From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Initial release | July 27, 1993; 30 years ago |
| Latest release | 2022 (10.0.20348.1906) / August 8, 2023; 50 days ago[1] |
| Latest preview | vNext (10.0.25931) / August 16, 2023; 42 days ago[2] |
| Update method |
|
| Default user interface |
|
| License | Trialware, SaaS, or volume licensing |
| Official website | www |
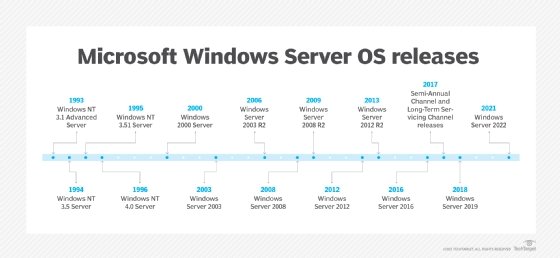
Windows Server (formerly Windows NT Server) is a group of operating systems (OS) for servers that Microsoft has been developing since 1993. The first OS that was released for this platform is Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server. With the release of Windows Server 2003, the brand name was changed to Windows Server. The latest release of Windows Server is Windows Server 2022, which was released in 2021.
Microsoft’s history of developing operating systems for servers goes back to Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server. Windows 2000 Server is the first OS to include Active Directory, DNS Server, DHCP Server, and Group Policy.
Members[edit]
Main releases[edit]
Main releases include:
- Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server (July 1993)
- Windows NT Server 3.5 (September 1994)
- Windows NT Server 3.51 (May 1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 Server (July 1996)
- Windows 2000 Server (December 1999)
- Windows Server 2003 (April 2003)[3]
- Windows Server 2003 R2 (December 2005)[4]
- Windows Server 2008 (February 2008)[5]
- Windows Server 2008 R2 (October 2009)[6]
- Windows Server 2012 (September 2012)[7]
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (October 2013)[8]
- Windows Server 2016 (October 2016)[9]
- Windows Server 2019 (October 2018)[10]
- Windows Server 2022 (August 2021)[11]
Traditionally, Microsoft supports Windows Server for 10 years, with five years of mainstream support and an additional five years of extended support. These releases also offer a complete desktop experience. Starting with Windows Server 2008 R2, Server Core and Nano Server configurations were made available to reduce the OS footprint.[12][13] Between 2015 and 2021, Microsoft referred to these releases as «long-term support» releases to set them apart from semi-annual releases (see below.)
For sixteen years, Microsoft released a major version of Windows Server every four years, with one minor version released two years after a major release. The minor versions had an «R2» suffix in their names. In October 2018, Microsoft broke this tradition with the release of Windows Server 2019, which should have been «Windows Server 2016 R2». Windows Server 2022 is also a minor upgrade over its predecessor.[14][15]
Branded releases[edit]
Certain editions of Windows Server have a customized name:
- Windows Storage Server (editions of Windows Server 2003 through 2016; editions of Windows Server IoT 2019 and its successors)[16][17][18]
- Windows HPC Server 2008
- Windows HPC Server 2008 R2
- Windows Home Server (an edition of Windows Server 2003)
- Windows Home Server 2011 (an edition of Windows Server 2008 R2)
- Hyper-V Server (a discontinued,[19] freeware edition of Windows Server 2008 through 2019)[20]
- Windows MultiPoint Server
- Windows Server Essentials[21][22]
- Windows Essential Business Server (discontinued)[23]
- Azure Stack HCI (an edition of Windows Server 2019 and later)[24]
Semi-annual releases (discontinued)[edit]
Following the release of Windows Server 2016, Microsoft attempted to mirror the lifecycle of Windows 10 in the Windows Server family, releasing new versions twice a year which were supported for 18 months. These semi-annual versions were only available as part of Microsoft subscription services, including Software Assurance, Azure Marketplace, and Microsoft Visual Studio subscriptions,[25] until their discontinuation in July 2021.[26][25]
The semi-annual releases do not include any desktop environments. Instead, they are restricted to the Nano Server configuration installed in a Docker container,[13][25] and the Server Core configuration, licensed only to serve as a container host.[13][25]
Semi-annual releases include:[27]
- Windows Server, version 1709 (unsupported as of April 9, 2019; 4 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1803 (unsupported as of November 12, 2019; 3 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1809 (unsupported as of November 10, 2020; 2 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1903 (unsupported as of December 8, 2020; 2 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 1909 (unsupported as of May 11, 2021; 2 years ago)
- Windows Server, version 2004 (unsupported as of December 14, 2021; 21 months ago)
- Windows Server, version 20H2 (unsupported as of August 9, 2022; 13 months ago)[28][29][30][31]
See also[edit]
- List of Microsoft Windows versions
- Microsoft Servers
- Linux range of use § Servers, mainframes and supercomputers
- NetWare
- Open Enterprise Server
References[edit]
- ^ «Windows Server 2022 update history». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved November 26, 2021.
