Service Control Manager (SCM) Events
|
EVENT ID |
Message |
|
7005 |
The %1 call failed with the following error: %2 |
|
7006 |
The %1 call failed for %2 with the following error: %3 |
|
7007 |
The system reverted to its last known good configuration. The system is restarting…. |
|
7008 |
No backslash is in the account name. |
|
7010 |
Timeout (%1 milliseconds) waiting for ReadFile. |
|
7012 |
Message returned in the transaction has incorrect size. |
|
7015 |
Boot-start or system-start driver (%1) must not depend on a service. |
|
7018 |
Detected circular dependencies auto-starting services. |
|
7025 |
At least one service or driver failed during system startup. Use Event Viewer to examine the event log for details. |
|
7026 |
The following boot-start or system-start driver(s) failed to load: %1 |
|
7027 |
Windows could not be started as configured. A previous working configuration was used instead. |
|
7028 |
The %1 Registry key denied access to SYSTEM account programs so the Service Control Manager took ownership of the Registry key. |
|
7033 |
The Service Control Manager did not initialize successfully. The security configuration server (scesrv.dll) failed to initialize with error %1. The system is restarting… |

- 7000 Служба не ответила на запрос своевременно
- 7001 Служба является зависимой от службы, которую не удалось запустить из-за ошибки Не удалось запустить дочернюю службу
- 7001 Служба является зависимой от службы, которую не удалось запустить из-за ошибки Присоединенное к системе устройство не работает
- 7011 Превышение времени ожидания (60000 мс) при ожидании ответа транзакции от службы
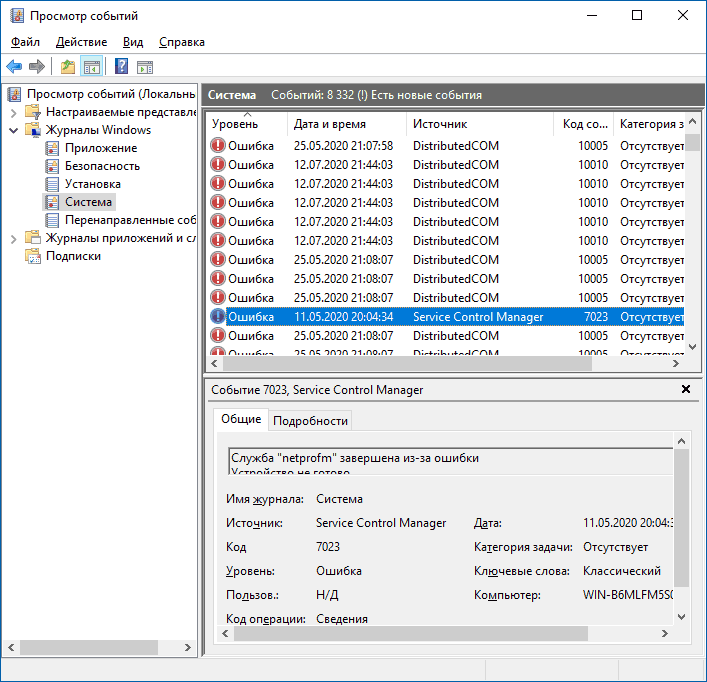
- 7023 Служба завершена из-за ошибки Устройство не готово
- 7031 Служба была неожиданно завершена. Это произошло (раз): 1
- 7034 Служба неожиданно прервана. Это произошло (раз): 1
- 7043 Служба не завершила работу должным образом после получения управления для выполнения предзавершающих операций
В этой инструкции подробно о том, что может вызывать такие ошибки в Windows 10, как исправить ошибки с указанными кодами от источника Service Control Manager в Windows 10, стоит ли это делать и дополнительная информация, которая может оказаться полезной.
Ошибки с источником Service Control Manager — причины, необходимость исправления
Прежде чем вы решите переживать и пытаться исправить ошибки с кодами события 7000, 7001, 7009, 7011, 7023, 7031, 7034, 7043 и источником Service Control Manager, учитывайте следующий важный момент: такие ошибки вы встретите на любой, даже самой чистой и беспроблемной системе Windows 10. Если в просмотре событий эти ошибки появляются время от времени, а не ежедневно при включении компьютера, работе и завершении работы, причинами могут быть обычные процессы работы Windows 10 связанные с:
- Установкой обновлений (при этом некоторые службы могут завершаться, а другие, зависимые от них, вызывать ошибку).
