In Windows Server 2022, File Server Resource Manager is the feature available to system administrators that gives the ability to set quotas and limit the types of files that can be saved to a file server.
File Server Resource Manager was initially released by Microsoft in 2005 for Windows Server 2003 to offer administrators greater control than the default Windows Explorer.
File Server Resource Manager’s Five Main Features
Quota Management
- Limit the allowed space on folders and volumes.
- Define quota templates on folders and volumes.
File Classification Infrastructure
- Manage data effectively with automated classification.
- Automatically or manually update selected folder or file properties.
- Some policy examples would be file expirations, file encryption, and restricting access with dynamic access control.
File Management Tasks
- Application of actions or conditional policies depending on file classification.
- Conditions can include: Location
- Classification properties
- Creation date
- Date last modified
- Date last accessed
- File management tasks can: Run custom commands
- Run file encryption
- File expiration
File Screening Management
- Controls types of files that can be stored on the file server.
- Limit file extensions, for example, block MP3 files from being saved to the server.
Storage Reports
- Identify disk usage trends.
- Monitor selected users attempting to save unauthorized files.
All these features can be configured via the graphical interface or via PowerShell.
File Server Resource Manager Examples
- Allow or deny access based on the location of data on the file server.
- Expire files that have not been modified in a specified time.
- Create quotas with warnings when a specified percentage of storage has been used.
- Scheduled reporting on usage.
- Prevent specified file types from being saved to shared locations.
- Classify data with multiple identifiers.
File Server Resource Manager Advantages
Advanced Quota Management
File Server Resource Manager offers centralized quota management for volumes, folders, and files. Multiple quotas can be applied to different paths within a volume. Quota templates assist to simplify management of both soft and hard quotas.
Content Regulation
In addition to managing quotas, there is a need to regulate the types of files that can be stored on file shares. This could be in the form of blocking executables that could contain malicious code, blocking content that could infringe on copyrights, or even specifying file extensions such as allowing only *.docx and blocking *.doc.
Reports On Utilization of Storage
File Server Resource Manager is currently able to generate the below reports:
- Location of files
- File duplication
- Last accessed date
- Last modified date
- File types
- Properties of files
- Properties of folders
- Least accessed files
- Recently accessed files
- Quota usage
Easy File Location
Files can be sorted in a wide variety of ways, for example, name, time created, properties, etc
File Server Resource Manager Installation
The File Server Resource Manager can be installed via the Graphical User Interface (GUI) installation or PowerShell.
PowerShell Installation
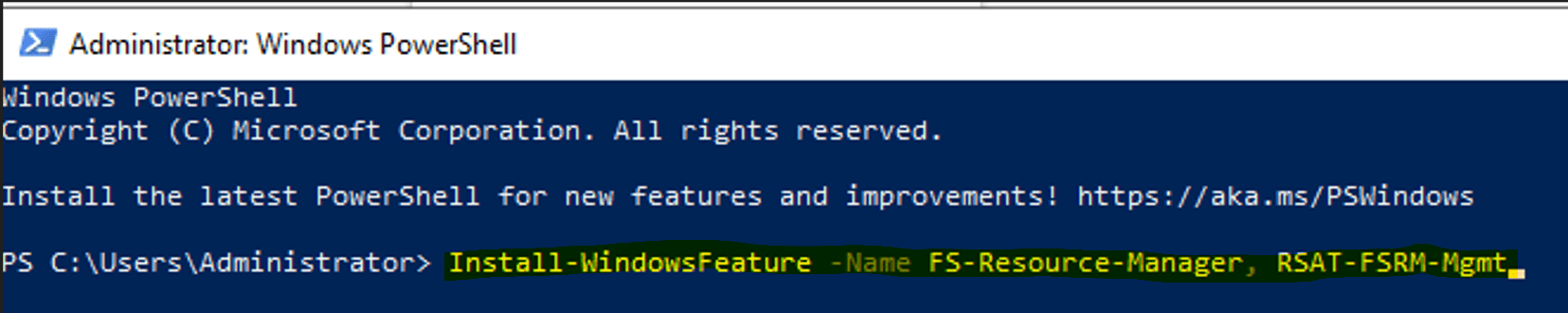
Open PowerShell, and enter the below command to install the File Server Resource Manager:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name FS-Resource-Manager, RSAT-FSRM-Mgmt
No reboot is necessary after installing this feature.
Graphical User Interface Installation
Follow the below steps to install via the GUI:
