4.3 Git на сервере — Генерация открытого SSH ключа
Генерация открытого SSH ключа
Как отмечалось ранее, многие Git-серверы используют аутентификацию по открытым SSH-ключам.
Для того чтобы предоставить открытый ключ, каждый пользователь в системе должен его сгенерировать, если только этого уже не было сделано ранее.
Этот процесс аналогичен во всех операционных системах.
Сначала вам стоит убедиться, что у вас ещё нет ключа.
По умолчанию пользовательские SSH ключи сохраняются в каталоге ~/.ssh домашнем каталоге пользователя.
Вы можете легко проверить наличие ключа перейдя в этот каталог и посмотрев его содержимое:
$ cd ~/.ssh
$ ls
authorized_keys2 id_dsa known_hosts
config id_dsa.pubИщите файл с именем id_dsa или id_rsa и соответствующий ему файл с расширением .pub.
Файл с расширением .pub — это ваш открытый ключ, а второй файл — ваш приватный ключ.
Если указанные файлы у вас отсутствуют (или даже нет каталога .ssh), вы можете создать их используя программу ssh-keygen, которая входит в состав пакета SSH в системах Linux/Mac, а для Windows поставляется вместе с Git:
$ ssh-keygen -o
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/schacon/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/home/schacon/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/schacon/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/schacon/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
d0:82:24:8e:d7:f1:bb:9b:33:53:96:93:49:da:9b:e3 schacon@mylaptop.localСначала программа попросит указать расположение файла для сохранения ключа (.ssh/id_rsa), затем дважды ввести пароль для шифрования.
Если вы не хотите вводить пароль каждый раз при использовании ключа, то можете оставить его пустым или использовать программу ssh-agent.
Если вы решили использовать пароль для приватного ключа, то настоятельно рекомендуется использовать опцию -o, которая позволяет сохранить ключ в формате, более устойчивом ко взлому методом подбора, чем стандартный формат.
Теперь каждый пользователь должен отправить свой открытый ключ вам или тому, кто администрирует Git-сервер (подразумевается, что ваш SSH-сервер уже настроен на работу с открытыми ключами).
Для этого достаточно скопировать содержимое файла с расширением .pub и отправить его по электронной почте.
Открытый ключ выглядит примерно так:
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAklOUpkDHrfHY17SbrmTIpNLTGK9Tjom/BWDSU
GPl+nafzlHDTYW7hdI4yZ5ew18JH4JW9jbhUFrviQzM7xlELEVf4h9lFX5QVkbPppSwg0cda3
Pbv7kOdJ/MTyBlWXFCR+HAo3FXRitBqxiX1nKhXpHAZsMciLq8V6RjsNAQwdsdMFvSlVK/7XA
t3FaoJoAsncM1Q9x5+3V0Ww68/eIFmb1zuUFljQJKprrX88XypNDvjYNby6vw/Pb0rwert/En
mZ+AW4OZPnTPI89ZPmVMLuayrD2cE86Z/il8b+gw3r3+1nKatmIkjn2so1d01QraTlMqVSsbx
NrRFi9wrf+M7Q== schacon@mylaptop.localБолее подробное руководство по созданию SSH-ключей и конфигурации клиента на различных системах вы можете найти в руководстве GitHub.
After you’ve checked for existing SSH keys, you can generate a new SSH key to use for authentication, then add it to the ssh-agent.
About SSH key passphrases
You can access and write data in repositories on GitHub.com using SSH (Secure Shell Protocol). When you connect via SSH, you authenticate using a private key file on your local machine. For more information, see «About SSH.»
When you generate an SSH key, you can add a passphrase to further secure the key. Whenever you use the key, you must enter the passphrase. If your key has a passphrase and you don’t want to enter the passphrase every time you use the key, you can add your key to the SSH agent. The SSH agent manages your SSH keys and remembers your passphrase.
If you don’t already have an SSH key, you must generate a new SSH key to use for authentication. If you’re unsure whether you already have an SSH key, you can check for existing keys. For more information, see «Checking for existing SSH keys.»
If you want to use a hardware security key to authenticate to GitHub, you must generate a new SSH key for your hardware security key. You must connect your hardware security key to your computer when you authenticate with the key pair. For more information, see the OpenSSH 8.2 release notes.
