on August 5, 2015
Deleting files is one of the frequently done operation from Windows command prompt. This post explains how to use ‘del’ command from CMD for different use cases like deleting a single file, deleting files in bulk using wild cards etc. Before we start to look at the syntax, note that the command works only for files and can’t handle folders.
How to delete a file
Run del command with the name of the file to be deleted, you are done!
del filename
You do not see message after running the command if the file is deleted successfully. Error message is shown only when something goes wrong.
Delete files in bulk
Del command recognizes wildcard(*) and so can be used to delete files in bulk from CMD. Some examples below.
To delete all the files in current folder
del *
To delete all the files with ‘log’ extension
del *.log
Delete all files having the prefix ‘abc’
del abc*
Delete all files having ‘PIC’ somewhere in the file name.
del *PIC*
The above are the basic use cases of del command. Continue to read below for non trivial use cases.
Delete multiple files
‘Del’ command can accept multiple files as argument
del filename1 filename2 filename3 filename4....
Example:
D:\>dir /s /b 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\>del 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\> D:\>dir /s /b D:\>
Delete Read only files
We can’t delete a read-only file using simple‘del’ command. We get access denied error in this scenario.
c:\>attrib readonlyfile.txt A R C:\readonlyfile.txt c:\>del readonlyfile.txt c:\readonlyfile.txt Access is denied. c:\>
A read-only file can be deleted by adding /F flag.
del /F readonlyfile.txt
Alternatively, we can use the below command too
del /A:R readonlyfile.txt
The Windows Command Processor cmd.exe has two internal commands for deletion of files and folders:
- The command DEL is for the deletion of files with usage help output on running in a Windows command prompt window either
help delordel /?. - The command RMDIR or with shorter name RD is for removal of directories with usage help output on running in a Windows command prompt window either
help rmdirorrmdir /?orhelp rdorrd /?.
Deletion of all *.svn files in an entire folder tree
There can be used in a Windows command prompt window or a Windows batch file the following command to delete really all files of which long or short 8.3 file name is matched by the wildcard pattern *.svn in the directory %USERPROFILE%\Projects or any of its subdirectories:
del /A /F /Q /S "%USERPROFILE%\Projects\*.svn" >nul 2>&1
The usage of option /A to match all files independent on the file attributes replaces the implicit default /A-H to ignore hidden files. So even files with hidden attribute are deleted by this command because of using the option /A. Files matched by wildcard pattern *.svn with hidden attribute set are ignored on not using the option /A.
The option /F forces a deletion of files with file extension .svn which have the read-only attribute set. There would be output the error message Access is denied. if a *.svn file has the read-only attribute set and the option /F is not used on running the command DEL.
The quiet option /Q prevents the user confirmation prompt Are you sure (Y/N)?.
The option /S results in searching not only in the specified directory, but also in all its subdirectories including those with hidden attribute set even on not using option /A for files of which long or short 8.3 name is matched by the wildcard pattern *.svn.
The two redirections >nul and 2>&1 result in redirecting the list of deleted files output to handle STDOUT (standard output) and the error messages output to handle STDERR (standard error) to the device NUL to suppress every output.
There are deleted also hard links and symbolic links matched by the wildcard pattern *.svn on using this command, but not the files linked to on having a file name not ending with .svn or being in a different directory tree.
Files matched by the wildcard pattern *.svn currently opened by a process (program/application) with using shared access permissions to deny all other processes to delete the file as long as being opened by this process are not deleted by this command. File system permissions can result also in files not being deleted by this command.
Deletion of all *.svn folders in an entire folder tree
There can be used in a Windows command prompt window the following command to remove really all folders matching in long or short 8.3 folder name the wildcard pattern *.svn in the directory %USERPROFILE%\Projects and all its subdirectories:
for /F "delims=" %I in ('dir "%USERPROFILE%\Projects\*.svn" /AD /B /S 2^>nul') do @rd /Q /S "%I" 2>nul
The same command line for usage in a batch file containing @echo off at top is:
for /F "delims=" %%I in ('dir "%USERPROFILE%\Projects\*.svn" /AD /B /S 2^>nul') do rd /Q /S "%%I" 2>nul
There is executed on more cmd.exe in background with option /c and the command line specified between ' as additional arguments to run in background the Windows Command Processor internal command DIR to search
- in the specified directory
%USERPROFILE%\Projects - and in all its subdirectories because of option
/S - for just directories because of using the option
/ADwhich includes also junctions and symbolic directory links - matching the wildcard pattern
*.svn.