- Установкой новых версий драйверов (в том числе и самой Windows 10, в этих случаях мы можем получить ошибки, связанных с тем, что устройство не готово или не работает).
- Установкой сторонних программ, взаимодействующих со службами (иногда лишь временно, для успешного выполнения установки).
- Автоматическим обслуживанием системы (редко).
Во всех случаях появление ошибок возможно не при самом процессе, а после повторного включения компьютера или ноутбука, так как многие процессы установки завершаются лишь после перезагрузки.
В случае же если у вас эти ошибки возникают ежедневно, причины могут быть самыми разными, среди них:
- Ручное вмешательство в тип запуска служб, отключение служб, использование различных программ «для оптимизации», «ускорения» и «отключения слежки» Windows Получить представление о том, как отключение одних служб может влиять на работу других можно получить из статьи Не удалось запустить дочернюю службу — как исправить.
- В случае, если ошибок нет после перезагрузки компьютера или ноутбука, но присутствуют после завершения работы и последующего включения (особенно по прошествии некоторого времени), можно попробовать отключить быстрый запуск Windows 10. Желательно также вручную установить все оригинальные драйверы чипсета с сайта производителя ноутбука или материнской платы, в случае если у вас ПК.
- Нестабильная работа каких-либо устройств (плохое подключение, неисправности). Иногда — проблемы при задействовании устройства после перехода в режим энергосбережения. Можно попробовать отключить экономию энергию для устройств в дополнительных параметрах схемы электропитания в панели управления и в свойствах устройства в диспетчере устройств на вкладке «Управление электропитанием» (присутствует не для всех устройств). Особенно часто это касается USB устройств, сетевых и Wi-Fi адаптеров.
- Иногда ошибки могут появляться при завершении работы, если какие-то сторонние программы (например, клиенты для загрузки файлов из Интернета) мешают завершиться какой-либо сетевой службе.
Также при регулярном появлении указанных ошибок стоит проверить, а появляются ли они, если выполнить чистую загрузку Windows 10 — если нет, можно предположить, что правильному запуску служб мешают какие-то сторонние программы или антивирусы. Также может оказаться, что эти программы инициируют запуск служб, которые не могут быть запущены из-за отключенных дочерних служб.
Если проблема появилась недавно, вам могут помочь точки восстановления системы на дату, предшествующую появлению ошибок.
Увеличение времени ожидания запуска служб для ошибок с кодами 7000, 7009 и 7011
Ошибки типа «Превышение времени ожидания» или «Не ответила на запрос своевременно» при запуске служб c кодами события 7000, 7009 и 7011 могут появляться на медленных компьютерах и ноутбуках с HDD. В таких ситуациях мы можем увеличить время ожидания запуска службы:
- Запустите редактор реестра, для этого нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, введите regedit и нажмите Enter.
- Перейдите в раздел реестра
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control
- В правой панели редактора реестра найдите параметр с именем ServicesPipeTimeout. Если такой параметр отсутствует, нажмите правой кнопкой мыши в пустом месте панели справа, выберите «Создать» — «Параметр DWORD» и задайте имя ServicesPipeTimeout для этого параметра.
- Дважды нажмите по параметру ServicesPipeTimeout, выберите «Десятичный» и задайте значение 60000.
- Нажмите Ок, закройте редактор реестра и перезагрузите компьютер.
Указанные действия установят время ожидания для запуска службы равным 60 секунд. Если этого окажется недостаточно, можно попробовать увеличить значение.
Надеюсь, предложенный материал поможет разобраться с ошибками Service Control Manager в просмотре событий Windows 10 и предпринять действия для исправления ситуации при необходимости.
The Service Control Manager Error (Event ID 7001) can occur due to installation issues or hardware problems. Thankfully, it’s an easy fix without needing professional assistance.
Before anything, what is the Service Control Manager and what function does it play?
What Is the Service Control Manager?
The Service Control Manager allows you to make changes to different Windows processes, features, and programs that run in the background. This tool lets you modify services like the Windows Defender, as well as other third-party apps, such as antivirus suites that protect your computer.
Depending on your Windows 10/11 computer’s software configuration, you can access this utility to modify a program or service’s execution pattern all while maintaining a certain level of efficiency with other existing apps. Here’s how to use the Service Control Manager:
- Right-click on the Windows menu and select Manage.
- Double-click on the Services and Applications section and choose Services.
- Double-click on the service that you want to modify. Doing this will launch the service’s Properties menu.
