How do I find out which process is listening on a TCP or UDP port on Windows?
Mateen Ulhaq
24.7k19 gold badges102 silver badges136 bronze badges
asked Sep 7, 2008 at 6:26
readonlyreadonly
344k107 gold badges204 silver badges205 bronze badges
11
PowerShell
TCP
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort YourPortNumberHere).OwningProcess
UDP
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetUDPEndpoint -LocalPort YourPortNumberHere).OwningProcess
cmd
netstat -a -b
(Add -n to stop it trying to resolve hostnames, which will make it a lot faster.)
Note Dane’s recommendation for TCPView. It looks very useful!
-a Displays all connections and listening ports.
-b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port. In some cases well-known executables host multiple independent components, and in these cases the sequence of components involved in creating the connection or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called, and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient permissions.
-n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
-o Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:28
15
There’s a native GUI for Windows:
-
Start menu → All Programs → Accessories → System Tools → Resource Monitor
-
or run
resmon.exe, -
or from TaskManager → Performance tab.
serge
14.1k35 gold badges124 silver badges206 bronze badges
answered May 18, 2014 at 5:02
bcorsobcorso
45.7k10 gold badges63 silver badges76 bronze badges
10
For Windows:
netstat -aon | find /i "listening"
xash
3,70210 silver badges22 bronze badges
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:32
akuaku
122k32 gold badges174 silver badges203 bronze badges
6
Use TCPView if you want a GUI for this. It’s the old Sysinternals application that Microsoft bought out.
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:38
DaneDane
9,7375 gold badges28 silver badges23 bronze badges
3
The -b switch mentioned in most answers requires you to have administrative privileges on the machine. You don’t really need elevated rights to get the process name!
Find the pid of the process running in the port number (e.g., 8080)
netstat -ano | findStr "8080"
Find the process name by pid
tasklist /fi "pid eq 2216"
Jaywalker
3,0793 gold badges29 silver badges44 bronze badges
answered Jan 24, 2018 at 3:50
Ram SharmaRam Sharma
2,4971 gold badge8 silver badges7 bronze badges
You can get more information if you run the following command:
netstat -aon | find /i "listening" |find "port"
using the ‘Find’ command allows you to filter the results. find /i "listening" will display only ports that are ‘Listening’. Note, you need the /i to ignore case, otherwise you would type find «LISTENING». | find "port" will limit the results to only those containing the specific port number. Note, on this it will also filter in results that have the port number anywhere in the response string.
answered Oct 8, 2013 at 18:56
Nathan24Nathan24
1,3721 gold badge11 silver badges20 bronze badges
4
-
Open a command prompt window (as Administrator) From «Start\Search box» Enter «cmd» then right-click on «cmd.exe» and select «Run as Administrator»
-
Enter the following text then hit Enter.
netstat -abno-a Displays all connections and listening ports.
-b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or
listening port. In some cases well-known executables host
multiple independent components, and in these cases the
sequence of components involved in creating the connection
or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable
name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called,
and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option
can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient
permissions.-n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
-o Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.
-
Find the Port that you are listening on under «Local Address»
-
Look at the process name directly under that.
NOTE: To find the process under Task Manager
-
Note the PID (process identifier) next to the port you are looking at.
-
Open Windows Task Manager.
-
Select the Processes tab.
-
Look for the PID you noted when you did the netstat in step 1.
-
If you don’t see a PID column, click on View / Select Columns. Select PID.
-
Make sure “Show processes from all users” is selected.
-
answered Nov 8, 2012 at 1:49
CyborgCyborg
1,24412 silver badges12 bronze badges
Get PID and Image Name
Use only one command:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr 9000') do tasklist /FI "PID eq %a"
where 9000 should be replaced by your port number.
The output will contain something like this:
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
java.exe 5312 Services 0 130,768 K
Explanation:
-
it iterates through every line from the output of the following command:
netstat -aon | findstr 9000 -
from every line, the PID (
%a— the name is not important here) is extracted (PID is the5th element in that line) and passed to the following commandtasklist /FI "PID eq 5312"
If you want to skip the header and the return of the command prompt, you can use:
echo off & (for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr 9000') do tasklist /NH /FI "PID eq %a") & echo on
Output:
java.exe 5312 Services 0 130,768 K
answered Feb 10, 2016 at 10:17
ROMANIA_engineerROMANIA_engineer
54.6k29 gold badges203 silver badges200 bronze badges
1
First we find the process id of that particular task which we need to eliminate in order to get the port free:
Type
netstat -n -a -o
After executing this command in the Windows command line prompt (cmd), select the pid which I think the last column. Suppose this is 3312.
