The Windows command line is one of the most powerful utilities on a Windows PC. With it, you can interact with the OS directly and do a lot of things not available in the graphical user interface (GUI).
In this article, I’ll show you 40 commands you can use on the Windows command line that can boost your confidence as a Windows user.
N.B.: You have to be careful while using the commands I’ll show you. This is because some commands can have a lasting negative or positive effect on your Windows PC until you reset it.
In addition, some of these commands require you to open the command prompt as an admin.
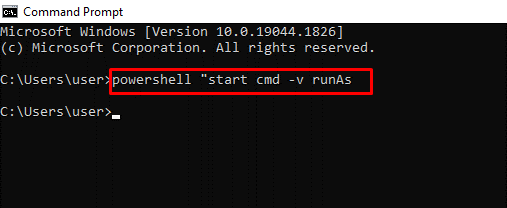
powershell start cmd -v runAs – Run the Command Prompt as an Administrator
Entering this command opens another command prompt window as an administrator:
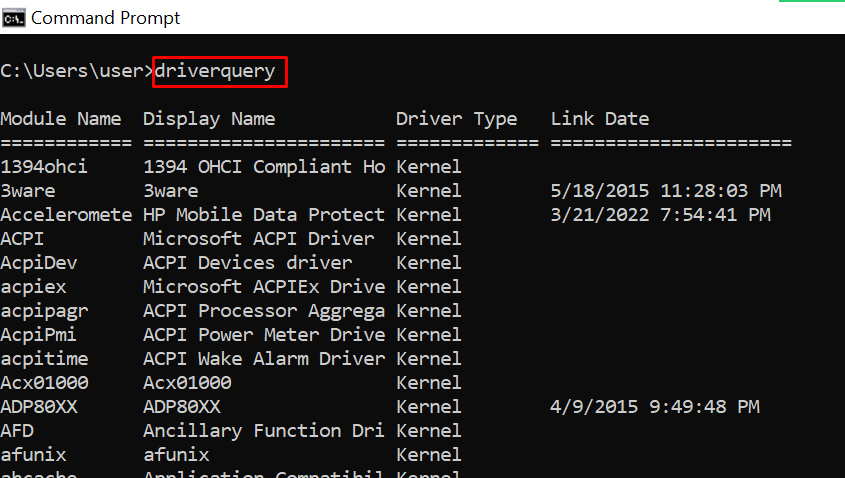
driverquery – Lists All Installed Drivers
It is important to have access to all drivers because they often cause problems.
That’s what this command does – it shows you even the drivers you won’t find in the device manager.
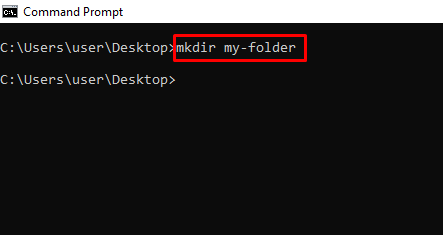
chdir or cd – Changes the Current Working Directory to the Specified Directory
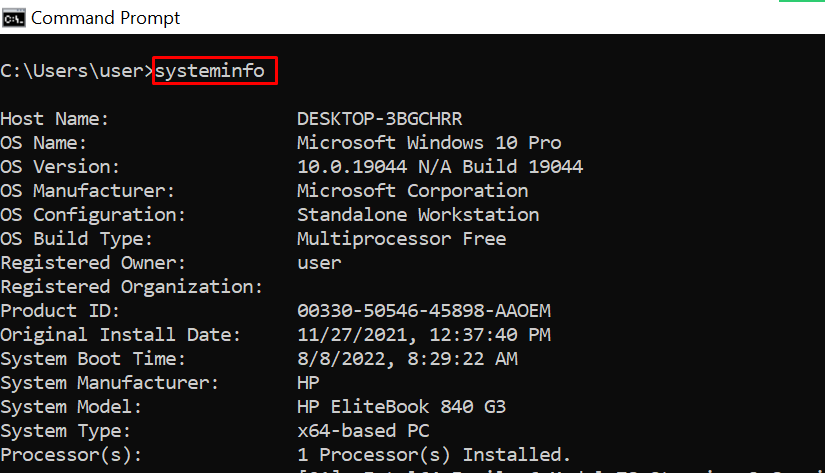
systeminfo – Shows Your PC’s Details
If you want to see more detailed information about your system you won’t see in the GUI, this is the command for you.