Open the Server Manager.
Click “Manage.”
Next, click “Add Roles and Features.”
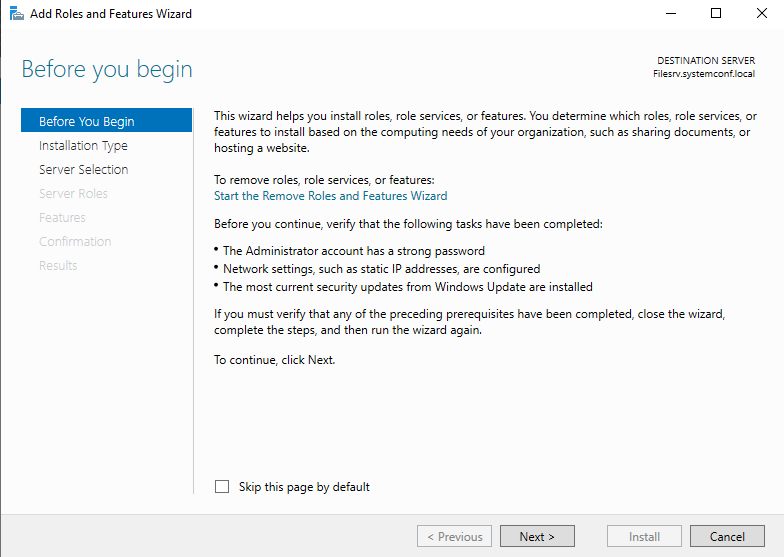
If prompted with the “Before You Begin” screen, click “Next.”
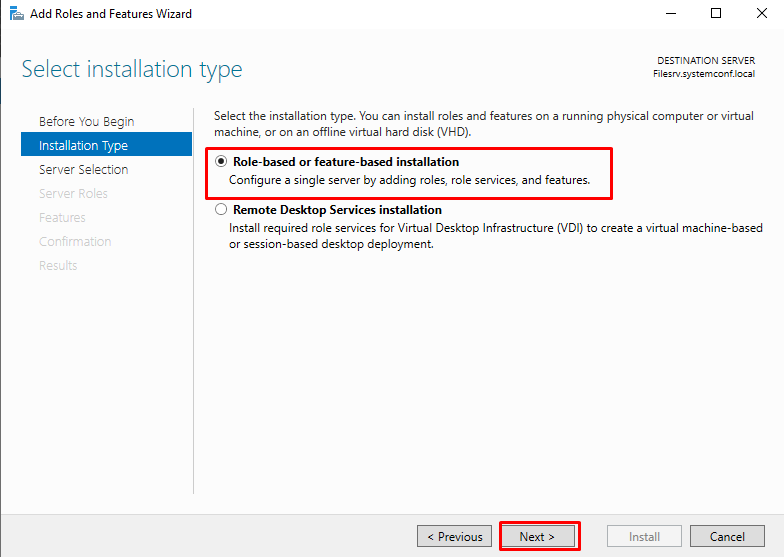
Then select “Role-based or feature-based installation” and click “Next.”
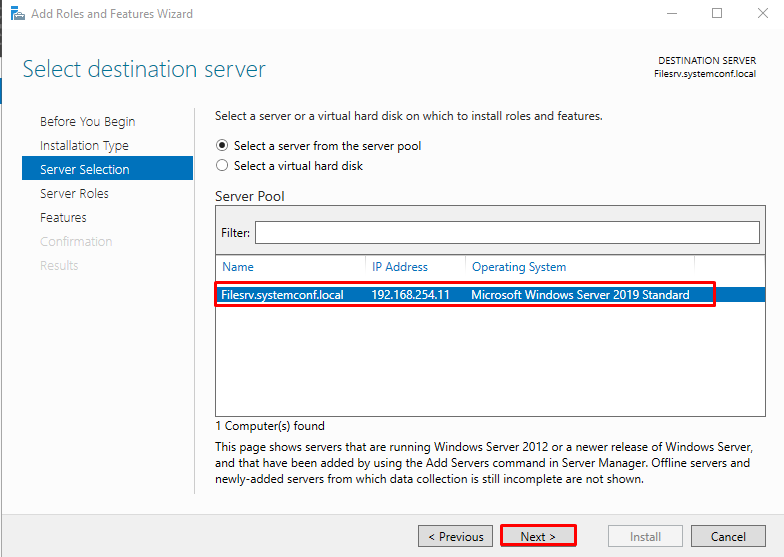
Select the server where the feature will be installed and click “Next.”
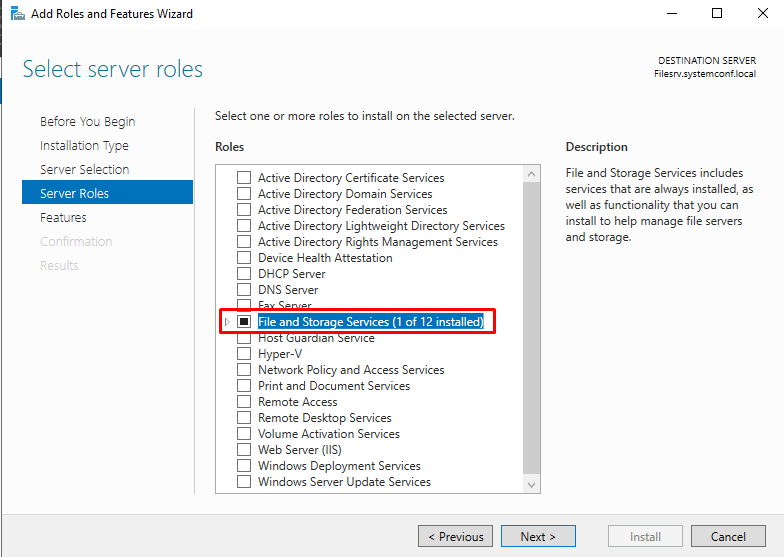
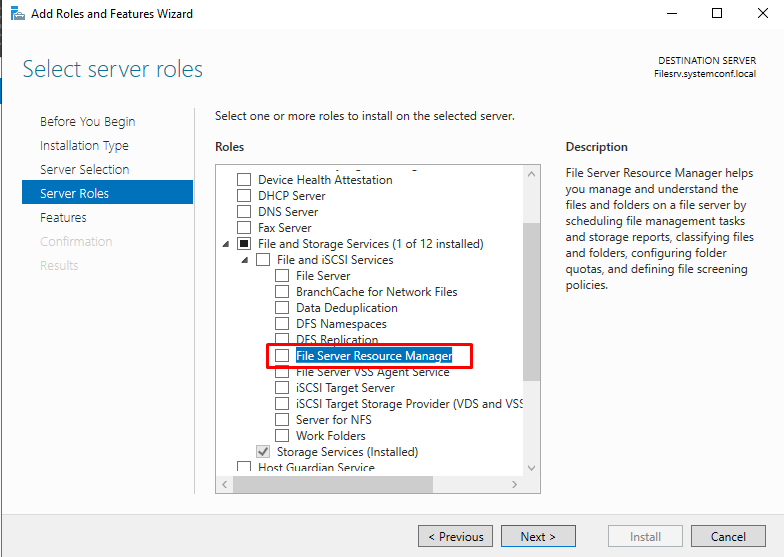
Expand “Select Server Roles,” then expand “File and Storage Services.”
Now expand “File and iSCSI Services.”
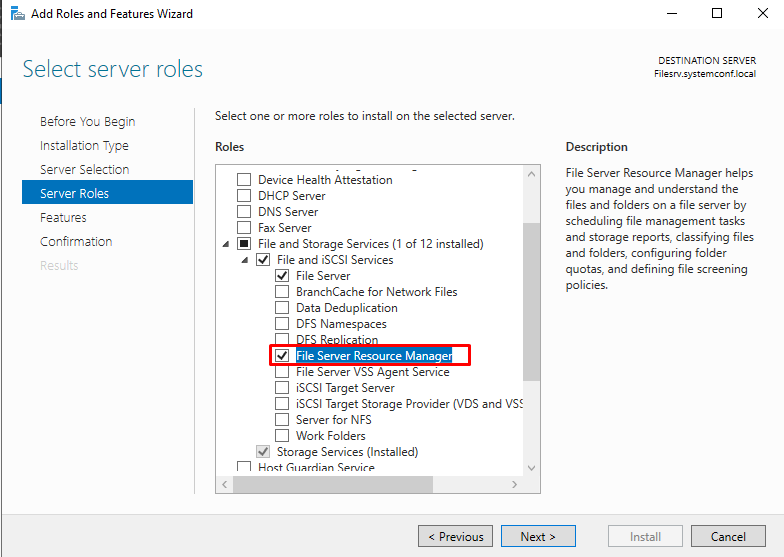
Select the “File Server Resource Manager” and click “Next.”
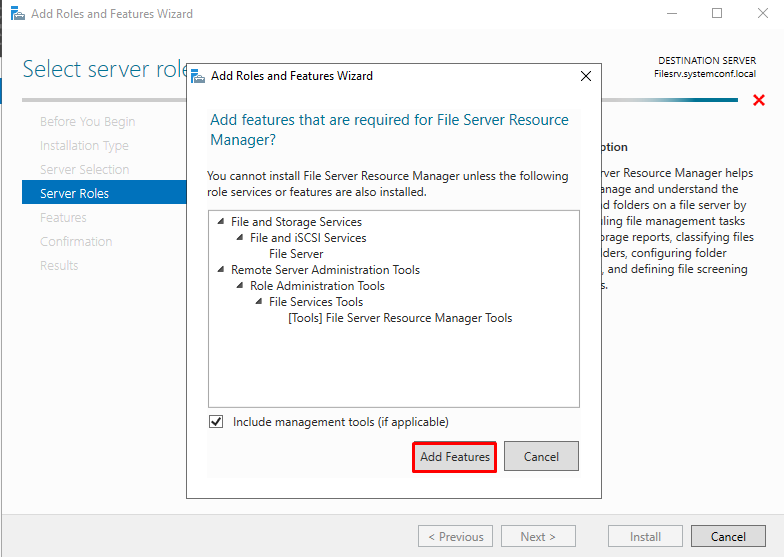
Select “Add Features”
Click “Next.”
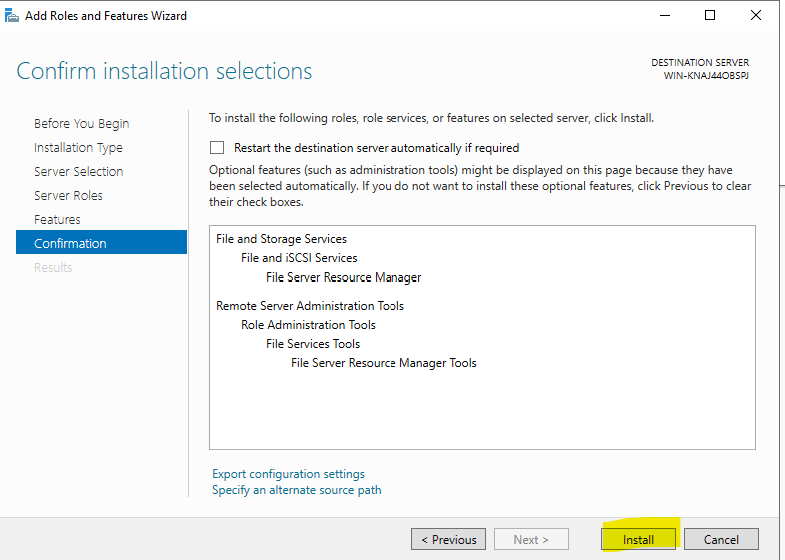
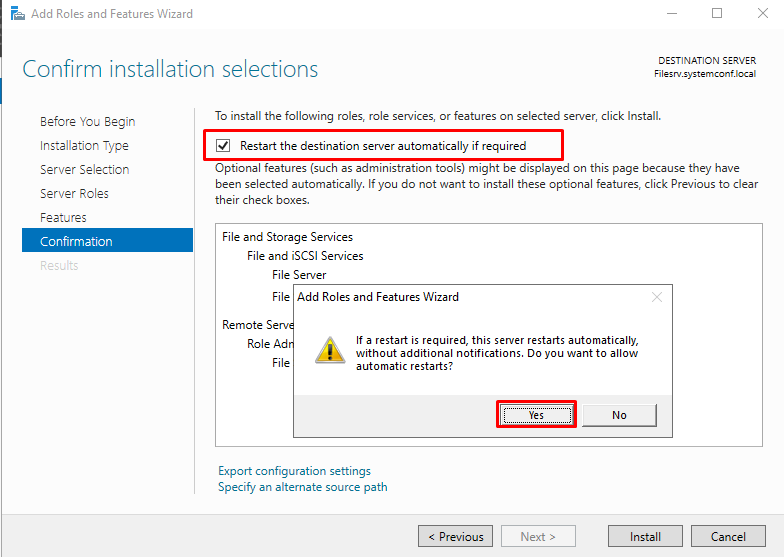
Start the installation process by clicking “Install.”
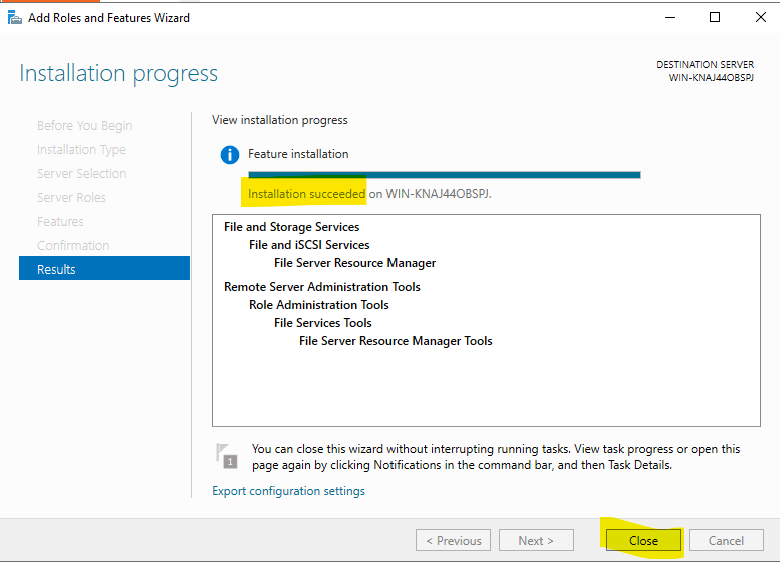
Once complete, select “Close.”
File Server Resource Manager is now installed.
Template Creation
Quotas setting requires a template to be created. This template can be custom or from a predefined template within the File Server Resource Manager.
Quotas management can be simplified by changing templates. In addition, centralizing control of quotas makes enforcement of storage policy rules easy.
To create a quota template:
Open the File Server Resource Manager.
Expand the “Quota Management” in the left-hand pane.
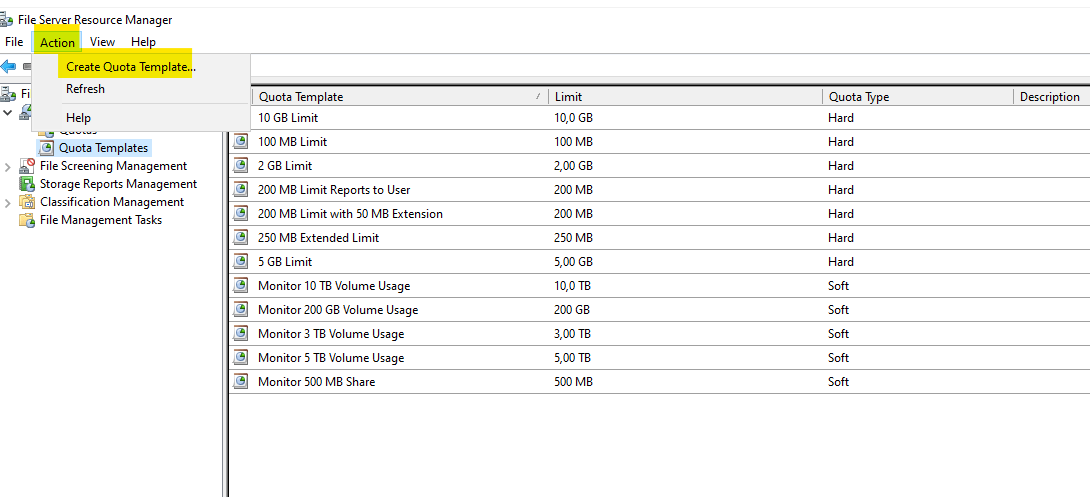
Right-click “Quota Templates.”
Select “Create Quota Template.”
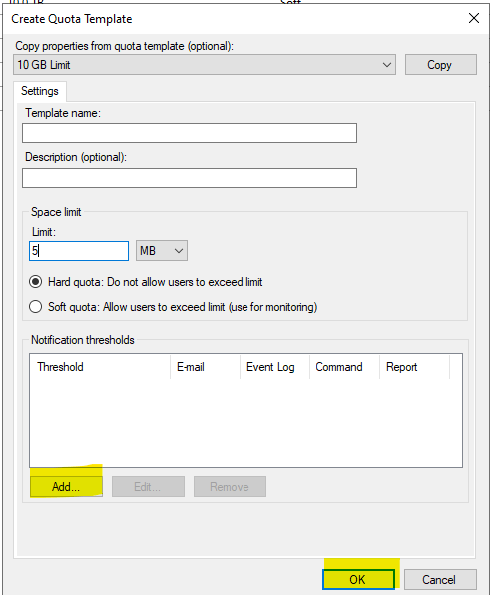
Mandatory fields for creating a template are the name, space limit, and selecting either a hard or soft quota.
Hard quotas will not allow users to exceed the limits.
Soft quotas will allow users to exceed limits but will produce a warning.
To set threshold notifications, select “Add.”
Configure the options.
Select “OK.”
Quota Creation
After setting up the quota template or using a default quota template, create the quota.
Quota creation steps:
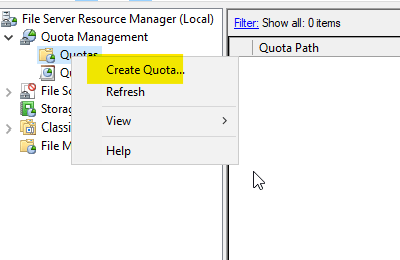
Right-click on the File Server Resource Manager’s dashboard “Quotas.”
Select “Create Quota.”
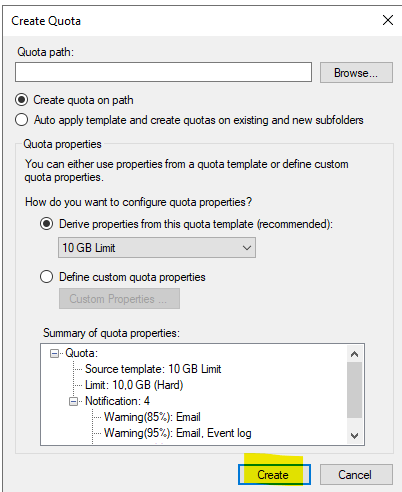
On the “Create Quota” window, in the “Quota path” section, select “Browse.”
Browse to the path that requires quota enablement
Select “Create quota on the path” or “Auto apply template and create quotas on existing and new subfolders…” option.
To only apply a quota to the top-level folder, select the first option.
To apply the quota to a folder and all subfolders, select the second option.
Select “Derive properties from this quota template”.
Select the previously created template.
Select “Create.”
File Server Resource Manager’s dashboard will show the new quota where limits are applied.
File Screening Configuration
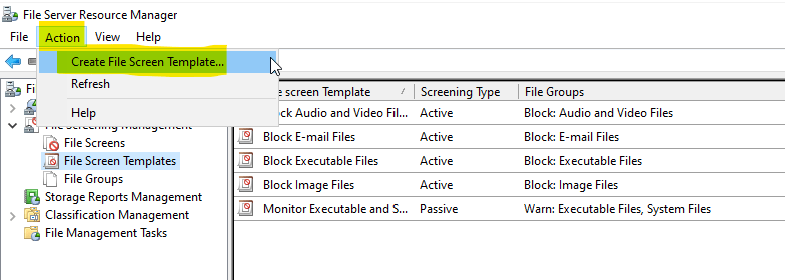
To create a file screening template, select “Action.”
Next, select “Create File Screen Template.”
In the new window that opens up, configure the desired options and click “OK.”
Report Generation
File Server Resource Manager allows a variety of reports to be generated.
For example, disk usage or monitoring groups of users to check for non-compliance.
To create reports:
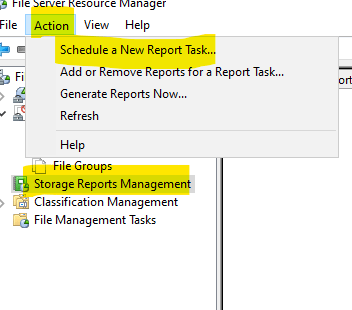
Select “Storage Reports Management.”
Click “Action.”
Choose “Schedule a New Report Task.”
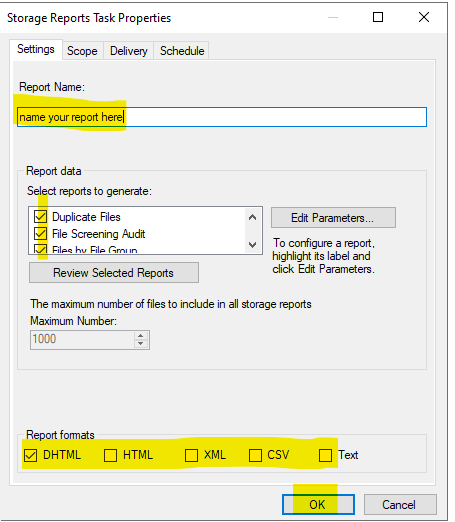
Create a unique name for the report.
Select the desired information the report should contain.
