Время на прочтение
3 мин
Количество просмотров 147K
Недавно Microsoft презентовала более подробную информацию о Windows Server 2016. Уже есть некоторые технические сведения о Hyper-V, Containers, Nano Server и многом другом. Но только сейчас появилась информация о лицензировании Windows Server 2016.
Небольшая оговорка: вся информация в статье взята с документации, выпущенной Microsoft в декабре 2015. В будущем она может меняться. Эта статья служит лишь для обзорного ознакомления с изменениями лицензирования. Если вы хотите убедиться в правильности приобретаемой лицензии, то необходимо связаться с Microsoft или партнером Microsoft.
Microsoft выпустит две версии Windows Server 2016 — Datacenter и Standard, как это было и с Windows Server 2012 и Windows Server 2012 R2. Будет два больших изменения в лицензировании Windows Server 2016:
Первое, Microsoft перейдет от по-процессорного лицензирования на по-ядерное лицензирование в Windows Server 2016 Datacenter и Standard Editions.
И второе большое изменение в том, что не будет функционального равенства между Standard Edition и Datacenter Edition. В Windows Server 2012 R2 в основном были те же самые функции в обоих изданиях и единственная разница была в правах использования виртуальных машин. За исключением автоматической активации виртуальных машин в редакции Datacenter.
Некоторые интересные факты из документации выпущенной Microsoft:
Windows Server 2016 редакции:
- Datacenter Edition предназначается для высоко виртуализированной частной и гибридной облачной среды.
- Standard Edition для невиртуализованной или частично виртуализированной среды.
- Информация о других изданиях Windows Server 2016 и Windows Storage Server 2016 будет представлена в 1 квартале 2016 года.
Примерные цены на редакции Windows Server 2016 выглядят следующим образом:
Что означает изменение модели лицензирования на основе ядер:
Чтобы лицензировать физичесеий сервер, необходимо лицензировать все физические ядра. Минимум 8 лицензий требуется для каждого физического процессора на сервере, и минимум 16 ядер должны быть лицензированы для серверов с одним процессором:
- Цена 16-ядерной лицензий Windows Server 2016 Datacenter и Standard Edition будет такая же как на лицензию 2 процессоров соответствующих изданий Windows Server 2012 R2.
- Standard Edition дает право на установку 2 операционных сред или Hyper-V контейнерев, когда все физические ядра в сервере лицензированы. Несколько лицензий могут быть установлены на некоторые ядра для дополнительных операционных сред или Hyper-V контейнеров.
- Каждому пользователю и / или устройству, требующему доступ к лицензированной Windows Server Standard или Datacenter Edition, требуется Windows Server CAL. Каждый Windows Server CAL позволяет получить доступ к нескольким лицензиям Windows Servers.
- Windows Server CAL дает пользователям или устройствам право на доступ к любой редакции Windows Server той же или более ранней версии.
- Для лицензирования дополнительных или расширенных функций, таких как службы Remote Desktop Services или Active Directory Rights Management Services потребуется, как и ранее, покупка дополнительных лицензий клиентского доступа.
Как лицензировать физические ядра для Windows Server 2016 Standard и Datacenter Editions
- Лицензии для всех физических ядер сервера.
- Минимум 8 лицензий для ядер каждого процессора.
- Минимум 16 лицензий для ядер каждого сервера.
- Лицензии на ядро будут продаваться в паками. По две лицензии в паке.
- Покупка 8 паков будет минимальным требованием для лицензирования каждого физического сервера.
- Стоимость 2х лицензий(паков) для каждого издания составит 1/8-й цены лицензии двух процессоров соответствующих 2012 R2 изданий.
Более детально с лицензированием Windows Server 2016 можно ознакомится на www.microsoft.com/en-us/server-cloud/products/windows-server-2016
C уважением коллектив компании Servilon
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows Server 2016 with Desktop Experience |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Written in |
|
| OS family | Windows Server |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
September 26, 2016; 6 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
October 12, 2016; 6 years ago[2] |
| Latest release | 1607 (10.0.14393.6252) (September 12, 2023; 13 days ago[3]) [±] |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) Windows PowerShell (Command line) |
| License | Trialware, Volume licensing, Microsoft Software Assurance, MSDN subscription, Microsoft Imagine |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2012 R2 (2013) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2019 (2018) / Windows Server, version 1709 (2017) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2016 (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
|
Windows Server 2016 is the eighth release of the Windows Server operating system developed by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was developed alongside Windows 10 and is the successor to the Windows 8.1-based Windows Server 2012 R2. The first early preview version (Technical Preview) became available on October 1, 2014 together with the first technical preview of System Center.[5] Windows Server 2016 was released on September 26, 2016 at Microsoft’s Ignite conference[1] and broadly released for retail sale on October 12, 2016.[2] It was succeeded by Windows Server 2019 and the Windows Server Semi-Annual Channel.