- Now, you will see a set of execution options. Choose whatever you prefer. The Automatic Startup option sets the service to launch at startup, while the Manual Startup option lets you launch the service only when needed. The Disabled option will deactivate the service entirely.
- Hit OK to apply the changes.
Like other Windows 10/11 services and utilities, the Service Control Manager is also at risk of errors. One particular error associated with it is the Service Control Manager Event ID 7001.
What Is Service Control Manager Event ID 7001 on Windows 10/11?
Some Windows 10/11 users have reportedly encountered the Service Control Manager Error with Event ID 7001 while using the Event Viewer. It seems that this error is a result of a system issue associated with the Service Control Manager. If you go to the Event Viewer’s General tab, you should see the detailed error and have an idea about what’s causing it.
Generally, the Event ID 7001 error comes with this error message:
<System>
<Provider Name=”Service Control Manager” Guid=”{555908d1-a6d7-4695-8e1e-26931d2012f4}” EventSourceName=”Service Control Manager” />
<EventID Qualifiers=”49152″>7001</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>2</Level>
<Task>0</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8080000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime=”2018-10-
13T17:00:04.618596100Z” />
<EventRecordID>13970</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID=”884″ ThreadID=”3636″ />
<Channel>System</Channel>
<Computer>My Computer</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
– <EventData>
<Data Name=”param1″>RasMan</Data>
<Data Name=”param2″>SstpSvc</Data>
<Data Name=”param3″>%%0</Data>
<Binary> 5200610073004D0061006E000000 </ Binary>
</ EVENTDATE>
</ Event>
But then again, there could be other factors that could cause the Service Control Manager Error with Event ID 7001. And we will share them with you in the next part.
What Causes ‘Service Control Manager Error 7001’ on Windows 10/11?
There are various culprits that can contribute to the occurrence of this error. Below, we have listed some scenarios or instances where the Service Control Manager Event ID 7001 error will show:
- Mandatory Services Are Disabled – For the Computer Browser service to run efficiently, there are many different mandatory services that must be enabled. When they are not running, the error 7001 may appear. In this case, you need to access the Services utility to enable all the essential services.
- There Are Missing Network Discovery Dependencies – If you see that the Event IDs on the Event Viewer window is associated with the Network Discovery function, then the fix will involve running different commands using an elevated Command Prompt.
- Some System Files Are Corrupted – In some cases, you will see the error if your system has experienced system file In such a scenario, the best solution is to refresh Windows by performing a clean install.
- A Software Conflict Has Happened – According to some users, this error may occur after performing a system change like a driver installation or update. To fix this, you may need to use the System Restore utility.
- Malware Infection – It is possible that some sort of malware entity has infected your computer, resulting in the error.
How to Fix ‘Service Control Manager Error 7001’ on Windows 10/11
If you encounter the Service Control Manager Event ID 7001 on your Windows 10/11 device, then there is good news. You can easily resolve it by following the solutions below.
However, before you proceed, try easy troubleshooting methods first. Your Windows 10/11 device may just need a quick restart as plenty of processes are already running in the background, and that there are no sufficient resources to be allocated for new processes, which leads to the error.
It could also be the case of malware entities wreaking havoc on your system. Malware infection may have affected essential services, causing them not to run properly and throw the error message that you’re seeing.
If the basic troubleshooting methods did not work, then move on with the following solutions:
Solution #1: Enable All Essential and Related Services
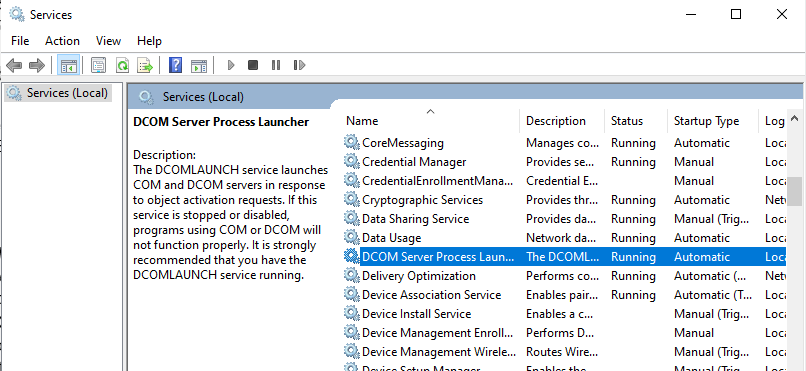
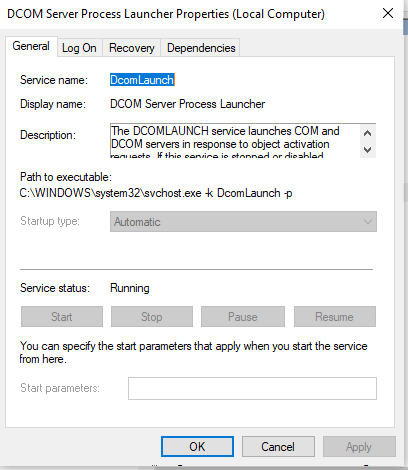
As mentioned above, the error may surface if the essential services required by the Service Control Manager are disabled. These include the DCOM Server Process Launcher, Security Accounts Manager, Server, and RPC Endpoint Mapper. By making sure these services are enabled, you can get rid of the error.
