in Blog / Citrix / Containers / FSLogix / Outlook / Search / UPM / Windows
Windows Search challenges in Server 2019 and Windows 10 Multi Session
- Intro
- First Logon for the user
- User Logoff
- Restarting the search service
- Summary
Intro
As always in our industry, small changes in one platform can result in significant impact across what is “standard practice” in many other areas. This week’s lucky contender is Windows Search.
Update 25/10/2021: There is a new update from Microsoft available stating the fix as follows:
Addresses an issue that causes searchindexer.exe to keep handles to the per user search database in the path below after you sign out:
C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{SID}
As a result, searchindexer.exe stops working and duplicate profile names are created.
Windows Search in both Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 Multi-Session has changed how it operates, introducing the concept of per-user search natively into the Search Service. This is fundamentally different from previous versions (namely Windows Server 2016 etc) and changes how we need to think about search roaming with supporting technologies such as FSLogix Containers and Citrix UPM.
The biggest change is that the Windows Search index is now stored per user in the user profile, specifically
C:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{UserSID}\{UserSID}.edb
On each login, the Windows Search process creates a new instance of the search database for the user based on the existing EDB. If no EDB file exists, a new one is created by the Operating System.
There are two components associated with the Search functionality split into individual processes:
- SearchIndexer.exe: This process runs under the
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEMaccount and accesses the index database for each user (profile based) - SearchProtocolHost.exe: an instance of this process runs per user and is a child process of SearchIndexer.exe. This process handles amongst other things, the indexing of the Outlook OST file, not the searching of the index file, but the actual index creation of it making content available to search. Searching should be operational with or without this process running. When new items need to be indexed, the process will run, once finished, it will stop
The impacts here, should you have dealt with FSLogix or Citrix UPM Search roaming should start to become obvious when you think about how these solutions tackle the Search side of things (they rip out a component of the index and store them within a container). The long and short of it is as follows:
- For FSLogix environments, you must NOT enable search roaming within the FSLogix GPO. Specifically, you want SearchRoam set to 0 in the registry. This needs to be reversed in your master image should you have enabled it previously, in fact, given the what we know of Search challenges and the attempted hooks into it, I would be tempted to suggest that should you have enabled search roaming in either Windows Server 2019 or Windows 10 multi-session previously, then revert the setting, reinstall Microsoft Office and make sure that the event logs are clear from a Windows Search perspective
- For Citrix UPM environments, the following article has been released which is quite confusing. TLDR, the key it’s discussing should not be set to anything other than 0, and ideally shouldn’t exist as a whole in Windows Server 2019. Citrix UPM configurations will need to cater for the new location of the Search Index, however, the OST container can stay in place and do its thing. I haven’t had time to test, but I would assume that the new search location in the user profile is an ideal candidate for the UPM container feature
