The Windows command line is one of the most powerful utilities on a Windows PC. With it, you can interact with the OS directly and do a lot of things not available in the graphical user interface (GUI).
In this article, I’ll show you 40 commands you can use on the Windows command line that can boost your confidence as a Windows user.
N.B.: You have to be careful while using the commands I’ll show you. This is because some commands can have a lasting negative or positive effect on your Windows PC until you reset it.
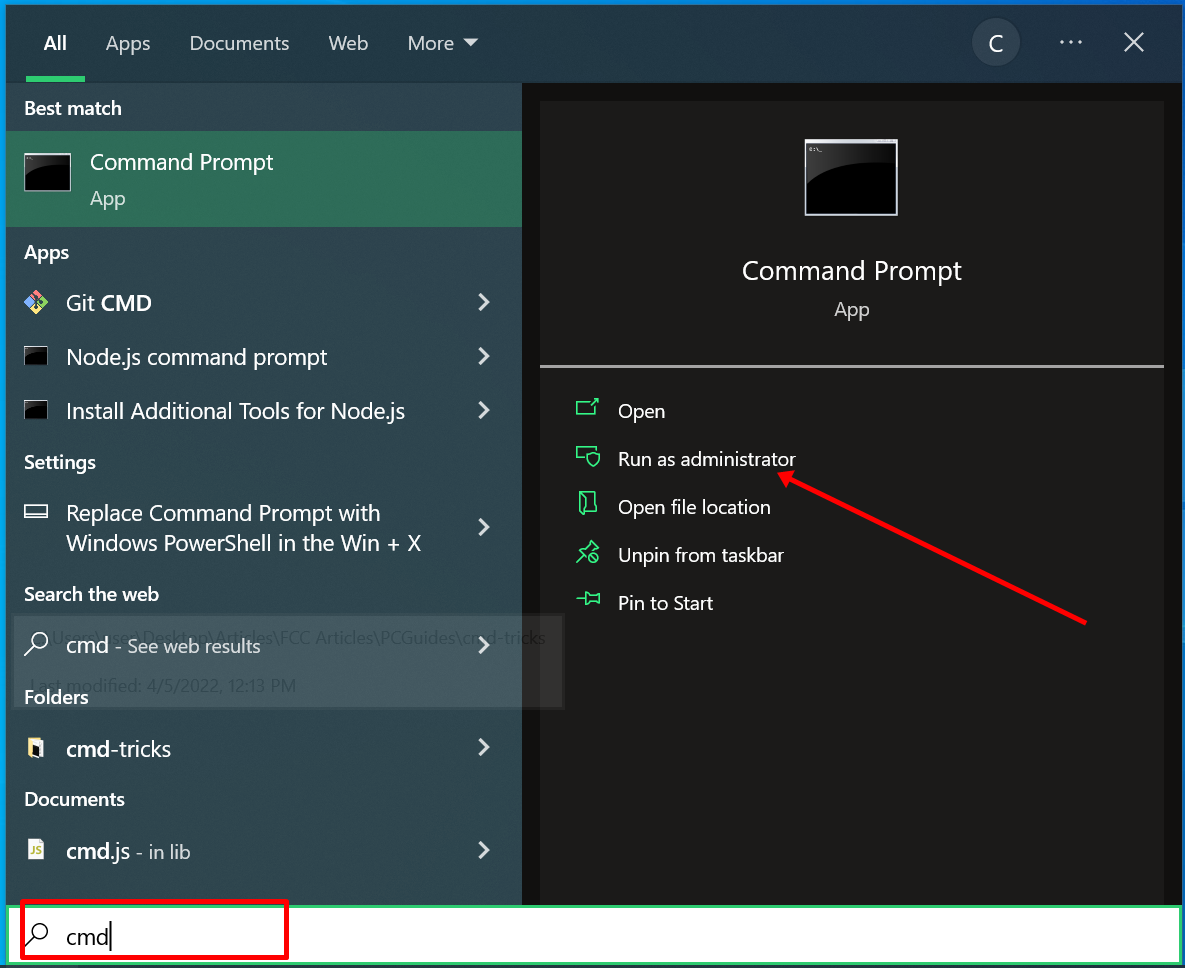
In addition, some of these commands require you to open the command prompt as an admin.
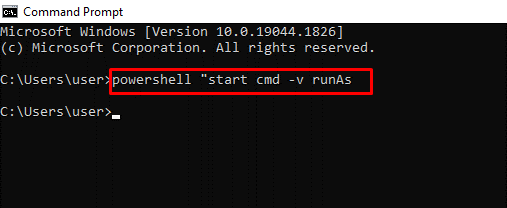
powershell start cmd -v runAs – Run the Command Prompt as an Administrator
Entering this command opens another command prompt window as an administrator:
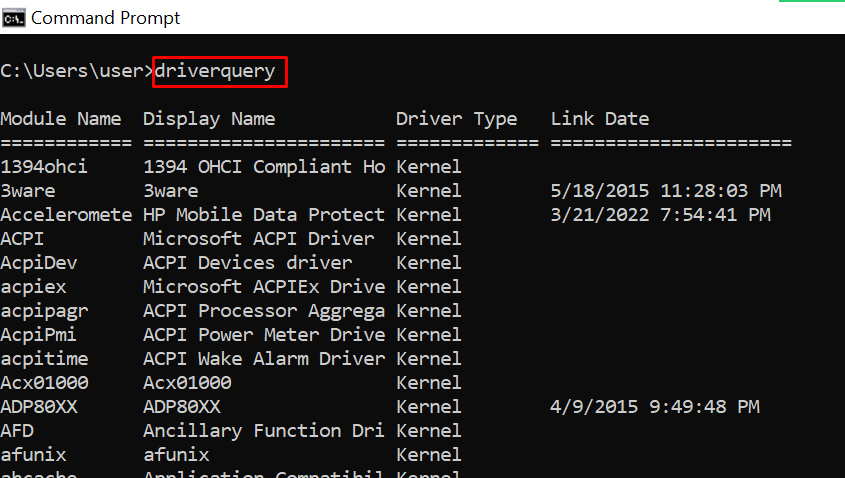
driverquery – Lists All Installed Drivers
It is important to have access to all drivers because they often cause problems.
That’s what this command does – it shows you even the drivers you won’t find in the device manager.
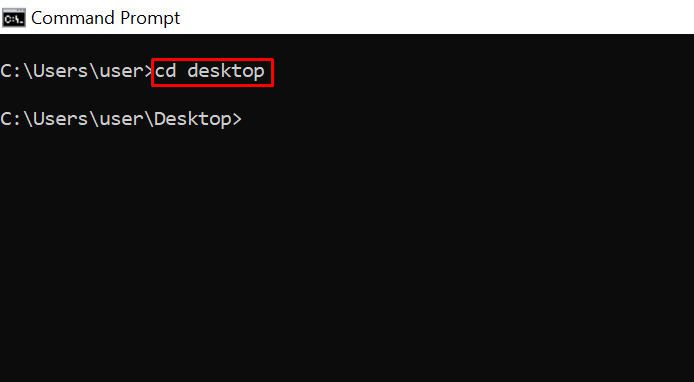
chdir or cd – Changes the Current Working Directory to the Specified Directory
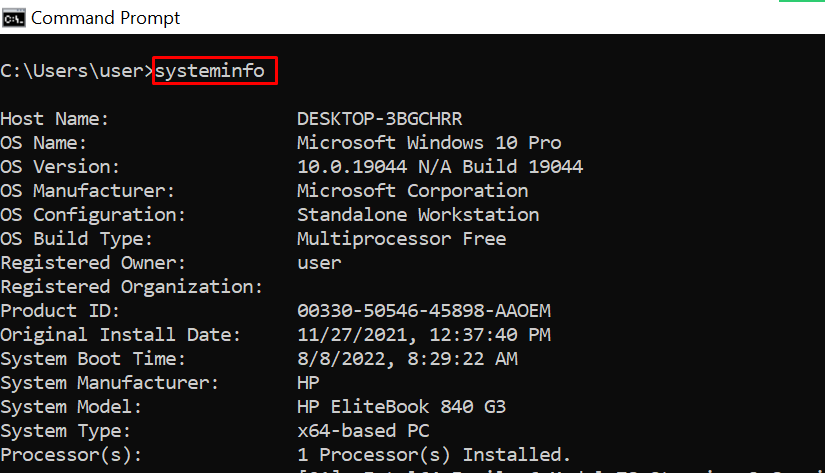
systeminfo – Shows Your PC’s Details
If you want to see more detailed information about your system you won’t see in the GUI, this is the command for you.
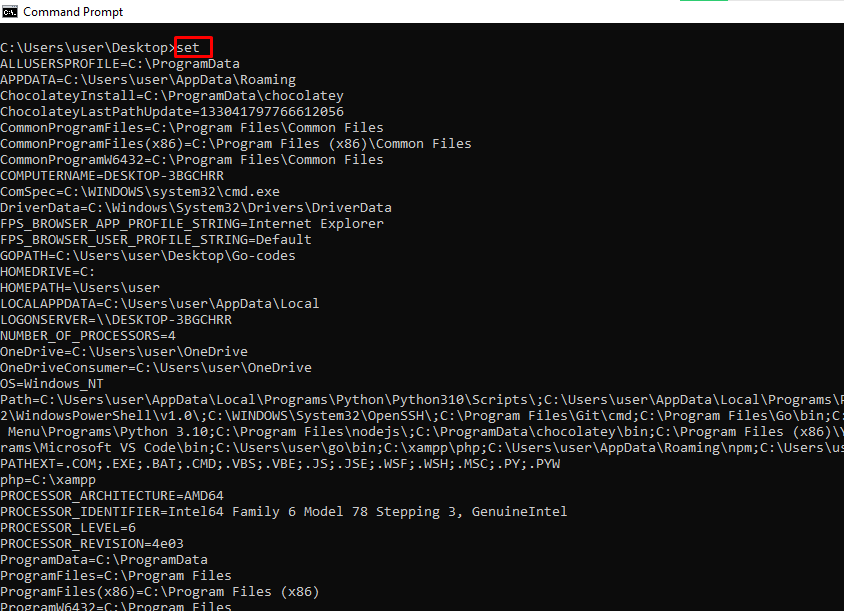
set – Shows your PC’s Environment Variables
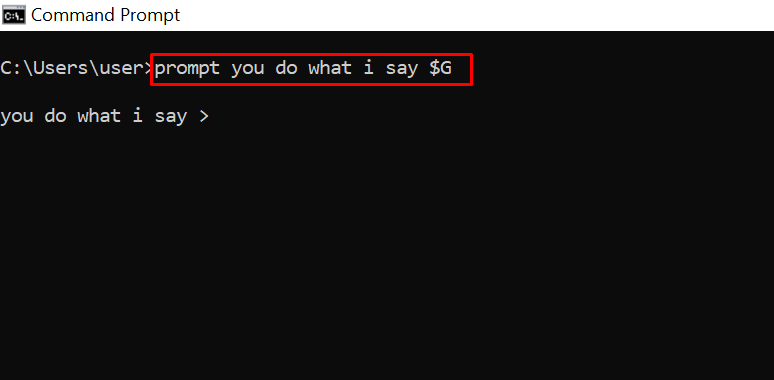
prompt – Changes the Default Text Shown before Entering Commands
By default, the command prompt shows the C drive path to your user account.
