide Security Essentials virus definitions and updates for its Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT) for XP until July 14, 2015.[133] As the end of extended support approached, Microsoft began to increasingly urge XP customers to migrate to newer versions such as Windows 7 or 8 in the interest of security, suggesting that attackers could reverse engineer security patches for newer versions of Windows and use them to target equivalent vulnerabilities in XP.[134] Windows XP is remotely exploitable by numerous security holes that were discovered after Microsoft stopped supporting it.[135][136]
Similarly, specialized devices that run XP, particularly medical devices, must have any revisions to their software—even security updates for the underlying operating system—approved by relevant regulators before they can be released. For this reason, manufacturers often did not allow any updates to devices’ operating systems, leaving them open to security exploits and malware.[137]
Despite the end of support for Windows XP, Microsoft has released three emergency security updates for the operating system to patch major security vulnerabilities:
- A patch released in May 2014 to address recently discovered vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer 6 through 11 on all versions of Windows.[138]
- A patch released in May 2017 to address a vulnerability that was being leveraged by the WannaCry ransomware attack.[139]
- A patch released in May 2019 to address a critical code execution vulnerability in Remote Desktop Services which can be exploited in a similar way as the WannaCry vulnerability.[140][141]
Researchers reported in August 2019 that Windows 10 users may be at risk for «critical» system compromise because of design flaws of hardware device drivers from multiple providers.[142] In the same month, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Microsoft Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[143] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from the older Windows XP version to the most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[144]
Microsoft announced in July 2019 that the Microsoft Internet Games services on Windows XP and Windows Me would end on July 31, 2019 (and for Windows 7 on January 22, 2020).[145] Others, such as Steam, had done the same, ending support for Windows XP and Windows Vista in January 2019.[146]
In 2020, Microsoft announced that it would disable the Windows Update service for SHA-1 endpoints; since Windows XP did not get an update for SHA-2, Windows Update Services are no longer available on the OS as of late July 2020.[147] However, as of October 2021, the old updates for Windows XP are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog,[148] or through Legacy Update, a community-driven third party replacement for the Windows XP update servers.
Reception
On release, Windows XP received critical acclaim. CNET described the operating system as being «worth the hype», considering the new interface to be «spiffier» and more intuitive than previous versions, but feeling that it may «annoy» experienced users with its «hand-holding». XP’s expanded multimedia support and CD burning functionality were also noted, along with its streamlined networking tools. The performance improvements of XP in comparison to 2000 and Me were also praised, along with its increased number of built-in device drivers in comparison to 2000. The software compatibility tools were also praised, although it was noted that some programs, particularly older MS-DOS software, may not work correctly on XP because of its differing architecture. They panned Windows XP’s new licensing model and product activation system, considering it to be a «slightly annoying roadblock», but acknowledged Microsoft’s intent for the changes.[149] PC Magazine provided similar praise, although noting that a number of its online features were designed to promote Microsoft-owned services, and that aside from quicker boot times, XP’s overall performance showed little difference over Windows 2000.[150] Windows XP’s default theme, Luna, was criticized by some users for its childish look.[151][152]
Despite extended support for Windows XP ending in 2014, many users – including some enterprises – were reluctant to move away from an operating system they viewed as a stable known quantity despite the many security and functionality improvements in subsequent releases of Windows. Windows XP’s longevity was viewed as testament to its stability and Microsoft’s successful attempts to keep it up to date, but also as an indictment of its direct successor’s perceived failings.[153]
According to web analytics data generated by Net Applications, Windows XP was the most widely used operating system until August 2012, when Windows 7 overtook it (later overtaken by Windows 10),[154] while StatCounter indicates it happening almost a year earlier.[155] In January 2014, Net Applications reported a market share of 29.23%[156] of «desktop operating systems» for XP (when XP was introduced there was not a separate mobile category to track), while W3Schools reported a share of 11.0%.[157]
As of September 2022, in most regions or continents, Windows XP market share on PCs, as a fraction of the total Windows share, has gone below 1% (0.5% in Africa[158]). XP still has a double-digit market share in a few countries, such as Armenia at over 50%,[159][160][161][162] at 57%, where Windows 7 was highest ranked, and with it being replaced by Windows 10, Windows XP got highest ranked for the longest time, and had over 60% share on some weekends in the summer of 2019.[163][164]
Source code leak
On September 23, 2020, source code for Windows XP with Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2003 was leaked onto the imageboard 4chan by an unknown user. Anonymous users managed to compile the code, as well as a Twitter user who posted videos of the process on YouTube proving that the code was genuine.[165] The videos were later removed on copyright grounds by Microsoft. The leak was incomplete as it was missing Winlogon and some other components.[166][167] The original leak itself was spread using magnet links and torrent files whose payload originally included Server 2003 and XP source code and which was later updated with additional files, among which were previous leaks of Microsoft products, its patents, media about conspiracy theories on Bill Gates by anti-vaccination movements and an assortment of PDF files on different topics.[168]
Microsoft issued a statement stating that it was investigating the leaks.[167][169][170]
See also
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of operating systems
- List of operating systems
References
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ a b «An Inside Look at the Months-long Process of Getting Windows XP Ready for Release to Manufacturing | Stories». Microsoft Stories. Microsoft. August 24, 2001. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Kelly, Gordon (April 16, 2008). «Windows XP SP3 Release Date(s) Confirmed». Trusted Reviews. Trusted Reviews. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows XP». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 20, 2012. Retrieved May 14, 2022.
