Товарищи, добрый день. Так как у меня появились несколько идей для написания будущих статей, я решил немного подготовить сайт. В будущем, нам скорее всего понадобится инструмент PowerShell, который уже сейчас превосходит по возможностям стандартную командную строку, но все равно развивается параллельно ей. Подробнее лучше прочитать на википедии, а у нас практические знания, поэтому переходим к инструкции. И снова у нас несколько способов:
- Через меню «Пуск»
- Через командную строку
- Через проводник
- Заменой командной строки в контекстном меню «Пуск» (только современные операционные системы)
Самый популярный способ у нас будет первым, для Windows 10: открываем меню «Пуск» → «Все программы» → ищем каталог «Windows PowerShell» и выбираем файл нужной разрядности. На 32 битных системах будет только 32 битный исполняющий файл.
Если необходим PowerShell с правами администратора, то кликаем правой клавишей мыши по файлу, выбираем «Дополнительно» и жмем «Запуск от имени администратора».
Для Windows 8.x и старше: Открываем меню «Пуск» → открываем раздел «Все программы» → листаем до раздела служебные и открываем Windows PowerShell этот сриншот сделан на 32 битной системе и здесь уже видно, что файл будет только один.
Запуск от имени администратора по тому же сценарию, правой клавишей по файлу и выбираем «Запустить от имени администратора»
2. Запуск PowerShell через командную строку
Да, для любителей нестандартных путей, тоже способ есть)) Много способов запуска командной строки описаны здесь. Здесь же я опишу способ, который подходит для современных операционных систем. Нажимаем правой клавишей мыши по углу пуск или жмем Win+X, а в открывшемся меню выбираем подходящую командную строку. Если вам необходим PowerShell с правами администратора, то выбираем и командную строку с правами администратора.
В открывшееся окно вводим powershell и жмём Enter. После этого командная строка будет работать полностью как Windows PowerShell.
3. Запуск Windows PowerShell через окно проводника Windows.
Открываем проводник и переходим в одну из папок:
a) 64bit PowerShell если стоит 64 битная система или 32bit PowerShell, если стоит 32 битная система
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0
b) 32bit PowerShell на 64 битных системах находится в папке:
C:\Windows\syswow64\Windowspowershell\v1.0
Можно просто вставить ссылку в адресную строку.
Если вам нужен PowerShell с обычными правами, просто запускаем выделенный файл. Если же с правами администратора, жмём правой клавишей мыши и выбираем «Запуск от имени администратора».
4. Замена командной строки на PowerShell в контекстном меню «Пуск».
Вот во втором способе, мы использовали контекстное меню «Пуска» и там по-умолчанию добавлена командная строка. Это можно исправить. Скажем для системных администраторов, все чаще нужен PowerShell, вместо командной строки и вместе с добавлением контекстного меню, Microsoft добавили возможность замены командной строки на Windows PowerShell. Для этого, необходимо кликнуть правой клавишей мыши по пустому месту на «Панели задач». И выбрать её «Свойства».
На вкладке «Навигация» ставим галочку на «Заменить командную строку оболочкой Windows PowerShell…» и жмём ОК.
Теперь в контекстном меню можно сразу же запускать Windows PowerShell.
Вроде всё. Надеюсь эта статья оказалась вам полезной, нажмите одну из кнопок ниже, чтобы рассказать о ней друзьям. Также подпишитесь на обновления сайта, введя свой e-mail в поле справа или подписавшись на группу во Вконтакте и канал YouTube.
Спасибо за внимание
Материал сайта geekteam.pro
I have Windows 10 and run some PowerShell commands through the Outlook COM object. This requires PowerShell to be running the same level of access (running as admin or user) as Outlook.
As I need PowerShell to be running as administrator for other pieces I set Outlook to always run as admin too, no problem. The issue is when I open the ISE I now can’t access the Outlook objects.