- ^ «Announcing Windows Server Preview Build 25931». Microsoft Tech Community. August 16, 2023. Retrieved August 16, 2023.
when reporting issues please refer to «VNext» rather than Windows Server 2022 which is currently in market.
- ^ «Windows Server 2003 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. March 8, 2008. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server 2003 R2 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. March 8, 2008. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved September 25, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved September 25, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. January 2012. Retrieved October 10, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 R2 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft.com. Retrieved December 27, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Server 2016 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved December 7, 2016.
- ^ «Windows Server 2019 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server 2022 – Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ «What is Microsoft Windows Server LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel)? – Definition from WhatIs.com». SearchWindowsServer. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- ^ a b c «Windows Server – Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) vs Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) – Thomas Maurer». Thomas Maurer. November 19, 2017. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- ^ Sommergut, Wolfgang (August 24, 2021). «Windows Server 2022 released: Overview of new features». 4sysops. Archived from the original on August 24, 2021.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (August 20, 2021). «Microsoft’s Windows Server 2022 is rolling out to mainstream users». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 22, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Storage Server Lifecycle (EOL)». EndOfLife.Software.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 for Storage». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2022». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ Christensen, Elden (March 25, 2022). «Hyper-V in the 2022 Wave». Microsoft Tech Community. Self-published.
- ^ «Hyper-V Server». Search Product and Services Lifecycle Information. Microsoft. Retrieved September 2, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2008 Technical FAQ». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft. December 14, 2010 – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (September 3, 2011). «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials». Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved September 26, 2011.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server». TechNet Archive. Microsoft. February 7, 2012 – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Deploy the Azure Stack HCI operating system». Azure Docs. Microsoft. October 22, 2021.
- ^ a b c d «Windows Server servicing channels». Windows Server Library. Microsoft. July 5, 2022. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022.
- ^ «Microsoft to retire semi-annual Windows Server updates, will move entirely to LTSC releases». Neowin. July 28, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server». Search Product and Services Lifecycle Information. Microsoft. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- ^ «Windows message center: Windows Server, version 20H2 has reached end of servicing». August 9, 2022. Archived from the original on August 10, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server release information». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 9, 2022. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows Server, version 20H2». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 9, 2022. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ Popa, Bogdan. «Microsoft Retires Windows Server Version 20H2». news.softpedia.com. Archived from the original on August 10, 2022. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
External links[edit]
- Official website
Microsoft Windows Server OS (operating system) is a series of enterprise-class server operating systems designed to share services with multiple users and provide extensive administrative control of data storage, applications and corporate networks.
Development for Windows Server started in the early 1980s when Microsoft produced two operating system lines: MS-DOS and Windows NT. Microsoft engineer David Cutler developed the kernel of Windows NT with the intent to provide speed, security and reliability that large organizations require in a server operating system.
Prior to the release of Windows NT, many companies relied on the Unix operating system that required expensive RISC-based hardware to run file and printing services. Windows NT had the ability to run on less costly x86 machines.
A key feature in the NT architecture is symmetric multiprocessing, which makes applications run faster on machines with several processors.
Later iterations of Windows Server can be deployed either on hardware in an organization’s data center or on a cloud platform, such as Microsoft Azure.
Key features in later versions of Windows Server include Active Directory, which automates the management of user data, security and distributed resources, and enables interoperation with other directories; and Server Manager, which is a utility to administer server roles and make configuration changes to local or remote machines.
