-
Home
-
News
- Fix “Not Recognized As an Internal or External Command” Win 10
By Alisa |
Last Updated
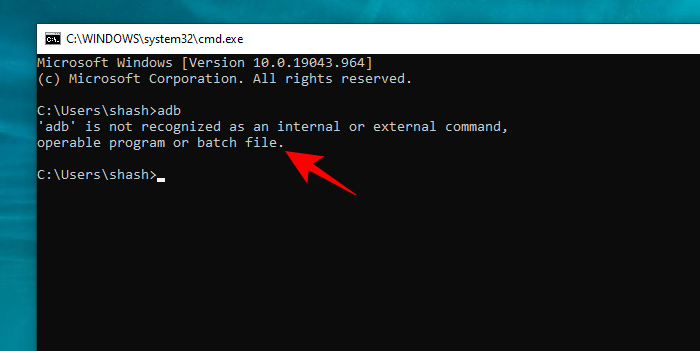
If a command is not recognized as an internal or external command, it may be due to the messed up environment variables. Check how to fix this error in this post. To help you tackle data loss, manage hard drive partitions, backup and restore system, MiniTool software provides professional tools.
If you meet the error “command is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file” problem in Command Prompt in Windows 10, the reason may be that the Windows Environment Variables are messed up. Check what Windows Environment Variables are and how to fix this error below.
Windows Environment Variables
Windows OS has a list of path to record the locations of most common system applications. When you use the Run prompt or CMD.exe to open a program, it can launch easily. This list is called Windows Environment Variables.
Your operating system uses the PATH system variable to locate needed executables from the Command Prompt or Terminal application.
If the Windows Environment Variables are messed up, it may cause some programs not working like Command Prompt not working.
You can learn how to fix not recognized as an internal or external command error in Windows 10 when you try to execute a command or open a system program in Command Prompt.
How to Fix Not Recognized As an Internal or External Command
Step 1. Go to C:\Windows\System32\ to check if the program actually exists. You can search and find the target exe file in System32 folder. If the program exists, then you can continue to modify the Windows Environment Variables to fix Command Prompt not recognizing commands errors.
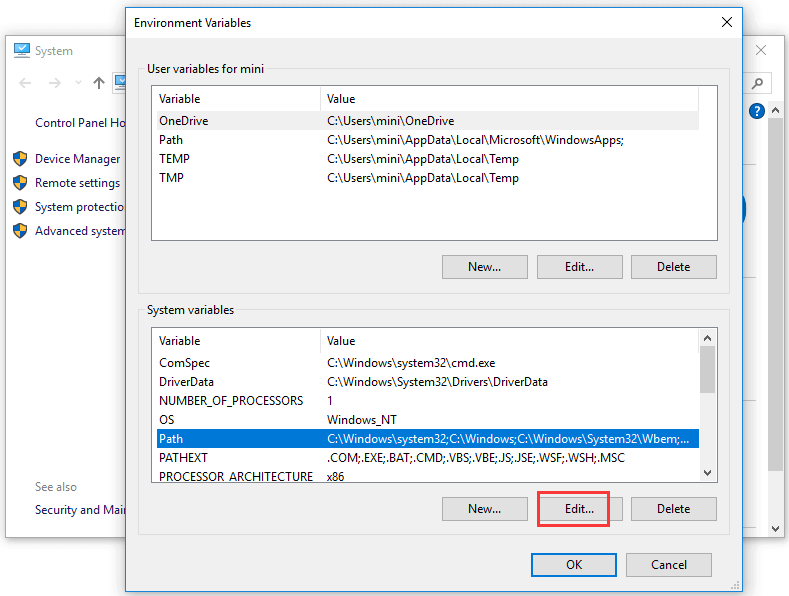
Step 2. You can right-click This PC icon and select Properties. Click Advanced system settings to open System Properties window. After that, click Advanced tab and click Environment Variables.
Step 3. Then you can click Path under System variables, and click Edit button. Before you edit the PATH system variable, it’s advised you copy and paste the old environment variables to a text file to make a backup. In case something goes wrong, you can easily revert them.
Step 4. Check if there is a directory path of the executable file location, if not, enter the location of the executable file’s parent folder. After you edit the value, you can click OK.
Step 5. Then you can reboot your computer and execute the command again to see if the “not recognized as an internal or external command” problem is fixed in your Windows 10 computer.
How to Recover Deleted/Lost EXE Files in Windows 10
If some exe files are automatically or mistakenly deleted or unexpectedly lost in your Windows 10 computer, you can use MiniTool Power Data Recovery to easily recover exe files.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery is a professional easy-to-use data recovery program for Windows 10. You can use it to recover any deleted/lost files (incl. application exe files) from Windows 10 computer with ease. Still, this best data recovery software also allows you to recover deleted/lost files from external hard drive, USB flash drive, pen drive, thumb drive, SD card, and more. The free edition allows you to recover up to 1GB data totally for free. 100% clean and safe software, and extremely intuitive interface.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Alisa is a professional English editor with 4-year experience. She loves writing and focuses on sharing detailed solutions and thoughts for computer problems, data recovery & backup, digital gadgets, tech news, etc. Through her articles, users can always easily get related problems solved and find what they want. In spare time, she likes basketball, badminton, tennis, cycling, running, and singing. She is very funny and energetic in life, and always brings friends lots of laughs.
The Command Prompt is a handy way to perform specific tasks, but sometimes it doesn’t recognize what you want from it. Here’s how to fix that.
The Command Prompt in Windows is a handy utility. It allows you to perform many tasks quickly; however, the command processor may show the «not recognized as an internal or external command» error when you try to execute a command.
It is a common error and usually occurs due to incorrect command execution. This article explains the causes and a few troubleshooting steps to help you fix this error.
Why the Not Recognized as an Internal or External Command Error Occurs?
Windows OS keeps a list of paths known as Windows Environment Variables to launch and execute programs quickly. Any issues with it can cause the error.
Potential issues that cause this error include:
- Incorrect commands.
- Registry entries interrupting the functioning of commands and more.
- Executable programs or scripts not installed.
- An incorrectly specified path or filename.
- A missing file directory in Windows Environment Variables.
How to Fix the «Not Recognized as an Internal or External Command» Error
This error is often triggered when you run a program or CMD command, and something goes wrong. We have listed fixes for both versions of the error, so follow the relevant one to your case.
