I’ve got a Windows Server 2003 R2 Standard SP2 running. When I try to connect to this server using Remote Desktop I get the following error popup:
«The system cannot log you on due to the following error: The RPC server is unavailable.»
In the event log of the server I get the following event:
«Logon rejected for Domain\administrator. Unable to obtain Terminal Server User Configuration. Error: The RPC server is unavailable.» (Source: Winlogon, Event ID: 1219)
What can I do to fix this problem? I got no clue which RPC server this refers to.
asked Nov 9, 2009 at 12:01
Create the following Registry key
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
Name: IgnoreRegUserConfigErrors
Type: REG_DWORD
Value: 1
Reboot the server, and try logging in via RDP.
Massimo
70.4k57 gold badges200 silver badges324 bronze badges
answered Aug 1, 2013 at 4:13
user183932user183932
511 silver badge2 bronze badges
3
Are there any other errors in the event log, not related to terminal services? We need to determine if this is a problem with Terminal Services, or with the RPC service.
I have often seen this error ‘TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper’ service running? I’ve often seen the fact that this service was stopped cause this error.
The fact that you have an error accessing your group policy file may be related. One thing you can try is to check if «File and Print Sharing» is enabled on the adapter your trying to RDP too, if its not, turn it on and see if you can connect then.
answered Nov 9, 2009 at 12:50
Sam CoganSam Cogan
38.8k6 gold badges79 silver badges115 bronze badges
6
I’m having the same problem. Do you find an answer for this?
I found this link http://support.microsoft.com/kb/555839 that says
There can be a few reasons for this problem:
1. Incorrect DNS settings. 2. Incorrect Time and Time zone settings. 3. The "TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper" service isn't running. 4. The "Remote Registry" service isn't running.
I have checked all of these and file and print sharing and still get the error.
answered Aug 31, 2010 at 13:28
Adam ButlerAdam Butler
3793 silver badges10 bronze badges
Check it is accessible the Domain controller by \\<domain Controller>
Check the date, time and Time Zone
Check if any AV/firewall is blocking the traffic(software/hardware) or any traffic filtering device block the traffic
sysadmin1138♦
133k18 gold badges176 silver badges300 bronze badges
answered Jan 1, 2014 at 6:42
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Dear All
Recently I am facing remote desktop login problem in on Windows 2003 Server.
While I am enter user name and password server give me logon error.«The system cannot log you on due to the following error:
The RPC server is unavailable.Please try again or consult your system administrator.
Kindly help me………
Answers
-
Hi Michael,
Try putting this registry key in your regedit
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
Create a new kwy selecting Dword and name it as IgnoreRegUserConfigErrors
now double click it and give a value as 1
Now try doing an RDP it should work for you .
It should work for you .
This issue is normally seen in 2003 servers and suggest using my fix only on 2003 servers.
Senior Windows Server System Administrator
-
Proposed as answer by
Monday, April 9, 2012 9:18 PM
-
Edited by
Pankajvg
Thursday, July 26, 2012 4:59 AM
Update on server version -
Marked as answer by
Yagmoth555MVP
Thursday, September 3, 2015 11:41 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
Hi,
Whenever u face such an issue…goto ur domain controller machine. Open up services.msc
here u can check for two services :-1.Computer browser and
2.Secondary logon.Somehow these two services might have stopped. Just restart these services n u will be able to login
-
Marked as answer by
Sainath IRP_MJ_CREATE
Thursday, August 26, 2010 1:37 AM
-
Marked as answer by
-
Hi Goel,
please remember RPC is service independent , it completely relies on IPC ( interprocess communication ) and developers uses this technology to develop stable client server applications which helps in calling different subroutines.
And to answer your question , every service will be hosted by the SCM and SCM itself is a RPC server so falling back to different services ( computer broswer and secon logon) doesnt validate unless we have concrete technical evidence
Remember service can either run in its own process or can be shared. So we need to check the components involved in the error
sainath
!analyze-
Marked as answer by
Sainath IRP_MJ_CREATE
Thursday, August 26, 2010 1:37 AM
-
Marked as answer by
-
Hi,
Whenever u face such an issue…goto ur domain controller machine. Open up services.msc
here u can check for two services :-1.Computer browser and
2.Secondary logon.Somehow these two services might have stopped. Just restart these services n u will be able to login
Thanks, you saved my day! I had the same problem, then noticed that the Computer Browser service on my domain controller was down. Starting the service solved the problem.
-
Marked as answer by
Sainath IRP_MJ_CREATE
Thursday, August 26, 2010 1:37 AM
-
Marked as answer by
I’ve got a Windows Server 2003 R2 Standard SP2 running. When I try to connect to this server using Remote Desktop I get the following error popup:
«The system cannot log you on due to the following error: The RPC server is unavailable.»
In the event log of the server I get the following event:
«Logon rejected for Domain\administrator. Unable to obtain Terminal Server User Configuration. Error: The RPC server is unavailable.» (Source: Winlogon, Event ID: 1219)
What can I do to fix this problem? I got no clue which RPC server this refers to.
asked Nov 9, 2009 at 12:01
Create the following Registry key
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
Name: IgnoreRegUserConfigErrors
Type: REG_DWORD
Value: 1
Reboot the server, and try logging in via RDP.
Massimo
70.4k57 gold badges200 silver badges324 bronze badges
answered Aug 1, 2013 at 4:13
user183932user183932
511 silver badge2 bronze badges
3
Are there any other errors in the event log, not related to terminal services? We need to determine if this is a problem with Terminal Services, or with the RPC service.
I have often seen this error ‘TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper’ service running? I’ve often seen the fact that this service was stopped cause this error.
The fact that you have an error accessing your group policy file may be related. One thing you can try is to check if «File and Print Sharing» is enabled on the adapter your trying to RDP too, if its not, turn it on and see if you can connect then.
answered Nov 9, 2009 at 12:50
Sam CoganSam Cogan
38.8k6 gold badges79 silver badges115 bronze badges
6
I’m having the same problem. Do you find an answer for this?
I found this link http://support.microsoft.com/kb/555839 that says
There can be a few reasons for this problem:
1. Incorrect DNS settings. 2. Incorrect Time and Time zone settings. 3. The "TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper" service isn't running. 4. The "Remote Registry" service isn't running.
I have checked all of these and file and print sharing and still get the error.
answered Aug 31, 2010 at 13:28
Adam ButlerAdam Butler
3793 silver badges10 bronze badges
Check it is accessible the Domain controller by \\<domain Controller>
Check the date, time and Time Zone
Check if any AV/firewall is blocking the traffic(software/hardware) or any traffic filtering device block the traffic
sysadmin1138♦
133k18 gold badges176 silver badges300 bronze badges
answered Jan 1, 2014 at 6:42
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
The RPC server is unavailable, Windows Server 2003.
Hello Everyone,
I’ve searched and found similar issues, but this one is interesting.
I am trying to remote desktop connect to a win2k3 server in our domain. When doing so I get the following error:
The RPC server is unavailable.
Please try again or consult your system administrator.
I was able to connect fine until today, the only changes have been an installation of SQL Server 2005 and a recruiting tool called WinSearch. The strange thing is I have mapped network drives on this particular server that I can access with no problem. Also, when I try to login locally to the server, it just hangs during the login process. I enter user name and password, and it hangs for about an hour.
Any ideas?
Thanks
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The RPC Server
- The RPC Client
- RPC Quick Fixes
- Unable to resolve DNS or NetBIOS names in an Active Directory environment.
- The RPC service or related services may not be started
- Network Connectivity
- Verify ports needed by RPC are open
- File and Printer Sharing is not enabled
- Name Resolution
- DNS Name Resolution
- NetBIOS Name Resolution
- TCP Session Establishment
- Firewall/Network
- RPC Discovery
- Discovery — RPC Over TCPIP
- Discovery — RPC Over SMB
- RPC Communication
- How to identify the RPC traffic in a trace
- RPC over TCPIP
- RPC over HTTP Port 80
- RPC over HTTP Port 443
- RPC over SMB aka “Named Pipes”
- Kerberos Authentication
- NTLM Authentication
- Troubleshooting Authentication
- Active Directory Symptoms:
- Troubleshooting Tools and Methods
- Methods to generate RPC Traffic
- Tools for Testing RPC
- Tools for monitoring RPC
- Using PortQry
- Resources
- RPC Blogs
- External TechNet Magazine article
- KB Article
Introduction
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is an inter-process communication technique to allow client and server software to communicate on a network. The RPC protocol is based on a client/server model. The client makes a procedure call that appears to be local but is
actually run on a remote computer. During this process, the procedure call arguments are bundled and passed through the network to the server. The arguments are then unpacked and run on the server. The result is again bundled and passed back to the client,
where it is converted to a return value for the client’s procedure call.
RPC is used by several components in Windows Server, such as the File Replication Service (FRS), Active Directory Replication, Certificate services, DCOM, domain join, DCPromo and RDP, NLB and Cluster, Microsoft Operations Master, Exchange and SQL.
An RPC server is a communications interface provided by an application or service that allows remote clients to connect, pass commands, and transfer data using the RPC protocol. A typical example of an RPC server is Microsoft Exchange Server. Microsoft Exchange
Server is an application running on a computer that supplies an RPC communications interface for an RPC client.
An application will register its RPC server with the operating system’s End Point Mapper (EPM) service so that the remote client can locate the RPC server. When the application registers with the EPM it will indicate the IP address and TCP port that it is
listening on.
The RPC Client
An RPC client is an application running on any given computer that uses the RPC protocol to communicate with an RPC server. An example of a typical RPC client is the Microsoft Outlook application.
NOTE: In this document the terms RPC server and
RPC client refer to the application running at both ends of an RPC communication.
↑
Back to top
RPC Quick Fixes
Common causes of RPC errors include:
- Errors resolving a DNS or NetBIOS name.
- The RPC service or related services may not be running.
- number of connectivity Problems with network connectivity.
- File and printer sharing is not enabled.
Use the following procedures to diagnose and repair common causes of RPC errors.
Unable to resolve DNS or NetBIOS names in an Active Directory environment.
- Use the following commands to verify DNS is working for all DC’s or specific DC’s:
- To get a DNS status for all DCs in forest, run the following command:
- DCDIAG /TEST:DNS /V /E /F:<filename.log>
- The «/e» switch runs the DNS test against all DCs in an Active Directory Forest
- To get DNS health on a single DC, run the command below.
- DCDIAG /TEST:DNS /V /S:<DCNAME> /F:<filename.log>
- The «/s:» switch runs the DNS test against a specified domain controller.
- To verify that a domain controller can be located for a specific domain, run the command below.
- NLTEST /DSGETDC:<NetBIOS or DNS domain name>
- Servers and clients that are receiving the error should be checked to verify that they are configured with the appropriate DNS server. Servers should not be pointing to their ISP’s DNS servers in the preferred or alternate DNS server portion of the TCP/IP
settings. The ISP’s DNS servers should only be used as forwarders in DNS.
- Ensure that at least one correct DNS record is registered on each domain controller.
- To ensure that a correct DNS record is registered on each domain controller, find this server’s Active Directory replication partners that run DNS.
- Open DNSManager and connect in turn to each of these replication partners.
- Find the host (A) resource record registration for this server on each of the other replication partner domain controllers.