You can use the prompt command to change that default text with the syntax prompt prompt_name $G:
N.B: If you don’t append $G to the command, you won’t get the greater than symbol in front of the text.
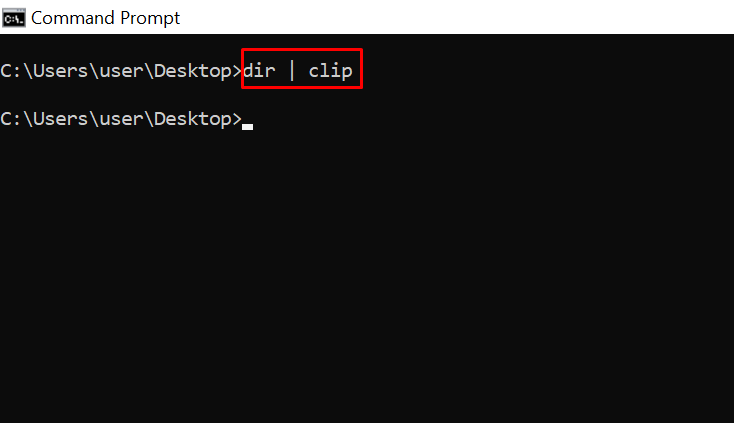
clip – Copies an Item to the Clipboard
For example, dir | clip copies all the content of the present working directory to the clipboard.
You can type clip /? and hit ENTER to see how to use it.
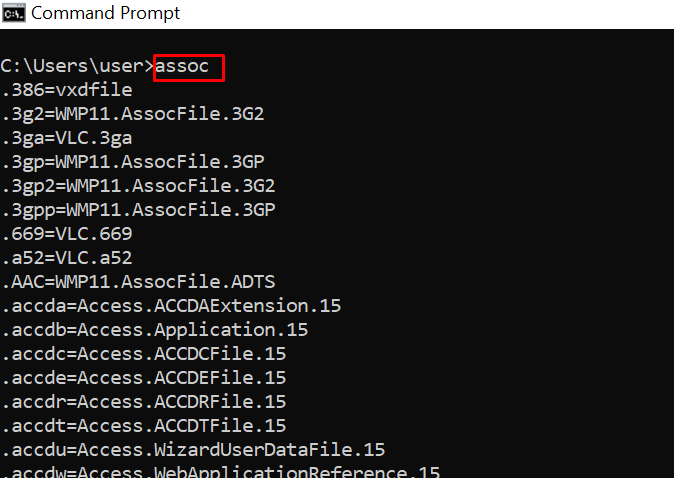
assoc – Lists Programs and the Extensions They are Associated With
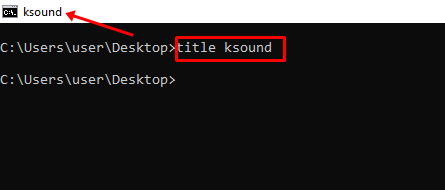
title – Changes the Command Prompt Window Title Using the Format title window-title-name
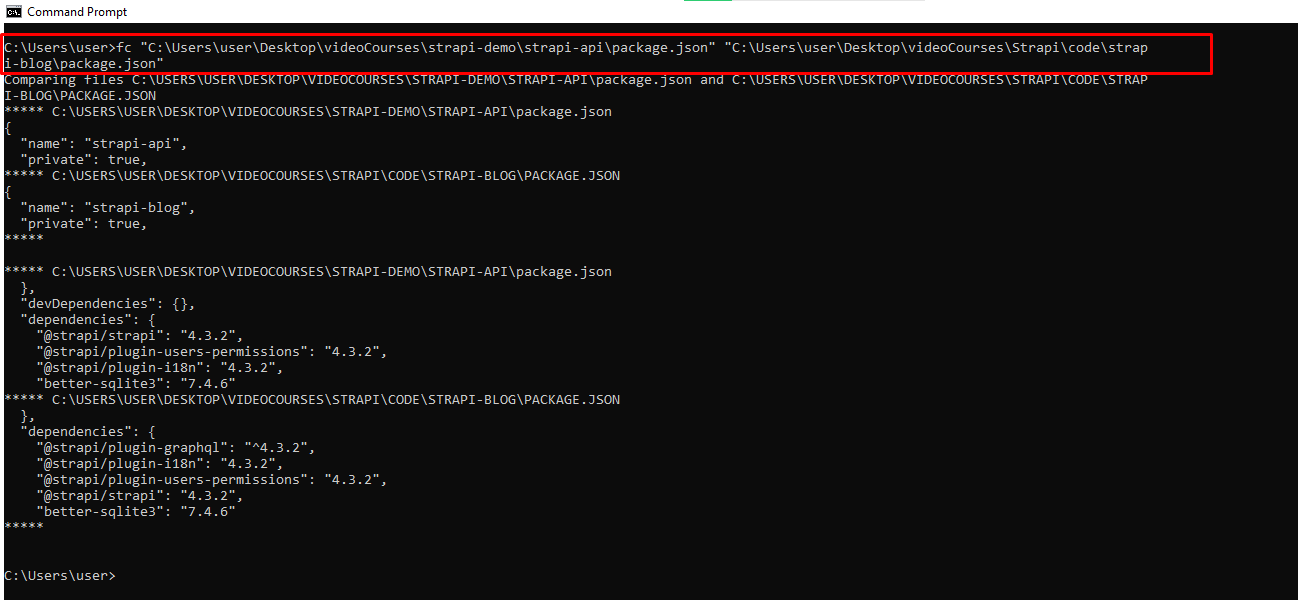
fc – Compares Two Similar Files
If you are a programmer or writer and you want to quickly see what differs between two files, you can enter this command and then the full path to the two files. For example fc “file-1-path” “file-2-path”.
cipher – Wipes Free Space and Encrypts Data
On a PC, deleted files remain accessible to you and other users. So, technically, they are not deleted under the hood.
You can use the cipher command to wipe the drive clean and encrypt such files.