The file system entries (= directory names) matched by these criteria are output in bare format because of option /B with full path because of option /S to handle STDOUT of the background command process without surrounding " even on full directory name containing a space or one of these characters &()[]{}^=;!'+,`~. The error message output by DIR on not finding any name matching these criteria is redirected to device NUL to suppress it.
The redirection operator > must be escaped with caret character ^ on FOR command line to be interpreted as literal character when the Windows Command Processor parses this command line before executing the command FOR which executes the embedded dir command line with using a separate command process started in background.
The output list of directory names with their full paths to handle STDOUT is captured by cmd.exe processing the batch file and processed by FOR after started cmd.exe closed itself.
The FOR /F option delims= defines an empty list of string delimiters which results in each entire directory name is assigned completely one after the other to the specified loop variable I.
The command RD is executed to delete quietly because of option /Q the directory with all files and all subdirectories because of option /S.
There are deleted also junctions (soft links) and symbolic directory links matched by the wildcard pattern *.svn on using this command, but not the directories linked to on having a directory name not ending with .svn or being in a different directory tree.
A directory matched by the wildcard pattern *.svn in which a file is currently opened by a process (program/application) with using shared access permissions to deny all other processes to delete the file as long as being opened by this process is not deleted by this command and of course also no directory above the directory containing the file which cannot be deleted at the moment. File system permissions can result also in directories not being deleted by this command. Windows prevents by default also the deletion of a directory which is the current working directory of any running process.
Other useful information regarding to deletion of files and folders
The directory path %USERPROFILE%\Projects\ can be removed completely or replaced by .\ in the commands above to delete the files and folders matching the wildcard pattern *.svn in the current directory of the Windows Command Processor process which executes the commands.
The directory path %USERPROFILE%\Projects\ can be replaced by %~dp0 to delete the files and folders matching the wildcard pattern *.svn in the directory of the batch file on using the command lines above in a batch file independent on which directory is the current directory on execution of the batch file.
The directory path %USERPROFILE%\Projects\ can be replaced also by a relative path. Please read the Microsoft documentation about Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces for more details about relative paths.
To understand the commands used and how they work, open a command prompt window, execute there the following commands, and read the displayed help pages for each command, entirely and carefully.
del /?dir /?for /?rd /?
Run mklink /? for help on how to create file and directory links explained very well by MKLink.
See also:
- Microsoft documentation for the Windows commands
- SS64.com — A-Z index of Windows CMD commands
Командная строка – мощный инструмент для автоматизации и упрощения многих задач, которые возникают при администрировании компьютера с операционной системой Windows. В этой статье мы рассмотрим команды DEL, ERASE, RD и RMDIR. С их помощью вы сможете удалять файлы и папки прямо из командной строки.
Удаление файлов через командную строку
Если вам нужно удалить файл через командную строку, то для этого нужно использовать команду DEL или ERASE. Эти команды являются синонимами и работают одинаково. Вы можете получить подробную информацию об этих командах, если введете их в командную строку с параметром «/?». Например, вы можете ввести «del /?» и в консоль выведется вся основная информация о команде del.
Команда DEL (или ERASE) предназначена для удаления одного или нескольких файлов и может принимать следующие параметры:
- /P – удаление с запросом подтверждения для каждого файла;
- /F – удаление файлов с атрибутом «только для чтения»;
- /S – удаление указанного файла из всех вложенных папок;
- /Q – удаление без запроса на подтверждение ;
-
/A – удаление файлов согласно их атрибутам;
- S — Системные;
- H — Скрытые;
- R – Только для чтения;
- A — Для архивирования
- Также перед атрибутами можно использовать знак минус «-», который имеет значение «НЕ». Например, «-S» означает не системный файл.
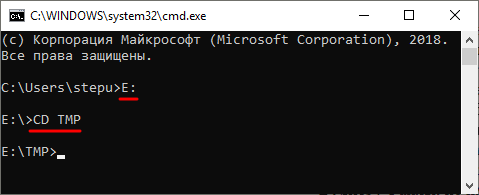
Обычно, для того чтобы воспользоваться командной DEL нужно сначала перейти в папку, в которой находится файл для удаления, и после этого выполнить команду. Для того чтобы сменить диск нужно просто ввести букву диска и двоеточие. А для перемещения по папкам нужно использовать команду «CD».