Features[edit]
Windows Server 2016 has a variety of new features, including
- Active Directory Federation Services: It is possible to configure AD FS to authenticate users stored in non-AD directories, such as X.500 compliant Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories and SQL databases.[6]
- Windows Defender: Windows Server Antimalware is installed and enabled by default without the GUI, which is an installable Windows feature.[7]
- Remote Desktop Services: Support for OpenGL 4.4 and OpenCL 1.1, performance and stability improvements; MultiPoint Services role (see Windows MultiPoint Server)[8]
- Storage Services: Central Storage QoS Policies; Storage Replicas (storage-agnostic, block-level, volume-based, synchronous and asynchronous replication using SMB3 between servers for disaster recovery).[9] Storage Replica replicates blocks instead of files; files can be in use. It’s not multi-master, not one-to-many and not transitive. It periodically replicates snapshots, and the replication direction can be changed.
- Failover Clustering: Cluster operating system rolling upgrade, Storage Replicas[10]
- Web Application Proxy: Preauthentication for HTTP Basic application publishing, wildcard domain publishing of applications, HTTP to HTTPS redirection, Propagation of client IP address to backend applications[11]
- IIS 10: Support for HTTP/2
- Windows PowerShell 5.1[12]
- Windows Server Containers [13]
Networking features[edit]
- DHCP: As Network Access Protection was deprecated in Windows Server 2012 R2, in Windows Server 2016 the DHCP role no longer supports NAP[14]
- DNS:
- DNS client: Service binding – enhanced support for computers with more than one network interface[15]
- DNS Server: DNS policies, new DDS record types (TLSA, SPF, and unknown records), new PowerShell cmdlets and parameters[16]
- Windows Server Gateway now supports Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnels[17]
- IP address management (IPAM): Support for /31, /32, and /128 subnets; discovery of file-based, domain-joined DNS servers; new DNS functions; better integration of DNS, DHCP, and IP Address (DDI) Management[18]
- Network Controller: A new server role to configure, manage, monitor, and troubleshoot virtual and physical network devices and services in the datacentre[19]
- Hyper-V Network virtualization: Programmable Hyper-V switch (a new building block of Microsoft’s software-defined networking solution); VXLAN encapsulation support; Microsoft Software Load Balancer interoperability; better IEEE Ethernet standard compliance.[20]
Hyper-V[edit]
- Rolling Hyper-V cluster update: Unlike upgrading clusters from Windows 2008 R2 to 2012 level, Windows Server 2016 cluster nodes can be added to a Hyper-V Cluster with nodes running Windows Server 2012 R2. The cluster continues to function at a Windows Server 2012 R2 feature level until all of the nodes in the cluster have been upgraded and the cluster functional level has been upgraded.[21]
- Storage quality of service (QoS) to centrally monitor end-to-end storage performance and create policies using Hyper-V and Scale-Out File Servers
- New, more efficient binary virtual machine configuration format (.VMCX extension for virtual machine configuration data and the .VMRS extension for runtime state data)
- Production checkpoints
- Hyper-V Manager: Alternate credentials support, down-level management, WS-Management protocol
- Integration services for Windows guests distributed through Windows Update
- Hot add and remove for network adapters (for generation 2 virtual machines) and memory (for generation 1 and generation 2 virtual machines)
- Linux secure boot
- Connected Standby compatibility
- Storage Resiliency feature of Hyper-V is formed for detecting transitory loss of connectivity to VM storage. VMs will be paused until connectivity is re-established.[22]
- RDMA compatible Virtual Switch[23]
Nano Server[edit]
Microsoft announced a new installation option, Nano Server, which offers a minimal-footprint headless version of Windows Server. It excludes the graphical user interface, WoW64 (support for 32-bit software) and Windows Installer. It does not support console login, either locally or via Remote Desktop Connection. All management is performed remotely via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), Windows PowerShell and Remote Server Management Tools (a collection of web-based GUI and command line tools).[24] However, in Technical Preview 5, Microsoft has re-added the ability to administer Nano Server locally through PowerShell.
According to Microsoft engineer Jeffrey Snover, Nano Server has 93% lower VHD size, 92% fewer critical security advisories, and 80% fewer reboots than Windows Server.[25][26]
Nano Server is only available to Microsoft Software Assurance customers[2] and on cloud computing platforms such as Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services.
Starting with the new feature release of Windows Server version 1709, Nano Server can only be installed inside a container host.[27]
Development[edit]
Microsoft has been reorganized by Satya Nadella, putting the Server and System Center teams together. Previously, the Server team was more closely aligned with the Windows client team. The Azure team is also working closely with the Server team.[28]
In March 2017, Microsoft demonstrated an internal version of Server 2016 running on the ARMv8-A architecture. It was reported that Microsoft was working with Qualcomm Centriq and Cavium ThunderX2 chips. According to James Vincent of The Verge, this decision endangers Intel’s dominance of the server CPU market.[29][30][31] However, later inquiry from Microsoft revealed that this version of Windows Server is only for internal use and only impacts subscribers of Microsoft Azure service.[32]
Preview releases[edit]
A public beta version of Windows Server 2016 (then still called vNext) branded as «Windows Server Technical Preview» was released on October 1, 2014; the technical preview builds are aimed toward enterprise users. The first Technical Preview was first set to expire on April 15, 2015 but[33] Microsoft later released a tool to extend the expiry date, to last until the second tech preview of the OS in May 2015.[34] The second beta version, «Technical Preview 2», was released on May 4, 2015. Third preview version, «Technical Preview 3» was released on August 19, 2015. «Technical Preview 4» was released on November 19, 2015. «Technical Preview 5» was released on April 27, 2016.