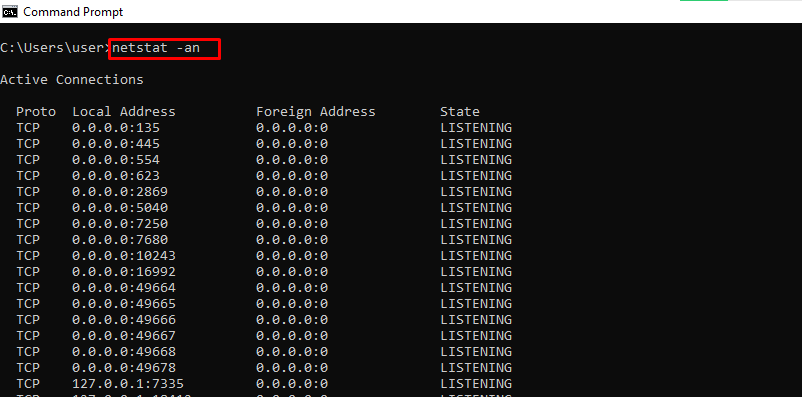
netstat -an – Shows Open Ports, their IP Addresses and States
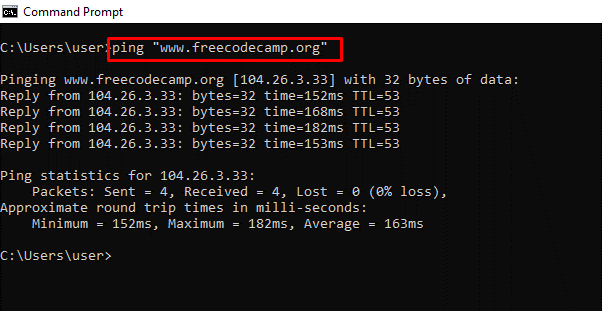
ping – Shows a Website IP Address, Lets you Know How Long it Takes to Transmit Data and a Get Response
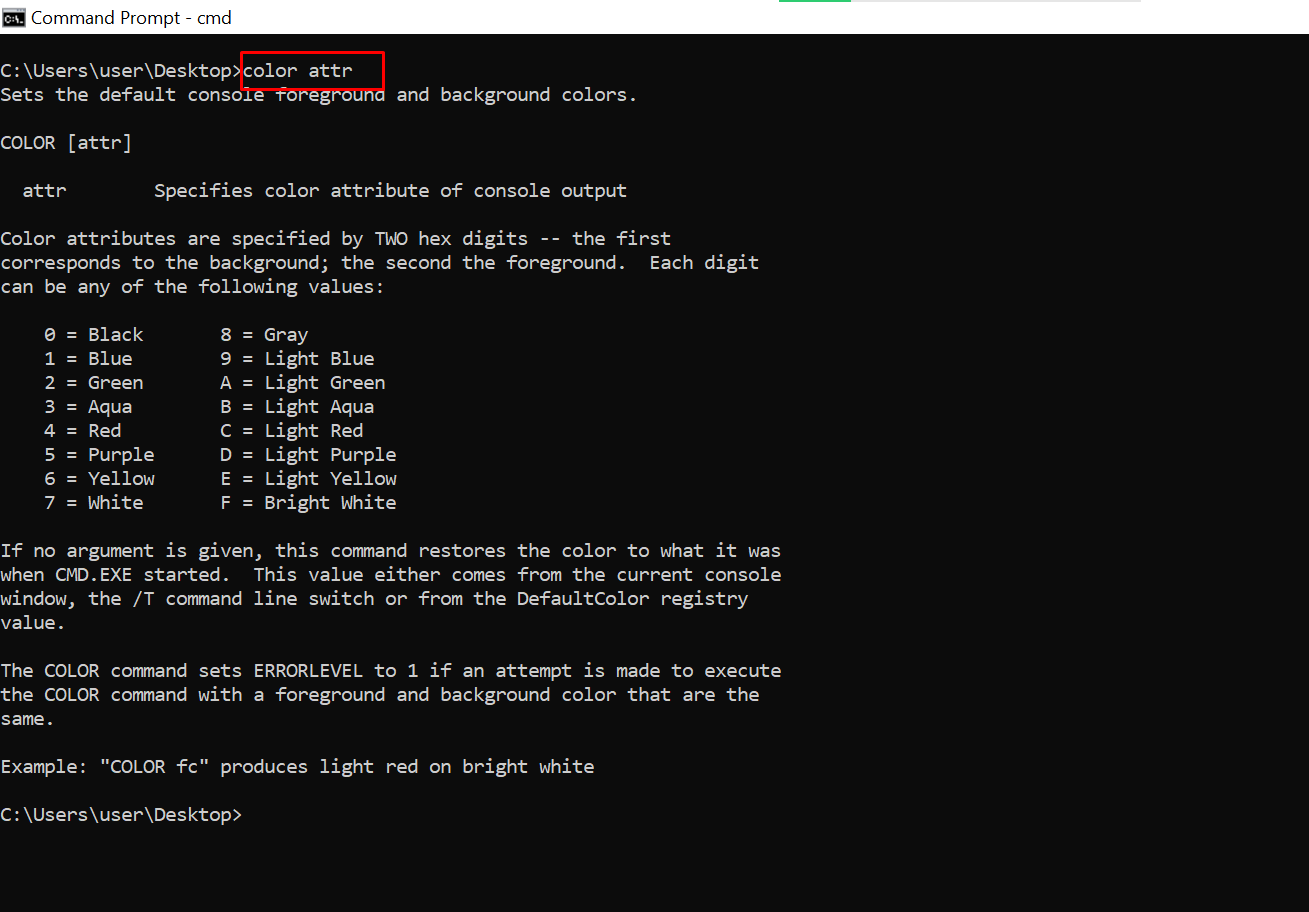
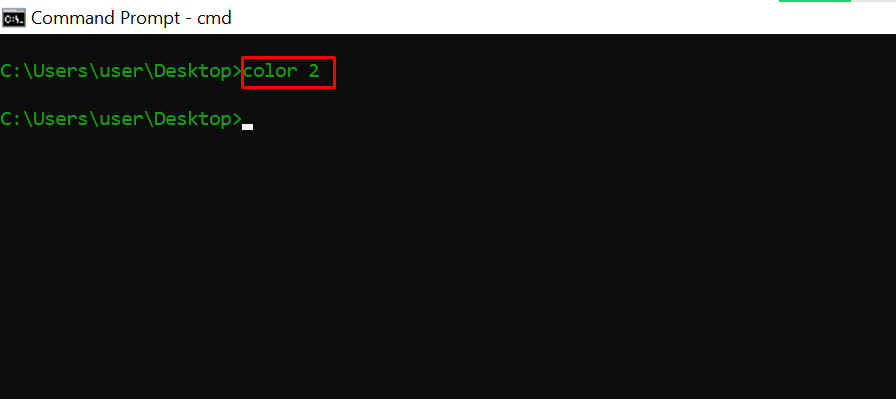
color – Changes the Text Color of the Command Prompt
Enter color attr to see the colors you can change to:
Entering color 2 changes the color of the terminal to green:
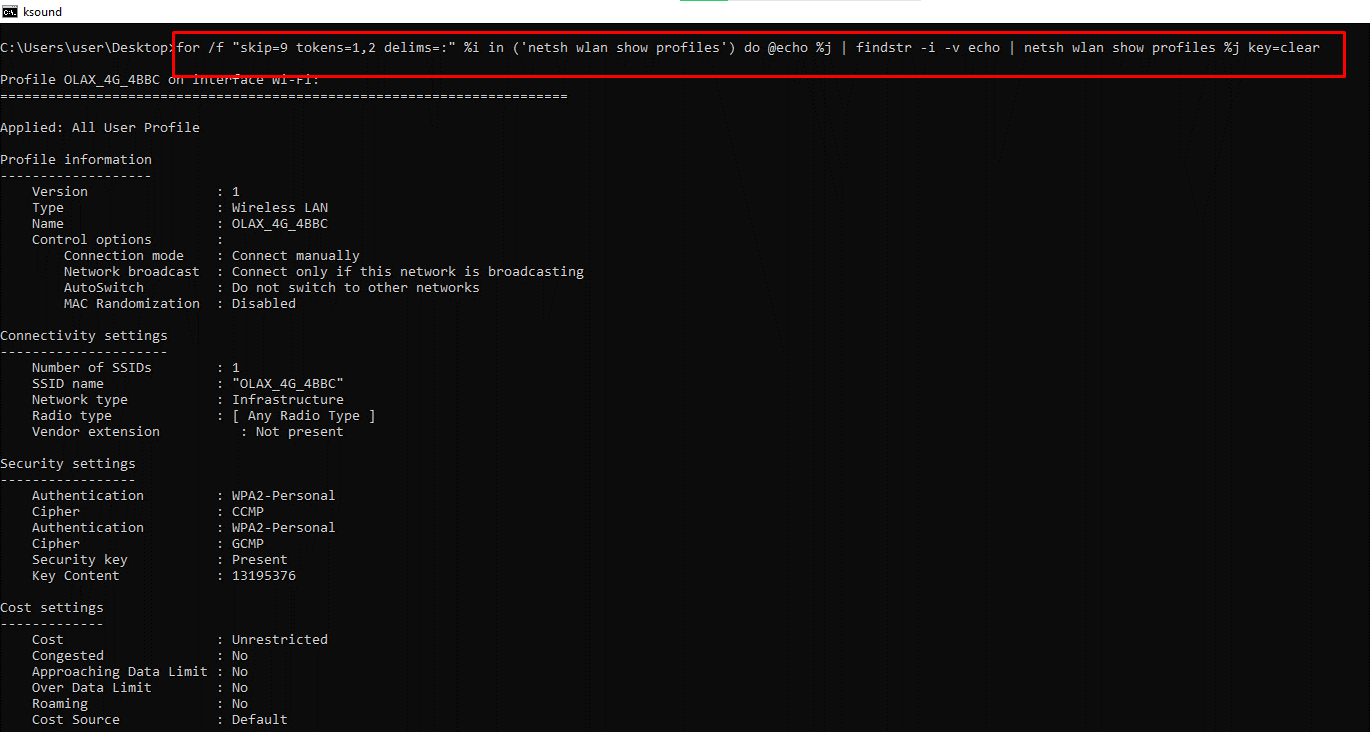
for /f "skip=9 tokens=1,2 delims=:" %i in ('netsh wlan show profiles') do @echo %j | findstr -i -v echo | netsh wlan show profiles %j key=clear – Shows All Wi-Fi Passwords
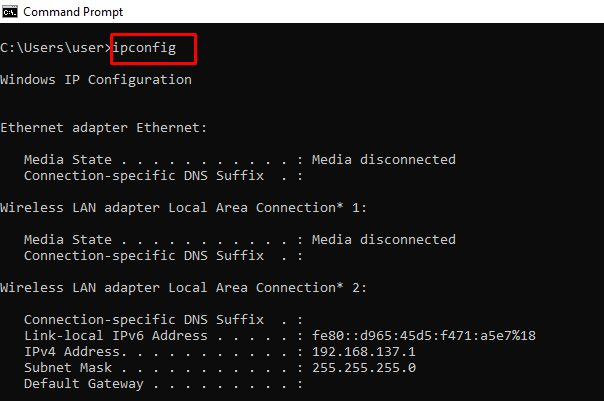
ipconfig – Shows Information about PC IP Addresses and Connections
This command also has extensions such as ipconfig /release, ipconfig /renew, and ipconfig /flushdns which you can use to troubleshoot issues with internet connections.
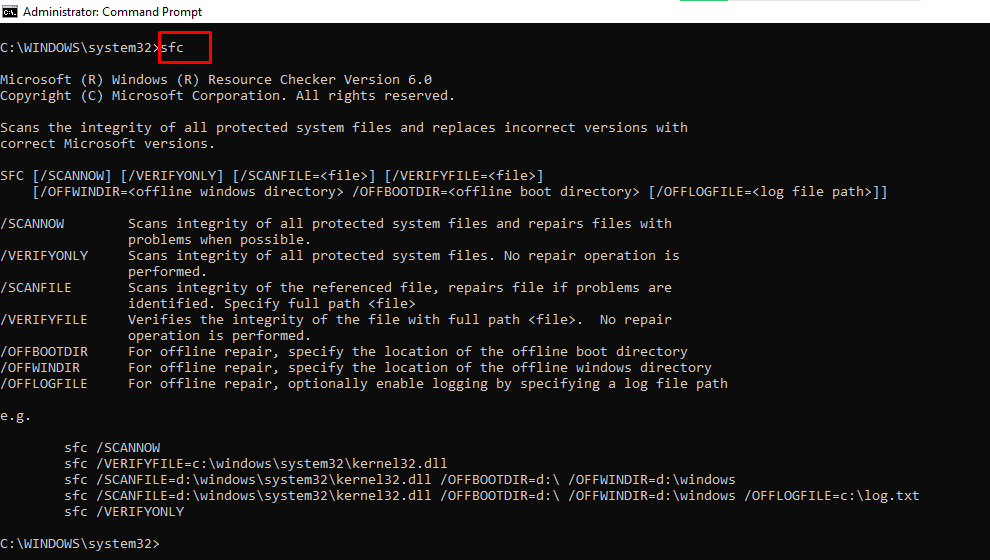
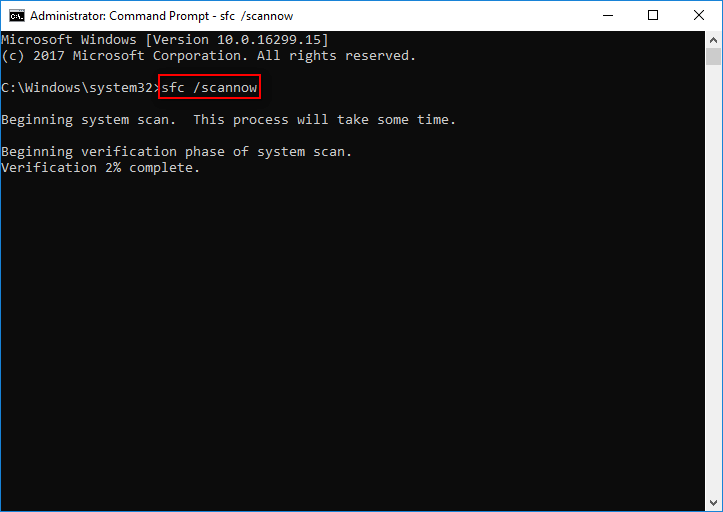
sfc – System File Checker
This command scans your computer for corrupt files and repairs them. The extension of the command you can use to run a scan is /scannow.