Microsoft released its Windows NT operating system in two formats: one for workstations and the other for servers. The 32-bit operating system featured a hardware abstraction layer (HAL), which provided more system stability by blocking applications from direct access to system hardware. Companies could use Advanced Server as a domain controller to store user and group rights. Microsoft updated key networking features in this server release and added integrated support for TCP/IP and Winsock. Other networking improvements allowed users on other non-Microsoft operating systems to access files and applications on the domain. Microsoft fine-tuned this release to boost performance and reduce the amount of required memory. This server OS was optimized to deliver services faster to users through its updated networking stack. Microsoft added more connectivity support for companies in a mixed environment with both Windows NT and NetWare servers to allow users to get services from each with a single credential. Microsoft borrowed the Windows 95 interface for this server OS release and also used many of the applications in the client OS, such as the File Explorer. Microsoft expanded the networking protocol capabilities in this release to make network resources available to a wider array of non-Microsoft machines. Key features in this release were the ability to use a server as an Internet Information Server — now called Internet Information Services (IIS) — and a domain name system server. This server OS also could walk administrators through various tasks, such as sharing a hard disk with a feature called Administrative Wizards. Windows 2000 introduced Active Directory, a directory service that stores and manages information about network objects, including user data, systems and services. Active Directory lets administrators perform various tasks, such as virtual private network configuration, data encryption and granting access to file shares on networked computers. Microsoft also introduced several other key features in this release, including: Windows 2000 had three editions — Server, Advanced Server and Datacenter — that were built to work with Windows 2000 Professional, the client OS. Microsoft introduced the «Windows Server» brand with the release of Windows Server 2003 and touted its security improvements over Windows 2000. Microsoft hardened IIS, the web server feature, and disabled more default services to reduce exploit opportunities. Microsoft introduced server roles with this release, which allowed administrators to assign a specific function to a server, such as domain controller or DNS server. Other new features in this release included expanded encryption functionality, built-in firewall, greater Network Address Translation (NAT) support and Volume Shadow Copy Service. Windows Server 2003 had four editions: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter and Web. Rather than a version number, Microsoft began using the R2 — or release two — designation with Windows Server 2003 R2. Organizations always need to buy a new Windows Server license to use the new server operating system, but R2 releases used the client access licenses (CALs) of the immediately preceding server version to eliminate the need to upgrade those licenses. This version improved on the security and safety features in Windows Server 2003. Key new features in this release were: This version also added enhancements to file replication and data compression for branch office servers. Among the security improvements in this release was the Security Configuration Wizard, which let administrators apply consistent security policies to multiple machines. Windows Server 2008 added new features such as: Microsoft also overhauled the networking stack and Active Directory to enhance its Group Policy and identity management capabilities. Windows Server 2008 came in four editions: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter and Web. Microsoft used its Windows 7 kernel for this server operating system and touted its improved scalability and availability features. Microsoft enhanced Active Directory for improved handling of user accounts and more granular control with policies. The company also updated Terminal Services functionality and rechristened it to Remote Desktop Services (RDS). New features in this release include BranchCache and DirectAccess, both aimed at improving how users in remote locations are able to get their work done. This server OS, like its predecessor, shares some of the administrative and security functionality used in the Windows Vista client operating system. Windows Server 2008 R2 also marked a change from a 32-bit server operating system to a 64-bit version. Microsoft embedded a number of cloud-related features to Windows Server 2012, going so far as to dub it the «Cloud OS,» so organizations could run services more easily in public or private clouds. The company also made significant updates to the operating system’s storage infrastructure and Hyper-V virtualization platform. New features worth noting in this release were the Hyper-V virtual switch, Hyper-V Replica, Storage Spaces and ReFS file system. In another change with this release, Microsoft switched the default installation option to Server Core, which requires administrators to use PowerShell. Upon this release, PowerShell had 2,300 cmdlets available for management. This server version came in four editions: Essentials, Foundation, Standard and Datacenter. The Standard and Datacenter editions had the same feature set, but a Standard license permitted organizations to run two virtual machines (VMs), while