Данная статья представляет краткий обзор всех версий операционной системы Windows.
Версия Вашей системы: Windows 7
Версии для настольных компьютеров
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows 1 | 1985 | Не поддерживается Не используется |
 |
Windows 2 | 1987 | |
 |
Windows 3 | 1990 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.1 | 1993 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows 95 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 98 | 1998 | |
 |
Windows Millenium | 2000 | |
 |
Windows 2000 (NT 5.0) | 2000 | |
 |
Windows XP (NT 5.1) | 2001 | Не поддерживается Встречается редко |
 |
Windows Vista (NT 6.0) | 2006 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 7 (NT 6.1) | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока используется |
 |
Windows 8 (NT 6.2) | 2012 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 8.1 (NT 6.3) | 2013 | Поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 10 (NT 10) | 2015 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows 11 (NT 10) | 2021 | Поддерживается Начинает применяться |
Серверные Windows
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server | 1993 | Не поддерживается Как правило, не используется |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Server | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 Server | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 Server | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 2000 Server | 2000 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 | 2003 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 | 2008 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока еще используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 | 2012 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013 | |
 |
Windows Server 2016 | 2016 | |
 |
Windows Server 2019 | 2018 | |
 |
Windows Server 2022 | 2021 | Начало использования |
Все версии Windows по линейкам + хронология
| Линейка | Годы | Перечисление версий |
|---|---|---|
| 16 бит | 1985 — 1995 | Windows 1 / 2 / 3 |
| 32 бита (9x) |
1995 — 2001 | Windows 95 / 98 / ME |
| NT (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Workstation / 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10 |
| NT Servers (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Server / 2000 Server / 2003 / 2003 R2 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 / 2019 / 2022 |
История успеха
Данная история успеха отражает частоту использования системы; количество глюков, с которыми столкнулись пользователи; отзывы.
 |
Windows 1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 2 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows 3 | Успех |
 |
Windows 95 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 98 | Успех |
 |
Windows Millenium | Провал |
 |
Windows 2000 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows XP | Большой успех |
 |
Windows Vista | Провал |
 |
Windows 7 | Успех |
 |
Windows 8 | Провал |
 |
Windows 8.1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 10 | Успех |
 |
Windows 11 | Нейтрально |
* несмотря на провал некоторых версий операционной системы, они несли новые функции, которые перешли в уже успешные версии. Например, в миллениум появились красивые иконки и окна, которые перешли в Windows 2000. Поэтому провал не стоит оценивать, как неудачную работу.
 Windows 1
Windows 1
Годы поддержки: 1985 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
До Windows 1 был MS-DOS, поэтому самое главное новшество — графический интерфейс и возможность управления при помощи мыши.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 2
Windows 2
Годы поддержки: 1989 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Возможность использования сочетания клавиш.
- Появились перекрывающиеся окна.
- Возможность увеличить и уменьшить окно.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 3
Windows 3
Годы поддержки: 1990 — 2008. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первый (от Microsoft) удобный для пользователя интерфейс.
- Появление диспетчера программ.
- Появление мультимедийных возможностей.
- Поддержка сети (с 3.1).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 8086/8088 | 80486DX 33 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 640 Кбайт | 4 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 6,5 Мб | 60 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первая система на базе ядра NT.
- Поддержка файловой системы NTFS.
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера и клиента DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows 95
Windows 95
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 80386 DX | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 4 Мб | 8 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 50 Мб | 100 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 98
Windows 98
Годы поддержки: 1998 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486DX 66 МГц | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows Millenium
Windows Millenium
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 150 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows 2000
Windows 2000
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows XP
Windows XP
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Редакции: XP, XP Professional
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | от 1,5 Гб |
 Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Годы поддержки: 2006 — 2017. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Premium), Бизнес (Business), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 20 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows 7
Windows 7
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Home Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Home Premium), Профессиональная (Professional), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8
Windows 8
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2016. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 10
Windows 10
Годы поддержки: 2015 — 2025. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания
- Домашняя (Home). Для большинства домашних компьютеров. Нет возможности настроить удаленный рабочий стол для того, чтобы к систему можно было подключиться удаленно; нет возможности использования групповых политик и присоединения к домену.
- Профессиональная (Pro). Содержит все функции домашней версии + возможность присоединения к домену, использования групповых политик, возможность подключения к компьютеру с использованием удаленного рабочего стола.
- Корпоративная (Enterprise). Урезаны некоторые функции домашней версии. Есть все дополнительные функции версии Pro + DirectAccess, AppLocker.
- S. Является урезанной версией; предустановлена на некоторые устройства. Не поддерживает стандартную установку приложений — возможна установка только из магазина Windows.