Generating a new SSH key
You can generate a new SSH key on your local machine. After you generate the key, you can add the public key to your account on GitHub.com to enable authentication for Git operations over SSH.
Note: GitHub improved security by dropping older, insecure key types on March 15, 2022.
As of that date, DSA keys (ssh-dss) are no longer supported. You cannot add new DSA keys to your personal account on GitHub.com.
RSA keys (ssh-rsa) with a valid_after before November 2, 2021 may continue to use any signature algorithm. RSA keys generated after that date must use a SHA-2 signature algorithm. Some older clients may need to be upgraded in order to use SHA-2 signatures.
-
Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
-
Paste the text below, substituting in your GitHub email address.
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com"Note: If you are using a legacy system that doesn’t support the Ed25519 algorithm, use:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"This creates a new SSH key, using the provided email as a label.
> Generating public/private ALGORITHM key pair.When you’re prompted to «Enter a file in which to save the key», you can press Enter to accept the default file location. Please note that if you created SSH keys previously, ssh-keygen may ask you to rewrite another key, in which case we recommend creating a custom-named SSH key. To do so, type the default file location and replace id_ssh_keyname with your custom key name.
-
At the prompt, type a secure passphrase. For more information, see «Working with SSH key passphrases.»
> Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase] > Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again]
Adding your SSH key to the ssh-agent
Before adding a new SSH key to the ssh-agent to manage your keys, you should have checked for existing SSH keys and generated a new SSH key. When adding your SSH key to the agent, use the default macOS ssh-add command, and not an application installed by macports, homebrew, or some other external source.
Generating a new SSH key for a hardware security key
If you are using macOS or Linux, you may need to update your SSH client or install a new SSH client prior to generating a new SSH key. For more information, see «Error: Unknown key type.»
-
Insert your hardware security key into your computer.
-
Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
-
Paste the text below, substituting in the email address for your account on GitHub.
Note: If the command fails and you receive the error
invalid formatorfeature not supported,you may be using a hardware security key that does not support the Ed25519 algorithm. Enter the following command instead.ssh-keygen -t ecdsa-sk -C "your_email@example.com" -
When you are prompted, touch the button on your hardware security key.
-
When you are prompted to «Enter a file in which to save the key,» press Enter to accept the default file location.
-
When you are prompted to type a passphrase, press Enter.
> Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase] > Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again] -
Add the SSH public key to your account on GitHub. For more information, see «Adding a new SSH key to your GitHub account.»
Last updated: Jul 30, 2023 | Published: Jul 25, 2019
Securing your Git interactions with SSH keys is a fundamental aspect of software development today, offering a secure and convenient way to authenticate with remote repositories. Whether you’re an experienced developer or just starting your coding journey, understanding how to generate SSH keys for Git authorization is an essential skill to ensure the integrity and privacy of your code. In this quick guide, we’ll walk you through the process of creating SSH keys on Windows, Mac, and Linux systems, empowering you to access and collaborate on your Git projects with enhanced security.
Windows
Just follow these 5 steps:
- Go to this address, and download Git for Windows, after the download install it with default settings
- Open Git Bash that you just installed (Start->All Programs->Git->Git Bash)
- Type in the following: ssh-keygen -t rsa (when prompted, enter password, key name can stay the same)
- Open file your_home_directory/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with your favorite text editor, and copy contents to your Git repository’s keys field (GitHub, beanstalk, or any other repository provider), under your account.
- Be sure that you don’t copy any whitespace while copying public key’s content (id_rsa.pub)
Note: your_home_directory is either C:\Users\your_username (on Windows Vista / 7 / 8 / 10), or C:\Documents and Settings\your_username (on Windows XP)
Mac
Follow these 5 steps:
- Start the terminal
- Navigate to your home directory by typing: cd ~/
- Execute the following command: ssh-keygen -t rsa (when prompted, enter password, key name can stay the same)
- Open the file you’ve just created ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with your favorite text editor, and copy contents to your Git repository’s keys field (GitHub, beanstalk, or any other repository provider), under your account.
- Be sure that you don’t copy any whitespace while copying public key’s content (id_rsa.pub)
Linux (Ubuntu)
Follow these 5 steps:
- Open console
- cd ~
- ssh-keygen -t rsa (when prompted, enter password, key name can stay the same)
- open file /home/your_username/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with your favorite text editor, and copy contents to your Git repository’s keys field (GitHub, beanstalk, or any other repository provider), under your account.