Windows Server 2016 Insider Preview Build 16237 was released to Windows Insiders on July 13, 2017.[35][36]
Public release[edit]
Windows Server 2016 was officially released at Microsoft’s Ignite Conference on September 26, 2016. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2016 is licensed by the number of CPU cores rather than number of CPU sockets—a change that has similarly been adopted by BizTalk Server 2013 and SQL Server 2014.[37] The new licensing structure that has been adopted by Windows Server 2016 has also moved away from the Windows Server 2012/2012R2 CPU socket licensing model in that now the amount of cores covered under one license is limited. Windows Server 2016 Standard and Datacenter core licensing now covers a minimum of 8 core licenses for each physical processor and a minimum of 16 core licenses for each server. Core licenses are sold in packs of two with Standard Edition providing the familiar rights to run 2 virtualized OS environments. If the server goes over 16 core licenses for a 2 processor server additional licenses will now be required with Windows Server 2016.[38]
Version history[edit]
Technical Preview[edit]
Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview, released on October 1, 2014, was the first beta version of the operating system made publicly available. Its version number was 6.4.9841.[5]
Technical Preview 2[edit]
Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2 was made available on May 4, 2015. Its version number was 10.0.10074. (A similar jump in the most significant part of the version number from 6 to 10 is seen in Windows 10.) Highlights of this version include:[39]
- Nano Server installation option[40][41]
- Hyper-V: hot add and remove memory and NIC; resilient virtual machines to keep running even when their cluster fabric fails[42]
- Rolling upgrades for Hyper-V and Storage clusters[40][42]
- Networking: Converged NIC across tenant and RDMA traffic; PacketDirect on 40G[42]
- Storage: Virtual Machine Storage Path resiliency; Storage Spaces Direct to aggregate Storage Spaces across multiple servers; Storage Replica[42]
- Security: Host Guardian Service, helping to keep trust and isolation boundary between the cloud infrastructure and guest OS layers; Just Enough Administration, restricting users to perform only specific tasks[42]
- Management: PowerShell Desired State Configuration; PowerShell Package Manager; Windows Management Framework 5.0 April Preview and DSC Resource Kit[42]
- Other: Conditional access control in AD FS; application authentication support for OpenID Connect and OAuth; full OpenGL support with RDS for VDI; Server-side support for HTTP/2, including header compression, connection multiplexing and server push[42]
- Installation options: Minimal Server Interface was made default and renamed the Server installation option to “Server with local admin tools”.[43]
Technical Preview 3[edit]
The third technical preview of Windows Server 2016 was made available on August 19, 2015. Its version number was 10.0.10514. Highlights of this version include:
- Windows Server Containers[44]
- Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS): authentication of users stored in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories[44]
- Installation options: The Server installation option had been renamed to “Server with Desktop Experience” having the shell and Desktop Experience installed by default. Due to the structural changes required to deliver the Desktop Experience on Server, it is no longer possible to convert from Server with Desktop Experience to Server Core or to convert Server Core up to Server with Desktop Experience.[43]
Technical Preview 4[edit]
The fourth technical preview of the operating system was made available on November 19, 2015, one year and one month after the initial technical preview. Its version number was 10.0.10586, based on Windows 10 version 1511. Its highlights include:
- Nano Server supports the DNS Server and IIS server roles, as well as MPIO, VMM, SCOM, DSC push mode, DCB, Windows Server Installer, and the WMI provider for Windows Update. Its Recovery Console supports editing and repairing the network configuration. A Windows PowerShell module is now available to simplify building Nano Server images.[45]
- Hyper-V Containers encapsulates each container in a light weight virtual machine.[45]
Technical Preview 5[edit]
The last technical preview of Windows Server 2016 was made available on April 27, 2016. Its version number was 10.0.14300. Its highlights include:[46]
- Mostly general refinements. Greater time accuracy in both physical and virtual machines
- Container support adds performance improvements, simplified network management, and support for Windows containers on Windows 10
- Nano Server: an updated module for building Nano Server images, including more separation of physical host and guest virtual machine functionality as well as support for different Windows Server editions. Improvements to the Recovery Console, including separation of inbound and outbound firewall rules as well as the ability to repair configuration of WinRM
- Networking: traffic to new or existing virtual appliances can now be both mirrored and routed. With a distributed firewall and Network security groups, this enables dynamically segmented and secure workloads in a manner similar to Azure. One can deploy and manage the entire Software-defined networking (SDN) stack using System Center Virtual Machine Manager. Docker can be used to manage Windows Server container networking, and associate SDN policies not only with virtual machines but containers as well
- Remote Desktop Services: a highly available RDS deployment can leverage Azure SQL Database for the RD Connection Brokers in high availability mode
- Management: ability to run PowerShell.exe locally on Nano Server (no longer remote only), new Local Users & Groups cmdlets to replace the GUI, added PowerShell debugging support, and added support in Nano Server for security logging & transcription and JEA (Just Enough Administration)
- Shielded Virtual Machines:
- New «Encryption Supported» mode that offers more protections than for an ordinary virtual machine, but less than «Shielded» mode, while still supporting vTPM, disk encryption, Live Migration traffic encryption, and other features, including direct fabric administration conveniences such as virtual machine console connections and Powershell Direct
- Full support for converting existing non-shielded Generation 2 virtual machines to shielded virtual machines, including automated disk encryption
- Shielded virtual machines are compatible with Hyper-V Replica
Release to manufacturing[edit]