Что нового
Windows 10 претерпевает сильные изменения с выходом новых билдов. Поэтому нововведения будем рассматривать исходя из этого.
Билд 1507 (ноябрь 2015):
- Улучшенная производительность.
- Новый встроенный браузер Microsoft Edge.
- Автоматическое сжимание соседнего окна, при прижимании активного окна в одной из сторон рабочего стола.
- «Все приложения» в «Пуск» поддерживают отображение в 2048 элементов (раньше только 512).
- Принудительная установка обновлений.
- Использование виртуального голосового помощника Кортана.
- Обновленный меню пуск — представляет из себя гибрид предыдущих версий и Windows 8 (вернулся старый вариант раскрытия, а в правой части появились плитки).
- Возможность создания нескольких рабочих столов.
- Отказ от плиточной системы Windows 8.
1607 (август 2016):
- Возможность рукописного ввода (Windows Ink).
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры.
- Синхронизация с мобильного устройства уведомлений.
- Изменение меню параметров системы.
1703 (апрель 2017):
- Встроенная поддержка шлемов виртуальной реальности.
- Игровой режим
- По умолчанию предлагается командная строка в Powershell.
- Доступ к классической панели управления скрыт из контекстного меню. Теперь его можно вызвать командой control.
- Улучшение работы встроенного антивируса.
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры для Active Directory.
- Возможность создавать скриншот с выделением области с помощью сочетания клавиш Win + Shaft + S.
- Поддержка шрифта Брайля.
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи.
1709 (октябрь 2017):
- Возможность работы Cortana на одном устройстве и окончание работы на другом.
- Отключение протокола SMBv1. Включить можно вручную.
- Появление панели «Люди».
- Информация о GPU в диспетчере задач.
- Полноэкранный режим Microsoft Edge
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи (функция Power Throttling).
- Появление панели эмодзи.
- Выборочная синхронизация OneDrive.
- Исправление проблемы торможения в играх.
1803 (апрель 2018):
- Возможность восстановить пароль с помощью контрольных вопросов.
1809 (октябрь 2018):
- Темная тема для проводника.
- Возможность получения доступа к сообщениям с телефона (функция «Ваш телефон»).
1903 (май 2019):
- Изолированный рабочий стол для безопасного запуска приложений.
1909 (ноябрь 2019):
- Универсальный поиск в Проводнике.
- Улучшение производительности.
2004 (май 2020):
- Функция «Загрузка из облака» для переустановки Windows 10.
- Регулирование пропускной способности для обновлений Windows.
- Отображение температуры видеоядра в Диспетчере задач.
- Возможность удаления Блокнот, Paint, WordPad.
- Возможность использование Windows без пароля.
* данный список содержит часть нововведений. Полный список на странице в Википедии.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: только 64 бита.
Основные издания: Домашняя (Home), Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise).
Дополнительные издания: для обучения (Education), для облаков (Cloud).
Системные требования
| Процессор | 2 ядра, 1 ГГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 64 Гб |
| БИОС (прошивка) | UEFI |
| Видеоадаптер | Совместимый с DirectX 12 / WDDM 2.x |
| Интернет | Для Home необходим вход под учетной записью Microsoft. |
 Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Server
Windows NT 3.5 Server
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Server
Windows NT 3.51 Server
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Server
Windows NT 4.0 Server
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Server
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Годы поддержки: 2003 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Web, Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003 R2
Windows Server 2003 R2
Годы поддержки: 2005 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008
Годы поддержки: 2008 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Storage, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб | ||
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Small Business, Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2016
Годы поддержки: 2016 — 2026. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Лицензирование на физические ядра процессора (минимум 16).
- Новый режим установки — Nano.
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Шифрование виртуальных машин и внутреннего сетевого трафика.
- Блочная репликация файловых хранилищ.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
Более подробно в обзоре Windows Server 2016.
 Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019
Годы поддержки: 2018 — 2029. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность — встроенные технологии Defender ATP и Defender Exploit Guard.
- Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL) — контейнеры для поддержки приложений Linux.
- Для построения кластера с четным количеством узлов в качестве диска-свидетеля может выступать USB-диск.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) |
4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность.
- Больше возможностей для работы с облаками, особенно, Microsoft Azure.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) Поддержка ECC |
4 Гб
Поддержка ECC |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
| Сетевой адаптер | 1 гигабит в секунду |
Microsoft has been making client operating systems since 1985, when Windows 1.01 was first launched. However, the first server was not released till 1993 after the introduction of New Technology (NT). Since then, 14 different versions have been released (Windows Server 2022 is the latest version available at the time of writing this post).
Windows Servers are used for enterprise-level management, data storage, applications, and communications. Using this group of operating systems, administrators can apply and implement policies while enhancing their network’s security infrastructure.
