Символическая ссылка (симлинк, символьная ссылка, Symbolic link) это специальный файл на файловой системе, которые сам не содержит данных, а является по сути ярлыком, указывающим на какой-то другой объект (файл или папку). При обращении к симлику операционная система считает, что это оригинальный файл (папка) и работает с ними совершенно прозрачно.
Символические ссылки используются в Windows довольно часто для системных файлов и каталогов. Пользователь может их применять, когда нужно перенести часть “тяжелых” файлов на другой диск, но чтобы Windows считала, что файлы все еще находятся в исходном каталоге (например в ситуациях, когда нужно экономить место на SSD, перенеся некоторые каталоги на более медленный и емкий SSD, не нарушая работоспособности программ). Можно использовать симлинки на SMB файловом сервере, когда каталоги с разных LUN должны быть доступны через одну точку входа.
В Windows есть три типа файловых ссылок для NTFS томов: жесткие, мягкие (симлинки), точки соединения (Junction point).
- Hard Links (жесткие ссылки) – могут указывать только на локальный файл, но не на папку. Такой файл – это ссылка на другой файла на этом же диске без фактического дублирования самого файла. У него отображается такой же размер и свойства, как у целевого файла (но реальное место на диске он не занимает);
- Junction Points (Directory Hard Link, точка соединения) – могут указывать только на папку (на этом же или на другом разделе);
- Symbolic Links (мягкая ссылка, симлинк) – могут указывать на локальный файл, папку и сетевой каталог на удаленном компьютере (UNC), поддерживаются относительные пути.
В подавляющем большинстве случаев вам будет достаточно функционала symbolic link, как наиболее универсального средства создания ссылки на любой объект.
Как создать символическую ссылку в Windows?
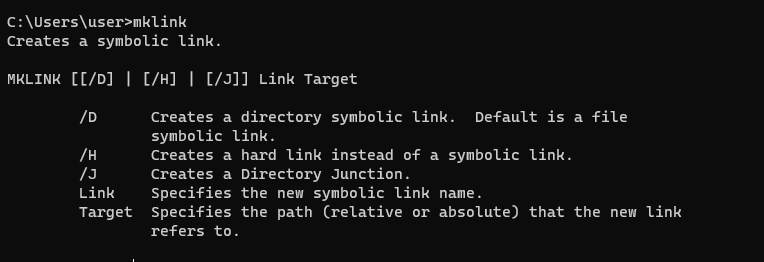
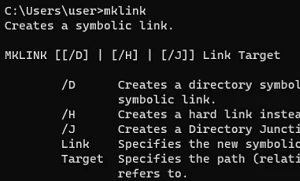
Для создания символических и жестких ссылок в Windows можно использовать встроенную утилиты mklink или PowerShell.
Синтаксис у утилиты
mklink
простой. Чтобы создать символическую ссылку на файл, нужно указать имя ссылки и целевой объект, на который она должна указывать. Можно указать тип ссылки:
/D
— символьная (мягкая) ссылка на каталог,
/H
— жесткая ссылка,
/J
– точка соединения (Junction point).
Чтобы использовать mklinkдля создания символических ссылок нужно запустить командную строку с правами администратора. Иначе при запуске команды появится ошибка “
You do not have sufficient privilege to perform this operation
”.