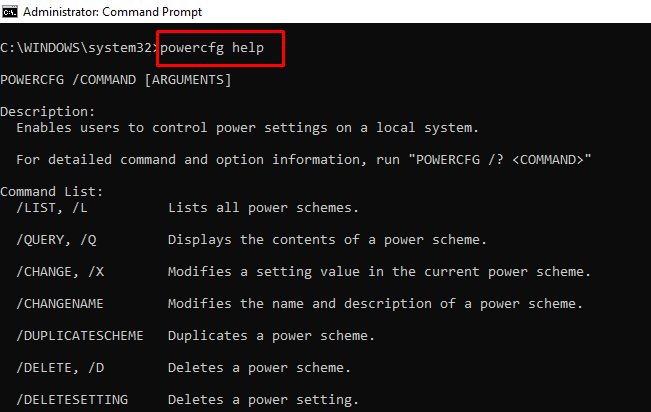
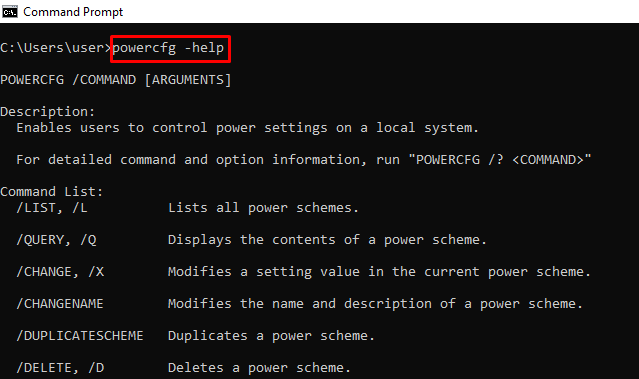
powercfg – Controls Configurable Power Settings
You can use this command with its several extensions to show information about the power state of your PC.
You can enter powercfg help to show those extensions.
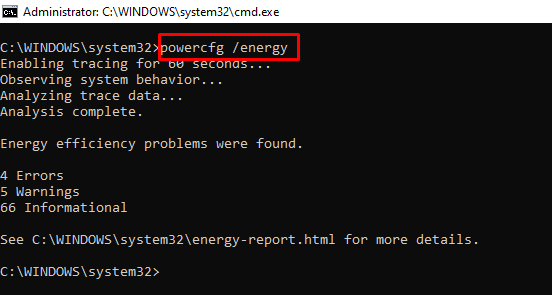
For example, you can use powercfg /energy to generate a battery health report.
The powercfg /energy command will generate an HTML file containing the report. You can find the HTML file in C:\Windows\system32\energy-report.html.
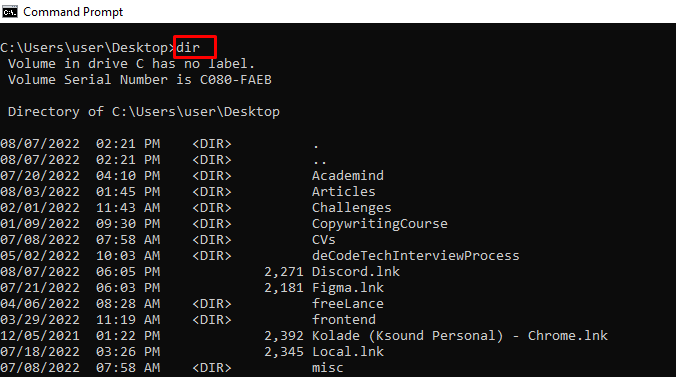
dir – Lists Items in a Directory
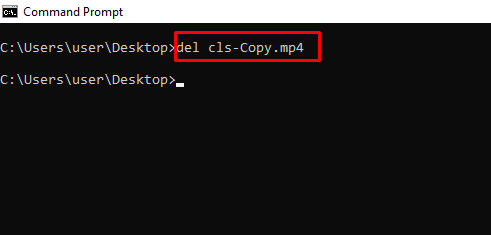
del – Deletes a File
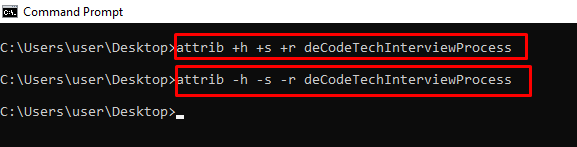
attrib +h +s +r folder_name – Hides a Folder
You can hide a folder right from the command line by typing in attrib +h +s +r folder_name and then pressing ENTER.
To show the folder again, execute the command – attrib -h -s -r folder_name.
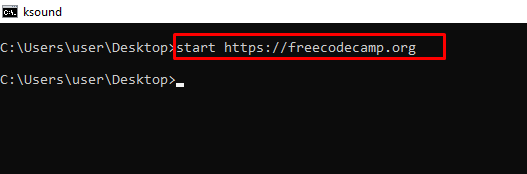
start website-address – Logs on to a Website from the Command Line
tree – Shows the Tree of the Current Directory or Specified Drive
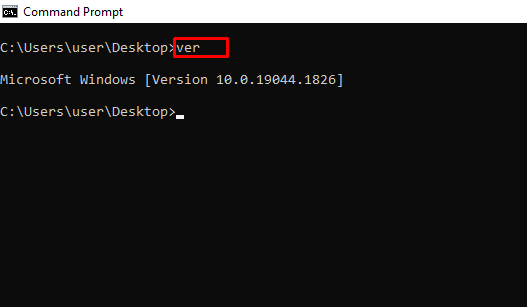
ver – Shows the Version of the OS
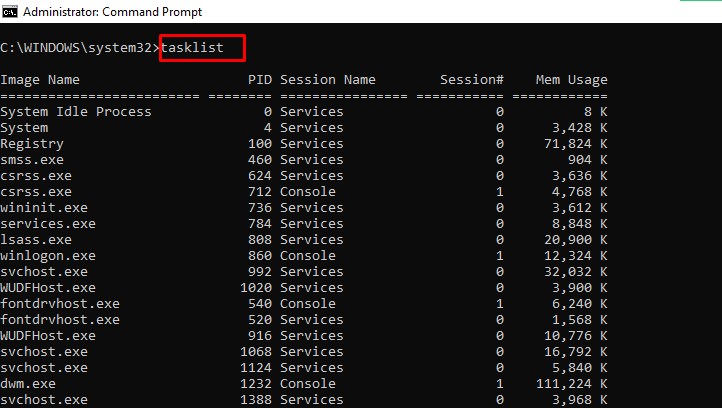
tasklist – Shows Open Programs
You can do the same thing you do with the task manager with this command:
The next command shows you how to close an open task.