In this post, we will discuss the different Windows Server versions, what unique feature(s) they brought, and in what order they were released.
Table of contents
- Windows Server Timeline
- Windows Server History
- Windows Server NT Versions
- Windows NT Server 3.1
- Windows NT Server 3.5
- Windows NT Server 3.51
- Windows NT Server 4.0
- Rebranded Windows Server Versions
- Windows Server 2000
- Windows Server 2003
- Windows Server 2003 R2
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2022
- Final Thoughts
A common misunderstanding some people have is between the Server versions and their editions. The version of the server is either denoted by integers (this naming convention is no longer used) or suffixed with its corresponding year. For example, previously, Microsoft named a server version “Windows NT 3.5” or “Windows NT 4.0.” Now, they use “Windows Server 2003” or “Windows Server 2019.”
If you are confusing this with the Server editions, click on the link to read more about it.
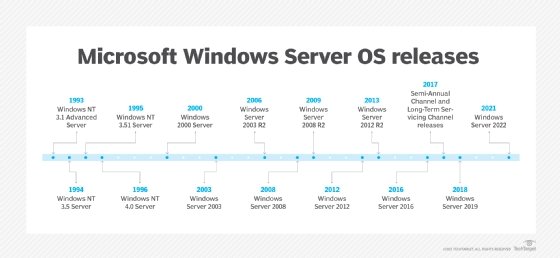
Windows Server Timeline
The image below illustrates when a Windows Server version was initially released. You can then continue to read below to understand how each of these is different.
Windows Server History
The table below briefly describes the important aspects of each of the Windows Server versions along with some other useful information.
| Server Version | Release Year | Editions | Currently Supported | Details |
| Windows NT 3.1 | 1993 | – | No | First Server version. 32-bit. |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 1994 | – | No | Supports Unix and Novell Netware connectivity. Can be used with existing networks. |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995 | – | No | Support for Windows 95 with remote software license management. |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 1996 | – | No | With IIS, Server-edition Terminal, UI similar to Windows 95 |
| Server 2000 | 2000 | Server, Advanced Server, Datacenter Server | No | Integration with Active Directory for user authentication and support for Extensible Market Language. |
| Server 2003 | 2003 | Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter | No | Define Server roles and features, inclusion of .NET. |
| Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter | No | With Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), a Security configuration wizard, and improved data compression capabilities. |
| Server 2008 | 2008 | Web, Foundation, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter | No | Introduced Hyper-Virtualization, Event Viewer, and Server Manager. |
| Server 2008 R2 | 2009 | Web, Foundation, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter | No | 64-bit OS, enhanced Group Policy implementation, with Remote Desktop Services. |
| Server 2012 | 2012 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter | Mainstream ended, extended ending October 2023 | Improved Hyper-V functionality and support added for cloud integration |
| Server 2012 R2 | 2013 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter | Mainstream ended, extended ending October 2023 | Windows PowerShell updated and improved storage management. |
| Server 2016 | 2016 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter | Mainstream ended, extended ending January 2027 | Inclusion of Network Controller and Nano Server, support for containers added. |
| Server 2019 | 2018 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter | Yes | With Hyper-converged infrastructure, Advanced Threat Protection, and Windows Admin Center. |
| Server 2022 | 2021 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Azure edition | Yes | With Azure Arc, Storage Migration Service, support for hot-patching. |
The table above briefly describes all the significant changes as well as the release details of individual Windows Server versions since Microsoft first launched the operating system back in 1993.
Let us now dig into the details of each version.
Windows Server NT Versions
Initially, Microsoft used the New Technology (NT) terminology when releasing Windows Server. Moreover, the first version ever to be released publicly wasn’t version 1, but it was 3.1.
Another thing to note is that the different editions of each version did not kick in until 2000, with Windows Server 2000. Before that, Servers were only offered as a single, standard edition.
Windows NT Server 3.1
Windows NT Server 3.1 was the first Server by Microsoft. This was an operating system with a 32-bit architecture that was released in 1993. This was released in 2 variants: one for Terminals and another for Servers.
The version for Servers is what evolved into the Server family which continues to date.
Windows NT Server 3.5
Microsoft then skipped directly to version 3.5. Since most networks ran Unix or Novell servers, Windows NT Server 3.5 allowed interconnectivity with these systems for convenient data transmission.
This was a major feature for the sustainability of NT Servers since they were relatively new to the market.
Windows NT Server 3.51
Windows NT Server 3.51 had the capabilities to manage computers running Windows 95 on the same network. Server 3.51 also supported the management of software licenses for client computers and update other Windows 95 machines over the network.
Windows NT Server 4.0
This Server version included a UI similar to Windows 94 and was released in 1996. This included the Internet Information Server (IIS) which was in direct competition with Apache HTTP Server.