- ^ a b Seltzer, Larry (May 26, 2014). «Registry hack enables continued updates for Windows XP». ZDNet. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
[UPDATE:] Late Monday we received a statement from a Microsoft spokesperson: We recently became aware of a hack that purportedly aims to provide security updates to Windows XP customers. The security updates that could be installed are intended for Windows Embedded and Windows Server 2003 customers and do not fully protect Windows XP customers. Windows XP customers also run a significant risk of functionality issues with their machines if they install these updates, as they are not tested against Windows XP. The best way for Windows XP customers to protect their systems is to upgrade to a more modern operating system, like Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share in Armenia – September 2022». September 30, 2022. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats». gs.statcounter.com. Statcounter. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved May 8, 2022.
- ^ Miles, Stephanie (January 24, 2000). «Microsoft consolidates Windows development efforts». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Windows «Longhorn» FAQ». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. June 22, 2005. Archived from the original on April 4, 2008. Retrieved April 4, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold: The development of Windows XP Reviewed». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (July 17, 2000). «Introducing the Whistler Preview, Build 2250». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold (Part Two)». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft to christen Windows, Office with new name». CNET. CNET Networks. February 5, 2001. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ a b «Windows XP marketing tab to hit $1 billion». CNET. CNET Networks. January 2, 2002. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft changes XP slogan in wake of US attacks». Computerworld NZ. IDG. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved August 7, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2001). «The Road to Gold (Part Three)». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ a b «HOW TO: Use ClearType to Enhance Screen Fonts in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on August 5, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Esposito, Dino (November 2001). «New Graphical Interface: Enhance Your Programs with New Windows XP Shell Features». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Turner, Paul (February 22, 2004). «No view of Palouse from Windows». The Spokesman-Review. Spokane. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved September 19, 2012.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Jason (August 6, 2015). «The Start Menu Should Be Sacred (But It’s Still a Disaster in Windows 10)». How-To Geek. Archived from the original on March 13, 2017. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ «How To Use the Fast User Switching Feature in Windows XP (Revision 1.5)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. March 27, 2007. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ». Archived from the original on December 23, 2018. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Manually Configuring Windows Firewall in Windows XP Service Pack 2». May 5, 2010. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Firewall feature in Windows XP SP2». Archived from the original on September 17, 2009. Retrieved September 18, 2009.
- ^ «Hotfix for Windows XP that adds support for SDHC cards that have a capacity of more than 4 GB». Support (5.0 ed.). May 22, 2013. Archived from the original on February 5, 2014. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- ^ a b «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». Windows Hardware Developer Center (WHDC). Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 7, 2008. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «HOW TO: Use the Driver Roll Back Feature to Restore a Previous Version of a Device Driver in Windows XP». Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on February 18, 2006.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (February 2, 2001). «Windows Product Activation: an early look». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP Networking Features and Enhancements». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 8, 2001. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions About Remote Desktop». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 4, 2007.
- ^ Otey, Michael (October 2001). «Discover Windows XP». Microsoft Developer. Archived from the original on April 20, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Program Compatibility Wizard». ServerWatch. March 12, 2002. Archived from the original on November 13, 2021. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ «How to Enable Application Compatibility-Mode Technology in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2». Active Win. 2000. Archived from the original on August 18, 2001. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ Proffit, Brian (September 2, 2002). «Old Apps Find A New Home On Windows XP». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 10, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ Karp, David; O’Reilly, Tim; Mott, Troy (2005). Windows XP in a Nutshell : [a desktop quick reference] (2nd ed.). Beijing [u.a.]: O’Reilly. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-596-00900-7.