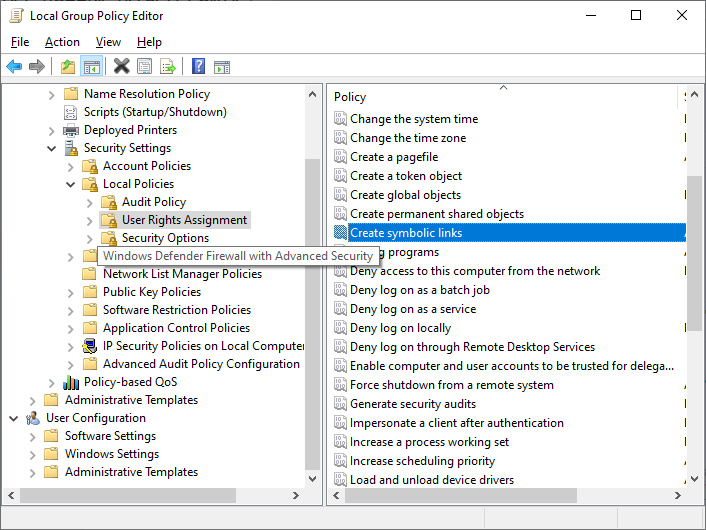
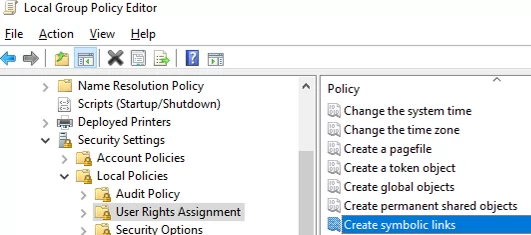
Если вам нужно разрешить создавать символические ссылки обычным пользователям, нужно добавить группу пользователей в параметр групповой политики Create Symbolic Links (Computer configuration -> Window Settings -> Security settings -> User Rights Assignment в редакторе GPO). По умолчанию в этой политике добавлена только локальная группа «Administrators». Обновите локальные политики после изменения параметра: gpupdate /force
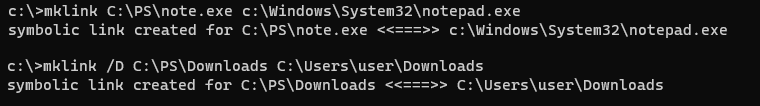
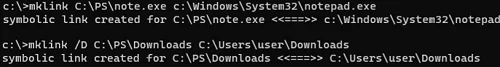
Создадим в каталоге C:\PS символическую ссылку на файл notepad.exe:
mklink C:\PS\note.exe c:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe
Должно появится сообщение:
symbolic link created for C:\PS\note.exe <<===>> c:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe
Теперь для запуска процесса notepad.exe можно использовать символическую ссылку note.exe.
Теперь создадим в этом каталоге симлинк на другой каталог на этом же диcке:
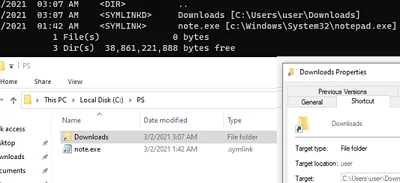
mklink /D “C:\PS\Downloads” “C:\Users\user\Downloads”
Теперь при переходе в каталог C:\PS\Downloads вы будете видеть содержимое каталога, на который он ссылается.
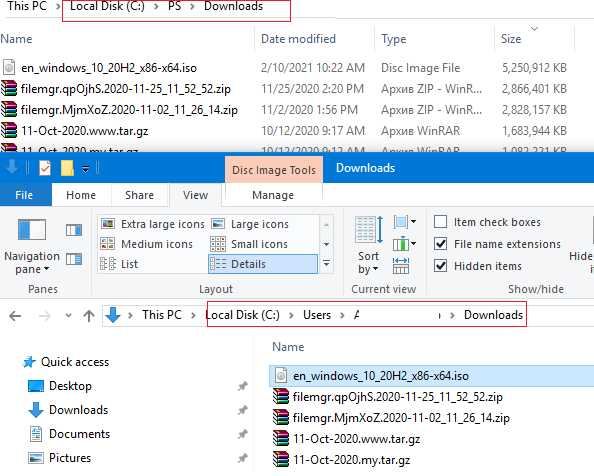
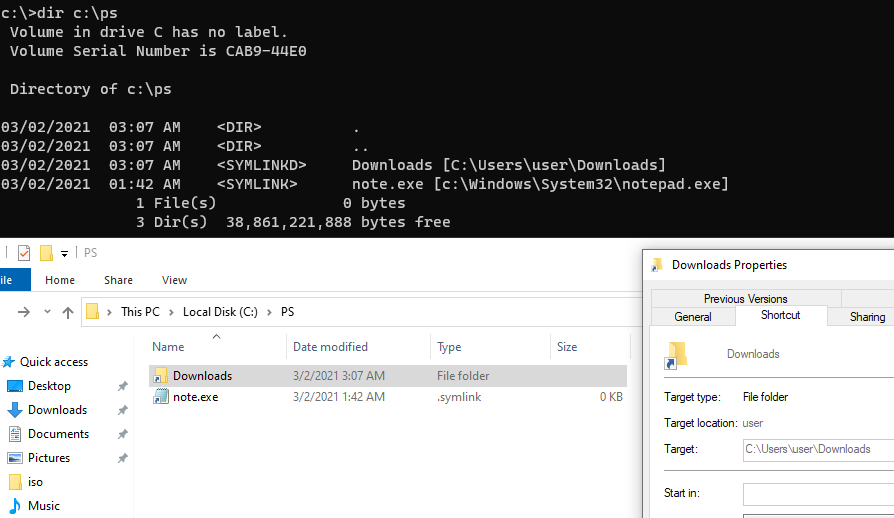
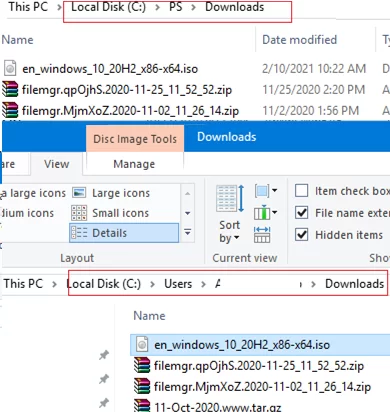
Выведем содержимое каталога C:\PS:
Dir c:\ps
Как вы видите, в атрибутах некоторых файлов указано, что это symlink/simlinkd. Также указан объект, на который они ссылаются. В Windows File Explorer симлинки отображаются с иконками ярлыков, а в их свойствах можно посмотреть целевой объект на который они ссылаются.
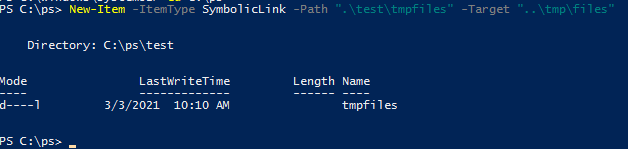
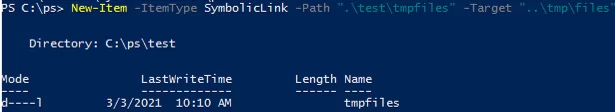