Here’s how to enable the mentioned services:
- Press the Windows + R keys to launch the Run utility.
- Type services.msc into the text field and hit OK. This will open the Services utility.
- Next, double-click on any of the above services to open Properties.
- Go to the General tab. Make sure that the status is Running.
- Navigate to Startup Type and select Automatic.
- Hit Apply then OK to apply your changes.
- Repeat the above steps for all other services.
- Restart your computer and see if the error still shows.
Solution #2: Repair All the Faulty Discovery Dependencies
You may also see the Service Control Manager Event ID 7001 if there is a problem with any of the Network Discovery dependencies. By cleaning the PeerNetworking folder, some users were able to resolve the problem.
Here’s a guide on how to do so:
- Launch the Run utility by pressing the Windows + R keys.
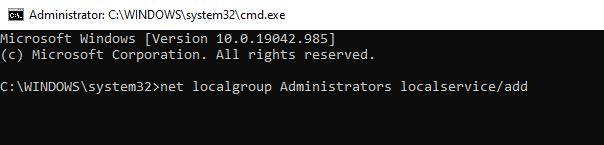
- Type cmd into the text field and press the CTRL + Shift + Enter keys simultaneously. This will open an elevated Command Prompt.
- Next, type the following commands and hit Enter after each one of them:
- net localgroup Administrators localservice /add
- net localgroup Administrators service /add
- Launch File Explorer and navigate to this location: C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\LocalService\AppData\Roaming.
- Go to the PeerNetworking folder and delete all its contents.
- Restart your computer and see if the Service Control Manager Event ID error 7001 is resolved.
Solution #3: Adjust the Service Logon User Rights
Based on the error’s general information, we can assume that it could be caused by a service that failed to start. And in some cases, it could happen because the service does not have sufficient user rights.
To fix this, adjust the service’s logon user rights. Here’s how:
- Go to the Services app and right-click on the problematic service highlighted on the error information.
- Select Properties.
- Go to the Log On tab and select This Account.
- Provide your username and password. Hit the Apply and OK button to apply the changes.
Solution #4: Optimize Your Drives
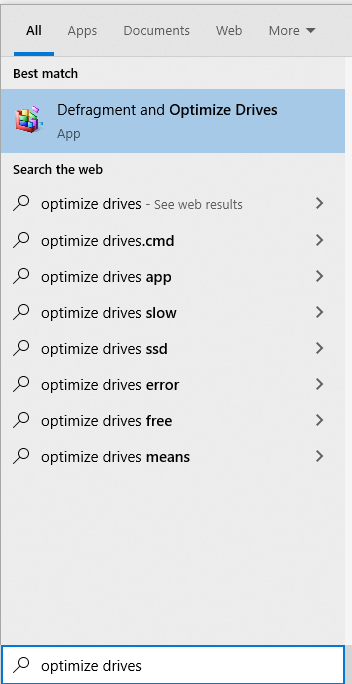
By optimizing your drives, you help improve your computer’s performance. If you want to optimize your Windows 10/11 drives, you may use the built-in Defragment and Optimize Drives tool.
To use it, follow these steps:
- Type optimize drives into the search field and click on the top-most result.
- Now, you will see a percentage of fragmentation of each disk in the Current Status column.
- Ideally, it must be less than 10%. If a disk’s fragmentation is more than 10%, then you have to optimize it. To do so, just click on the drive and hit the Optimize button.