1. Verify if the Program Is Installed
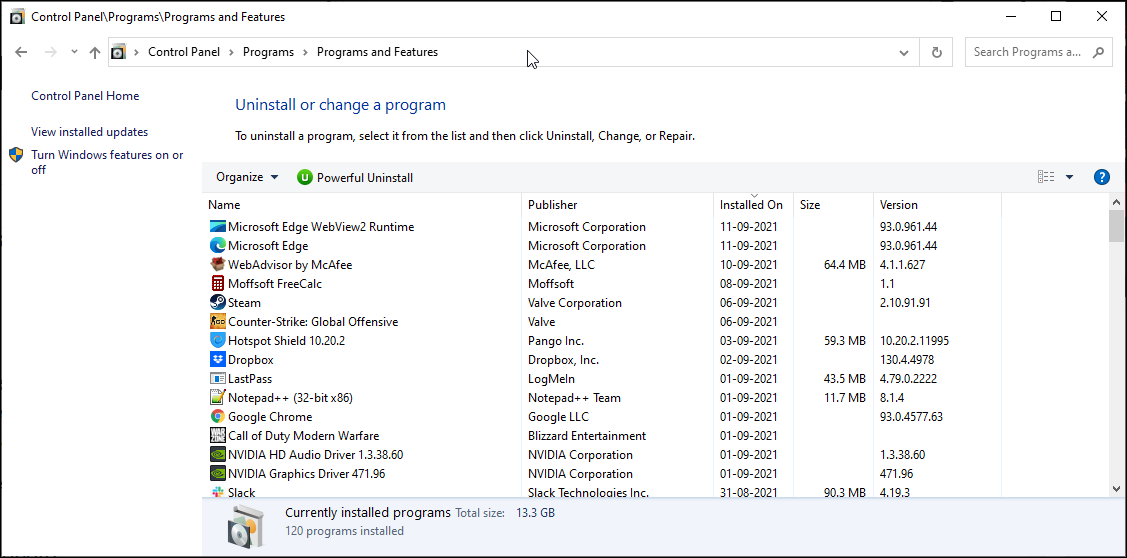
Command Prompt can’t run a program that does not exist. If you are trying to execute a newly installed program, ensure it is correctly installed.
To verify the installation:
- Press Win + R to open Run. Then, type control and click OK.
- Then, in the Control Panel, go to Programs > Programs and Features.
- Scroll through the list of installed apps and locate the app you want to run.
Alternatively, you can also view installed apps by accessing Apps and Features in Settings. To do this, press Windows key + I, click on Apps and locate the installed app.
By default, when you try to launch a program or a script from CMD, the command processor looks for the related files and paths in the System32 folder or environment variables. If the file is missing, it will return the not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program, or batch file error.
This is likely because Windows does not install most apps in the System32 folder, but C:\Program Files instead.
You can resolve this issue in three ways:
- First, use the full path of the executable file to launch the program.
- Second, add the program path to Windows environment variables.
- Finally, move the files to the System32 folder.
2. Use the Full File Path to Execute the Command
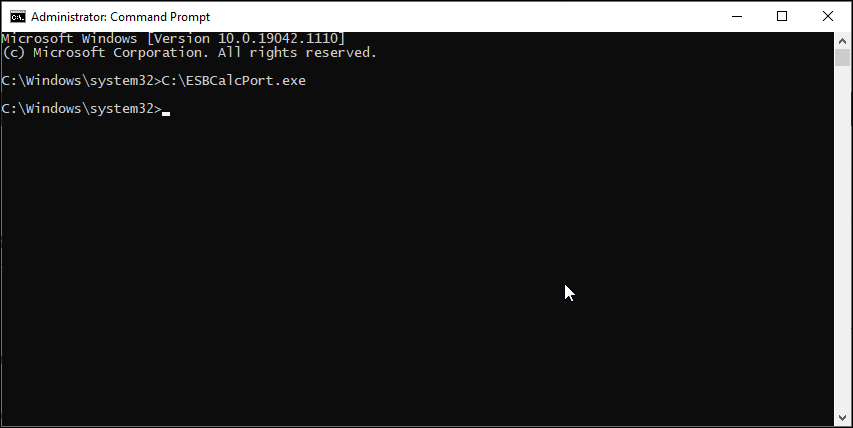
First, let’s try the full path method. Here, we will use the full file path instead of the app name to launch programs from Command Prompt. Here’s how to do it:
- First, open the Command Prompt as administrator.
- Next, type the full path of the application you want to launch. For example, if you want to open the ESBCalc Port located in the C:\ directory, then the command to open the app with the full path will look something like this:
C:\ESBCalcPort.exe - That said, this will only work if the file path does not have any white spaces. If your file path has a space, type the file path inside double-quotes.
3. Use the Full File Path Within Double Quotes
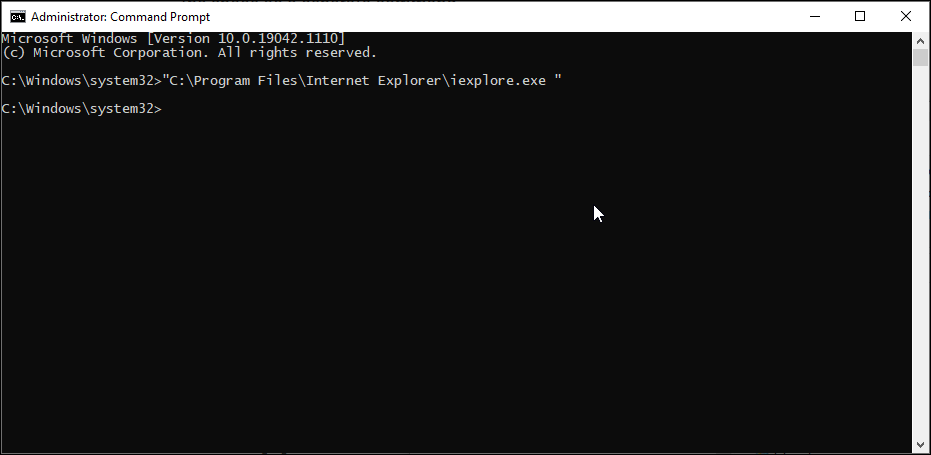
Command Prompt reads the white spaces as the end of a command and treats anything after the space as a separate command.
Let’s say you want to launch the Internet Explorer app located in C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe via CMD. However, running this file path will return an error due to the space between Program Files and Internet Explorer.