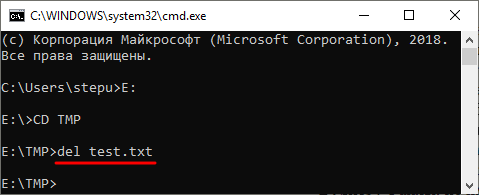
После того как вы попали в нужную папку можно приступать к удалению файлов. Для этого просто введите команду DEL и название файла.
del test.txt
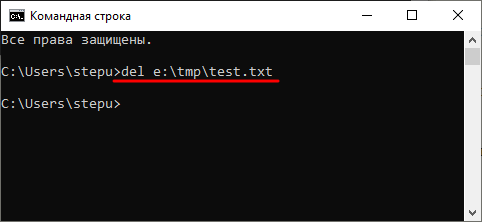
Также, при необходимости вы можете удалять файлы, не перемещаясь по папкам. В этом случае нужно указывать полный путь к документу.
del e:\tmp\test.txt
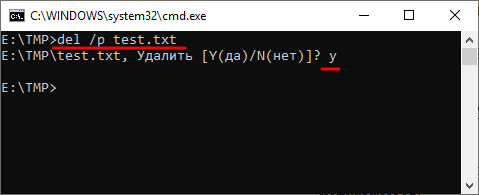
Если есть необходимость выполнить запрос на подтверждение удаления каждого из файлов, то к команде DEL нужно добавить параметр «/p». В этом случае в командной строке будет появляться запрос на удаление файла и пользователю нужно будет ввести букву «Y» для подтверждения.
del /p test.txt
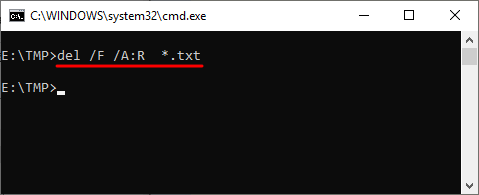
Нужно отметить, что при использовании параметра «/a», отвечающие за атрибуты буквы нужно вводить через двоеточие. Например, для того чтобы удалить все файлы с атрибутом «только для чтения» и с расширением «txt» нужно ввести:
del /F /A:R *.txt
Аналогичным образом к команде DEL можно добавлять и другие параметры. Комбинируя их вы сможете создавать очень мощные команды для удаления файлов через командную строку Windows. Ниже мы приводим еще несколько примеров.
Уничтожение всех файлов в корне диска D:
del D:\
Уничтожение всех файлов с расширением «txt» в корне диска D:
del D:\*.txt
Уничтожение всех файлов в папке d:\doc (документы с атрибутами будут пропущены):
del D:\doc
Уничтожение всех файлов с атрибутом «только для чтения» и расширением «txt» в папке d:\doc:
del /A:r d:\doc\*.txt
Удаление папок через командную строку
Если вам нужно удалить папку через командную строку Windows, то указанные выше команды вам не помогут. Для удаления папок существует отдельная команда RD или RMDIR (сокращение от английского Remove Directory).
