Командная строка – мощный инструмент для автоматизации и упрощения многих задач, которые возникают при администрировании компьютера с операционной системой Windows. В этой статье мы рассмотрим команды DEL, ERASE, RD и RMDIR. С их помощью вы сможете удалять файлы и папки прямо из командной строки.
Удаление файлов через командную строку
Если вам нужно удалить файл через командную строку, то для этого нужно использовать команду DEL или ERASE. Эти команды являются синонимами и работают одинаково. Вы можете получить подробную информацию об этих командах, если введете их в командную строку с параметром «/?». Например, вы можете ввести «del /?» и в консоль выведется вся основная информация о команде del.
Команда DEL (или ERASE) предназначена для удаления одного или нескольких файлов и может принимать следующие параметры:
- /P – удаление с запросом подтверждения для каждого файла;
- /F – удаление файлов с атрибутом «только для чтения»;
- /S – удаление указанного файла из всех вложенных папок;
- /Q – удаление без запроса на подтверждение ;
-
/A – удаление файлов согласно их атрибутам;
- S — Системные;
- H — Скрытые;
- R – Только для чтения;
- A — Для архивирования
- Также перед атрибутами можно использовать знак минус «-», который имеет значение «НЕ». Например, «-S» означает не системный файл.
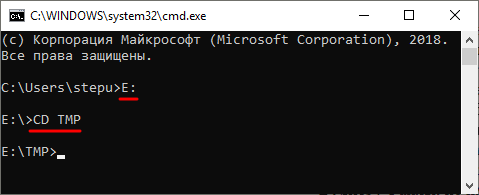
Обычно, для того чтобы воспользоваться командной DEL нужно сначала перейти в папку, в которой находится файл для удаления, и после этого выполнить команду. Для того чтобы сменить диск нужно просто ввести букву диска и двоеточие. А для перемещения по папкам нужно использовать команду «CD».
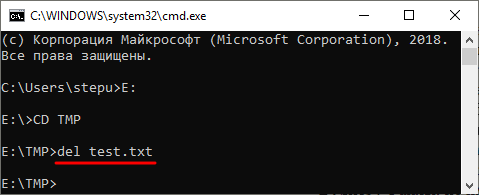
После того как вы попали в нужную папку можно приступать к удалению файлов. Для этого просто введите команду DEL и название файла.
del test.txt
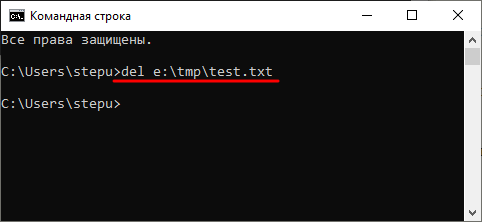
Также, при необходимости вы можете удалять файлы, не перемещаясь по папкам. В этом случае нужно указывать полный путь к документу.
del e:\tmp\test.txt
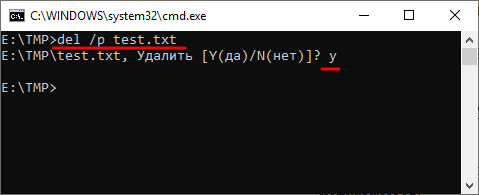
Если есть необходимость выполнить запрос на подтверждение удаления каждого из файлов, то к команде DEL нужно добавить параметр «/p». В этом случае в командной строке будет появляться запрос на удаление файла и пользователю нужно будет ввести букву «Y» для подтверждения.
del /p test.txt
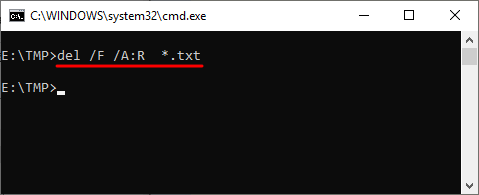
Нужно отметить, что при использовании параметра «/a», отвечающие за атрибуты буквы нужно вводить через двоеточие. Например, для того чтобы удалить все файлы с атрибутом «только для чтения» и с расширением «txt» нужно ввести:
del /F /A:R *.txt
Аналогичным образом к команде DEL можно добавлять и другие параметры. Комбинируя их вы сможете создавать очень мощные команды для удаления файлов через командную строку Windows. Ниже мы приводим еще несколько примеров.