- ^ Richtmyer, Richard (August 23, 2001). «Opening up Windows XP». CNN Money. CNN. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Picture and Fax Viewer overview». Windows XP Professional Product Documentation. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ Harder, Bobbie (April 2001). «Microsoft Windows XP System Restore». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 4, 2005.
- ^ Petri, Daniel (January 8, 2009). «What is ASR in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003?». Petri. Blue Whale Web Media Group. Archived from the original on March 12, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Columbus, Louis (June 29, 2001). «Exploring Windows XP’s Device Driver Rollback and System Restore». InformIT. Pearson Education. Archived from the original on January 5, 2014. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Norton, Peter; Mueller, John Paul (2002). Peter Norton’s Complete Guide to Windows XP. Pearson Education. p. N/A. ISBN 9780132715386. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ McNamee, Kieran (June 27, 2003). «Setting up dual monitors using Windows XP Home». PC World. Archived from the original on February 5, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Architecture of Fast User Switching». Microsoft Knowledgebase. Microsoft. January 15, 2006. Archived from the original on August 2, 2009. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Satran, Michael (May 31, 2018). «About Side-by-Side Assemblies». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 24, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Wienholt, Nick (August 14, 2006). «Simplify Application Deployment with Registration-Free COM — Developer.com». www.developer.com. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on December 16, 2010. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Honeycutt, Jerry (2003). Introducing Microsoft Windows Server 2003. Redmond, Wash.: Microsoft. pp. 293–298. ISBN 9780735615700.
- ^ «New ways to do familiar tasks». Windows XP Product Documentation. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 3, 2006. Retrieved May 21, 2014.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». MSDN. Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 6, 2013. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Pittsley, Steven (June 13, 2002). «Easy install guide for NetBEUI and IPX in Windows XP Pro». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 11, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Non-Plug and Play Network Device Support in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 18, 2001. Archived from the original on October 30, 2004. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
- ^ «TCP/IP Raw Sockets (Windows)». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ Pash, Adam (April 29, 2008). «Field Guide to Windows XP SP3». Lifehacker. Univision Communications. Archived from the original on January 15, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Differences with Windows XP Home Edition». TechNet. Microsoft. September 11, 2009. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Marti, Don (November 6, 2006). «Dell customer gets Windows refund». LinuxWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on September 27, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ «HP must reimburse Italian PC buyer the amount paid for Microsoft software». Heise online. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe (July 16, 2002). «Microsoft reveals media XP details». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe; Junnarkar, Sandeep (November 7, 2002). «Microsoft launches tablet PC drive». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Evers, Joris (January 5, 2005). «Microsoft nixes Windows XP for Itanium». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Raises the Speed Limit with the Availability of 64-Bit Editions of Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional» (Press release). Microsoft. April 25, 2005. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (January 3, 2005). «Windows XP Starter Edition». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 28, 2013. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ Fried, Ina (May 23, 2006). «Microsoft pitches pay-as-you-go PCs». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft and EU reach agreement». BBC. March 28, 2005. Archived from the original on September 22, 2015.
- ^ Bishop, Todd (December 24, 2004). «Europe gets ‘reduced’ Windows». Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Corporation. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- ^ Anderson, Nate (December 7, 2005). «South Korea fines Microsoft for antitrust abuses». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on April 22, 2008. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ «Changes to Windows XP Home Edition K and Windows XP Professional K from earlier versions of Windows XP (MSKB 922474)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. September 15, 2006. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Service Pack and Update Center». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2016. Archived from the original on August 31, 2017.
- ^ «Installing Windows XP Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. Microsoft. November 18, 2011. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ Purdy, Kevin. «Slipstream Service Pack 3 into Your Windows XP Installation CD». Lifehacker. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP SP1 Irons out the Wrinkles». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward. «Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 1 review». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Differences Between Windows XP SP1 and Windows XP SP1a». February 3, 2003. Archived from the original on January 27, 2007. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ «How to obtain the latest Windows XP service pack». March 26, 2007. Archived from the original on October 14, 2004. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Shinder, Deb (August 26, 2004). «Windows XP Service Pack 2: How it affects wireless networking». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on June 13, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ – 2010». July 24, 2012. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ Menn, Joseph (2019). Cult of the Dead Cow: How the Original Hacking Supergroup Might Just Save the World. New York: Public Affairs. p. 49–50.
- ^ Grimes, Roger A. (2017). «46 — Profile: Window Snyder». Hacking the hacker : learn from the experts who take down hackers. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley. ISBN 978-1-119-39626-0. OCLC 983465946.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2003). «Windows XP SP2 to be ‘Springboard’ to Longhorn». Windows IT Pro. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 2 information». Microsoft. August 4, 2004. Archived from the original on October 16, 2007.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 21, 2006). «Why Windows XP SP2b and Windows Server 2003 SP2a?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 12, 2009.