Windows Server 2016 was released to manufacturing on September 26, 2016, bearing the version number of 10.0.14393 (same as Windows 10 Anniversary Update). Microsoft added the following final touches:
- Available for a 180-day evaluation
- Fixed Start menu corruptions
- Improved user experience and performance
- Windows Store apps have been removed
- Login screen now has a background
- The Windows Hello feature has been added
- Dark theme has been added
Semi-Annual Channel releases[edit]
Version 1709[edit]
Windows Server, version 1709 (version shared with Windows 10 Fall Creators Update) was released on October 17, 2017. The release has dropped the Windows Server 2016 name and is just called Windows Server by Microsoft.[47] It is offered to the Microsoft Software Assurance customers who have an active Windows Server 2016 license and has the same system requirements. This is the first Windows Server product to fall under the «Semi-Annual Channel» (SAC) release cadence.[48] This product only features the Server Core and the Nano Server modes. Of the two, only the Server Core mode of the OS can be installed on a bare system. The Nano Server mode is only available as an operating system container.[49]
Version 1803[edit]
Windows Server, version 1803 (version shared with Windows 10 April 2018 Update) is the second Semi-Annual Channel release of Windows Server.[50] It is also the final version to be branched off the Server 2016 codebase, as the next release shares the version number 1809 with Windows Server 2019.[51]
See also[edit]
- Microsoft Servers
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- History of Microsoft Windows
- Comparison of operating systems
- List of operating systems
References[edit]
- ^ a b Chapple, Erin (September 26, 2016). «Announcing the launch of Windows Server 2016». Hybrid Cloud. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 21, 2017. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ a b c Foley, Mary Jo (October 12, 2016). «Microsoft’s Windows Server 2016 hits general availability». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «September 12, 2023—KB5030213 (OS Build 14393.6252)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 2, 2019. Retrieved December 7, 2016.
- ^ a b «Announcing availability of Windows Server Technical Preview and System Center Technical Preview». Hybrid Cloud. Microsoft. March 17, 2015. Archived from the original on August 2, 2017. Retrieved April 1, 2015.
- ^ Mathers, Bill; Poggemeyer, Liza; Tobin, John (September 8, 2017). «What’s new in Active Directory Federation Services for Windows Server 2016». Microsoft Docs. Windows Server, Identity and access. Archived from the original on February 28, 2018. Retrieved January 22, 2018.
- ^ «TechNet: Windows Server Antimalware Overview for Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 19 February 2015)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Remote Desktop Services in the Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Storage Services in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Failover Clustering in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Web Application Proxy in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ O’Shea, Mark (September 4, 2016). «What’s New In Windows Server 2016 Standard Edition Part 9 – Management And Automation». Microsoft Australia OEM Team blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 17, 2016. Retrieved September 9, 2016.
- ^ «About Windows Containers». Archived from the original on November 4, 2016. Retrieved November 1, 2016.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in DHCP in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in DNS Client in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in DNS Server in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: GRE Tunneling in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in IPAM in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 6 February 2015)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: Network Controller (Updated: 18 December 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Hyper-V Network Virtualization in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 11 March 2015)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Hyper-V in Technical Preview (Updated: 12 November 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet Wiki: Hyper-V Features in Windows Server 2016». Archived from the original on March 12, 2016. Retrieved March 12, 2016.
- ^ «Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Switch Embedded Teaming (SET)». Microsoft. May 17, 2016. Archived from the original on August 10, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2016.
- ^ Jindal, Kriti (February 9, 2016). «Introducing Server management tools». Nano Server Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ Neil, Mike (April 8, 2015). «Microsoft Announces New Container Technologies for the Next Generation Cloud». Server & Cloud Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 27, 2016. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ Snover, Jeffrey; Mason, Andrew; Back, Alan (April 8, 2015). «Microsoft Announces Nano Server for Modern Apps and Cloud». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 19, 2016. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- ^ «Changes to Nano Server in the next release of Windows Server». Archived from the original on January 27, 2018. Retrieved June 18, 2017.
- ^ Patrizio, Andy (February 10, 2015). «Microsoft to release next generation of Windows Server in 2016». Network World. IDG. Archived from the original on March 21, 2015. Retrieved April 10, 2015.
- ^ Vincent, James (March 9, 2017). «Microsoft unveils new ARM server designs, threatening Intel’s dominance». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 8, 2017). «Windows Server on ARM: It’s happening». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on March 10, 2017. Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 8, 2017). «Microsoft’s latest open source servers shown off with Intel, AMD, and even ARM chips». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on March 10, 2017. Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 10, 2017). «Microsoft’s Windows Server on ARM move: More questions and answers». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on March 11, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ «Windows IT Pro: Windows Server Technical Preview expires 15 April 2015». Archived from the original on April 10, 2015. Retrieved April 5, 2015.
- ^ «Neowin: Second tech preview of Windows Server 2016 coming next month». Archived from the original on April 5, 2015. Retrieved April 5, 2015.