Solution #5: Reset the TCP/IP of Your Windows Device
You may also see the error on your Windows computer if the Net.Tcp Port Sharing service is unable to start. In this scenario, resetting the TCP/IP of your device may resolve the problem.
Here’s how:
- Click the Start menu and type cmd into the search field.
- Right-click on the most relevant search result and select Run as Administrator.
- When the elevated Command Prompt opens, type the netsh int ip reset command.
- Hit Enter.
Solution #6: Enable the Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service
If the above solutions did not resolve the error, then this solution is worth trying. Many affected users have reportedly fixed the problem by enabling the Net.Tcp Port Sharing service.
Here’s how they did it:
- Press the Windows + R keys to launch the Run utility.
- Launch the Services Management Console by typing services.msc into the Run dialog box and hitting Enter.
- Scroll down the list and find the Net.Tcp Port Service.
- Double-click on the service and set its startup type to Automatic.
- Click the Start button and hit OK to continue.
- Restart your computer and check if this solution helps.
Solution #7: Disable the TCP Port Sharing Feature
Another solution you should try involves disabling the TCP Port Sharing feature. You can do this by using the Control Panel.
Just follow the instructions below:
- Input Turn Windows Features On and Off into the search field.
- Click on the top-most result.
- Expand the .NET Framework 4.6 Advanced Services section.
- Next, expand the WCF Services.
- Disable the TCP Port Sharing feature by unticking the box next to it.
- Hit OK to save your settings.
- Restart your computer.
Solution #8: Perform a System Restore
If all else fails, you may need to perform a System Restore. This way, you can restore your system to a previous point when the error does not show.
For this solution to work, you need to have a restore point first. To create one, follow these instructions.
- Type create a restore point into the search field. The System Properties window should now appear.
- Click the Configure button.
- If System Protection is disabled, enable it.
- Hit OK to proceed.
- Next, go to the System Properties window and select the partition associated with your system.
- Press the Create button.
- Add a description to the restore point and click Create once again.
- At this point, your system will create a restore point. Wait for it to finish.
- Once done, hit the Close button.
To restore Windows 10/11 using a restore point, do the following:
- Press the Power button twice or thrice to enter the Troubleshoot window.
- Select Advanced Options and click System Restore.
- In the window that appears, hit the Next button.
- Choose a restore point and hit Next.
- Confirm your action and press Finish.
Solution #9: Reset Every Windows Component
If none of the solutions has worked so far, then it is possibly the case of your system dealing with a system file corruption. Unfortunately, this calls for a more complex fix. So, if you find yourself in such a situation, then try resetting every Windows component relevant to the process.
Reset Windows components by following any of these procedures:
Repair Install
This is the approach we recommend if you plan to retain your applications and personal files. But to proceed with this, you need compatible installation media. Here’s how to perform a repair install:
- Download the Windows 10/11 ISO file from here.
- Save it on your computer, preferably on your desktop.
- Next, mount the file.
- Double-click on the setup.exe file to begin the repair and installation process.
Alternatively, you can use a USB installation media, but you need to have a USB flash drive with a minimum of 4 GB space for 32-bit installation and 8 GB for 64-bit.
Solution #10: Install Any Pending Windows Update
As you may already know, Microsoft fixes previously reported bugs and issues on Windows 10/11 by rolling out regular updates. So, you may try installing any available Windows update to resolve the Service Control Manager Event ID 7001 error.
To install a Windows update, do the following:
- Go to the Start menu.
- Click on the Settings icon. It is the one that has a gear icon.
- Next, select Update and Security.
- Navigate to the Windows Update tab.
- Hit the Update button. If an update is detected, it should start downloading right away.
- Wait for the process to complete. Once done, restart your computer.
Clean Install
This is usually the default choice if you are looking for a fast method that allows you to reset every Windows component without having to insert an installation media. But remember that this method may cause you to lose your data, so make sure you have a backup file.
Windows 10/11 Error Prevention Tips
To avoid errors like the Service Control Manager Event ID 7001, make sure your computer is running at an optimal state. Below are some tips that can help speed things up. Try them in any order you desire.
Tip #1: Make Sure Everything Is Up to Date
One of the best ways to ensure you make the most of your Windows 10/11 PC is to have the latest Windows 10 version. When you install the latest version, you are also installing the latest device drivers and improving your computer’s performance.
Tip #2: Make It a Habit to Restart Your PC and Open Those That You Only Need
Opening too many programs, tabs, and apps can slow down your computer. Worse, it can trigger error messages to appear. If you feel that your computer is becoming sluggish, restart it and open only the apps that you need.