Furthermore, Microsoft also added the Transaction Server and the Message Queue Server to improve the OS. In the end, Microsoft improved the connectivity to non-Windows systems and also created a bridge from 16-bit DOS applications so that they could interface with the 32-bit Desktop environment.
Rebranded Windows Server Versions
In 2000, Microsoft dropped the “NT” version naming convention and shifted to a year-based release name. For example, “Windows Server 2000” was released in the year 2000.
Windows Server 2000
Windows Server 2000 was a major milestone for Microsoft since many of the features are still in use today by modern versions of the Server.
Windows Server 2000 included support for XML, creation of Active Server Pages (ASP), and the use of Active Directory for user authentication. It also introduced the concept of tailored editions, which included the standard Windows Server, Microsoft released Advanced Server, and Datacenter Server.
Editions: Server, Advanced Server, Datacenter Server
Windows Server 2003
The major change in Server 2003 was the reduction of system reboot requirements after an event. Microsoft also enhanced the security features of the operating system, and this was the first time that the .NET environment was included with the Windows Server operating system.
It was also the first time a Server was able to assign server roles, enabling the operating system to be tailored to specific specialized tasks, such as a DNS server.
Editions: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Windows Server 2003 R2
This was Revision 2 (R2) of Windows Server 2003. This allowed users with valid licenses for Server 2003 to automatically upgrade to Server 2003 R2 without any additional costs.
This version mostly focused on enhancing the security of the OS as well as the network. It introduced Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) for user authentication. The purpose of this AD extension was to enable external services to be included in the “single sign-on” permissions managed within the network.
Another improvement to this version was the Active Directory Application Mode, which improved security by creating an “arm’s length” relationship with third-party applications – it did not trust the apps that well.
Furthermore, administrators were now able to apply and implement Group Policies on other users and computers using the Security Configuration Wizard.
Editions: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008 was the first Server OS to include a Hyper-V virtualization system, upon which users can implement Virtual Machines (VMs) and install operating systems. Furthermore, the inclusion of the Event Viewer and the Server Manager made it easier for the administrators to troubleshoot any issues and then manage their Servers more conveniently.
Not only that, but Microsoft went a step ahead and also introduced the Core version of Windows Server 2008, which was a command line-based OS with a bare minimum User Interface (UI).
Editions: Web, Foundation, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Windows Server 2008 R2
This was the first Server to have a 64-bit architecture. Windows Server 2008 R2 made significant improvements to the Active Directory Group Policy implementation, with the inclusion of new policies. It also included Remote Desktop Services for the very first time on a Server OS.
Editions: Web, Foundation, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 included better features for off-site server integration. This was mainly done by Microsoft so it can be integrated with cloud servers and services. Furthermore, they also updated the storage system with this OS, which was mediated by Hyper-V itself.
Not only that, but the Hyper-V virtual switch and Hyper-V Replica were also introduced in Server 2012.
Editions: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Windows Server 2012 R2
This revision to Server 2012 made further improvements to the cloud integration. It also included updates to Windows PowerShell. Virtualization and storage technologies were also overhauled and the Web services were enhanced.
Editions: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Windows Server 2016
Server 2012 introduced the Nano Server – a minimal, lightweight server implementation to minimize the attack surface. An encryption system was also added for Hyper-V to secure the VMs.
Another milestone for Microsoft was the support for containers.
That said, at this point, Microsoft discontinued R2 versions of the Servers as they had shifted to the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC).
Server 2016 also included the Network Controller. This enabled administrators to manage both physical as well as virtual network devices using a single console. However, this feature is only available in the Datacenter edition.
Editions: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Windows Server 2019
Previously known as Project Honolulu, Windows Admin Center was launched for the first time and is an integrated all-in-one console to manage your Active Directory. Integrated servers, machines, and users can also be managed using this one console only, along with services and server roles.
It also includes Hyperconvereged Infrastructure (HCI) capabilities which is a software that combines all of the basic data center elements, such as computing, storage, networking, and management, into a single software. This facility aims to obtain all the functions of a miniature data center without the additional hardware costs.
You can read more about other enhancements and improvements in our post for Server 2019.
Editions: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Windows Server 2022
Windows Server 2022 is the latest version of Server at the time of writing this post.
This includes Azure Arc, which is used to manage and govern on-prem servers within Microsoft Azure. Furthermore, it also includes support for hotpatching – which is installing updates without having to reboot the target PC.
Improvements to networking have also been improved by the inclusion of software-defined networking capabilities. Supports SMB over QUIC capability for safer communications. It’s designed for VPN replacement and relies on UDP and TLS 1.3 protocols for faster and safer communication.
You can read more about other enhancements and improvements in our post for Server 2022.