Также можно создать символически ссылки в Windows 10 с помощью PowerShell (в этом примере я использую относительные пути, чтобы создать символическую ссылку):
New-Item -ItemType SymbolicLink -Path ".\test\tmpfiles" -Target "..\tmp\files"
Можно создать символическую ссылку на сетевую папку на удаленном компьютере/сервере. Адрес сетевой папки нужно указывать в формате UNC. Следующий пример создаст симлинк на сетевой каталог на сервере:
mklink /D c:\ps\share \\mskfs01\Share
Например, подключим административную шару C$ с удаленного компьютера по IP адресу:
mklink /D c:\remotePC\server1 \\192.168.31.15\С$
Если при доступе к сетевой папке через симлинк, вы получили ошибку
The symbolic link cannot be followed because its type is disabled
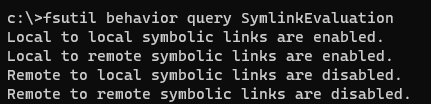
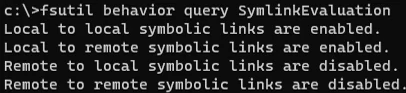
проверьте разрешенные способы использования символических ссылок на вашем компьютере:
fsutil behavior query SymlinkEvaluation
Local to local symbolic links are enabled. Local to remote symbolic links are enabled. Remote to local symbolic links are disabled. Remote to remote symbolic links are disabled.
Чтобы включить использование символических ссылок на удаленные ресурсы, выполните команды:
fsutil behavior set SymlinkEvaluation R2R:1
fsutil behavior set SymlinkEvaluation R2L:1
Вы можете работать с символическими ссылками, как с обычными объектами файловой системы, можно переименовать, переносить или удалить их. Система автоматически изменит настройки таких симлинков, чтобы они указывали на верные целевые объекты.
Для удаления симлинков используются обычные команды, как и для удаления файлов:
Del c:\ps\note.exe
RD c:\ps\downloads
Как найти и вывести все символические ссылки на диске?
В Windows нет простых инструментов для просмотра и управления всеми симлинками на диске.