- ^ Fletcher, Jefferson (April 8, 2008). «IE Automatic Component Activation Now Available». IEBlog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 11, 2008. Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft Windows XP Professional Service Pack 2c Release». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Emil Protalinski (April 29, 2008). «Microsoft releases the long-anticipated Windows XP SP3 (updated)». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on January 15, 2022. Retrieved February 10, 2022.
- ^ «Release Notes for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2». October 8, 2009. Archived from the original on November 11, 2019. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «64-Bit Windows XP Service Pack 3?». Softpedia. SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (July 8, 2008). «Microsoft sets XP SP3 automatic download for Thursday». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on July 9, 2008. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 3 Overview». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved May 7, 2008.
- ^ «List of fixes that are included in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «No, Internet Explorer 7 Will Not(!) Be a Part of Windows XP SP3». SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on January 18, 2012.
- ^ Howard, Michael (January 29, 2008). «New NX APIs added to Windows Vista SP1, Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2008». Michael Howard’s Web Log. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Description of the Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on October 9, 2009. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Enterprise IT Planet Staff (May 13, 2005). «Upgraded Wi-Fi Security for Windows XP SP2». Wi-Fi Planet. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Overview of Windows XP Service Pack 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 17, 2009.
- ^ «Information about Windows Imaging Component». Microsoft. August 13, 2002. Archived from the original on May 10, 2011.
- ^ Nanjappa, Ashwin (January 27, 2010). «Windows: ClearType on RDP». CodeYarns.com. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ «A hotfix is available that improves the stability of the Windows Management Instrumentation repository in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 8, 2011. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b «FAQs regarding SP3 RTM». Microsoft. April 22, 2008. Archived from the original on August 24, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Kaelin, Mark (May 8, 2008). «How do I… Return the Address bar Windows XP SP3 removed?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview surfaces on Web». PC World. IDG. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Sneak preview of Windows XP SP3 surfaces». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft employee blasts ‘fake’ service pack». PC World. IDG. October 14, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview a fake». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 15, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft leans on Vista SP1 site». PC World. IDG. October 4, 2007. Archived from the original on May 18, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- ^ «Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP». Memory Limits for Windows Releases. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ «Processor and memory capabilities of Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and of the x64-based versions of Windows Server 2003 (Revision 7.0)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Kumar, I. Suuresh (October 25, 2010). «Multi-core processor and multiprocessor limit for Windows XP». Microsoft Answers. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ «Processor Affinity Under WOW64». MSDN. Microsoft. January 27, 2011. Archived from the original on May 6, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Maximum quantity of logical processors in a PC supported by Microsoft Windows XP professional, x64 edition». Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on January 11, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 5, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS05-036 – Critical». July 12, 2015. Archived from the original on April 26, 2018. Retrieved April 26, 2018.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (February 19, 2014). «Windows XP Embedded Supported for Two or More Years». Redmond Magazine. 1105 Media. Archived from the original on February 20, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded Standard 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded POSReady 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 30, 2008. Retrieved June 5, 2008.
- ^ Lai, Eric (March 3, 2008). «Microsoft to keep Windows XP alive—but only for Eee PCs and wannabes». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on April 8, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ Tung, Liam (February 18, 2014). «Microsoft: ‘Remember, some XP-based embedded systems to get support to 2019’«. ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Newman, Jared (August 27, 2014). «Enthusiast developer keeps Windows XP alive with unofficial ‘Service Pack 4’«. PCWorld. Archived from the original on October 26, 2018. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ^ Satherley, Dan (April 9, 2013). «Businesses urged to ditch XP». 3 News NZ. Archived from the original on July 13, 2014. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (August 26, 2013). «Microsoft will craft XP patches after April ’14, but not for you». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved December 12, 2013.
- ^ a b Keizer, Gregg (March 11, 2014). «US-CERT urges XP users to dump IE». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on June 28, 2019. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ ATM Industry Association (collectively) (June 1, 2015). «ATMIA position paper recommending migration to Windows 10». www.atmia.com (Press release). ATM Industry Association. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Summers, Nick (January 16, 2014). «ATMs Face Deadline to Upgrade From Windows XP». Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on January 16, 2014. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ^ «Wannacry ransomware cyber attack: Indian ATMs could be at high risk as most run on Windows XP». Business Today. May 15, 2017. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- ^ «Windows 8 a ‘threat’ to China’s security». BBC. June 5, 2014. Archived from the original on October 8, 2018. Retrieved October 8, 2018.