- ^ «RedmondMag: Windows Server ‘Insider’ Testing Program Coming This Summer». Archived from the original on August 5, 2017. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- ^ «Announcing Windows Server Insider Preview Build 16237». Windows Blog. Microsoft. July 13, 2017. Archived from the original on December 3, 2017. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (December 4, 2015). «Windows Server 2016 moving to per core, not per socket, licensing». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on December 4, 2015. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft (2017). «Windows Server 2016 Licensing Datasheet — Microsoft» (PDF). Microsoft. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 26, 2017. Retrieved October 8, 2017.
- ^ Berkouwer, Sander (May 5, 2015). «Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2 now available». The things that are better left unspoken. Archived from the original on April 6, 2016. Retrieved March 26, 2016.
- ^ a b «The Register: Try to contain your joy: Microsoft emits Windows Server 2016 with nano-services». The Register. Archived from the original on September 11, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- ^ «WinBeta: Microsoft shows off what’s new in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2». Archived from the original on May 5, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g «Windows Server Blog: What’s new in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2». Archived from the original on May 7, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ a b «Windows Server Blog: Windows Server 2016 Installation Option Changes». August 27, 2015. Archived from the original on November 11, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ a b «TechNet: What’s New in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 3». Archived from the original on September 6, 2015. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- ^ a b Anderson, Kareem (November 19, 2015). «Microsoft has released Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 4». WinBeta. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved November 20, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 5». Archived from the original on June 3, 2016. Retrieved April 27, 2016.
- ^ «Windows Server, version 1709 available for download». October 17, 2017. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- ^ Jawad, Usama (September 25, 2017). «Microsoft launches Windows Server version 1709». Neowin. Archived from the original on March 13, 2018. Retrieved March 12, 2018.
- ^ «Introducing Windows Server, version 1709». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Windows Server. Archived from the original on January 21, 2018. Retrieved January 21, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Server servicing channels». Archived from the original on November 15, 2018. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019 update history». Archived from the original on December 18, 2019. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
External links[edit]
- PluralSight: Windows Server vNext First Look – An introduction to the new features of the Windows Server vNext operating system
- Our Server Journey – video session describing the path that Windows Server has taken from its creation to the current day and where it is going from here Archived April 9, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- Michael Pietroforte: Nano Server – Goodbye Windows Server?
- Microsoft Windows Nano Server, the future of Windows Server?
С выходом 2016 версии серверных продуктов Microsoft произошли существенные изменения в лицензировании.
Напомним, что семейство проприетарных операционных систем Microsoft Windows Server, начиная с первой версии NT, лицензируется по модели Server + CAL (серверная лицензия + лицензия на подключение). С появлением виртуализации и кластеризации расчет нужного количества лицензий потребовал особого внимания к будущему назначению этих лицензий на сервера и кластеры. Повышение производительности серверов также отразилось на лицензировании. Если в Windows Server 2008 одна лицензия покрывала 4 процессора, то с увеличением мощности серверного оборудования одна лицензия Windows Server 2012 покрывала уже 2 процессора.

Итак, Windows Server 2016 выпускается в следующих редакциях:
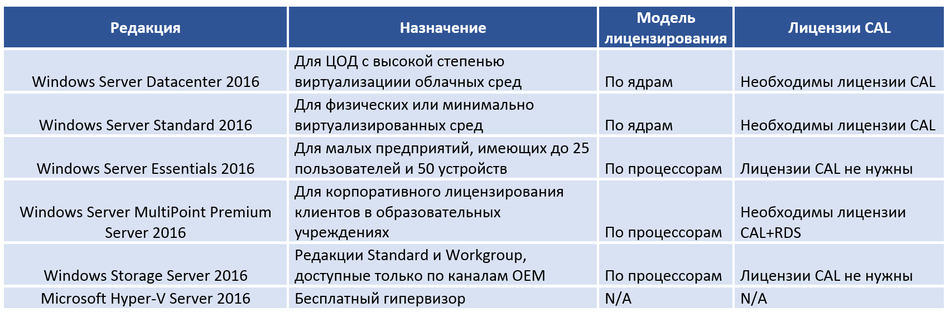
Мы будем рассматривать редакции Standard и Datacenter, которые наиболее часто используются в компаниях средних и крупных размеров.
Лицензирование рассматриваемых редакций в 2016 версии аналогично продукту SQL Server Enterprise, который, с версии 2012, лицензируется на основе количества ядер. Отличие заключается в том, что, согласно Product Terms, лицензии на подключение (CAL) входят в серверную лицензию SQL Server, а в Windows Server приобретаются отдельно.
Данная модель лицензирования обеспечит согласованное лицензирование частных и общедоступных облачных сред и упростит лицензирование в инфраструктурах с несколькими облаками. Переход на модель лицензирования по количеству ядер – один из этапов на пути к поддержке гибридного облака серверными лицензиями.
О СТОИМОСТИ
По словам правообладателя, стоимость одной лицензии Windows Server 2012 R2 (2 Proc) будет равна стоимости 8 лицензий Windows Server 2016 (2 Core).
1*Windows Server 2012 R2 (2 Proc) = 8* Windows Server 2016 (2 Core)*
* Это равенство работает в том случае, если вы используете до 8 ядер на 1 процессоре.