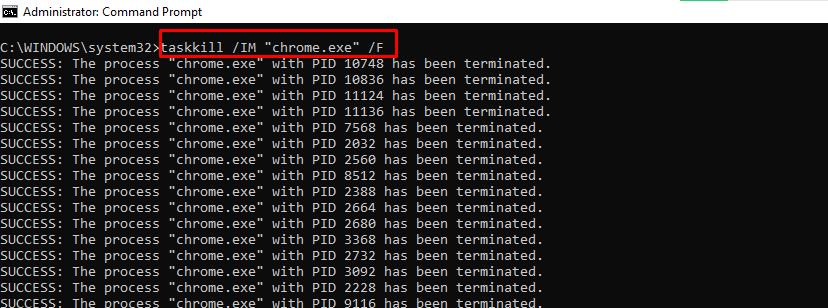
taskkill – Terminates a Running Task
To kill a task, run taskkill /IM "task.exe" /F. For example, taskkill /IM "chrome.exe" /F:
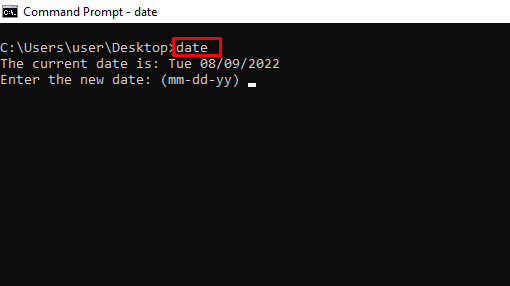
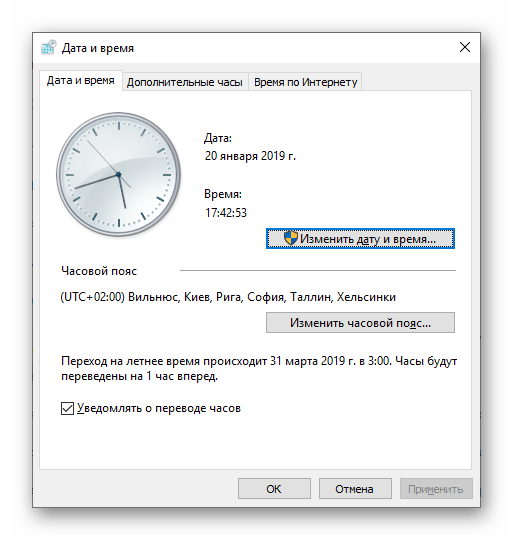
date – Shows and Changes the Current Date
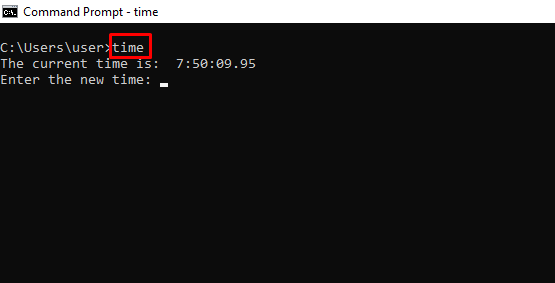
time – Shows and Changes the Current Time
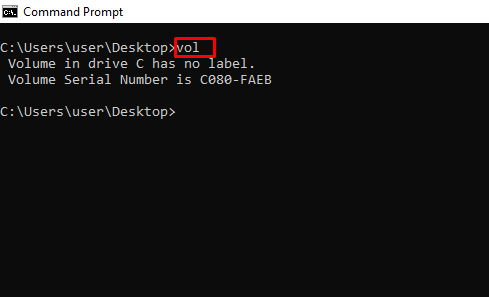
vol – Shows the Serial Number and Label Info of the Current Drive
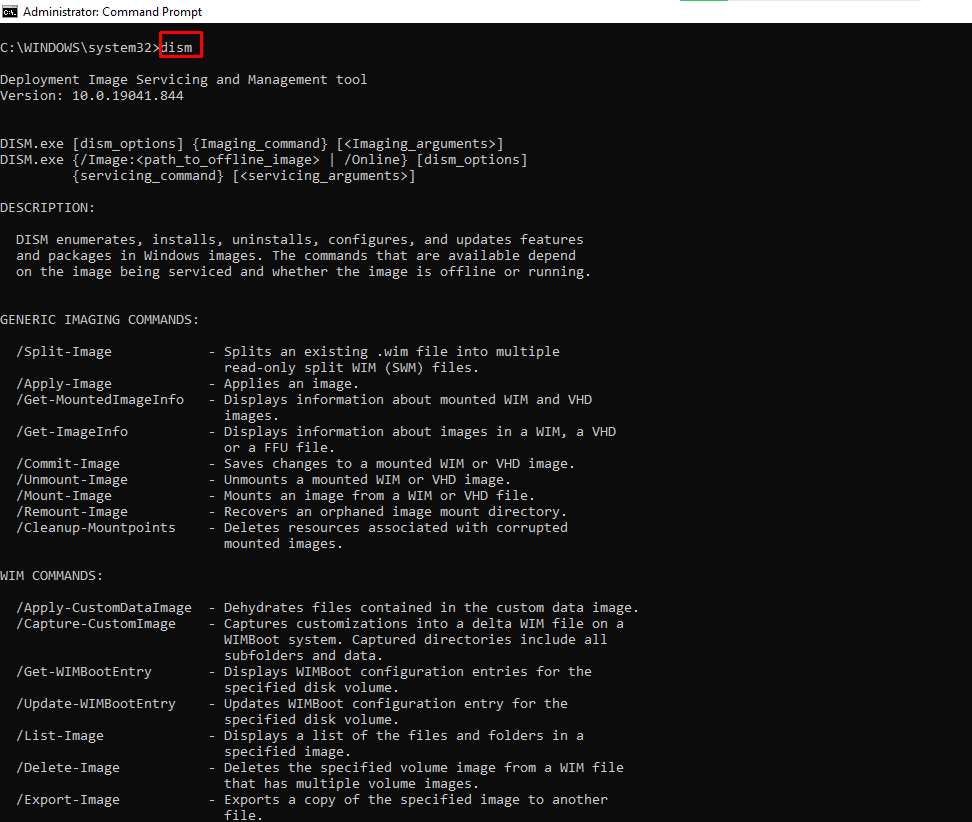
dism – Runs the Deployment Image Service Management Tool
CTRL + C – Stops the Execution of a Command
-help – Provides a Guide to other Commands
For example, powercfg -help shows how to use the powercfg command
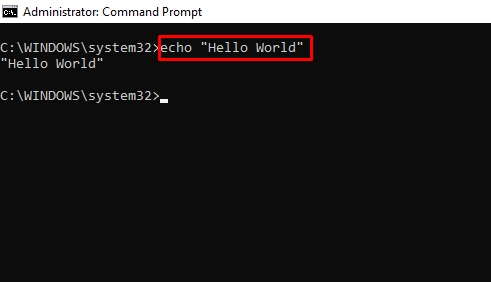
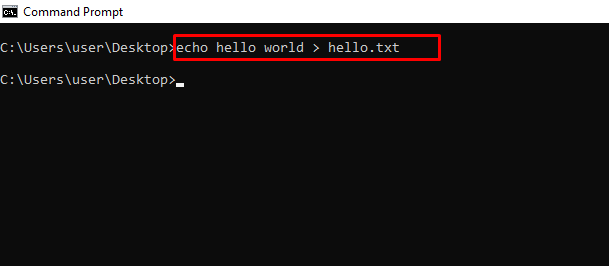
echo – Shows Custom Messages or Messages from a Script or File
You can also use the echo command to create a file with this syntax echo file-content > filename.extension.
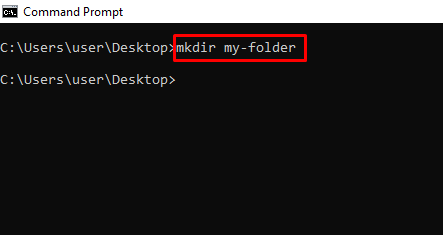
mkdir – Creates a Folder
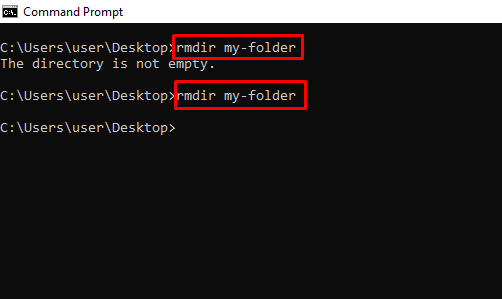
rmdir – Deletes a Folder
N.B.: The folder must be empty for this command to work.
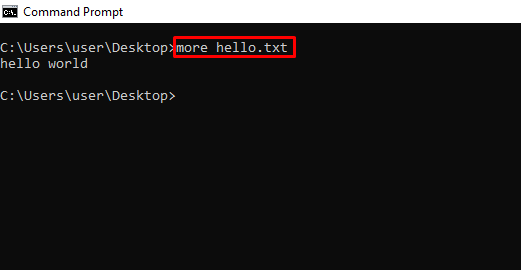
more – Shows More Information or the Content of a File
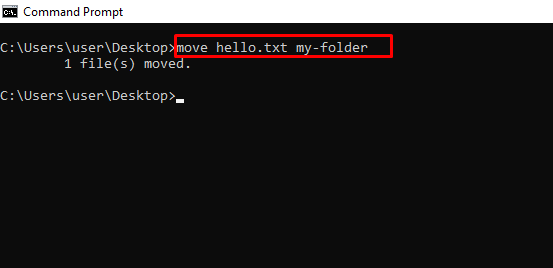
move – Moves a File or Folder to a Specified Folder
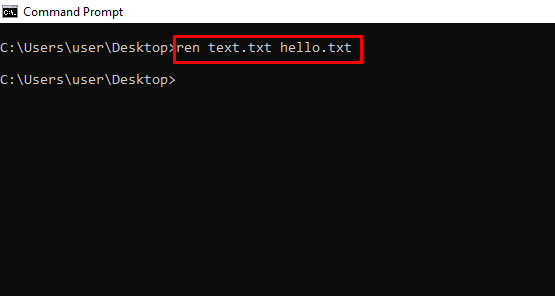
ren – Renames a File with the Syntax ren filename.extension new-name.extension
cls – Clears the Command Line
In case you enter several commands and the command line gets clogged up, you can use cls to clear all entries and their outputs.
exit – Closes the Command Line
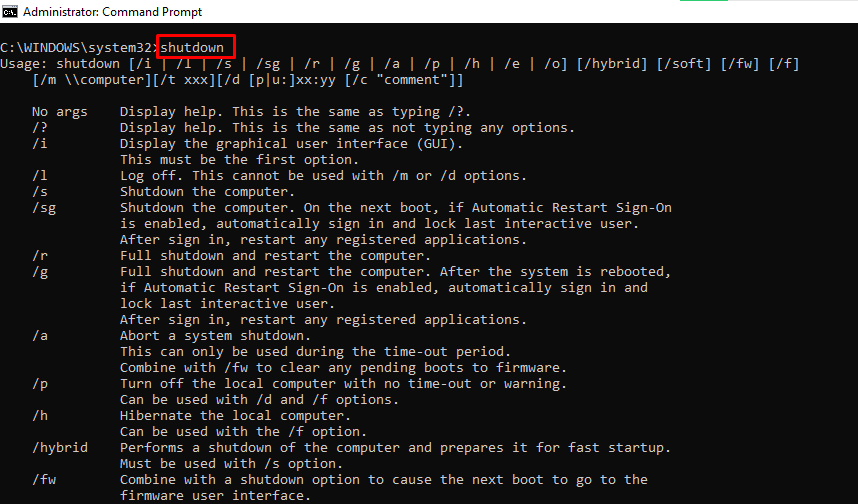
shutdown – Shuts down, Restarts, Hibernates, Sleeps the Computer
You can shut down, restart, hibernate, and sleep your PC from the command line.
Enter shutdown in the command line so you can see the extensions you can use to perform the actions. For example, shutdown /r will restart your computer.
Conclusion
This article showed you several “unknown-to-many” commands you can use to get access to hidden functionalities on your Windows PC.
Again, you should be careful while working with these commands because they can have a lasting effect on your OS.
If you find the commands helpful, share the article with your friends and family.
In case you know another useful command I did not list, tell me about it on Twitter. I will add it and mention you as the source.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Содержание
- Команды для «Командной строки» в Виндовс 10
- Запуск приложений и компонентов системы
- Действия, управление и настройка
- Настройка и использование оборудования
- Работа с данными и накопителями
- Сеть и интернет
- Заключение
- Вопросы и ответы
«Командная строка» или консоль — один из важнейших компонентов Windows, предоставляющий возможность быстрого и удобного управления функциями операционной системы, ее тонкой настройки и устранения множества проблем как с программной, так и с аппаратной составляющей. Но без знания команд, с помощью которых все это можно сделать, данный инструмент является бесполезным. Сегодня мы расскажем именно о них – различных командах и операторах, предназначенных для использования в консоли.