To avoid this, you can insert the file path within a double quote. Here, the command to launch Internet Explorer will look like this:
"C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe"
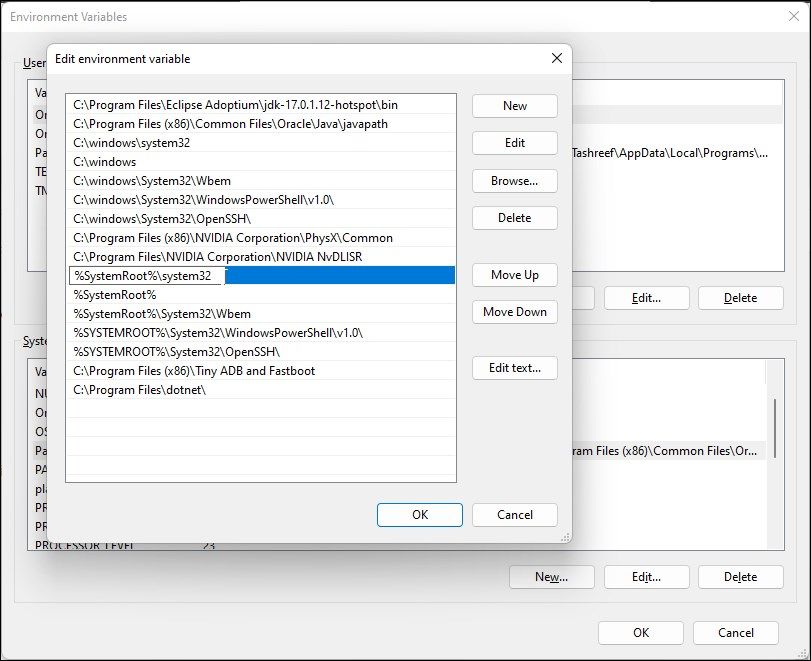
4. Add the File Path to the Windows Environment Variables
You can edit the Environment Variables and add the file path of your application to its directory. This way, Command Prompt will identify the path for the entered command and execute it without the error.
Adding a full file path to the Windows Environment Variable can help you resolve the not recognized as an internal or external command error for the Flex, nmake, make, cobra, Is, terraform, gcc, code, Android Studio, Python, Fastboot, and ADB commands.
To edit Windows Environment Variable:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Next, type control and click OK to open the Control Panel.
- In Windows 10, Go to System and Security > System. In the left pane, click on Advanced System Settings.
- On newer versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11, go to Settings > System > About. Then, click on Advanced system settings under the Related settings section.
- In the Advanced tab, click on the Environment Variables button.
- In the new window, under System variables, select the Path variable.
- Click the Edit button.
- In the Edit window, click on New.
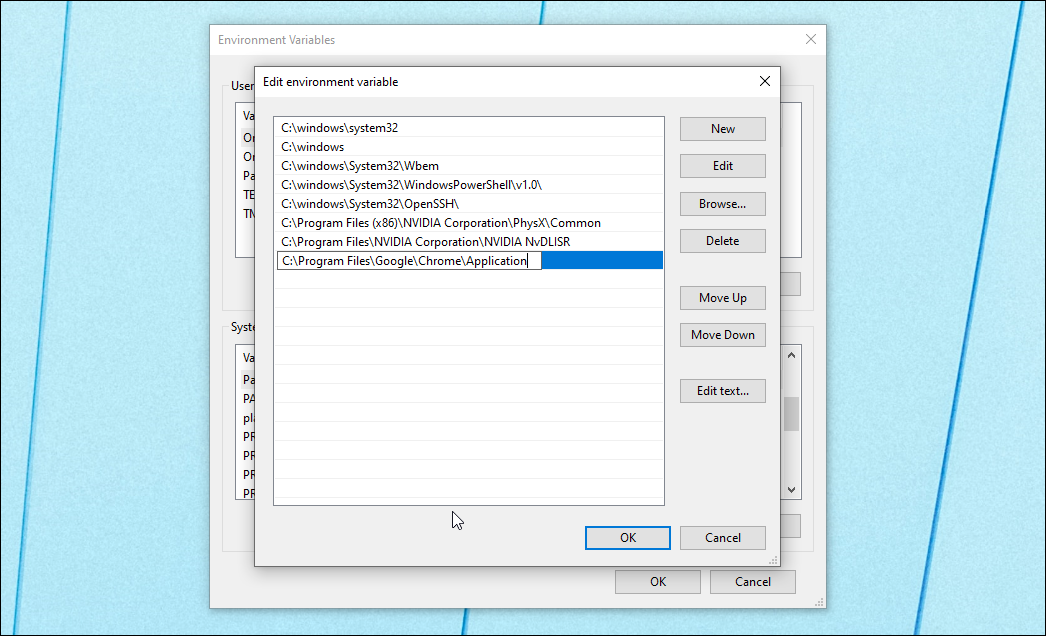
- Here, you have to paste the program’s file path you want to run from CMD. For example, if you want to run the Chrome browser located in C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application, then the full file path will look like this:
C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application - Click OK to add it to the Environment Variables.
- Then, click OK again.
- Next click OK and Apply to save the changes.
Once you have added the new environment variable, restart your PC to apply the changes. After the PC restarts, open Command Prompt, enter the program’s name, and CMD will open it without any error.
If you experience issues with the commands like ipconfig, netsh, cipher, etc., then add the Windows system root folder file path in the Environment Variable dialog. Here’s how to do it.
- Open the Environmental Variables dialog.
- Next, select the Path variable under the System variables section and click on Edit.
- Click New and paste the following:
%SystemRoot%\system32 - Click OK to save the changes.
- Click OK, and then click OK and Apply to save the changes.