Editions: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Datacenter: Azure edition
Final Thoughts
Windows Server has come a long way since its debut in 1993. This has improved UI as well as many other functional improvements for manageability. Such improvements are the reason why Microsoft releases new versions every few years – so organizations can take advantage of the new features.
Each of these versions then had different variants, which are known as editions. You may click on the link to learn about the different editions and how they differ from one another. But it doesn’t end here.
The Datacenter and Standard editions also come with different variants – which are the Core and Desktop Experience variants.
To sum up, the complete name of a Windows Server operating system can be as such: Windows Server 2022 Datacenter Core Evaluation. This means that the version is Server 2022, the edition is Datacenter with the bare minimum UI (Core), and is the Evaluation edition and only valid for a total of 180 days since its installation.
12
dows Server. Active Directory и административные шаблоны поз-
воляют применять параметры безопасности ко всем рабочим станциям и серверам вашего учреждения. Иными словами, вы настраиваете защиту данных не для каждого конкретного компьютера, а всего предприятия в целом.
Семейство ОС Windows 2000 Server состоит из версий
Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server.
Семейство ОС Windows Server 2003 состоит из версий
Standard Edition, Enterprise Edition, Datacenter Edition и Web Edition.
Семейство ОС Windows Server 2008 состоит из версий
Standard Edition, Enterprise Edition, Datacenter Edition.
Укаждой — свое назначение.
2.1.1.Windows Server 2003-2008 Standard Edition
(Windows 2000 Server)
Windows Server 2003-2008 Standard Edition и Windows 2000 Server разработаны для предоставления служб и ресурсов другим системам в сети. Они сменили Windows NT 4.0 Server и Windows 2000 Server, соответственно. Эти ОС обладают богатым набором функций и конфигурационных параметров. Windows Server 2003-2008 и Windows 2000 Server поддерживают до двух центральных процессоров и до 4 Гбайт оперативной памяти.
2.1.2.Windows Server 2003-2008 Enterprise Edition
иWindows 2000 Advanced Server
Эти системы расширяют возможности Windows Server 2003-2008, Standard Edition и Windows 2000 Server, соответ-
ственно, обеспечивая поддержку служб кластеров, служб метакаталогов и служб для Macintosh.
Windows 2000 Advanced Server обеспечивает поддержку конфигураций с большим объемом памяти (до 64 Гб) и четыр ь- мя процессорами.
В Windows Server 2003-2008 также поддерживаются
64-разрядные процессоры Intel Itanium, оперативная память с
13
возможностью «горячей» замены и неоднородный доступ к па-
мяти (no uniform memory access, NUMA). Эта версия поддержи-
вает до 32 Гбайт оперативной памяти на процессорах х86, до 64 Гбайт оперативной памяти на процессорах Itanium и до 8 центральных процессоров.
2.1.3.Windows Server 2003-2008 Datacenter Edition (Windows
2000 Datacenter Server)
Данные системы являются самыми надежными Windows — серверами и поддерживают более сложную кластеризацию
При этом Windows 2000 Datacenter Server поддерживает до 16 процессоров, а Server 2003-2008 Datacenter Edition способна работать с большими объемами оперативной памяти — до 64 Гбайт на процессорах х86 и до 128 Гбайт на процессорах Itanium. Минимальное количество процессоров для работы Datacenter Edition — 8, максимальное – 32.
2.1.4.Windows Server 2003 Web Edition
Windows Server 2003 Web Edition предназначена для за-
пуска служб Web при развертывании Web-узлов и Webприложений. Для решения этих задач в данную версию включе-
ны Microsoft.NET Framework, Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS), ASP.NET и функции для равномерного распределения нагрузки на сеть. Многие другие функции, в частности Active Directory, в ней отсутствуют. Строго говоря, из стандартных компонент Windows в этой версии предусмотрены лишь распределенная файловая система DFS, шифрованная файловая система EFS и удаленный рабочий стол. Версия Windows Server 2003, Web Edition поддерживает до 2 Гбайт оперативной памяти и до двух центральных процессоров.
Примечание. Все версии поддерживают одни и те же базовые функции и средства администрирования, т.е. рассматриваемые методики можно применять независимо от того, какой версией Windows Server вы пользуетесь. Помните, что в версии
Web Edition нет Active Directory, поэтому сервер, работающий под управлением этой версии, нельзя сделать контроллером домена. Он, тем не менее, может быть частью домена Active Directory .
Windows Server (formerly Windows NT Server) is a group of operating systems (OS) for servers that Microsoft has been developing since 1993. The first OS that was released for this platform is Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server. With the release of Windows Server 2003, the brand name was changed to Windows Server. The latest release of Windows Server is Windows Server 2022, which was released in 2021.