There doesn’t appear to be any way to set the ISE to always run as admin. The Compatibility tab is missing (though not on PowerShell itself?) and the registry keys in ...Windows NT\AppCompatibility did nothing. I’d disable UAC completely but of course it’s not possible in Windows 10 without screwing over a bunch of other stuff.
Any ideas? And no I don’t particularly feel like right clicking the icon each time as I often open scripts directly.
UPDATE: Outlook complains it can’t index as admin and the ISE doesn’t recognise my network drives as admin so the lesser of two evils is just run both as a user. Incidentally, the Compatibility tab has disappeared from the PowerShell exe now too, thanks Microsoft…
asked Oct 29, 2015 at 10:19
Deadly-BagelDeadly-Bagel
4231 gold badge3 silver badges13 bronze badges
Here are 2 different options you can use to start ISE as admin:
- You can create/edit a shortcut to the
powershell_ise.exeexecutable file and edit the properties for that shortcut toRun as Administrator.
- You can start PowerShell ISE as admin by
Start-Process powershell_ise -verb RunAs.
answered Oct 29, 2015 at 14:25
bentekbentek
6943 silver badges12 bronze badges
7
I came across this many months after the post, but I think my comment is helpful.
@Deadly-Bagel No, the script is just a file so it doesn’t «run».
While a script is just a file, it can certainly contain functions. One of those functions can be setup to run as the first process in that script file. That function can be used to determine whether or not the current session is running as an administrator. If it is not, it can self-elevate (assuming the logged-in user has admin rights).
function Use-RunAs
{
# Check if script is running as Adminstrator and if not use RunAs
# Use Check Switch to check if admin
param([Switch]$Check)
$IsAdmin = ([Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal] [Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()`
).IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole] "Administrator")
if ($Check) { return $IsAdmin }
if ($MyInvocation.ScriptName -ne "")
{
if (-not $IsAdmin)
{
try
{
$arg = "-file `"$($MyInvocation.ScriptName)`""
Start-Process "$psHome\powershell.exe" -Verb Runas -ArgumentList $arg -ErrorAction 'stop'
}
catch
{
Write-Warning "Error - Failed to restart script with runas"
break
}
exit # Quit this session of powershell
}
}
else
{
Write-Warning "Error - Script must be saved as a .ps1 file first"
break
}
}
Use-RunAs
I hope this helps your situation. If not, I’d be happy to revisit.
answered Jan 8, 2018 at 4:23
EricOEricO
211 bronze badge
1
I’m assuming you are admin on the said PC otherwise you wouldn’t be asking to do such,
You can Completely ignore UAC Prompt and just run everything in elevated mode without having to click Yes or No!
to do so, follow these steps:
- From the start menu, go to «Edit Group Policy»
- Go to this path: Computer Configuration >> Windows Settings >> Security Settings >> Local Policies >> Security Options
- Under «Policy», find «User Account Control: Behavior of the elevation prompt for administrators in Admin Approval mode
- Change settings to elevate without prompting.
That’s it!
answered Jun 26 at 22:35
3
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
PowerShell is a command-line shell that is used for administering windows OS and applications. Microsoft has built it using the .NET framework. CMDLETS are the command used by PowerShell to execute tasks. But while using PowerShell, you might often run into scenarios where you need administrator privileges to execute tasks. So, when I set up my PowerShell environment, I set up administrator privileges so that I can edit registry settings and do more complex tasks there. In this article, I will show you different solutions on how to run PowerShell script as admin.