- Be sure that you don’t copy any whitespace while copying public key’s content (id_rsa.pub)
Additional info
When you create private/public SSH keys on your machine (that’s what you did in the above steps), it’s not enough. You need to give your public key to the repository in order to pair the Git server with your local machine (that’d be steps 4. and 5. above).
Most of the popular repositories will give you web interface access to the application, and here’s how it looks like on Github:
After this step, you’re ready to start using Git.
Conclusion
I hope this wasn’t too complicated to follow, and also I hope it was helpful to someone!
Cheers!

What is a Git SSH Key?
An SSH key is an access credential for the SSH (secure shell) network protocol. This authenticated and encrypted secure network protocol is used for remote communication between machines on an unsecured open network. SSH is used for remote file transfer, network management, and remote operating system access. The SSH acronym is also used to describe a set of tools used to interact with the SSH protocol.
SSH uses a pair of keys to initiate a secure handshake between remote parties. The key pair contains a public and private key. The private vs public nomenclature can be confusing as they are both called keys. It is more helpful to think of the public key as a «lock» and the private key as the «key». You give the public ‘lock’ to remote parties to encrypt or ‘lock’ data. This data is then opened with the ‘private’ key which you hold in a secure place.
How to Create an SSH Key
SSH keys are generated through a public key cryptographic algorithm, the most common being RSA or DSA. At a very high level SSH keys are generated through a mathematical formula that takes 2 prime numbers and a random seed variable to output the public and private key. This is a one-way formula that ensures the public key can be derived from the private key but the private key cannot be derived from the public key.
SSH keys are created using a key generation tool. The SSH command line tool suite includes a keygen tool. Most git hosting providers offer guides on how to create an SSH Key.
Generate an SSH Key on Mac and Linux
Both OsX and Linux operating systems have comprehensive modern terminal applications that ship with the SSH suite installed. The process for creating an SSH key is the same between them.
1. execute the following to begin the key creation
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"This command will create a new SSH key using the email as a label
2. You will then be prompted to «Enter a file in which to save the key.»
You can specify a file location or press “Enter” to accept the default file location.
> Enter a file in which to save the key (/Users/you/.ssh/id_rsa): [Press enter]3. The next prompt will ask for a secure passphrase.
A passphrase will add an additional layer of security to the SSH and will be required anytime the SSH key is used. If someone gains access to the computer that private keys are stored on, they could also gain access to any system that uses that key. Adding a passphrase to keys will prevent this scenario.
> Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase]
> Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again]
At this point, a new SSH key will have been generated at the previously specified file path.
4. Add the new SSH key to the ssh-agent
The ssh-agent is another program that is part of the SSH toolsuite. The ssh-agent is responsible for holding private keys. Think of it like a keychain. In addition to holding private keys it also brokers requests to sign SSH requests with the private keys so that private keys are never passed around unsecurly.
Before adding the new SSH key to the ssh-agent first ensure the ssh-agent is running by executing:
$ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
> Agent pid 59566
Once the ssh-agent is running the following command will add the new SSH key to the local SSH agent.
ssh-add -K /Users/you/.ssh/id_rsaThe new SSH key is now registered and ready to use!
Generate an SSH Key on Windows
Windows environments do not have a standard default unix shell. External shell programs will need to be installed for to have a complete keygen experience. The most straight forward option is to utilize Git Bash. Once Git Bash is installed the same steps for Linux and Mac can be followed within the Git Bash shell.
Windows Linux Subsystem
Modern windows environments offer a windows linux subsystem. The windows linux subsystem offers a full linux shell within a traditional windows environment. If a linux subsystem is available the same steps previously discussed for Linux and Mac can be followed with in the windows linux subsystem.
Summary
SSH keys are used to authenticate secure connections. Following this guide, you will be able to create and start using an SSH key. Git is capable of using SSH keys instead of traditional password authentication when pushing or pulling to remote repositories. Modern hosted git solutions like Bitbucket support SSH key authentication.
Инструменты
Git SSH Windows — пошаговое руководство
Дата размещения статьи 08/12/2019 👁31067
Git SSH Windows — пошаговое руководство
Настроим пошагово Git SSH для Windows 10. Это позволит вам выполнять команды git без ввода пароля от своей учетной записи GitHub.
Порядок действий:
- Генерация ключа SSH.
- Добавление SSH-ключа в ssh-agent.
