it seems that whenever i open a program in windows 8, the process name is WWAHost.exe
i would like to be able to do something like TASKKILL /F /IM notepad.exe and terminate a specific process by name
if i kill WWAHost.exe then all open programs will die.
any ideas?
asked Mar 24, 2015 at 7:39
PatrioticcowPatrioticcow
26.5k75 gold badges217 silver badges337 bronze badges
2
You can kill the process and all its children (ie. all processes started by it) using the /t switch:
taskkill /f /t /im wwahost.exe
See the documentation for taskkill (ss64) and tskill (ss64) system utilities.
answered Mar 24, 2015 at 12:55
1
it seems that whenever i open a program in windows 8, the process name is WWAHost.exe
i would like to be able to do something like TASKKILL /F /IM notepad.exe and terminate a specific process by name
if i kill WWAHost.exe then all open programs will die.
any ideas?
asked Mar 24, 2015 at 7:39
PatrioticcowPatrioticcow
26.5k75 gold badges217 silver badges337 bronze badges
2
You can kill the process and all its children (ie. all processes started by it) using the /t switch:
taskkill /f /t /im wwahost.exe
See the documentation for taskkill (ss64) and tskill (ss64) system utilities.
answered Mar 24, 2015 at 12:55
1
Sometimes when an application in Windows hangs, freezes and stops responding the only way to terminate it is to kill from the command-line.
The taskkill command in Windows serves for terminating tasks by name or by process id (PID).
In this note i am showing how to find and kill a process by its name or by PID and how to identify a process by the listening port.
I am also showing how to troubleshoot “The process could not be terminated” and “Access denied” errors.
Cool Tip: Get the return code from the last command or application! Read more →
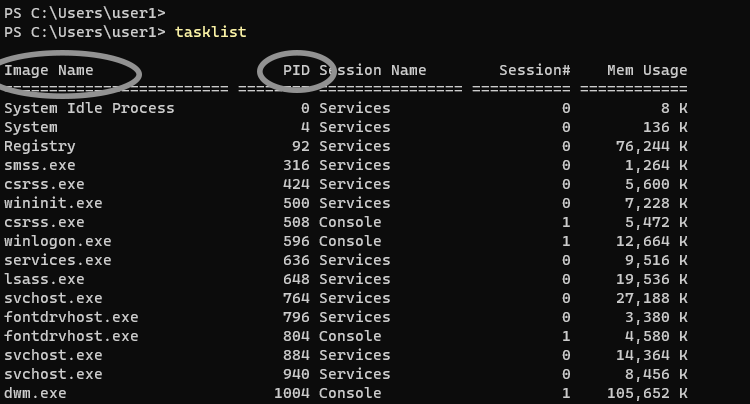
List all Windows processes and find the full name of a process to kill (case insensitive):
C:\> tasklist | findstr /I process_name
Kill the process by name:
C:\> taskkill /IM process_name.exe
Kill Process by PID
List all Windows processes and find the PID of a process to kill (case insensitive):
C:\> tasklist | findstr /I process_name
Kill the process by PID:
C:\> taskkill /PID process_id
Kill Process by Port
List all Windows processes listening on TCP and UDP ports and find the PID of a process running on a specific port:
C:\> netstat -ano | findstr :port
Find the name of a process by its PID:
C:\> tasklist /FI "pid eq process_id"
Kill the process by name or by PID:
C:\> taskkill /IM process_name.exe - or - C:\> taskkill /PID process_id
Cool Tip: Windows grep command equivalent in CMD and PowerShell! Read more →
Troubleshooting
Kill the process forcefully in case of the following error:
ERROR: The process with PID XXX could not be terminated.
Reason: This process can only be terminated forcefully (with /F option).
C:\> taskkill /F /IM process_name.exe - or - C:\> taskkill /F /PID process_id
If you get an “Access is denied” error, you should open the command prompt as an administrator:
ERROR: The process with PID XXX could not be terminated.
Reason: Access is denied
To run the CMD as an administrator, press ⊞ Win keybutton to open the start menu, type in cmd to search for the command prompt and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch it as administrator.
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
We use the taskkill command to terminate applications and processes in the Windows command prompt. Running taskkill is the same as using the End task button in the Windows Task Manager.
With taskkill, we kill one or more processes based on the process ID (PID) or name (image name). The syntax of this command is as follows:
taskkill /pid PID
taskkill /im nameYou can use the tasklist command to find the PID or image name of a Windows process.