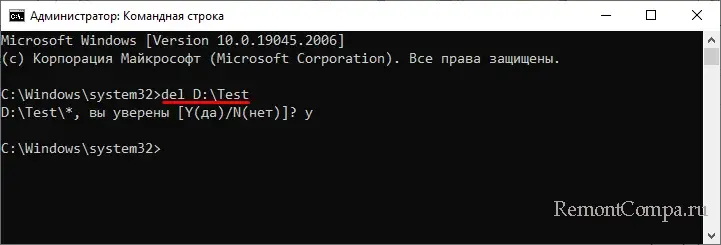
Уничтожение всех файлов в корне диска D:
del D:\
Уничтожение всех файлов с расширением «txt» в корне диска D:
del D:\*.txt
Уничтожение всех файлов в папке d:\doc (документы с атрибутами будут пропущены):
del D:\doc
Уничтожение всех файлов с атрибутом «только для чтения» и расширением «txt» в папке d:\doc:
del /A:r d:\doc\*.txt
Удаление папок через командную строку
Если вам нужно удалить папку через командную строку Windows, то указанные выше команды вам не помогут. Для удаления папок существует отдельная команда RD или RMDIR (сокращение от английского Remove Directory).
Команды RD и RMDIR являются синонимами и предназначены для удаления папок. Они могу принимать следующие параметры:
- /S — удаление всего дерева каталогов, при использовании данного параметра будет удалена не только сама папка, но и все ее содержимое;
- /Q – удаление дерева папок без запроса на подтверждение;
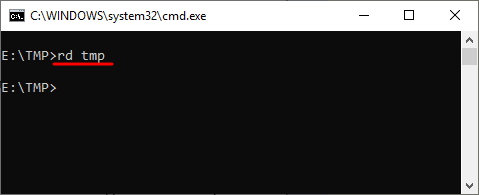
Например, для того чтобы удалить папку достаточно ввести команду RD и название папки. Например:
rd MyFolder
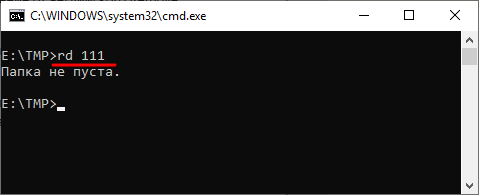
Если папка содержит вложенные папки или файлы, то при ее удалении будет выведена ошибка «Папка не пуста».
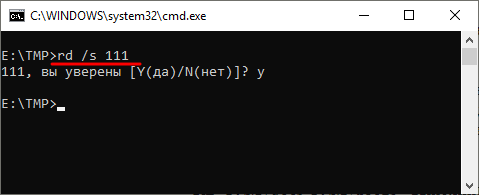
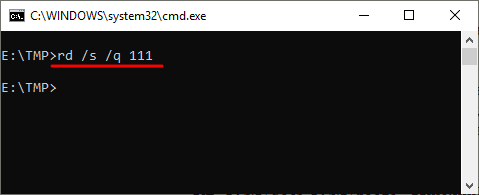
Для решения этой проблемы к команде RD нужно добавить параметр «/s». В этом случае удаление проходит без проблем, но появляется запрос на подтверждение удаления. Например:
rd /s MyFolder
Для того чтобы удаление дерева папок прошло без появления запроса на подтверждение к команде нужно добавить параметр «/q». В этом случае папка удаляется без лишних вопросов. Например:
rd /s /q MyFolder
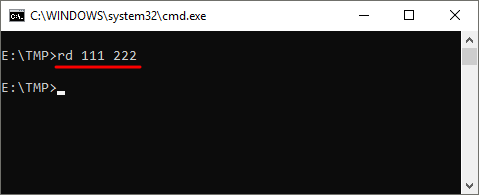
Также команда RD может принимать сразу несколько папок, для этого их нужно просто разделить пробелом. Например, чтобы сразу удалить
rd Folder1 Folder2
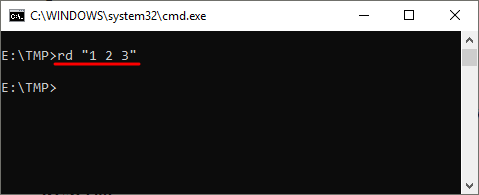
Если же вам нужно удалить через командную строку папку, которая сама содержит пробел, то в этом случае ее название нужно взять в двойные кавычки. Например:
rd "My Files"
Комбинируя команды DEL и RD, можно создавать мощные скрипты для очистки и удаления папок в операционной системе Windows.