Команды RD и RMDIR являются синонимами и предназначены для удаления папок. Они могу принимать следующие параметры:
- /S — удаление всего дерева каталогов, при использовании данного параметра будет удалена не только сама папка, но и все ее содержимое;
- /Q – удаление дерева папок без запроса на подтверждение;
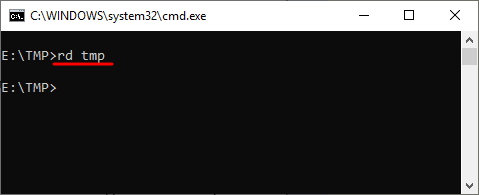
Например, для того чтобы удалить папку достаточно ввести команду RD и название папки. Например:
rd MyFolder
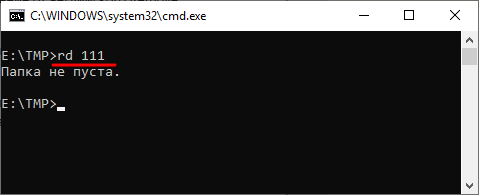
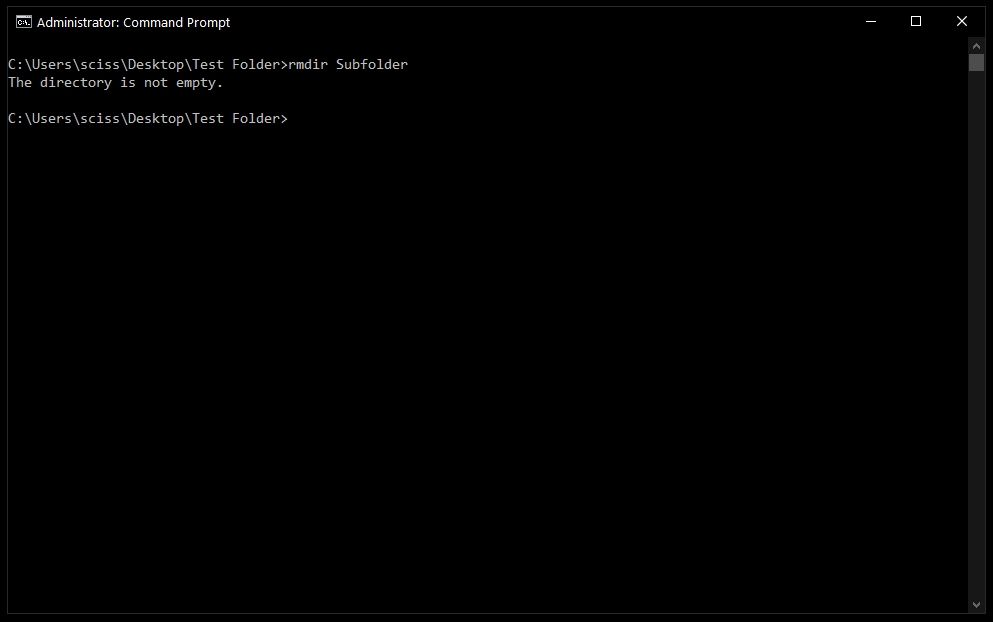
Если папка содержит вложенные папки или файлы, то при ее удалении будет выведена ошибка «Папка не пуста».
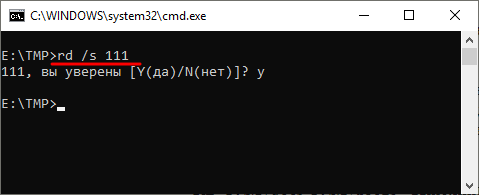
Для решения этой проблемы к команде RD нужно добавить параметр «/s». В этом случае удаление проходит без проблем, но появляется запрос на подтверждение удаления. Например:
rd /s MyFolder
Для того чтобы удаление дерева папок прошло без появления запроса на подтверждение к команде нужно добавить параметр «/q». В этом случае папка удаляется без лишних вопросов. Например:
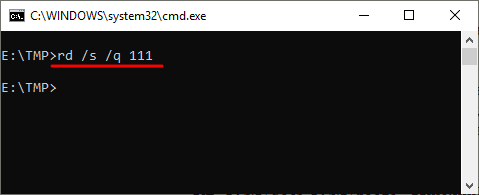
rd /s /q MyFolder
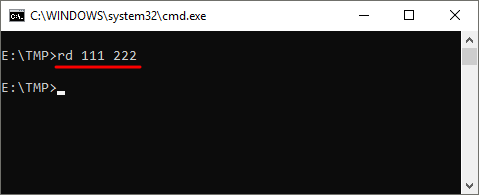
Также команда RD может принимать сразу несколько папок, для этого их нужно просто разделить пробелом. Например, чтобы сразу удалить
rd Folder1 Folder2
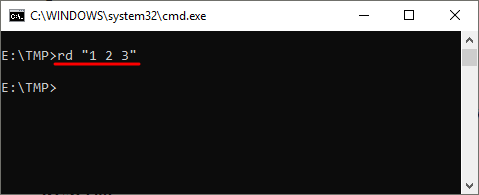
Если же вам нужно удалить через командную строку папку, которая сама содержит пробел, то в этом случае ее название нужно взять в двойные кавычки. Например:
rd "My Files"
Комбинируя команды DEL и RD, можно создавать мощные скрипты для очистки и удаления папок в операционной системе Windows.
Удаление файлов и папок в PowerShell
В консоли PowerShell вы можете использовать рассмотренные выше команды DEL и RD, либо «Remove-Item» — собственную команду (командлет) PowerShell. С помощью данной команды можно удалять можно удалять файлы, папки, ключи реестра, переменные и другие объекты.