The /F option tells Windows to force kill the process:
taskkill /f /im notepad.exeKill a Process by PID
In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate a process with a PID of 1000:
taskkill /f /pid 3688The multiple processes can be terminated at once, as shown in the following example:
taskkill /pid 3688 /pid 4248 /pid 4258Kill a Process by Name
To kill a process by its name, we use the /IM option. In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate the notepad.exe process:
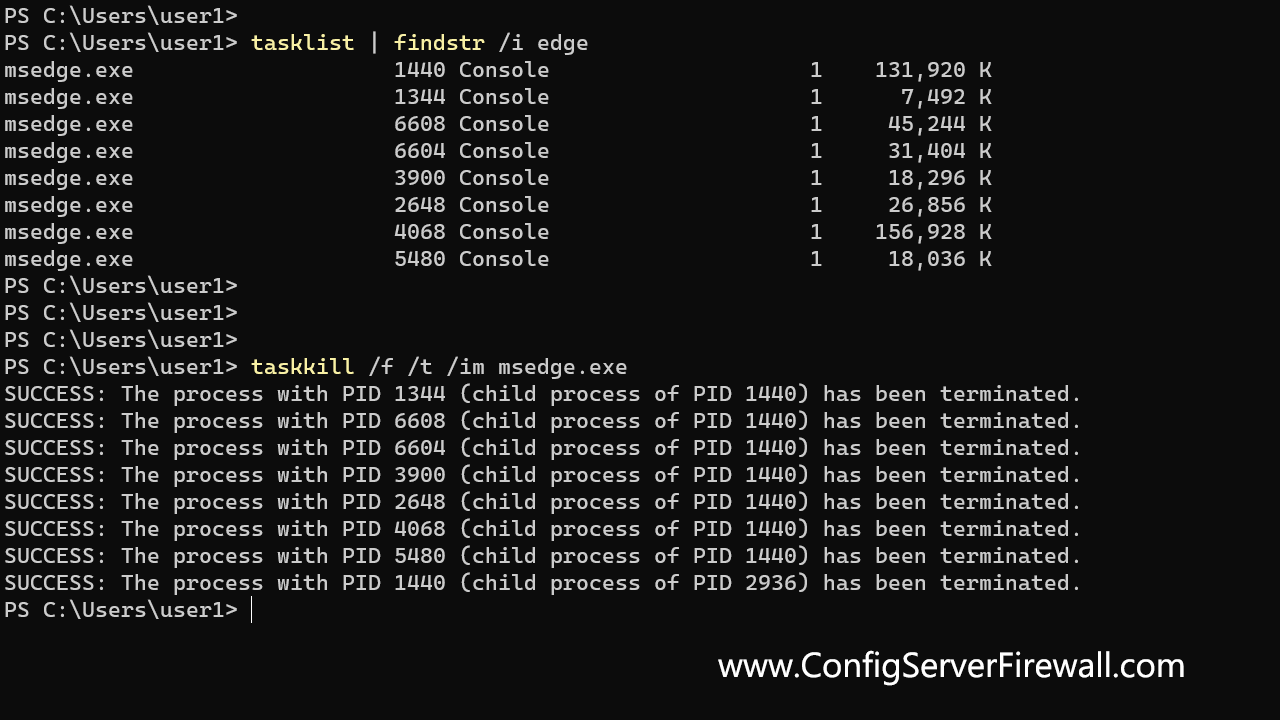
taskkill /im notepad.exeThe /t option tells Windows to terminate the specified process and all child processes. In the following example, we force kill Microsoft Edge and its child processes:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exeCommand Options
| /S | Specifies the IP Address or name of the remote system to connect to. |
| /U | Specifies the name of the Windows user under which the command should execute. |
| /P | Password for the user. Prompts for input if omitted. |
| /FI | This option is to apply filters (see examples below). |
| /PID | Specifies the PID of the process to be terminated. |
| /IM | Specifies the image name of the process to be terminated. |
| /T | Terminates the specified process and its child processes (end all tasks). |
| /F | Forcefully kill a process. |
Examples
Terminate a process with a PID of 4000:
taskkill /pid 4000Terminate spoolsv.exe (which is the Print Spooler service on Windows):
taskkill /im spoolsv.exeUsing /f and /t options to forcefully terminate the entire process tree of the Microsoft Edge browser:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exeForce kill any process that starts with the name note:
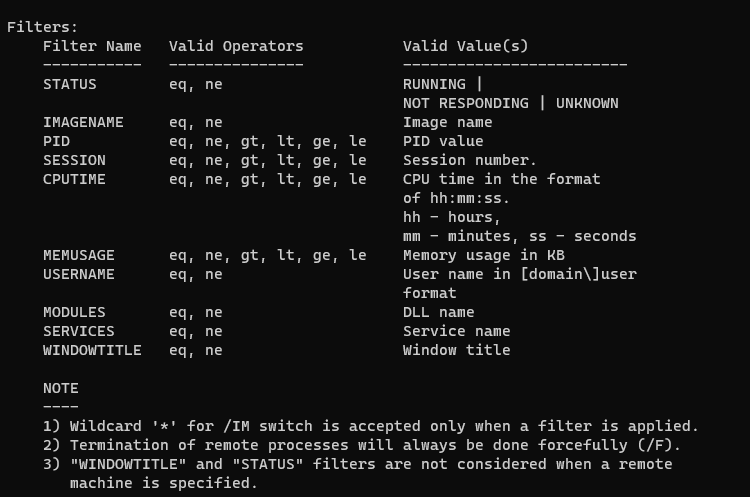
taskkill /f /t /im note*In the following example, we terminate all processes that are not responding by using a filter:
taskkill /f /fi "status eq not responding"In the above example, eq stands for equal. You can use the following filters with the /fi option.