Now type
taskkill /F /PID 3312
You can now cross check by typing the netstat command.
NOTE: sometimes Windows doesn’t allow you to run this command directly on CMD, so first you need to go with these steps:
From the start menu -> command prompt (right click on command prompt, and run as administrator)
answered Aug 23, 2014 at 15:25
1
With PowerShell 5 on Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016, run the Get-NetTCPConnection cmdlet. I guess that it should also work on older Windows versions.
The default output of Get-NetTCPConnection does not include Process ID for some reason and it is a bit confusing. However, you could always get it by formatting the output. The property you are looking for is OwningProcess.
-
If you want to find out the ID of the process that is listening on port 443, run this command:
PS C:\> Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 443 | Format-List LocalAddress : :: LocalPort : 443 RemoteAddress : :: RemotePort : 0 State : Listen AppliedSetting : OwningProcess : 4572 CreationTime : 02.11.2016 21:55:43 OffloadState : InHost -
Format the output to a table with the properties you look for:
PS C:\> Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 443 | Format-Table -Property LocalAddress, LocalPort, State, OwningProcess LocalAddress LocalPort State OwningProcess ------------ --------- ----- ------------- :: 443 Listen 4572 0.0.0.0 443 Listen 4572 -
If you want to find out a name of the process, run this command:
PS C:\> Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 443).OwningProcess Handles NPM(K) PM(K) WS(K) CPU(s) Id SI ProcessName ------- ------ ----- ----- ------ -- -- ----------- 143 15 3448 11024 4572 0 VisualSVNServer
answered Nov 2, 2016 at 19:19
bahrepbahrep
30k12 gold badges103 silver badges151 bronze badges
To get a list of all the owning process IDs associated with each connection:
netstat -ao |find /i "listening"
If want to kill any process have the ID and use this command, so that port becomes free
Taskkill /F /IM PID of a process
answered Apr 17, 2014 at 14:38
Monis MajeedMonis Majeed
1,35814 silver badges21 bronze badges
1
It is very simple to get the port number from a PID in Windows.
The following are the steps:
-
Go to run → type cmd → press Enter.
-
Write the following command…
netstat -aon | findstr [port number](Note: Don’t include square brackets.)
-
Press Enter…
-
Then cmd will give you the detail of the service running on that port along with the PID.
-
Open Task Manager and hit the service tab and match the PID with that of the cmd, and that’s it.
answered May 30, 2016 at 6:36
Nishat LakhaniNishat Lakhani
7331 gold badge8 silver badges20 bronze badges
0
netstat -aof | findstr :8080 (Change 8080 for any port)
answered Feb 16, 2021 at 23:59
David JesusDavid Jesus
1,9812 gold badges29 silver badges34 bronze badges
To find out which specific process (PID) is using which port:
netstat -anon | findstr 1234
Where 1234 is the PID of your process. [Go to Task Manager → Services/Processes tab to find out the PID of your application.]
answered Dec 14, 2018 at 6:55
Talha ImamTalha Imam
1,0461 gold badge20 silver badges22 bronze badges
2
In case someone need an equivalent for macOS like I did, here is it:
lsof -i tcp:8080
After you get the PID of the process, you can kill it with:
kill -9 <PID>
answered Aug 12, 2020 at 11:22
wzsowzso
3,5325 gold badges28 silver badges48 bronze badges
2
Just open a command shell and type (saying your port is 123456):
netstat -a -n -o | find "123456"
You will see everything you need.
The headers are:
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID
TCP 0.0.0.0:37 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1111
This is as mentioned here.
answered Jan 25, 2017 at 0:13
1
If you’d like to use a GUI tool to do this there’s Sysinternals’ TCPView.
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:40
David WebbDavid Webb
191k57 gold badges313 silver badges299 bronze badges
-
Open the command prompt — start → Run →
cmd, or start menu → All Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt. -
Type
netstat -aon | findstr '[port_number]'
Replace the [port_number] with the actual port number that you want to check and hit Enter.
