Операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2 расширяет базовые возможности операционной системы Windows Server и предоставляет новые мощные средства, помогая организациям всех размеров повышать управляемость, доступность и гибкость в соответствии с изменяющимися требованиями бизнеса. Новые веб-средства, технологии виртуализации, средства управления и расширенные возможности масштабирования экономят время, снижают затраты и предоставляют надежную платформу для создания ИТ-инфраструктуры организации.
Windows Server 2008 R2 содержит новые и усовершенствованные средства и возможности в следующих пяти категориях.
Платформа веб-приложений
В сервер Windows Server 2008 R2 включены множество усовершенствований, превращающих его в самую надежную платформу веб-приложений на основе Windows Server среди всех версий Windows. Он содержит обновленную роль веб-сервера и службы IIS 7.5 и обеспечивает расширенную поддержку .NET в режиме Server Core.
Виртуализация
Виртуализация играет важнейшую роль в работе современных центров обработки данных. Обеспечиваемое виртуализацией повышение эффективности работы позволяет организациям значительно снизить трудоемкость эксплуатации и энергопотребление. Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает следующие типы виртуализации: виртуализацию клиентских и серверных систем с помощью Hyper-V и виртуализацию представлений с помощью служб удаленных рабочих столов.
Масштабируемость и надежность
Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает недостижимые ранее объемы рабочих нагрузок, динамическую масштабируемость, доступность и надежность на всех уровнях, а также ряд других новых и обновленных возможностей, включая использование современных архитектур процессоров, повышение уровня компонентного представления операционной системы и повышение производительности и масштабируемости приложений и служб.
Управление
Постоянное управление серверами в центрах обработки данных — одна из тех задач, которые отнимают у ИТ-специалистов наибольшее время. Применяемая в организации стратегия управления должна поддерживать управление физическими и виртуальными средами. Чтобы помочь в решении этой задачи, в состав Windows Server 2008 R2 включены новые средства, уменьшающие трудоемкость управления серверами Windows Server 2008 R2 и выполнения повседневных задач по администрированию серверов.
Совместная работа с Windows 7
Операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает ряд функций, рассчитанных на работу с клиентскими компьютерами под управлением Windows 7.
Более подробно с основными возможностями ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Все редакции Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживают основные возможности, необходимые для решения задач, которые возникают в работе ИТ-систем и организаций любого размера. Основные особенности различных редакций Windows Server 2008 R2, которые поставляются совместно с серверами DEPO Storm, описаны в данной статье.
Сравнительные характеристики различных редакций ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 приведены в таблице.
| Технические характеристики | MultiPoint Server (ОЕМ) | Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise |
| Количество CPU | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Объем ОЗУ | 8 Гб | 8 Гб | 32 Гб | 32 Гб | 2 ТБ |
| Количество подключений для удаленного управления (Remote Desktop) | Нет | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Количество клиентских лицензий в комплекте | 0 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 25 |
| Кол-во CAL (Max) | 10 | Не требуются Ограничено подключением до 15 пользователей |
75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Кол-во терминальных лицензий (Max) | Нет | 15 | 75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (RRAS) | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (IAS) | Нет | 10 | 50 | 50 | Без ограничений |
| Количество одновременных подключений через Шлюз Терминальных Служб | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Поддержка виртуализации | Нет | Нет | Нет | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 1 виртуальную машину | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 4 виртуальных машины. При использовании 4 виртуальных машин — на физической машине роль только Hyper-V. |
Для работы с Windows Server 2008 R2 компьютер должен удовлетворять следующим требованиям*
| Компонент |
Требование |
| Процессор | 1,4 ГГц (процессор с архитектурой x64) |
| Память | Минимальный объем: 512 МБ Максимальный объем: Foundation — 8 ГБ, Standard — 32 ГБ, Enterprise — 2 ТБ |
| Требования к свободному пространству на диске |
Минимальный объем: 32 ГБ |
| Монитор |
Монитор с разрешением Super VGA (800×600) или более высоким |
| Прочее |
Дисковод для DVD-дисков, клавиатура и мышь (Microsoft) или совместимое указывающее устройство, доступ в Интернет |
* Фактические требования к системе зависят от конфигурации системы и от выбранных для установки приложений и компонентов. Производительность процессора зависит не только от его тактовой частоты, но и от числа ядер и объема кэша процессора. Необходимый объем свободного дискового пространства в системном разделе указан приблизительно. При установке по сети может потребоваться дополнительное место на диске.
Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 – продукт семейства Windows, при помощи которого несколько человек могут одновременно работать на одном компьютере. MultiPoint Server является идеальным решением для образовательных учреждений, поскольку предоставляет большему числу преподавателей и учащихся доступ к компьютерным технологиям, а также:
- сокращает начальные вложения в оборудование и текущие эксплуатационные расходы;
- сокращает потребление электроэнергии;
- упрощает управление ИТ-инфраструктурой.
Более подробно с возможностями Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation предназначена для небольших организаций, где рассматривается приобретение первого сервера или уже используется клиентская операционная система (например, Windows XP) для обеспечения базовой инфраструктуры. Это недорогая, удобная в развертывании и надежная платформа, на которой можно запускать распространенные бизнес-приложения и обеспечивать общий доступ к информации и ресурсам. Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation основан на Windows Server 2008 R2 и сможет обеспечить все ключевые элементы ИТ в Вашем бизнесе: совместная работа с файлами и принтерами, удаленный доступ, безопасность ИТ среды.
Однако Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation имеет ограничения по количеству клиентских подключений и не поддерживает функции виртуализации.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка 1 многоядерного процессора (количество ядер в процессоре неограниченно);
- поддержка 8 ГБ ОЗУ для 64-разрядных систем (4 ГБ для 32-разрядных систем);
- до 50 подключений службы сетевого доступа (RRAS);
- до 10 подключений сервера политики сети;
- до 50 подключений сервера терминалов;
- до 15 пользователей (учетных записей в Active Directory).
Более подробно с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Small Business Server 2008 – полностью интегрированное ИТ-решение, включающее в себя все, что нужно малым и средним компаниям. Оно позволяет улучшить защиту данных и повысить эффективность работы компании, значительно снизив при этом расходы на развертывание и поддержку.
Электронная почта, подключение к Интернету, внутренние веб-узлы, удаленный доступ к файлам и почте, поддержка мобильных устройств, совместное использование файлов и принтеров, резервное копирование и восстановление – неполный список возможностей Windows Small Business Server 2008.
Windows Small Business Server 2008 поставляется в двух вариантах: Standard и Premium.
Версия Standard содержит средства для подключения локальной сети предприятия к Интернету. В состав продукта входит надежный межсетевой экран, сервер сообщений Microsoft Exchange со встроенной системой web-почты Microsoft Outlook Web Access, динамический web-сайт Remote Web Workplace, позволяющий сотрудникам получать быстрый и безопасный доступ к данным через Интернет.
Версия Premium содержит необходимые средства для подключения локальной сети предприятия к Интернету. В состав продукта входит мощный и надежный межсетевой экран, сервер сообщений Microsoft Exchange со встроенной системой web-почты Microsoft Outlook Web Access, динамический web-сайт Remote Web Workplace, позволяющий сотрудникам получать быстрый и безопасный доступ к данным через Интернет.
Более подробно с возможностями Windows Small Business Server можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard – это самая надежная операционная система из семейства Windows Server на настоящее время. Эта система имеет встроенный веб-сервер и возможности виртуализации. Она поможет повысить надежность и гибкость серверной инфраструктуры при снижении расходов и экономии времени. Мощные инструменты обеспечивают более удобное управление серверами, упрощают настройку и управление. Надёжные средства безопасности этой операционной системы защищают сети и данные, что даёт возможность построить исключительно прочный фундамент для ИТ-среды вашего бизнеса.
Windows Server 2008 Standard обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка до 4-х многоядерных процессоров (количество ядер в процессоре неограниченно);
- поддержка 32 ГБ ОЗУ для 64-разрядных систем;
- до 250 подключений службы сетевого доступа (RRAS);
- до 50 подключений сервера политики сети;
- до 250 подключений сервера терминалов;
- практически неограниченное кол-во пользователей (учетных записей в Active Directory);
- поддержка виртуализации на базе технологии Hyper-V и один бесплатный виртуальный экземпляр.