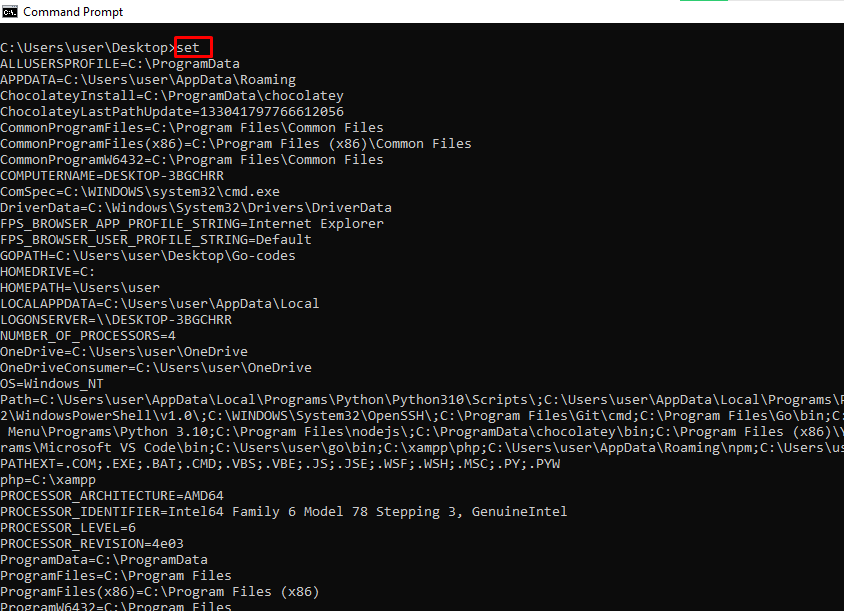
set – Shows your PC’s Environment Variables
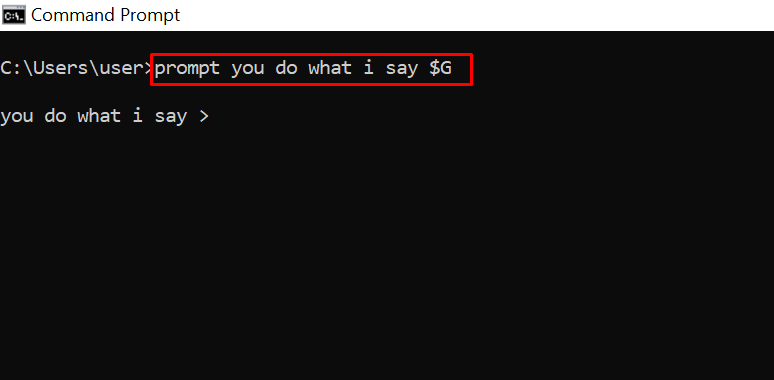
prompt – Changes the Default Text Shown before Entering Commands
By default, the command prompt shows the C drive path to your user account.
You can use the prompt command to change that default text with the syntax prompt prompt_name $G:
N.B: If you don’t append $G to the command, you won’t get the greater than symbol in front of the text.
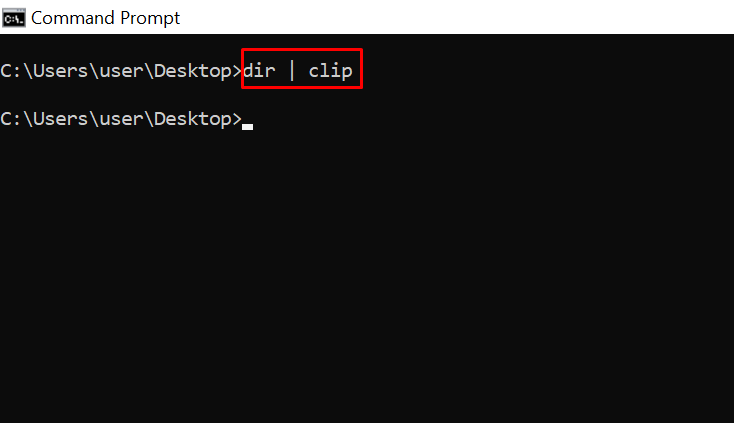
clip – Copies an Item to the Clipboard
For example, dir | clip copies all the content of the present working directory to the clipboard.
You can type clip /? and hit ENTER to see how to use it.