Choose a file format to save the output to.
Click “OK.”
Conclusion
The above examples will give you a good starting point to manage your Microsoft Windows Server 2022 storage. Once you are comfortable with these, explore more advanced options such as file classification.
В этой статье мы разберем методику использования функционала File Server Resource Manager (FSRM) на файловом сервере Windows Server 2012 R2 для детектировании и блокировки работы вирусов-шифровальщиков (троянов-энкодеров, Ransomware или CryptoLocker). В частности, разберемся, как установить службу FSRM, настроить детектирование определенных типов файлов и, в случае детектирования таких файлов, заблокировать доступ пользователя к каталогу на файловом сервере.
Содержание:
- Детектирование шифровальщиков с помощью FSRM
- Настройка SMTP параметров FSRM для отправки email уведомлений
- Создание группы расширений файлов, создаваемых шифровальщиками
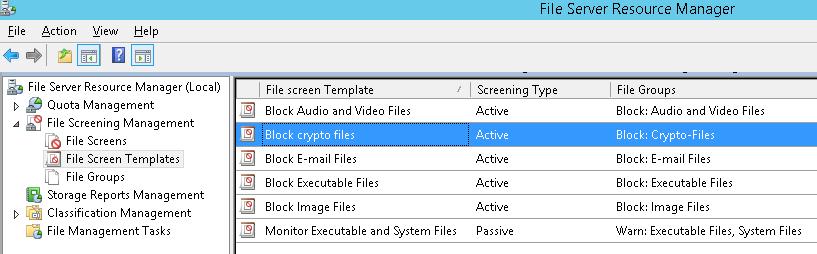
- Настройка File Screen Templates
- Применение шаблона File Screen к диску или папке
- Автоматическая блокировка доступа пользователя, зараженного шифровальщиком
- Тестирование защиты FSRM
Детектирование шифровальщиков с помощью FSRM
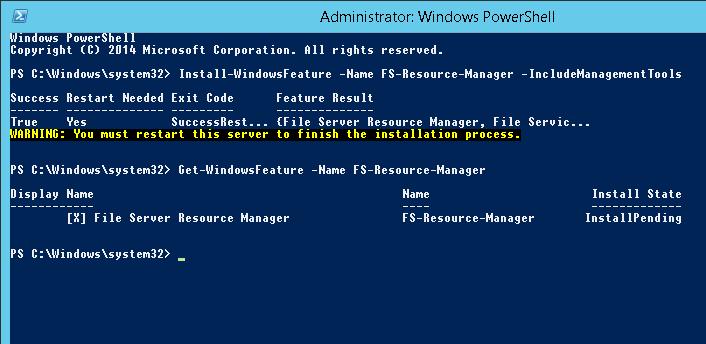
Если компонент File Server Resource Manager еще не установлен на сервере, его можно установить с помощью графической консоли Server Manager или из командной строки PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature FS-Resource-Manager -IncludeManagementTools
Проверим, что роль установилась:
Get-WindowsFeature -Name FS-Resource-Manager
Настройка SMTP параметров FSRM для отправки email уведомлений
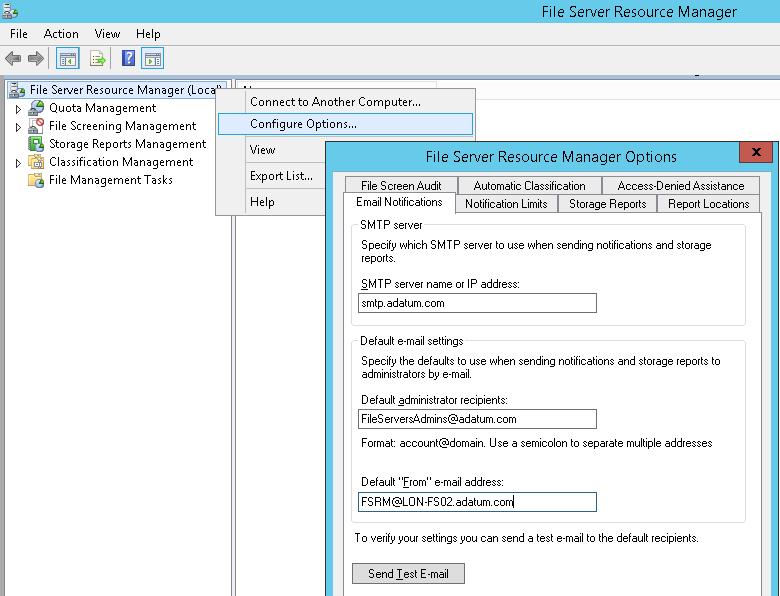
Следующий этап — конфигурация SMTP параметров службы FSRM, благодаря которым администратор может настроить отправку email уведомлений на свой ящик. Для этого запустите консоль fsrm.msc, щелкните ПКМ по корню консоли File Server Resource Manager и выберите пункт Configure Options.
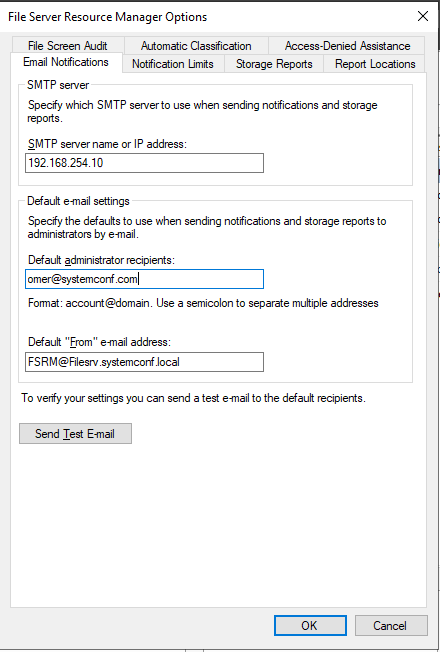
Укажите адрес SMTP сервера, почтовый ящик администратора и имя отправителя.
Совет. Если у вас отсутствует внутренний почтовый сервер, можно настроить пересылку через SMTP релей на внешние ящики.
Проверить корректность настройки SMTP сервера можно, отправив тестовое письмо с помощью кнопки Send Test E-mail.
Настроить параметры SMTP службы FSRM также можно выполнить с помощью Powershell:
Set-FsrmSetting -AdminEmailAddress "[email protected]" –smtpserver smtp.adatum.com –FromEmailAddress "[email protected]"
Создание группы расширений файлов, создаваемых шифровальщиками
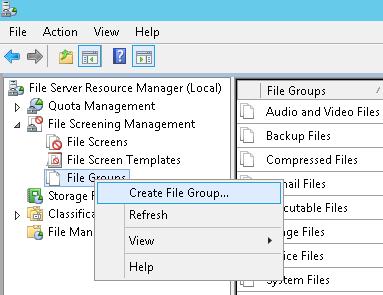
Следующий шаг – создать группу файлов, в которой будут содержаться известные расширения и имена файлов, которые создают шифровальщики в процессе работы.
Этот список можно задать из консоли FSRM. Для этого разверните раздел File Screening Management -> File Groups и в меню выберите Create File Group.
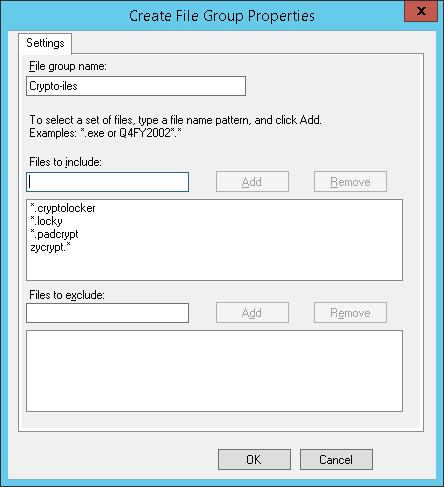
В Windows Server 2012 создать группу файлов с помощью PowerShell можно так:
New-FsrmFileGroup -Name "Crypto-files" –IncludePattern @("_Locky_recover_instructions.txt","DECRYPT_INSTRUCTIONS.TXT", "DECRYPT_INSTRUCTION.TXT", "HELP_DECRYPT.TXT", "HELP_DECRYPT.HTML", "DecryptAllFiles.txt", "enc_files.txt", "HowDecrypt.txt", "How_Decrypt.txt", "How_Decrypt.html", "HELP_RESTORE_FILES.txt", , "restore_files*.txt", "restore_files.txt", "RECOVERY_KEY.TXT", "how to decrypt aes files.lnk", "HELP_DECRYPT.PNG", "HELP_DECRYPT.lnk", "DecryptAllFiles*.txt", "Decrypt.exe", "AllFilesAreLocked*.bmp", "MESSAGE.txt","*.locky","*.ezz", "*.ecc", "*.exx", "*.7z.encrypted", "*.ctbl", "*.encrypted", "*.aaa", "*.xtbl", "*.abc", "*.JUST", "*.EnCiPhErEd", "*.cryptolocker","*.micro","*.vvv")