- If the port is being used by any application, then that application’s detail will be shown. The number, which is shown at the last column of the list, is the PID (process ID) of that application. Make note of this.
-
Type
tasklist | findstr '[PID]'
Replace the [PID] with the number from the above step and hit Enter.
- You’ll be shown the application name that is using your port number.
answered May 9, 2019 at 12:18
Anatole ABEAnatole ABE
5751 gold badge7 silver badges12 bronze badges
2
PowerShell
If you want to have a good overview, you can use this:
Get-NetTCPConnection -State Listen | Select-Object -Property *, `
@{'Name' = 'ProcessName';'Expression'={(Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).Name}} `
| select ProcessName,LocalAddress,LocalPort
Then you get a table like this:
ProcessName LocalAddress LocalPort
----------- ------------ ---------
services :: 49755
jhi_service ::1 49673
svchost :: 135
services 0.0.0.0 49755
spoolsv 0.0.0.0 49672
For UDP, it is:
Get-NetUDPEndpoint | Select-Object -Property *, `
@{'Name' = 'ProcessName';'Expression'={(Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).Name}} `
| select ProcessName,LocalAddress,LocalPort
answered Feb 27, 2022 at 22:16
Oliver GaidaOliver Gaida
1,7327 silver badges14 bronze badges
Netstat:
- -a displays all connection and listening ports
- -b displays executables
- -n stop resolve hostnames (numerical form)
-
-o owning process
netstat -bano | findstr "7002" netstat -ano > ano.txt
The Currports tool helps to search and filter
answered Sep 23, 2018 at 5:05
Blue CloudsBlue Clouds
7,3655 gold badges72 silver badges113 bronze badges
Type in the command: netstat -aon | findstr :DESIRED_PORT_NUMBER
For example, if I want to find port 80: netstat -aon | findstr :80
This answer was originally posted to this question.
answered Nov 22, 2016 at 15:36
TechnotronicTechnotronic
8,4744 gold badges40 silver badges53 bronze badges
netstat -ao and netstat -ab tell you the application, but if you’re not a system administrator you’ll get «The requested operation requires elevation».
It’s not ideal, but if you use Sysinternals’ Process Explorer you can go to specific processes’ properties and look at the TCP tab to see if they’re using the port you’re interested in. It is a bit of a needle and haystack thing, but maybe it’ll help someone…
answered Mar 13, 2014 at 19:57
Tony DelroyTony Delroy
103k15 gold badges177 silver badges253 bronze badges
1
Using Windows’ default shell (PowerShell) and without external applications
For those using PowerShell, try Get-NetworkStatistics:
> Get-NetworkStatistics | where Localport -eq 8000
ComputerName : DESKTOP-JL59SC6
Protocol : TCP
LocalAddress : 0.0.0.0
LocalPort : 8000
RemoteAddress : 0.0.0.0
RemotePort : 0
State : LISTENING
ProcessName : node
PID : 11552
answered Aug 25, 2016 at 13:36
mikemaccanamikemaccana
112k99 gold badges392 silver badges497 bronze badges
3
I recommend CurrPorts from NirSoft.
CurrPorts can filter the displayed results. TCPView doesn’t have this feature.
Note: You can right click a process’s socket connection and select «Close Selected TCP Connections» (You can also do this in TCPView). This often fixes connectivity issues I have with Outlook and Lync after I switch VPNs. With CurrPorts, you can also close connections from the command line with the «/close» parameter.
answered Jun 29, 2015 at 22:07
JoshJosh
2,1422 gold badges23 silver badges20 bronze badges
0
A single-line solution that helps me is this one. Just substitute 3000 with your port:
$P = Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 3000).OwningProcess; Stop-Process $P.Id
Edit: Changed kill to Stop-Process for more PowerShell-like language
answered Feb 3, 2019 at 14:46
Angel VenchevAngel Venchev
7071 gold badge7 silver badges18 bronze badges
2
Use:
netstat -a -o
This shows the PID of the process running on a particular port.
Keep in mind the process ID and go to Task Manager and services or details tab and end the process which has the same PID.