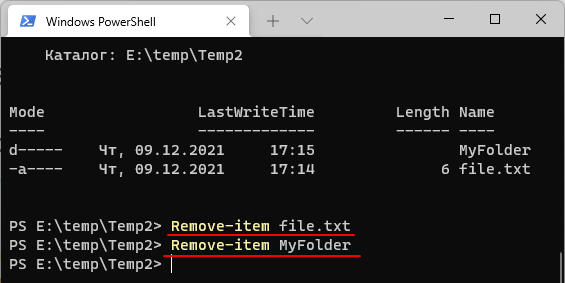
Например, для того чтобы удалить файл или папку в консоли PowerShell можно использовать команду:
Remove-item file.txt Remove-item MyFolder
Посмотрите также:
- Выключение компьютера через командную строку
- Как перезагрузить компьютер через командную строку
- Как вызвать командную строку в Windows 7
- Как поменять дату в Windows 7
- Как выключить компьютер через определенное время
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
Sometimes it’s just faster to do things with the command line.
In this quick tutorial we’ll go over how to open Command Prompt, some basic commands and flags, and how to delete files and folders in Command Prompt.
If you’re already familiar with basic DOS commands, feel free to skip ahead.
How to open Command Prompt
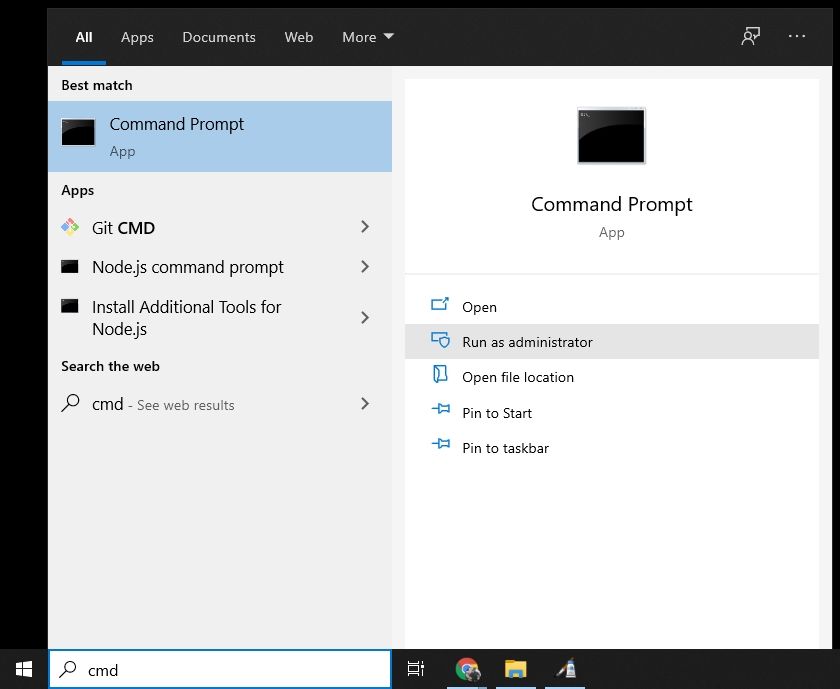
To open Command Prompt, press the Windows key, and type in «cmd».