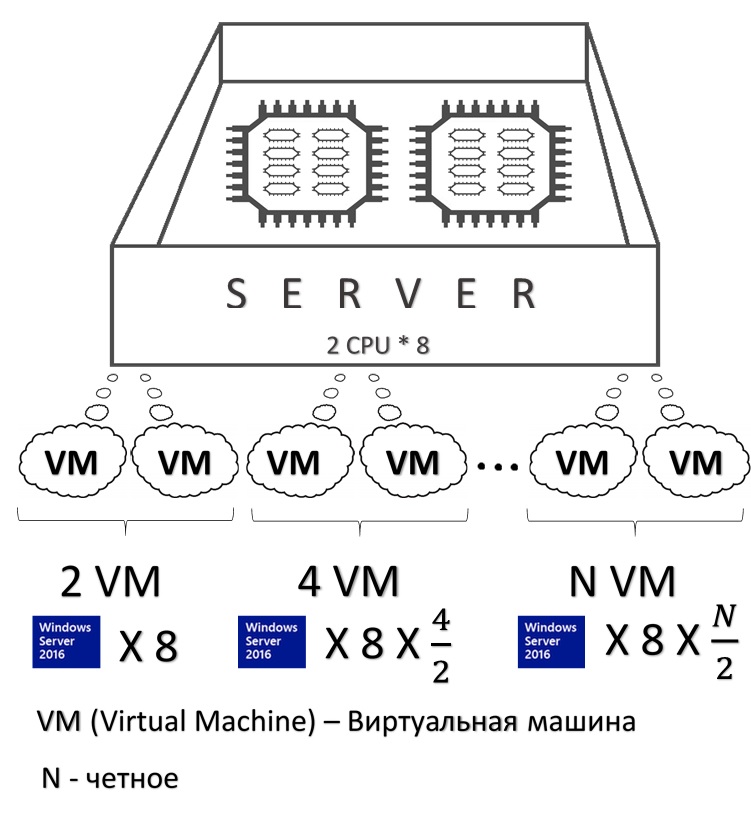
ВАЖНО!
- Для многопроцессорных серверов (более 1 физического процессора на 1 сервере): На каждый физический процессор для одного сервера необходимо приобрести не менее 4 лицензий Windows Server 2016 (2 Core).
- Для однопроцессорных серверов (1 физический процессор на 1 сервере): На каждом физическом сервере необходимо покрыть минимум 16 ядер – это 8 лицензий Windows Server 2016 (2 Core).
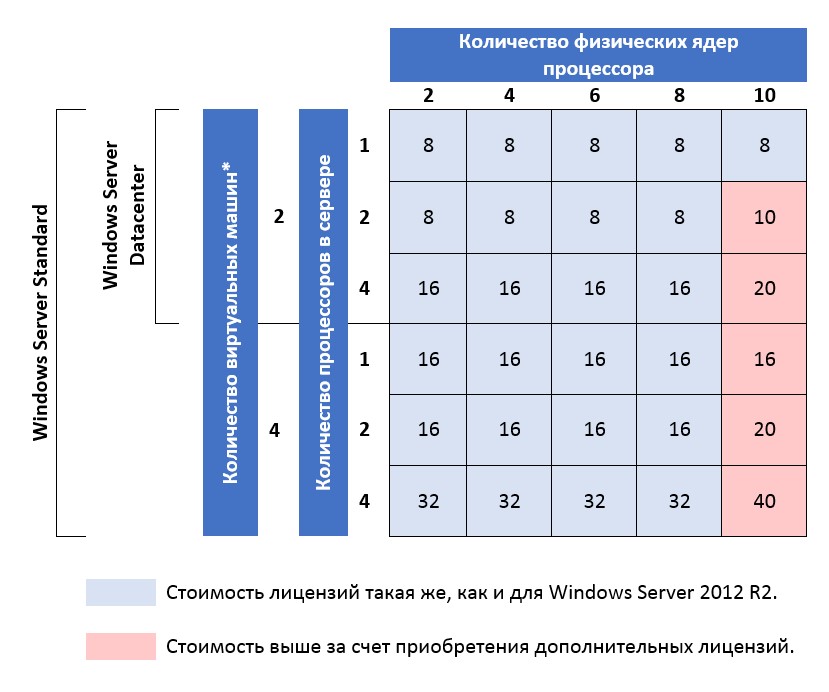
Калькулятор лицензий WINDOWS SERVER 2016
Количество ядер на процессор
Количество виртуальных машин
Количество лицензий:
Windows Server Standard 2016 (2 Core):
или
Windows Server Datacenter 2016 (2 Core):
Читайте статью «Лицензирование набора серверов. Windows Server 2008, 2008 R2, 2012, 2012 R2, 2016»
ЧТО НЕ ИЗМЕНИЛОСЬ?
- Windows Server Standard 2016 дает право на инсталляцию 2-х ОС в физической среде или 2 ВМ в виртуальной.
- Windows Server Datacenter 2016 дает право на инсталляцию неограниченного количества ОС в физической или виртуальной средах.
- Смешивать Редакции Standard и Datacenter на одном физическом сервере не допускается.
- Каждому пользователю или устройству, по-прежнему, необходима лицензия на доступ к Windows Server. Каждая лицензия Windows Server CAL предоставляет доступ к неограниченному количеству Windows Server в рамках одной компании, включая предыдущие версии Windows Server.