Datacenter permitted an unlimited number of VMs. Microsoft made expansive changes across the board with Windows Server 2012 R2, including significant updates to virtualization, storage, networking, information security and web services. New features of note: Microsoft nudged enterprises closer to the cloud with a number of new features tailored to ease workload migrations, such as support for Docker containers and software-defined enhancements in networking. Microsoft debuted Nano Server, a minimal server deployment option intended to boost security by shrinking the attack vector. Microsoft says Nano Server is 93% smaller than a full Windows Server deployment. Another nod to security comes in the new Hyper-V shielded VM feature, which uses encryption to prevent data inside a VM from being compromised. The Network Controller is a key new networking feature that allows administrators to manage the switches, subnets and other devices on the virtual and physical networks. This server OS comes in Standard and Datacenter editions. In previous Windows Server versions, the Standard and Datacenter editions had the same feature set, but different license rights and use restrictions. In Windows Server 2016, the Standard edition does not have the more advanced features in virtualization, storage and networking. In June 2017, Microsoft announced it would split Windows Server into two channels: the Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) and the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) — formerly the Long-Term Servicing Branch. The SAC caters to enterprises with a DevOps framework that prefer a shorter term between feature updates to get the most recent updates for rapid application development cycles. SAC releases will come every six months — one in the spring and one in the fall — with mainstream support of just 18 months. Microsoft tailors the LTSC for companies that prefer the more traditional release cycle of two to three years between major feature updates with the typical five years of mainstream support followed by five years of extended support. The LTSC naming convention will retain the Windows Server YYYY format — such as Windows Server 2016 — while the SAC releases will follow a format of Windows Server version YYMM. Microsoft said it plans to add most of the enhancements — with some variations — from the SAC releases into upcoming LTSC releases. Microsoft released its first SAC release — Windows Server version 1709 — in October 2017. Highlights of this release were support for Linux containers with kernel isolation provided by Hyper-V and a refactored Nano Server strictly for use as a base OS container image. Businesses with Software Assurance on their Windows Server Standard or Datacenter licenses or a Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN) license can download the SAC releases from Microsoft’s Volume Licensing Service Center. Organizations without Software Assurance can use SAC releases in Azure or another cloud or hosting environment.
History of Windows Server
1993: Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
1994: Windows NT 3.5 Server
1995: Windows NT Server 3.51
1996: Windows NT Server 4.0
2000: Windows 2000
2003: Windows Server 2003
2005: Windows Server 2003 R2
2008: Windows Server 2008
2009: Windows Server 2008 R2
2012: Windows Server 2012
2013: Windows Server 2012 R2
2016: Windows Server 2016
2017: Semi-Annual Channel and Long-Term Servicing Channel releases
Летом 2021 года Microsoft анонсировала релиз Windows Server 2022. Количество нововведений хоть и невелико, но среди них есть некоторые интересные особенности, причем две из них зарезервированы для старшего издания Azure. Ключевое внимание уделяется безопасности и модификациям для SMB и Hyper-V. Подробно обо всех возможностях новой серверной ОS от Microsoft читайте в нашей статье.
Что нового в MS Windows Server 2022
Во время анонса новой операционной системы Microsoft особо подчеркнула инновационные возможности, нацеленные на повышение безопасности. Новшества позволяют реализовать концепцию сервера с защищенным ядром, основанную на сочетании оборудования, микропрограмм и драйверов. Все заявленные функции можно будет вручную настроить в центре администрирования Windows.
Более того, впервые HTTPS и TLS 1.3 будут включены по дефолту. Также частью новой ОС стал Secure DNS (DNS поверх HTTPS), который будет включен еще и в клиентские Windows 10 21H2, а также Windows 11.
Улучшения в сетевом протоколе SMB
С появлением Server 2022 изменится и процедура шифрования для протокола Server Message Block, где с недавнего времени внедрены два надежных алгоритма AES-256. Алгоритм AES-128, как и раньше, будет работать для обеспечения совместимости.
Шифрование SMB настраивается в том числе отдельно для связи между узлами кластера, что сказывается как на CSV, так и на SSD.
Эти функции безопасности теперь также совместимы с SMB Direct, тогда как в предыдущих версиях Windows Server они вызывали снижение производительности при использовании сетевых адаптеров RDMA.
Еще одна новая функция — это возможность сжимать SMB-трафик. В Windows 10, начиная с выпуска 20H2, можно было включить сжатие SMB для xcopy и robocopy с отдельными переключателями для этих программ. В Server 2022 эту функцию теперь можно включить для обмена файлами через Центр администрирования Windows или PowerShell.
Еще одна новая функция для доступа к общим файловым ресурсам — поддержка SMB через QUIC. Протокол QUIC может использоваться как альтернатива TCP, а в сочетании с TLS 1.3 он также может использоваться для замены VPN. Однако эта функция доступна только в Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition.