Prerequisites
To follow all the steps mentioned in this article, you must have:
- A Windows 10 PC
- An account with administrator privileges
- PowerShell
Solution 1: Search Bar
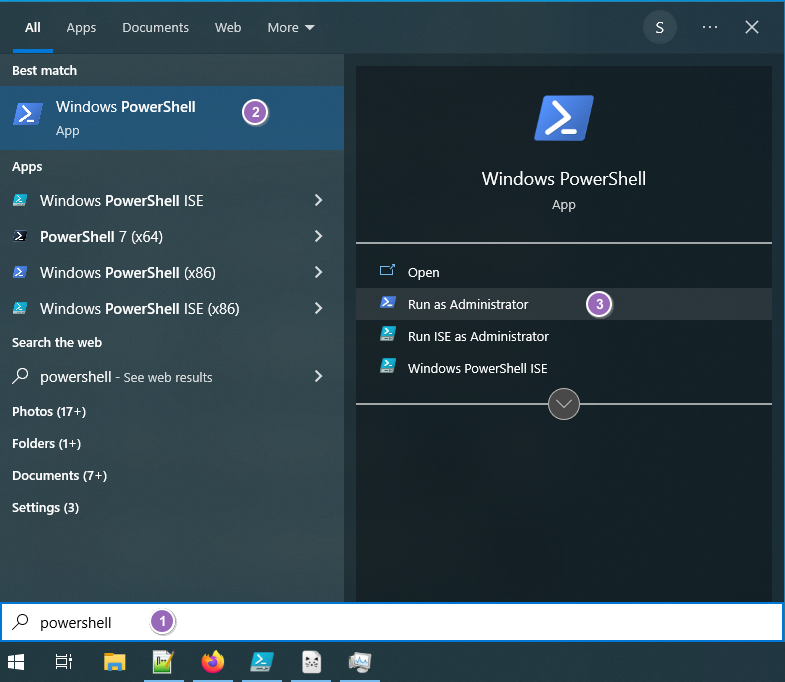
- Firstly, go to the search bar of windows 10.
- Search for PowerShell.
- You will get the best match Windows PowerShell option.
- Click on Run as Administrator.
- You might get a popup, which will ask if you want to allow this app to make changes on your device, click on Yes.
- The Windows PowerShell will start as Administrator.
Solution 2: Pinned Application
- Firstly, go to the search bar of windows 10.
- Search for PowerShell.
- Click on the Windows PowerShell ISE application arrow.
- Click on Pin to Start.
- Now when you click on the start sign, you will see the Windows PowerShell ISE application pinned.
- Right click on the application.
- Click on more.
- Click on Run as Administrator.
Solution 3: Taskbar
- Go to the search bar of windows 10.
- Search for PowerShell.
- You will get the best match Windows PowerShell option.
- Click on Pin to the taskbar.
- The Windows PowerShell application will now appear on your taskbar.
- Right click on the PowerShell taskbar application.
- Click on Run as Administrator.
Solution 4: PowerShell Executable
Whether you are using a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system, you can run PowerShell as administrator from its respective location.
- Go to the search bar of windows 10.
- Search for PowerShell.
- You will get the best match Windows PowerShell option.
- Click on Open file location.
- Select the powershell.exe file.
- Right-click on powershel.exe and select Run as Administrator.
Solution 5: Shortcut
- Go to the search bar of windows 10.
- Search for PowerShell.
- You will get the best match Windows PowerShell option.
- Click on Open file location.
- Select a PowerShell application and create a shortcut on the desktop.
- Go to your desktop.
- Right click on the PowerShell application.
- Click on Properties.
- Windows PowerShell Properties will open.
- Click on Advanced.
- Click on the Run as Administrator checkbox and click on Ok.
- Finally, click on Apply and Ok.
Now, whenever you run the PowerShell shortcut application on the desktop, it will run as administrator.
Solution 6: Run Command Window
The Run Command Window is a powerful tool that lets you run programs without searching for them using the Search Bar, Start Menu or File Explorer.
- To run PowerShell as administrator by using the Run command window, press Win Key + R to open the run application.
- Type powershell and press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
This will open the PowerShell as administrator
Solution 7: Command Line
- Go to the search bar of windows 10.
- Search and select Command Prompt application.
- Click on Run as Administrator.
- Run this command in the command prompt -> powershell Start-Process powershell -Verb runAs
- This will open Windows PowerShell as admin.
- Note: Even if you don’t run command prompt application as administrator, this command will still open Windows PowerShell as admin.