5. Move Files to System32 Folder
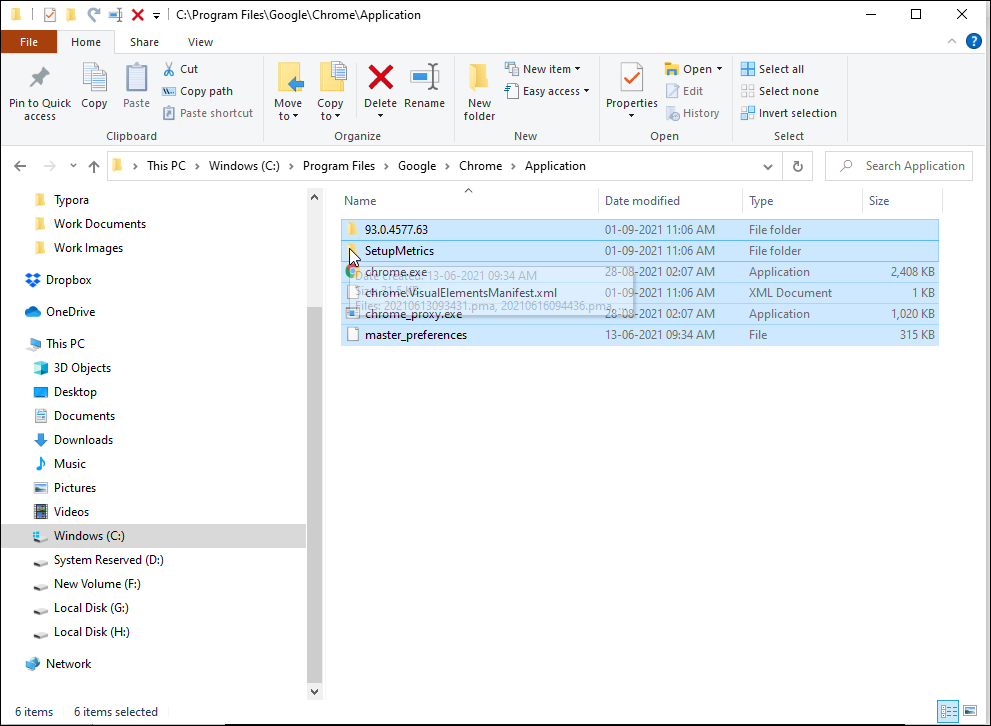
System32 is a protected system folder, and it is protected for a good reason. When you try to launch a program as an administrator, Command Prompt looks for the executable file in the System32 folder. However, since all the programs are not installed in the System32 folder, you may end up with an error.
If you still want to run the program from CMD and don’t want to type a full file path, you can move the program files to the System32 folder.
To move program files to the System32 folder:
- Navigate to the installation directory for your program and copy all the files in the folder. Here, we will move Google Chrome files located in C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application to the System32 folder.
- Next, navigate to the C:\Windows\System32 folder and paste the copied files. Click Yes if a UAC prompt appears.
- Next, open the Command Prompt as administrator, type chrome, and hit enter. CMD will instantly open the Google Chrome browser.
Fixing the CMD Not Recognized as an Internal or External Command Error
Command Prompt commands are not case-sensitive, but it does not forgive the use of extra spaces. To resolve this error, check if the commands are correct and use file paths with spaces within double-quotes. For the programs not installed in the System32 folder, add an environment variable with your application’s full file path to launch apps through CMD.
This is a very common question seen on Stackoverflow.
The important part here is not the command displayed in the error, but what the actual error tells you instead.
a Quick breakdown on why this error is received.
cmd.exe Being a terminal window relies on input and system Environment variables, in order to perform what you request it to do. it does NOT know the location of everything and it also does not know when to distinguish between commands or executable names which are separated by whitespace like space and tab or commands with whitespace as switch variables.
How do I fix this:
When Actual Command/executable fails
First we make sure, is the executable actually installed? If yes, continue with the rest, if not, install it first.
If you have any executable which you are attempting to run from cmd.exe then you need to tell cmd.exe where this file is located. There are 2 ways of doing this.
-
specify the full path to the file.
"C:\My_Files\mycommand.exe" -
Add the location of the file to your environment Variables.
Goto:
——> Control Panel-> System-> Advanced System Settings->Environment Variables
In the System Variables Window, locate path and select edit
Now simply add your path to the end of the string, seperated by a semicolon ; as:
;C:\My_Files\
Save the changes and exit. You need to make sure that ANY cmd.exe windows you had open are then closed and re-opened to allow it to re-import the environment variables.
Now you should be able to run mycommand.exe from any path, within cmd.exe as the environment is aware of the path to it.
When C:\Program or Similar fails
This is a very simple error. Each string after a white space is seen as a different command in cmd.exe terminal, you simply have to enclose the entire path in double quotes in order for cmd.exe to see it as a single string, and not separate commands.
So to execute C:\Program Files\My-App\Mobile.exe simply run as:
"C:\Program Files\My-App\Mobile.exe"
The Command Prompt lets you run a variety of executable files and get complex tasks done in a jiffy. Through it, anyone with an administrator’s account can access and change settings that otherwise wouldn’t be possible.
But this command interpreter has a specific language that one must know how to read and write. Even the smallest mistake can render the command useless and generate error messages. One of the most common ones being the “not recognized as an internal or external command…” error.
So, what exactly causes this “not recognized as an internal or external command” error and how can one fix it? We’ll explain.
Related: Common Windows 10 2004 issues and available fixes: Detailed list
What does the “is not recognized as an internal or external command” mean?
This error message could basically mean one of two things:
- The filename of the executable was entered without extension and without the whole path.
- Windows didn’t find the executable that matched the filename, including its extension, in any directory mentioned in Environment Variables “Path”.
The error occurs, as the message itself suggests, when the Command Prompt program cannot recognize the file or program that you wanted to use or execute. But there can be other problems too.
1. Executable or script not installed
It is possible that the program that you want to execute via command prompt isn’t installed properly on your system. A corrupt installer is the most common cause for this. Either that or the installed executable file is not located in the directory where the command interface is looking for it.
2. Filename and path not specified correctly
The most common cause of the error is a typing mistake while entering the command. Moreover, if you haven’t specified the path properly, the command prompt wouldn’t know where to look for the file and thus, render the error.
If you’re getting the error, it is important to check your command character by character to ensure it is specified correctly.
3. File Directory not found in Windows Environment Variables
Another possibility is that the directory of the file that you’re trying to execute doesn’t exist in Windows Environment Variables. The series of directories known as “Path” resides under System Variables in Windows Environment Variables, and is required for the commands to be executed. That is where your file directory must be as well, especially if you’re not specifying the complete path of your file in the command prompt.
But some programs, viruses, and malware can change these environment variables. If this happens, then the command Prompt wouldn’t be able to recognize the commands or execute them.
4. Executables in system32 not found on 64-bit Windows
For those using 64-bit Windows, there can be another potential cause of the error.
Windows 64-bit programs have “C:\Windows\System32” as their directory, while 32-bit programs have “C:\Windows\SysWOW64” as their directory.
Although most of the executables are found in both of these directories, there are some that exist only in System32, and only a handful in SysWOW64.
By default, the Windows Environment Variables “Path” contains the folder C:\Windows\System32. That means when running in a 64-bit environment, the command prompt is looking for the path directory in C:\Windows\System32. Therefore if you want to run 32-bit programs, you have to execute them in a 32-bit environment.
6 ways to fix the “is not recognized as an internal or external command” error
Fixing the “not recognized as an internal or external command” error mainly has to do with correcting the problems mentioned above. With that in mind, let us look at the fixes one at a time.