Раздел конфигурации SMB в центре администрирования Windows однако не содержит настроек для SMB через QUIC в Server 2022 Datacenter.
В случае «горячего исправления» Microsoft резервирует для Azure еще одну интересную новую функцию. Она позволяет внедрять обновления без перезапуска сервера. Операционная система использует для этого службу автоматического управления Azure.
Помимо новых вариантов гибридных конфигураций (таких как управление локальными серверами через Azure Arc) и расширенной поддержки контейнеров, новая операционная система достигла определенных результатов, соответствующих традиционному использованию ОС.
Вложенная виртуализация для AMD
Еще одна немаловажная «фича» гарантирует поддержку вложенной виртуализации на чипах производства AMD, которая прежде была доступна лишь для процессоров Intel, начиная с версии ОС Windows Server 2016.
Касательно поддержки ЦП новых поколений, то новая версия ОС поддерживает процессоры Intel Ice Lake. На этой платформе система может оперировать объемами оперативной памяти до 48 ТБ и обеспечивать работу до 2048 ядер логического процессора.
Edge включен в Server Core
С прекращением поддержки IE 15 июня 2022 года Microsoft Edge заменит устаревший браузер на сервере. Таким образом, Edge включен в Server 2022 и также может опционально использоваться при установке Server Core. Такая конфигурация ранее уже поддерживалась, однако при ручной установке возникали некоторые препятствия.
Улучшение для Storage Spaces Direct
Для работы с гиперконвергентной инфраструктурой все будущие инновации войдут в Azure Stack HCI, однако в Windows Server по-прежнему будут улучшаться существующие функции.
Теперь это отражено в версиях Server 2022, которые по-прежнему не располагают функциями, такими как расширяемые кластеры, но при этом получили новую возможность восстановления для локальных хранилищ. Администраторы могут использовать эту функцию для контроля за ресурсами, необходимыми для восстановления копий данных или активных рабочих нагрузок.
Другие нововведения в области хранения данных
Пока Storage Spaces Direct соединяет хранилище узлов кластера в пул, Storage Spaces оперирует хранилищем лишь одного сервера. В обновленной версии операционной системы для кэширования доступно многоуровневое хранилище с поддержкой высокоскоростных накопителей по типу твердотельных SSD или NVMe.
Наконец, в Server 2022 Microsoft расширила службу миграции хранилища, представленную в выпуске 2019 года. Первоначально он был предназначен для переноса общих файловых ресурсов из устаревших систем на более новые версии Windows Server. Теперь он поддерживает отказоустойчивые кластеры, серверы Samba и NetApp FAS в качестве источников, а также переносит локальных пользователей и группы.
Формы издания
Начиная с версии 2012, Microsoft предлагает серверную ОС в двух основных редакциях, которые различаются в первую очередь правами на виртуализацию. Однако, начиная с Server 2016, Datacenter Edition получил эксклюзивные функции, которые отсутствуют в стандартной версии. К ним относятся Shielded VMs, Storage Replica и программно-определяемое хранилище с локальными дисковыми пространствами.
Это различие сохраняется в версии 2022 года, где Standard Edition ограничивается двумя виртуальными экземплярами и включает только урезанную версию Storage Replica, которая ограничена максимальным объемом томов в 2 ТБ.
К двум выпускам теперь присоединяется третий, который называется Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition. Как следует из названия, он предназначен только для работы в облаке Microsoft.
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Standard
Стандартная версия предназначена для пользователей, которым требуется всего несколько виртуальных машин Windows Server. Помимо установки на физическое оборудование, с серверной лицензией также возможны две виртуальные машины под управлением Windows Server. На виртуальные машины Linux нет ограничений. Почти все функции и роли серверов из Datacentre Edition также включены в стандартную версию.
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Essentials
Версия Essentials, рассчитанная на 25 пользователей или 50 устройств, является идеальной серверной ОС для малого бизнеса. Она включает в себя многие функции старших выпусков, таких как Windows Admin Center и System Insights, однако ограничена поддержкой одного процессора с максимум 10 ядрами.
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Datacenter
С выпуском Datacenter пользователи получат максимально возможную гибкость в развертывании серверов и могут реализовывать крупные, быстро меняющиеся рабочие нагрузки. Количество виртуальных машин не ограничено, и программно определяемое хранилище может быть реализовано с помощью Storage Spaces Direct.