Solution 8: Batch File
- Open your favorite text editor.
- Paste this line in the file -> Powershell.exe -Command “& {Start-Process Powershell.exe -Verb RunAs}”
- Save it as a batch file with .bat extension as your preferred location.
- Double click and run the batch file.
- It will open a PowerShell window running as administrator.
Solution 9: Using Elevated Script
On UAC-enabled systems, to make sure a script is running with full admin privileges, add this code at the beginning of your script:
param([switch]$Elevated)
function Test-Admin {
$currentUser = New-Object Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal $([Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent())
$currentUser.IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltinRole]::Administrator)
}
if ((Test-Admin) -eq $false)
{
if ($elevated) {
# tried to elevate, did not work, aborting
} else {
Start-Process powershell.exe -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList ('-noprofile -noexit -file "{0}" -elevated' -f ($myinvocation.MyCommand.Definition))
}
Exit
}
'running with full privileges'Now, when running your script, it will call itself again and attempt to elevate privileges before running. The -elevated switch
prevents it from repeating if something fails.
So, those were the multiple ways how you could run the PowerShell script as admin.
В этой базовой инструкции подробно описано 7 способов запустить PowerShell от имени администратора, в Windows.
Запуск PowerShell с правами администратора, частая необходимость при получении доступа или изменении параметров системы.
Содержание
Запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, с помощью:
- Меню Пуск
- Меню Быстрые ссылки
- Меню Файл
- Меню Поиск
- Командная строка
- PowerShell (с правами пользователя)
- Меню Выполнить
Article in other languages:
?? — How to Run PowerShell as Administrator
?? — Cómo ejecutar PowerShell como administrador
?? — Comment exécuter PowerShell en tant qu’administrateur
?? — So führen Sie PowerShell als Administrator aus
?? — Hoe te PowerShell uitvoeren als administrator
Меню Пуск
Первый способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, используя кнопку Пуск.
- Нажмите кнопку Пуск;
- В списке программ нажмите Windows PowerShell;
- Щелкните по Windows PowerShell правой клавишей мыши, выберите Дополнительно и Запуск от имени администратора.
Меню Быстрые ссылки
Второй способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, используя меню Быстрые ссылки.
- Щёлкните по кнопке Пуск правой клавишей мыши (или нажмите сочетание Windows+X);
- Нажмите Windows PowerShell (администратор).
Меню Файл
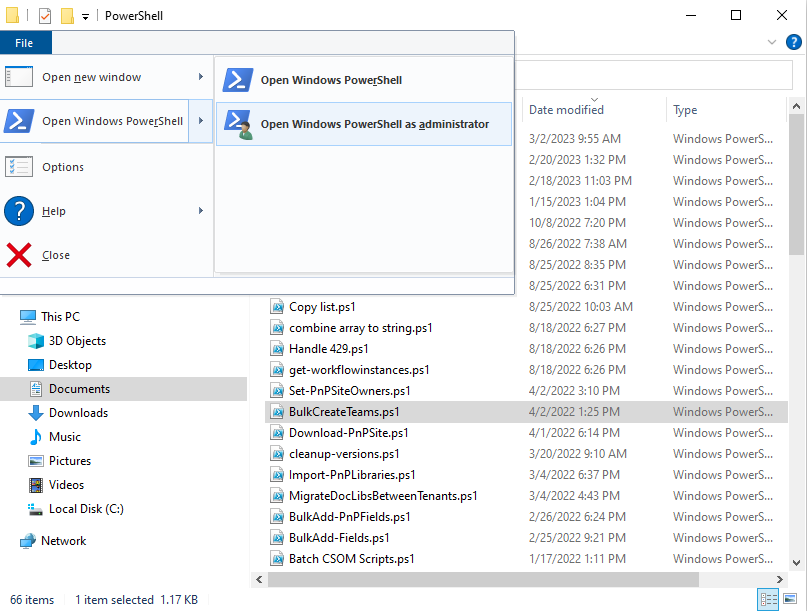
Третий способ запустить PowerShell от имени администратора — это используя меню Файл при выделении файла или папки в проводнике Windows.