Method #01: Check if the Program is installed
First and foremost, ensure that the program that you’re trying to execute through Command Prompt is actually installed on your system and is at the appropriate location. You can check if the program is actually installed on your PC in a couple of different ways.
One way is to check the list of “Apps & Features” from Windows Settings. Here is how you can do so:
Press Win+I to open Settings and select Apps.
With Apps & features selected in the left pane, you will see the list of programs in the right pane.
If the program is not displayed here, open up File Explorer (Win+E) and navigate to the following folder:
C:\Windows\System32
This directory contains all your applications’ system files. Scroll through and check if the program you’re trying to run is available (with its executable file). If it’s not, the application is not installed in this folder and you most likely can’t execute the application by simply typing in its file name. This matter can be addressed by the following.
Method #02: Move the file to the System32 Folder
When you’re trying to run a program or an executable file from Command Prompt, the latter searches through the System32 folder and runs the file. But if the file is not there, as can be the case with some programs, you can move it to the System32 folder. Here’s how you can do so.
Note: You will need to be logged in to an administrative account for the following.
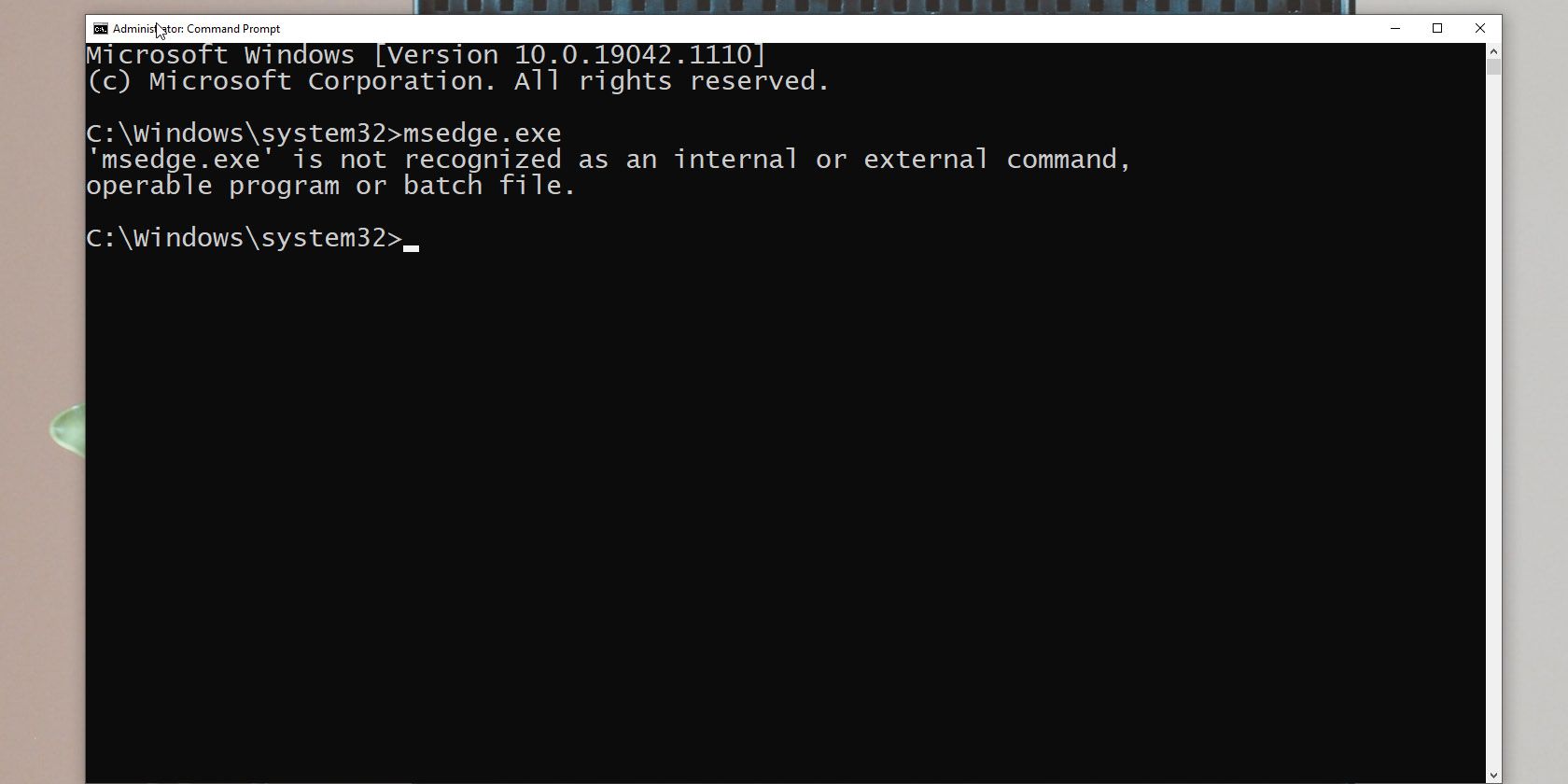
First up, go to your program’s location and copy all the files that are in the folder (select all the files and press Ctrl+C for this). In our example, we want to run Microsoft Edge (msedge.exe) through the command prompt and are copying all the files present in the application’s folder.
And pasting the files (Ctrl+V) in the C:\Windows\System32 folder.
Now, if you just enter the name of the executable file, your command will run without errors.
Method #03: Provide the full path of the file
Another important thing to keep in mind while typing the command is that the Command Prompt doesn’t know where the file is located. If you don’t want to copy the files to the System32 folder, you will have to specify the exact location of the executable that you want to run.
For instance, if you’re trying to execute PowerToys.exe located in the PowerToys folder in C drive, the command might look like this:
C:\PowerToys\PowerToys.exe
This method works only if there are no spaces in your command. But if there is a space somewhere in your file’s path, then you have to do the following.
Method #04: Insert the whole file path within double quotes
The “not recognized as an internal or external command” error can also be the result of improper use of the command lines, especially when inserting file paths.
In the command prompt, a “space” is read as the end of the command. Anything entered after a space entered through the “space” or “tab” key will be read as an argument. So, if there are spaces in your file path’s location, ensure that you enclose the path within double quotes.
In our example below, we have to run the steamservice.exe file which is within the folder C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Steam. So, to ensure that the space in the ‘Common Files’ folder is not read as the end of the command, we will insert the whole file path within double-quotes. Like this:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Steam\steamservice.exe"
Method #05: Change Environment Variables
Windows Environment Variables is the list of paths to common system applications that the Command Prompt uses to execute programs swiftly. If these environment variables are altered, the command interface won’t be able to find the location of the executable and render the error.