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Initial release | July 27, 1993; 30 years ago |
| Latest release | 2022 (10.0.20348.1906) / August 8, 2023; 50 days ago[1] |
| Latest preview | vNext (10.0.25931) / August 16, 2023; 42 days ago[2] |
| Update method |
|
| Default user interface |
|
| License | Trialware, SaaS, or volume licensing |
| Official website | www |
Microsoft’s history of developing operating systems for servers goes back to Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server. Windows 2000 Server is the first OS to include Active Directory, DNS Server, DHCP Server, and Group Policy.
Members
Edit
Main releases
Edit
Main releases include:
- Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server (July 1993)
- Windows NT Server 3.5 (September 1994)
- Windows NT Server 3.51 (May 1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 Server (July 1996)
- Windows 2000 Server (December 1999)
- Windows Server 2003 (April 2003)[3]
- Windows Server 2003 R2 (December 2005)[4]
- Windows Server 2008 (February 2008)[5]
- Windows Server 2008 R2 (October 2009)[6]
- Windows Server 2012 (September 2012)[7]
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (October 2013)[8]
- Windows Server 2016 (October 2016)[9]
- Windows Server 2019 (October 2018)[10]
- Windows Server 2022 (August 2021)[11]
Traditionally, Microsoft supports Windows Server for 10 years, with five years of mainstream support and an additional five years of extended support. These releases also offer a complete desktop experience. Starting with Windows Server 2008 R2, Server Core and Nano Server configurations were made available to reduce the OS footprint.[12][13] Between 2015 and 2021, Microsoft referred to these releases as «long-term support» releases to set them apart from semi-annual releases (see below.)
For sixteen years, Microsoft released a major version of Windows Server every four years, with one minor version released two years after a major release. The minor versions had an «R2» suffix in their names. In October 2018, Microsoft broke this tradition with the release of Windows Server 2019, which should have been «Windows Server 2016 R2». Windows Server 2022 is also a minor upgrade over its predecessor.[14][15]
Branded releases
Edit
Certain editions of Windows Server have a customized name:
- Windows Storage Server (editions of Windows Server 2003 through 2016; editions of Windows Server IoT 2019 and its successors)[16][17][18]
- Windows HPC Server 2008
- Windows HPC Server 2008 R2
- Windows Home Server (an edition of Windows Server 2003)
- Windows Home Server 2011 (an edition of Windows Server 2008 R2)
- Hyper-V Server (a discontinued,[19] freeware edition of Windows Server 2008 through 2019)[20]
- Windows MultiPoint Server
- Windows Server Essentials[21][22]
- Windows Essential Business Server (discontinued)[23]
- Azure Stack HCI (an edition of Windows Server 2019 and later)[24]
Semi-annual releases (discontinued)
Edit
Following the release of Windows Server 2016, Microsoft attempted to mirror the lifecycle of Windows 10 in the Windows Server family, releasing new versions twice a year which were supported for 18 months. These semi-annual versions were only available as part of Microsoft subscription services, including Software Assurance, Azure Marketplace, and Microsoft Visual Studio subscriptions,[25] until their discontinuation in July 2021.[26][25]
The semi-annual releases do not include any desktop environments. Instead, they are restricted to the Nano Server configuration installed in a Docker container,[13][25] and the Server Core configuration, licensed only to serve as a container host.[13][25]
Semi-annual releases include:[27]
- Windows Server, version 1709 (unsupported as of April 9, 2019; 4 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1803 (unsupported as of November 12, 2019; 3 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1809 (unsupported as of November 10, 2020; 2 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1903 (unsupported as of December 8, 2020; 2 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1909 (unsupported as of May 11, 2021; 2 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 2004 (unsupported as of December 14, 2021; 21 months ago)
- Windows Server, version 20H2 (unsupported as of August 9, 2022; 13 months ago)[28][29][30][31]
See also
Edit
- List of Microsoft Windows versions
- Microsoft Servers
- Linux range of use § Servers, mainframes and supercomputers
- NetWare
- Open Enterprise Server
References
Edit
- ^ «Windows Server 2022 update history». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved November 26, 2021.
- ^ «Announcing Windows Server Preview Build 25931». Microsoft Tech Community. August 16, 2023. Retrieved August 16, 2023.
when reporting issues please refer to «VNext» rather than Windows Server 2022 which is currently in market.
- ^ «Windows Server 2003 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. March 8, 2008. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server 2003 R2 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. March 8, 2008. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved September 25, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved September 25, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. January 2012. Retrieved October 10, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 R2 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft.com. Retrieved December 27, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Server 2016 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved December 7, 2016.