Thus you can kill a process running on a particular port in Windows.
answered Aug 13, 2013 at 2:32
nishanisha
7112 gold badges14 silver badges28 bronze badges
To find pid who using port 8000
netstat -aon | findstr '8000'
To Kill that Process in windows
taskkill /pid pid /f
where pid is the process id which you get form first command
answered Jul 14, 2020 at 6:13
jizjiz
3083 silver badges7 bronze badges
2
Follow these tools: From cmd: C:\> netstat -anob with Administrator privileges.
Process Explorer
Process Dump
Port Monitor
All from sysinternals.com.
If you just want to know process running and threads under each process, I recommend learning about wmic. It is a wonderful command-line tool, which gives you much more than you can know.
Example:
c:\> wmic process list brief /every:5
The above command will show an all process list in brief every 5 seconds. To know more, you can just go with /? command of windows , for example,
c:\> wmic /?
c:\> wmic process /?
c:\> wmic prcess list /?
And so on and so forth. 
1
You can also check the reserved ports with the command below. Hyper-V reserve some ports, for instance.
netsh int ipv4 show excludedportrange protocol=tcp
answered Nov 24, 2020 at 14:50
При запуске новых сервисов в Windows, вы можете обнаружить что нужный порт уже занят (слушается) другой программой (процессом). Разберемся, как определить какая программ прослушивает определенный TCP или UDP порт в Windows.
Например, вы не можете запустить сайт IIS на стандартном 80 порту в Windows, т.к. этот порт сейчас занят (при запуске нескольких сайтов в IIS вы можете запускать их на одном или на разных портах). Как найти службу или процесс, который занял этот порт и завершить его?
Чтобы вывести полный список TCP и UDP портов, которые прослушиваются вашим компьютером, выполните команду:
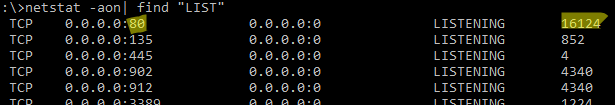
netstat -aon| find "LIST"
Или вы можете сразу указать искомый номер порта:
netstat -aon | findstr ":80" | findstr "LISTENING"
Используемые параметры команды netstat:
- a – показывать сетевые подключения и открытые порты
- o – выводить идентфикатор професса (PID) для каждого подключения
- n – показывать адреса и номера портов в числовом форматер
По выводу данной команды вы можете определить, что 80 порт TCP прослушивается (статус
LISTENING
) процессом с PID 16124.
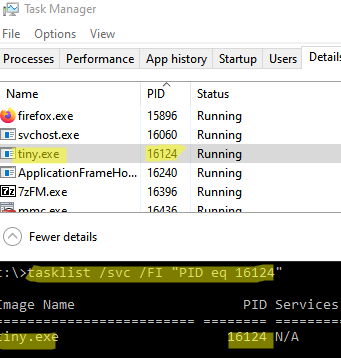
Вы можете определить исполняемый exe файл процесса с этим PID с помощью Task Manager или с помощью команды:
tasklist /FI "PID eq 16124"
Можно заменить все указанные выше команды одной:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr :80') do tasklist /FI "PID eq %a"
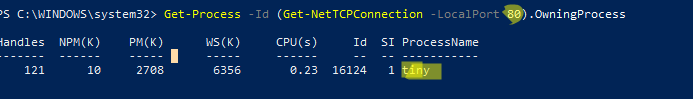
С помощью однострочной PowerShell команды можно сразу получить имя процесса, который прослушивает:
- TCP порт:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80).OwningProcess - UDP порт:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetUDPEndpoint -LocalPort 53).OwningProcess
Можно сразу завершить этот процесс, отправив результаты через pipe в командлет Stop-Process:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80).OwningProcess| Stop-Process
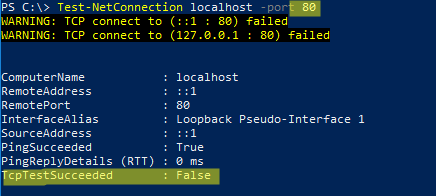
Проверьте, что порт 80 теперь свободен:
Test-NetConnection localhost -port 80
Чтобы быстрой найти путь к исполняемому файлу процесса в Windows, используйте команды:
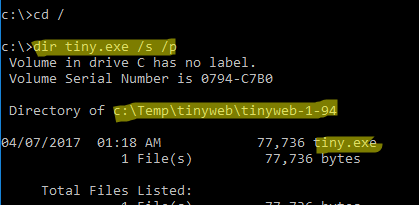
cd /
dir tiny.exe /s /p
Или можно для поиска файла использовать встроенную команду where :
where /R C:\ tiny
В нашем случае мы нашли, что исполняемый файл
tiny.exe
(легкий HTTP сервер), который слушает 80 порт, находится в каталоге c:\Temp\tinyweb\tinyweb-1-94
You may encounter errors such as «port is currently in use…» and be unable to reassign the same port to another application. As a result, you may need to determine which processes and applications are using that port. So, in this tutorial in our tech room, I’ll walk you through the steps to determine the port’s process.