Unfortunately, Windows Search is an ongoing challenge and there is a fair number of customers who are experiencing issues with the native multi-user search capability in both Windows 10 Multi-Session and Windows Server 2019. Some are experiencing repeated crashing of the service others are finding that search index files are not released on logoff resulting in locked files and corrupt indexes.
In the below walkthrough, I will try and outline what happens with Windows Search in Server 2019, and where things fall apart, along with a temporary resolution which may help until the problems are properly addressed by Microsoft.
First of all, an outline of the environment I am using to demonstrate the situation
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, latest rollup at the time of writing
- FSLogix release 2.9.7237.48865
- Profile and Office Container configured
- Microsoft Office 365 ProPlus, x64, Semi-Annual channel
- No PVS or MCS provisioning
Secondly, below is an outline of some of the event log entries we will be referring to:
| ID | Detail | |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Windows Search Service has created default configuration for new user KINDO\JKindon5 |
|
| 2 | SearchIndexer (4400,P,98) {S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine (10.00.17763.0000) is starting a new instance (3) |
|
| 102 | SearchIndexer (4400,P,98) {S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine (10.00.17763.0000) is starting a new instance (3) |
|
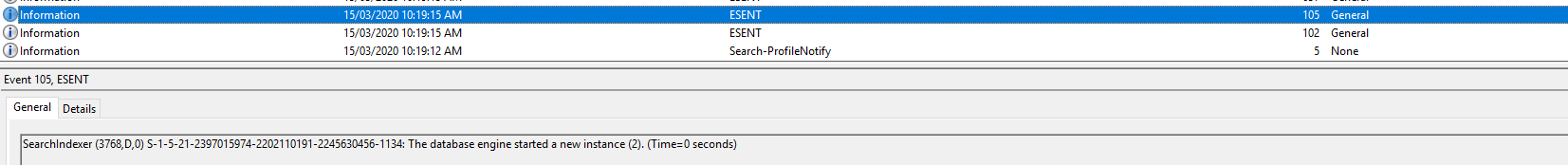
| 105 | SearchIndexer (4400,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine started a new instance (3). (Time=0 seconds) |
|
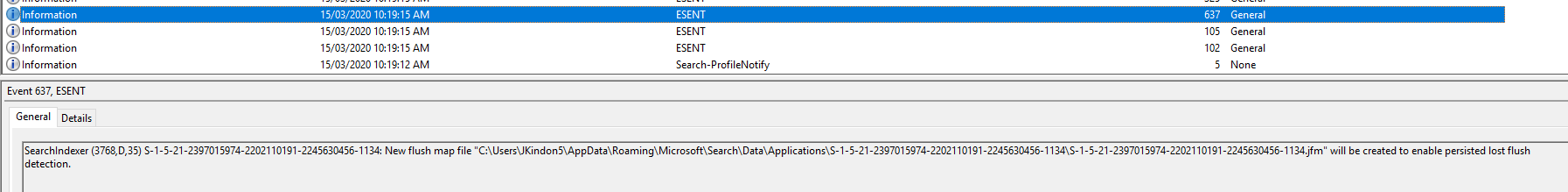
| 637 | SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: New flush map file C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.jfm will be created to enable persisted lost flush detection |
|
| 325 | SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) {S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine created a new database (6, C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.edb). (Time=0 seconds) |
|
| 103 | SearchIndexer (6672,T,97) {S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine stopped the instance (3) |
|
| 2 | Unable to remove Windows Search Service indexed data for user ‘KINDO\JKindon5’ in response to user profile deletion. Error code 0x80004002 | |
| 482 | SearchIndexer (3768,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: An attempt to write to the file C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.jfm at offset 0 (0x0000000000000000) for 8192 (0x00002000) bytes failed after 0.000 seconds with system error 21 (0x00000015): “The device is not ready.”. The write operation will fail with error -1022 (0xfffffc02). If this error persists then the file may be damaged and may need to be restored from a previous backup |
|
| 492 | SearchIndexer (9200,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The logfile sequence in C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\ has been halted due to a fatal error. No further updates are possible for the databases that use this logfile sequence. Please correct the problem and restart or restore from backup |
|
| 439 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: Unable to write a shadowed header for file |
C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.edb. Error -1022 |
| 104 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine stopped the instance (2) with error (-1022) |
|
| 103 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) Windows: The database engine stopped the instance (0) | |
| 300 | SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine is initiating recovery steps. |
|
| 301 | SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has finished replaying logfile C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\edb.jtx |