Run taskkill command on a remote computer:
taskkill /s 192.168.1.100 /u robst /pid 5936In the above example, the process with PID 5936 will be terminated on a remote computer with an IP address of 192.168.1.100.
Note that the Windows Firewall must be configured on the remote computer to allow the taskkill command. Click the link below for instructions on how to do it.
How to allow tasklist and taskkill commands from Windows Firewall
All right, here’s the end of this tutorial. While working on the CMD, you can run taskkill /? to display the help page, command options, and filters of the tasklist command.
The PowerShell equivalent to the taskkill is the Stop-Process cmdlet. But you can always use taskkill in PowerShell as well.
When you start an app, the operating system creates a process for an executable file of the app. It contains the program code and its current activity. Windows assigns a special number known as Process Identifier (PID) which is unique for every process. There are a number of reasons you might want to kill a process, and different methods you can use to terminate it. Here is how it can be done.
If an app stops responding, consumes a lot of system resources or behaves unexpectedly and doesn’t allow you to quit it, you might want to kill its process to forcefully close the app. Traditionally, Windows allowed using Task Manager and the command prompt for these tasks. In addition to these methods, you can use PowerShell. Here is how.
To kill a process in Windows 10, do the following.
- Open Task Manager.
- Click on «More details» in the bottom right corner to enter Full view mode.
- Select the desired app in the app list.
- Click on the End task button or hit the Del key on the keyboard.
You are done.
This is Task Manager’s most well known method.
Note: The same can be done from the Details tab. It is a special tab which lists process names instead of app names. There you can select a process in the list and either click on the End process button or hit the Del key.
Using the End Task button means Windows first tries to see for a certain timeout if the process has really stopped responding, and attempts to collect a crash or memory dump of the process. It then terminates the app.
Tip: We highly recommend you read the article How to end a process quickly with Task Manager in Windows 10 to learn all Task Manager tricks. Also, you can get the classic Task Manager app in Windows 10 to end processes or tasks.
Another classic method to close a process is the console tool taskill. It comes bundled with modern versions of Windows.
Kill a process using Taskkill
Note: Some processes are running as Administrator (elevated). In order to kill them, you need to open an elevated command prompt instance.
- Open the command prompt as the current user or as Administrator.
- Type tasklist to see the list of running processes and their PIDs. Since the list might be very long, you can use a pipe character with the more command.
tasklist | more
- To kill a process by its PID, type the command:
taskkill /F /PID pid_number
- To kill a process by its name, type the command
taskkill /IM "process name" /F
For example, to kill a process by its PID:
taskkill /F /PID 1242
To kill a process by its name:
taskkill /IM "notepad.exe" /F
Taskkill supports many useful options which you can use to terminate apps. You can learn them by running it as follows: taskkill /?. Using taskkill, you can close all not responding tasks at once in Windows 10.
Kill a process using PowerShell
Note: To kill a process which runs elevated, you need to open PowerShell as Administrator.
- Open PowerShell. If required, run it as Administrator.
- Type the command
Get-Processto see the list of running processes. - To kill a process by its name, execute the following cmdlet:
Stop-Process -Name "ProcessName" -Force
- To kill a process by its PID, run the command:
Stop-Process -ID PID -Force
Examples:
This command will close the notepad.exe process.
Stop-Process -Name "Notepad" -Force
The next command will close a process with PID 2137.
Stop-Process -ID 2137 -Force
If you need to kill a Store app, see the following article:
How to Terminate Store Apps in Windows 10
That’s it.
Support us
Winaero greatly relies on your support. You can help the site keep bringing you interesting and useful content and software by using these options:
If you like this article, please share it using the buttons below. It won’t take a lot from you, but it will help us grow. Thanks for your support!