- Delete those host (A) records that do not have IP addresses corresponding to any of this server’s IP addresses.
- If a domain controller has no host (A) records for this server, add at least one that corresponds to an IP address on this server. (If there are multiple IP addresses for this server, add at least one that is on the same network as the domain controller
you are updating.)
- Name resolution may also fail with the RPC Server is unavailable error if NetBIOS over TCP/IP is disabled on the WINS tab in the advanced section of the TCP/IP properties. The NetBIOS over TCP/IP setting should be either enabled or default (use DHCP).
- Verify that a single label domain name is not being configured. DNS names that do not contain a suffix such as .com, .corp, .net, .org or .local are considered to be single-label DNS names. Microsoft doesn’t recommend using single label domain names because
they cannot be registered with an Internet registrar and domain members do not perform dynamic updates to single-label DNS zones. Knowledge base article
826743 — «Clients cannot dynamically register DNS records in a single-label domain» provides instructions on how to configure your domain to allow dynamic registration of DNS records in a single label domain.
The RPC service or related services may not be started
Verify the status and startup type for the RPC and RPC locator services on the server that gets the error:
- By default, Windows server 2003 domain controllers and member servers all should have the RPC service started and set to Automatic startup and the RPC Locator service stopped and set to Manual Startup.
- Windows 2000 domain controllers should have the RPC and RPC Locator services both set to started and automatic startup, while Windows 2000 member servers should have the RPC service started and set to automatic startup while the RPC locator service should
be started and set to manual startup. - If you make any changes to the RPC service or to the RPC Locator service settings, restart the computer, and then test for the problem again.
- Additional Services that may result in «The RPC Server is Unavailable» errors are the TCP/IP NetBIOS helper service, Distributed File System service and Remote Registry service. These services should both be set to automatic and started. The Kerberos Key
Distribution Center (KDC) should be Started and Automatic on Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 DCs. It should not be started and set to Disabled in all other cases.
↑
Back to top
Network Connectivity
Verify ports needed by RPC are open
Verify that ports greater than 1024 are not blocked. Clients connect to RPC Endpoint Mapper on port 135. RPC Endpoint Mapper then tells the client which randomly assigned port between 1024-65535 a requested service is listening on.
Ports may be blocked by a hardware firewall or a software firewall. Software firewalls include Internet Connection Firewall on computers running Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP, and Windows Firewall on computers running Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows
Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. A computer might also have third-party firewall software installed, or antivirus software with built-in firewall functionality. By default, port 135 TCP/UDP and ports 1024-65535 TCP must be open for RPC to work. You
can restrict the ports greater than 1024 that RPC uses. However, RPC Endpoint Mapper is always on port 135.
File and Printer Sharing is not enabled
File and Printer sharing for Microsoft Networks will produce the error RPC Server is unavailable” when you try to view or manage services on a remote computer using the Services snap-in. See the following example:
Unable to open service control manager database on \<computer>.
Error 1722: The RPC server is unavailable.
This error message may occur if the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks component is not enabled on the remote computer.
Troubleshooting RPC
The process of an RPC client connecting to an RPC server can be broken down into four phases. This troubleshooting guide will discuss the events that occur at each phase, how to test these events, and how to identify if the phase completed successfully.
Phase 1: Name Resolution: Name resolution is the act of resolving a name to an IP address. This normally takes two forms: NetBIOS Name Resolution or the more common DNS Name Resolution.
Phase 2: TCP session establishment: TCP session establishment is the act of establishing a TCP connection between the RPC client and the RPC server. TCP sessions will be initiated by the RPC client via a TCP 3-way handshake with the RPC
server.
Phase 3: RPC Discovery: When a client wants to connect to the RPC server supplied by the application it will contact the computer that hosts the RPC Server and discover how to connect to the RPC Server.
Phase 4: RPC Communication: RPC Communication is the act of making RPC requests to the application endpoint and receiving RPC responses from this application.
Data needed to troubleshoot the issue:
- Identify the client and server computers reporting the RPC error. Identify the DNS and WINS servers used by these computers. To do this:
- On each machine, open a command prompt and run ipconfig /all.
- Determine the IP address of both machines. If the server is part of a cluster get the cluster resource IP address as well. Identify the DNS servers and WINS servers that the RPC client is configured to use.
Note: You can also obtain this information by opening Control PanelNetwork and Sharing Center, clicking Local Area Connection and selecting Properties.
- Identify the application(s) reporting RPC Server Unavailable
- Simultaneous network traces (using Wireshark, Netmon, or a comparable network sniffer) from the machines hosting the RPC client and RPC Server while reproducing the task that results in a “RPC Server Unavailable” error.
- The network captures on both hosts should be started first.
- From a command prompt on the client run ipconfig /flushdns and nbtstat –R to clear the name resolution caches.
- Reproduce the error.
- Stop the traces and save them.
↑
Back to top
Name Resolution
Name Resolution consists of one or possibly more NetBIOS or DNS queries to locate the IP address for the RPC Server. Troubleshooting this phase requires verifying that a response is received to the name resolution request and that the response contains the
correct IP address for the RPC server. Compare the IP address reported by DNS or NetBIOS in the network trace for the server with the IP addresses you noted earlier. If it does not match then check DNS and WINS and note if there is a difference.
DNS Name Resolution
To identify DNS Name Resolution in a network trace use the following filter in Network Monitor or Wireshark: dns. DNS resolution will be occurring at the client so open the network trace taken from the RPC client machine. You will be looking for one packet
that is the query from the client to the DNS server and then the response packet from the DNS server. It will look similar to this:
If the trace shows the correct IP address for the RPC server was returned by the DNS server proceed to TCP Session Establishment.
If the trace does not show a correct IP address returned or you do not see any answer from the DNS server then reference the following resources to help with DNS name resolution troubleshooting.
For details on troubleshooting Active Directory related DNS issues go
here.
For general DNS troubleshooting:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;330511
NetBIOS Name Resolution
NetBIOS queries come in two forms, WINS or NetBIOS Broadcasts. WINS will consist of a unicast query to a WINS server and a response from the WINS server.
NetBIOS broadcasts are queries broadcast to all hosts on the local subnet so name resolution is limited to only hosts on the subnet. The host with the name listed in the NetBIOS Broadcast will respond with its IP address.
To identify NetBIOS Name Resolution in a network trace, use the following filter in Network Monitor — “nbtns”. For Wireshark, use the following filter — nbns”. If the trace shows a successful resolution using WINS or NetBIOS queries proceed to TCP Session
Establishment.
For details on troubleshooting this NetBIOS Name Resolution further:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc940110.aspx
TCP Session Establishment
TCP Sessions always begin with a TCP 3-way handshake. The handshake should look similar to what is shown below. The RPC Client will send the first packet, known as the SYN packet. The computer hosting the RPC Server will send a SYN/ACK response, and then
the RPC Client will send an ACK packet.
Scenarios that may cause the TCP session to fail
Firewall/Network
If a firewall or network problem is the culprit, it is likely a failure will occur during this phase. To diagnose this you will want to look at the network traces taken from the RPC Client and RPC Server. If a firewall or other network device is causing a problem
it will usually manifest as a retransmit of the TCP SYN packet by the RPC Client about 3 seconds after the first TCP SYN is sent. This can be seen in a Netmon network trace using the display filter specification of “tcpsynretransmit==1”. In other cases, firewalls
will allow the 3-way handshake to succeed but may block the RPC packets due to the contents of the packet at a higher level. In these cases it is possible to see the retransmit of the RPC packet within half a second of the original packet being sent. To identify
this condition in a Netmon network trace use the display filter specification of “tcpretransmit==1”. To see either of these retransmit conditions in a trace taken using Wireshark use the display filter specification of “tcp.analysis.retransmission”.
The RPC Server is not actively listening.
It was noted earlier that an RPC Server will register itself and listen on a particular port and IP address of the host computer. If for some reason that fails the TCP layer will answer the SYN packet from the client with a Reset packet.
A device in the middle between the RPC Client and RPC Server will be resetting the connection attempt.
In the client side trace it will appear as if the server sent the TCP Reset while the trace from the server indicates the client is the source of the TCP Reset.
For both these scenarios, check for the presence of a Reset packet in the TCP three way handshake by using the display filter specification of “TCP.flags.reset==1”.
For troubleshooting this step see the following sections in this document:
- How to identify RPC traffic in a trace
- Connectivity
- RPC Services
- RPC Client Registry
If the 3-way handshake is successful, continue to the RPC Discovery phase.
↑
Back to top
RPC Discovery
The RPC Discovery phase will occur one of two ways. In both methods the client will know the identifier for the RPC Server it wants to contact and will supply that to the computer hosting the RPC Server and ask for information on how to contact the RPC Server.
The identifier is different depending on which method is used and the RPC client will know ahead of time which method it wishes to use.
Discovery — RPC Over TCPIP
This method is a two-step process. First the RPC client will contact the End Point Mapper (EPM) on the machine hosting the RPC Server to find out what port and IP address that Server is listening on. Upon successful completion of this the RPC client will
contact the RPC Server directly on the indicated IP address and Port. Below is a sample of what this would look like and a step by step explanation below it. This step depends on the successful TCP session establishment twice, first to the EPM and then to
the RPC Server.
- The RPC Client will open a TCP session with TCP port 135 on the computer hosting RPC Server of interest. This can be picked out using the following filter syntax in Netmon or Wireshark: “tcp.port==135”
- The RPC Client will send an RPC Bind request using the UUID of the End Point Mapper and the RPC EPM should respond with a Bind ACK packet.
- The RPC Client will make a MAP request to the EPM to locate the IP address and port of the RPC Server of interest, identifying the RPC Server based on its UUID.
- The EPM will send back a MAP Response that indicates the IP and port the RPC Server is listening on.
- The RPC Client will then open a TCP session with the IP and port it received in the EPM MAP response.
- The client will send an RPC Bind Request to the RPC Server specifying the UUID of the RPC Server application and should get back a Bind ACK from the RPC Server.
- There will be an RPC Alter Context Request/Response in which authentication will take place. If an error is noted here then see the following section for help determining why the error is occurring —
Authentication
- Perform some RPC operations…(Go to RPC Communication phase)
Discovery — RPC Over SMB
The second method an RPC Client may use to contact an RPC Server is RPC over SMB. This method depends upon first establishing an SMB session with the computer hosting the RPC Server and then using the Named Pipes protocol to communicate using RPC. So in
effect there are several levels of encapsulation – RPC over Named Pipes over SMB over TCP. We will not address the SMB session setup in this document and the TCP session establishment has already been discussed.
With a successfully opened TCP and SMB session, next:
- The RPC Client will issue a SMB TreeConnectAndX for the tree name “IPC$”. This is a special hidden share for inter-process communication. It should get a positive response from the computer hosting the RPC Server.
- The RPC Client will then issue an SMB NTCreateAndX for the name of the PIPE of the RPC Server Application and should get back a positive response. Some examples are:
EVENTLOG = The Event log service
winreg = Remote Registry
svcctl = Service Control Manager
srvsvc = Server Service
- Next there is a Bind handshake. This is to “bind” the RPC client to the RPC server. There are a total of four packets involved:
- The RPC Client bind request containing the UUID of the desired RPC Server.