|
| 302 | SearchIndexer (10076,U,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has successfully completed recovery steps |
|
| 326 | SearchIndexer (9808,D,50) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1104: The database engine attached a database (2, C:\Users\JKindon\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1104\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1104.edb). (Time=0 seconds) |
My findings here are an aggregation of existing posts, as well as feedback from colleagues in the World of EUC slack channel. Testing has been validated in my own environments.
First Logon for the user
On the first logon for a new user, the following event logs entries will occur, basically detecting a new user without an index, creating a new database, configuring and leveraging the new instance as below:
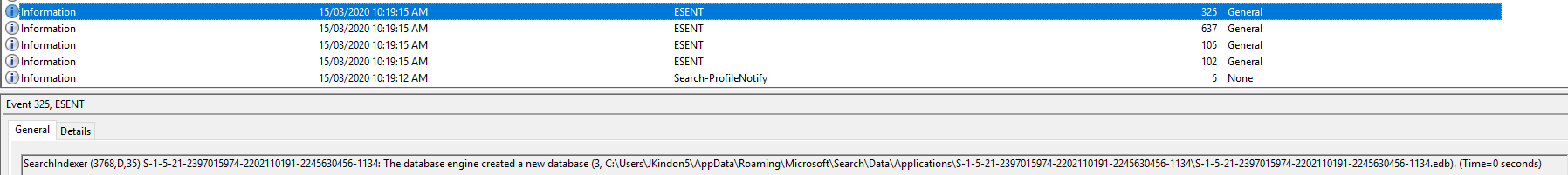
Event ID 5: Windows Search Service has created the default configuration for new user Kindo\JKindon5
Event ID 102: SearchIndexer (4400,P,98) {S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine (10.00.17763.0000) is starting a new instance (3)
Event ID 105: SearchIndexer (4400,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine started a new instance (3). (Time=0 seconds)
Event ID 637: SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: New flush map file C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.jfm will be created to enable persisted lost flush detection
Event ID 325: SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) {S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine created a new database (6, C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.edb`). (Time=0 seconds)
In summary, in a healthy operational state, for a new user, the following event log patterns will occur on logon:
- 5 = Search Creates a default configuration
- 102 = Search Indexer creates a new instance for the user
- 105 = Search Indexer starts the new instance for the user
- 637 = New flush map file created for the user
- 325 = Search Indexer creates the new database
User Logoff
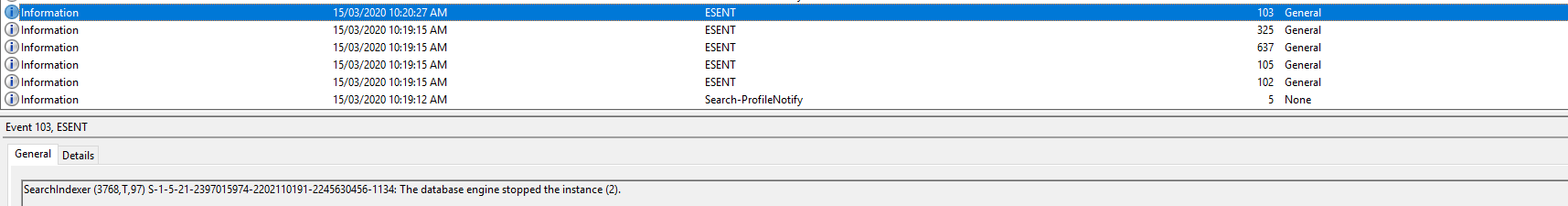
When the user logs off for the first time, the following event entry is logged:
Event ID 103: Event 103: SearchIndexer (6672,T,97) {S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine stopped the instance (3)
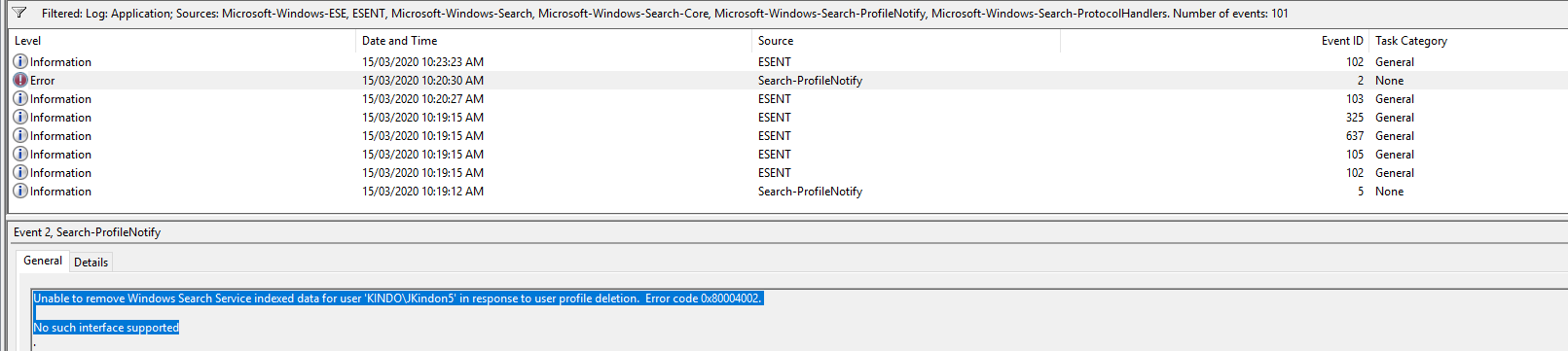
And this is where things go pear-shaped, you will most probably find the 103 entry is quickly followed by this one:
Event ID 2: Unable to remove Windows Search Service indexed data for user KINDO\JKindon5 in response to user profile deletion. Error code 0x80004002
In this state, when the user next connects, they are going to be hit with a problem. What we are looking for, is a happy combination of the following events when the user logs on for the second time:
- 102 = Search Indexer creates a new instance for the user
- 105 = Search Indexer starts the new instance for the user
- 326 = Search Indexer attaches an existing database
What we end up with though due to the above event ID 2 on Logoff, is the following:
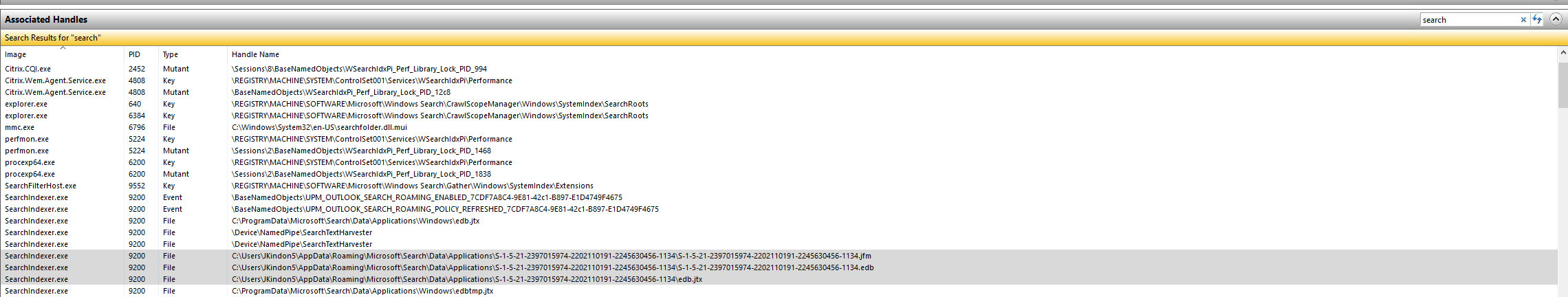
Event ID 482: SearchIndexer (3768,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: An attempt to write to the file C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.jfm at offset 0 (0x0000000000000000) for 8192 (0x00002000) bytes failed after 0.000 seconds with system error 21 (0x00000015): The device is not ready. The write operation will fail with error -1022 (0xfffffc02). If this error persists then the file may be damaged and may need to be restored from a previous backup.
The root cause of this is due to the following handles still being kept open by the SearchIndexer.exe process
These files are held open; however, the physical files have gone (detached) and thus we loop.