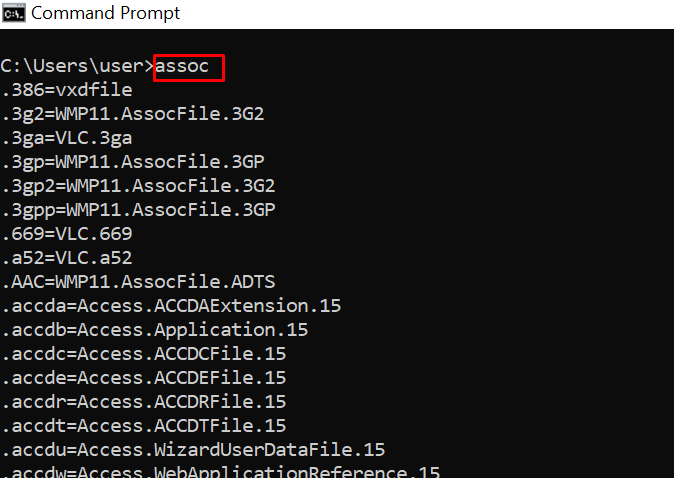
assoc – Lists Programs and the Extensions They are Associated With
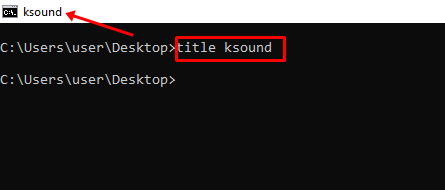
title – Changes the Command Prompt Window Title Using the Format title window-title-name
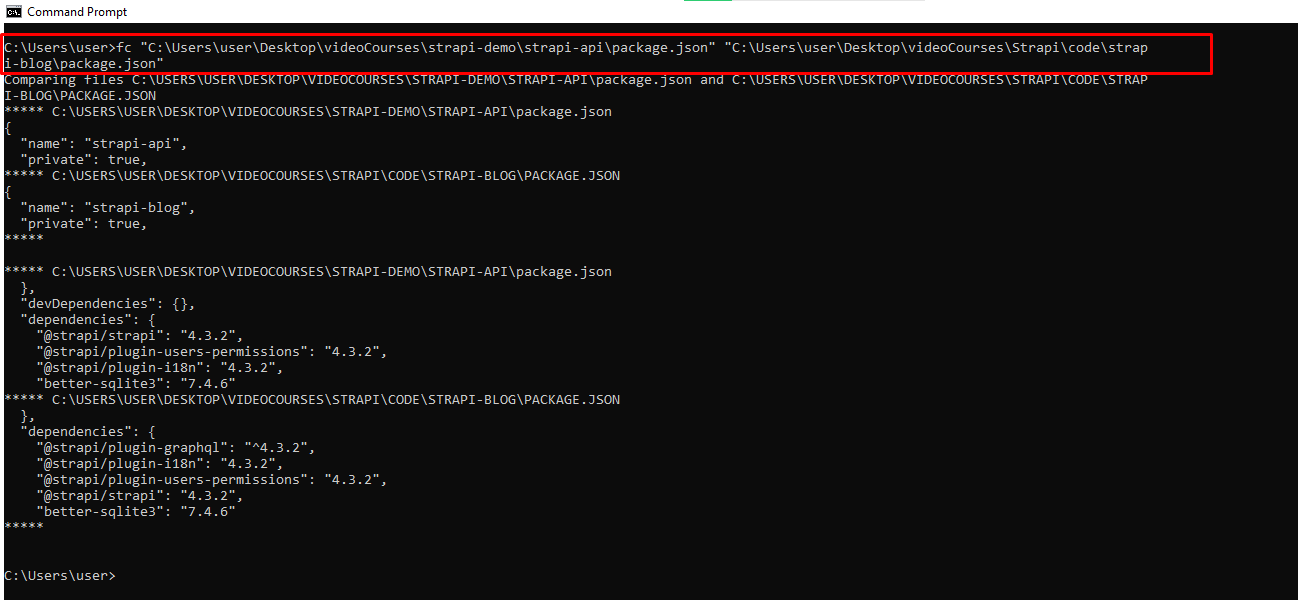
fc – Compares Two Similar Files
If you are a programmer or writer and you want to quickly see what differs between two files, you can enter this command and then the full path to the two files. For example fc “file-1-path” “file-2-path”.
cipher – Wipes Free Space and Encrypts Data
On a PC, deleted files remain accessible to you and other users. So, technically, they are not deleted under the hood.