- A Write AndX response from the RPC Server
- A Read AndX request from the RPC Client.
- A Bind ACK response from the RPC Server.
- At this time a RPC request to the RPC server component is expected.
RPC Communication
At this point RPC communication is occurring between the RPC Client and RPC Server. The troubleshooting steps involved at this stage are largely based on the application reporting the RPC failure.
For Active Directory processes or services please see
Active Directory Symptoms.
For Microsoft Exchange related RPC errors please see:
Analyzing Exchange RPC traffic over TCP/IP
↑
Back to top
How to identify the RPC traffic in a trace
RPC network traffic can take multiple forms. It is important to understand which form is in use in order to identify which TCP session is responsible for the RPC communication.
RPC over TCPIP
This is sometimes referred to as Traditional RPC or Sockets based RPC. An example of this is Outlook without “Outlook anywhere” or without http settings configured. A TCP session on TCP port 135 is established with the RPC server. To view this traffic in
a trace use the filter: “tcp.port==135”. This session will be used in the RPC Discovery phase to locate the endpoint of the desired application.
RPC over HTTP
RPC connectivity for Internet connected hosts will typically use RPC over HTTP in order to traverse firewalls. Some examples of this can be seen with Terminal Services Gateway, Outlook Web Access, Outlook via “Outlook Anywhere”. This communication will be
established on one or more connections to either TCP port 80 or 443(SSL). Since this typically traverses a public network, SSL or TCP port 443 is the more common method. Use the filter “tcp.port==80 or tcp.port==443” to locate either form inside network trace.
RPC over HTTP Port 80
For sessions over TCP port 80, the HTTP requests associated with RPC over HTTP will include a UserAgent header that contains the text “OutlookConnectorDS” and the version number of the connector.
RPC over HTTP Port 443
Sessions using TCP port 443 will initially establish a TLS session. After this TLS negotiation, the TCP Payload will be encrypted in TLS/SSL and the contents of the frames will not be readable in the trace. In this phase, look for failures due to improper
certificates, inaccessible Certificate Revocation Lists, or untrusted certificate chains.
For more information on troubleshooting SSL/TLS see:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc783349(WS.10).aspx
↑
Back to top
RPC over SMB aka “Named Pipes”
RPC can also take advantage of SMB sessions for the purpose of RPC communication. Some examples of this can be seen with Computer Management or the Remote Registry service. With the use of RPC over SMB:
- Establish TCP connection on TCP port 139 or 445.
- Negotiate dialect request/response
- SessionSetupANDX request/response. This sequence is used to establish the SMB Session. Authentication occurs during the SessionSetupANDX exchange.
If a failure in step 1 occurs, see additional troubleshooting steps see:
File and Printer Sharing.
Kerberos Authentication
If Kerberos is used, and the client doesn’t currently have a Kerberos ticket for the RPC server, just after the Negotiate Dialect response is received, the client will obtain a Kerberos ticket for the Servername/cifs SPN of the RPC server. This exchange
will occur over the Kerberos ports TCP or UDP port 88 between the client and a Domain Controller. SessionSetupANDX follows and will consist of a single SessionSetupANDX request which includes the Kerberos ticket, followed by a SessionSetupANDX Response indicating
success or failure of the authentication.
For additional troubleshooting steps during authentication, see
Authentication.
NTLM Authentication
If NTLM is used, SessionSetup will result in a SessionSetupANDX response with a status of STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED. This response includes the NTLM challenge. The subsequent SessionSetupANDX Request will include the hashed credentials of the client.
At this time, the RPC server must validate the credentials supplied by the user. To do this, the RPC server will contact a domain controller, and validate the credentials with the netlogon service, via RPC, on the domain controller. If this is successful,
the RPC server will then respond to the client with a SessionSetupANDX Response indicating STATUS_SUCCESS.
For additional troubleshooting steps during authentication, see
Authentication.
Troubleshooting Authentication
Verify that authentication is working correctly by checking for Time skew, UDP Fragmentation or an Invalid Kerberos Realm.
- Time skew can be verified by running net time /querysntp and net time /setsntp:<PDCe server name>. The /querysntp switch allows you to determine if a specific DC is manually configured as the authoritative time server. The /setsntp:<PDCe server name> switch
can be used to synchronize the computer receiving the error with the PDC emulator. The PDC emulator is the authoritative time server by default. - UDP fragmentation can cause replication errors that appear to have a source of RPC server is unavailable. Symptoms of UDP fragmentation being at the root of this problem include clients being unable to log on to the domain, administrators being unable
join computers to the domain and Event ID 40960 & 40961 errors with a source of LSASRV and Kerberos errors with an Event ID of 10 in the system log.Knowledge base article 244474 — «How to force Kerberos to use TCP instead of UDP in Windows Server 2003, in Microsoft Windows and XP, and in Microsoft Windows 2000» provides the steps to resolve this
problem. - An incorrect Kerberos realm can also be at the root of RPC server is unavailable problems. The symptoms that will be experience when the Kerberos realm is incorrect include the following errors when opening AD management tools:
Naming Convention could not be located because: No authority could be contacted for authentication. Contact your system administrator to verify that your domain is properly configured and is currently online.
-or-
Naming information cannot be located because: No authority could be contacted for authentication. Contact your system administrator to verify that your domain is properly configured and is currently online.
To verify that the correct Kerberos realm is configured, follow the steps in 837513 — «Domain controller is not functioning correctly».
↑
Back to top
Active Directory Symptoms:
1. If you are experiencing replication problems and getting RPC server is unavailable errors as is reported in repadmin /showreps below, use Portqry or Network Monitor to determine if RPC traffic is being blocked is the first step when attempting
to troubleshoot RPC Server is unavailable errors.
[Replications Check,DC2] A recent replication attempt failed:
From DC1 to DC2
Naming Context: CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=xl
The replication generated an error (1722):
The RPC server is unavailable.
The failure occurred at 2003-10-30 11:59.47.
The last success occurred at 2003-10-28 20:50.22.
26 failures have occurred since the last success.
[DC1] DsBind() failed with error 1722,
The RPC server is unavailable..
The source remains down. Please check the machine.
BermudaDC1 via RPC objectGuid: 28c78c72-3c95-499a-bcda137a250f069f
Last attempt @ 2003-10-30 11:58.15 failed, result 1722:
The RPC server is unavailable.
Troubleshooting: If IP Security Policies in Active Directory had the Assigned Value to Server (Request Security) set to Yes then these errors will result. Knowledge base article 313190
— «How to use IPSec IP filter lists in Windows 2000» provide details about where to check these settings and more information about their impact.
2. If you are blocking all ICMP traffic between separate AD sites, you will receive the errors below in the output of DCDIAG when trying to replicate inter-site:
Testing server: contosoDC1
Starting test: Replications
* Replications Check
[Replications Check,DC1] A recent replication attempt failed:
From DC2 to DC1
Naming Context: CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=litware,DC=com
The replication generated an error (1722):
The RPC server is unavailable.
The failure occurred at 2003-08-24 23:00.51.
The last success occurred at (never).
553 failures have occurred since the last success.
[DC2] DsBind() failed with error 1722,
The RPC server is unavailable..
The source remains down. Please check the machine.
REPLICATION LATENCY WARNING
DC1: A full synchronization is in progress
from DC2 to DC1
Replication of new changes along this path will be delayed.
[DC2] LDAP connection failed with error 58,
The specified server cannot perform the requested operation.
Troubleshooting: To resolve this issue, remove the ICMP traffic restriction between domain controllers. When establishing an RPC session prior to AD replication, ICMP traffic is used. If the ICMP fails, so does the RPC session establishment,
and hence AD replication also fails. ISA 2004 can prevent ICMP traffic with the exception of computers specified in the Remote Management Computers computer set which can be configured in system policy.
3. The following error will appear when attempting to connect to the computer.
«computer <\servername.domain.local> cannot be managed. The network path was not found. RPC server is unavailable.
Or when viewing the properties of the remote computer you will receive the error:
«Win32: The RPC server is unavailable».
Troubleshooting: Computer management is one of the better tools for testing RPC connectivity. When RPC traffic is being blocked, connections to other computers using the computer management console will fail.
4. When attempting to promote an additional domain controller in an Active Directory domain while the RPC service is blocked or not running, the following error will appear:
«The domain «domain.local» is not an Active Directory domain, or an Active Directory domain controller for the domain could not be contacted.
Troubleshooting:
5. Connections to computers via Remote Desktop may fail if RPC connectivity cannot be established. When attempting to logon on to the domain via Remote Desktop the following error will be produced in the form of a popup error message if RPC connectivity
is the root of the problem:
«The system cannot log you on due to the following error: The RPC server is unavailable.”
You may also see the following errors on the Terminal server:
Error 1727: The remote procedure call failed and did not execute
Error 1722: The RPC server is unavailable.
Error 1723: The RPC server is too busy to complete this operation.
Error 1721: Not enough resources are available to complete this operation.
-or-
Event ID 5719:
Source: NetLogon
Description: No Windows NT Domain Controller is available for domain domain_name.
The following error occurred: There are currently no logon servers available to
service the logon request.
Event ID: 1219
Source: Winlogon
Details: Logon rejected for CONTOSO<computername>. Unable to obtain Terminal Server
User
Configuration. Error: The RPC server is unavailable.
Troubleshooting: These errors can be a result of the TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper service being disabled on the Terminal server or NetBIOS over TCP/IP being disabled on one of the NIC’s used to access the Terminal server. You should also verify
that the Client for Microsoft networks is bound to the adapter used to access the Terminal server. You can tell if this is happening by looking at a Netdiag /v from the box for the following output:
Testing redirector and browser… Failed
NetBT transports test. . . . . . . : Failed
List of NetBt transports currently configured:
[FATAL] No NetBt transports are configured.
Redir and Browser test . . . . . . : Failed
List of transports currently bound to the Redir
NetBIOSSmb
[FATAL] The redir isn’t bound to any NetBt transports.
List of transports currently bound to the browser
[FATAL] The browser isn’t bound to any NetBt transports.
↑
Back to top
Troubleshooting Tools and Methods
Methods to generate RPC Traffic
Computer Management MMC to a remote host
Outlook to an Exchange server
RPCPing — http://support.microsoft.com/kb/831051
Tools for Testing RPC
RPCPing — http://support.microsoft.com/kb/831051
PortQry —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;832919
Pipelist —
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/dd581625.aspx
RPCDump —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;325930
NSLookup —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;200525
NBLookup —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;830578
Tools for monitoring RPC
Network Monitor —
Download –
FAQ
Wireshark — Download
Using PortQry
You can use the Portqry tool to verify that the required ports are open. You should run the Portqry tool on a computer that is not receiving any RPC errors against a computer that is receiving RPC errors by using the -n switch. To this, follow these steps:
a. Click «Start», click «Run», type «cmd» in the «Open» box, and then click OK».
b. Type «portqry -n <problem_server> -e 135» (without the quotation marks).