Системные требования
Процессор. На эффективность процессора влияют два ключевых фактора: число ядер и тактовая частота. Для установки Windows Server система должна быть оборудована как минимум одним 64-разрядным процессором с тактовой частотой 1,4 ГГц, совместимым с набором инструкций x64. В числе прочего должна быть обеспечена поддержка функций безопасности DEP и NX Bit.
Оперативная память. Минимальные требования к оперативной памяти на сервере — это не менее 512 МБ. Кроме того, требуется поддержка ECC.
Сетевые адаптеры. Адаптер Ethernet должен обеспечивать скорость не менее 1 гигабита в секунду. Также сетевые адаптеры также должны соответствовать спецификации архитектуры PCI Express.
Дисковое пространство. В конфигурацию сервера должен быть включен жесткий диск объемом не менее 32 ГБ данных для работы Windows Server, в то время как для установки графического интерфейса потребуются дополнительные 4 ГБ.
Резюме
Windows Server 2022 не привносит новых ролей или функций, но вместе с тем дополняет и вносит коррективы в ряд существующих функций и протоколов, некоторые из которых существенно повышают безопасность сервера.
Тем не менее, продукт от Microsoft остается одним из наиболее востребованных и надежных серверных ОС на рынке. Выбор лицензии и издания Windows Server 2022 следует делать на основе специфики бизнеса, численности штата и имеющегося оборудования — помочь в этой ситуации в любой момент готовы наши специалисты, просто обратитесь по номеру на сайте или свяжитесь с нами по электронной почте.

Microsoft’s Windows Server operating system shares multi-user services and extensive control over data storage, applications, and shared networks. This article talk about Windows Server history and what it is used for.
What Is Windows Server?
To answer the question of what is Windows Server, it must be said that Microsoft’s Windows Server operating system is designed as a series of enterprise-class server operating systems that share multi-user services and extensive control over data storage, applications, and shared networks.
Windows Server development began in the early 1980s when Microsoft produced two operating systems: MS-DOS and Windows NT. At the time, a Microsoft engineer named David Cutler developed the Windows NT kernel to provide the speed, security, and reliability that large organizations need on server operating systems.
Before Windows NT was released, many companies relied on Unix (OS), which required expensive RISC-based hardware to run files and print services. But Windows NT was available on cheap x86 machines. One of the critical features in NT architecture is multi-processor symmetry, which makes it faster for applications to work on devices with multiple processors.
Subsequent windows server duplicates are implemented on the hardware in an organization’s data center and on a cloud platform such as Microsoft Azure.
Critical features in later versions of Windows Server include Active Directory, which automatically manages user data, security, and distributed resources and enables collaboration with other directories. Server Manager is also a tool for managing the server and making configuration changes on local or remote devices. However, what you are familiar with is the Windows Server concept.
If you aim to know what is tomcat , check this article out!
what is windows server used for?
Windows servers use for enterprise purposes, covering an extensive network and virtually unlimited connections.
What Is Windows Server History?
Now that you are familiar with the concept of Windows Server let’s take a look at its history throughout this article.
1993: Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Microsoft released its Windows NT operating system in two formats: one for workstations and one for servers. The 8-bit operating system had a Hardware Abstraction Layer that provided system stability by blocking applications’ direct access to system hardware.
1994: Windows NT 3.5 Server
Microsoft updated key network features in this server version and added integrated support for TCP / IP and Winsock. Other network enhancements allow users of operating systems other than Microsoft to access files and applications in the domain.
1995: Windows NT Server 3.51
Microsoft fine-tuned this version to increase performance and reduce the amount of memory required. This server operating system is optimized through its updated network stack to provide faster service to users. Microsoft added more communication support for companies in an environment with Windows NT and NetWare servers so users with a single credit can benefit from both.
1996: Windows NT Server 4.0
Microsoft used the Windows 8 UI for this server operating system version and expanded network protocol capabilities to allow network resources in a broader array of non-Microsoft devices. Key features in this release were the ability to use a server as an Internet information server, now known as the Internet Information Services (IIS).
I you want to know more about what is iis and how it works, read our article.
2000: Windows 2000
Windows 2000 introduced Active Directory, which stores and manages information about network objects, including data, systems, and user services. Active Directory allows administrators to perform various tasks such as configuring a virtual private network, encrypting data, and accessing file sharing on network computers.