You can use the cipher command to wipe the drive clean and encrypt such files.
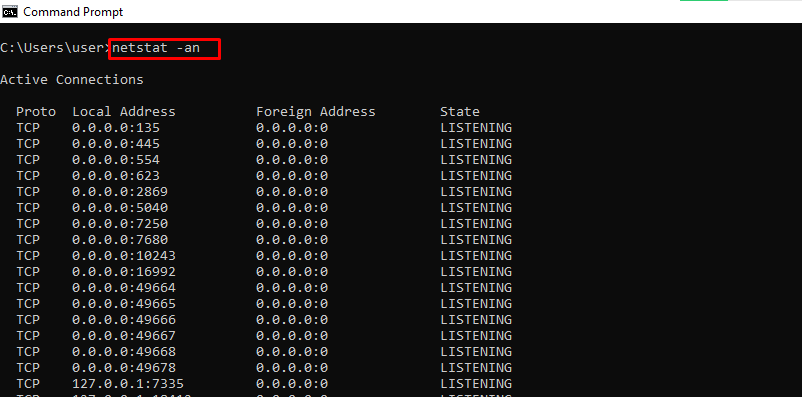
netstat -an – Shows Open Ports, their IP Addresses and States
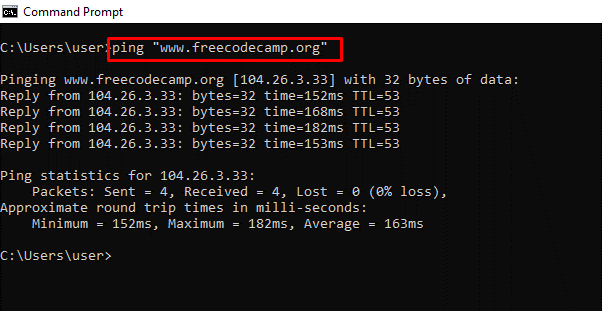
ping – Shows a Website IP Address, Lets you Know How Long it Takes to Transmit Data and a Get Response
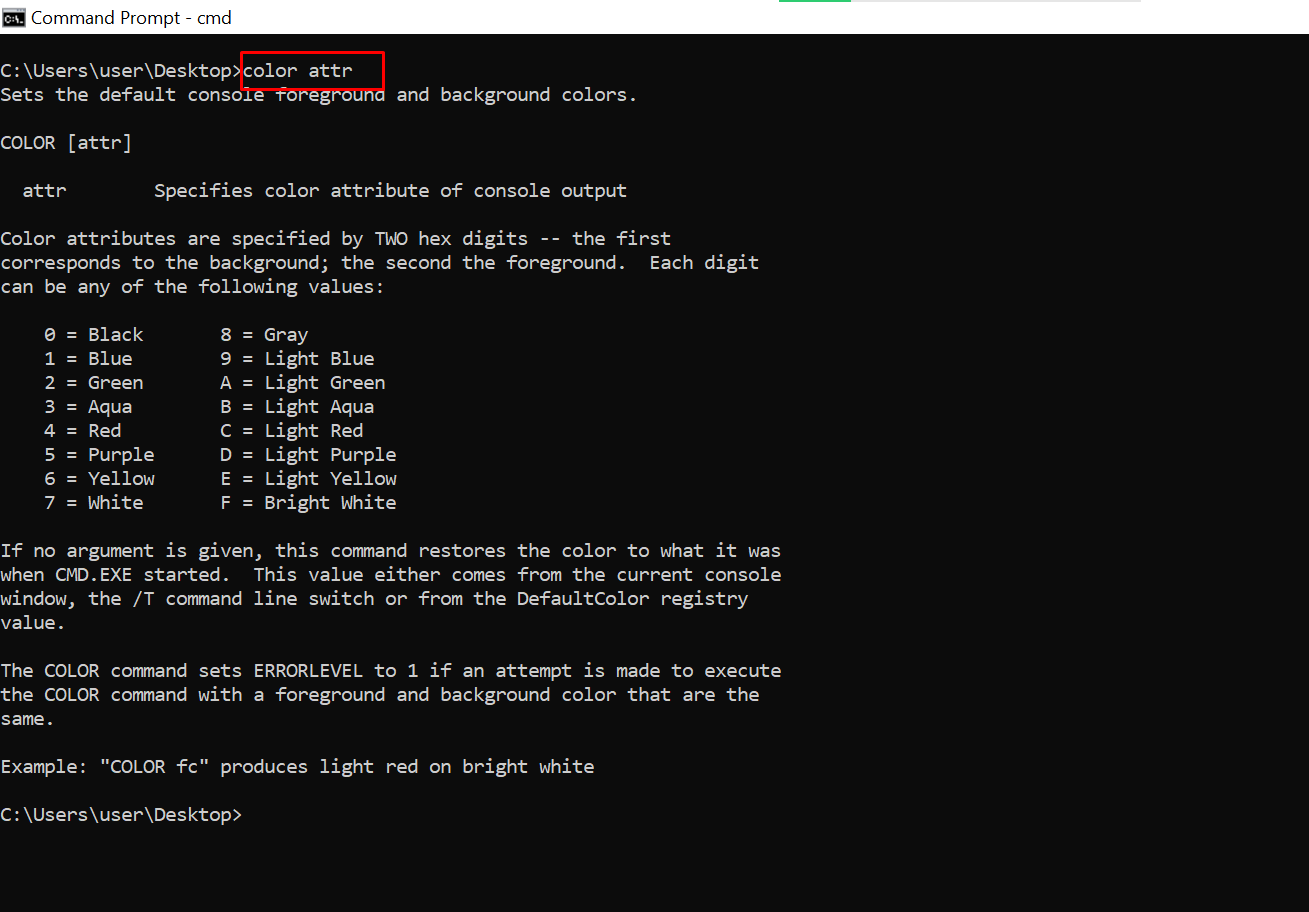
color – Changes the Text Color of the Command Prompt