The output will appear similar to the following examples:
Querying target system called:
<problem_server>
Attempting to resolve name to IP address…
Name resolved to 169.254.1.1
querying…
<problem_server>
TCP port 135 (epmap service): LISTENING
Using ephemeral source port
Querying Endpoint Mapper Database…
Server’s response:
UUID: f5cc59b4-4264-101a-8c59-08002b2f8426 NtFrs Service
ncacn_ip_tcp:65.53.63.16[1094]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_ip_tcp:65.53.63.16[1025]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_http:65.53.63.16[1029]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_http:65.53.63.16[6004]
If port 135 is blocked, the following will appear:
TCP port 135 (epmap service): NOT LISTENING However, for these RPC Endpoint Mapper errors it is likely that ports greater than 1024 are blocked, and not port 135.From the output, you know the DC is using port 1094 for FRS and 1025, 1029, and 6004 for Active
Directory replication. You can use the Portqry tool again to check those ports. For example, you can test all the ports at the same time by using the Portqry tool with the -o switch. For example, type
«portqry -n <problem_server> -o 1094,1025,1029,6004″(Without the quotation marks)
If the ports all respond as «LISTENING,» it’s likely that blocked ports are not causing this problem. If any ports respond as «NOT LISTENING,» the ports are probably blocked.
↑
Back to top
Resources
RPC Blogs
Basics of RPC are covered here:
RPC to Go v.1:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2008/10/24/rpc-to-go-v-1.aspx
Architecture and a closer look at a connection to the RPC Endpoint mapper in a network capture.
RPC to Go v.2:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2008/12/04/rpc-to-go-v-2.aspx
This describes how RPC commands can be sent over Named Pipes in SMB via the IPC$ Tree.
RPC to Go v.3:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2009/04/28/rpc-to-go-v-3-named-pipes.aspx
Troubleshooting “RPC server is unavailable” error, reported in failing
AD replication scenario.
http://blogs.technet.com/b/abizerh/archive/2009/06/11/troubleshooting-rpc-server-is-unavailable-error-reported-in-failing-ad-replication-scenario.aspx
External TechNet Magazine article
This one is good. It lays out RPC basics really quickly and then moves on RPC errors. The information on MaxUserPort would need to be updated with the information about the dynamic port ranges that are used in Vista/W2008 are the high range of ports compared
to the 1025-5000 for W2003.
How IT Works, Troubleshooting RPC Errors by Zubair Alexander:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/2007.07.howitworks.aspx
KB Article
Troubleshooting RPC Endpoint Mapper errors using the Windows Server 2003 Support Tools from the product CD
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/839880/troubleshooting-rpc-endpoint-mapper-errors-using-the-windows-server-20
↑
Back to top
Обновлено 15.02.2022
Добрый день! Уважаемые читатели и гости одного из крупнейших IT блогов в рунете Pyatilistnik.org. В прошлый раз мы с вами разобрали замечательную утилиту командной строки robocopy, и с ее помощью научились создавать точные копии папок, двигать их в нужное расположение и многое другое. В сегодняшней публикации я покажу вам, как устранять ошибку «Сервер RPC недоступен (The rpc server is unavailable)», покажу примеры, когда ее мониторинг очень важен в работе корпоративных сервисов.
Для чего нужна служба «Удаленный вызов процедур (RPC)»
Удаленный вызов процедур (RPC) — это протокол, который одна программа может использовать для запроса услуги у программы, расположенной на другом компьютере в сети, без необходимости разбираться в деталях сети. RPC используется для вызова других процессов на удаленных системах, таких как локальная система. Вызов процедуры также иногда называют вызовом функции или вызовом подпрограммы .
RPC использует модель клиент-сервер. Запрашивающая программа — это клиент, а программа, предоставляющая услуги, — это сервер. Подобно обычному или локальному вызову процедуры, RPC — это синхронная операция, требующая приостановки запрашивающей программы до тех пор, пока не будут возвращены результаты удаленной процедуры. Однако использование облегченных процессов или потоков, которые совместно используют одно и то же адресное пространство, позволяет одновременно выполнять несколько RPC.
Язык определения интерфейса (IDL) — язык спецификации, используемый для описания интерфейса прикладного программирования (API) программного компонента — обычно используется в программном обеспечении удаленного вызова процедур. В этом случае IDL обеспечивает мост между машинами на обоих концах связи, которые могут использовать разные операционные системы (ОС) и компьютерные языки.
Процедура сообщения RPC
Когда программные операторы, использующие структуру RPC, компилируются в исполняемую программу, в скомпилированный код включается заглушка, которая выступает в качестве представителя кода удаленной процедуры. Когда программа запускается и выполняется вызов процедуры, заглушка получает запрос и пересылает его клиентской программе и времени выполнения на локальном компьютере. При первом вызове клиентской заглушки она связывается с сервером имен, чтобы определить транспортный адрес, по которому находится сервер.
Программа среды выполнения клиента знает, как обращаться к удаленному компьютеру и серверному приложению, и отправляет сообщение по сети, которое запрашивает удаленную процедуру. Точно так же сервер включает исполняющую программу и заглушку, которая взаимодействует с самой удаленной процедурой. Протоколы ответа-запроса возвращаются таким же образом.
Данная служба есть в любой операционной системе Windows, начиная от Windows 7 и заканчивая Windows 11 и в любой из Windows Server редакции.
Как работает RPC?
Когда вызывается служба RPC (удаленный вызов процедуры), вызывающая среда приостанавливается, параметры процедуры передаются по сети в среду, в которой должна выполняться процедура, а затем процедура выполняется в этой среде. Когда процедура завершается, результаты передаются обратно в вызывающую среду, где выполнение возобновляется, как если бы оно возвращалось из обычного вызова процедуры.
Во время RPC выполняются следующие шаги:
- Клиент вызывает клиентскую заглушку. Вызов представляет собой вызов локальной процедуры с параметрами, помещенными в стек обычным способом.
- Клиентская заглушка упаковывает параметры процедуры в сообщение и выполняет системный вызов для отправки сообщения. Упаковка параметров процедуры называется маршалингом.
- Локальная ОС клиента отправляет сообщение с клиентского компьютера на удаленный сервер.
- Серверная ОС передает входящие пакеты на серверную заглушку.
- Заглушка сервера распаковывает параметры из сообщения — это называется демаршалингом .
- Когда серверная процедура завершается, она возвращается к серверной заглушке, которая маршалирует возвращаемые значения в сообщение. Затем заглушка сервера передает сообщение на транспортный уровень.
- Транспортный уровень отправляет полученное сообщение обратно на клиентский транспортный уровень, который возвращает сообщение клиентской заглушке.
- Клиентская заглушка не упорядочивает возвращаемые параметры, и выполнение возвращается вызывающей стороне.
Клиент RPC по 135 порту подключается к службе RPC Endpoint Mapper (сопоставления конечных точек), а далее уже запрашивает номер порта, где запущено нужное RPC приложение. Служба сопоставления конечных точек вернет клиенту RPC номер динамического RPC порта (диапазон 1024 – 65535), на котором работает нужная служба. Дальше уже все взаимодействие идет по TCP порту
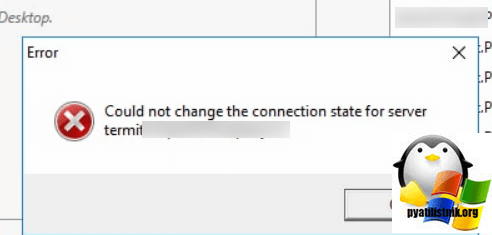
Если вы видите ошибку «Сервер RPC недоступен” (The RPC server is unavailable)», то у вас точно недоступен порт 135. Это может быть критичным для ряда ситуации. Например вы не сможете сохранить настройки RDS фермы, если у одного из хостов RDSH есть проблемы с RPC, то вы будите видеть ошибку «Could not change the connection state for server», вы не сможете перевести его в режим обслуживания (Drain Mode)
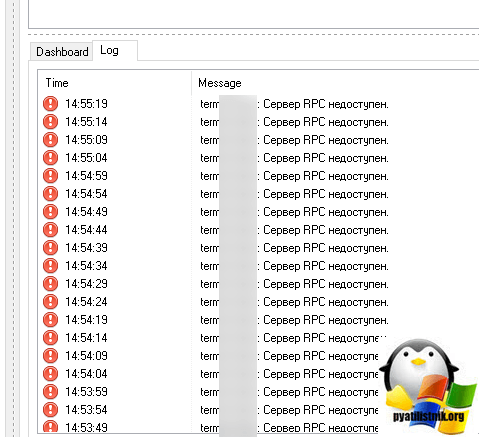
Или в приложении Terminal Services Manager будет ошибка при попытке получения данных «Сервер RPC недоступен«.
Так же RPC может быть причиной проблемы в репликации контроллеров домена, где в логах Windows будет фигурировать ошибка ID 1722. Это очень не приятный момент, который может привести к большим проблемам.
Типы RPC
Существует пять типов RPC:
- Обычный метод работы, при котором клиент выполняет вызов и не продолжает работу до тех пор, пока сервер не вернет ответ.
- Клиент звонит и продолжает свою обработку. Сервер не отвечает.
- Средство для отправки нескольких клиентских неблокирующих вызовов в одном пакете.
- У клиентов RPC есть средство широковещательной рассылки, т. е. Они могут отправлять сообщения на множество серверов, а затем получать все полученные ответы.
- Клиент делает неблокирующий вызов клиент/сервер; сервер сигнализирует о завершении вызова путем вызова процедуры, связанной с клиентом.
Почему может не работать служба RPC
- Удаленный компьютер с которым идет взаимодействие выключен
- На удаленном сервере не запущена или перестала работать служба RPC
- Подключение по RPC происходит не к тому серверу (Может быть проблема с DNS или IP адресом)
- Есть блокировки между клиентом и сервером на фаэрволе
- Используются некорректные настройки сетевого подключение на клиенте или сервере
Преимущества удаленного вызова процедур
К преимуществам удаленного вызова процедур можно отнести следующее:
- помогает клиентам общаться с серверами посредством традиционного использования вызовов процедур на языках высокого уровня;
- может использоваться как в распределенной, так и в локальной среде;
- поддерживает процессно-ориентированные и поточно-ориентированные модели;
- скрывает внутренний механизм передачи сообщений от пользователя;
- требует минимальных усилий для переписывания и повторной разработки кода;
- обеспечивает абстракцию, т. е. характер передачи сообщений по сети скрыт от пользователя;
- опускает многие уровни протокола для повышения производительности.
Недостатки RPC
Некоторые из недостатков RPC включают следующее:
- Клиент и сервер используют разные среды выполнения для своих соответствующих подпрограмм, и использование ресурсов, например файлов, также является более сложным. Следовательно, системы RPC не подходят для передачи больших объемов данных.
- RPC очень уязвим для сбоев, потому что он включает в себя систему связи, другую машину и другой процесс.
- Единого стандарта для RPC не существует; это может быть реализовано множеством способов.
- RPC основан только на взаимодействии и, как таковой, не предлагает гибкости, когда дело касается аппаратной архитектуры.