Удаление файлов и папок в PowerShell
В консоли PowerShell вы можете использовать рассмотренные выше команды DEL и RD, либо «Remove-Item» — собственную команду (командлет) PowerShell. С помощью данной команды можно удалять можно удалять файлы, папки, ключи реестра, переменные и другие объекты.
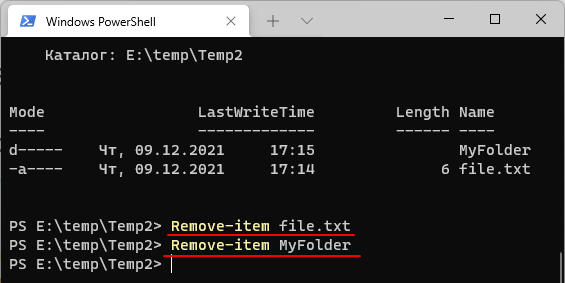
Например, для того чтобы удалить файл или папку в консоли PowerShell можно использовать команду:
Remove-item file.txt Remove-item MyFolder
Посмотрите также:
- Выключение компьютера через командную строку
- Как перезагрузить компьютер через командную строку
- Как вызвать командную строку в Windows 7
- Как поменять дату в Windows 7
- Как выключить компьютер через определенное время
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
Вы можете столкнуться с ситуацией, когда файл в проводнике Windows не удаляется. Это может быть связанно с какой-нибудь ошибкой или файлы или папки заняты каким-то процессом. В таких случаях для удаления файлов и папок можно использовать командную строку. Это не гарантирует удаление файлов и папок, но попробовать можно.
Будьте осторожны удаляя файлы из командной строки! Неправильное использование командной строки может сделать вашу систему неработоспособной, и даже привести к фатальным ошибкам, которые могут повлиять на работоспособность операционной системы.
Содержание
- Удалить файл или папку из командной строки
- Удалить файл через командную строку
- Удалить папку через командную строку
- Заключение
Удалить файл или папку из командной строки
Чтобы удалить файлы с помощью командной строки откройте ее с правами администратора.
РЕКОМЕНДУЕМ:
Выключение Windows из командной строки
Кстати, вы можете использовать те же команды и параметры в PowerShell.
Удалить файл через командную строку
Когда откроется окно командной строки CMD, перейдите к папку, в которой необходимо удалить файл. Для перехода по папкам используйте команду «cd». Затем введите следующую команду с параметрами:
Синтаксис:
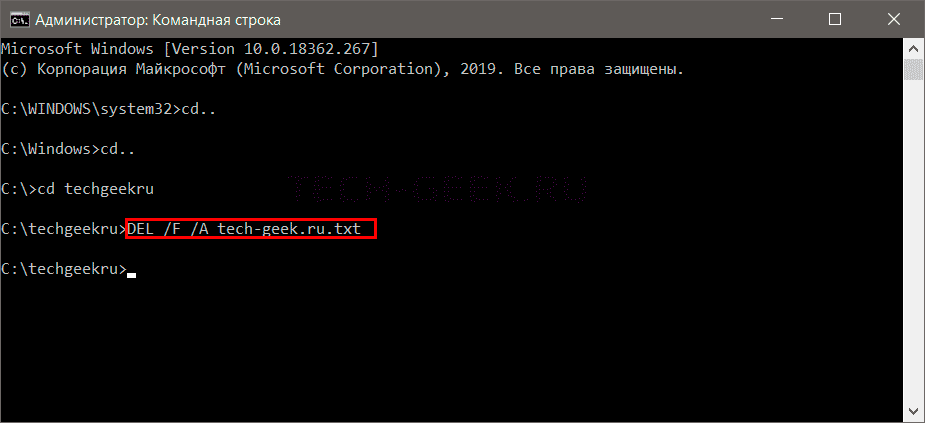
|
DEL /F /A <путь к файлу вместе с расширением> |
Пример:
|
DEL /F /A tech—geek.ru.txt |
Параметры:
- /F — означает принудительное удаление.
- /A — выбирает только файлы с атрибутом «Готово к архивированию».