Then, click on «Run as Administrator»:
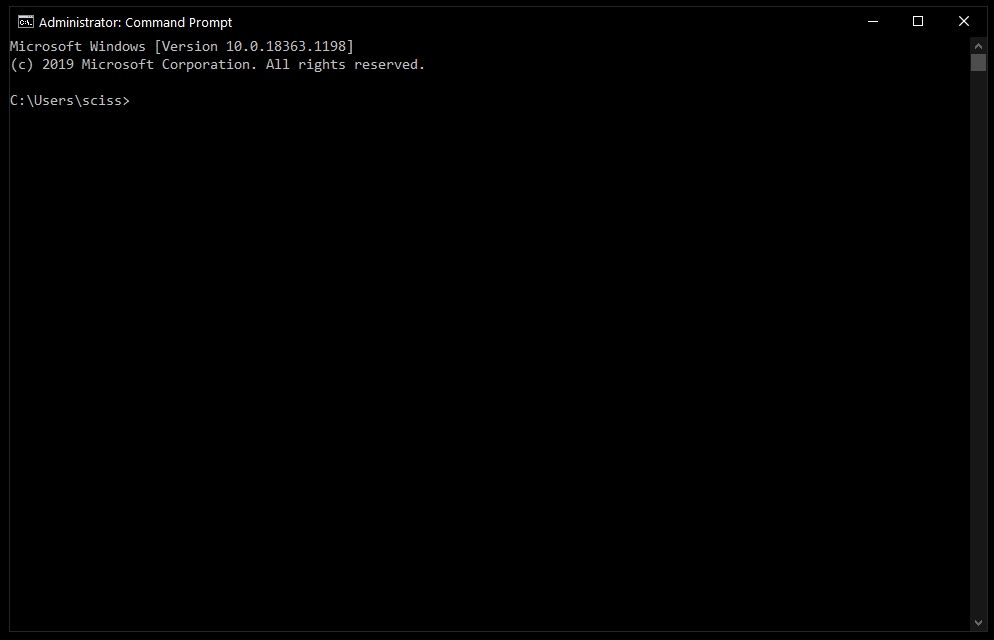
After that, you’ll see a Command Prompt window with administrative privileges:
If you can’t open Command Prompt as an administrator, no worries. You can open a normal Command Prompt window by clicking «Open» instead of «Run as Administrator».
The only difference is that you may not be able to delete some protected files, which shouldn’t be a problem in most cases.
How to delete files with the del command
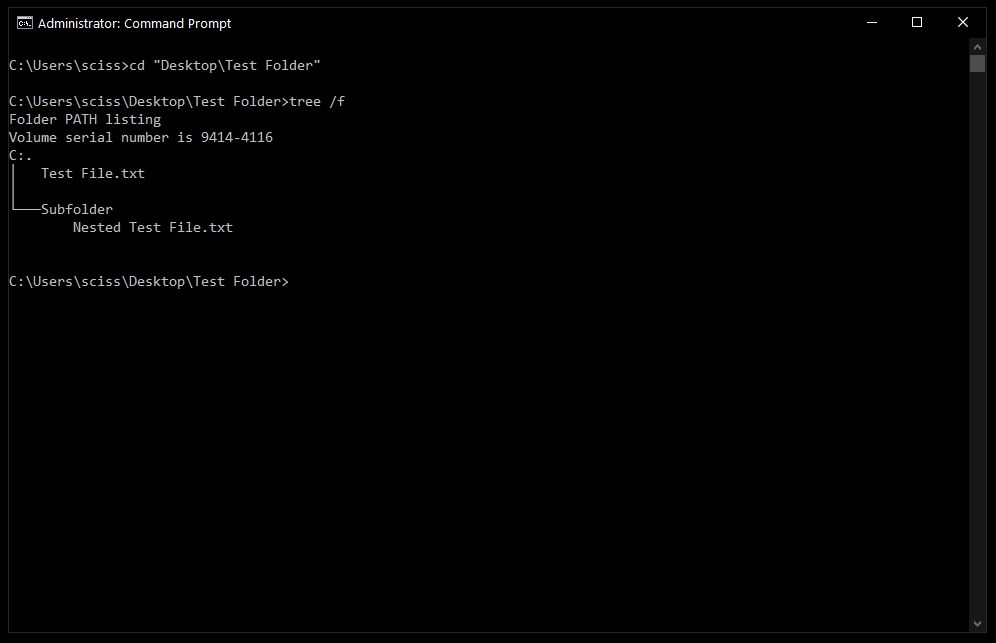
Now that Command Prompt is open, use cd to change directories to where your files are.