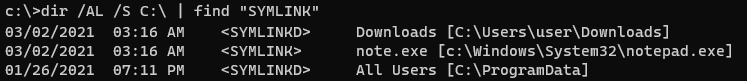
Вы можете вывести список всех символических ссылок на диске с помощью команды:
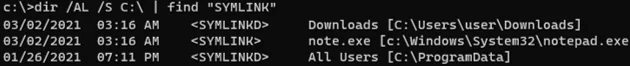
dir /AL /S C:\ | find "SYMLINK"
-
/A
– вывести файлы с атрибутом L (симлинк); -
/S
–выполнить команду рекурсивно для всех вложенных каталогов; -
C:\
— укажите имя диска, на котором нужно найти все символические ссылки (если вы не хотите сканировать весь диск, укажите путь к нужному каталогу)
Также можно вывести список всех символических ссылок на диске с помощью PowerShell. Для этого нужно просканировать все каталоги и найти NTFS объекты с атрибутом ReparsePoint:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Force -Recurse -ErrorAction 'silentlycontinue' | Where { $_.Attributes -match "ReparsePoint"}
Want to easily access folders and files from different folders without maintaining duplicate copies?
Quick Links
- What Are Symbolic Links?
- How to Create Symbolic Links with mklink
- How to Create Symbolic Links with a Graphical Tool
- How to Delete Symbolic Links
Key Takeaways
- Symbolic links are advanced shortcuts in Windows 11 and Windows 10 that can point to a file or folder, redirecting applications to access them as if they were in a different location.
- There are two types of symbolic links: soft links, which redirect to the location where files are stored, and hard links, which make it appear as though the file or folder exists at the location of the symbolic link.
- Symbolic links can be created using the mklink command in Command Prompt, with different options for creating symbolic links to files or directories. Alternatively, you can use the Link Shell Extension, a graphical tool, to create symbolic links with more options.
Windows 11 and Windows 10 both support symbolic links — also known as symlinks — that point to a file or folder on your system. You can create them using the Command Prompt or a third-party tool called Link Shell Extension.
What Are Symbolic Links?
Symbolic links are basically advanced shortcuts. Create a symbolic link to an individual file or folder, and that link will appear to be the same as the file or folder to Windows — even though it’s just a link pointing at the file or folder.
For example, let’s say you have a program that needs its files at C:\Program. You’d really like to store this directory at D:\Stuff, but the program requires that its files be at C:\Program. You could move the original directory from C:\Program to D:\Stuff, and then create a symbolic link at C:\Program pointing to D:\Stuff. When you relaunch the program, it will try to access its directory at C:\Program. Windows will automatically redirect it to D:\Stuff, and everything will just work as if it were in C:\Program.
This trick can be used for all sorts of things, including syncing any folder with programs like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive.
There are two type of symbolic links: Hard and soft. Soft symbolic links work similarly to a standard shortcut. When you open a soft link to a folder, you will be redirected to the folder where the files are stored. However, a hard link makes it appear as though the file or folder actually exists at the location of the symbolic link, and your applications won’t know any better. That makes hard symbolic links more useful in most situations.
Note that Windows doesn’t actually use the terms «hard link» and «soft link». Instead, it uses the terms «hard link» and «symbolic link». In the Windows documentation, a «symbolic link» is the same thing as a «soft link». However, the mklink command can create both hard links (known as «hard links» in Windows) and soft links (known as «symbolic links» in Windows).
How to Create Symbolic Links with mklink
You can create symbolic links using the mklink command in a Command Prompt window as Administrator or as a regular user. To do this without an Administrator Command Prompt window, you must first enable Developer Mode from Settings > Update & Security > For Developers.
To open Command Prompt as admin, click the Start button, search «cmd» or «Command Prompt,» then select «Run as Administrator».
Windows 11 doesn’t require administrative privileges to create symbolic links.