If the user was to log back on at this point, we will experience some problematic symptoms and events:
Outlook indexing will present as below:
And no files in the %AppData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{UserSID}` directories will be touched
Restarting the search service
If we restart the Windows Search Service, a few things happen:
All existing handles are closed for SearchIndexer operations, both for any logged off users in a fail state, and for any other user on the Server, and the following event logs are written
| ID | Detail |
|---|---|
| 439 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: Unable to write a shadowed header for file C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.edb. Error -1022. |
| 104 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine stopped the instance (2) with error (-1022) |
| 103 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) Windows: The database engine stopped the instance (0) |
| 102,105,326 | (happy combination representing success) |
| 300 | SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine is initiating recovery steps |
| 301 | SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has finished replaying logfile |
| 302 | SearchIndexer (10076,U,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has successfully completed recovery steps |
| 105,326 | (Search index is OK again) |
Outlook indexing is now OK
Along with successful alterations to the %AppData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{UserSID}` directories.
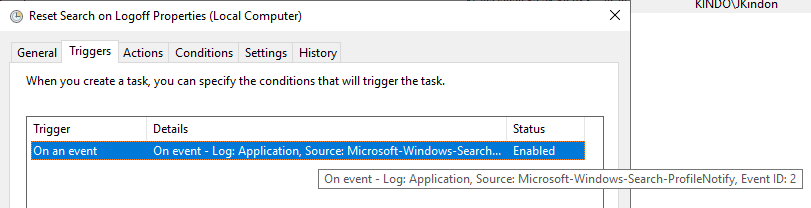
Fixed it would seem. So, logically here, we know that the resolution is to restart the Windows Search Service based on the failure Event, which is represented by Event ID 2. Specifically:
- Event Log: Application
- Event Level: Error
- Event Source: Search-ProfileNotify
- Event ID: 2
- Event Data: Unable to remove Windows Search Service indexed data for user
KINDO\JKindon5in response to user profile deletion. Error code 0x80004002
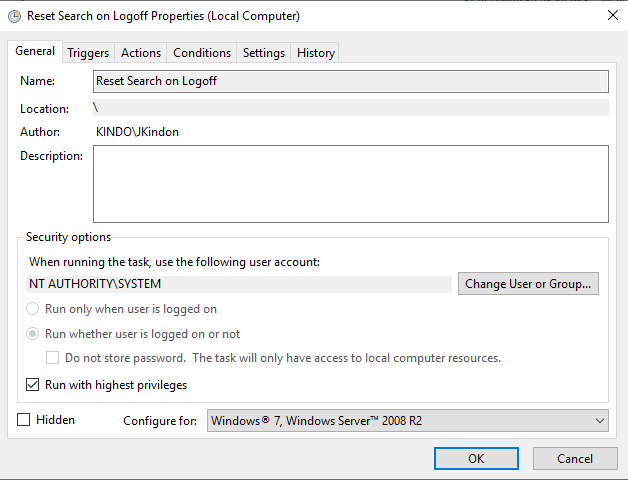
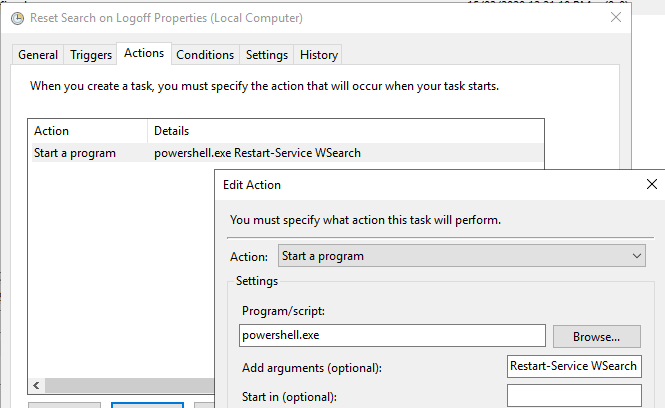
By implementing a scheduled task with the above Event ID as the trigger, and a simple configuration of PowerShell to restart the search service as the action:
We can successfully clear the errors on log-off, release the files, and ensure that when the user logs back in, their index is good to go. The process will now look like the below when a user logs off:
| ID | Detail |
|---|---|
| 103 | for the user logging off |
| 2 | This triggers the restart of the service, which also triggers an Event ID: 103 for all other users on the Server |
| 102, 105, 326 | for all remaining user accounts on the server |
Based on testing so far, this process does not hurt user experience, inclusive of existing Outlook sessions with existing search indexes, however, your mileage will vary, and this is at the end of the day, simply a workaround for a problem that needs to be fixed.
Summary
There are multiple streams of issues associated with native multi-user search currently, a running an interesting stream is located here on the Microsoft forums which pointed to the end resolution of a scheduled restart of the Search Service on the specific Event ID trigger, however, there have been multiple discussions around the World of EUC slack channel with people willing to test and share results – namely Kasper Johansen, Mike Streetz, Dennis Mohrmann
Windows Search является мощным инструментом, предоставляемым в операционной системе Windows Server 2019. Это инструмент поиска файлов и папок, который значительно облегчает работу с данными на сервере.
Основной функционал Windows Search включает в себя индексацию и поиск файлов, позволяя пользователям быстро находить нужные документы или папки. С его помощью можно настроить различные параметры индексации, такие как типы файлов, которые нужно исключить или включить в поиск, а также определить, какие папки будут индексироваться.