A simple way to fix this is by editing the environment variables and adding the appropriate file path there. Doing so will also allow you to run the executable by entering just the name of the file. This is how you can do so:
Press Win+R to open the RUN box and search for “Control Panel”.
Click on System and Security.
Click on System.
In the left sidebar, click on Advanced system settings.
In the “System properties” window, click on Environment Variables at the bottom.
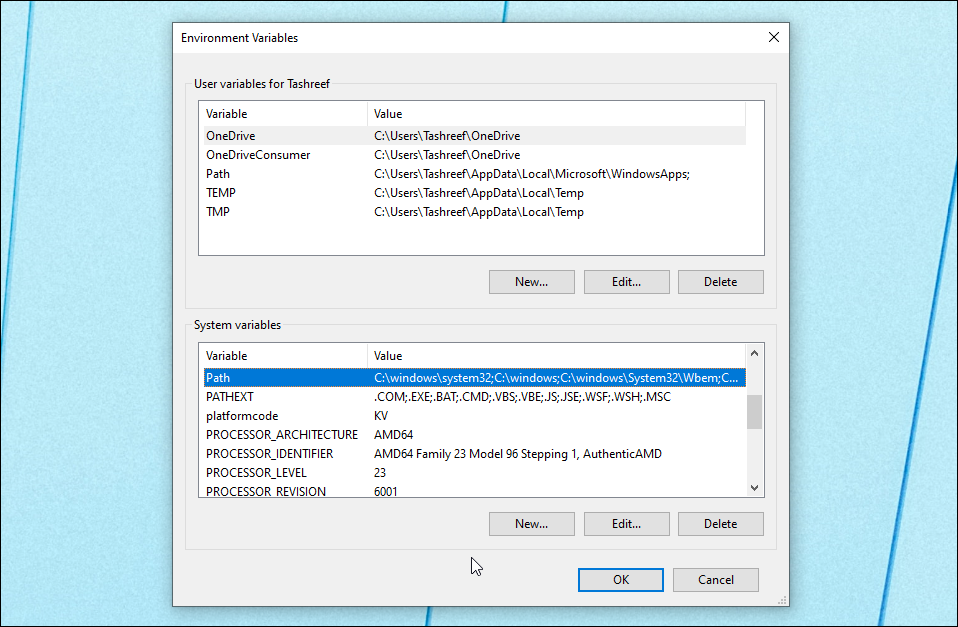
This will open up the “Environment Variables” window. Here, under “System variables” click to select the Variable that says Path, and then click on Edit.
Now, to add a new variable value (file location), click on New.
Here, add the folder path to the program/application you want to run through Command Prompt.
You can either do this by simply going to where your application (chrome.exe in our example) is installed and copying the path…
… and pasting it in the environment variable window;
Or through the environment variable window itself. For this, click on Browse.
Then navigate to the folder, select it, and click on OK.
Once you have added this new environment variable for the Command Prompt to access, click OK on all open windows. If you now open Command Prompt and simply enter the name of the executable file, your application will open promptly.
Method #06: Change directory to SysWOW64
As mentioned earlier, there are some 32-bit programs that only work in a 32-bit environment. And since the directory for these is C:\Windows\SysWOW64, you will have to tell the command prompt to look for it here, and not in the usual system32.
To do so, simply type in the following command:
cd c:\windows\SysWOW64
Doing this will change the directory in which the command prompt looks for your 32-bit executable.
Fix: Python is not recognized as an internal or external command
If you’re getting the same error when running Python through the command prompt, it is highly likely that Python’s executable file is missing from the environment variables.
To fix this issue, all one needs to do is to find where Python is installed and add the path of the executable Python file to the “Path” variable in Environment Variables (as shown before).
You will be able to run Python from the command prompt.
Fix: Python command opening Microsoft Store
On Windows 10, many have also found that sometimes, after adding Python’s path to the environment variables and running “python.exe” in the command prompt, a new problem comes up. Instead of opening python.exe directly, they are taken to the Microsoft Store.
This is because Microsft embeds a couple of ‘fake’ executables in the folder and puts their app executable aliases in the On position. To fix this, simply search for and open “Manage app execution aliases” from the Start Menu. Then turn Off python.exe and python3.exe.
You should be able to run python.exe from the command prompt now without being redirected to where you don’t want to go.
Android Studio: is not recognized as an internal or external command
Android Studio has its own terminal command for executing commands. And the same error is encountered here when trying to run the ‘adb’ command.
The cause of the problem here tends to be the incorrect path to the adb folder. But it can be solved with ease if you know where the adb.exe file is located.
By default, the adb is located in the following folder:
C:\Users\(username)\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\platform-tools
So, all one needs to do is to open Android Studio, click on File>Settings. In the next window, under Tools, click on Terminal. Then enter the complete location to adb in the Start Directory.
Restart Android Studio and your adb command should execute now.
Alternatively, you can change the directory in Android Studio’s terminal itself. Simply type in the following command:
cd C:\Users\(username)\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\platform-tools
Now, you should be able to run adb from Android Studio’s terminal command.
CMD: Fastboot or ADB is not recognized as an internal or external command
Lastly, if you have downloaded Fastboot and are not able to execute the adb command from cmd, then it means you have to set the path to ADB in System Variables (in Environment Variables).
Open Windows Environment Variables (as shown earlier), under “System Variables”, select Path and click “Edit”. Then add the full path to where the platform-tools folder is located (which contains adb.exe). Apply the changes.
Restart the command prompt, and you should be able to execute the adb command.
Entering the right commands in the interface and ensuring that the latter has access to the executable file is all that it takes for the command prompt to run the program/file/application that you have commanded it to. So make sure you follow the fixes mentioned herein and run your commands without any more errors.
RELATED
- How to solve Microsoft OneDrive “cannot connect to Windows” error on Windows 10 version 2004
- How to fix DISM ‘incorrectly reporting corruption’ error on Windows 10 version 2004
- How to fix the issue: This site can’t be reached. Server IP address could not be found.
- How to Fix “ERROR: x86_64 emulation currently requires hardware acceleration” on Windows
One of the great things about Windows is that you can get many of your tasks done from the Command Prompt on your machine. You just need to enter cmd.exe and Windows will run it for you. But occasionally, you might come across errors like “is not recognized as an internal command”.