Without any extra options, mklink creates a symbolic link to a file. The below command creates a symbolic, or «soft», link at Link pointing to the file Target :
mklink Link Target
Use /D when you want to create a soft link pointing to a directory. like so:
mklink /D Link Target
Use /H when you want to create a hard link pointing to a file:
mklink /H Link Target
Use /J to create a hard link pointing to a directory, also known as a directory junction:
mklink /J Link Target
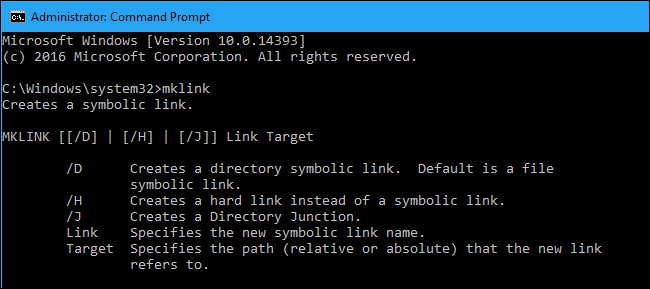
So, for example, if you wanted to create a directory junction (a hard link to a folder) at «C:\LinkToFolder» that pointed to «C:\Users\Name\OriginalFolder,» you’d run the following command:
mklink /J C:\LinkToFolder C:\Users\Name\OriginalFolder
You’ll need to put quotation marks around paths with spaces. For example, if the folders are instead named «C:\Link To Folder» and «C:\Users\Name\Original Folder,» you’d use the following command instead:
mklink /J "C:\Link To Folder" "C:\Users\Name\Original Folder"
If you see the message «You do not have sufficient privilege to perform this operation.», you need to launch the Command Prompt as Administrator before running the command.
If you’re like to do this with a graphical tool, download Link Shell Extension. Be sure to download the appropriate prerequisite package before the tool itself — both are linked to on the tool’s download page.
Once it’s installed, locate the file or folder you want to create a link to, right-click it, and select «Pick Link Source» in the menu.
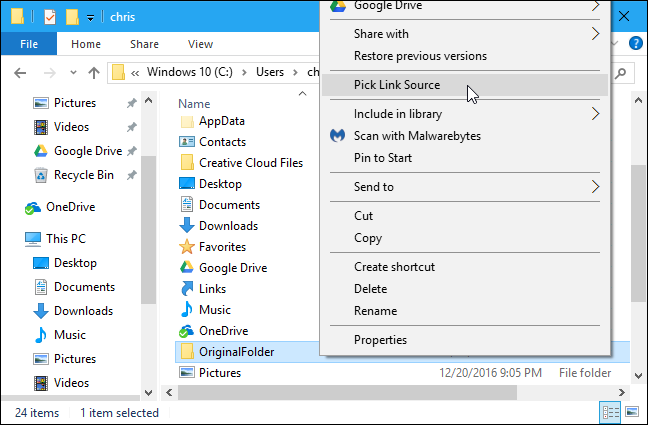
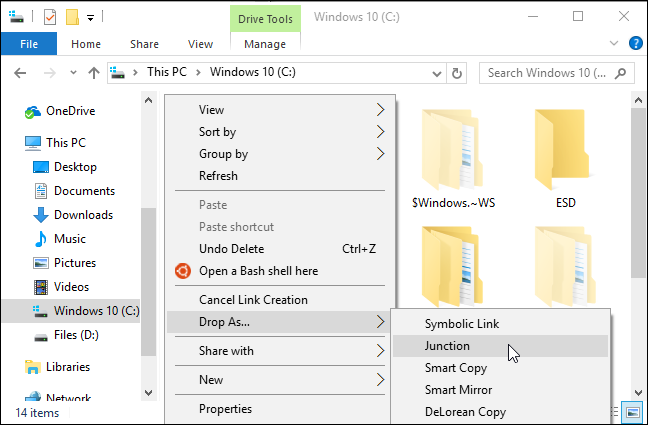
You can then right-click inside a different folder, point to the «Drop As» menu and select «Hardlink» to create a hard link to a file, «Junction» to create a hard link to a directory, or «Symbolic Link» to create a soft link to a file or directory.
How to Delete Symbolic Links
To get rid of a symbolic link, you can simply delete it like you would any other file or directory. Just be careful to delete the link itself rather than the file or directory it’s linking to.