Так как команд для консоли существует огромное множество, мы рассмотрим лишь основные из них — те, которые рано или поздно могут прийти на помощь рядовому пользователю Windows 10, ведь именно на них и ориентирована эта статья. Но прежде чем приступить к изучению информации, рекомендуем вам ознакомиться с представленным по ссылке ниже материалом, в котором рассказывается обо всех возможных вариантах запуска консоли как с обычными, так и с административными правами.
Читайте также:
Как открыть «Командную строку» в Виндовс 10
Запуск консоли от имени администратора в Windows 10
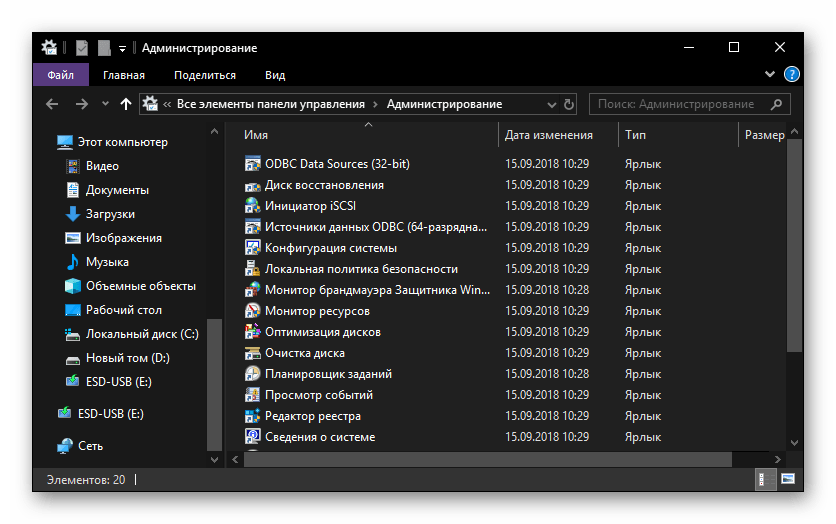
Запуск приложений и компонентов системы
Первым делом рассмотрим простые команды, с помощью которых можно быстро запускать стандартные программы и оснастки. Напомним, что после ввода любой из них нужно нажимать «ENTER».
Читайте также: Установка и удаление программ в Виндовс 10
| appwiz.cpl | Запуск средства «Программы и компоненты» |
| certmgr.msc | Консоль управления сертификатами |
| control | «Панель управления» |
| control printers | «Принтеры и факсы» |
| control userpasswords2 | «Учетные записи пользователя» |
| compmgmt.msc | «Управление компьютером» |
| devmgmt.msc | «Диспетчер устройств» |
| dfrgui | «Оптимизация дисков» |
| diskmgmt.msc | «Управление дисками» |
| dxdiag | Средство диагностики DirectX |
| hdwwiz.cpl | Еще одна команда для вызова «Диспетчера устройств» |
| firewall.cpl | Брандмауэр Защитника Windows |
| gpedit.msc | «Редактор локальной групповой политики» |
| lusrmgr.msc | «Локальные пользователи и группы» |
| mblctr | «Центр мобильности» (по понятным причинам доступен только на ноутбуках) |
| mmc | Консоль управления системными оснастками |
| msconfig | «Конфигурация системы» |
| odbcad32 | Панель администрирования источника данных ODBC |
| perfmon.msc | «Системный монитор», предоставляющий возможность просмотра изменений в производительности компьютера и системы |
| presentationsettings | «Параметры режима презентации» (доступно только на ноутбуках) |
| powershell | PowerShell |
| powershell_ise | «Интегрированная среда сценариев» оболочки PowerShell |
| regedit | «Редактор реестра» |
| resmon | «Монитор ресурсов» |
| rsop.msc | «Результирующая политика» |
| shrpubw | «Мастер создания общих ресурсов» |
| secpol.msc | «Локальная политика безопасности» |
| services.msc | Средство управления службами операционной системы |
| taskmgr | «Диспетчер задач» |
| taskschd.msc | «Планировщик заданий» |
Действия, управление и настройка
Здесь будут представлены команды для выполнения различных действий в среде операционной, а также управления и настройки входящих в ее состав компонентов.
| date | Просмотр текущей даты с возможностью ее изменения |
| displayswitch | Выбор экранов |
| dpiscaling | Параметры дисплея |
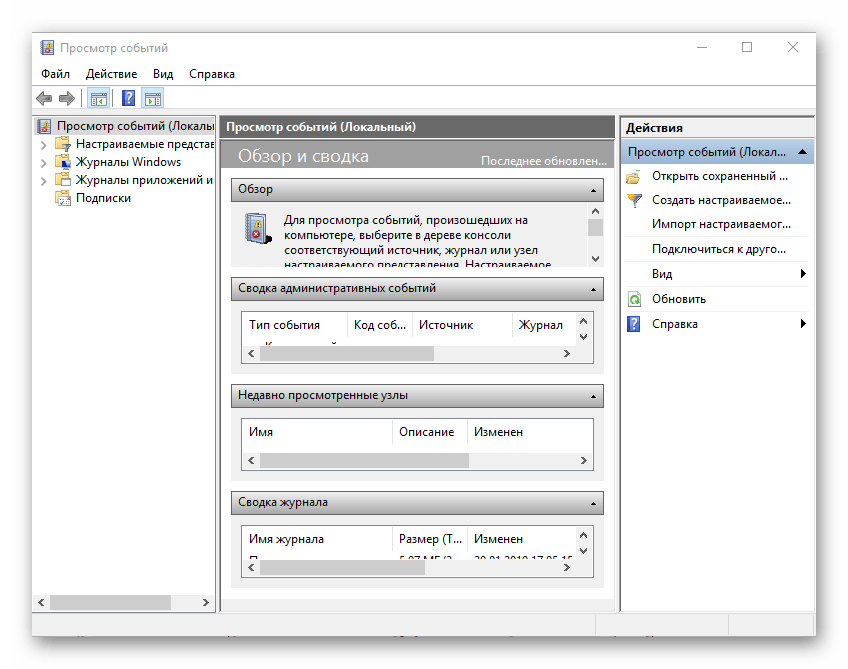
| eventvwr.msc | Просмотр журнала событий |
| fsmgmt.msc | Средство работы с общими папками |
| fsquirt | Отправка и прием файлов по Bluetooth |
| intl.cpl | Региональные настройки |
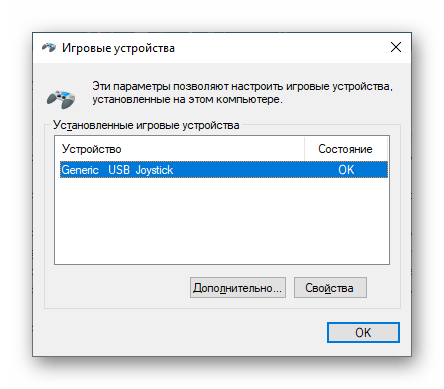
| joy.cpl | Настройка внешних игровых устройств (геймпадов, джойстиков и т.д.) |
| logoff | Выход из системы |
| lpksetup | Установка и удаление языков интерфейса |
| mobsync | «Центр синхронизации» |
| msdt | Официальное средство диагностики службы поддержки Microsoft |
| msra | Вызов «Удаленного помощника Windows» (может использоваться как для получения, так и для оказания помощи удаленно) |
| msinfo32 | Просмотр сведений об операционной системе (отображает характеристики программных и аппаратных компонентов ПК) |
| mstsc | Подключение к удаленному Рабочему столу |
| napclcfg.msc | Настройка конфигурации операционной системы |
| netplwiz | Панель управления «Учетными записями пользователей» |
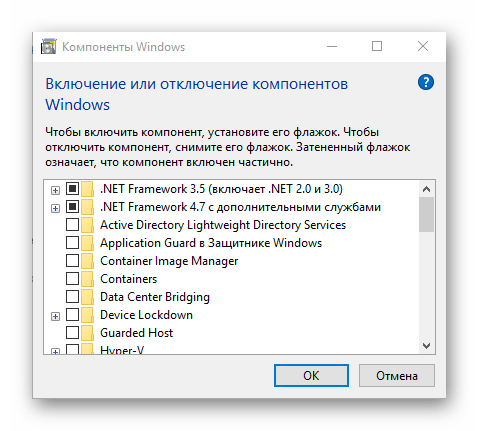
| optionalfeatures | Включение и отключение стандартных компонентов операционной системы |
| shutdown | Завершение работы |
| sigverif | Средство проверки подлинности файлов |
| sndvol | «Микшер громкости» |
| slui | Средство активации лицензии ОС Windows |
| sysdm.cpl | «Свойства системы» |
| systempropertiesperformance | «Параметры быстродействия» |
| systempropertiesdataexecutionprevention | Запуск службы DEP, компонента «Параметров быстродействия» ОС |
| timedate.cpl | Изменение даты и времени |
| tpm.msc | «Управление доверенным платформенным модулем TPM на локальном компьютере» |
| useraccountcontrolsettings | «Параметры управления учетными записями пользователей» |
| utilman | Управление «Специальными возможностями» в разделе «Параметров» операционной системы |
| wf.msc | Активация режима повышенной безопасности в стандартном Брандмауэре ОС Windows |
| winver | Просмотр общих (кратких) сведений об операционной системе и ее версии |
| WMIwscui.cpl | Переход к Центру поддержки операционной системы |
| wscript | «Параметры сервера сценария» ОС Windows |
| wusa | «Автономный установщик обновлений Windows» |
Настройка и использование оборудования
Есть ряд команд, предназначенных для вызова стандартных программ и элементов управления и предоставляющих возможность настройки оборудования, подключенного к компьютеру или ноутбуку либо интегрированного.
| Команда | Описание |
|---|---|
| main.cpl | Настройка мыши |
| mmsys.cpl | Панель настройки звука (устройства ввода/вывода аудиосигнала) |
| printui | «Пользовательский интерфейс принтера» |
| printbrmui | Средство переноса принтера, предоставляющее возможность экспорта и импорта программных компонентов и драйверов оборудования |
| printmanagement.msc | «Управление печатью» |
| sysedit | Редактирование системных файлов с расширениями INI и SYS (Boot.ini, Config.sys, Win.ini и др.) |
| tabcal | Средство калибровки дигитайзера |
| tabletpc.cpl | Просмотр и настройка свойств планшета и пера |
| verifier | «Диспетчер проверки драйверов» (их цифровой подписи) |
| wfs | «Факсы и сканирование» |
| wmimgmt.msc | Вызов «Элемента управления WMI» стандартной консоли |
Работа с данными и накопителями
Ниже представим ряд команд, предназначенных для работы с файлами, папками, дисковыми устройствами и накопителями, как внутренними, так и внешними.