В Windows Server 2019 имеется множество возможностей для настройки Windows Search, чтобы удовлетворить потребности вашего предприятия. Вы можете оптимизировать индексацию для повышения производительности сервера, настроить поиск по содержимому файлов, чтобы найти нужную информацию в текстовых документах или почтовых сообщениях, а также использовать расширенные фильтры для точного и быстрого поиска.
Этот руководство предлагает подробное описание всех функций и настроек Windows Search в Windows Server 2019. В нем вы найдете полезные советы по оптимизации поиска, а также примеры использования различных функций для решения различных задач в вашей организации.
Не упустите возможность использовать полные возможности Windows Search в Windows Server 2019! Воспользуйтесь этим руководством, чтобы настроить его по своим потребностям и упростить поиск файлов и папок на вашем сервере.
Содержание
- Руководство по настройке и использованию Windows Search в Windows Server 2019
- Установка и настройка Windows Search
- Основные функции и возможности Windows Search
- Советы по использованию Windows Search
Руководство по настройке и использованию Windows Search в Windows Server 2019
Ниже приведены шаги по настройке и использованию Windows Search в Windows Server 2019:
- Установка Windows Search: Windows Search является стандартной функцией в Windows Server 2019 и обычно включается по умолчанию. Если Windows Search не работает, убедитесь, что функция установлена и включена.
- Индексация файлов: Чтобы Windows Search мог найти нужные файлы, необходимо проиндексировать данные на сервере. Это можно сделать с помощью специальной функции индексации, которая автоматически сканирует и создает индекс для всех файлов и папок на сервере.
- Настройка параметров поиска: Windows Search позволяет настраивать параметры поиска, такие как типы файлов, расположение и дополнительные фильтры. Настройте параметры поиска, чтобы они отвечали вашим потребностям и предпочтениям.
- Использование поиска: После настройки Windows Search можно начать использовать его для поиска файлов и приложений на сервере. Просто введите ключевые слова или фразы в поле поиска и Windows Search найдет соответствующие результаты в индексе.
- Управление индексацией: При использовании Windows Search можно управлять процессом индексации, добавлять или исключать определенные файлы и папки из поиска, а также изменять параметры индексации в соответствии с потребностями вашей организации.
Windows Search предлагает мощный инструмент для быстрого и удобного поиска файлов и приложений на сервере Windows Server 2019. Настройка и использование Windows Search может значительно упростить процесс поиска и повысить производительность работы. Следуйте этому руководству, чтобы получить максимальную отдачу от Windows Search на вашем сервере.
Установка и настройка Windows Search
Вот пошаговая инструкция, как установить и настроить Windows Search:
- Откройте «Центр управления сервером» и выберите «Установить роли и компоненты».
- Выберите «Роль» и установите галочку рядом с «Файловые и сторонние службы».
- Перейдите в «Подробности» и выберите «Поиск Windows».
- Нажмите «Дальше» и примите лицензионное соглашение.
- Нажмите «Далее» и подождите завершения установки.
- Перезагрузите сервер для завершения установки.
После установки Windows Search, необходимо настроить параметры поиска. Вот несколько полезных советов по настройке:
- Откройте «Панель управления» и выберите «Параметры индексации».
- Выберите папки и диски, которые вы хотите индексировать.
- Настройте параметры индексации, такие как тип файлов, включаемые и исключаемые папки, и т.д.
- Нажмите «ОК», чтобы сохранить настройки.
После завершения настройки, Windows Search будет начинать индексацию выбранных папок и дисков. Поиск файлов и папок станет более быстрым и удобным.
Важно отметить, что для работы Windows Search требуется достаточно мощный сервер с достаточным объемом памяти и процессора. Убедитесь, что ваш сервер соответствует минимальным системным требованиям для Windows Search.
Надеемся, эта статья помогла вам установить и настроить Windows Search на сервере Windows Server 2019. Пользуйтесь поиском эффективно!
Основные функции и возможности Windows Search
Одной из основных функций Windows Search является индексация файлов и папок. При активации этой функции операционная система автоматически сканирует все диски и создает индекс, который содержит информацию о наименованиях файлов, содержимом и других атрибутах. Благодаря индексации пользователи могут быстро находить нужные файлы и документы, используя поисковые запросы.
Windows Search также предоставляет возможность поиска по ключевым словам внутри файлов. Эта функция позволяет найти определенные фрагменты текста или информацию в документах, электронных таблицах, презентациях и других типах файлов. Пользователи могут указать ключевое слово или фразу в поле поиска, и Windows Search отобразит результаты, содержащие это ключевое слово.
Дополнительно, Windows Search предлагает расширенные параметры поиска, которые позволяют уточнить результаты. Пользователи могут фильтровать результаты по типу файла, дате создания или изменения, а также размеру файла. Это упрощает процесс поиска и позволяет найти нужную информацию с большей точностью.
Windows Search также интегрирован с функцией «Мгновенный поиск» операционной системы Windows Server 2019. Эта функция предварительно показывает результаты поиска по мере ввода пользователем поискового запроса. Пользователи могут увидеть предполагаемые результаты внизу окна поиска и мгновенно перейти к нужному файлу или приложению.