В Windows Server 2008 R2 придется воспользоваться утилитой filescrn.exe:
filescrn.exe filegroup add /filegroup:"Crypto-files" /members:"DECRYPT_INSTRUCTIONS.TXT|DECRYPT_INSTRUCTION.TXT| DecryptAllFiles.txt|enc_files.txt|HowDecrypt.txt|How_Decrypt.txt| How_Decrypt.html|HELP_TO_DECRYPT_YOUR_FILES.txt|HELP_RESTORE_FILES.txt| HELP_TO_SAVE_FILES.txt|restore_files*.txt| restore_files.txt|RECOVERY_KEY.TXT|HELP_DECRYPT.PNG|HELP_DECRYPT.lnk| DecryptAllFiles*.txt|Decrypt.exe|ATTENTION!!!.txt|AllFilesAreLocked*.bmp| MESSAGE.txt|*.locky|*.ezz|*.ecc|*.exx|*.7z.encrypted|*.ctbl| *.encrypted|*.aaa|*.xtbl|*.EnCiPhErEd|*.cryptolocker|*.micro|*.vvv| *.ecc|*.ezz|*.exx|*.zzz|*.xyz|*.aaa|*.abc|*.ccc|*.vvv|*.xxx| *.ttt|*.micro|*.encrypted|*.locked|*.crypto|*_crypt|*.crinf| *.r5a|*.XRNT|*.XTBL|*.crypt|*.R16M01D05|*.pzdc|*.good| *.LOL!|*.OMG!|*.RDM|*.RRK|*.encryptedRSA|*.crjoker| *.LeChiffre|*.keybtc@inbox_com|*.0x0|*.bleep|*.1999| *.vault|*.HA3|*.toxcrypt|*.magic|*.SUPERCRYPT|*.CTBL|*.CTB2|*.locky"
Совет. Список известных расширений файлов различных шифровальщиков можно составить самостоятельно, или воспользоваться готовыми периодически обновляемым списками, ведущимися энтузиастами:
https://www.bleib-virenfrei.de/ransomware/
https://fsrm.experiant.ca/api/v1/combined
Во втором случае актуальный список расширений файлов для FSRM можно грузить прямо с веб сервера с помощью Invoke-WebRequest
new-FsrmFileGroup -name "Anti-Ransomware File Groups" -IncludePattern @((Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://fsrm.experiant.ca/api/v1/combined").content | convertfrom-json | % {$_.filters})
Либо воспользоваться готовым файлом: crypto_extensions.txt. Данный файл можно сохранить на диск и обновить с его помощью созданную группу файлов FSRM:
$ext_list = Get-Content .\crypto_extensions.txt
Set-FsrmFileGroup -Name "Crypto-files" -IncludePattern ($ext_list)
Настройка File Screen Templates
Создадим новый шаблон File Screen Template, в котором определяются действия, которые FSRM должен выполнить при обнаружении указанных файлов. Для этого в консоли FSRM перейдите в раздел File Screen Management -> File Screen Templates. Создадим новый шаблон Create File Screen Template.
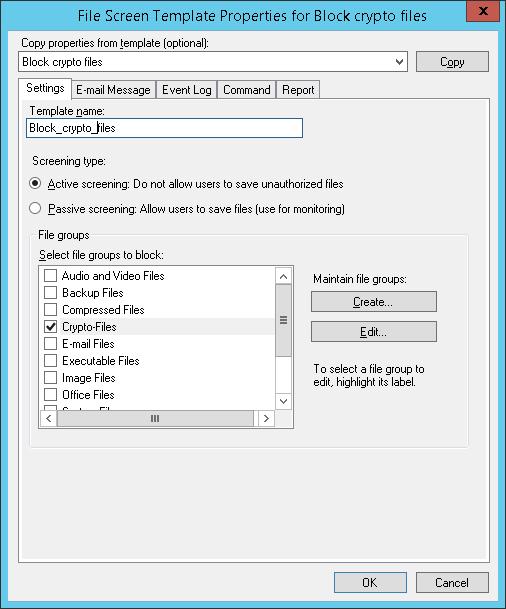
На вкладке Command можно указать действие, которое нужно выполнить при обнаружении такого типа файла. Об этом чуть ниже.
Сохраните изменения. В списке шаблонов должен появится еще один.
Применение шаблона File Screen к диску или папке
Осталось назначить созданный шаблон к диску или сетевой папке на сервере. В консоли FSRM создадим новое правило Create File Screen.
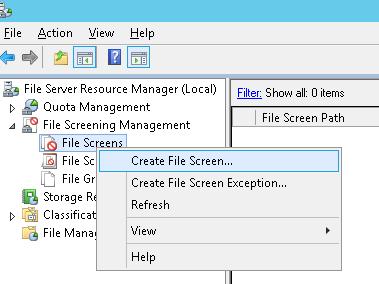
Автоматическая блокировка доступа пользователя, зараженного шифровальщиком
Осталось настроить действие, которое FSRM будет выполнять при обнаружении файлов, созданных шифровальщиками. Мы воспользуемся готовым скриптом: Protect your File Server against Ransomware by using FSRM and Powershell (https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/Protect-your-File-Server-f3722fce). Что делает этот скрипт? При попытке записать «запрещенный» тип файла в сетевой каталог, FSRM запускает данный скрипт, который анализирует журнал событий и на уровне шары запрещает запись пользователю, из-под осуществлялась попытка записать запрещенный тип файла. Таким образом, мы заблокируем доступ зараженного пользователя к сетевой папке.