To restart your computer, click the Start button. Go to Power and select Restart.
Tip #3: Free Up Disk Space
You can significantly improve your device’s performance by freeing up some disk space on your computer. To check if a disk has no sufficient space, go to Start and select Settings. Next, click System then Storage. All your drives will be listed in the Storage area. Take note of the total amount of free space and delete files from disks that are running low in space.
Tip #4: Pause Cloud Syncing
We know how handy the cloud is, especially when it comes to backing up files. However, syncing your files all the time can take a toll on your PC. Syncing real-time can slow down your PC. If you notice your PC is performing poorly, pause automatic syncing temporarily.
Tip #5: Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs
Whenever you switch on your computer, some programs will automatically launch and start in the background. You can disable them if you notice your computer is running slow.
Summary
The Service Control Manager plays an essential role in the Windows 10/11 platform. Not only does it allow you to make changes in core processes, but it also lets you modify various services like Windows Defender.
But as with other services, this tool may also encounter errors, and one of the most notorious ones is the Service Control Manager Error with Event ID 7001.
This error can be triggered by many different factors. The most common ones include disabled mandatory services, missing network discovery dependencies, corrupted system files, and software conflict.
Regardless of the cause, the error can be resolved. While some fixes are complex like clean installing Windows 10/11, others are easy to do such as enabling some services and disabling some features. And if you feel that the issue requires the help of professionals, you can always turn to the experts at Microsoft. They should be able to provide you with a solution that is suited for your scenario.
Have you used the Service Control Manager before? What errors did you encounter while using it? Share your experience in the comments!
Give us some love and rate our post!
Introduction
Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager is a Windows system event that is triggered when a service fails to start. It is used to log information about the service, such as the service name, the error code, and the cause of the failure. This event can be used to troubleshoot service-related issues and can help identify the root cause of the problem. It is important to note that this event is not an error, but rather a notification that a service has failed to start.
What is Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager and How Can It Help You?
Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager is a Windows system event that is triggered when a service fails to start. It is used to help diagnose and troubleshoot problems with services that are not starting correctly. The event contains information about the service that failed to start, including the service name, the error code, and the service-specific error message. This information can be used to identify the cause of the problem and take corrective action. Additionally, the event can be used to monitor the health of services on a system, as well as to detect malicious activity. By monitoring the Service Control Manager, administrators can ensure that services are running correctly and take action when they are not.
How to Troubleshoot Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager Errors
The Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager (SCM) error is a common issue that can occur when attempting to start a service or driver on a Windows computer. This error can be caused by a variety of issues, including missing or corrupt files, incorrect permissions, or a problem with the service or driver itself. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot and resolve this error.
First, check the system log in Event Viewer for any related errors. This can help you identify the cause of the issue. If the log does not provide any useful information, you can try restarting the computer. This can often resolve the issue.
If the error persists, you can try disabling the service or driver in question. To do this, open the Services window by typing “services.msc” in the Run dialog box. Then, right-click the service or driver and select “Properties.” In the Properties window, select the “Disable” option and click “OK.”
If disabling the service or driver does not resolve the issue, you can try reinstalling it. To do this, open the Device Manager by typing “devmgmt.msc” in the Run dialog box. Then, right-click the service or driver and select “Uninstall.” Once the uninstallation is complete, restart the computer and reinstall the service or driver.
Finally, if none of the above steps resolve the issue, you can try restoring the computer to an earlier point in time. To do this, open the System Restore window by typing “rstrui.exe” in the Run dialog box. Then, follow the on-screen instructions to restore the computer to an earlier point in time.
By following these steps, you should be able to troubleshoot and resolve the Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager error. If the issue persists, you may need to contact a qualified technician for further assistance.
Understanding the Different Types of Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager Events
Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager (SCM) events are generated when a service fails to start or stops unexpectedly. These events are logged in the System log and can be used to troubleshoot service-related issues.
The Event ID 7000 can be divided into three categories:
1. Service Start Failure: This type of event is generated when a service fails to start. The event will contain information about the service name, the error code, and the service-specific error code.
2. Service Stop Unexpectedly: This type of event is generated when a service stops unexpectedly. The event will contain information about the service name, the error code, and the service-specific error code.
3. Service Timeout: This type of event is generated when a service fails to respond within the specified timeout period. The event will contain information about the service name, the timeout period, and the service-specific error code.