- ^ «Windows Server 2019 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server 2022 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «What is Microsoft Windows Server LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel)? – Definition from WhatIs.com». SearchWindowsServer. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- ^ a b c «Windows Server – Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) vs Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) – Thomas Maurer». Thomas Maurer. November 19, 2017. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- ^ Sommergut, Wolfgang (August 24, 2021). «Windows Server 2022 released: Overview of new features». 4sysops. Archived from the original on August 24, 2021.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (August 20, 2021). «Microsoft’s Windows Server 2022 is rolling out to mainstream users». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 22, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Storage Server Lifecycle (EOL)». EndOfLife.Software.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 for Storage». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2022». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ Christensen, Elden (March 25, 2022). «Hyper-V in the 2022 Wave». Microsoft Tech Community. Self-published.
- ^ «Hyper-V Server». Search Product and Services Lifecycle Information. Microsoft. Retrieved September 2, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2008 Technical FAQ». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft. December 14, 2010 – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (September 3, 2011). «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials». Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved September 26, 2011.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server». TechNet Archive. Microsoft. February 7, 2012 – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Deploy the Azure Stack HCI operating system». Azure Docs. Microsoft. October 22, 2021.
- ^ a b c d «Windows Server servicing channels». Windows Server Library. Microsoft. July 5, 2022. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022.
- ^ «Microsoft to retire semi-annual Windows Server updates, will move entirely to LTSC releases». Neowin. July 28, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server». Search Product and Services Lifecycle Information. Microsoft. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- ^ «Windows message center: Windows Server, version 20H2 has reached end of servicing». August 9, 2022. Archived from the original on August 10, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server release information». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 9, 2022. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows Server, version 20H2». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 9, 2022. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ Popa, Bogdan. «Microsoft Retires Windows Server Version 20H2». news.softpedia.com. Archived from the original on August 10, 2022. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
External links
Edit
- Official website
Microsoft Windows Server OS (operating system) is a series of enterprise-class server operating systems designed to share services with multiple users and provide extensive administrative control of data storage, applications and corporate networks.
Development for Windows Server started in the early 1980s when Microsoft produced two operating system lines: MS-DOS and Windows NT. Microsoft engineer David Cutler developed the kernel of Windows NT with the intent to provide speed, security and reliability that large organizations require in a server operating system.
Prior to the release of Windows NT, many companies relied on the Unix operating system that required expensive RISC-based hardware to run file and printing services. Windows NT had the ability to run on less costly x86 machines.
A key feature in the NT architecture is symmetric multiprocessing, which makes applications run faster on machines with several processors.
Later iterations of Windows Server can be deployed either on hardware in an organization’s data center or on a cloud platform, such as Microsoft Azure.
Key features in later versions of Windows Server include Active Directory, which automates the management of user data, security and distributed resources, and enables interoperation with other directories; and Server Manager, which is a utility to administer server roles and make configuration changes to local or remote machines.
Microsoft released its Windows NT operating system in two formats: one for workstations and the other for servers. The 32-bit operating system featured a hardware abstraction layer (HAL), which provided more system stability by blocking applications from direct access to system hardware. Companies could use Advanced Server as a domain controller to store user and group rights. Microsoft updated key networking features in this server release and added integrated support for TCP/IP and Winsock. Other networking improvements allowed users on other non-Microsoft operating systems to access files and applications on the domain. Microsoft fine-tuned this release to boost performance and reduce the amount of required memory. This server OS was optimized to deliver services faster to users through its updated networking stack. Microsoft added more connectivity support for companies in a mixed environment with both Windows NT and NetWare servers to allow users to get services from each with a single credential. Microsoft borrowed the Windows 95 interface for this server OS release and also used many of the applications in the client OS, such as the File Explorer. Microsoft expanded the networking protocol capabilities in this release to make network resources available to a wider array of non-Microsoft machines. Key features in this release were the ability to use a server as an Internet Information Server — now called Internet Information Services (IIS) — and a domain name system server. This server OS also could walk administrators through various tasks, such as sharing a hard disk with a feature called Administrative Wizards. Windows 2000 introduced Active Directory, a directory service that stores and manages information about network objects, including user data, systems and services. Active Directory lets administrators perform various tasks, such as virtual private network configuration, data encryption and granting access to file shares on networked computers. Microsoft also introduced several other key features in this release, including: Windows 2000 had three editions — Server, Advanced Server and Datacenter — that were built to work with Windows 2000 Professional, the client OS. Microsoft introduced the «Windows Server» brand