Удалить папку через командную строку
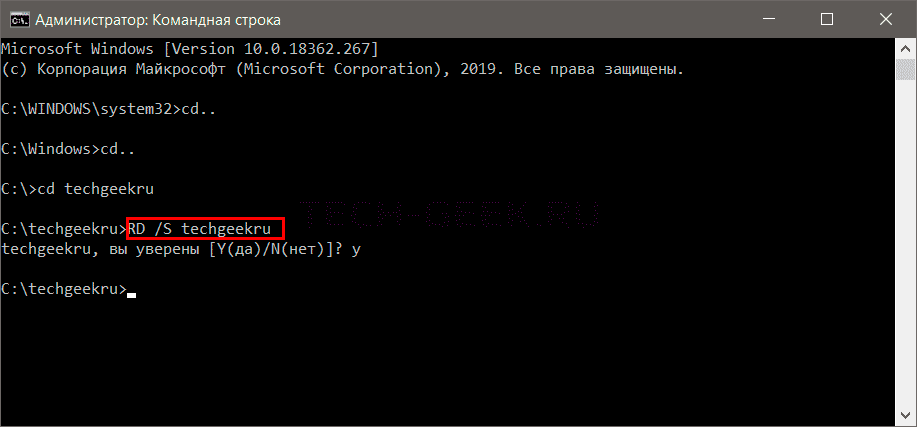
С помощью команды «cd» перейдите в каталог, содержащий папку, которую следует удалить. Введите следующую команду в командной строке:
Синтаксис:
Пример:
Параметры:
- RD — удаляет папку из каталога.
- /S — удаляет все подпапки и файлы.
Если использовать параметр /Q, то вас не спросят о подтверждении Y / N.
Если папка или файл заблокированы, вы можете следовать этим инструкциям, чтобы удалить заблокированные или не подлежащие восстановлению файлы и папки.
РЕКОМЕНДУЕМ:
История выполнения команд в командной строке Windows
Заключение
Как вы видите удаление папок и файлов командной строки — дело несложное. Попробуйте эти способы удаления и дайте знать в разделе комментариев ниже, если описанный метод работает помог вам.
Удалить файл или папку с диска или флешки – что, казалось бы, может быть проще? Да, это действительно просто, если только вы не работаете в среде восстановления, в которой Проводник недоступен. В таких случаях вам придется использовать командную строку – мощный инструмент управления Windows, о котором многие пользователи уже начали забывать. Консоль может вам понадобиться и в работающей системе, например, при удалении скрытых и недоступных только для чтения файлов, а также файлов, используемых процессом explorer.exe (после его завершения).
Для удаления файлов в классической командной строке Windows используются две команды – DEL и ERASE, которые функционально ничем не отличаются, имея одинаковый набор аргументов. Команда имеет следующий синтаксис:
del /key full path
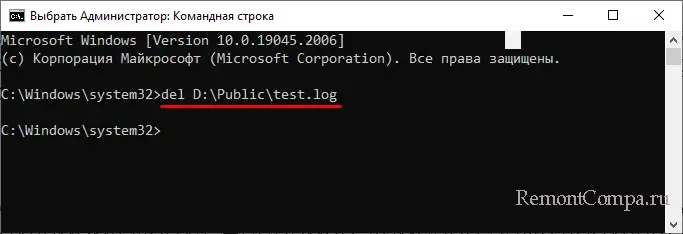
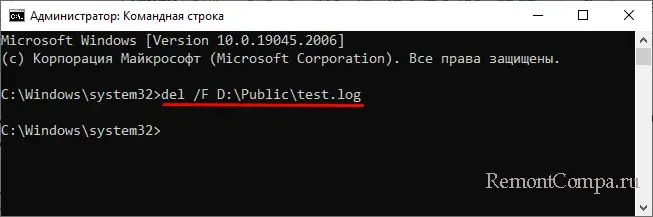
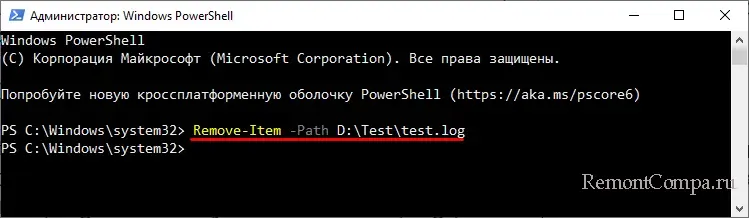
del или erase – это сама команда удаления, /key – это необязательный аргумент, а full path – полный путь к удаляемому файлу. Например, команда ниже удаляет файл test.log в папке Public на диске D:
del D:\Public\test.log
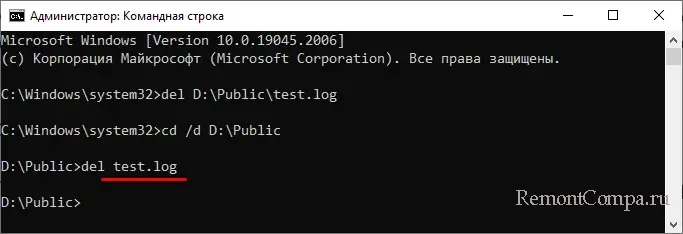
Кстати, указывать полный путь необязательно, если вы заранее перешли в папку с файлов. В этом случае указывается только команда удаления и сам файл:
del test.log