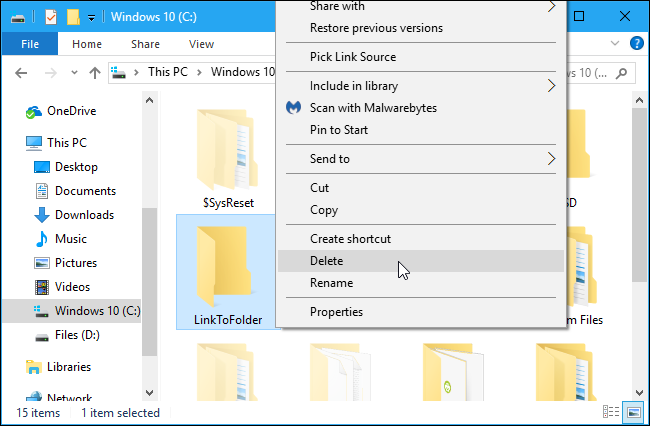
That is a major advantage of a symbolic link — you can freely delete the symbolic link whenever you want without worrying about the associated files or folders.
It seems like the junction command has been retired in Windows 10.
You can download junction from Windows SysInternals (which is part of Microsoft):
Junction not only allows you to create NTFS junctions, it allows you to see if files or directories are actually reparse points. Reparse points are the mechanism on which NTFS junctions are based, and they are used by Windows’ Remote Storage Service (RSS), as well as volume mount points.
Please read this Microsoft KB article for tips on using junctions.
Note that Windows does not support junctions to directories on remote shares.
So how do I create junctions or directory symbolic links in Windows 10?
Download junction as instructed above.
Now you can use the following commands.
Create a junction:
junction "C:\Documents and Settings\UserName\My Documents\My Dropbox\My Games" "C:\Documents and Settings\UserName\My Documents\My Games"
Create a directory symbolic link:
mklink /D "C:\Documents and Settings\UserName\My Documents\My Dropbox\My Games" "C:\Documents and Settings\UserName\My Documents\My Games"
You can use either mklink /j or junction in Windows 10 to create junctions.
You can use mklink /d in Windows 10 to create directory symbolic links.
Notes:
-
junctioncan also list junctions and determine if a file is a junction unlikemklink. -
mklinkis an internal command only available within acmdshell. -
By default Administrator privileges are required to create symbolic links.
It can also be granted to other users. The security setting «Create symbolic links» can be granted at:
Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\
Examples
Using mklink to create a directory symbolic link:
F:\test>mklink /d test-dir-sym-link test
symbolic link created for test-dir-sym-link <<===>> test
Using mklink to create a junction:
F:\test>mklink /j test-junction test
Junction created for test-junction <<===>> test
Using junction to create a junction:
F:\test>C:\apps\NirSoft\SysinternalsSuite\junction.exe test-junction test
Junction v1.06 - Windows junction creator and reparse point viewer
Copyright (C) 2000-2010 Mark Russinovich
Sysinternals - www.sysinternals.com
Created: F:\test\test-junction
Targetted at: F:\test\test
Further Reading
- An A-Z Index of the Windows CMD command line — An excellent reference for all things Windows cmd line related.
- mklink — Create a symbolic link to a directory or a file, or create a hard file link or directory junction.
Symlinks or Symbolic Links is one of the lesser known, yet useful, features in Windows. You can think of symbolic links as the shortcuts you create in Windows. However, symbolic links are much more powerful and helpful than regular shortcuts. This tutorial discusses what symbolic links are and shows how you can easily create them in Windows.
Content
- Create Symbolic Link Using Link Shell Extension
- Create Symbolic Link Using Mklink
- Frequently Asked Questions
Also read: Latest Windows 10 and 11 Update Problems and How to Fix Them
What Are Symbolic Links?
When you create a shortcut for a file or folder, all you are doing is pointing it to that specific file or folder, nothing more. Symbolic links are much more than a simple shortcut. They act as a virtual file or folder that links to the actual file or folder.
When you create a symlink for a file, it appears as if it is the actual file, when in reality, it is redirecting you toward the real file in the background. Besides files, you can also create symlinks for folders. Simply put, a symlink is nothing more than a build of the text string, which lets the operating system know that it is just a path for another file or folder.
For instance, most cloud service apps you install will only sync files and folders located in their own folder. But there may be times when you have a folder in some other drive you want to sync with the cloud storage service.