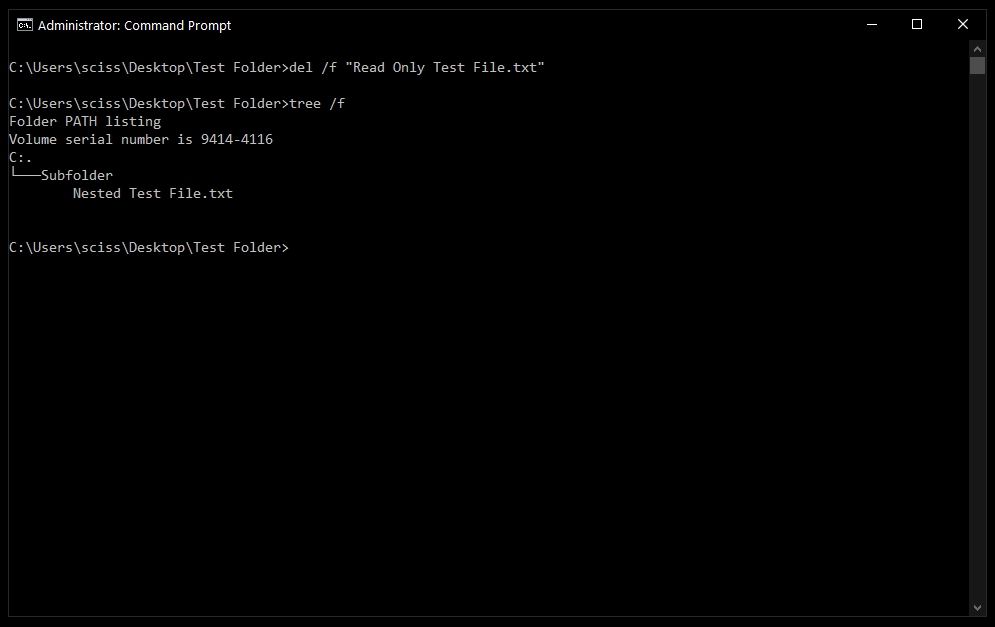
I’ve prepared a directory on the desktop called Test Folder. You can use the command tree /f to see a, well, tree, of all the nested files and folders:
To delete a file, use the following command: del "<filename>".
For example, to delete Test file.txt, just run del "Test File.txt".
There may be a prompt asking if you want to delete the file. If so, type «y» and hit enter.
Note: Any files deleted with the del command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
After that, you can run tree /f to confirm that your file was deleted:
Also, bonus tip – Command Prompt has basic autocompletion. So you could just type in del test, press the tab key, and Command Prompt will change it to del "Test File.txt".
How to force delete files with the del command
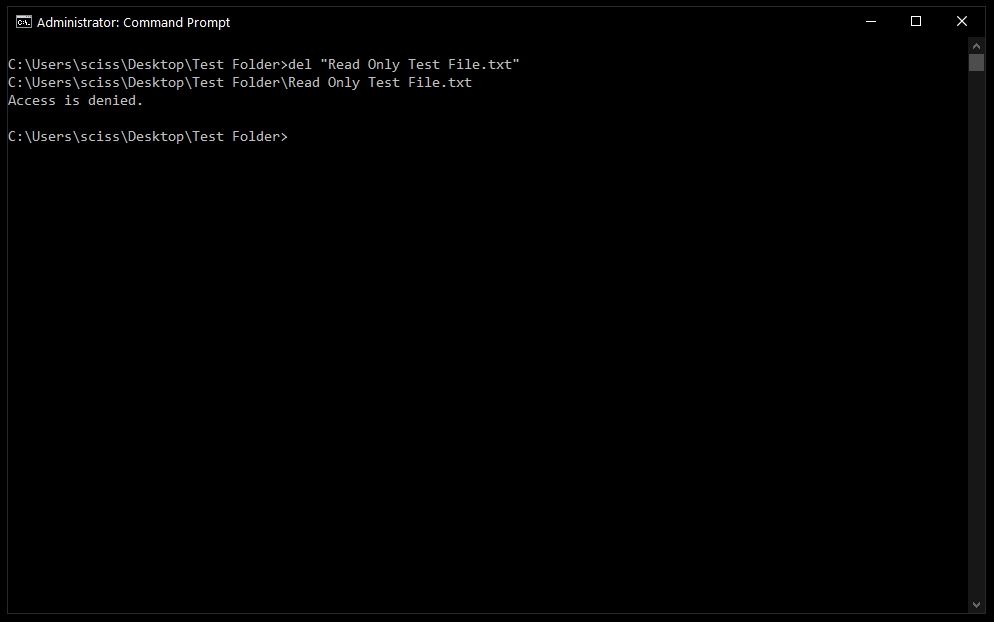
Sometimes files are marked as read only, and you’ll see the following error when you try to use the del command:
To get around this, use the /f flag to force delete the file. For example, del /f "Read Only Test File.txt":
How to delete folders with the rmdir command
To delete directories/folders, you’ll need to use the rmdir or rd command. Both commands work the same way, but let’s stick with rmdir since it’s a bit more expressive.
Also, I’ll use the terms directory and folder interchangeably for the rest of the tutorial. «Folder» is a newer term that became popular with early desktop GUIs, but folder and directory basically mean the same thing.