Кроме того, Windows Search поддерживает поиск по сетевым ресурсам, таким как файловые серверы. Пользователи могут использовать поисковые запросы, чтобы найти файлы на сетевых дисках и получить к ним быстрый доступ.
Общие функции и возможности Windows Search делают поиск файлов и приложений быстрым и удобным процессом для пользователей Windows Server 2019. Благодаря индексации, функции поиска внутри файлов и расширенным параметрам поиска, пользователи могут быстро находить нужные файлы и документы, сохраняя свое время и увеличивая производительность.
Советы по использованию Windows Search
1. Правильно настройте индексацию.
Перед использованием Windows Search важно убедиться, что файлы и папки, которые вы хотите индексировать, настроены для индексации. Для этого откройте панель управления и выберите «Параметры индексации». Затем выберите нужные папки или файлы и нажмите «Изменить».
2. Используйте правильные ключевые слова.
Для получения наиболее точных результатов поиска в Windows Search рекомендуется использовать ключевые слова, которые наиболее точно описывают то, что вы ищете. Например, если вы ищете файл с названием «отчет», уточните его дату или расширение, чтобы сузить результаты поиска.
3. Запустите поиск из проводника.
Наиболее удобным способом использования Windows Search является запуск поиска прямо из проводника. Просто откройте проводник, выберите нужную папку, введите ключевые слова в поле поиска и нажмите «Enter». Windows Search покажет вам все файлы, соответствующие вашим критериям.
4. Ограничьте область поиска.
Если у вас огромный объем данных и поиск занимает слишком много времени, вы можете ограничить область поиска для более быстрого результата. Например, вы можете искать только в определенных папках или типах файлов, чтобы уменьшить объем индексации.
5. Используйте синтаксис расширенного поиска.
Windows Search поддерживает множество операторов и синтаксисов для более точного поиска. Например, вы можете использовать операторы AND, OR и NOT для комбинирования условий поиска. Также вы можете использовать кавычки для поиска точных фраз и использовать знаки >, < для поиска по размеру файлов.
Следуя этим простым советам, вы сможете использовать Windows Search более эффективно и быстро находить нужные вам файлы и папки.
Hi,
So nothing like being on the cutting edge……
I have been testing Server 2019 RDS and so-far-so-good apart from an issue with the Windows Search Service.
It appears that in Server 2019 each user gets their own search database EDB file in their profile path (appdata\roaming). e.g.
C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-3901271148-1553943383-1671037523-1629\S-1-5-21-3901271148-1553943383-1671037523-1629.edb
When they log on and log off; this is connected to the search service and the following event log is generated
Source:ESENT
EventID: 326
SearchIndexer (10896,D,50) S-1-5-21-3901271148-1553943383-1671037523-1629: The database engine attached a database (3, C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-3901271148-1553943383-1671037523-1629\S-1-5-21-3901271148-1553943383-1671037523-1629.edb).
(Time=0 seconds)
Unfortunately it appears that this process is not very stable and on some logons the database in the users profile does not attach and the following error is generated
Source:Search
EventID: 3057
The plug-in manager <Search.TripoliIndexer> cannot be initialized.
Context: S-1-5-21-3901271148-1553943383-1671037523-1629 Application
Source:Search
EventID: 3028
The gatherer object cannot be initialized.
Context: S-1-5-21-3901271148-1553943383-1671037523-1629 Application, SystemIndex Catalog
Details: The specified object cannot be found. Specify the name of an existing object. (HRESULT : 0x80040d06) (0x80040d06)
And a few more similar but related errors….
No subsequent logon/off will succeed in attaching the database until the Windows Search service is restarted
I am not testing with User Profile Disks or Roaming Profiles
There is no AV on the server
Any ideas?
Andy
Andrew
-
Edited by
Thursday, December 6, 2018 10:18 AM
As always in our industry, small changes in one platform can result in significant impact across what is “standard practice” in many other areas. This week’s lucky contender is Windows Search.
Windows Search in both Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 Multi-Session has changed how it operates, introducing the concept of per-user search natively into the Search Service. This is fundamentally different from previous versions (namely Windows Server 2016 etc) and changes how we need to think about search roaming with supporting technologies such as FSLogix Containers and Citrix UPM.
The biggest change is that the Windows Search index is now stored per user in the user profile, specifically C:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{UserSID}\{UserSID}.edb. On each login, the Windows Search process creates a new instance of the search database for the user based on the existing EDB. If no EDB file exists, a new one is created by the Operating System.