- Для удаленного доступа к Windows Server, также необходима клиентская лицензия Windows Remote Desktop.
КАК БЫТЬ ПРИ ПРОДЛЕНИИ ПОДПИСКИ SOFTWARE ASSURANCE?
До окончания действия подписки Software Assurance у вас ничего не меняется. Вы сможете обновиться до Windows Server 2016 по текущей модели лицензирования в рамках вашего действующего лицензионного соглашения. После продления Software Assurance вы переходите на модель лицензирования по ядрам. Для владельцев локальных сред на каждую лицензию Windows Server 2012 R2 (2 Proc) вы получаете минимум 8 лицензий Windows Server 2016 (2 Core), а для поставщиков услуг – минимум 4 лицензии Windows Server 2016 (2 Core) на каждую лицензию Windows Server 2012 R2 (1 Proc). Если в лицензированных серверах с действующей подпиской Software Assurance больше 8 ядер на процессоре или больше 16 ядер на сервере, то у вас есть возможность получить дополнительные лицензии со стороны вендора. Без действующей подписки Software Assurance на момент выхода версии 2016 дополнительные ядерные лицензии не предоставляются. Для получения дополнительных лицензий «на ядро» необходимо предоставить Microsoft датированный перечень инвентаризации производственных серверов с указанием количества физических процессоров и ядер, и назначенных на них лицензий Windows Server.
Читайте статью «Миссия: выполнима. Внедрить SAM»
ОБРАТИТЕ ВНИМАНИЕ!
Если у вас отключены физические ядра процессора и недоступны для использования операционной системой, вам необходимо приобрести такое количество лицензий, которое покроет все имеющиеся ядра, в т.ч. недействующие. Например, если у вас на сервере 20 физических ядер и 8 из них отключены, лицензии необходимо приобрести для покрытия не 12, а 20 ядер.
ПОДВЕДЕМ ИТОГИ
ИТ-специалисты и разработчики найдут много ценного и интересного в выпусках Windows Server и System Center 2016 года. Корпорация Майкрософт оптимизирует Windows Server 2016 для использования инновационных облачных технологий, а System Center 2016 — для управления частными и общедоступными облачными средами. Лицензирование выпусков Datacenter и Standard Edition будет осуществляться не по числу процессоров, а по числу физических ядер. Это обеспечивает согласованное лицензирование частных и общедоступных облачных сред и упрощает лицензирование в инфраструктурах с несколькими облаками. Клиенты, лицензирующие серверы с восьмью (и меньше) ядрами на процессор для Windows Server 2016 и System Center 2016, будут платить ту же сумму (стоимость единицы × количество), что и при лицензировании 2012 R2 на базе модели лицензирования с двумя процессорами. Лицензия на выпуск Standard Edition Windows Server 2016 и System Center 2016 распространяется не более чем на две виртуальные машины или два контейнера Hyper-V, если все физические ядра на сервере лицензированы.
- На физическом сервере все физические ядра должны быть лицензированы.
- Минимум 8 ядерных лицензий требуется для каждого физического процессора в сервере. Минимум 16 ядер необходимо лицензировать на сервере с одним физическим процессором.
- «Ядерные» лицензии продаются пакетами на 2 ядра.
- Редакция «Standard» Windows Server позволит запускать до 2 виртуальных машин/ОС, если все физические ядра сервера лицензированы (минимум 8 ядер на каждый процессор и 16 ядер на сервер).
- Цена 16-ти ядерной лицензии Windows Server 2016 редакций Datacenter и Standard не отличается от цены 2-х процессорной лицензии соответствующей редакции Windows Server 2012 R2. В таком сценарии никаких изменений в цене.
- Если у вас есть действующая подписка Software Assurance, то вы можете досрочно продлить Windows Server с процессорной лицензией.
Если у вас остались вопросы или требуется помощь в расчёте необходимого количества лицензий на ПО, обращайтесь к нашим консультантам по лицензированию и управлению программными активами, будем рады помочь!
- Больше информации и практических советов по теме лицензирования ПО вы можете получить на курсе «Лицензирование продуктов Microsoft»
- Научиться управлять лицензионным ПО и получать от этого выгоды на курсе «Управление программными активами на предприятии»
When installing Windows Server 2016 you need to know the right version to use. Microsoft licensing is very particular when it comes to what edition of Windows Server 2016 you’re using on what type of hardware. Picking the right version can be the different between saving a lot of money and losing a lot of money (when Microsoft comes knocking with a license audit request).
Now it’s not just licensing and hardware that determines the best version of Windows Server 2016 to use, it’s also how you plan to use it. I’ll explain in a bit.
Let’s compare the different editions.
Server 2016 is available in four major editions:
- Hyper-V
- Essentials
- Standard
- Datacenter
Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V
Hyper-V Server is a free version of Server 2016 that it meant for running the Hyper-V role only. Its purpose is to be a hypervisor for your virtual environment only. It does not have a GUI. It’s essentially a stripped out version of Server Core. You’ll use sconfig.cmd to stand up the hypervisor and then manage the environment using Hyper-V Manager (as part of RSAT) from a Windows 10 workstation within your network. I highly recommend using this version for your hypervisor to keep licensing clean and simple.