Подробнее с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise обеспечивает бесперебойное функционирование, безопасность на основе новейших технологий и высокую масштабируемость, которая необходима для поддержки расширения критически важных приложений. Кроме того, она позволяет недорого и эффективно виртуализировать оборудование.
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка до 8-ми многоядерных CPU для обработки пиковых нагрузок;
- 2 ТБ ОЗУ для эксплуатации ресурсоемких приложений;
- поддержка неограниченного количества VPN-подключений;
- проверка подлинности и авторизация для неограниченного количества подключений службы сетевого доступа и сервера политики сети;
- практически неограниченное количество подключений шлюза удаленных служб;
- поддержка виртуализации на базе технологии Hyper-V (лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 4 виртуальных машины).
Кроме того, в Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise имеется функция горячего добавления памяти, которая позволяет без перезагрузки устанавливать на сервере дополнительные блоки памяти и сразу делать их доступными для операционной системы и приложений в рамках обычного пула памяти.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — оптимальная операционная система для серверов с приложениями для управления работой сети, обмена сообщениями, инвентаризации, обслуживания заказчиков и приложениями баз данных. Она поддерживает все функциональные возможности Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, а также имеет ряд преимуществ. Благодаря таким возможностям, как отказоустойчивые кластеры, Server Core, отказоустойчивая синхронизация памяти и распределенной файловой репликации (DFS-R), ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise обеспечивает высокий уровень доступности для критически важных приложений, например баз данных, систем обмена сообщениями, файловых служб и служб печати.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise является идеальной платформой для виртуализации в масштабах всей компании с помощью гибкой и высокопроизводительной технологии Hyper-V™. Лицензия Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise включает право на использование до четырех дополнительных виртуальных экземпляров Windows Server на одном сервере с лицензией Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise.
Подробнее с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Приложение
В процессе эксплуатации Windows Server 2008 R2 системный администратор может столкнутся с ограничениями установленной редакции ОС, которые не позволяют воспользоваться тем или иным функционалом сервера, например в редакции 2008 R2 Standard нельзя использовать более 32 Гб оперативной памяти, или развертывать решения Failover Cluster, RRAS, RDS и т.д. В предыдущих версиях Windows Server в такой ситуации приходилось полностью переустанавливать систему на «старшую» редакцию ОС. В Windows Server 2008 R2 из этой ситуации есть выход, т.к. в ней существует возможность обновиться до старшей версии ОС (например, с редакции Standard до Enterprise) без переустановки сервера.
Обновление выполняется при помощи утилиты DISM, и может быть выполнено как в автономном (офлайн) режиме, так и прямо в процессе работы сервера (онлайн режим). Обновление не требует переустановки системы, и текущие настройки сервера (роли, компоненты и другие приложения) сохраняются. Обновление возможно, как в режиме Server Core, так и в Full GUI версии Windows 2008 R2, однако следует понимать, что переход от версии Server Core к полной установке 2008 R2 невозможен (в Windows Server 2012 возможно переключатся между Full и Core режимами). Возможно обновление с младшей редакции Windows Server 2008 R2 до старшей версии, обратная процедура понижения редакции (даунгрейд) невозможна.
Доступные варианты обновления редакции Windows Server 2008 R2:
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard —> Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise —> Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Server Core —> Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Server Core —> Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Server Core
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation —> Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard
Итак, утилита DISM.exe уже входит в комплект поставки Windows Server 2008 R2 и дополнительно устанавливать ничего не нужно.
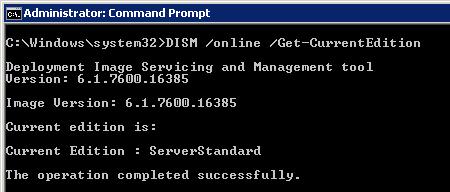
Чтобы узнать текущую версию Windows Server 2008 R2, в командной строке выполните команду:
DISM /online /Get-CurrentEdition
Если команда вернет ServerStandard, это означает что текущая редакция установленной ОС — Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard.