Enter color attr to see the colors you can change to:
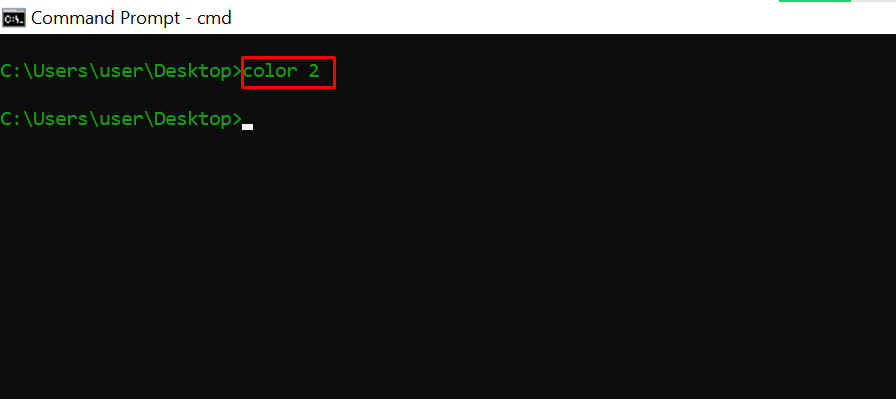
Entering color 2 changes the color of the terminal to green:
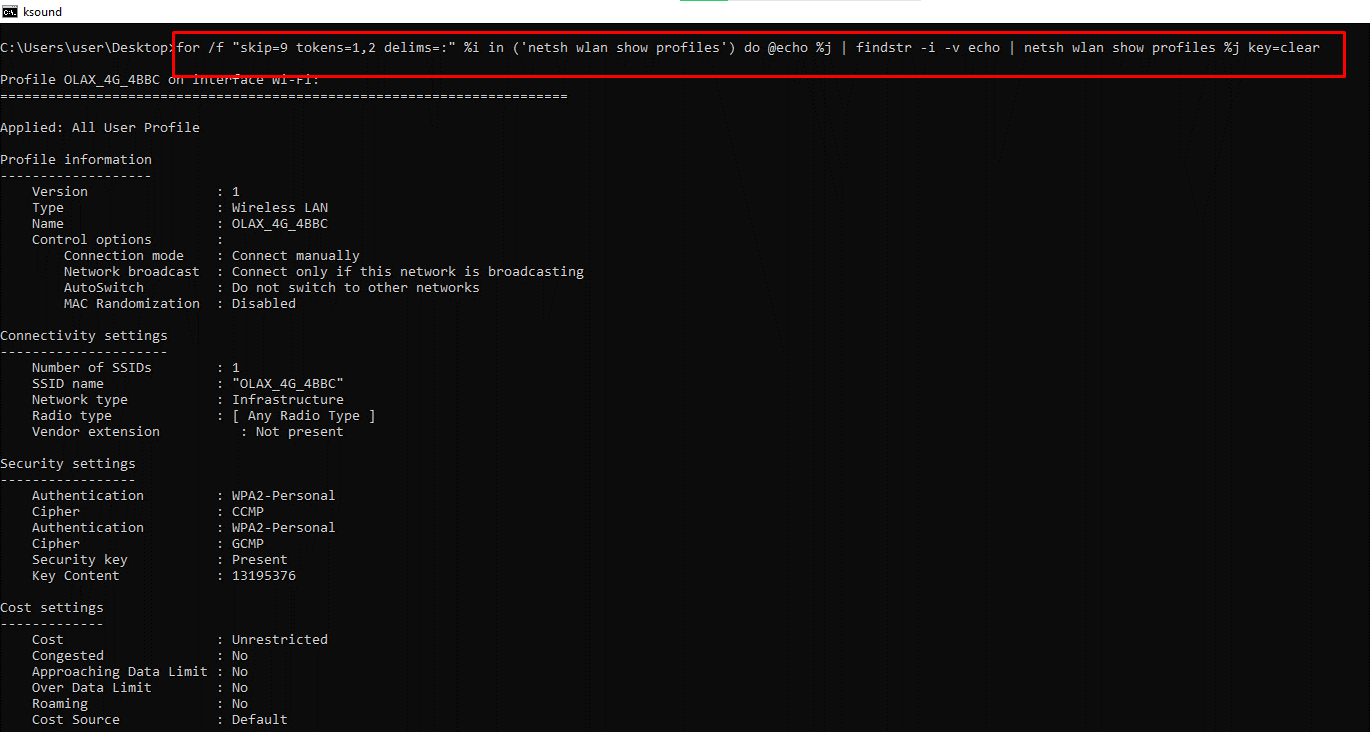
for /f "skip=9 tokens=1,2 delims=:" %i in ('netsh wlan show profiles') do @echo %j | findstr -i -v echo | netsh wlan show profiles %j key=clear – Shows All Wi-Fi Passwords
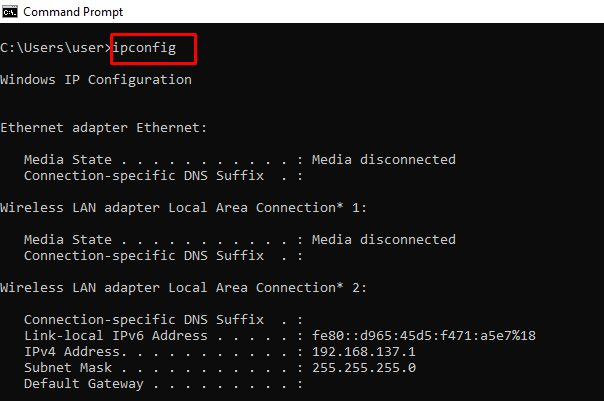