- Выделите файл или папку в окне Проводника Windows;
- Щелкните по меню Файл, наведите курсор на треугольник расширенного выбора в пункте Windows PowerShell;
- Выберите Запустить Windows PowerShell от имени администратора.
Меню Поиск
Четвертый способ запуска PowerShell с правами администратора — это используя Поиск Windows из начального меню.
- Щелкните по строке Поиск на панели задач (или нажмите сочетание Windows+S);
- Введите текст PowerShell;
- Щелкните по треугольнику расширенные результаты в пункте Windows PowerShell и нажмите Запуск от имени администратора.
Пятый способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, с помощью командной строки.
Запустите командную строку и выполните команду:
powershell "start-process powershell -verb runas"Запуск PowerShell от имени администратора с помощью PowerShell (с правами пользователя)
Шестой способ — это запуск PowerShell от имени администратора, с помощью консоли PowerShell запущенной с правами пользователя.
Запустите консоль PowerShell и выполните команду:
start-process powershell –verb runasМеню Выполнить
Седьмой способ — используйте меню Выполнить, для запуска Windows PowerShell с правами администратора.
Откройте меню Выполнить.
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Windows+R (или щелкните по кнопке Пуск правой клавишей мыши, выберите Выполнить);
- Введите команду powershell;
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
? В этой статье обсуждалось как запустить PowerShell с правами администратора, для запуска программ или изменения параметров системы требующих повышенных прав. Я надеюсь, вы смогли запустить консоль PowerShell с повышенными правами выбранным способом. Однако, если вы столкнулись с каким-то проблемами при запуске PowerShell, не стесняйтесь написать в комментариях. Я постараюсь помочь.
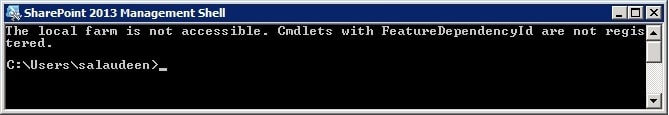
PowerShell is an incredibly powerful tool for managing and automating tasks in Windows environments. It’s a common Administrator’s pitfall – forgetting to run a PowerShell script using the “Run as Administrator” option. Failing so could lead to many *weird* issues while running PowerShell scripts. E.g., In SharePoint, we get the “The local farm is not accessible. Cmdlets with FeatureDependencyId are not registered.” error.
Running a PowerShell script as an administrator is often necessary when executing scripts that require elevated privileges to modify system settings, install software, or manage resources. This article will guide you through running a PowerShell script as an administrator.
You need to run PowerShell as an administrator to install software, modify registry keys, or manage system settings. Without administrative privileges, PowerShell may not be able to execute certain commands, and you may receive errors or access denied messages.
So, How to run PowerShell as an administrator? The Solution is simple! To open Windows PowerShell as admin, Type “PowerShell” in the start menu >> Choose “Run as Administrator”. You can also right-click “Windows PowerShell” from the search results and select “Run as administrator”. I assume you have Administrative privileges on your Windows 10 or 7 computers, BTW!
Use Ctrl+Shift+Enter key shortcut key combination on your keyboard to launch PowerShell (or any program) with the “Run as Administrator” option!
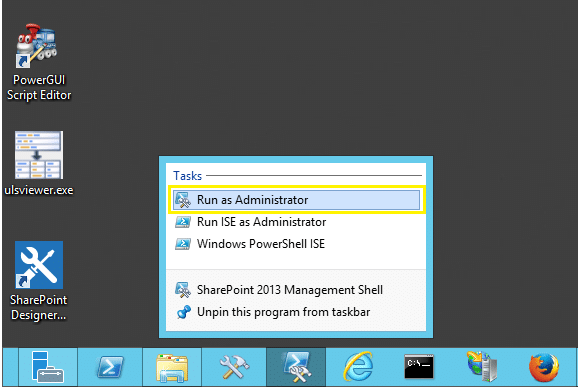
In the case of Snap-in, Right-click the SharePoint 2013 PowerShell Snap-in and choose “Run as Administrator”.