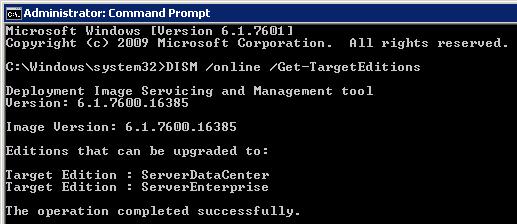
Получим список редакций, до которых нам можно проапгрейдится:
DISM /online /Get-TargetEditions
В данном случае возможно обновление до версий:
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter (ServerDataCenter)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise (ServerEnterprise)
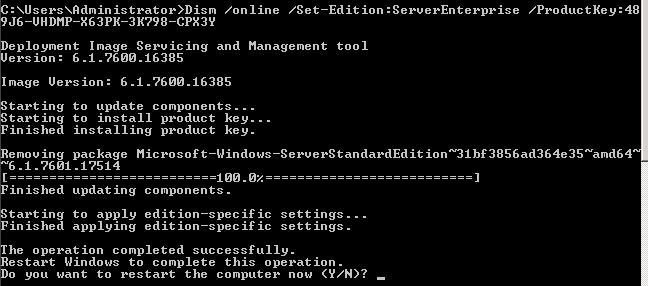
Чтобы выполнить обновление до Windows 2008 R2 Enterprise выполните команду:
DISM /online /Set-Edition:ServerEnterprise /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
Где XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX – приобретенный Вами ключ продукта для соответствующей редакции Windows 2008 R2.
В том случае, если для активации планируется использовать сервер KMS, воспользуйтесь KMS ключом для Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise (так называемый GVLK ключ).
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise | 489J6-VHDMP-X63PK-3K798-CPX3Y |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter | 74YFP-3QFB3-KQT8W-PMXWJ-7M648 |
KMS ключ поможет также в том случае, если с помощью Вашего MAK / retail ключа от соответствующей версии Windows Server обновиться не получается. Не забудьте после обновления изменить KMS ключ на ваш с помощью команды:
slmgr /ipk XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
В том случае если сервер, который планируется обновить, является контроллером домена Active Directory, необходимо перед обновлением версии ОС выполнить с помощью команды DCPROMO понижение роли сервера до рядового сервера домена, и лишь затем выполнить апгрейд версии ОС. После этого сервер нужно перезагрузить и опять поднять на нем контроллер домена.
В процессе обновления версий могут появиться такие ошибки:
- Setting an Edition is not supported with online images – скорее всего на сервере развернута роль контроллера домена Active Directory (роль AD DS). Как мы уже говорили выше – необходимо понизить роль сервера для рядового сервера домена.
- The specified product key is not valid for the target edition. Run this command again with a product key specific to the target edition – по какой-то причине ОС не принимает указанный ключ, если вы уверены, что ключ валидный и соответствует редакции Windows Server, до которой проводится обновление, проведите обновление с KMS ключом (список ключей выше)
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2</google>
Before embarking on the installation of Windows Server 2008 R2, it is important to first gain an understanding of the different editions available and the corresponding hardware requirements. It is also important to be aware of the upgrade options available with each edition. With this objective in mind, this chapter will focus on providing an overview of both the different Windows Server 2008 R2 editions and the recommended hardware requirements.
Contents
Contents
|
||
CPU Requirements
The first item of note for users familiar with the first version of Windows Server 2008 is that the R2 edition is only available for 64-bit systems. Whilst some editions of the original Windows Server 2008 operating system were available in 32-bit versions, this is now no longer the case for the R2 version.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation Edition
The Foundation edition of Windows Server 2008 R2 is the new entry level edition and is designed specifically with the small business in mind. It is the least expensive of the various editions and lacks some of the more advanced functionality typically found in the higher end editions such as full Active Directory support and Hyper-V virtualization capabilities. In addition, the Foundation edition limits some of the included features, such as restricting the number of concurrent remote desktop services connections to 50 and is able to access a maximum of 1 processor and 8GB of RAM.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Edition
<google>ADSDAQBOX_FLOW</google>
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard is another one of Microsoft’s entry level server offerings (alongside Windows Web Server R2 2008 and Windows Server R2 2008 Foundation). As previously stated, whilst the original version of Windows Server 2008 supported both 32-bit and 64-bit versions, the R2 version supports only 64-bit processors. In terms of hardware, Standard Edition supports up to 4GB of RAM and 4 processors.