ipconfig – Shows Information about PC IP Addresses and Connections
This command also has extensions such as ipconfig /release, ipconfig /renew, and ipconfig /flushdns which you can use to troubleshoot issues with internet connections.
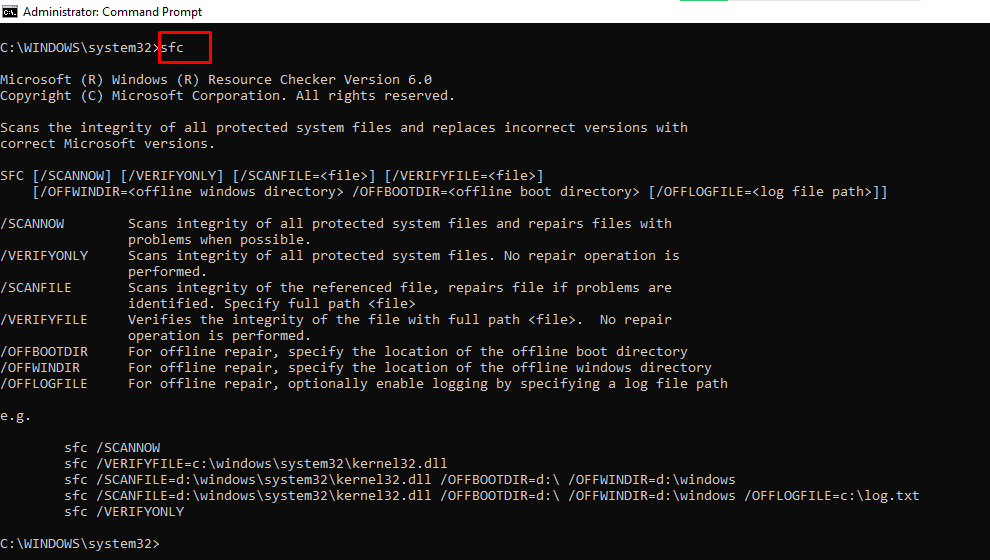
sfc – System File Checker
This command scans your computer for corrupt files and repairs them. The extension of the command you can use to run a scan is /scannow.