- Добавление ключа SSH в учетную запись GitHub.
Генерация ключа SSH
Откройте bash/терминал. Добавьте следующий текст, подставив свой адрес электронной почты GitHub.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "ваша@почта.com"Будет создан ключ ssh, используя e-mail в качестве метки.
Когда вам будет предложено «Введите файл, в котором вы хотите сохранить ключ», нажмите Enter. Это установит в местоположение по умолчанию.
Enter a file in which to save the key (/c/Users/you/.ssh/id_rsa):[Press enter]
Далее введите безопасную фразу-пароль дважды или просто нажмите Enter.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase]
Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again]
Добавление SSH-ключа в ssh-agent
Чтобы запустить ssh-агент введите следующую команду.
На экране отобразится похожая строка.
Agent pid 31724
Добавим свой закрытый ключ SSH в ssh-agent. Если вы создали свой ключ с другим именем (или добавляете существующий ключ с другим именем), замените в команде id_rsa на имя вашего файла закрытого (приватного) ключа.
Ключ будет успешно добавлен в ssh-агент.
Добавление ключа SSH в учетную запись GitHub
Мы сгенерировали у себя на компьютере закрытый ключ SSH и добавили его в ssh-агент. Теперь нам необходимо добавить SSH ключ в учетную запись GitHub.
Сейчас нам необходимо скопировать SSH ключ в буфер обмена.
Способов есть несколько, но я же вам предлагаю следующее решения для Windows 10: введите команду ниже.
Прямо в терминале вы увидите содержимое необходимого файла с ключем. Скопируйте его в буфер.
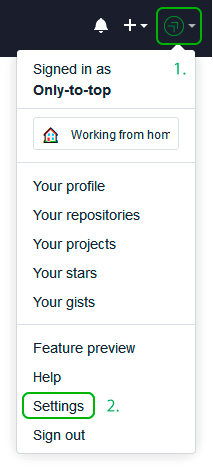
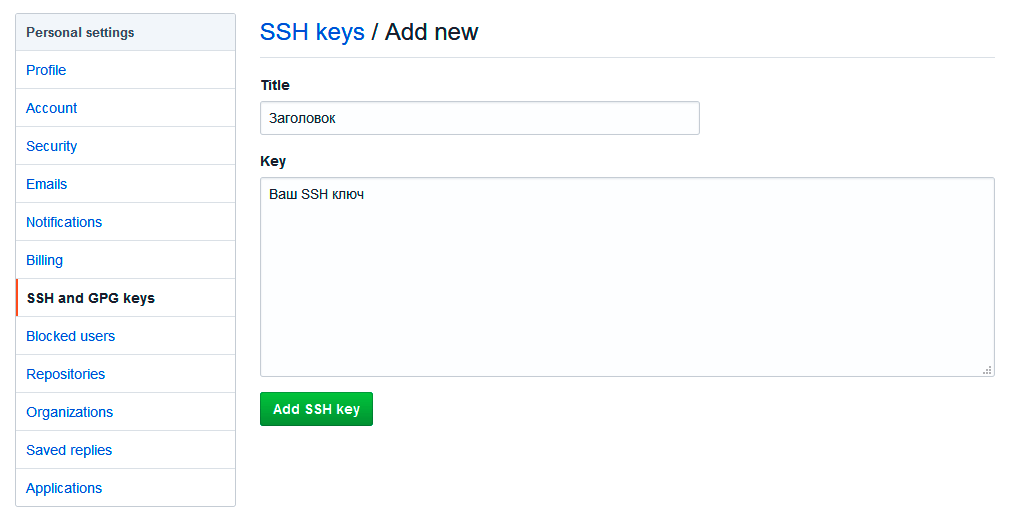
Теперь зайдите на вашу страницу GitHub » Settings.