Файлы можно удалять не только по одному, но и все сразу, так, следующая команда удалит все файлы из папки Test:
del D:\Test
Будут пропущены лишь те файлы, которые имеют атрибуты «Только для чтения», «Скрытые», «Системные» и т. д. Для удаления таких файлов в команду добавляются специальные ключи, например, чтобы удалить файл с меткой «Только для чтения», в команду нужно добавить ключ /F, вот так:
del /F D:\Public\test.log
Помимо ключа /F, командой DEL поддерживает параметры /P, /S, /Q и /A. Рассмотрим их назначение чуть более подробно.
● /P – включает запрос на подтверждение удаления файла.
● /Q – отключает запрос на подтверждение удаления файла, обычно используется при удалении групп файлов.
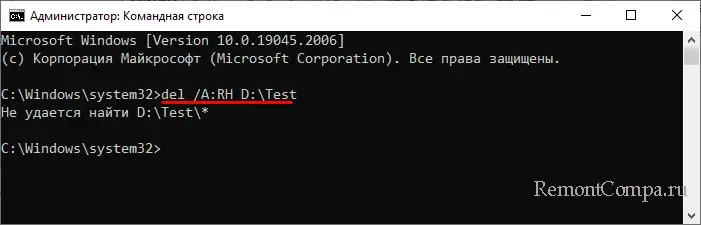
● /A – ключ используется, когда нужно удалить группу файлов с определенными атрибутами – del /A:RH D:\Test – в результате выполнения этой команды из папки Test будут удалены все файлы с атрибутами R (только для чтения) и Н (скрытые).
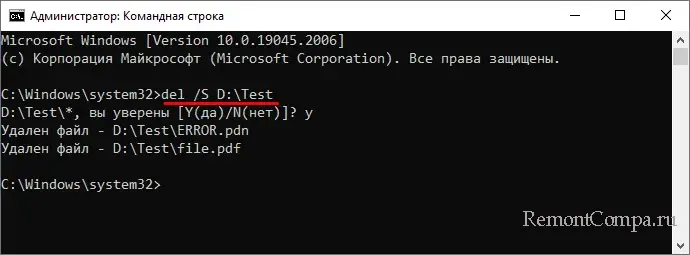
● /S – если нужно удалить файлы рекурсивно, то есть не только в указанной папке, но и во всех вложенных в нее папках, добавьте в команду ключ S, вот так:
del /S D:\Test.
В принципе, этих знаний достаточно, чтобы удалить любой несистемный файл, но рассмотренная нами тема была бы не раскрыта без упоминания о другом консольном инструменте Windows – PowerShell. Помимо поддержки ею команд DEL и ERASE, PowerShell располагает собственным командлётом для удаления объектов файловой системы. Он называется Remove-Item и имеет следующий синтаксис:
Remove-Item -Path -key
Командлёт очень похож на DEL, Path принимает значение пути к удаляемому объекту, а key – дополнительный параметр или несколько параметров. В отличие от DEL и ERASE, Remove-Item универсален и может использоваться для удаления как файлов, так и каталогов. Удалим файл test.log из папки Test:
Remove-Item -Path D:\Test\test.log
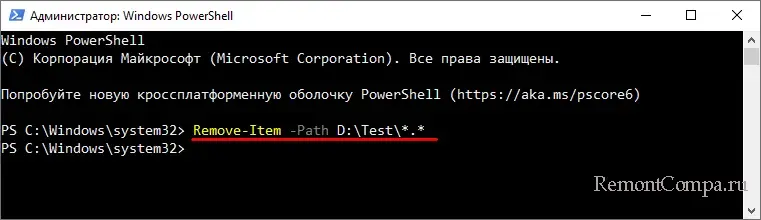
Использовать «-Path» необязательно, так как PowerShell и так понимает, что нужно делать. Папки удаляются аналогично, если нужно удалить только файлы, используется подстановочный знак, в данном случае точка перед расширением.