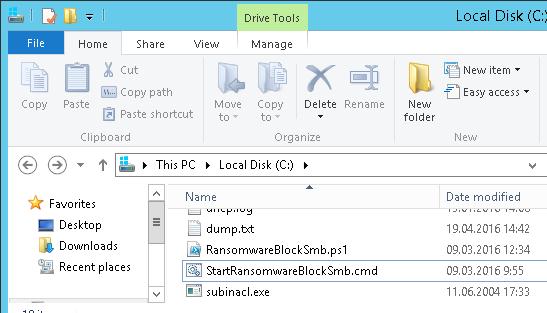
Скачайте указанный скрипт и распакуйте его в корень каталога C:\ на файловом сервере. В эту же папку скопируйте утилиту SubInACL (нужна для изменения разрешений на сетевой каталог). В каталоге должны оказаться следующие файлы:
- RansomwareBlockSmb.ps1
- StartRansomwareBlockSmb.cmd
- subinacl.exe
Примечание. В PS скрипте пришлось изменить строки:
$SubinaclCmd = "C:\subinacl /verbose=1 /share \\127.0.0.1\" + "$SharePart" + " /deny=" + "$BadUser"
и
if ($Rule -match "Crypto-Files")
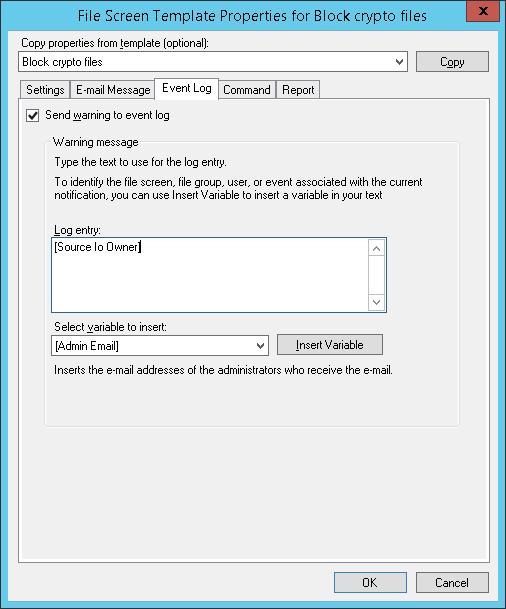
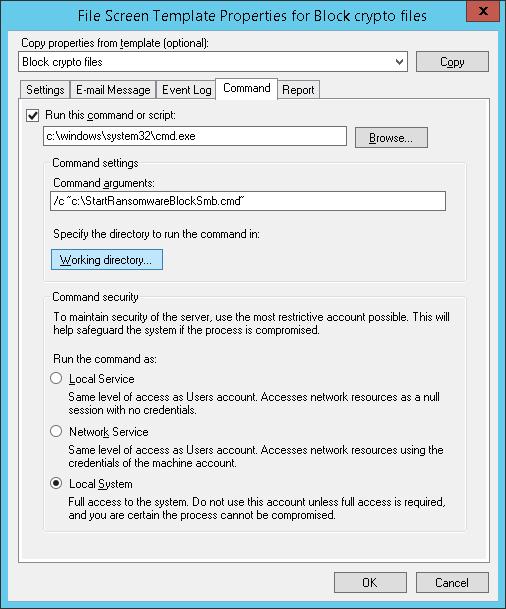
Осталось в настройках шаблона “Block crypto files” на вкладке Command указать, что должна запуститься командная строка с аргументом StartRansomwareBlockSmb.cmd:
Run this command or script:
c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe
Command arguments:
/c “c:\StartRansomwareBlockSmb.cmd”
Команда должна выполняться с правами локальной системы (Local System).
Тестирование защиты FSRM
Протестируем, как работает защита FSRM от шифровальщиков. Для чего в защищаемом каталоге создадим файл с произвольным расширением, и попробуем изменить его на запрещенное .locky.
При попытке сохранить запрещенный файл FSRM запишет в журнал событие:
Event ID: 8215
Source: SRMSVC
Скрипт RansomwareBlockSmb.ps1на основании данных из события запретит текущему пользователю доступ к данному каталогу, выставив в разрешениях на шару персональный deny:
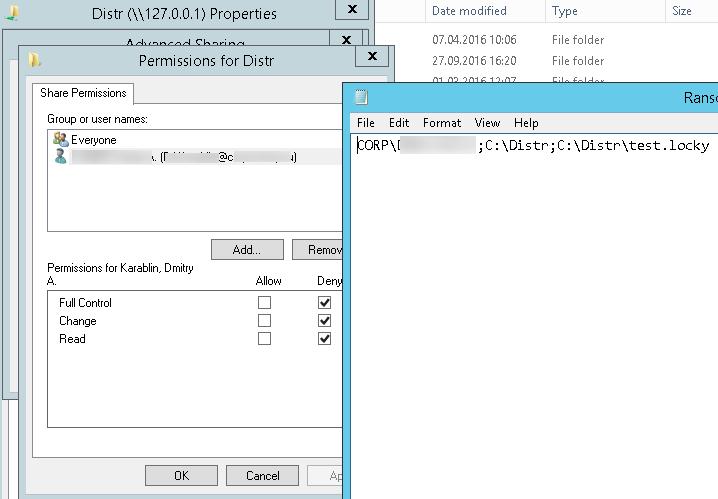
Если нужно обеспечить еще более высокий уровень зашиты, можно перейти от черного списка файлов к белому, когда на файловом сервере можно сохранять только файлы разрешенных типов.
Итак, мы рассмотрели, как с помощью FSRM автоматически блокировать доступ к сетевым каталогам пользователям, компьютеры которых заражены вирусом-шифровальщиком. Естественно, использование FSRM в таком режиме не может дать 100% гарантию защиты файлов на серверах от этого класса вирусов, но как один из эшелонов защиты, методика вполне себе пригодна. В следующих статьях мы рассмотрим еще несколько вариантов противодействия вирусам-шифровальщикам:
- Как восстановить файлы пользователя из снимков VSS после заражения шифровальщиком
- Блокировка вирусов и шифровальщиков с помощью Software Restriction Policies
The File Server Resource Manager (FSRM) has been around for quite a while but seems to be an underutilized feature on a Windows Server. The FSRM helps system administrators with anything related to managing files on file servers.
With FSRM, you can put a size limit on a directory, filter the files users share, and more.
Stick around and discover the benefits of setting up the File Server Resource Manager and how to use its features to your advantage!
Prerequisites
This tutorial will be a hands-on demonstration. This tutorial assumes you already have a working domain controller, file server, and network-shared folder. You must also have a domain administrator account to set up FSRM.
Installing File Server Resource Manager on Windows Server
Like most roles and features, FSRM does not come pre-installed on a Windows Server. You need to install FSRM yourself.
In real-world use cases, FSRM and File server roles and features are installed together on a dedicated Windows Server. But if you don’t have a dedicated server, you can install the file server and FSRM roles onto your domain controller as part of a testing environment.
1. Log in using your domain administrator account to your file server.
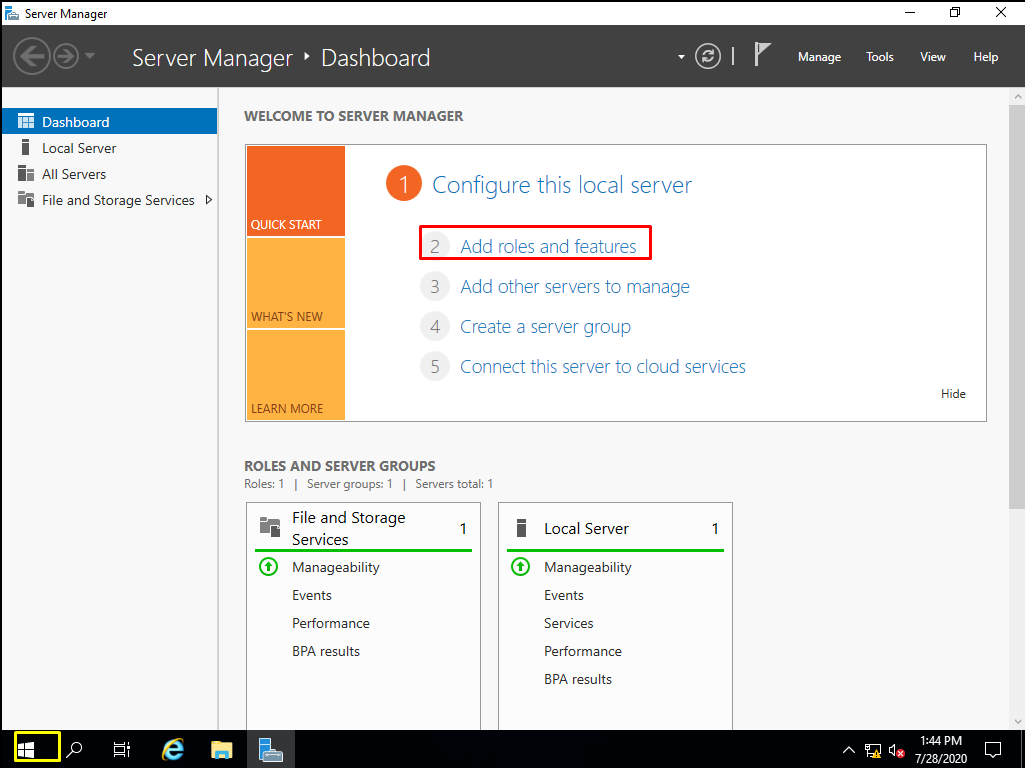
2. Click Manage → Add roles and features.