Once the PowerShell console is in Administrator mode, you can start typing cmdlets to execute them in Administrator mode.
Switch from Normal User to Administrator in PowerShell
When you open the PowerShell console, it launches in normal user mode by default. To switch to Administrator mode, use the following:
start-process PowerShell -verb runas
This command will launch an elevated Windows PowerShell as an administrator.
How to run a ps1 file in PowerShell as an Administrator?
To run PowerShell scripts as an Administrator, do the following:
- Launch the PowerShell console or PowerShell ISE as Administrator using the above “Run as Administrator” method.
- Navigate to the script location using the “CD” cmdlet. E.g., “CD C:\Scripts”
- Run the PowerShell script by typing its name followed by the “.ps1” extension. E.g., “.\YourScriptName.ps1”
Enable the “Run as Administrator” elevated privilege for PowerShell by default
If you frequently run PowerShell scripts as an admin, you may find it tedious to click “Yes” every time the UAC (User Account Control) prompt appears. Fortunately, there’s a way to bypass the prompt and automatically Open PowerShell in admin mode.
To automatically run the PowerShell script as administrator without a prompt, create a shortcut to your PowerShell console on your desktop.
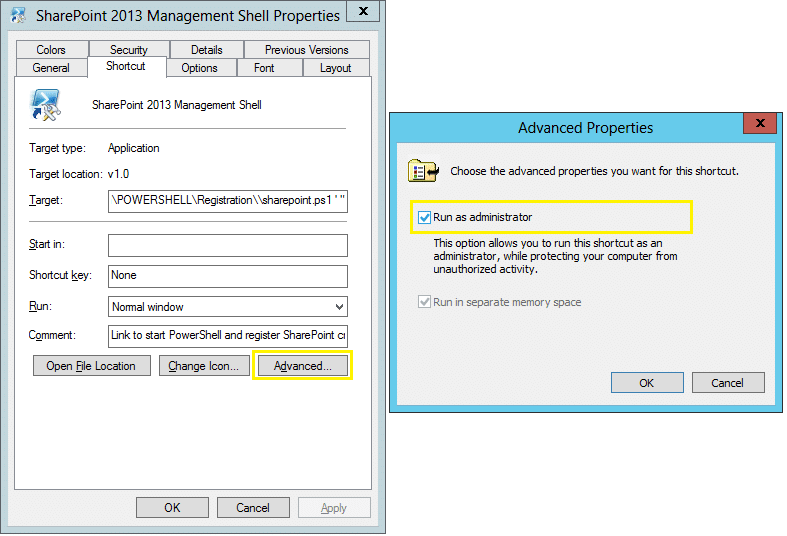
- Right-click the “SharePoint 2013 Management Shell” shortcut (or Windows PowerShell) and click Properties.
- Click the “Advanced” button under the Shortcut tab
- Enable “Run as Administrator” and click the “OK” button.
From now on, you can run PowerShell in elevated mode by double-clicking the new shortcut on your desktop. It opens the PowerShell in Administrative mode always.
Run PowerShell as an administrator in scheduled tasks:
The Task scheduler allows you to schedule scripts to run at specific times or events, allowing them to run with administrative privileges. If you are scheduling a PowerShell script, make sure you select the “Run With the Highest Privileges” check box. Otherwise, your scheduled task may run unattended, invoking a UAC prompt. To do this,
- Open the Task Scheduler and create a new task.
- In the General tab, give the task a name and description, and select “Run with highest privileges.”
- In the Triggers tab, specify when and how often the task should run.