Remove-Item -Path D:\Test\*.*
Если путь содержит пробелы или кириллицу, его нужно взять в прямые двойные кавычки. Командлёт поддерживает около дюжины параметров, из которых вам наверняка пригодятся -Force и -Recurse.
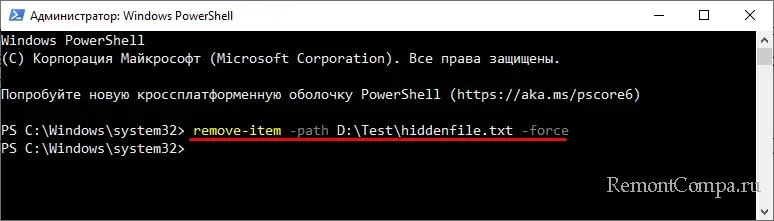
Параметр -Force используется для принудительного удаления файлов с атрибутами «Только чтения», «Скрытый», «Архивный» и «Системный».
remove-item -path D:\Test\hiddenfile.txt -force
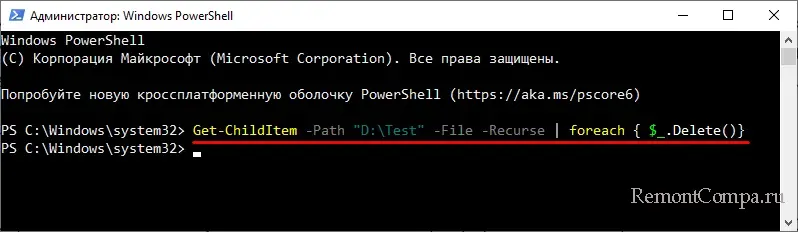
Параметр -Recurse служит для удаления файлов в указанной папке и всех вложенных в нее каталогах. Поскольку параметр Remove-Item в связке с командлётом -Recurse работает корректно не во всех версиях PowerShell, вместо Remove-Item лучше использовать Get-ChildItem.
Get-ChildItem -Path «D:\Test» -File -Recurse | foreach { $_.Delete()}
Обращаем внимание, что эта команда удалит все файлы из папок в директории Test мимо Корзины, такова особенность ее работы. И на этом, пожалуй, достаточно. Более подробные сведения об использовании команд DEL, ERASE и Remove-Item можно получить в самой консоли, выполнив интересующую вас команду с ключом /? в классической командной строке и get-help название-командлёта в PowerShell.
In some cases, for whatever reason, Windows will make sure that the provided file is used by the system and prevent it from being deleted. This file situation is very frustrating, especially if you know the file is not in use.
If you are having trouble in deleting any file or folder directly by right-clicking, then you can delete it using cmd. The commands below delete the specific file or folder and place them in the recycle bin:
- del
- rmdir
Here we have created a sample File and a Folder to delete it using CMD:
del command
del command is used to delete a file. Here, we will take our sample file “hello.txt” located at the desktop and try to delete it using the del command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the file:
Step 1: Change the path of the directory in CMD and set it to the path of the file. Type the following command in cmd and press Enter:
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the file “hello.txt” with following command:
del hello.txt
rmdir command
rmdir command is used to delete the entire folder or directory. Here, we will take our sample folder named “Tasks” placed at desktop and try to delete it using rmdir command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the folder:
Step 1: Change the path of the directory in CMD and set it to the path of the folder. Type the following command in cmd and press Enter:
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the folder “Tasks” with following command:
rmdir tasks
Last Updated :
03 Jul, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
Some folders and files are impossible to delete using Windows Explorer. These include files with long paths, names or reserved names like CON, AUX, COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, LPT1, LPT2, LPT3, PRN, NUL etc. You will get an Access Denied error message when you try to delete these files using Windows Explorer, even if you are an administrator.