3. Click Next on the Before you begin tab.

4. Select Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next.

5. Since installing on the local server, keep the default values on the Server Selection tab and click Next.

6. On the Select server roles tab, expand File and Storage Services. Expand File and iSCSI Services, and tick File Server Resource Manager.

7. Click Add Features on the popup window.

8. The wizard will tick the File Server and File Server Resource Manager after you click Add Features. The wizard will disable the File Server option if you have already installed it.

9. Keep the default selected values on the Select features tab. Click Next to advance to the Confirmation tab.

10. On the Confirmation tab, confirm that the File Server Resource Manager is part of the installation. Click Install.

11. Within a few minutes, the installation will be complete. Click Close.

In this instance, the installation did not require restarting the server.
Accessing File Server Resource Manager
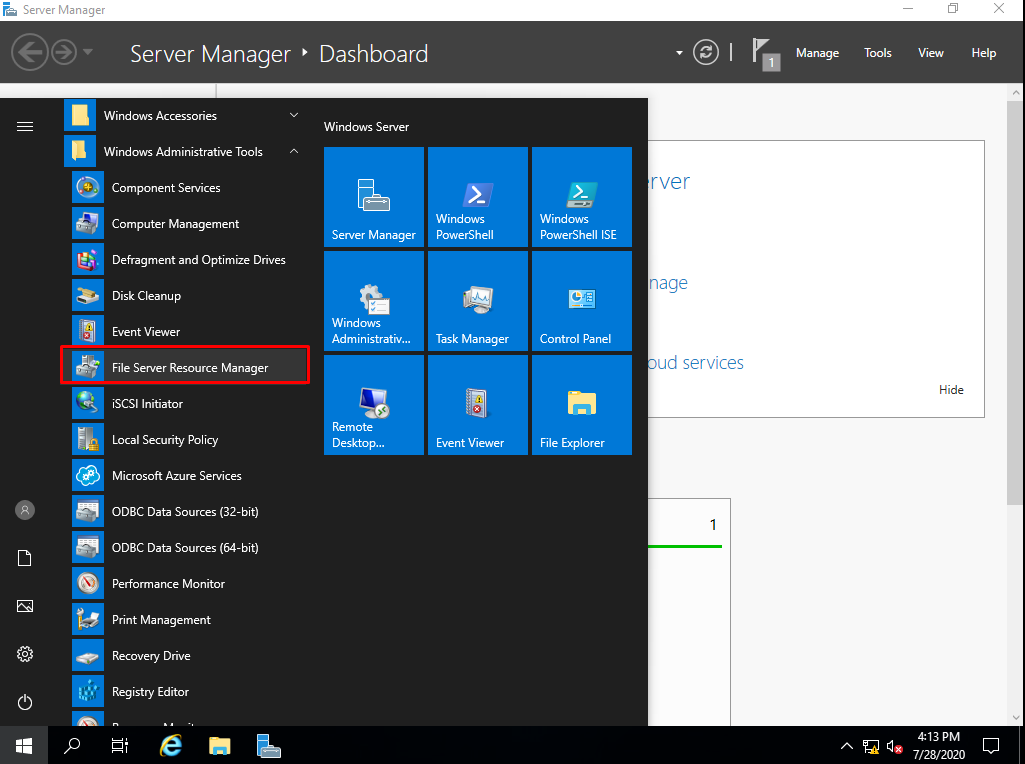
After installing FSRM and restarting the destination server, you can pull up FSRM from the Server Manager’s Tools menu.
1. Click Tools on the Server Manager → File Server Resource Manager.

2. FSRM has five primary nodes that you can configure:
- Quota Management – To create user file size quotas to conserve storage space.
- File Screening Management – Create filters that allow or deny users to save specific file types.
- Storage Report Management – To Schedule report tasks and generate reports in real-time.
- Classification Management – To categorize files depending on their classification property type.
- File Management Tasks – Create tasks to automate file management, such as creating expiration tasks.

Tweaking File Server Resource Manager Options
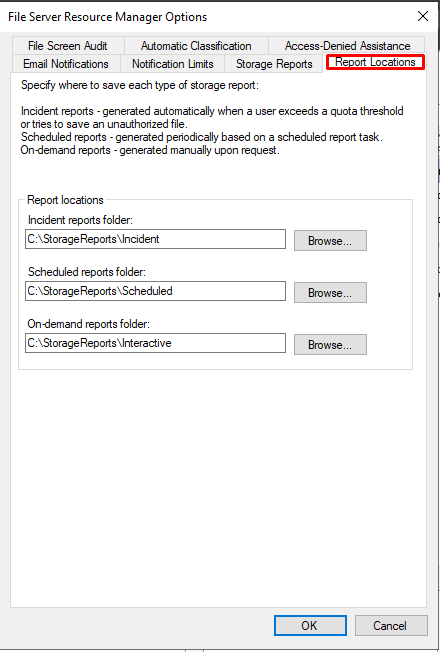
Before configuring any nodes of FSRM, there are some configurations you need to perform in the FSRM options. The following settings will be helpful in your implementation of FSRM. Feel free to navigate all the other tabs not tackled here.
1. To configure FSRM options, click File Server Resource Manager (Local) → right-click File Server Resource Manager (Local), → click Configure Options.