Проверка доступности службы RPC
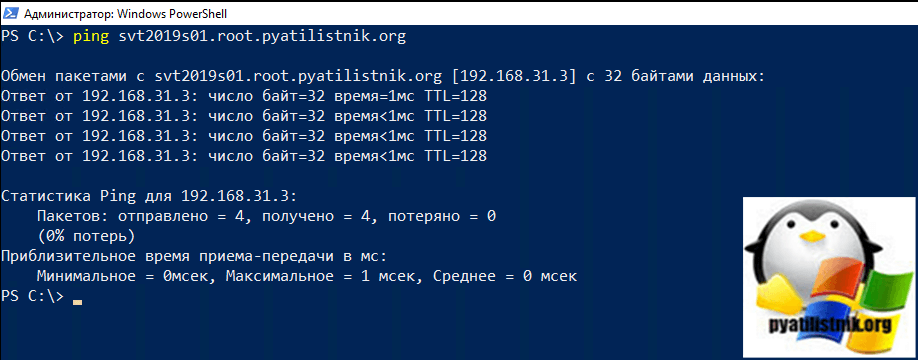
- Как я и писал выше, в первую очередь вы должны убедиться, что удаленный компьютер к которому вы делаете проверку RPC доступен по сети. Для этого элементарно откройте командную строку или оболочку PowerShell и воспользуйтесь командой Ping, NSlookup, Test-NetConnection. Я буду производить проверку службы удаленного вызова в PowerShell. Выполним для начала команду Ping. Мой удаленный сервер называется SVT201S01.root.pyatilistnik.org. Пишем команду:
ping SVT201S01.root.pyatilistnik.org
Если вдруг компьютер не ответил, то это не значит, что он не работает, может работать брандмауэр и просто блокировать ping пакеты.
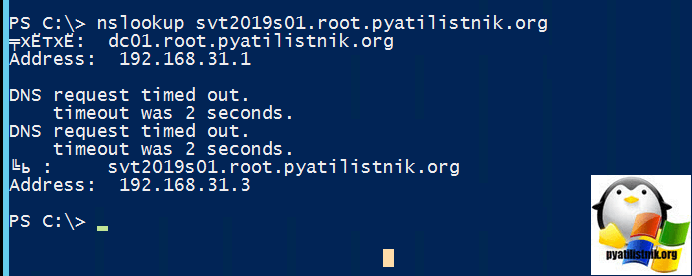
- Далее выполните Nslookup, чтобы удостовериться, что нужное вам имя компьютера преобразовывается в нужный IP-адрес. Выполните:
nslookup SVT201S01.root.pyatilistnik.org
Небольшой пример из практики, предположим, что вы мигрировали сервер в другую подсеть, в итоге в DNS должна быть изменена соответствующая запись, но Windows это поймет не сразу, так как у нее есть свой локальный кэш, он живет 15 минут, поэтому если при проверке DNS имени вам выдается не тот IP-адрес, вам необходимо произвести очистку кэша DNS.
- Далее я вам советую проверить отвечает ли порт. Напоминаю, что служба RPC Endpoint Mapper слушает порт под номером 135. В PowerShell введите команду:
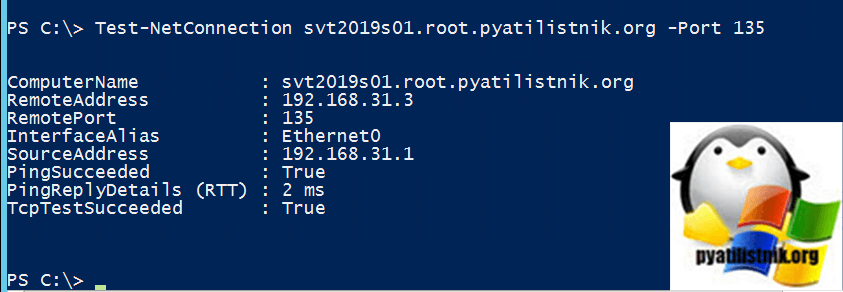
Test-NetConnection svt2019s01.root.pyatilistnik.org -Port 135
Если удаленный RPC порт доступен вы в в строке TcpTestSucceeded будет стоять статус «True».
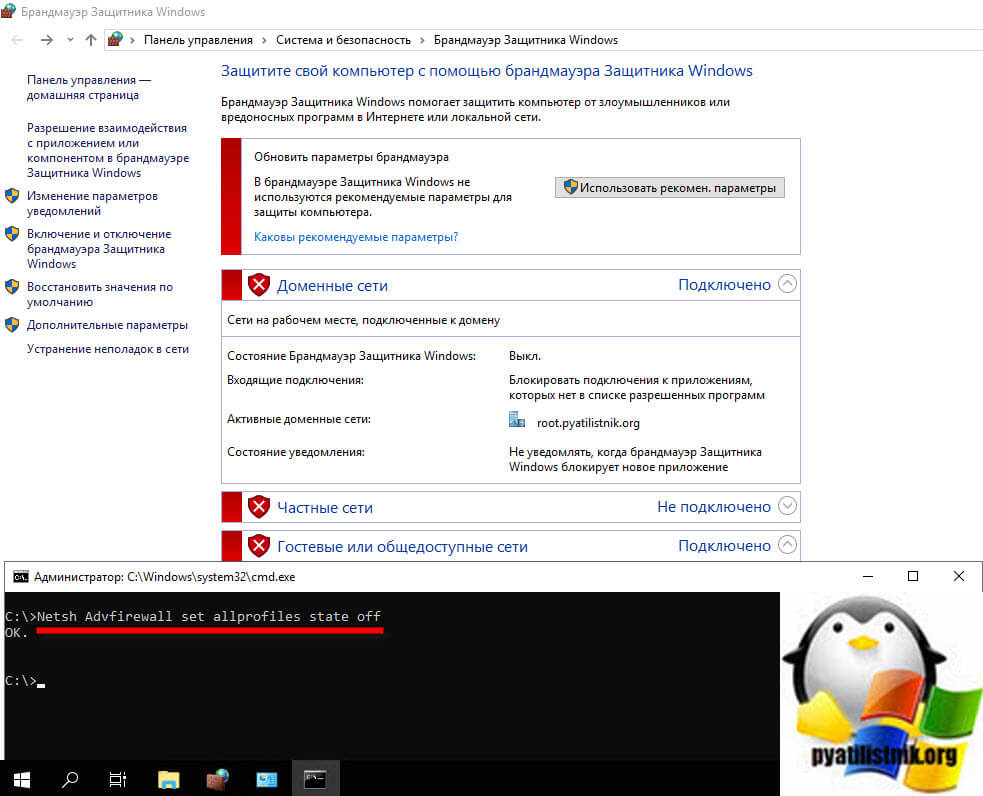
Если будет порт закрыт или блокируется, то ошибка «Сервер RPC недоступен (The rpc server is unavailable)» вам обеспечена. Поняв, что порт не отвечает, нужно удостовериться, что трафик от клиента до сервера не блокирует фаервол. По умолчанию в любой версии Windows есть встроенный брандмауэр. На время тестирования и поиска причины, я советую его выключить для всех профилей. Сделаем мы это через командную строку:
Netsh Advfirewall set allprofiles state off
Данная команда выключит брандмауэр на всех трех профилях сетевой карты.
Далее если порт 135 стал доступен, то можно делать правила на удаленном сервере. Напоминаю, что нужно сделать правило для трех служб:
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC) — Удаленный вызов процедур (RPC)
- RPC Endpoint Mapper — Сопоставитель конечных точек RPC
- COM Server Process Launcher — Модуль запуска процессов DCOM-сервера
Подробнее, о том как сделать правила — https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/windows-firewall/create-inbound-rules-to-support-rpc)
Еще хочу отметить, что если у вас есть сторонние антивирусные решения, например Касперский, то там так же есть встроенный сетевой экран, где так же нужно будет создать необходимые, разрешающие правила, которые корректно будут обрабатывать трафик динамических RPC портов.
Проверка работы служб RPC
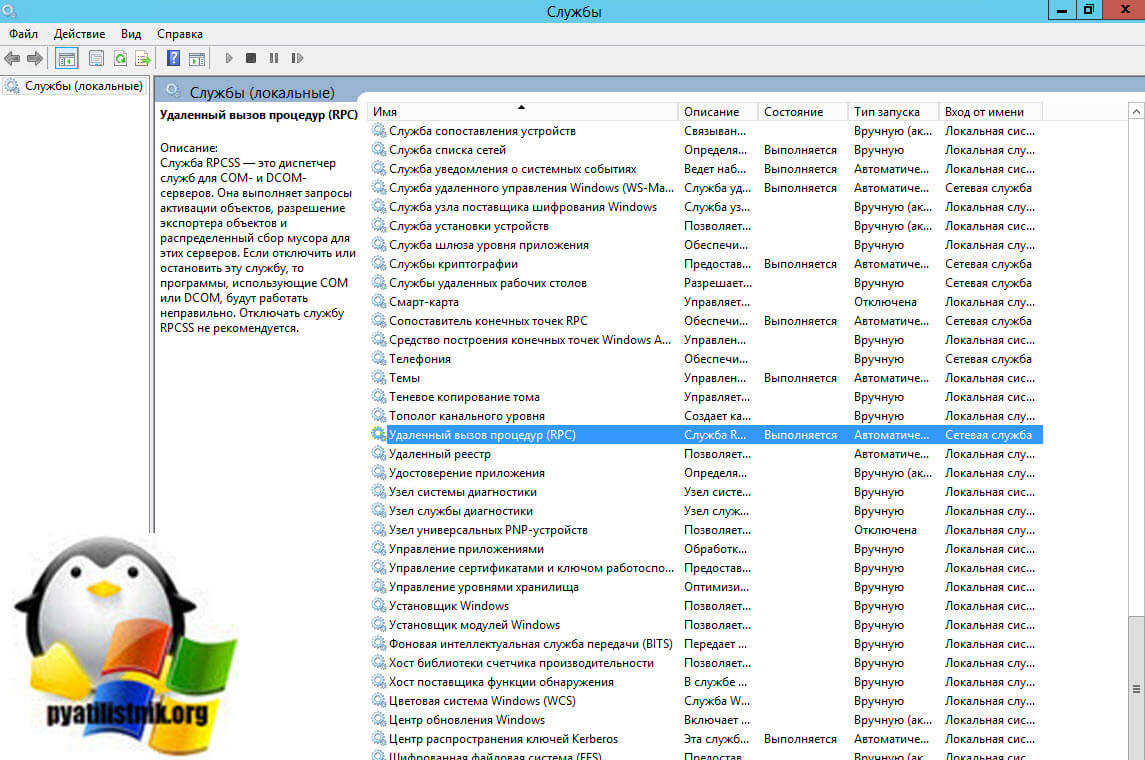
Следующим шагом является проверка состояния службы на нужном вам сервере или компьютере. Проверять следует три службы:
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC) — Удаленный вызов процедур (RPC)
- RPC Endpoint Mapper — Сопоставитель конечных точек RPC
- COM Server Process Launcher — Модуль запуска процессов DCOM-сервера
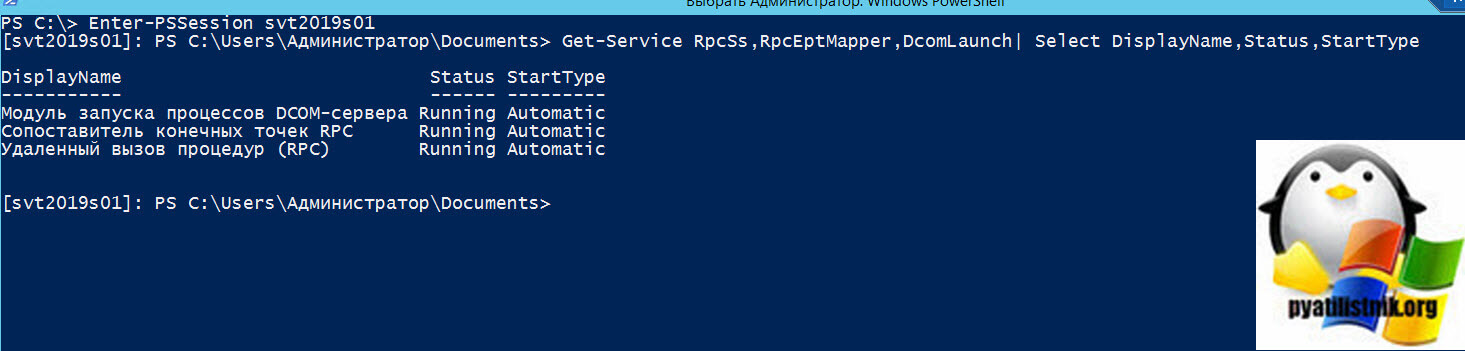
В оболочке PowerShell выполните команду:
Для локального сервера — Get-Service RpcSs,RpcEptMapper,DcomLaunch| Select DisplayName,Status,StartType
Для удаленного выполнения Enter-PSSession svt2019s01 далее Get-Service RpcSs,RpcEptMapper,DcomLaunch| Select DisplayName,Status,StartType
Напоминаю, что в команде svt2019s01, это имя удаленного сервера. Как видно из примера, все службы RPC запущены и имею автоматический тип запуска.