This guide will also cover the fundamental concepts of program, process, and port, as well as how they interact with one another. Then we’ll show you how to find out what process the port is using in Windows, Mac, and Linux. Doesn’t that sound fantastic? Let’s get this party started right away.
Process and Port are different things. A program or application is a piece of information that does specific things and is stored in some physical storage. When the program is loaded into memory then the process comes into existence. The process is a program that is currently running on your computer. The process can be anything like MS Word, Google Chrome tab, small background task. Process in a computer system is identified by a certain number called a PID number. This PID tag is used by the operating system to identify each process.
A port is the endpoint of communication. If you open two tabs in your Chrome browser you will find different processes running on different port numbers. This process ID and port number identify which port that process is using to communicate.
Within the same network(local or remote), No two applications can listen to the same port at the same.ie.NO TWO PROGRAMS CAN respond TO THE SAME SOCKET ie( IP ADDRESS: PORT COMBINATION ). If you open two notepads, then you will find two separate processes in the task manager each using a separate port.
Windows Environment
Find process/program using Port in Windows Using Command Prompt
Netstat is a useful command-line scripting utility available for Windows, Mac, Linux, and Unix. Netstat helps to show network statistics and connections of your system. and is taken as a powerful networking tool for troubleshooting and network configuration. With the help of the netstat command, we can easily find out the process using the port.
In Windows OS just find a port number and apply the following command in the command prompt
netstat -ano | findstr
Here,
| -a | Helps to display all the active ports. |
| -b | Helps to display the executable file of listening ports. |
| -o | Helps to display the process identifier(PID) associated with each connection. |
| -n | Helps to display port and address in numeric format. |
| | | Called a Pipe which is used to combine two or more commands. Here, the output of one command is input to another. Here, the output of netstat -ano is the input to findstr |
| findStr | Helps to find the string present left to it. |
| port_number | Any port whose process you want to find. |
Here, I am going to find out the process used by port number:1434 as below.
This will give information like which protocol is used either TCP or UDP, which local address and port are used, which remote address and port are used, what is the current state of the process, PID number of the process/program using the port, etc.
Now, we can scan the Process / Program with the help of PID because PID is associated with the process. Let’s find Process/Program using the given port by following the command.
tasklist /FI «PID eq 5720»
Here, we have 5720 PID, and let’s find the process associated with it.
Here, The tasklist cmdlet allows us to retrieve a list of all currently running processes./FI is a filter that helps in the finding of matches defined by the filter. In this case, the ‘eq’ filter on PID is used. You can also use other filters like eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le, and so on. Also, the PID number must be positive.
Find process/program using Port in Windows Using Powershell
You can simply type the below command:
For TCP:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort ).OwningProcess
- Get-Process is a Powershell cmdlet that returns all background processes that are currently running in Windows.
- Get-NetTCPConnection cmdlet helps to get current TCP connections.
- -LocalPort helps to find current TCP connections having a local port.