2. The first tab to appear under File Server Resource Manager Options is Email Notifications. Enter your SMTP server address here. This article does not have an email server for this demonstration. To set up an email server, consider reading the related guide below.
3. Next, click the File Screen Audit tab. Tick the Record file screening activity in auditing database to record file screening activity audits.

4. Navigate to Report Locations to see the report paths. You can keep or change these locations as you wish. Click OK to save your changes.

Configuring Quota Management
Quota Management allows you to create quotas for shared drives and folders. Quota Management has two subcomponents: Quotas and Quota Templates.
Creating a Quota Template and a Quota
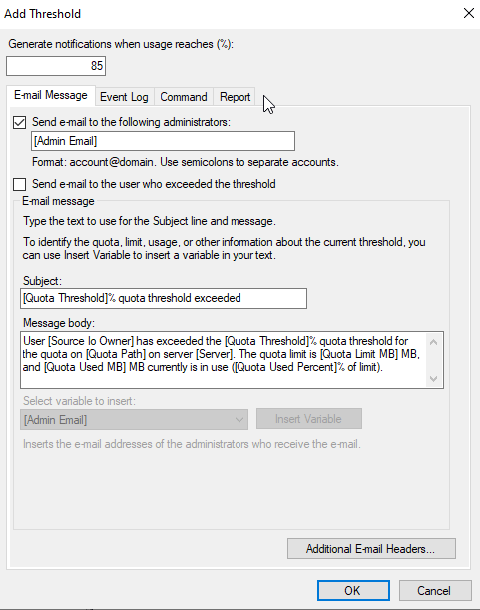
You can create a quota to set a data limit to a shared folder. Aside from limiting data or volume usage, a quota can send threshold notifications via email, event log, report, and run a script or command.
1. Expand Quota Management → click Quota Templates → right click Quota Templates → click Create Quota Template.

2. Input the following details:
Template name: 4 GB Limit
Space Limit: 4 GB
Click Hard quota → Click Add in the Notification thresholds part.

3. Keep 85% usage to generate a notification. Click Event Log → tick Send warning to event log → click OK.

4. Click OK to finish creating the quota template.

5. Click Quotas on FSRM→ right click Quotas → select Create Quota to create a quota.

6. Specify the quota path. Click Create quota on path→ click Derive properties from this quota template. Select 4 GB Limit. Click OK to finish creating the quota.

Testing the Quota
You can test your quota to generate notification/s and let users know they can’t exceed the size limit. First, trigger a notification by adding files to the folder to reach the threshold. And second, add more files that exceed the size limit warning the user.
1. Navigate to your quota path in File Explorer and add files greater than or equal to 85% but less than 100% of the 4 GB quota.

2. To see the event log, click Tools on Server Manager → click Event Viewer.

3. Expand Custom Views → click Administrative Events → click the most recent warning from the source SRMSVC. The Event Viewer will display the event log text and other details below. Close the event viewer when done.

4. Navigate to your quota path in File Explorer again and add more files to the shared folder. When you’re about to exceed the quota limit, you’ll get a prompt saying, “There is not enough space on…”

Setting Up File Screening
File screening is another excellent feature of FSRM; it can help define which files are allowed and which are not. File screening ensures users only upload appropriate and approved files on a shared drive or folder.
Creating a File Screen
A file screen acts as a filter for which files the users can upload to the shared folder. A file screen either allows or denies users to add files upload. In this example, you will create a file screen template and a file screen to block compressed files.
1. Expand File Screening Management on FSRM → click File Screen Templates → right-click File Screen Templates → click Create File Screen Template.

2. In the Template name, type Block Compressed Files. Click Active screening → tick Compressed Files from the file groups to block.

3. Click Event Log → tick Send warning to event log.

4. Click Report → tick Generate reports → tick File Screen Audit → click OK.

5. Click File Screens Management → right-click File Screens → click Create File Screen.

6. Specify the file screen path → click Derive properties from this file screen template → select Block Compressed Files → click Create.

Testing the File Screen
To test the file screen, try to save a compressed file to the file screen path to trigger a warning.
Navigate to the file screen path and add a compressed file. You should get a message like the one below.

Open the Event Viewer and click the most recent warning from SRMSVC. The event log text and other details are below.

The default location of the generated file screening audit report is C:\StorageReports\Incident.

Managing Storage Reports
Storage Reports Management helps you generate reports in real-time, schedule a weekly or monthly report task, and add or remove reports for a report task. In this example, you will learn to schedule a report task.
1. Click Storage Reports Management → right-click Storage Reports Management → click Schedule a New Report Task.

2. Type File Screen and Quota Usage in the Report Name. Tick File Screening Audit and Quota Usage under reports to generate.

3. Click the Scope tab. Click Add and specify the folder to add to the task’s scope.

4. Click the Schedule tab. Set the time and frequency for automatic storage reports, and click OK. The default location for scheduled reports is C:\StorageReports\Scheduled.

5. Right click the task name → click Run Report Task Now to run the report task on demand.

6. Click the Wait to display the generated option, and click OK.

Below is an example of storage reports generated on demand.

Working on Classification Management
Classification properties and rules help categorize files within a specified directory. You will create a yes or no classification property, classification rule, and an additional parameter for this demonstration.
Creating Classification Properties
Classification properties help assign values to files within a designated folder or location. There are different classification property types you can choose from depending on your needs.
Expand the Classification Management. Right click Classification Properties → click Create Local Property.

Type the name of your new classification property, add a description, select Yes/No property type, and click OK.

Creating Classification Rules
Create a classification rule to set the value for a single classification property. Here, you learn to create a classification rule as a content classifier with a parameter to look for the word password within files.
1. Create two text files in the directory of files to classify, and one must contain the word password.

2. Click Classification Rules → right-click Classification Rules → click Create Classification Rule.

3. Type the rule name and description on the General tab and tick Enabled.

4. Click the Scope tab. Click Add and specify the folder or folders you want to include in the scope.

5. Click the Classification tab and set the following fields.
- Classification method: Folder Classifier
- Property to assign to files: your yes/no rule.
- Specify a value: Yes.
Click Configure.

6. Type password under Expression. Click OK.

7. Right click Classification Rules → click Run Classification With All Rules Now.

8. Click Wait for classification to complete and click OK.

After running classification, the reports will open in a browser.

9. Open File Explorer, right-click one of the files in the reports → click Properties, → click Classification to verify classification. Click OK to close the file properties.

Creating File Management Tasks
Manual file management is prone to user error and time-consuming. What if you have a lot of files to process? Automate file management tasks by schedule or on demand. Here, you’ll learn to create a file management task based on the classification property and rule you made earlier.
1. Click File Management Tasks → right-click File Management Tasks → click Create File Management Task.

2. Type the task name and description on the tick Enabled.

3. Click the Scope tab → click Add to add a folder or folders to include in the scope.

4. Click the Action tab and choose File expiration as the action type. Specify the expiration directory.

5. Click the Condition tab → click Add under property conditions and choose the following values:
- Property: your yes/no property.
- Operator: Equal.
- Value: Yes.
Click OK.

6. Click the Schedule tab, set the time, choose how often this task runs, and click OK. In this example, the schedule is 5:00 PM every Friday.

7. Right click the File Management Tasks node → click Run File Management Task Now → click Wait for the task to complete, → click OK. This step is for testing if the task works.

8. On the top part of the report, click on the expiration directory to confirm the text file that contains the word password is there.