Microsoft also introduced several other critical features in this release, including:
- Microsoft Management Console (MMC / Microsoft Management Console)
- NTFS 3.0 file system
- Dynamic disk volume support
Windows 2000 had three versions – Server, Advanced Server, and Datacenter.
2003: Windows Server 2003
Microsoft introduced the Windows Server brand with Windows Server 2003 and promoted its security enhancements on Windows 2000. Microsoft IIS has made the web server feature more difficult and disables default services to reduce deployment opportunities.
Microsoft introduced server roles with this release. The use of Windows Server 2003 is to allow administrators to assign a specific function, such as a domain controller or DNS server, to a server.
This release’s other new features include enhanced encryption, firewall, more network address support (NAT), and Volume Shadow Copy Service.
Windows Server 2003 had four versions: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, and Web.
2005: Windows Server 2003 R2
Instead of the version number, Microsoft started using R2. Organizations had to purchase a new windows server license to use the new server operating system. Still, this version did not need to be upgraded, and R2 releases used client access licenses (CALs) of the previous server version.
This release has improved security and safety features in Windows Server 2003.
2008: Windows Server 2008
- Hyper-V virtualization software
- failover clustering
- event viewer
- Server Core
- Server Manager console
The Windows 2008 server was released in four versions: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, and Web.
2009: Windows Server 2008 R2
Microsoft used its Windows 7 kernel for the operating system and improved its scalability and accessibility features.
Microsoft has expanded Active Directory rules and features to improve user account editing and more node control. The company also updated Terminal Services and reinstalled Remote Desktop Services (RDS).
New features in the server version of Windows 2009 include BranchCache and DirectAccess, improving users’ remote use.
Like the previous version, this server operating system shares some of the management and security features used in the Windows Vista client operating system. Windows Server 2008 R2 changes from a 32-bit operating system to a 64-bit version.
2012: Windows Server 2012
And what about Windows Server 2012? Microsoft embedded several cloud features for Windows Server 2012, as far as Cloud OS is concerned. The company has also made significant updates to its operating system storage infrastructure and Hyper-V virtualization platform.
New features notable in this release include Hyper-V Virtual Switch, Replica Hyper-V, storage, and ReFS file system.
This version of Windows Server was released in four versions: Essentials, Foundation, Standard, and Datacenter.
2013: Windows Server 2012 R2
Microsoft Windows Server 2013 R2 has undergone several changes, including significant updates to virtualization, storage, networking, information security, and web services.
New features include:
-
Desired State Configuration / DSC was built on PowerShell to prevent configuration crashes and maintain compatibility across enterprise devices.
-
The addition of multiple storages to the storage space enhances the mechanical movement of commonly used data blocks to solid-state storage.
-
Folders allow users to retrieve and save company files on work and personal devices.
2016: Windows Server 2016
Microsoft has come close to the cloud with new features in this release. Microsoft introduced the Nano Server, a minimal server-side option to increase security by reducing the attack vector.
Another security issue is the new Hyper-V shielded VM feature that uses encryption to prevent data damage in the VM.
Network Controller is a critical new network feature that allows administrators to manage switches, subnets, and other virtual and physical network devices.
This server operating system is available in standard versions of the Datacenter. Windows Server 2016 Standard Edition does not have advanced features in virtualization, storage, and networking.
2017: Semi-Annual Channel and Long-Term Servicing Channel releases
In June 2017, Microsoft announced dividing the windows server into two channels: the Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) and the Long Term Service Channel (LTSC).
The LTSC naming convention will maintain the Windows Server YYYY format. (Such as Windows Server 2016). While the SAC release follows the Windows version of the YYMM server version. Microsoft released its first version of SAC, Windows Server 17.9, in October 2017.
2019: Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019 is the latest version of Microsoft’s server operating system and is part of the Windows NT operating system family. Windows Server 2019 is an operating system that connects to Azure locally, adds additional layers of security, and helps you modernize your applications and infrastructure.
Windows Server 2019 was introduced on March 20, 2018, and the first version of Windows preview was released the same day. But it was released for public access on October 1, 2018.
Windows Server 2019 has the following new features:
Other graphical elements from Windows 7 and later:
-
Storage Spaces Direct
-
Storage Migration Service
-
Storage Replica
-
System Insights
If you need more details, don’t miss this article