It is important to note that the Event ID 7000 is not an error code, but rather a notification that a service has failed to start or has stopped unexpectedly. In order to troubleshoot the issue, it is necessary to review the event details and determine the root cause of the issue.
Best Practices for Configuring Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager
The Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager (SCM) is an important component of the Windows operating system. It is responsible for managing the services and drivers that are installed on the system. Properly configuring the SCM is essential for ensuring the stability and security of the system. Here are some best practices for configuring the SCM:
1. Ensure that all services and drivers are up to date. Outdated services and drivers can cause system instability and security vulnerabilities.
2. Configure the SCM to start services and drivers automatically when the system is booted. This will ensure that all services and drivers are running when the system is in use.
3. Configure the SCM to stop services and drivers when they are not in use. This will help to conserve system resources and improve system performance.
4. Configure the SCM to log events when services and drivers are started or stopped. This will help to identify any issues with the services and drivers.
5. Configure the SCM to alert administrators when services and drivers fail to start or stop. This will help to quickly identify and address any issues with the services and drivers.
By following these best practices, administrators can ensure that the Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager is properly configured and that the system is secure and stable.
How to Use Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager to Monitor System Performance
Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager (SCM) is a powerful tool for monitoring system performance. It is a component of the Windows operating system that is responsible for managing the services and drivers that are running on the system. SCM can be used to monitor the performance of services and drivers, as well as to detect and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
To use SCM to monitor system performance, first open the Event Viewer. This can be done by typing “eventvwr” into the search box in the Start menu. Once the Event Viewer is open, navigate to the Windows Logs section and select the System log. This will display all of the events that have occurred on the system.
Next, look for the Event ID 7000. This is the event that is triggered when a service or driver fails to start. It will provide information about the service or driver that failed to start, as well as the reason for the failure. This information can be used to identify any potential issues with the service or driver, and can help to troubleshoot any problems that may be occurring.
Finally, use the information provided by the Event ID 7000 to monitor system performance. If the same service or driver is failing to start multiple times, it may indicate that there is an issue with the service or driver that needs to be addressed. Additionally, if the same service or driver is failing to start on a regular basis, it may indicate that the system is not performing optimally and may need to be tuned or upgraded.
By using Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager to monitor system performance, administrators can quickly identify and troubleshoot any issues that may be occurring on the system. This can help to ensure that the system is running optimally and can help to prevent any potential problems from occurring.
How to Automate Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager Tasks for Improved Efficiency
The Windows Event ID 7000 Service Control Manager (SCM) is a powerful tool that can be used to automate tasks and improve efficiency. This article will provide an overview of how to use the SCM to automate tasks and improve efficiency.
The SCM is a Windows service that is responsible for managing the services and drivers that are installed on a computer. It is used to start, stop, and configure services and drivers. It also provides a way to monitor the status of services and drivers.
The SCM can be used to automate tasks by creating a script that will run when a specific event occurs. For example, if a service fails to start, the SCM can be used to automatically restart the service. This can be done by creating a script that will run when the event ID 7000 is triggered.
The SCM can also be used to improve efficiency by scheduling tasks to run at specific times. For example, if a service needs to be restarted every day at a certain time, the SCM can be used to schedule the task to run at that time. This can help to ensure that the service is running properly and that it is not causing any problems.
Finally, the SCM can be used to monitor the status of services and drivers. This can help to identify any potential problems that may be occurring and can help to ensure that the system is running properly.
By using the SCM to automate tasks and improve efficiency, organizations can save time and money. This can help to ensure that the system is running properly and that it is not causing any problems.
Q&A
Q1: What is Windows Event ID 7000?
A1: Windows Event ID 7000 is an event generated by the Service Control Manager (SCM) when a service fails to start. It indicates that the service failed to start due to some error.
Q2: What information does Windows Event ID 7000 provide?
A2: Windows Event ID 7000 provides information about the service that failed to start, the error code associated with the failure, and the time the failure occurred.
Q3: How can I troubleshoot Windows Event ID 7000?
A3: To troubleshoot Windows Event ID 7000, you should first check the service’s configuration and ensure that it is set up correctly. You should also check the system log for any related errors.
Q4: What are some common causes of Windows Event ID 7000?
A4: Common causes of Windows Event ID 7000 include incorrect service configuration, missing or corrupt files, and incompatible drivers.
Q5: How can I prevent Windows Event ID 7000 from occurring?