Regardless of the reason, these can only be force deleted using command line only. This article explains using cmd to delete folder or file successfully.
Table of contents
- Before we begin
- How to remove files and folders using Command Prompt
- Del/Erase command in cmd
- Rmdir /rd command in cmd
- Delete multiple files and folders
- Delete files and folders in any directory
- Check the existence of file or folder then remove using IF command
- How to remove files and folders using Windows PowerShell
- Delete multiple files and folders
- Delete files and folders in any directory
- Delete files and folders with complex and long paths using the command line
- Closing words
Before we begin
Here are some important things for you to understand before we dig into removing files and folders using Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell. These tips will help you understand the terms and some basic rules of the commands that will be used further in the article.
The most important thing to remember here is the syntax of the path and file/folder name. When typing file name, notice whether there is a gap (space) in it. For example, if the folder name has no space in it, it can be written as-is. However, if there is a gap in it, it will need to be written within parenthesis (“”). Here is an example:
Another thing to remember is that you might see different outcomes while removing folders that are already empty, and folders that have some content in them. Having said that, you will need to use the dedicated options in the command to remove content from within a folder along with the main folder itself. This is called a recursive action.
Furthermore, you must also know how to change your working directory when inside a Command Line Interface. Use the command cd to change your directory, followed by the correct syntax. Here are some examples:
One last thing that might come in handy is being able to view what content is available in the current working directory. This is especially helpful so that you type in the correct spelling of the target file or folder. To view the contents of the current working directory in Command Prompt and PowerShell, type in Dir.
Now that we have the basic knowledge, let us show you how you can delete files and folders using the command line on a Windows PC.
By default, there are 2 command-line interfaces built into Windows 10 – Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell. Both of these are going to be used to delete content from a computer.
How to remove files and folders using Command Prompt
Let us start with the very basic commands and work our way up from there for Command Prompt. We recommend that you use Command Prompt with administrative privileges so that you do not encounter any additional prompts that you already might have.
Del/Erase command in cmd
Del and Erase commands in Command Prompt are aliases of one another. Meaning, both perform the same function regardless of which one you use. These can be used to remove individual items (files) in the current working directory. Remember that it cannot be used to delete the directories (folders) themselves.
Use either of the following commands to do so:
Tip: Use the Tab button to automatically complete paths and file/folder names.
Del File/FolderName Erase File/FolderName
Replace File/FolderName with the name of the item you wish to remove. Here is an example of us removing files from the working directory:
If you try to remove items from within a folder, whether empty or not, you will be prompted for a confirmation action, such as the one below:
In such a scenario, you will need to enter Y for yes and N for no to confirm. If you select yes, the items directly within the folder will be removed, but the directory (folder) will remain. However, the subdirectories within the folder will not be changed at all.
This problem can be resolved by using the /s switch. In order to remove all of the content within the folder and its subdirectories, you will need to add the recursive option in the command (/s). The slash followed by “s” signifies the recursive option. Refer to the example below to fully understand the concept:
We will be using the Del command here to recursively remove the text files within the folder “Final folder,” which also has a subdirectory named “Subfolder.” Subfolder also has 2 sample text files that we will be recursively removing with the following command:
Del /s "Final folder"
Here is its output:
As you can see in the image above, we had to enter “y” twice – once for each folder. with each confirmation, 2 text files were removed, as we had stated earlier in this example. However, if we use File Explorer, we can still see that both the directories – “Final folder” and “Subfolder” – are still there, but the content inside them is removed.
You can also make another tweak to the command so that it is executed silently and you will not be prompted for confirmation. Here is how:
Del /s /q "Final folder"
The /q illustrates that the action be taken quietly.