- ^ Kan, Michael (May 20, 2014). «China bans government purchases of Windows 8». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 20, 2014. Retrieved May 20, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Partners Lenovo, Tencent to Offer XP Tech Support in China». Voanews.com. Reuters. April 9, 2014. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Gallagher, Sean (April 6, 2014). «Not dead yet: Dutch, British governments pay to keep Windows XP alive». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft to start nagging Windows XP users about April 8 end-of-support date». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Yegulalp, Serdar (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft: Use Laplink’s Windows XP migration tools, not ours». Infoworld. Archived from the original on October 15, 2019.
- ^ Ward, Mark (March 5, 2014). «XP – the operating system that will not die». BBC News. Archived from the original on March 24, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Egan, Matt (April 7, 2014). «What should XP users do when Microsoft ends support? Upgrade to Windows 8, buy a new PC, keep running XP?». PC Advisor. Archived from the original on February 14, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ «Alert (TA14-069A): Microsoft Ending Support for Windows XP and Office 2003». March 11, 2014. Archived from the original on March 16, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 19, 2014). «Microsoft will furnish malware assassin to XP users until mid-2015». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on January 22, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Warns of Permanent Zero-Day Exploits for Windows XP». Infosecurity. Reed Exhibitions. August 20, 2013. Archived from the original on August 26, 2013. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS15-011 JASBUG». February 10, 2015. Archived from the original on August 11, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Freeman, Robert (November 11, 2014). «IBM X-Force Researcher Finds Significant Vulnerability in Microsoft Windows». Securityintelligence.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Talbot, David (October 17, 2012). «Computer Viruses Are «Rampant» on Medical Devices in Hospitals». MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on October 19, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (May 1, 2014). «Emergency patch for critical IE 0-day throws lifeline to XP laggards, too». Ars Technica. Conde Nast. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 13, 2017). «Microsoft issues ‘highly unusual’ Windows XP patch to prevent massive ransomware attack». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on May 14, 2017. Retrieved May 13, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 14, 2019). «Microsoft warns of major WannaCry-like Windows security exploit, releases XP patches». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on September 2, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ «Prevent a worm by updating Remote Desktop Services (CVE-2019-0708) – MSRC». blogs.technet.microsoft.com. May 14, 2019. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ Winder, Davey (August 11, 2019). «Critical Windows 10 Warning: Millions Of Users At Risk». Forbes. Archived from the original on August 11, 2019. Retrieved August 11, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Farewell to Microsoft Internet Games on Windows XP, Windows ME, and Windows 7». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows XP and Windows Vista Support – Steam – Knowledge Base – Steam Support». support.steampowered.com. Archived from the original on August 12, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». support.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Catalog». www.catalog.update.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ Lake, Matt (October 10, 2002). «Microsoft Windows XP – Home Edition review». CNET. Archived from the original on May 31, 2007. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (September 3, 2001). «Microsoft Ships Its Biggest OS Upgrade Ever—Early!». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Manes, Stephen (August 26, 2004). «Full Disclosure: Your Take on Windows’ Worst Irritations». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 8, 2009.
- ^ Bright, Peter (April 10, 2014). «Memory lane: Before everyone loved Windows XP, they hated it». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on April 24, 2014. Retrieved June 20, 2014.
- ^ Bright, Peter (October 25, 2011). «Ten years of Windows XP: how longevity became a curse». Ars Technica. WIRED Media Group. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ «Operating system market share». September 9, 2012. Archived from the original on September 9, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2018.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
- ^ Crothers, Brooke (February 2, 2014). «Oops, Windows XP gains in January but so does Windows 8.1». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved March 16, 2014.
- ^ «OS Platform Statistics». w3schools. Archived from the original on September 17, 2015. Retrieved September 14, 2015.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Africa». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved March 2, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Windows XP leak confirmed after user compiles the leaked code into a working OS». ZDNet. Archived from the original on September 30, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ Warren, Tom (September 25, 2020). «Windows XP source code leaks online». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 29, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ a b Alcorn, Paul (September 30, 2020). «Windows XP Source Code Leaked, Posted to 4chan (Update, It Works)». Tom’s Hardware. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP Source Code Leaked By Apparent Bill Gates Conspiracist». Gizmodo. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on October 1, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «The Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 source code leaks online». Graham Cluley. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on September 26, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP source code leaked online». www.computing.co.uk. September 28, 2020. Archived from the original on October 2, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
Further reading
- Joyce, Jerry; Moon, Marianne (2004). Microsoft Windows XP Plain & Simple. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2112-1.
External links
- Windows XP End of Support
- Security Update for Windows XP SP3 (KB4012598)