Also read: 4 Easy Ways to Copy a Large Number of Files Quickly in Windows
However, you don’t want to move the folder from its actual location or don’t want to create a copy of the folder. In those situations, you can simply create a symlink in the cloud service folder so that you can sync the contents of the target folder without actually moving or copying the real folder.
Since a symlink is just a virtual folder that just acts as a path to the real folder, you don’t have to worry about the symlink consuming your disk space.
Create Symbolic Link Using Link Shell Extension
If you don’t want to faff around in the Command Prompt and are prepared to faff around a little bit by installing a tool that lets you create symlinks to an existing file or directory using the right-click context menu, then try the following. Link Shell Extension is a tool that lets you create hard links and symbolic links by right-clicking whatever folder you want to create a link to.

There are a few hoops with the installation. You’ll get a warning that it can’t be downloaded securely, and Windows Defender may warn you that it’s «unsigned.»
We can assure you that the tool is safe. Go ahead and install it. During installation, explorer.exe will restart, so make sure you have important stuff backed up.
- Once LSE is installed, right-click the target file or folder you want to create a symlink to, then click «Pick Link Source.»
Note: in Windows 11, you’ll have to click «Show more options» first before you will see «Pick Link Source» or any of the other right-click menu options below.

- Go to the folder where you want the symlink to appear, right-click it, then select «Drop As -> Symbolic Link.»

Also read: How to Sort Folders by Size in Windows
Create Symbolic Link Using Mklink
Note: although these instructions are shown using Windows 11, the commands shown here are applicable for Windows Vista and later.
- Creating symlinks in Windows is pretty easy with the
mklinkcommand. To start, press Win, then search for «Command Prompt.» Right-click on «Command Prompt» in the results, then select «Run as administrator» to open the Command Prompt with admin rights.

- Once the command prompt has been opened, use the below command format to create a symlink for a file.
- In my case, I want to create a symlink in the C: drive for a text file located on the F: drive, so the command looks something like this:
mklink "C:\Path\Symlink_File.txt" "F:\Real_File.txt"

The first path you see in the above command is where you will create your symlink. This path is called a «Link.» The second path belongs to the actual file on your disk and is called «Target.»
- Once the symlink has been created, this is how it looks in the File Explorer. Though the icon looks like a regular shortcut, it is a symlink.

Along with individual files, you can create symlinks for entire directories.
- To do that, use the below command. The switch
/Dallows you to do this.
mklink /D "C:\Path\Symlink_Books" "F:\Books"

- As soon as you execute the command, the symlink will be created for the target directory. You can use it to access all the files and folders inside the real folder.
- If you ever want to, you can delete the symbolic link like any other file or folder. Just select the symlink, press the delete key on your keyboard, and you are good to go.

Also read: Find and Open Files Using Command Prompt in Windows
Frequently Asked Questions
Why am I getting an error when I try to install links shell extension?
You most likely do not have the right Microsoft Visual C files installed on your computer, probably when using Windows 11. Download and install the 64-bit or 32-bit runtime DLLs from the same page you downloaded Link Shell Extension, then try installing it again.
Why can’t I use Powershell instead of Command Prompt?
PowerShell is now the default terminal in Windows 11, but unfortunately, it does not work with the mklink command, so you’ll have to fall back on the trusty Command Prompt.
Why can’t I create a symlink in the root of the C: drive?
You can only create folders in the root of the C: drive, assuming that «C» is your system drive. To create symbolic links on this drive, you must make a folder for them first.
Image credit: Pexels. All screenshots by Sydney Butler.
Sydney Butler is a technology writer with a background in Psychology who has written for a wide variety of technology outlets including How-To-Geek, Online Tech Tips, Helpdesk Geek, 9to5Mac, 9to5Google, and many more.
He has 25 years of technology troubleshooting experience as a technician and user-education practitioner.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox
A symbolic link (symlink) is a special file on a file system that doesn’t contain any data but is actually a shortcut pointing to another object (file or folder). When accessing a symlink, the operating system thinks that it is an original file (folder) and works with it completely transparently.