with the release of Windows Server 2003 and touted its security improvements over Windows 2000. Microsoft hardened IIS, the web server feature, and disabled more default services to reduce exploit opportunities. Microsoft introduced server roles with this release, which allowed administrators to assign a specific function to a server, such as domain controller or DNS server. Other new features in this release included expanded encryption functionality, built-in firewall, greater Network Address Translation (NAT) support and Volume Shadow Copy Service. Windows Server 2003 had four editions: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter and Web. Rather than a version number, Microsoft began using the R2 — or release two — designation with Windows Server 2003 R2. Organizations always need to buy a new Windows Server license to use the new server operating system, but R2 releases used the client access licenses (CALs) of the immediately preceding server version to eliminate the need to upgrade those licenses. This version improved on the security and safety features in Windows Server 2003. Key new features in this release were: This version also added enhancements to file replication and data compression for branch office servers. Among the security improvements in this release was the Security Configuration Wizard, which let administrators apply consistent security policies to multiple machines. Windows Server 2008 added new features such as: Microsoft also overhauled the networking stack and Active Directory to enhance its Group Policy and identity management capabilities. Windows Server 2008 came in four editions: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter and Web. Microsoft used its Windows 7 kernel for this server operating system and touted its improved scalability and availability features. Microsoft enhanced Active Directory for improved handling of user accounts and more granular control with policies. The company also updated Terminal Services functionality and rechristened it to Remote Desktop Services (RDS). New features in this release include BranchCache and DirectAccess, both aimed at improving how users in remote locations are able to get their work done. This server OS, like its predecessor, shares some of the administrative and security functionality used in the Windows Vista client operating system. Windows Server 2008 R2 also marked a change from a 32-bit server operating system to a 64-bit version. Microsoft embedded a number of cloud-related features to Windows Server 2012, going so far as to dub it the «Cloud OS,» so organizations could run services more easily in public or private clouds. The company also made significant updates to the operating system’s storage infrastructure and Hyper-V virtualization platform. New features worth noting in this release were the Hyper-V virtual switch, Hyper-V Replica, Storage Spaces and ReFS file system. In another change with this release, Microsoft switched the default installation option to Server Core, which requires administrators to use PowerShell. Upon this release, PowerShell had 2,300 cmdlets available for management. This server version came in four editions: Essentials, Foundation, Standard and Datacenter. The Standard and Datacenter editions had the same feature set, but a Standard license permitted organizations to run two virtual machines (VMs), while Datacenter permitted an unlimited number of VMs. Microsoft made expansive changes across the board with Windows Server 2012 R2, including significant updates to virtualization, storage, networking, information security and web services. New features of note: Microsoft nudged enterprises closer to the cloud with a number of new features tailored to ease workload migrations, such as support for Docker containers and software-defined enhancements in networking. Microsoft debuted Nano Server, a minimal server deployment option intended to boost security by shrinking the attack vector. Microsoft says Nano Server is 93% smaller than a full Windows Server deployment. Another nod to security comes in the new Hyper-V shielded VM feature, which uses encryption to prevent data inside a VM from being compromised. The Network Controller is a key new networking feature that allows administrators to manage the switches, subnets and other devices on the virtual and physical networks. This server OS comes in Standard and Datacenter editions. In previous Windows Server versions, the Standard and Datacenter editions had the same feature set, but different license rights and use restrictions. In Windows Server 2016, the Standard edition does not have the more advanced features in virtualization, storage and networking. In June 2017, Microsoft announced it would split Windows Server into two channels: the Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) and the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) — formerly the Long-Term Servicing Branch. The SAC caters to enterprises with a DevOps framework that prefer a shorter term between feature updates to get the most recent updates for rapid application development cycles. SAC releases will come every six months — one in the spring and one in the fall — with mainstream support of just 18 months. Microsoft tailors the LTSC for companies that prefer the more traditional release cycle of two to three years between major feature updates with the typical five years of mainstream support followed by five years of extended support. The LTSC naming convention will retain the Windows Server YYYY format — such as Windows Server 2016 — while the SAC releases will follow a format of Windows Server version YYMM. Microsoft said it plans to add most of the enhancements — with some variations — from the SAC releases into upcoming LTSC releases. Microsoft released its first SAC release — Windows Server version 1709 — in October 2017. Highlights of this release were support for Linux containers with kernel isolation provided by Hyper-V and a refactored Nano Server strictly for use as a base OS container image. Businesses with Software Assurance on their Windows Server Standard or Datacenter licenses or a Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN) license can download the SAC releases from Microsoft’s Volume Licensing Service Center. Organizations without Software Assurance can use SAC releases in Azure or another cloud or hosting environment.
History of Windows Server
1993: Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
1994: Windows NT 3.5 Server
1995: Windows NT Server 3.51
1996: Windows NT Server 4.0
2000: Windows 2000
2003: Windows Server 2003
2005: Windows Server 2003 R2
2008: Windows Server 2008
2009: Windows Server 2008 R2
2012: Windows Server 2012
2013: Windows Server 2012 R2
2016: Windows Server 2016
2017: Semi-Annual Channel and Long-Term Servicing Channel releases