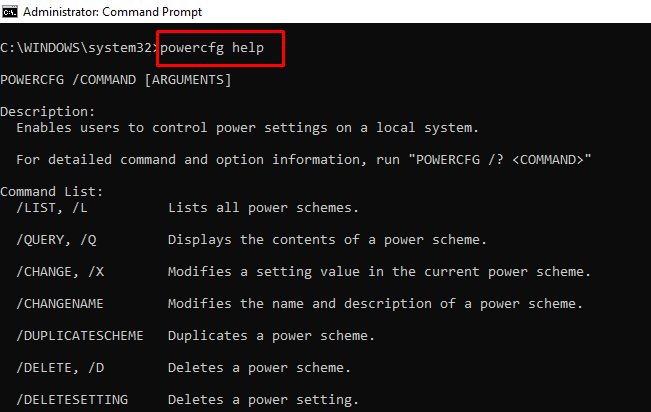
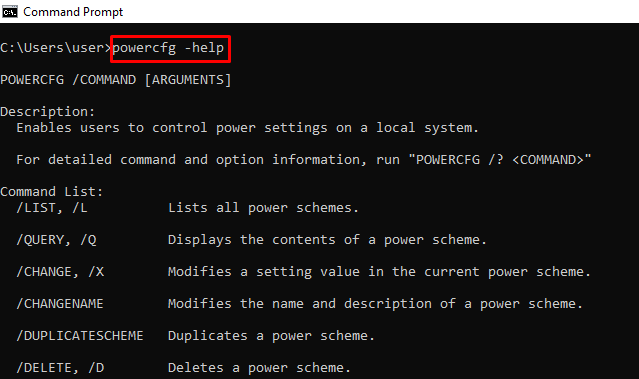
powercfg – Controls Configurable Power Settings
You can use this command with its several extensions to show information about the power state of your PC.
You can enter powercfg help to show those extensions.
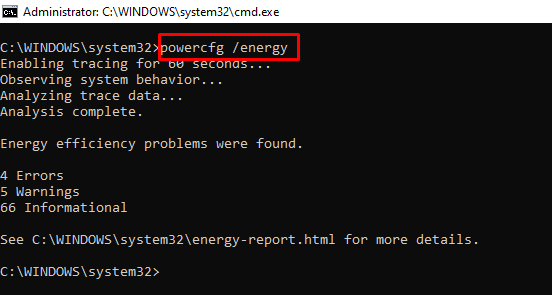
For example, you can use powercfg /energy to generate a battery health report.
The powercfg /energy command will generate an HTML file containing the report. You can find the HTML file in C:\Windows\system32\energy-report.html.
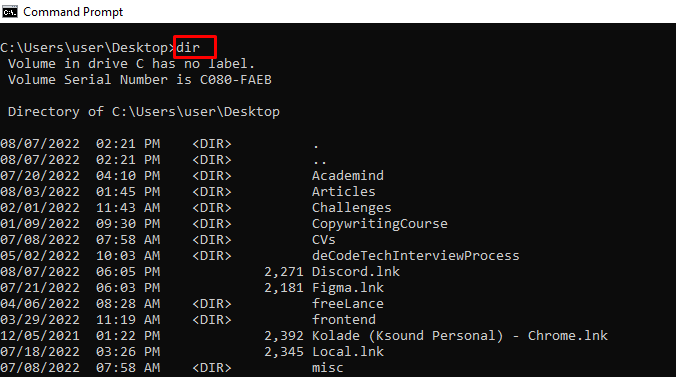
dir – Lists Items in a Directory
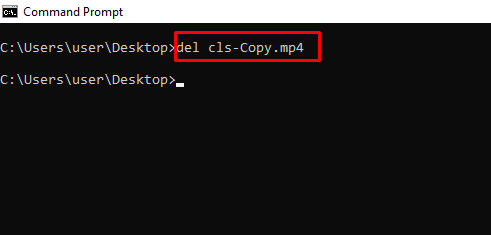
del – Deletes a File
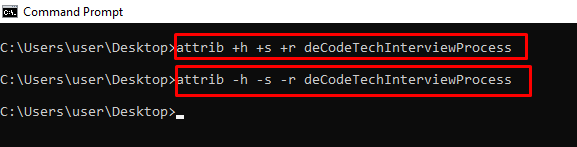
attrib +h +s +r folder_name – Hides a Folder
You can hide a folder right from the command line by typing in attrib +h +s +r folder_name and then pressing ENTER.