A5: To prevent Windows Event ID 7000 from occurring, you should ensure that all services are configured correctly and that all necessary files and drivers are present and up-to-date.
Q6: What should I do if I receive a Windows Event ID 7000 error?
A6: If you receive a Windows Event ID 7000 error, you should first check the service’s configuration and ensure that it is set up correctly. You should also check the system log for any related errors. If the issue persists, you should contact Microsoft Support for further assistance.
Service Control Manager#
The service control manager (SCM) is started at system boot. It is a remote procedure call (RPC) server, so that service configuration and service control programs can manipulate services on remote machines.
The service functions provide an interface for the following tasks performed by the SCM:
-
Maintaining the database of installed services.
-
Starting services and driver services either upon system startup or upon demand.
-
Enumerating installed services and driver services.
-
Maintaining status information for running services and driver services.
-
Transmitting control requests to running services.
-
Locking and unlocking the service database.
Database of Installed Services#
The SCM maintains a database of installed services in the registry. The database is used by the SCM and programs that add, modify, or configure services. The following is the registry key for this database: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services. This key contains a subkey for each installed service and driver service. The name of the subkey is the name of the service.
This database is also known as the ServicesActive database or the SCM database. You must use the functions provided by the SCM, instead of modifying the database directly.
Services and RPC/TCP#
Starting with Windows Vista, the service control manager (SCM) supports remote procedure calls over both Transmission Control Protocol (RPC/TCP) and named pipes (RPC/NP). Client-side SCM functions use RPC/TCP by default. RPC/TCP is appropriate for most applications that use SCM functions remotely, such as remote administration or monitoring tools. The server interface is identified by UUID 367ABB81-9844-35F1-AD32-98F038001003, version 2.0, using the RPC well-known endpoint “\PIPE\svcctl”. The server MUST use RPC over SMB, ncacn_np or RPC over TCP, or ncacn_ip_tcp as the RPC protocol sequence to the RPC implementation.
When a service calls a remote SCM function, the client-side SCM first attempts to use RPC/TCP to communicate with the server-side SCM. If the server is running a version of Windows that supports RPC/TCP and allows RPC/TCP traffic, the RPC/TCPP connection will succeed. If the server is running a version of Windows that does not support RPC/TCP, or supports RPC/TCP but is operating behind a firewall which allows only named pipe traffic, the RPC/TCP connection times out and the SCM retries the connection with RPC/NP.
SCM Handles#
The SCM supports handle types to allow access to the following objects.
-
The database of installed services.
-
A service.
-
The database lock.
An SCManager object represents the database of installed services. It is a container object that holds service objects. The OpenSCManager function returns a handle to an SCManager object on a specified computer. This handle is used when installing, deleting, opening, and enumerating services and when locking the services database.
A service object represents an installed service. The CreateService and OpenService functions return handles to installed services.
The OpenSCManager, CreateService, and OpenService functions can request different types of access to SCManager and service objects. The requested access is granted or denied depending on the access token of the calling process and the security descriptor associated with the SCManager or service object.
OpenSCManagerA function#
Establishes a connection to the service control manager on the specified computer and opens the specified service control manager database.
SC_HANDLE OpenSCManagerA( LPCWSTR lpMachineName, LPCWSTR lpDatabaseName, DWORD dwDesiredAccess );
lpMachineName
The name of the target computer. If the pointer is NULL or points to an empty string, the function connects to the service control manager on the local computer.
lpDatabaseName
The name of the service control manager database. This parameter should be set to SERVICES_ACTIVE_DATABASE. If it is NULL, the SERVICES_ACTIVE_DATABASE database is opened by default.
dwDesiredAccess
The access to the service control manager. For a list of access rights, see Service Security and Access Rights.
Before granting the requested access rights, the system checks the access token of the calling process against the discretionary access-control list of the security descriptor associated with the service control manager.
The SC_MANAGER_CONNECT access right is implicitly specified by calling this function.
Before granting the requested access rights, the system checks the access token of the calling process against the discretionary access-control list of the security descriptor associated with the service control manager.
References#
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/services/service-control-manager
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/services/scm-handles
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/winsvc/nf-winsvc-openscmanagera
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/winsvc/nf-winsvc-openscmanagerw
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/services/database-of-installed-services
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/services/service-security-and-access-rights
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/services/services-and-rpc-tcp
-
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/openspecs/windows_protocols/ms-scmr/4c8b7701-b043-400c-9350-dc29cfaa5e7a