Если службы не запущены, то откройте оснастку «services.msc’, зайдите в свойства службы и выставите автозапуск и попробуйте запустить вручную.
Если по каким, то причинам вы не можете запустить службу из оснастки, то можно это сделать через реестр (Кстати реестр можно править и удаленно). Для этого есть несколько веток, но для начала откройте окно «Выполнить» и введите regedit.
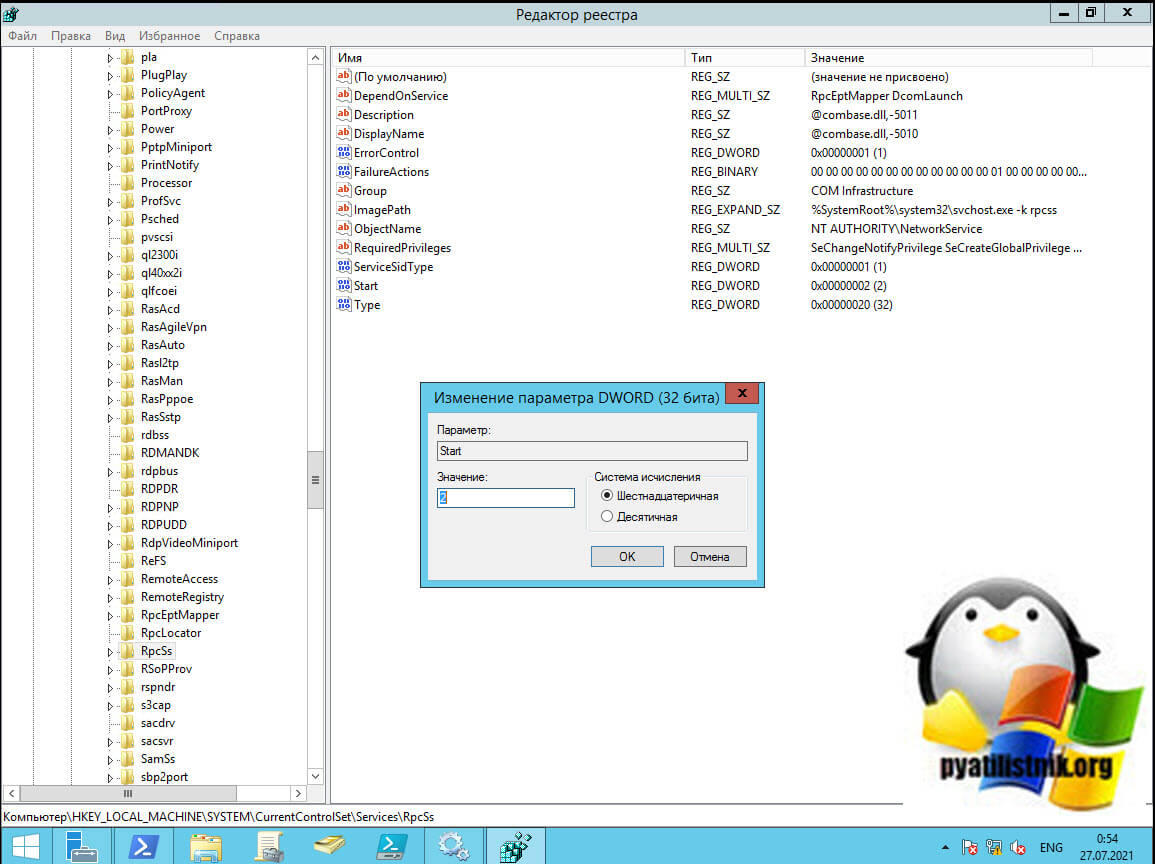
- Модуль запуска процессов DCOM-сервера — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesDcomLaunch
- Сопоставитель конечных точек RPC — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesRpcEptMapper
- Удаленный вызов процедур (RPC) — ветка реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesRpcSs
В каждом из этих расположений есть ключик «Start«, выставите ему значение «2«, это будет означать автоматический запуск службы.
Дополнительные сетевые проверки
В некоторых случаях причиной ошибок с доступностью RPC выступает сбой на сетевых адаптерах. Помогает сброс сетевых настроек и перезагрузка. В сети с Active Directory, старайтесь, чтобы на всех ваших сетевых адаптерах в свойствах были выставлены обе галки IPV4 и IPV6, особенно это актуально для контроллеров домена, где вы легко можете получать ошибку 1722. Еще может помочь отключение протокола Teredo у IPv6. В командной строке выполните:
netsh interface teredo set state disabled
Для включения обратно введите:
netsh interface teredo set state enabled
Еще на сайте Майкрософт пишут, что необходимо на сервере RPC иметь включенную службу «Удаленный реестр«. На этом у меня все, с вами был Иван Сёмин, автор и создатель IP портала Pyatilistnik.org.
Refer – http://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/4494.troubleshooting-the-rpc-server-is-unavailable.aspx
Introduction
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is an inter-process communication technique to allow client and server software to communicate on a network. The RPC protocol is based on a client/server model. The client makes a procedure call that appears to be local but is actually run on a remote computer. During this process, the procedure call arguments are bundled and passed through the network to the server. The arguments are then unpacked and run on the server. The result is again bundled and passed back to the client, where it is converted to a return value for the client’s procedure call.
RPC is used by several components in Windows Server, such as the File Replication Service (FRS), Active Directory Replication, Certificate services, DCOM, domain join, DCPromo and RDP, NLB and Cluster, Microsoft Operations Master, Exchange and SQL.
The RPC Server
An RPC server is a communications interface provided by an application or service that allows remote clients to connect, pass commands, and transfer data using the RPC protocol. A typical example of an RPC server is Microsoft Exchange Server. Microsoft Exchange Server is an application running on a computer that supplies an RPC communications interface for an RPC client.
An application will register its RPC server with the operating system’s End Point Mapper (EPM) service so that the remote client can locate the RPC server. When the application registers with the EPM it will indicate the IP address and TCP port that it is listening on.
The RPC Client
An RPC client is an application running on any given computer that uses the RPC protocol to communicate with an RPC server. An example of a typical RPC client is the Microsoft Outlook application.
NOTE: In this document the terms RPC server and RPC client refer to the application running at both ends of an RPC communication.
RPC Quick Fixes
Common causes of RPC errors include:
- Errors resolving a DNS or NetBIOS name.
- The RPC service or related services may not be running.
- Problems with network connectivity.
- File and printer sharing is not enabled.
Use the following procedures to diagnose and repair common causes of RPC errors.
Unable to resolve DNS or NetBIOS names in an Active Directory environment
- Use the following commands to verify DNS is working for all DC’s or specific DC’s:
- To get a DNS status for all DCs in forest, run the following command:
- DCDIAG /TEST:DNS /V /E /F:<filename.log>
- The «/e» switch runs the DNS test against all DCs in an Active Directory Forest
To get DNS health on a single DC, run the command below.
- DCDIAG /TEST:DNS /V /S:<DCNAME> /F:<filename.log>
- The «/s:» switch runs the DNS test against a specified domain controller.
To verify that a domain controller can be located for a specific domain, run the command below.
- NLTEST /DSGETDC:<NetBIOS or DNS domain name>
- Servers and clients that are receiving the error should be checked to verify that they are configured with the appropriate DNS server. Servers should not be pointing to their ISP’s DNS servers in the preferred or alternate DNS server portion of the TCP/IP settings. The ISP’s DNS servers should only be used as forwarders in DNS.
- Ensure that at least one correct DNS record is registered on each domain controller.
- To ensure that a correct DNS record is registered on each domain controller, find this server’s Active Directory replication partners that run DNS.
- Open DNSManager and connect in turn to each of these replication partners.
- Find the host (A) resource record registration for this server on each of the other replication partner domain controllers.
- Delete those host (A) records that do not have IP addresses corresponding to any of this server’s IP addresses.
- If a domain controller has no host (A) records for this server, add at least one that corresponds to an IP address on this server. (If there are multiple IP addresses for this server, add at least one that is on the same network as the domain controller you are updating.)
- Name resolution may also fail with the RPC Server is unavailable error if NetBIOS over TCP/IP is disabled on the WINS tab in the advanced section of the TCP/IP properties. The NetBIOS over TCP/IP setting should be either enabled or default (use DHCP).
- Verify that a single label domain name is not being configured. DNS names that do not contain a suffix such as .com, .corp, .net, .org or .local are considered to be single-label DNS names. Microsoft doesn’t recommend using single label domain names because they cannot be registered with an Internet registrar and domain members do not perform dynamic updates to single-label DNS zones. Knowledge base article 826743
– «Clients cannot dynamically register DNS records in a single-label domain» provides instructions on how to configure your domain to allow dynamic registration of DNS records in a single label domain.
The RPC service or related services may not be started
Verify the status and startup type for the RPC and RPC locator services on the server that gets the error:
- By default, Windows server 2003 domain controllers and member servers all should have the RPC service started and set to Automatic startup and the RPC Locator service stopped and set to Manual Startup.
- Windows 2000 domain controllers should have the RPC and RPC Locator services both set to started and automatic startup, while Windows 2000 member servers should have the RPC service started and set to automatic startup while the RPC locator service should be started and set to manual startup.
- If you make any changes to the RPC service or to the RPC Locator service settings, restart the computer, and then test for the problem again.
- Additional Services that may result in «The RPC Server is Unavailable» errors are the TCP/IP NetBIOS helper service, Distributed File System service and Remote Registry service. These services should both be set to automatic and started. The Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) should be Started and Automatic on Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 DCs. It should not be started and set to Disabled in all other cases.