Symbolic links are quite often used in Windows for system files and directories. You may use them when you need to move large files to another disk and Windows must consider that they are still located in the original directory (for example, when you want to save space on an SSD by moving some directories to a slower and larger HDD without disrupting programs). You can use symlinks on your SMB file server when directories located in different LUNs must be available in a single entry point.
The three types of file links available in Windows for NTFS volumes: hard links, soft links (symlinks), and Junction Points.
- Hard Links can only point to a local file, but not to a folder. A hard link is a file link to another file on the same volume without duplicating the file. It has the same size and properties as the source file (but it does not take up real space on the drive);
- Junction Points (Directory Hard Link) can only point to a directory (on the same or another volume);
- Symbolic Links (soft link, symlink) can point to a local file, folder, or network share on a remote computer (by the UNC path). Relative paths are supported.
In most cases, you can use a symlink for most tasks when you need to create a reference to an object.
How to Create a Symbolic Link in Windows?
To create symbolic or hard links in Windows, you can use the built-in mklink tool or PowerShell.
mklink has a simple syntax. To create a symbolic link to a file, specify the link name and the target object you want it to point to. You can set the link type: /D — a symbolic (soft) link to a directory, /H — a hard link, /J – a Junction point.
In order to use mklink for creating symbolic links, run the command prompt as administrator. Otherwise, when you run the command, the following error will appear: You do not have sufficient privilege to perform this operation.
If you want to allow non-admin users to create symbolic links, add the user group to Create Symbolic Links GPO option (Computer Configuration -> Window Settings -> Security Settings -> User Rights Assignment in the GPO editor). By default, only the local Administrators group is added to the policy. Update local Group Policy after changing the setting: gpupdate /force
Create a symbolic link to the notepad.exe file in C:\PS:
mklink C:\PS\note.exe c:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe
You will see the following message:
symbolic link created for C:\PS\note.exe <<===>> c:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe
Now you can use the note.exe symlink to run notepad.exe.
Create a symlink to another folder on the same drive:
mklink /D "C:\PS\Downloads" "C:\Users\user\Downloads"
Now, when you open the C:\PS\Downloads folder you will see the contents of the directory it refers to.
Display the contents of C:\PS:
dir c:\ps
As you can see, the attributes of some files show that it is a symlink (simlinkd). The object they refer to is also displayed. In File Explorer, symlinks are displayed as shortcut icons, and the target object they point to is shown in their properties.
You can also create a symbolic link in Windows using PowerShell (in this example I use relative paths to create symlink):
New-Item -ItemType SymbolicLink -Path ".\test\tmpfiles" -Target "..\tmp\files"
You can create a symbolic link to a shared network folder on a remote computer or server. Specify the network share address in the UNC format.
mklink /D c:\ps\share \\hq-fs01\Share
For example, let’s connect the administrative share C$ on a remote computer using its IP address:
mklink /D c:\remotePC\server1 \\192.168.13.10\C$
If you see the following error when accessing a share using a symlink:
The symbolic link cannot be followed because its type is disabled.
Check the allowed ways of using symbolic links on your computer:
fsutil behavior query SymlinkEvaluation
Local to local symbolic links are enabled. Local to remote symbolic links are enabled. Remote to local symbolic links are disabled. Remote to remote symbolic links are disabled.
To enable symbolic links to remote resources, run the following commands:
fsutil behavior set SymlinkEvaluation R2R:1
fsutil behavior set SymlinkEvaluation R2L:1
You can work with symbolic links in the same way as with ordinary file system objects: move, rename, or delete them. Windows will automatically change the settings of the symlinks so that they point to the correct targets.
To remove symlinks, the usual commands are used (like you do for files):
Del c:\ps\note.exe
RD c:\ps\downloads
How to Find All Symbolic Links on a Windows Drive?
There are no built-in tools in Windows to view and manage all symlinks on a disk.
You can list all symbolic links on a disk using this command:
dir /AL /S C:\ | find "SYMLINK"
/A– to display files with L attribute (symlinks)/S–run the command recursively for all subfoldersC:\— specify a drive name or path to a folder to search for symlinks
You can also get a list of all symbolic links on a disk using PowerShell. Just scan all folders and find NTFS objects with the ReparsePoint attribute:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Force -Recurse -ErrorAction 'silentlycontinue' | Where { $_.Attributes -match "ReparsePoint"}