To remove a directory, just use the command rmdir <directory name>.
Note: Any directories deleted with the rmdir command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
In this case I want to remove a directory named Subfolder, so I’ll use the command rmdir Subfolder:
But, if you remember earlier, Subfolder has a file in it named Nested Test File.
You could cd into the Subfolder directory and remove the file, then come back with cd .. and run the rmdir Subfolder command again, but that would get tedious. And just imagine if there were a bunch of other nested files and directories!
Like with the del command, there’s a helpful flag we can use to make things much faster and easier.
How to use the /s flag with rmdir
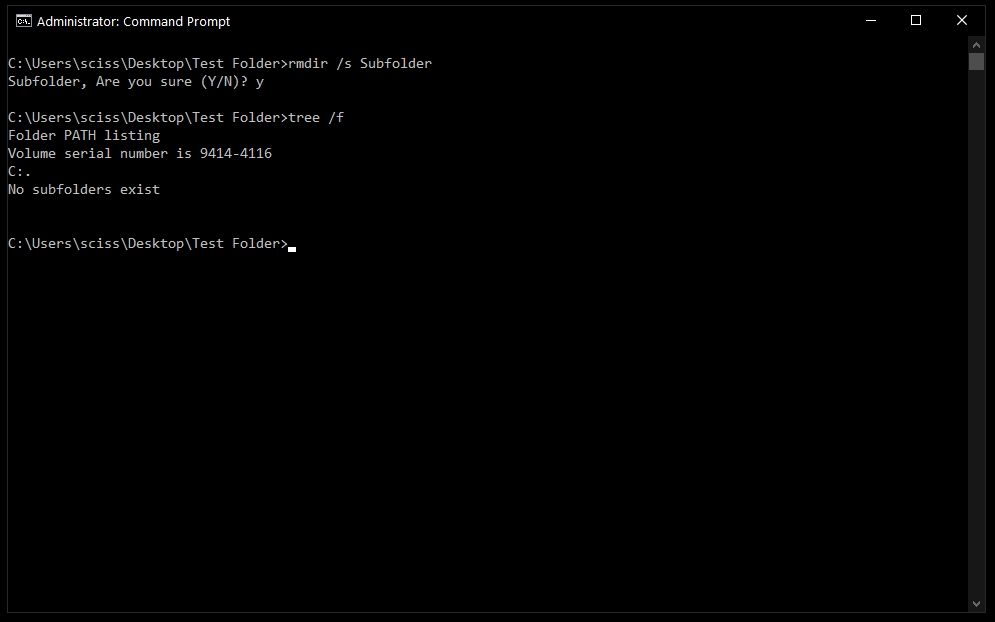
To remove a directory, including all nested files and subdirectories, just use the /s flag:
There will probably be a prompt asking if you want to remove that directory. If so, just type «y» and hit enter.
And that’s it! That should be everything you need to know to remove files and folders in the Windows Command Prompt.
All of these commands should work in PowerShell, which is basically Command Prompt version 2.0. Also, PowerShell has a bunch of cool aliases like ls and clear that should feel right at home if you’re familiar with the Mac/Linux command line.
Did these commands help you? Are there any other commands that you find useful? Either way, let me know over on Twitter.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
In some cases, for whatever reason, Windows will make sure that the provided file is used by the system and prevent it from being deleted. This file situation is very frustrating, especially if you know the file is not in use.
If you are having trouble in deleting any file or folder directly by right-clicking, then you can delete it using cmd. The commands below delete the specific file or folder and place them in the recycle bin:
- del
- rmdir
Here we have created a sample File and a Folder to delete it using CMD:
del command
del command is used to delete a file. Here, we will take our sample file “hello.txt” located at the desktop and try to delete it using the del command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the file:
Step 1: Change the path of the directory in CMD and set it to the path of the file. Type the following command in cmd and press Enter:
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the file “hello.txt” with following command:
del hello.txt
rmdir command
rmdir command is used to delete the entire folder or directory. Here, we will take our sample folder named “Tasks” placed at desktop and try to delete it using rmdir command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the folder:
Step 1: Change the path of the directory in CMD and set it to the path of the folder. Type the following command in cmd and press Enter:
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the folder “Tasks” with following command:
rmdir tasks
Last Updated :
03 Jul, 2022
Like Article
Save Article