This is actually one of the most common errors you can face with the Command Prompt. As the error itself suggests, it couldn’t recognize the tool you were trying to use with the Command Prompt. There are various reasons why it happens, and also there are multiple ways to get around the “not recognized as an internal or external command” error on your Windows PC.
Why The “not recognized as an internal command” Error Occurs
Before you start applying fixes, it’s a good idea to learn why the error occurred so you can ensure it doesn’t happen again in the future.
Other Apps Messing Up Your System
One of the most common reasons you may get this error on your PC is because another installed app modified your system variables. This prevents the Command Prompt from recognizing commands to launch other apps or tools.
Not Having The Program Installed On Your Computer
The second possible reason the “not recognized as an internal or external command” occurs is that you don’t have the appropriate program installed on your computer. It may be that the installer didn’t install the application files at the appropriate location, or the installer didn’t enable the tool to be launched with Command Prompt.
Regardless of the cause, there are ways to fix this error and get the Command Prompt to recognize the program that you’re trying to use.
Ensure The Program Actually Exists On Your PC
The first thing to do is verify if the program that you’re trying to use with the Command Prompt actually exists on your computer. You may have used a fake installer that told you that the program was successfully installed on your machine, but that may not be true.
There’s an easy way to check if the program is indeed installed on your machine.
- Launch a File Explorer window on your PC.
- Head over to the following path.
C:\Windows\System32\
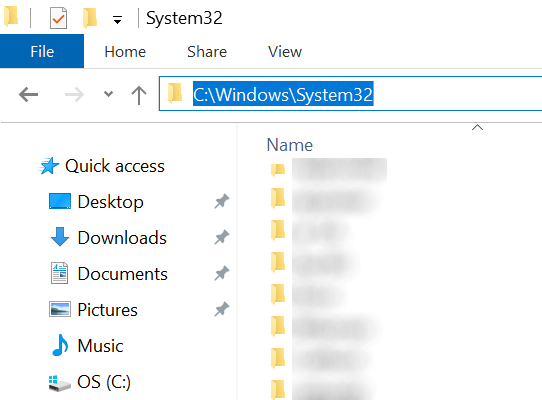
- Ensure the executable that you’re trying to run from the Command Prompt is available in this folder. If it’s not, the program is likely not installed on your computer.
The above isn’t a surefire way to check if a program is installed on your computer. This is because not all programs keep their files in the Windows’ System32 folder. However, it should help you locate most programs.
Use The Full Path To The Executable File
The “is not recognized as an internal command” error usually occurs because the computer can’t find the executable that you’re asking it to launch. However, you can provide it with the full path to your executable file and it should then be able to run it without any issues.
- Launch a Command Prompt window on your PC.
- Type in the full path of the executable that you want to use and hit Enter on your keyboard.
- For example, if you’re trying to use adb.exe that’s located in a folder called adb on your desktop, you’ll type something like the following.
C:\Users\<username>\Desktop\adb\adb.exe
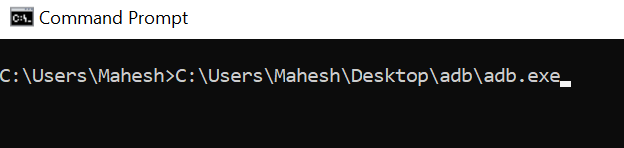
- The file should launch without an issue.
Enclose The File Path With Double Quotes
Specifying the full path to your executable file isn’t a bulletproof method. It can also cause the “is not recognized as an internal or external command” error if it isn’t used properly. The problem lies in the path that you specify in your Command Prompt window.
If your executable file’s full path has any spaces in it, that’s going to cause the error. This is because the utility can’t recognize the spaces, and it uses the characters up to the first space as a program name. Since that isn’t the correct path, you’ll get the aforementioned error.
You can fix this using the following method.
- While typing in a path that has spaces (whether single or multiple), enclose the path with double quotes.
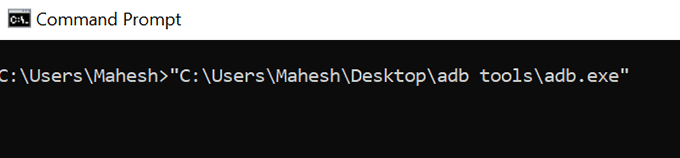
- Command Prompt will then recognize the entire path as a single item and launch the program appropriately on your machine.
Move The File To System32 Folder
By now, you know that when you try to run an executable from the Command Prompt utility, it looks into the System32 folder of your Windows installation and then opens the file, if it’s available there.
What if you could place your executable file there and then access it from the Command Prompt? You can do this as long as you have admin access on your computer.
- Copy the executable file along with all other files associated with it to the following folder on your computer.
C:\Windows\System32
- Close Command Prompt if it was already open and relaunch it.
- Enter the name of your executable file without any path, and you’ll find it launches successfully.
While this method works great and helps you fix the “is not recognized as an internal or external command” error on your computer, you may want to use it cautiously.
This is because each time you want to use something from the Command Prompt, you’ll need to put the appropriate executable in the System32 folder. Eventually, the folder will grow large and you’ll have a large number of files sitting in there.
It also won’t work for executable tools that require installation into a specific directory. You won’t be able to move those into the System32 folder since the installation path is defined in the Windows Registry.
We recommend you only use this solution if you can’t fix the issue using the other methods and as long as the application doesn’t require installation.
Add The Executable File Path To Environment Variables
The most efficient way to fix the “is not recognized as an internal command” error is to edit your environment variable and add the appropriate file path there. This is because the Command Prompt utility looks at those paths when you enter a command, and then opens the file if it finds it in one of those directories.
By adding your file path there, you’re telling Command Prompt where a certain executable is located when you want to use it by its short-name in a CMD window.
It’s pretty easy to edit your variables and add a new path there.
- Launch Control Panel using the Cortana search on your PC.
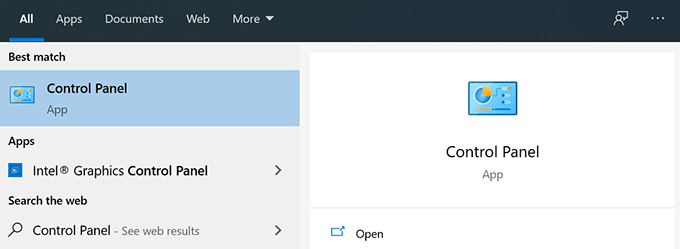
- Click on the option that says System and Security.