- In the Actions tab, select “Start a program” and type “powershell.exe” in the Program/script field. Then, add the path to your PowerShell script in the Add arguments (optional) field.
- Finally, click “OK” to save the task.
More on creating a scheduled task to run the PowerShell script is here: How to Run a PowerShell script using Windows Task scheduler?
Handle Run as Administrator within PowerShell script:
Let’s handle it in our PowerShell code, even if you forget to use the “Run as Administrator” option!
Function Check-RunAsAdministrator()
{
#Get current user context
$CurrentUser = New-Object Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal $([Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent())
#Check user is running the script is member of Administrator Group
if($CurrentUser.IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltinRole]::Administrator))
{
Write-host "Script is running with Administrator privileges!"
}
else
{
#Create a new Elevated process to Start PowerShell
$ElevatedProcess = New-Object System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo "PowerShell";
# Specify the current script path and name as a parameter
$ElevatedProcess.Arguments = "& '" + $script:MyInvocation.MyCommand.Path + "'"
#Set the Process to elevated
$ElevatedProcess.Verb = "runas"
#Start the new elevated process
[System.Diagnostics.Process]::Start($ElevatedProcess)
#Exit from the current, unelevated, process
Exit
}
}
#Check Script is running with Elevated Privileges
Check-RunAsAdministrator
#Place your script here.
write-host "Welcome"
Add this code at the beginning of your script.
Run as a Different User in PowerShell scripts:
$credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PsCredential("Domain\UserID", (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password" -AsPlainText -Force))
Start-Process powershell -Credential $credential -NoNewWindow
How to run PowerShell as administrator from the command prompt?
To run PowerShell as an administrator in the command line:
- Click on the Windows start icon >> Type “Cmd” to launch the command prompt.
- Type : PowerShell to enter into the PowerShell console
- Now, Type: Start-Process PowerShell -Verb RunAs
BTW, There could be some more reasons for “The local farm is not accessible. Cmdlets with FeatureDependencyId are not registered” issues, such as:
- .Net framework version compatibility (SharePoint 2010 isn’t compatible with .Net Framework 4.xx), append “-version 2” to the command line to resolve.
- Logged-in Administrator may not be a member of “SharePoint_Shell_Access” role. (Run “Add-SPShellAdmin” cmdlet to resolve – https://www.sharepointdiary.com/2014/07/the-local-farm-is-not-accessible-cmdlets-with-featuredependencyid-are-not-registered-powershell-error.html )
Conclusion
Running a PowerShell script as an administrator is often necessary to execute tasks requiring elevated privileges. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily launch PowerShell with administrative rights and run your script. This ensures you have the necessary permissions to perform advanced system modifications, install software, or manage resources as needed.
How do I run PowerShell as an administrator in Windows 10?
From Windows 10 File Explorer, You can select any PowerShell file (.ps1) >> Click on the “File” menu >> Open Windows PowerShell >> Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator.
How do you run PowerShell as an administrator from a command line?
To run PowerShell as administrator from cmd, Open the command prompt, type PowerShell, and then enter “Start-Process powershell -Verb RunAs”. This will open a new PowerShell window with administrator privileges.
Can you run PowerShell without admin rights?
Yes, you can run PowerShell without admin rights. To do so, simply open the Start menu, type “PowerShell” in the search bar, and click “Windows PowerShell.”. However, any system operation, such as changing system settings, making registry edits, or installing software, etc., requires PowerShell in Admin rights.
How do you detect if PowerShell is running as an administrator?
Use “([Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal] [Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()).IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole]::Administrator)”. This will return “True” if PowerShell is running as an administrator, and “False” if it is not.
How to run PowerShell as administrator from a batch file?
Use: powershell -noprofile -command “&{ start-process powershell -ArgumentList ‘-noprofile -file C:\script\psfile.ps1’ -verb RunAs}”
How do I run PowerShell as an administrator remotely?
When you execute commands remotely, they are run with administrative privileges because only administrators can execute them remotely in PowerShell.