Rmdir /rd command in cmd
Similar to Del and Erase, rmdir and rd are also aliases for one another, which means to remove directory. These commands are used to remove the entire directory and subdirectories (recursively) including their contents. Use the command below to do so:
rmdir "New Folder"
The above command will remove the “New folder” only if it is empty. If a folder has subdirectories, you might get the following prompt:
In this case, we will need to apply the option for recursive deletion of items as we have done earlier with the Del command.
rmdir /s "Final folder"
Of course, this can also be performed with the /q option so that you are not prompted with a confirmation.
rmdir /s /q "Final folder"
Delete multiple files and folders
Up until now, we have completed the task of deleting single items per command. Now let’s see how you can remove multiple selective files or folders. Use the command below to do so:
For files:
Del "File1.txt" "File3.txt" "File5.txt"
For directories:
rd "Folder1" "Folder3" "Folder5"
Here is a before and after comparison of the directory where both of the above commands were executed:
You can also use an asterisk (*) concatenated with a file type or file name to perform bulk removal of files with the Del command. However, Microsoft has removed the support for the use of asterisks with rmdir so that users do not accidentally remove entire folders.
Here is an example of us removing all .txt files from our current working directory:
Del "*.txt"
Delete files and folders in any directory
We are working on removing content within the current working directory. However, you can also use the commands we have discussed till now to remove files and folders from any directory within your computer.
Simply put the complete path of the item you want to delete in enclosed parenthesis, and it shall be removed, as in the example below:
Check the existence of file or folder then remove using IF command
We have already discussed that you can view the contents of the working directory by typing in Dir in Command Prompt. However, you can apply an “if” condition in Command Prompt to remove an item if it exists. If it will not, the action would not be taken. Here is how:
if exist File/FolderName (rmdir /s/q File/FolderName)
Replace File/FolderName in both places with the name of the item (and extension if applicable) to be deleted. Here is an example:
if exist Desktop (rmdir /s/q Desktop)
How to remove files and folders using Windows PowerShell
The commands in Windows PowerShell to delete and remove content from your PC are very much similar to those of Command Prompt, with a few additional aliases. The overall functionality and logic are the same.
We recommend that you launch Windows PowerShell with administrative privileges before proceeding.
The main thing to note here is that unlike Command Prompt, all commands can be used for both purposes – removing individual files as well as complete directories. We ask you to be careful while using PowerShell to delete files and folders, as the directory itself is also removed.
The good thing is that you do not need to specify recursive action. If a directory has sub-directories, PowerShell will confirm whether you wish to continue with your deletion, which will also include all child objects (subdirectories).
Here is a list of all the commands/aliases that can be used in PowerShell to remove an item:
- Del
- Rm-dir
- remove-item
- Erase
- Rd
- Ri
- Rm
We tested all of these commands in our working directory and each of them was successful in deleting the folders as well as individual items, as can be seen below:
As can be seen above, the syntax of all the aliases is the same. You can use any of the commands below to delete an item using PowerShell:
Del File/FolderName Rm-dir File/FolderName remove-item File/FolderName Erase File/FolderName Rd File/FolderName Ri File/FolderName Rm File/FolderName
Delete multiple files and folders
You can also delete multiple selective files and folders just as we did while using Command Prompt. The only difference is that you will need to provide the complete path of each item, even if you are in the same working directory. Use the command below to do so:
Del "DriveLetter:\Path\ItemName", "DriveLetter:\Path\ItemName"
Remember to append the file type if the item is not a directory (.txt, .png, etc.), as we have done in the example below:
You can also use an asterisk (*) concatenated with a file type or file name to perform bulk removal of files with the Del command, as done in Command Prompt. Here is an example:
The command shown above will remove all.txt files in the directory “New folder.”
Delete files and folders in any directory
You can also remove an item in a different directory, just like we did in Command Prompt. Simply enter the complete path to the item in PowerShell, as we have done below:
Delete files and folders with complex and long paths using the command line
Sometimes you may encounter an error while trying to delete an item that may suggest that the path is too long, or the item cannot be deleted as it is buried too deep. Here is a neat trick you can apply using both Command Prompt and PowerShell to initially empty the folder, and then remove it using any of the methods above.
Use the command below to copy the contents of one folder (which is empty) into a folder that cannot be deleted. This will also make the destination folder empty, hence making it removable.
robocopy "D:\EmptyFolder" D:\FolderToRemove /MIR
In this scenario, the EmptyFolder is the source folder that we have deliberately kept empty to copy it to the target folder “FolderToRemove.”
You will now see that the folder that was previously unremovable is now empty. You can proceed to delete it using any of the methods discussed in this article.
Closing words
The command line is a blessing for Windows users. You can use any of these commands to remove even the most stubborn files and folders on your computer.
Let us know which solution worked for you in the comments section down below.