Примечание: Некоторые из представленных ниже команд работают только в контексте – внутри предварительно вызванных консольных утилит или с обозначенными файлами, папками. Для получения более подробных сведений по ним вы всегда можете обратиться к справке, воспользовавшись командой «help» без кавычек.
| attrib | Редактирование атрибутов предварительно обозначенного файла или папки |
| bcdboot | Создание и/или восстановление системного раздела |
| cd | Просмотр наименования текущей директории или переход в другую |
| chdir | Просмотр папки или переход к другой |
| chkdsk | Проверка жестких и твердотельных дисков, а также подключенных к ПК внешних накопителей |
| cleanmgr | Инструмент «Очистка диска» |
| convert | Преобразование файловой системы тома |
| copy | Копирование файлов (с указанием конечного каталога) |
| del | Удаление выбранных файлов |
| dir | Просмотр файлов и папок по указанному пути |
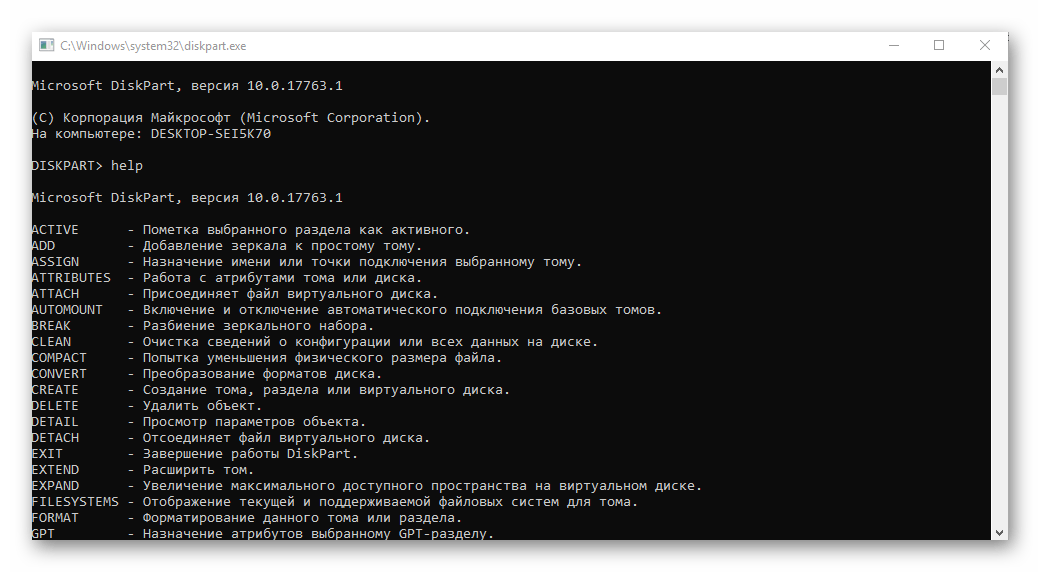
| diskpart | Консольная утилита для работы с дисками (открывается в отдельном окне «Командной строки», для просмотра поддерживаемых команд обратитесь к справке – help) |
| erase | Удаление файлов |
| fc | Сравнение файлов и поиск различий |
| format | Форматирование накопителя |
| md | Создание новой папки |
| mdsched | Проверка оперативной памяти |
| migwiz | Средство миграции (переноса данных) |
| move | Перемещение файлов по заданному пути |
| ntmsmgr.msc | Средство работы с внешними накопителями (флешками, картами памяти и т.д.) |
| recdisc | Создание диска восстановления операционной системы (работает только с оптическими накопителями) |
| recover | Восстановление данных |
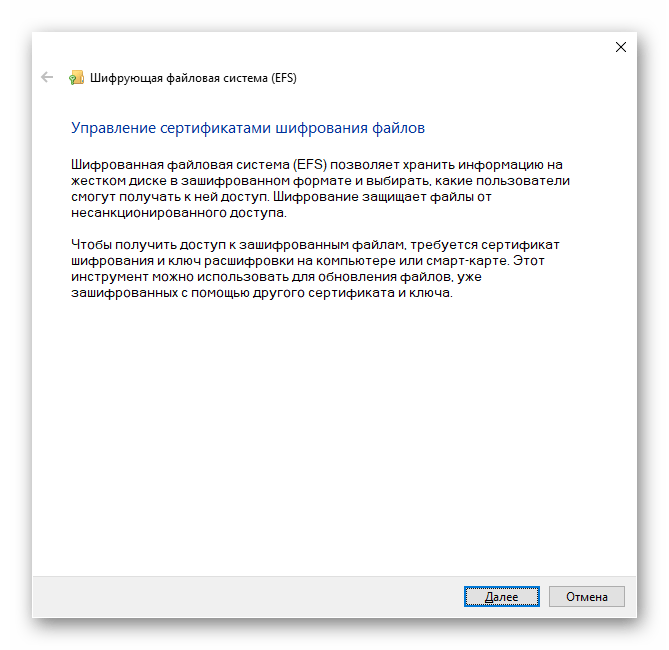
| rekeywiz | Инструмент для шифрования данных («Шифрующая файловая система (EFS)») |
| RSoPrstrui | Настройка средства «Восстановление системы» |
| sdclt | «Резервное копирование и восстановление» |
| sfc /scannow | Проверка целостности системных файлов с возможностью их восстановления |
Читайте также: Форматирование флешки через «Командную строку»
Сеть и интернет
Напоследок ознакомим вас с несколькими простыми командами, предоставляющими возможность получения быстрого доступа к сетевым параметрам и настройке интернета.
| control netconnections | Просмотр и настройка доступных «Сетевых подключений» |
| inetcpl.cpl | Переход к свойствам интернета |
| NAPncpa.cpl | Аналог первой команды, предоставляющий возможность настройки сетевых подключений |
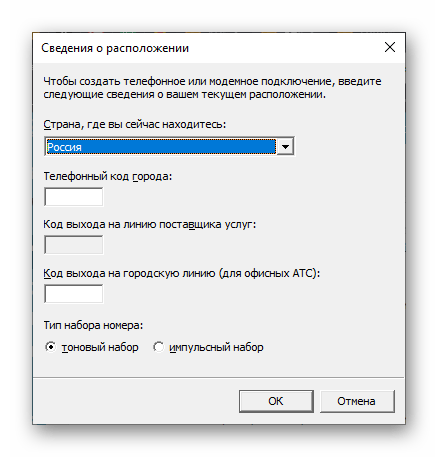
| telephon.cpl | Настройка модемного подключения к интернету |
Заключение
Мы ознакомили вас с довольно большим количеством команд для «Командной строки» в Windows 10, но по факту это лишь малая их часть. Запомнить все получится вряд ли, но этого и не требуется, тем более что при необходимости вы всегда можете обратиться к данному материалу или встроенной в консоль справочной системе. Кроме того, если у вас остались вопросы по рассмотренной нами теме, смело задавайте их в комментариях.
I’m using Windows 7, and my problem is running this file from a console (cmd.exe):
W:\software\projects\myproject\build\msvc\build.bat
When I move into the folder containing the file manually and run it from there using the following command sequence, it works:
W:\>cd software
W:\software>cd projects
W:\software\projects>cd myproject
W:\software\projects\myproject>cd build
W:\software\projects\myproject\build>cd msvc
W:\software\projects\myproject\build\msvc>build.bat
However, when I try to run the file from the root directory in any of these ways:
W:\>software\projects\myproject\build\msvc\build.bat
W:\>call software\projects\myproject\build\msvc\build.bat
W:\>@call software\projects\myproject\build\msvc\build.bat
W:\>"software\projects\myproject\build\msvc\build.bat"
W:\>call "software\projects\myproject\build\msvc\build.bat"
W:\>@call "software\projects\myproject\build\msvc\build.bat"
I get the following error message:
The system cannot find the path specified.
I’m pretty sure you didn’t have to navigate to the folder containing the file in order to run it when I was using Windows XP (though I could be wrong, of course), but this apparently seems to be the case with Windows 7. Or am I missing something?
Download Article
Easily run .BAT files in Windows and troubleshoot common problems
Download Article
- Running from the Batch File’s Folder
- Running from Anywhere
- Troubleshooting
- Other Ways to Run Batch Files
- Expert Q&A
- Warnings
|
|
|
|
|
If you need to run a batch file at the Windows Command Prompt, you’ll just need to know the location of the batch file. To run the file at the command line, simply type the full path to the batch file and press Enter. Or, if you don’t want to type the full path to the file, you can use the cd command to enter the folder containing the .BAT file, type the batch file’s name, and then press Enter. This wikiHow guide will teach you 2 simple ways to run a batch file from the Command Prompt in Windows, help you fix common errors, and show you a few other cool ways to run batch files on your PC.
Things You Should Know
- Use the «cd» command to enter the folder that contains your batch file.
- To run the batch file, type its name and press «Enter.»
- You can also type the full path to the batch file from any folder to run batch files from anywhere.
-
1
Open the Command Prompt. If your batch file performs administrative tasks, open Command Prompt as an administrator. If the batch file only requires access to files in your user account, you don’t need to start it as an administrator.
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type cmd.
- If your batch file doesn’t need administrator rights, click Command Prompt.
- If your batch file does require administrator rights:
- Right-click Command Prompt.
- Select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes.
-
2
Type cd followed by the full path to your batch file’s folder. The cd command stands for «change directories.» For example:
- If the file is at D:\Music\MP3s\Unsorted, you’d type cd D:\Music\MP3s\Unsorted.
- If the batch file is on your desktop, you’d type cd \Users\YourLoginName\Desktop.
- If you use OneDrive to automatically back up your personal files, you’d use cd \Users\YourLoginName\OneDrive\Desktop instead.
- If you don’t know your login name, type cd \Users and press Enter. Then, type dir and press Enter to see a list of users.