Windows Server 2008 is primarily targeted at small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) and is ideal for providing domain, web, DNS, remote access, print, file and application services. Support for clustering, however, is notably absent from this edition.
An upgrade path to Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard is available from Windows Server 2008, Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition provides greater functionality and scalability than the Standard Edition. As with Standard Edition both 32-bit and 64-bit versions are available. Enhancements include support for as many as 8 processors and up to 2TB of RAM.
Additional features of the Enterprise edition include support for clusters of up to 16 nodes and Active Directory Federated Services (AD FS).
Windows Server 2000, Windows 2000 Advanced Server, Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition and Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition may all be upgraded to Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Edition
<google>WIN28BOX</google>
The Datacenter edition represents the top end of the Windows Server 2008 R2 product range and is targeted at mission critical enterprises requiring stability and high uptime levels.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter edition supports up to 2TB of RAM and a minimum of 8 processors up to a maximum of 64.
Upgrade paths to Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Edition are available from the Datacenter editions of Windows Server 2008, Windows 2000 and 2003.
Windows Web Server 2008 R2
Windows Web Server R2 2008 is essentially a version of Windows Server 2008 R2 designed primarily for the purpose of providing web services. It includes Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.0 along with associated services such as Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and Telnet. It supports up to 4 processors but RAM is limited to 32GB.
As with other entry level editions, Windows Web Server 2008 R2 lacks many of the features present in other editions such as clustering, BitLocker drive encryption, multipath I/O, Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS), Removable Storage Management and SAN Management.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Features Matrix
Now that we have covered in general terms the various different editions of Windows Server 2008 R2 we can now look in a little more detail at a feature by feature comparison of the four different editions. This is outlined in the following feature matrix:
|
Feature |
Enterprise |
Datacenter |
Standard |
Itanium |
Web |
Foundation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Certificate Services | Yes | Yes | Limited | No | No | Limited |
| Active Directory Domain Services | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Active Directory Federation Services | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Active Directory Rights Management Services | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Application Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| DHCP Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| DNS Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Fax Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| File Services | Yes | Yes | Limited | No | No | Limited |
| Hyper-V | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Network Policy and Access Services | Yes | Yes | Limited | No | No | Limited |
| Print and Document Services | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Remote Desktop Services | Yes | Yes | Limited | No | No | Limited |
| Web Services (IIS) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Windows Deployment Services | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hardware Requirements
Before investing time and resources into downloading and installing Windows Server 2008 R2, an important first step is to gain an appreciation of the hardware requirements necessary to effectively run the operating system. The following table provides an overview of Microsoft’s recommended minimum hardware requirements:
|
Category |
Minimum / Recommended Requirements |
| Processor | • Minimum: 1.4GHz (x64 processor) • Recommended: 2GHz or faster Note: For Itanium based systems an Intel Itanium 2 processor is required. |
| Memory | • Minimum: 512MB RAM • Recommended: 2GB RAM or greater • Maximum (32-bit systems): 4GB (Standard) or 64GB (Enterprise and Datacenter) • Maximum: 8GB (Foundation) 32GB (Standard) or 2TB (Enterprise, Datacenter and Itanium-Based Systems) |
| Available Disk Space | • Minimum: 10GB • Recommended: 40GB or greater Note: Systems with RAM in excess of 16GB will require greater amounts of disk space to accommodate paging, hibernation, and dump files |
| Drive | DVD-ROM drive |
| Display and Peripherals | • Super VGA or greater-resolution monitor (800×600) • Keyboard • Microsoft Mouse or compatible pointing device |
As with the specified system requirements for all Windows systems, it is best to aim for the Recommended values rather than the Minimum values to ensure acceptable levels of performance. For example, whilst it is possible to run Windows Server 2008 R2 in 512MB of RAM it is unlikely that performance levels will be optimal with such a configuration.