For UDP:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetUDPEndpoint -LocalPort ).OwningProcess
Find process/program using the port in Windows using Resource Manager
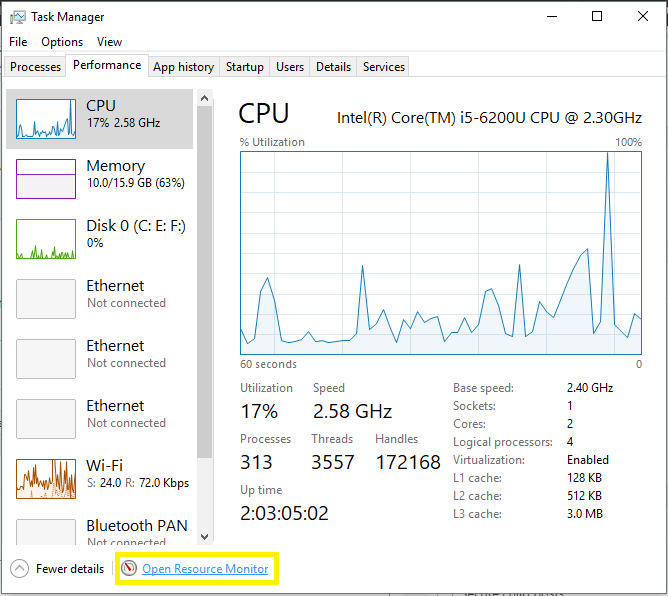
Resource Monitor is a powerful GUI tool available for Windows 7/8/10/11 for finding out how much hardware resources(disk, network, memory, and CPU)and software resources are being used by the process in real time.
- Goto run and type «resmon.exe» without quote and press enter.
- Under Overview, you will find the process name as Image, PID, Description, Status, and many more.
Find Process/program using the port in Windows using third-party Tools
There are lots of third-party tools which help to easily find out the process/program using the port. Some of them are TCPView.Here I will explain to you how to use TCPView to find processes using the port.
TCPView is a third-party network monitoring Windows application that provides detailed information of all TCP and UDP endpoints on a system.
1. First, install TCPView from here.
2. Open TCPView and its interface look as below:

Check Process Name / Program using TCPView.
1 In Search bar type port number. In my case, I am searching process name or program name using port 1434 so I used 1434 in the search field.
2 Then you will get the process name and module name as shown above.
This shows that the 1434 port is used by MSSQL Server.
Linux Environment
Find process/program using Port in Linux Using Netstat Command
You can simply use netstat command to find out the program using the port in Linux. We can do it by typing the below command in the terminal.
netstat -tulpn | grep :
eg. netstat -tulpn | grep : 3030
This will find out the process using 3030 PID.
In the CentOS version, you could try like below:
netstat -vanp —tcp | grep 3030
macOS Environment
Find Process/program using Port in MacOs using Netstat Command
netstat -vanp tcp | grep
eg. netstat -vanp tcp | grep 3030
Find Process/Program using Port in For macOS El Capitan and newer using the below command will work.
lsof -i tcp:
eg. lsof -i tcp:3030
see man lsof for detail
Using Activity Monitor
This tool is a built-in tool that helps you to view all the processes that are running on your Mac Computer.
Steps to view the process using Activity Monitor:
- First of all open Activity Monitor tools
- Then click on the Network Tab.
- Then look for the process (under the «Name» column) that is using the port you are interested in.
There are also other tools like TCPView and Little Snitch.
Many times we know the port number and want to get the details of the process running on that port on windows. Reasons may be
- to find which program is using the port.
- the process name running on that port.
- to find the process id(PID) of the process using its port so that we can kill the process.
Windows provides netstat command. This command has different options which can be used to extract port and process related information.
Find process running on given port
Use the below command if you know the port and want to get the PID of process running on it.
netstat -aon | findStr “<port number>”
Example,
netstat -aon | findStr “49691”
returned the following output on my windows machine
TCP [::1]:49691 [::]:0 LISTENING 8864
Rightmost column is the PID of the process and second column from the left shows the port number.
Above command options can be explained in detail as below.
-a : Displays all ports of the local machine that have been connected by a process.
-o : Displays the PID of the process running on a port. Removing this option will not display the process ID(PID).
-n : Displays the port numbers in numeric format.
Pipe(|) followed by findStr operator and the port number is used to filter the processes running on that port.
If you simply execute command netstat -aon, then it will list all the busy ports on the machine.
Another method to list all the above information along with the name of executable responsible for the process is by using command
netstat -a -b -n -o
But for this you should have administrator privileges, that is, the command prompt should be opened with Administrator rights where
-b : Lists the executable which started the process.
Find listening ports
If you want to check which all ports have a process which is Listening for incoming connections or to check open ports, then use the below command.
netstat -aon | find /i “LISTENING”
where find is a windows command for searching for a value in the string provided to it and /i is its option for case insensitive search.