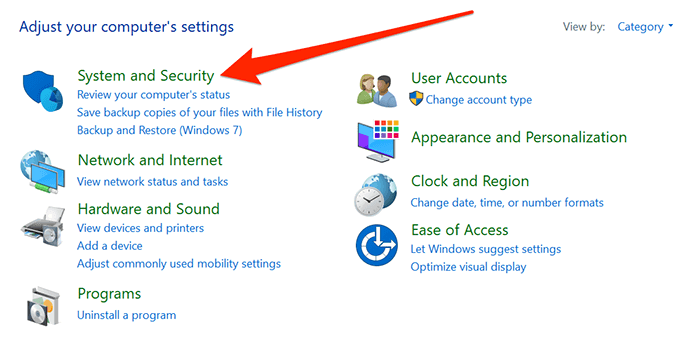
- Find and click on System on the following screen.
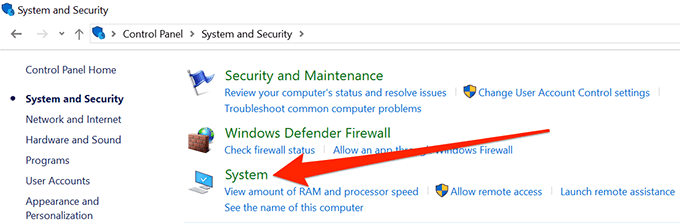
- Select Advanced system settings from the left sidebar on your screen.
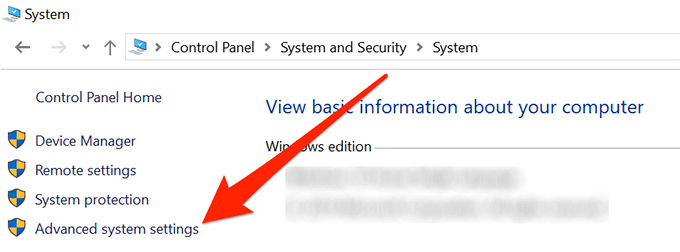
- A box will open on your screen. Click on the Environment Variables button which is located at the bottom of the box.

- You’ll see all the user variables for your account. Click on the one that says Path and then click on the Edit button.
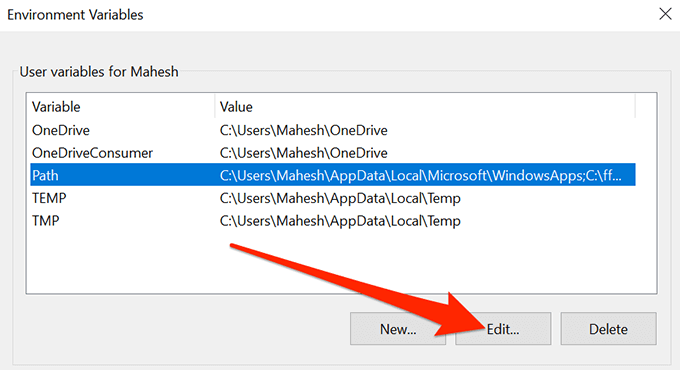
- You can now add the new path to the application you want to use with the Command Prompt. Click on Browse in the right sidebar to add a directory to the list.
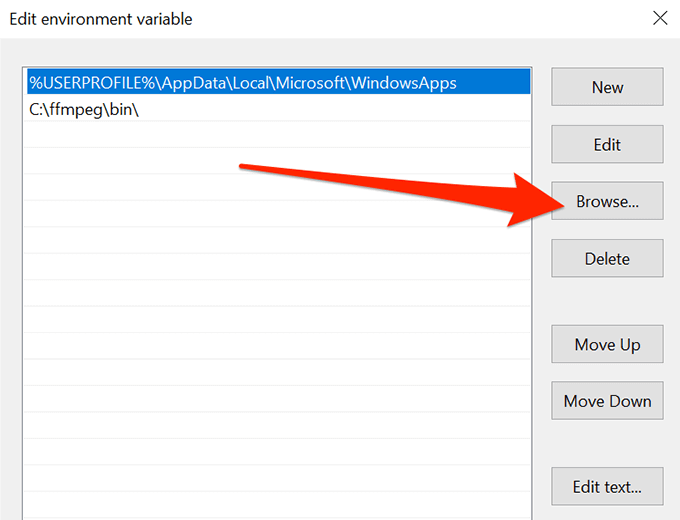
- Navigate to the folder where your executable is located and select it.
- You should see your newly added path is listed in the variables list. Click on OK at the bottom to save the changes.
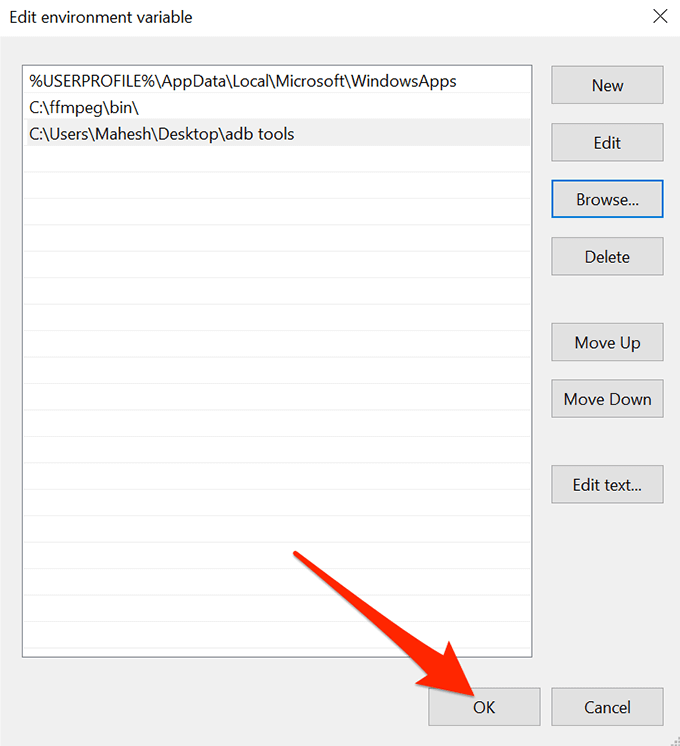
- Click on OK in all other boxes as you close them.
- Open a Command Prompt window and type the name of the executable file. You’ll see that the file opens without CMD throwing any errors on your screen.
The “is not recognized as an internal command” error can sometimes be very frustrating, as it won’t let you use a program that you know you’ve installed on your computer.
Using the methods above, you should be able to get rid of this error and run any program from a Command Prompt window without any issues. If any of the methods above helped you fix the issue, we’d like to know about it in the comments section below.