Conclusion
Thank you for sticking around. You have learned how File Server Resource Manager helps keep file management more effortless. FSRM also acts as a safety feature for blocking unapproved and potentially harmful files from being uploaded to the file server.
The scenarios and what you learned in this tutorial only covered the basics of File Server Resource Manager. Keep learning, and remember to have fun while you’re at it!
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests…
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
The File Server Role, which has been in our lives since Windows Server 2008, continues with Windows Server 2019. It is used for assigning sharing quotas to our users in our environments, preventing unnecessary content from being copied to these areas or adding only allowed content, receiving reports, seeing the event log in case of violations here, receiving e-mail related to the situations.
We can start the steps to add roles by using one of the Manage menu on Server Manager or the area shown by the picture below.
On the screen that opens, information is given on what we can do with the wizard. With the “Next” button, we can proceed to our next screen.
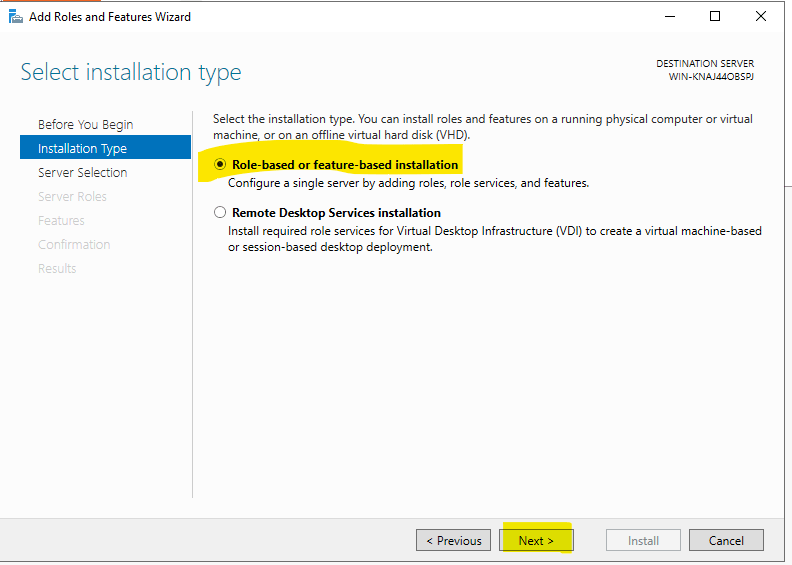
There are two options on our screen that opens. The first one is;
Role-based or feature-based installation: Allows to add and install on role and feature basis. According to the version we have in Windows Server 2016, we can add and remove the roles and features we need.
Remote Desktop Services installation: In the old days called Terminal Service and now we can make RDS (Remote Desktop Services) remote desktop configuration fast and as standard here.
For this reason, we will proceed with the Next button by choosing Role-based or feature-based installation since we will not do RDS installation and configuration.
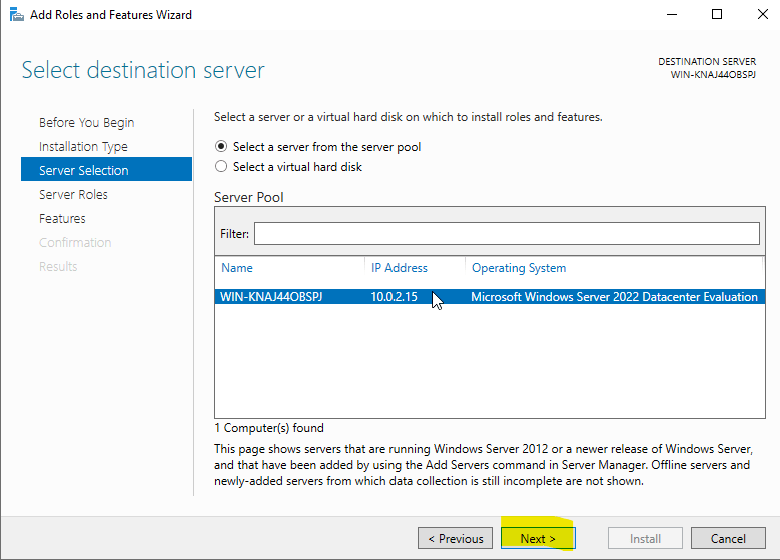
By creating a server cluster with Windows Server 2008 and 2012, it was able to add and remove Roles and Features on this cluster collectively and over a different server. Of course, this process can be done directly on Windows Server 2012, while we had to add some features to Windows Server 2008. Since we have a single server in our environment and we will install the Resources Manager feature of the File Server role on this server, we proceed with the “Next” button by selecting our server whose Name, IP address and version information are provided.
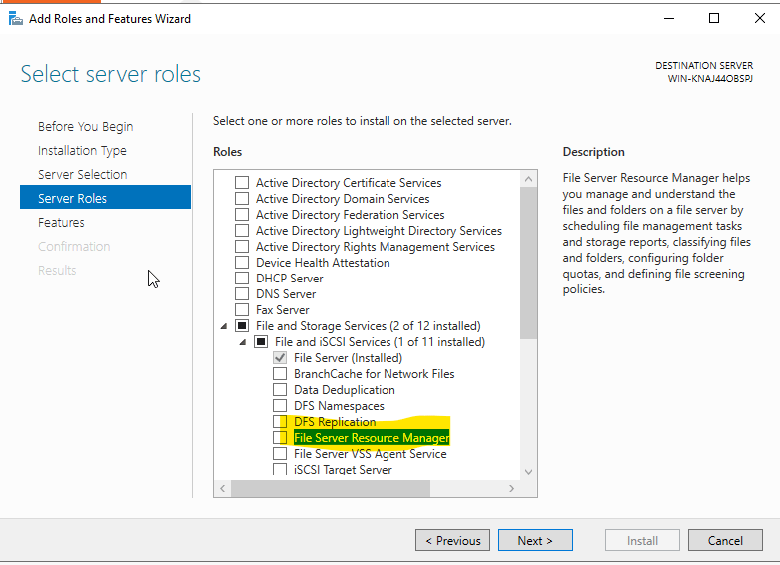
We select and expand the File and Storage Services role for the feature that we will install from the screen we see.
We select the File Server Resource Manager feature.
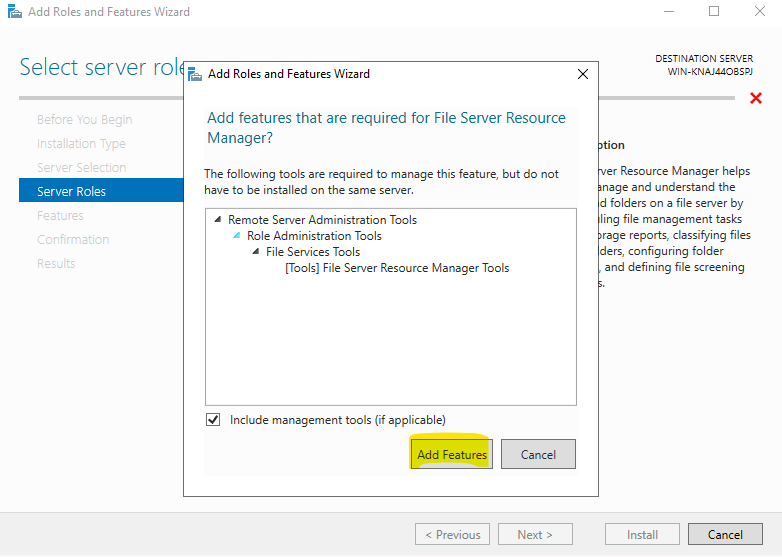
After selecting this feature, the screen of the components required to install this feature is displayed. Since we want it to be installed automatically on these components, we click on the Add Features button.
After our selections are completed, we proceed to the next screen with the “Next” button.
By selecting “Restart the destination server automatically if required”, we can ensure that this process happens automatically if a reboot is required after installing the roles. Let’s click the YES button on the problem screen that comes to our mix and let us state that we give consent to start again.
On this screen, we can start our installation process by clicking our Install button.
File Server Installation has started and continues.
Role feature setup is complete. We can close our screen with the “Close” button.
A shortcut of our File Server Resource Manager feature has occurred on the start menu. We can open our console by clicking here.
Our console is opened. A screen that is simple to use and manage welcomes us.
First, let’s right-click on the console main menu and click on “Configure Options…” to configure our main settings.
We just need to make a few settings on our screen in general. One of them will be notifications by mail when there is a violation or report situation. Therefore, first of all, let us enter an SMTP server information in our environment or outside in the Email Notifications section. Then we can enter the address information that will send and receive mail.
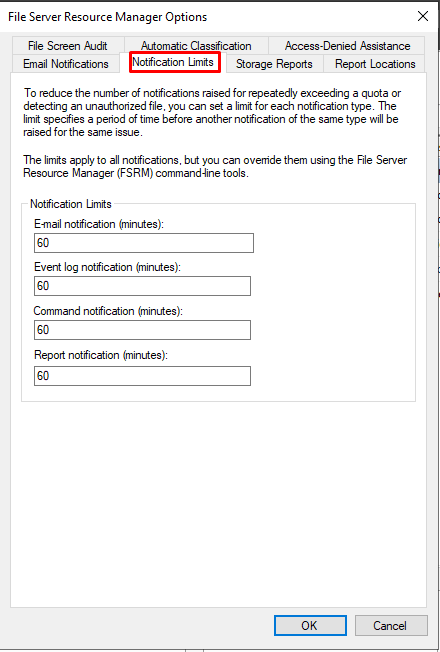
In the Notifications Limits section, we can edit the values or leave them as is.
In the Reports Locations section, we can change the area where the reports are stored or leave them as is.
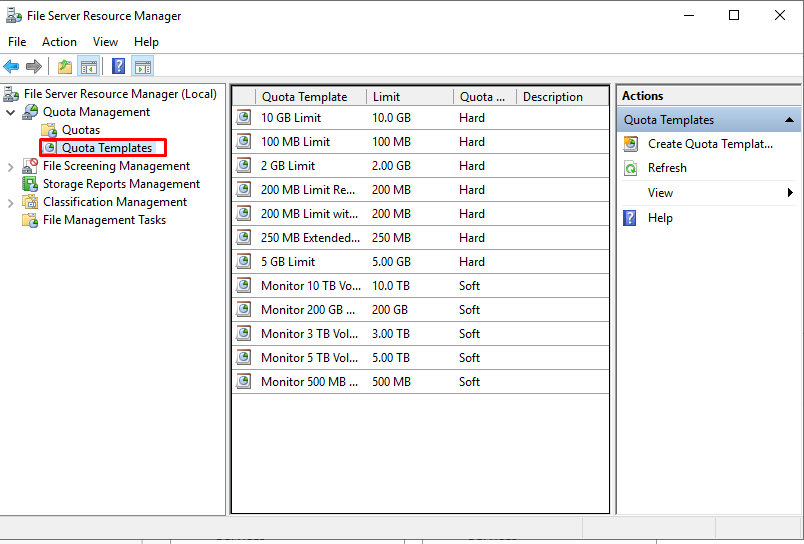
Finally, let’s start our settings after general settings. When we first look at the QUOTA Templates section, we can see ready templates prepared in MB, GB and TB.