Network Connectivity
Verify ports needed by RPC are open
Verify that ports greater than 1024 are not blocked. Clients connect to RPC Endpoint Mapper on port 135. RPC Endpoint Mapper then tells the client which randomly assigned port between 1024-65535 a requested service is listening on.
Ports may be blocked by a hardware firewall or a software firewall. Software firewalls include Internet Connection Firewall on computers running Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP, and Windows Firewall on computers running Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. A computer might also have third-party firewall software installed, or antivirus software with built-in firewall functionality. By default, port 135 TCP/UDP and ports 1024-65535 TCP must be open for RPC to work. You can restrict the ports greater than 1024 that RPC uses. However, RPC Endpoint Mapper is always on port 135.
File and Printer Sharing is not enabled
File and Printer sharing for Microsoft Networks will produce the error “RPC Server is unavailable” when you try to view or manage services on a remote computer using the Services snap-in. See the following example:
Unable to open service control manager database on <computer>.
Error 1722: The RPC server is unavailable.
This error message may occur if the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks component is not enabled on the remote computer.
Troubleshooting RPC
The process of an RPC client connecting to an RPC server can be broken down into four phases. This troubleshooting guide will discuss the events that occur at each phase, how to test these events, and how to identify if the phase completed successfully.
Phase 1: Name Resolution: Name resolution is the act of resolving a name to an IP address. This normally takes two forms: NetBIOS Name Resolution or the more common DNS Name Resolution.
Phase 2: TCP session establishment: TCP session establishment is the act of establishing a TCP connection between the RPC client and the RPC server. TCP sessions will be initiated by the RPC client via a TCP 3-way handshake with the RPC server.
Phase 3: RPC Discovery: When a client wants to connect to the RPC server supplied by the application it will contact the computer that hosts the RPC Server and discover how to connect to the RPC Server.
Phase 4: RPC Communication: RPC Communication is the act of making RPC requests to the application endpoint and receiving RPC responses from this application.
Data needed to troubleshoot the issue:
- Identify the client and server computers reporting the RPC error. Identify the DNS and WINS servers used by these computers. To do this:
- On each machine, open a command prompt and run ipconfig /all.
- Determine the IP address of both machines. If the server is part of a cluster get the cluster resource IP address as well. Identify the DNS servers and WINS servers that the RPC client is configured to use.
Note: You can also obtain this information by opening Control PanelNetwork and Sharing Center, clicking Local Area Connection and selecting Properties.
- Identify the application(s) reporting RPC Server Unavailable
- Simultaneous network traces (using Wireshark, Netmon, or a comparable network sniffer) from the machines hosting the RPC client and RPC Server while reproducing the task that results in a “RPC Server Unavailable” error.
- The network captures on both hosts should be started first.
- From a command prompt on the client run ipconfig /flushdns and nbtstat –R to clear the name resolution caches.
- Reproduce the error.
- Stop the traces and save them.
Name Resolution
Name Resolution consists of one or possibly more NetBIOS or DNS queries to locate the IP address for the RPC Server. Troubleshooting this phase requires verifying that a response is received to the name resolution request and that the response contains the correct IP address for the RPC server. Compare the IP address reported by DNS or NetBIOS in the network trace for the server with the IP addresses you noted earlier. If it does not match then check DNS and WINS and note if there is a difference.
DNS Name Resolution
To identify DNS Name Resolution in a network trace use the following filter in Network Monitor or Wireshark: “dns”. DNS resolution will be occurring at the client so open the network trace taken from the RPC client machine. You will be looking for one packet that is the query from the client to the DNS server and then the response packet from the DNS server. It will look similar to this:
If the trace shows the correct IP address for the RPC server was returned by the DNS server proceed to TCP Session Establishment.
If the trace does not show a correct IP address returned or you do not see any answer from the DNS server then reference the following resources to help with DNS name resolution troubleshooting.
For details on troubleshooting Active Directory related DNS issues go here.
For general DNS troubleshooting: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;330511
NetBIOS Name Resolution
NetBIOS queries come in two forms, WINS or NetBIOS Broadcasts. WINS will consist of a unicast query to a WINS server and a response from the WINS server.
NetBIOS broadcasts are queries broadcast to all hosts on the local subnet so name resolution is limited to only hosts on the subnet. The host with the name listed in the NetBIOS Broadcast will respond with its IP address.
To identify NetBIOS Name Resolution in a network trace, use the following filter in Network Monitor – “nbtns”. For Wireshark, use the following filter – ”nbns”. If the trace shows a successful resolution using WINS or NetBIOS queries proceed to TCP Session Establishment.
For details on troubleshooting this NetBIOS Name Resolution further:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc940110.aspx
TCP Session Establishment
TCP Sessions always begin with a TCP 3-way handshake. The handshake should look similar to what is shown below. The RPC Client will send the first packet, known as the SYN packet. The computer hosting the RPC Server will send a SYN/ACK response, and then the RPC Client will send an ACK packet.
Scenarios that may cause the TCP session to fail
Firewall/Network
If a firewall or network problem is the culprit, it is likely a failure will occur during this phase. To diagnose this you will want to look at the network traces taken from the RPC Client and RPC Server. If a firewall or other network device is causing a problem it will usually manifest as a retransmit of the TCP SYN packet by the RPC Client about 3 seconds after the first TCP SYN is sent. This can be seen in a Netmon network trace using the display filter specification of “tcpsynretransmit==1”. In other cases, firewalls will allow the 3-way handshake to succeed but may block the RPC packets due to the contents of the packet at a higher level. In these cases it is possible to see the retransmit of the RPC packet within half a second of the original packet being sent. To identify this condition in a Netmon network trace use the display filter specification of “tcpretransmit==1”. To see either of these retransmit conditions in a trace taken using Wireshark use the display filter specification of “tcp.analysis.retransmission”.
The RPC Server is not actively listening.
It was noted earlier that an RPC Server will register itself and listen on a particular port and IP address of the host computer. If for some reason that fails the TCP layer will answer the SYN packet from the client with a Reset packet.
A device in the middle between the RPC Client and RPC Server will be resetting the connection attempt.
In the client side trace it will appear as if the server sent the TCP Reset while the trace from the server indicates the client is the source of the TCP Reset.
For both these scenarios, check for the presence of a Reset packet in the TCP three way handshake by using the display filter specification of “TCP.flags.reset==1”.
For troubleshooting this step see the following sections in this document:
- How to identify RPC traffic in a trace
- Connectivity
- RPC Services
- RPC Client Registry
If the 3-way handshake is successful, continue to the RPC Discovery phase.
RPC Discovery
The RPC Discovery phase will occur one of two ways. In both methods the client will know the identifier for the RPC Server it wants to contact and will supply that to the computer hosting the RPC Server and ask for information on how to contact the RPC Server. The identifier is different depending on which method is used and the RPC client will know ahead of time which method it wishes to use.
Discovery – RPC Over TCPIP
This method is a two-step process. First the RPC client will contact the End Point Mapper (EPM) on the machine hosting the RPC Server to find out what port and IP address that Server is listening on. Upon successful completion of this the RPC client will contact the RPC Server directly on the indicated IP address and Port. Below is a sample of what this would look like and a step by step explanation below it. This step depends on the successful TCP session establishment twice, first to the EPM and then to the RPC Server.
- The RPC Client will open a TCP session with TCP port 135 on the computer hosting RPC Server of interest. This can be picked out using the following filter syntax in Netmon or Wireshark: “tcp.port==135”
- The RCP Client will send an RPC Bind request using the UUID of the End Point Mapper and the RPC EPM should respond with a Bind ACK packet.
- The RPC Client will make a MAP request to the EPM to locate the IP address and port of the RPC Server of interest, identifying the RPC Server based on its UUID.
- The EPM will send back a MAP Response that indicates the IP and port the RPC Server is listening on.
- The RPC Client will then open a TCP session with the IP and port it received in the EPM MAP response.
- The client will send an RPC Bind Request to the RPC Server specifying the UUID of the RPC Server application and should get back a Bind ACK from the RPC Server.
- There will be an RPC Alter Context Request/Response in which authentication will take place. If an error is noted here then see the following section for help determining why the error is occurring – Authentication
- Perform some RPC operations…(Go to RPC Communication phase)
Discovery – RPC Over SMB
The second method an RPC Client may use to contact an RPC Server is RPC over SMB. This method depends upon first establishing an SMB session with the computer hosting the RPC Server and then using the Named Pipes protocol to communicate using RPC. So in effect there are several levels of encapsulation – RPC over Named Pipes over SMB over TCP. We will not address the SMB session setup in this document and the TCP session establishment has already been discussed.
With a successfully opened TCP and SMB session, next:
- The RPC Client will issue a SMB TreeConnectAndX for the tree name “IPC$”. This is a special hidden share for inter-process communication. It should get a positive response from the computer hosting the RPC Server.
- The RPC Client will then issue an SMB NTCreateAndX for the name of the PIPE of the RPC Server Application and should get back a positive response. Some examples are:
EVENTLOG = The Event log service
winreg = Remote Registry
svcctl = Service Control Manager
srvsvc = Server Service
- Next there is a Bind handshake. This is to “bind” the RPC client to the RPC server. There are a total of four packets involved:
- The RPC Client bind request containing the UUID of the desired RPC Server.
- A Write AndX response from the RPC Server
- A Read AndX request from the RPC Client.
- A Bind ACK response from the RPC Server.
At this time a RPC request to the RPC server component is expected.
RPC Communication
At this point RPC communication is occurring between the RPC Client and RPC Server. The troubleshooting steps involved at this stage are largely based on the application reporting the RPC failure.
For Active Directory processes or services please see Active Directory Symptoms.
For Microsoft Exchange related RPC errors please see: Analyzing Exchange RPC traffic over TCP/IP
How to identify the RPC traffic in a trace
RPC network traffic can take multiple forms. It is important to understand which form is in use in order to identify which TCP session is responsible for the RPC communication.
RPC over TCPIP
This is sometimes referred to as Traditional RPC or Sockets based RPC. An example of this is Outlook without “Outlook anywhere” or without http settings configured. A TCP session on TCP port 135 is established with the RPC server. To view this traffic in a trace use the filter: “tcp.port==135”. This session will be used in the RPC Discovery phase to locate the endpoint of the desired application.
RPC over HTTP
RPC connectivity for Internet connected hosts will typically use RPC over HTTP in order to traverse firewalls. Some examples of this can be seen with Terminal Services Gateway, Outlook Web Access, Outlook via “Outlook Anywhere”. This communication will be established on one or more connections to either TCP port 80 or 443(SSL). Since this typically traverses a public network, SSL or TCP port 443 is the more common method. Use the filter “tcp.port==80 or tcp.port==443” to locate either form inside network trace.
RPC over HTTP Port 80
For sessions over TCP port 80, the HTTP requests associated with RPC over HTTP will include a UserAgent header that contains the text “OutlookConnectorDS” and the version number of the connector.
RPC over HTTP Port 443
Sessions using TCP port 443 will initially establish a TLS session. After this TLS negotiation, the TCP Payload will be encrypted in TLS/SSL and the contents of the frames will not be readable in the trace. In this phase, look for failures due to improper certificates, inaccessible Certificate Revocation Lists, or untrusted certificate chains.