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2_BOTTOM</google>
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 |
|

Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 R2 showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Windows Server |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
July 22, 2009; 14 years ago |
| General availability |
October 22, 2009; 13 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 1 with security update rollup (6.1.7601.24499) / March 19, 2019; 4 years ago[2] |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Commercial software (Retail, volume licensing, Microsoft Software Assurance) |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2008 (2008) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2012 (2012) |
| Official website | docs |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015.[3] Extended support ended January 14, 2020.[3] Windows Server 2008 R2 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) program.[4] This program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system until January 10, 2023,[5] only for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions. The program is included with Microsoft Azure purchases, and offers Azure customers an additional year of support, until January 9, 2024.[6][7][8] Installing Service Pack 1 is required for users to receive updates and support after April 9, 2013.[9][10] |
Windows Server 2008 R2, codenamed «Windows Server 7», is the fifth version of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft and released as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009,[11] and became generally available on October 22, 2009, shortly after the completion of Windows 7.[12] It is the successor to Windows Server 2008, which is derived from the Windows Vista codebase, released the previous year, and was succeeded by the Windows 8-based Windows Server 2012.
Enhancements in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new functionality for Active Directory, new virtualization and management features, version 7.5 of the Internet Information Services web server and support for up to 256[13] logical processors. It is built on the same kernel used with the client-oriented Windows 7, and is the first server operating system released by Microsoft which dropped support for 32-bit processors, a move which was followed by the consumer-oriented Windows 11 in 2021.
Windows Server 2008 R2 is the final version of Windows Server that includes Enterprise and Web Server editions, the final that got a service pack from Microsoft and the final version that supports IA-64 and processors without PAE, SSE2 and NX (although a 2018 update dropped support for non-SSE2 processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2012, requires a processor with PAE, SSE2 and NX, in any supported architecture.
Seven editions of Windows Server 2008 R2 were released: Foundation, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web, HPC Server and Itanium, as well as Windows Storage Server 2008 R2. A home server variant called Windows Home Server 2011 was also released.
History[edit]
Microsoft introduced Windows Server 2008 R2 at the 2008 Professional Developers Conference as the server variant of Windows 7, based on the Windows NT kernel.
On January 7, 2009, a beta release of Windows Server 2008 R2 was made available to subscribers of Microsoft’s TechNet and MSDN programs, as well as those participating in the Microsoft Connect program for Windows 7. Two days later, the beta was released to the public via the Microsoft Download Center.[14]
On April 30, 2009, the release candidate was made available to subscribers of TechNet and MSDN.[15] On May 5, 2009, the release candidate was made available to the public via the Microsoft download center.[16]
According to Windows Server Blog,[17] the following are the dates of the year 2009 when Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 has been made available to various distribution channels:
- OEMs received Windows Server 2008 R2 in English and all language packs on July 29. The remaining languages were available around August 11.
- Independent software vendor (ISV) and independent hardware vendor (IHV) partners have been able to download Windows Server 2008 R2 from MSDN starting on August 14.
- IT professionals with TechNet subscriptions were able to download Windows Server 2008 R2 and obtain product keys for English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish variants beginning August 14 and all remaining languages beginning August 21.
- Developers with MSDN subscriptions have been able to download and obtain product keys for Windows Server 2008 R2 in English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish starting August 14 and all remaining languages starting August 21.
- Microsoft Partner Program (MPP) gold/certified members were able to download Windows Server 2008 R2 through the MPP portal on August 19.
- Volume licensing customers with an existing Software Assurance (SA) contracts were able to download Windows Server 2008 R2 on August 19 via the Volume License Service Center.
- Volume licensing customers without an SA were able to purchase Windows Server 2008 R2 through volume licensing by September 1.
Additionally, qualifying students have been able to download Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard edition in 15 languages from the Microsoft Imagine program (known as DreamSpark at the time).[18]
Microsoft announced that Server 2008 R2 would be the last version of Windows supporting the Itanium architecture, with extended support to end on July 10, 2018.[19][20][21] However, monthly security updates continued until January 14, 2020,[22] and a final unscheduled update appeared in May 2020 via WSUS.[23]
New features[edit]
A reviewer guide published by the company describes several areas of improvement in R2.[24] These include new virtualization capabilities (Live Migration, Cluster Shared Volumes using Failover Clustering and Hyper-V), reduced power consumption, a new set of management tools and new Active Directory capabilities such as a «recycle bin» for deleted objects. IIS 7.5 has been added to this release which also includes updated FTP server services. Security enhancements include encrypted clientless authenticated VPN services through DirectAccess for clients using Windows 7, and the addition of DNSSEC support for DNS Server Service. Even though DNSSEC as such is supported, only one signature algorithm is available:[25] #5/RSA/SHA-1. Since many zones use a different algorithm – including the root zone – this means that in reality Windows still can’t serve as a recursive resolver.