There are two components associated with the Search functionality split into individual processes:
- SearchIndexer.exe: This process runs under the “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM” account and accesses the index database for each user (profile based)
- SearchProtocolHost.exe: an instance of this process runs per user and is a child process of SearchIndexer.exe. This process handles amongst other things, the indexing of the Outlook OST file, not the searching of the index file, but the actual index creation of it making content available to search. Searching should be operational with or without this process running. When new items need to be indexed, the process will run, once finished, it will stop
The impacts here, should you have dealt with FSLogix or Citrix UPM Search roaming should start to become obvious when you think about how these solutions tackle the Search side of things (they rip out a component of the index and store them within a container). The long and short of it is as follows:
- For FSLogix environments, you must NOT enable search roaming within the FSLogix GPO. Specifically, you want SearchRoam set to 0 in the registry. This needs to be reversed in your master image should you have enabled it previously, in fact, given the what we know of Search challenges and the attempted hooks into it, I would be tempted to suggest that should you have enabled search roaming in either Windows Server 2019 or Windows 10 multi-session previously, then revert the setting, reinstall Microsoft Office and make sure that the event logs are clear from a Windows Search perspective
- For Citrix UPM environments, the following article has been released which is quite confusing. TLDR, the key it’s discussing should not be set to anything other than 0, and ideally shouldn’t exist as a whole in Windows Server 2019. Citrix UPM configurations will need to cater for the new location of the Search Index, however, the OST container can stay in place and do its thing. I haven’t had time to test, but I would assume that the new search location in the user profile is an ideal candidate for the UPM container feature
Unfortunately, Windows Search is an ongoing challenge and there is a fair number of customers who are experiencing issues with the native multi-user search capability in both Windows 10 Multi-Session and Windows Server 2019. Some are experiencing repeated crashing of the service others are finding that search index files are not released on logoff resulting in locked files and corrupt indexes.
In the below walkthrough, I will try and outline what happens with Windows Search in Server 2019, and where things fall apart, along with a temporary resolution which may help until the problems are properly addressed by Microsoft.
First of all, an outline of the environment I am using to demonstrate the situation
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, latest rollup at the time of writing
- FSLogix release 2.9.7237.48865
- Profile and Office Container configured
- Microsoft Office 365 ProPlus, x64, Semi-Annual channel
- No PVS or MCS provisioning
Secondly, below is an outline of some of the event log entries we will be referring to:
| ID | Detail |
| 5 | Windows Search Service has created default configuration for new user ‘KINDO\JKindon5’ |
| 102 | SearchIndexer (4400,P,98) { S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine (10.00.17763.0000) is starting a new instance (3). |
| 105 | SearchIndexer (4400,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine started a new instance (3). (Time=0 seconds) |
| 637 | SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: New flush map file “C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.jfm” will be created to enable persisted lost flush detection. |
| 325 | SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) { S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine created a new database (6, C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.edb). (Time=0 seconds) |
| 103 | SearchIndexer (6672,T,97) { S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine stopped the instance (3). |
| 2 | Unable to remove Windows Search Service indexed data for user ‘KINDO\JKindon5’ in response to user profile deletion. Error code 0x80004002. |
| 482 | SearchIndexer (3768,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: An attempt to write to the file “C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.jfm” at offset 0 (0x0000000000000000) for 8192 (0x00002000) bytes failed after 0.000 seconds with system error 21 (0x00000015): “The device is not ready. “. The write operation will fail with error -1022 (0xfffffc02). If this error persists then the file may be damaged and may need to be restored from a previous backup. |
| 492 | SearchIndexer (9200,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The logfile sequence in “C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\” has been halted due to a fatal error. No further updates are possible for the databases that use this logfile sequence. Please correct the problem and restart or restore from backup. |
| 439 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: Unable to write a shadowed header for file C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.edb. Error -1022. |
| 104 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine stopped the instance (2) with error (-1022). |
| 103 | SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) Windows: The database engine stopped the instance (0). |
| 300 | SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine is initiating recovery steps. |
| 301 | SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has finished replaying logfile C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\edb.jtx. |
| 302 | SearchIndexer (10076,U,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has successfully completed recovery steps. |
| 326 | SearchIndexer (9808,D,50) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1104: The database engine attached a database (2, C:\Users\JKindon\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1104\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1104.edb). (Time=0 seconds) |
My findings here are an aggregation of existing posts, as well as feedback from colleagues in the World of EUC slack channel. Testing has been validated in my own environments.
First Logon for the user
On the first logon for a new user, the following event logs entries will occur, basically detecting a new user without an index, creating a new database, configuring and leveraging the new instance as below:
Event ID 5: Windows Search Service has created the default configuration for new user “Kindo\JKindon5”
Event ID 102: SearchIndexer (4400,P,98) { S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine (10.00.17763.0000) is starting a new instance (3)
Event ID 105: SearchIndexer (4400,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine started a new instance (3). (Time=0 seconds)
Event ID 637: SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: New flush map file “C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.jfm” will be created to enable persisted lost flush detection
Event ID 325: SearchIndexer (4400,D,35) { S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine created a new database (6, C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}\{ S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}.edb). (Time=0 seconds)
In summary, in a healthy operational state, for a new user, the following event log patterns will occur on logon:
- 5 = Search Creates a default configuration
- 102 = Search Indexer creates a new instance for the user
- 105 = Search Indexer starts the new instance for the user
- 637 = New flush map file created for the user
- 325 = Search Indexer creates the new database
User Logoff
When the user logs off for the first time, the following event entry is logged:
Event ID 103: Event 103: SearchIndexer (6672,T,97) { S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134}: The database engine stopped the instance (3)
And this is where things go pear-shaped, you will most probably find the 103 entry is quickly followed by this one:
Event ID 2: Unable to remove Windows Search Service indexed data for user ‘KINDO\JKindon5’ in response to user profile deletion. Error code 0x80004002
In this state, when the user next connects, they are going to be hit with a problem. What we are looking for, is a happy combination of the following events when the user logs on for the second time:
- 102 = Search Indexer creates a new instance for the user
- 105 = Search Indexer starts the new instance for the user
- 326 = Search Indexer attaches an existing database
What we end up with though due to the above event ID 2 on Logoff, is the following:
Event ID 482: SearchIndexer (3768,D,0) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: An attempt to write to the file “C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.jfm” at offset 0 (0x0000000000000000) for 8192 (0x00002000) bytes failed after 0.000 seconds with system error 21 (0x00000015): “The device is not ready. “. The write operation will fail with error -1022 (0xfffffc02). If this error persists then the file may be damaged and may need to be restored from a previous backup.