Advertisement
-
3
Press ↵ Enter. This will move you into the folder containing your batch file.
- Type dir and press Enter to see a list of all files in the current folder. You should see your batch file (ending with .bat) here.
-
4
Type the name of the batch file and press ↵ Enter. For example, if your batch file is called program.bat, type program.bat and press Enter. This runs the batch file.
Advertisement
-
1
Get the full path to your batch file. If you want to run a batch file without using cd to enter its folder first, you’ll just need to know the full path to the file. For example, C:\Users\wikiHow\Scripts\mybatchfile.bat. Here’s an easy way to find the full path to your batch file:
- Navigate to your batch file. If you’re not sure where you saved it, you can search for it.
- If you’re using Windows 11, right-click the file and select Copy as path (Windows 11).
- On Windows 10 and earlier, right-click the file and select Properties. Highlight the path next to «Location» and press Ctrl + C to copy it to your clipboard.
-
2
Open the Command Prompt. If your batch file performs administrative tasks, open Command Prompt as an administrator. If it only requires access to files in your user account, you don’t need to start it as an administrator.
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type cmd.
- If your batch file doesn’t need administrator rights, click Command Prompt.
- If your batch file does require administrator rights:
- Right-click Command Prompt.
- Select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes.
-
3
Type or paste the full path to your batch file. To paste the path you copied earlier, press Ctrl + V.
- Alternatively, you can type the full path to your file manually (e.g., C:\Users\wikiHow\Scripts\mybatchfile.bat).
- Because the .BAT extension is executable, you don’t need to type any commands before pasting or entering the path to the file.
-
4
Press ↵ Enter to run the batch file. The batch file will now run. Any commands in the batch file will execute as specified in the script.
Advertisement
-
1
Running the batch file at the prompt just takes me to the next line. Depending on the commands in your batch file, you may not see confirmation or output when you run a .BAT file from Command Prompt. You’ll only see output if there’s a command in the batch file that’s supposed to display output.
- For example, if the batch file is just working with files on your PC, such as moving, renaming, and/or deleting, you won’t see the commands as they run unless @echo on is at the top of the .BAT file.[1]
- You can also add echo "your text here" to your batch file to display a custom message when run.
- For example, if the batch file is just working with files on your PC, such as moving, renaming, and/or deleting, you won’t see the commands as they run unless @echo on is at the top of the .BAT file.[1]
-
2
I see «The syntax of the command is incorrect» when I run a batch file. This means that there’s an error with one of the commands in the batch file. The error could be due to missing or incorrect symbols, leaving out a flag required by a command, or even missing quotation marks around paths. Open the batch file in an editor like Notepad and inspect the code for errors.
-
3
I’m getting the error «x is not recognized as an internal or external command.» This error also indicates an error in the batch file. But in this case, the error occurs because a command in the batch file is not recognized by Command Prompt. Fortunately, the error tells you exactly which command is failing, so it should be simple to fix.
- For example, if a command in the .BAT file is misspelled or incorrect (e.g., «ifconfig» instead of «ipconfig»), or trying to start a program using its name instead of its full path.
-
4
When I double-click a batch file, the window just closes. If double-clicking your .BAT file quickly opens and closes a Command Prompt window, it just means the batch file doesn’t have a «pause» at the end. If you want to keep the window open after the commands have run, just add «pause» to the end of the batch file.
- Right-click the batch file.
- Select Open with > Notepad (Windows 10) or Show more options > Edit (Windows 11).
- Add «pause» to the last line of the batch file.
- Save the file and run it again. Now, when you run the batch file, the window will stay open while displaying «Press any key to continue…» Once you press a key, the window will close.[2]
Advertisement
-
1
Double-click any .BAT file to run it instantly. If you don’t want to use the Command Prompt, you can easily run a batch file from any location on your Windows PC just by double-clicking it.
- If double-clicking the batch file opens and closes a window without showing you any details, see this troubleshooting tip.
-
2
Use the Run dialog. To call up a batch script from the Run dialog:
- Press Windows key + R to open Run.
- Click Browse.
- Navigate to and select your batch file.
- Click Open.
- Click OK to run the batch file.
-
3
Run the batch file at a specific time and date. Use Windows Task Scheduler to automatically run a batch file at the time and date of your choice. You can have the batch file run once or on a regular schedule.
- Press the Windows key and type task scheduler.
- Click Task Scheduler.
- Expand the «Task Scheduler Library» folder.
- Create a new folder: Right-click Task Scheduler Library, click New Folder…, type a name, and click OK.
- Right-click your new folder and select Create basic task. Type a name for your task and click Next.
- Choose when (and how often) you want the batch file to run. For example, if you want it to run at a certain date, select the date. Then, click Next.
- Select Start a program, click Next, and then click Browse to select your .BAT file.
- Click Finish. The batch file will now run automatically at the selected time and date.
-
4
Run the batch file automatically when Windows starts. If you want the batch file to start automatically when your PC boots into Windows, you can copy or move the file to your Windows startup scripts folder. Here’s how:
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type shell:startup and click OK. This opens a File Explorer window to your Startup folder.
- Drag or copy the .BAT file into the folder.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
After I run the batch script, it just opens another line and nothing happens.
Nicole Levine is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. She has more than 20 years of experience creating technical documentation and leading support teams at major web hosting and software companies. Nicole also holds an MFA in Creative Writing from Portland State University and teaches composition, fiction-writing, and zine-making at various institutions.
wikiHow Technology Writer
Expert Answer
Many batch scripts won’t display any confirmation that the commands have run. If you wrote the batch script yourself, you can switch the value of «echo» to «on» to display the commands at the prompt as they run. You can also add «pause» to the end of the script to make it prompt the user to press a key to continue. But in general, as long as you don’t see an error, that means the batch script executed properly.
-
Question
What does this error mean? ‘.’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
The batch script is trying to run «.» as a command, which is not a recognized command. Look for the extra period somewhere in the script and remove it.
-
Question
How do I get out after I run my batch file ?
This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
Just click the »’X»’ at the top corner of the command prompt window to close it. Or, if the batch script is hung on a process and not letting you go to the next line, you can press Ctrl + C to stop the batch file from running.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
-
Never run a .BAT file as an administrator unless you know exactly what the file does. If the batch file is malicious, running it as an administrator could steal your data, install malware and viruses, and other dirty deeds.
-
Be careful when downloading .BAT files from the web or as email attachments. Make sure your PC is always protected by Microsoft Defender (or your preferred antivirus software) before running files from unknown sources.
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Press the Windows + R keys.
2. Click Browse.
3. Select the .bat file.
4. Click Open.
5. Click OK.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 343,904 times.
Is this article up to date?
-
Home
-
News
- Command Line Windows: Basic CMD/Command Line Commands
By Alisa |
Last Updated
Why do people still bother with command line Windows? Check what you can do with Windows command line commands and what the basic cmd commands are in Windows Command Prompt. If you want to repair, recover, backup and restore Windows 10/8/7, MiniTool software offers full sets of solutions.
CMD, also known as Command Prompt, is the command-line interpreter in Windows operating systems. cmd.exe interacts with the user through a command-line interface but not a graphical users interface (GUI). It offers hundreds of DOS command line commands to allow users to find and manipulate files or conduct some other actions like running CHKDSK, SFC commands to repair Windows 10 errors.
The command line Windows is almost 50 years old, but it’s still being used by many users. Why do people still use command line commands in Windows 10/8/7?
Why Do People Still Use Command Line Commands in Windows
The command line was once the only option for users to interact with a computer. The command lines are standardized thanks to POSIX. Each of the command line commands is designed to do a particular thing and it can do that thing well. Some users are favor of the benefits of using command line commands for the appropriate tasks. Compare to using GUI to do some operations, using CMD is often faster and agile.
How to Open Windows Command Line Window
You have several ways to get into command line Windows screen. Here we introduces two simple ways to quickly run Windows 10 Command Prompt as administrator.
You can press Windows + R keys simultaneously to open Windows Run box, type cmd, and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter together to open Windows cmd.exe and run it as administrator.
You can also click Start or the Search Box on Windows 10 computer screen, type cmd, and right-click Command Prompt app to choose Run as administrator.
After you get into Windows Command Prompt, you can type certain command lines to perform different tasks with the Windows command line commands.
Basic CMD Commands List Windows 10/8/7
As for what are the basic commands in Command Prompt, below we list some commonly used Windows command line commands incl. those related to hard drive partition management and Windows 10 repair.
Dir. You can type dir in the Command Prompt window to list files in the current directory. If you want to list files or directories that begin with the letter “B”, you could type dir b*.
Run a program. You can open and run any executable (.exe) file from the Command Prompt by typing the name of the file.
Change the directory. You can use the cd command to change the folder directory in Command Prompt. After you enter into Windows command line window, you can type cd\ and press Enter on the keyboard, and it will take you to the top directory. Then if you want to access the system32 folder located in C:\Windows, you should type cd windows\system32\, and press Enter.
Change the drive. To switch drives with command line Windows, you can type the drive letter of the drive followed by a colon “:”. For instance, if you want to change to D drive, you can type d: and press Enter.
Diskpart. The diskpart command is used to create, manage, and delete hard drive partitions.
Convert. Convert FAT to NTFS.
Diskcopy. Copy the contents of one disk and place them on another disk.
Fixboot. Write a new boot sector.
Fixmbr. Write a new boot record for a disk drive.
Format. Wipe a disk drive and prepare a disk drive.
CHKDSK. You can use CHKDSK command line to diagnose and fix hard drive errors. The command line is like this: chkdsk c /f /r. You should replace “c” with the drive letter of a specific partition.
SFC. The System File Checker can help detect and repair corrupted or missing system files.
DISM. The DISM command-line tool is used to manage and repair Windows images.
For more Windows command lines, you may refer these two posts below. They list all the basic CMD commands in alphabetical order and provide explanation of the usage of each command line Windows.
List of DOS commands – Wiki
List of Command Prompt Commands
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Alisa is a professional English editor with 4-year experience. She loves writing and focuses on sharing detailed solutions and thoughts for computer problems, data recovery & backup, digital gadgets, tech news, etc. Through her articles, users can always easily get related problems solved and find what they want. In spare time, she likes basketball, badminton, tennis, cycling, running, and singing. She is very funny and energetic in life, and always brings friends lots of laughs.