If you are using /i, then you can also use “listening”, “Listening” etc., values for search.
Resource Monitor
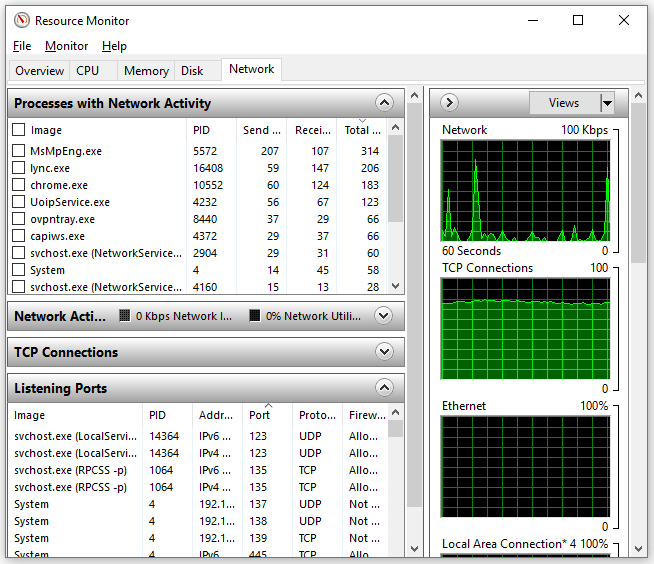
If you do not want to go with the command line option, then you can use a GUI in the form of Resource Monitor on Windows.
With Resource Monitor, you can get information about the process name, its PID, IP address and Port which it is running on.
You can open Resource Monitor from the Performance tab of Task Manager as shown below.
When you click on the highlighted link in the above image, it opens up a new Resource Monitor window as shown below.
As evident from the above image, Resource Manager contains information about process names, their PIDs, port etc.
If you do not want to open Resource Monitor through Task Manager, you can also open it directly running command resmon.exe from Windows command prompt.
Hope this post helped you out. Click the clap below to appreciate.
Find Process ID of Process using given port in Windows
Once a while it happens that you try to start Tomcat and it complains “Port 8080 required by Tomcat v7.0 Server at localhost is already in use”. So that means there is already a process running in background that has occupied 8080 port. So how to identify the process in Windows task manager that is using port 8080? I am sure there must be a javaw.exe. But is there a better way to identify which process in windows is using a given port number? Yes…
How to Find Process ID of process that uses a Port in Windows
Our friend netstat will help us in identifying the process. netstat can list the running process and display information such as process id, port, etc. From this list we can filter the processes that has given port using findstr command.
List process by port number
Code language: Bash (bash)
netstat -ano | findstr 8080
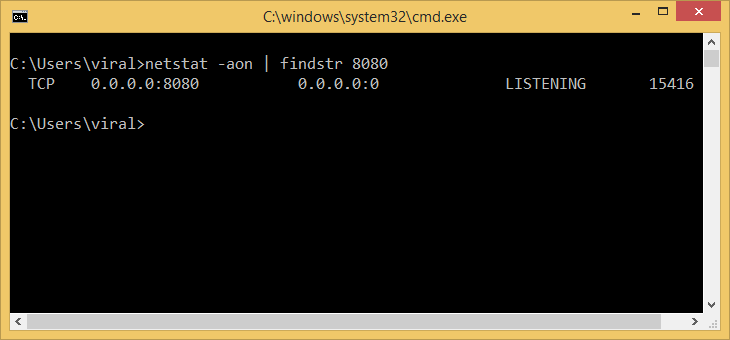
Output
Code language: Bash (bash)
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID TCP 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 29848
-a– Displays all connections and listening ports.-o– Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.-n– Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
We can use netstat to list all the processes.
List all processes by PID
Code language: Bash (bash)
netstat -ano
Kill the Process by PID
Once we identify the process PID, we can kill the process with taskkill command.
Code language: Bash (bash)
taskkill /F /PID 12345
Where /F specifies to forcefully terminate the process(es). Note that you may need an extra permission (run from admin) to kill some certain processes.
Or else you can use our old trusted Windows Task Manager to kill the process for given process id. If PID is not visible in your task manager then you can enable it by Right clicking on table header under Details tab, click Select Columns and then check PID.