The root cause of this is due to the following handles still being kept open by the SearchIndexer.exe process
These files are held open; however, the physical files have gone (detached) and thus we loop.
If the user was to log back on at this point, we will experience some problematic symptoms and events:
Outlook indexing will present as below:

And no files in the %AppData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{UserSID} directories will be touched
Restarting the search service
If we restart the Windows Search Service, a few things happen:
All existing handles are closed for SearchIndexer operations, both for any logged off users in a fail state, and for any other user on the Server, and the following event logs are written
- Event ID 439: SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: Unable to write a shadowed header for file C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134.edb. Error -1022.
- Event ID 104: SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine stopped the instance (2) with error (-1022).
- Event ID 103: SearchIndexer (3768,T,97) Windows: The database engine stopped the instance (0).
- Event ID: 102, 105, 326: (happy combination representing success)
- Event ID 300: SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine is initiating recovery steps.
- Event ID 301: SearchIndexer (10076,R,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has finished replaying logfile C:\Users\JKindon5\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134\edb.jtx.
- Event ID 302: SearchIndexer (10076,U,98) S-1-5-21-2397015974-2202110191-2245630456-1134: The database engine has successfully completed recovery steps
- Event ID: 105, 326 (Search index is OK again)
Outlook indexing is now OK

Along with successful alterations to the %AppData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\{UserSID} directories.
Fixed it would seem. So, logically here, we know that the resolution is to restart the Windows Search Service based on the failure Event, which is represented by Event ID 2. Specifically:
- Event Log: Application
- Event Level: Error
- Event Source: Search-ProfileNotify
- Event ID: 2
- Event Data: Unable to remove Windows Search Service indexed data for user ‘KINDO\JKindon5’ in response to user profile deletion. Error code 0x80004002
By implementing a scheduled task with the above Event ID as the trigger, and a simple configuration of PowerShell to restart the search service as the action:



We can successfully clear the errors on log-off, release the files, and ensure that when the user logs back in, their index is good to go. The process will now look like the below when a user logs off:
- Event ID: 103 for the user logging off
- Event ID: 2 -> This triggers the restart of the service, which also triggers an Event ID: 103 for all other users on the Server
- Event ID: 102, 105, 326 for all remaining user accounts on the server
Based on testing so far, this process does not hurt user experience, inclusive of existing Outlook sessions with existing search indexes, however, your mileage will vary, and this is at the end of the day, simply a workaround for a problem that needs to be fixed.
Summary
There are multiple streams of issues associated with native multi-user search currently, a running an interesting stream is located here on the Microsoft forums which pointed to the end resolution of a scheduled restart of the Search Service on the specific Event ID trigger, however, there have been multiple discussions around the World of EUC slack channel with people willing to test and share results – namely Kasper Johansen, Mike Streetz, Dennis Mohrmann
Enable the Windows Search Service if you Want to Use the …
Click Add Roles in the Roles Summary pane. On the Server Roles page, select the File Services role, and then click Next. On the Role Services page, select the Windows Search Service role service, and then click Next. On the Confirmation page, verify that Windows Search Service is listed, and then click Install.
How do I Reinstall Windows Search Service?
1. Type Start PowerShell in the Command Prompt window to start Windows PowerShell. 2. Type InstallWindowsFeature SearchService and press Enter to install the Windows Search Service.
How do I Enable Windows Search Server 2019?
Start Server Manager .
Click Manage, and then click Add Roles and Features.
On the “Before you Begin” page, click Next.
Select Rolebased or Featurebased Installation, and then click Next.
On the Features page, select Windows Search Service, and then click Next.
How do I Enable Windows Search Server 2016?
Enter services. msc into the field and then press Enter.
Rightclick Windows Search , and then click Properties.
Change the «Startup type» to Automatic Delayed Start.
Click Apply, and then click Start.
Click OK, and then close the Services console.
Where is the Search Option in Windows Server 2012?
Using Search in Windows Server 2012
If you cant find something in Windows Server 2012, search is the first place to head. The easiest way to access search is to press the Windows key and swap the desktop for the Start screen. You can then type the term you want to search for. The results will be displayed by category.
How do I Install Windows Search Service in Outlook?
In Outlook click on File and then then click on Options.
In the Outlook Options window click on Search and then under Sources click on the tab Indexing Options .
In the Indexing Options window click on Advance.
Under Index Settings click on Rebuild.
How do I Turn on Windows Search Service?
a. Click on start, go to control panel .
b. Open administrative tools, right click on services and click on run as administrator.
c. Scroll down for Windows search service, check if it is started.
d. If no, then right click on the service and click on start.