Windows Server 2016 Essentials
Essentials is ideal for SMBs or Small Businesses and individuals with very basic server needs. The GUI is pretty much the same as Standard with the exception of the Essentials Wizard that runs. While you can disable this Wizard, the system is really meant to be used with it.
Virtualization Rights
You’re allowed to run one physical instance of Essentials as a Hyper-V host, hosting one virtual instance of Essentials. You’ll need to remove all roles except the Hyper-V role from the physical Essentials instance to be in compliance. Essentials is also good for one virtual instance on any other hypervisor.
Licensing Model
CPU based. No CALs are required but you’re limited to 25 users and 50 devices connecting to the server.
Hardware Limits
Essentials is limited to a max of 64GB of RAM and 2 CPUs on the machine it’s installed on.
Learn more from Microsoft and Download the licensing sheet here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-cy/cloud-platform/windows-server-pricing
Windows Server 2016 Standard
Standard is ideal for any company or individual that that needs advanced features but will still not be virtualizing heavily.
Virtualization Rights
You’re allowed to run up to two virtual machines or Hyper-V containers or one physical instance with a Standard License. If you only use the Hyper-V role on the physical instance you can use it as a Hyper-V host and then host two Hyper-V VMs on that host. If you want to use multiple roles on the physical instance you cannot run vm’s on top with the same license.
Licensing Model
Core based. CALs are required for every user or device that connects indirectly or directly to the server. For example, if you use the server as a file server you will need a CAL for every user account or computer that access that file server on the network.
Hardware Limits
Standard is limited a max of 24TB of RAM and 512 cores.
Learn more from Microsoft and Download the licensing sheet here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-cy/cloud-platform/windows-server-pricing
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter
Datacenter is ideal for any company that is highly virtualized. You purchasing licensing according to how many cores your hosts have that any VM running Datacenter can live on (run or potentially run on after a vmotion). This licensing seems expensive at first but it allows you to create an unlimited amount of VMs running Server 2016 Datacenter on the hosts you’ve accounted for. If you have a low number of hosts (and subsequently cores) and high number of potential VMs then this license is a no brainer.
Virtualization Rights
Unlimited virtual machines or Hyper-V containers. As stated above, you’ll purchase licenses according to how many cores you have within your hosts. At that point you can spin up as many VMs on those hosts as your heart desires using whatever roles you want.
Licensing Model
Core Based. Make sure you don’t accidentally choose this edition on install on a physical server that won’t host virtual machines. You’ll be out several thousands of dollars should Microsoft request a license audit. CALs are required for every user or device that connects indirectly or directly to the servers in your environment.
Learn more from Microsoft and Download the licensing sheet here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-cy/cloud-platform/windows-server-pricing
Windows Server 2016 Installation Options Comparison
Within the Standard and Datacenter editions of Server 2016 there are also different installation options you can choose. These versions affect what features are available after install such as the presence of a GUI and a multitude of services. The installation options are:
- Desktop Experience
- Core
- Nano
Desktop Experience
Desktop Experience is the install option most people are familiar with. This options installs the most features and roles out of the box including the desktop GUI interface. You’ll get the Server Manager which allows you to add and remove Roles and Features. The benefit is the system may be easier to manage for people used to using a GUI. The drawback is you have more updates, reboots, and open ports to deal with.
Learn more from Microsoft here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/get-started/getting-started-with-server-with-desktop-experience
Core
Server Core lacks a gui and few roles that are installed by default under the Desktop Experience option. Server Core has a smaller disk footprint, and therefore a smaller attack surface due to a smaller code base. You also have less updates, reboots, and open ports to deal with. It’s a great option for infrastructure servers such as Active Directory Domain Controllers and DNS servers.
When installing server Core there are no accessibility tools, out of box experience for setting up the server, and no audio support. It really is a no frills install. Just make sure you’re comfortable with command line based administration.
Learn more from Microsoft here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/server-core/what-is-server-core
Nano
Starting with 1803, Nano is available only as a container base OS image. It’s meant to be run as a container within a container host like Server Core mentioned above. If you rely on containerized applications meant for server OSs then this is the edition you would use to compile those apps.
Nano can be deployed with either Standard or Datacenter but you must have attached Software Assurance to the licensing of the host server.
Learn more from Microsoft here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/get-started/nano-in-semi-annual-channel
Recommended for You: SolarWinds Hybrid Systems Monitoring Bundle (Free Trial)

Know which applications are having issues in your environment before users complain? Know which systems are causing those problems or were recently changed by someone? How about which servers are about to have problems like running out of space or memory?
Automate collection of data and alerting on your local or cloud applications and servers with SolarWinds Hybrid Systems Bundle so you have these answers.
Download a free trial now and get insight into Active Directory, DNS, DHCP, and your Virtual and Applications environments, both locally and cloud hosted, without needing to mess with complex templates or knowing a single line of code.
Network Engineer III
I am a CCNP certified Network Engineer III who has spent the last decade elbow deep in enterprise System Administration and Networking in the local government and energy sectors. I can usually be found trying to warm up behind the storage arrays in the datacenter.
Item Preview

cover.jpeg
1,953
Views
4
Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
Uploaded by
wailord284
on