For more information on troubleshooting SSL/TLS see:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc783349(WS.10).aspx
RPC over SMB aka “Named Pipes”
RPC can also take advantage of SMB sessions for the purpose of RPC communication. Some examples of this can be seen with Computer Management or the Remote Registry service. With the use of RPC over SMB:
- Establish TCP connection on TCP port 139 or 445.
- Negotiate dialect request/response
- SessionSetupANDX request/response. This sequence is used to establish the SMB Session. Authentication occurs during the SessionSetupANDX exchange.
If a failure in step 1 occurs, see additional troubleshooting steps see: File and Printer Sharing.
Kerberos Authentication
If Kerberos is used, and the client doesn’t currently have a Kerberos ticket for the RPC server, just after the Negotiate Dialect response is received, the client will obtain a Kerberos ticket for the Servername/cifs SPN of the RPC server. This exchange will occur over the Kerberos ports TCP or UDP port 88 between the client and a Domain Controller. SessionSetupANDX follows and will consist of a single SessionSetupANDX request which includes the Kerberos ticket, followed by a SessionSetupANDX Response indicating success or failure of the authentication.
For additional troubleshooting steps during authentication, see Authentication.
NTLM Authentication
If NTLM is used, SessionSetup will result in a SessionSetupANDX response with a status of STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED. This response includes the NTLM challenge. The subsequent SessionSetupANDX Request will include the hashed credentials of the client. At this time, the RPC server must validate the credentials supplied by the user. To do this, the RPC server will contact a domain controller, and validate the credentials with the netlogon service, via RPC, on the domain controller. If this is successful, the RPC server will then respond to the client with a SessionSetupANDX Response indicating STATUS_SUCCESS.
For additional troubleshooting steps during authentication, see Authentication.
Troubleshooting Authentication
Verify that authentication is working correctly by checking for Time skew, UDP Fragmentation or an Invalid Kerberos Realm.
- Time skew can be verified by running net time /querysntp and net time /setsntp:<PDCe server name>. The /querysntp switch allows you to determine if a specific DC is manually configured as the authoritative time server. The /setsntp:<PDCe server name> switch can be used to synchronize the computer receiving the error with the PDC emulator. The PDC emulator is the authoritative time server by default.
- UDP fragmentation can cause replication errors that appear to have a source of RPC server is unavailable. Symptoms of UDP fragmentation being at the root of this problem include clients being unable to log on to the domain, administrators being unable join computers to the domain and Event ID 40960 & 40961 errors with a source of LSASRV and Kerberos errors with an Event ID of 10 in the system log.
Knowledge base article 244474
– «How to force Kerberos to use TCP instead of UDP in Windows Server 2003, in Microsoft Windows and XP, and in Microsoft Windows 2000» provides the steps to resolve this problem.
- An incorrect Kerberos realm can also be at the root of RPC server is unavailable problems. The symptoms that will be experience when the Kerberos realm is incorrect include the following errors when opening AD management tools:
Naming Convention could not be located because: No authority could be contacted for authentication. Contact your system administrator to verify that your domain is properly configured and is currently online.
-or-
Naming information cannot be located because: No authority could be contacted for authentication. Contact your system administrator to verify that your domain is properly configured and is currently online.
To verify that the correct Kerberos realm is configured, follow the steps in 837513
– «Domain controller is not functioning correctly».
Active Directory Symptoms:
1. If you are experiencing replication problems and getting RPC server is unavailable errors as is reported in repadmin /showreps below, use Portqry or Network Monitor to determine if RPC traffic is being blocked is the first step when attempting to troubleshoot RPC Server is unavailable errors.
[Replications Check,DC2] A recent replication attempt failed:
From DC1 to DC2
Naming Context: CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=xl
The replication generated an error (1722):
The RPC server is unavailable.
The failure occurred at 2003-10-30 11:59.47.
The last success occurred at 2003-10-28 20:50.22.
26 failures have occurred since the last success.
[DC1] DsBind() failed with error 1722,
The RPC server is unavailable..
The source remains down. Please check the machine.
BermudaDC1 via RPC objectGuid: 28c78c72-3c95-499a-bcda137a250f069f
Last attempt @ 2003-10-30 11:58.15 failed, result 1722:
The RPC server is unavailable.
Troubleshooting: If IP Security Policies in Active Directory had the Assigned Value to Server (Request Security) set to Yes then these errors will result. Knowledge base article 313190 
2. If you are blocking all ICMP traffic between separate AD sites, you will receive the errors below in the output of DCDIAG when trying to replicate inter-site:
Testing server: contosoDC1
Starting test: Replications
* Replications Check
[Replications Check,DC1] A recent replication attempt failed:
From DC2 to DC1
Naming Context: CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=litware,DC=com
The replication generated an error (1722):
The RPC server is unavailable.
The failure occurred at 2003-08-24 23:00.51.
The last success occurred at (never).
553 failures have occurred since the last success.
[DC2] DsBind() failed with error 1722,
The RPC server is unavailable..
The source remains down. Please check the machine.
REPLICATION LATENCY WARNING
DC1: A full synchronization is in progress
from DC2 to DC1
Replication of new changes along this path will be delayed.
[DC2] LDAP connection failed with error 58,
The specified server cannot perform the requested operation.
Troubleshooting: To resolve this issue, remove the ICMP traffic restriction between domain controllers. When establishing an RPC session prior to AD replication, ICMP traffic is used. If the ICMP fails, so does the RPC session establishment, and hence AD replication also fails. ISA 2004 can prevent ICMP traffic with the exception of computers specified in the Remote Management Computers computer set which can be configured in system policy.
3. The following error will appear when attempting to connect to the computer.
«computer <servername.domain.local> cannot be managed. The network path was not found. RPC server is unavailable.
Or when viewing the properties of the remote computer you will receive the error:
«Win32: The RPC server is unavailable».
Troubleshooting: Computer management is one of the better tools for testing RPC connectivity. When RPC traffic is being blocked, connections to other computers using the computer management console will fail.
4. When attempting to promote an additional domain controller in an Active Directory domain while the RPC service is blocked or not running, the following error will appear:
«The domain «domain.local» is not an Active Directory domain, or an Active Directory domain controller for the domain could not be contacted.
Troubleshooting:
5. Connections to computers via Remote Desktop may fail if RPC connectivity cannot be established. When attempting to logon on to the domain via Remote Desktop the following error will be produced in the form of a popup error message if RPC connectivity is the root of the problem:
«The system cannot log you on due to the following error: The RPC server is unavailable.”
You may also see the following errors on the Terminal server:
Error 1727: The remote procedure call failed and did not execute
Error 1722: The RPC server is unavailable.
Error 1723: The RPC server is too busy to complete this operation.
Error 1721: Not enough resources are available to complete this operation.
-or-
Event ID 5719:
Source: NetLogon
Description: No Windows NT Domain Controller is available for domain domain_name.
The following error occurred: There are currently no logon servers available to
service the logon request.
Event ID: 1219
Source: Winlogon
Details: Logon rejected for CONTOSO<computername>. Unable to obtain Terminal Server
User
Configuration. Error: The RPC server is unavailable.
Troubleshooting: These errors can be a result of the TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper service being disabled on the Terminal server or NetBIOS over TCP/IP being disabled on one of the NIC’s used to access the Terminal server. You should also verify that the Client for Microsoft networks is bound to the adapter used to access the Terminal server. You can tell if this is happening by looking at a Netdiag /v from the box for the following output:
Testing redirector and browser… Failed
NetBT transports test. . . . . . . : Failed
List of NetBt transports currently configured:
[FATAL] No NetBt transports are configured.
Redir and Browser test . . . . . . : Failed
List of transports currently bound to the Redir
NetBIOSSmb
[FATAL] The redir isn’t bound to any NetBt transports.
List of transports currently bound to the browser
[FATAL] The browser isn’t bound to any NetBt transports.
Troubleshooting Tools and Methods
Methods to generate RPC Traffic
Computer Management MMC to a remote host
Outlook to an Exchange server
RPCPing – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/831051
Tools for Testing RPC
RPCPing – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/831051
PortQry – http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;832919
Pipelist – http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/dd581625.aspx
RPCDump – http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;325930
NSLookup – http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;200525
NBLookup – http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;830578
Tools for monitoring RPC
Network Monitor – Download 
Wireshark – Download
Using PortQry
You can use the Portqry tool to verify that the required ports are open. You should run the Portqry tool on a computer that is not receiving any RPC errors against a computer that is receiving RPC errors by using the -n switch. To this, follow these steps:
a. Click «Start», click «Run», type «cmd» in the «Open» box, and then click OK».
b. Type «portqry -n <problem_server> -e 135» (without the quotation marks).
The output will appear similar to the following examples:
Querying target system called:
<problem_server>
Attempting to resolve name to IP address…
Name resolved to 169.254.1.1
querying…
<problem_server>
TCP port 135 (epmap service): LISTENING
Using ephemeral source port
Querying Endpoint Mapper Database…
Server’s response:
UUID: f5cc59b4-4264-101a-8c59-08002b2f8426 NtFrs Service
ncacn_ip_tcp:65.53.63.16[1094]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_ip_tcp:65.53.63.16[1025]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_http:65.53.63.16[1029]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_http:65.53.63.16[6004]
If port 135 is blocked, the following will appear:
TCP port 135 (epmap service): NOT LISTENING However, for these RPC Endpoint Mapper errors it is likely that ports greater than 1024 are blocked, and not port 135.From the output, you know the DC is using port 1094 for FRS and 1025, 1029, and 6004 for Active Directory replication. You can use the Portqry tool again to check those ports. For example, you can test all the ports at the same time by using the Portqry tool with the -o switch. For example, type
«portqry -n <problem_server> -o 1094,1025,1029,6004″(Without the quotation marks)
If the ports all respond as «LISTENING,» it’s likely that blocked ports are not causing this problem. If any ports respond as «NOT LISTENING,» the ports are probably blocked.
Resources
RPC Blogs
Basics of RPC are covered here:
RPC to Go v.1: http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2008/10/24/rpc-to-go-v-1.aspx
Architecture and a closer look at a connection to the RPC Endpoint mapper in a network capture.
RPC to Go v.2: http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2008/12/04/rpc-to-go-v-2.aspx
This describes how RPC commands can be sent over Named Pipes in SMB via the IPC$ Tree.
RPC to Go v.3: http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2009/04/28/rpc-to-go-v-3-named-pipes.aspx
Troubleshooting “RPC server is unavailable” error, reported in failing AD replication scenario.
http://blogs.technet.com/b/abizerh/archive/2009/06/11/troubleshooting-rpc-server-is-unavailable-error-reported-in-failing-ad-replication-scenario.aspx 
External TechNet Magazine article
This one is good. It lays out RPC basics really quickly and then moves on RPC errors. The information on MaxUserPort would need to be updated with the information about the dynamic port ranges that are used in Vista/W2008 are the high range of ports compared to the 1025-5000 for W2003.
How IT Works, Troubleshooting RPC Errors by Zubair Alexander:

KB Article
Troubleshooting RPC Endpoint Mapper errors using the Windows Server 2003 Support Tools from the product CD
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb%3bEN-US%3b839880
This entry was posted on May 16, 2012 at 3:10 PM and is filed under Active Directory.
You can follow any responses to this entry through the RSS 2.0 feed.
You can leave a response, or trackback from your own site.