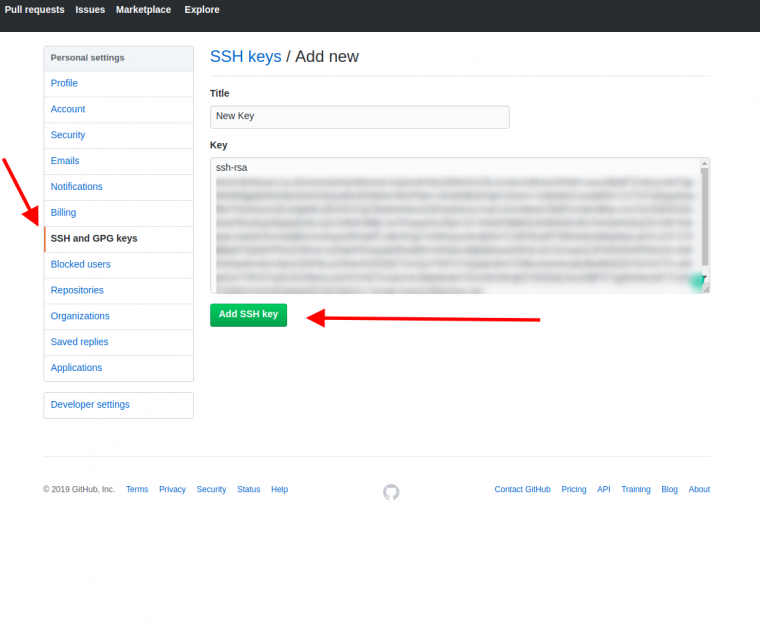
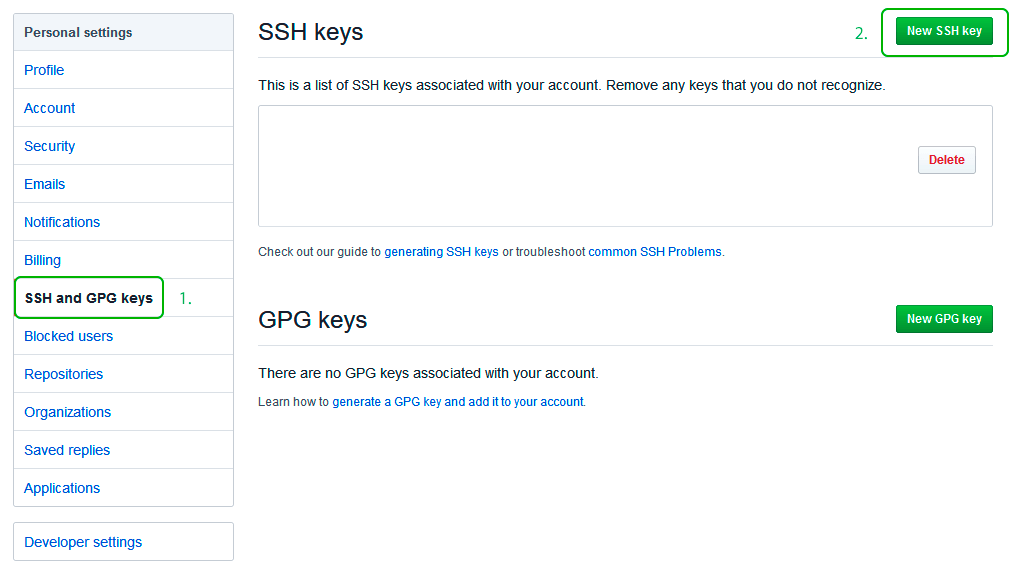
Перейдите во вкладку SSH and GPG keys и нажмите на кнопку New SSH key для добавления SSH ключа в вашу учетную запись GitHub.
В поле Title добавьте заголовок для данного ключа. Например, если вы захотите настроить SSH доступ на нескольких устройствах, то вы будите понимать какой ключ принадлежит какому устройству.
В поле Key добавьте свой ssh-ключ, который вы скопировали в буфер обмена на предыдущем шаге.
Нажмите Add SSH key.
Для подтверждения вам потребуется ввести свой пароль от учетной записи GitHub.
На этом настройка SSH для вашего устройства завершена, теперь вы можете работать с git без ввода пароля от своей учетной записи.
Если вам понравилась данная статья, можете прочитать как настроить моментальную загрузку сайта на хостинг и синхронизацию файлов.
JavaScript: Window Location Checkbox Checked — Проверка Состояния Чекбокса ✔️
Надеюсь, вам понравилась данная информация. Если вам интересна тема web-разработки,
то можете следить за выходом новых статей в Telegram.
- Настройка Gulp Babel
- Микроразметка сайта
- Как перенести сайт WordPress на хостинг
- Настройте показ всего текста во время загрузки веб-шрифтов
- Сниппеты в VS Code
- Не удается проверить так как не задан исполняемый PHP-файл