The DHCP server supports a large number of enhancements[26] such as MAC address-based control filtering, converting active leases into reservations or link layer based filters, DHCppP Name protection for non-Windows machines to prevent name squatting, better performance through aggressive lease database caching, DHCP activity logging, auto-population of certain network interface fields, a wizard for split-scope configuration, DHCP Server role migration using WSMT, support for DHCPv6 Option 15 (User Class) and Option 32 (Information Refresh Time). The DHCP server runs in the context of the Network Service account which has fewer privileges to reduce potential damage if compromised.
Windows Server 2008 R2 supports up to 64 physical processors[27] or up to 256 logical processors per system. (Only the Datacenter and Itanium editions can take advantage of the capability of 64 physical processors. Enterprise, the next-highest edition after those two, can only use 8.)[28] When deployed in a file server role, new File Classification Infrastructure services allow files to be stored on designated servers in the enterprise based on business naming conventions, relevance to business processes and overall corporate policies.[29]
Server Core includes a subset of the .NET Framework, so that some applications (including ASP.NET web sites and Windows PowerShell 2.0) can be used.
Performance improvement was a major area of focus for this release; Microsoft has stated that work was done to decrease boot time, improve the efficiency of I/O operations while using less processing power, and generally improve the speed of storage devices, especially iSCSI.
Active Directory has several new features when raising the forest and domain functional levels[30] to Windows Server 2008 R2: Two added features are Authentication Mechanism Assurance and Automatic SPN Management. When raising the forest functional level, the Active Directory recycle bin feature is available and can be enabled using the Active Directory Module for PowerShell.[31]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 R2 ended on April 9, 2013.[9][10] Users had to install Service Pack 1 to continue receiving updates.[32]
On January 13, 2015, Windows Server 2008 R2 exited mainstream support and entered the extended support phase; Microsoft continued to provide security updates every month for Windows Server 2008 R2, however, free technical support, warranty claims, and design changes were no longer offered. Extended support ended on January 14, 2020, about ten years after the release of Windows Server 2008 R2.[33] On July 12, 2018, Microsoft announced a paid «Extended Security Updates» service that will offer additional updates for Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter for up to 3 years after the end of extended support, lasting until January 10, 2023. In November 2021, Microsoft extended ESU support for Windows Server 2008 R2 until January 9, 2024, only for Microsoft Azure customers. ESU support for Itanium systems is not available.
In August 2019, researchers reported that «all modern versions of Microsoft Windows» may be at risk for «critical» system compromise due to design flaws of hardware device drivers from multiple providers.[34] In the same month, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Microsoft Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[35] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from the older Windows XP version to the most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[36]
Service Pack[edit]
On February 9, 2011, Microsoft officially released Service Pack 1 (SP1) for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 to OEM partners. Apart from bug fixes, it introduces two new major functions, RemoteFX and Dynamic Memory. RemoteFX enables the use of graphics hardware support for 3D graphics in a Hyper-V based VM. Dynamic Memory makes it possible for a VM to only allocate as much physical RAM as is needed temporarily for its execution. On February 16, SP1 became available for MSDN and TechNet subscribers as well as volume licensing customers. As of February 22, SP1 is generally available for download via the Microsoft Download Center and available on Windows Update.[37]
System requirements[edit]
System requirements for Windows Server 2008 R2 are as follows:[38]
- Processor
- 1.4 GHz x86-64 or Itanium 2 processor
- Memory
- Minimum: 512 MB RAM (may limit performance and some features)
- Recommended: 2 GB RAM
- Maximum: 8 GB RAM (Foundation), 32 GB RAM (Standard), or 2 TB RAM (Enterprise, Datacenter and Itanium)
- Display
- Super VGA (800×600) or higher
- Disk Space Requirements
- Minimum (editions higher than Foundation): 32 GB or more
- Minimum (Foundation edition) 10 GB or more.
- Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM require more disk space for paging and dump files.[38]
- Other
- DVD drive, keyboard and mouse, Internet access (required for updates and online activation)
Editions[edit]
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
References[edit]
- ^ http://www.microsoft.com/presspass/features/2009/Jun09/06-02SteveGuggenheimer.mspx
- ^ http://blogs.technet.com/windowsserver/archive/2009/07/22/windows-server-2008-r2-rtm.aspx
- ^ a b Microsoft. «Windows Server 2008 R2 Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved 2012-09-01.
- ^ «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-01-02.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ «Product Lifecycle FAQ – Extended Security Updates».
- ^ «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». Microsoft.
- ^ «Microsoft starts selling extended support for Windows Server 2008».
- ^ a b «Microsoft Support Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 20, 2012.
- ^ a b Rose, Stephen L (February 14, 2013). «Windows 7 RTM End Of Support Is Right Around The Corner». Springboard Series Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 2, 2013. Retrieved March 27, 2013.
- ^ Server and Cloud Platform Team (2009-07-22). «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone!». Blogs.technet.com. Archived from the original on July 23, 2009. Retrieved 2011-06-15.
- ^ «Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Timelines Shared at Computex». News Center. Taipei, Taiwan: Microsoft. June 3, 2009.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Edition Overview». Microsoft.com. Archived from the original on September 14, 2008. Retrieved 2011-06-15.
- ^ Emil Protalinski (9 January 2009). «Windows 7 public beta is available now».
- ^ «Announcing Windows Server 2008 R2 Release Candidate (RC)». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on May 15, 2009.
- ^ «Download Windows Server 2008 R2 RC .iso images (May2009)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 11, 2009.
- ^ House, Crissy (22 July 2009). «When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2009.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 on DreamSpark». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 18, 2011.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 to Phase Out Itanium». Windows Server Blog. 2 April 2010.
Why the change? The natural evolution of the x86 64-bit («x64») architecture has led to the creation of processors and servers which deliver the scalability and reliability needed for today’s «mission-critical» workloads.
- ^ «Microsoft ending support for Itanium». 4 April 2010.
SQL Server 2008 R2 and Visual Studio 2010 are also the last versions to support Itanium.
- ^ «Microsoft Dropping Itanium Support – Redmond Channel Partner». Redmond Channel Partner. Retrieved 2018-05-14.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Catalog (search=Itanium)». Retrieved 2023-03-20.
- ^ «Itanium KB4552965 direct link». Retrieved 2023-03-20.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reviewers Guide». Microsoft. November 2008. Archived from the original on February 5, 2009. Retrieved 2009-08-31.
- ^ «Understanding DNSSEC in Windows». Technet.microsoft.com. 2009-10-07. Retrieved 2011-06-15.
- ^ «New features in DHCP for Windows Server 2008 R2/Windows 7». Blogs.technet.com. Archived from the original on March 1, 2009. Retrieved 2011-06-15.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2: Scalability for the Enterprise Customer». Microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 13, 2008. Retrieved 2011-06-15.
- ^ «Windows7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 support more than 64 Processors in one System». Microsoft. November 2008. Archived from the original on December 17, 2008. Retrieved 2009-03-06.
- ^ «R2: How Would You Manage Without It?». MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on May 8, 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ «Appendix of Functional Level Features». Microsoft Technet. Retrieved 2009-10-06.
- ^ «Server 2008 R2: Active Directory Functional Levels». Praetorian Prefect. Archived from the original on October 12, 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-06.
- ^ «Windows 7 users: Move to SP1 to continue receiving Microsoft support». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Retrieved February 14, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 End-of-Life Support is Near». June 24, 2019. Retrieved October 26, 2019.
- ^ Winder, Davey (August 11, 2019). «Critical Windows 10 Warning: Millions Of Users At Risk». Forbes. Retrieved August 11, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1». Archived from the original on February 11, 2011.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2008 R2: System Requirements». Microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved 2011-06-15.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Editions Comparison by Technical Specifications». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 22 December 2010.
- ^ Archiveddocs. «What’s New in Distributed File System». technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
External links[edit]
- Windows Server 2008 R2 on Microsoft TechNet
- Thurrott, Paul (6 October 2010). «Windows Server 2008 R2 Preview». Supersite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 10, 2011.
- Convert Windows Server 2008 R2 to Workstation
Hardware
Software
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 1992-2020 Майкролэб Инвестмент |