To show the folder again, execute the command – attrib -h -s -r folder_name.
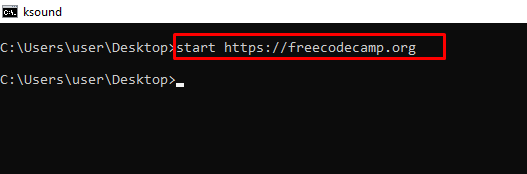
start website-address – Logs on to a Website from the Command Line
tree – Shows the Tree of the Current Directory or Specified Drive
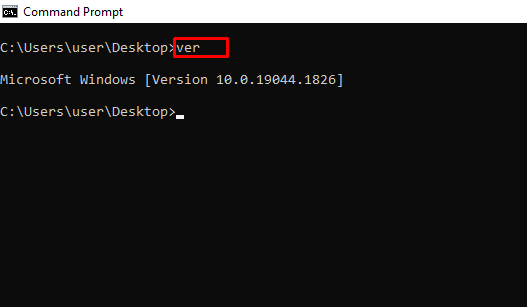
ver – Shows the Version of the OS
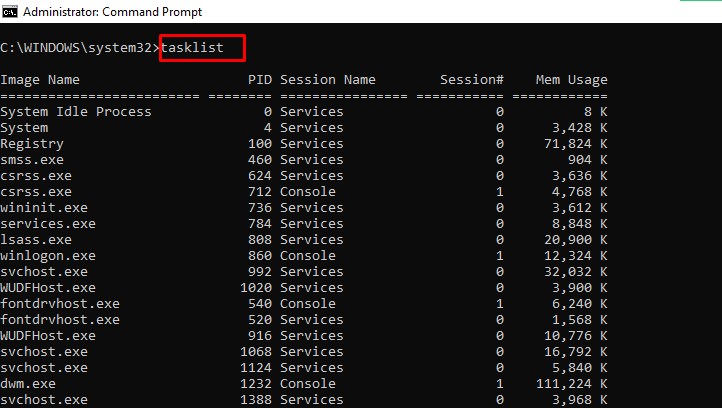
tasklist – Shows Open Programs
You can do the same thing you do with the task manager with this command:
The next command shows you how to close an open task.
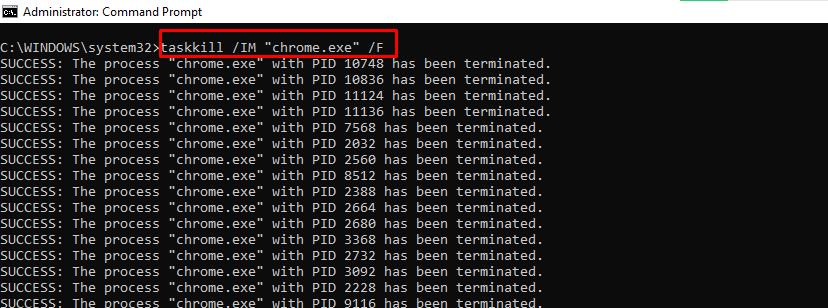
taskkill – Terminates a Running Task
To kill a task, run taskkill /IM "task.exe" /F. For example, taskkill /IM "chrome.exe" /F:
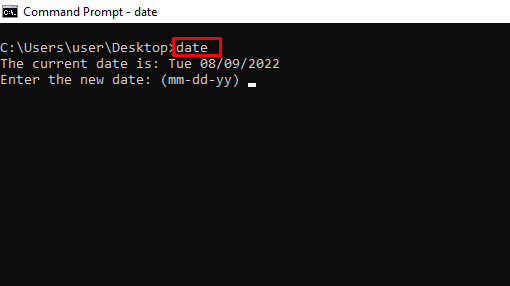
date – Shows and Changes the Current Date
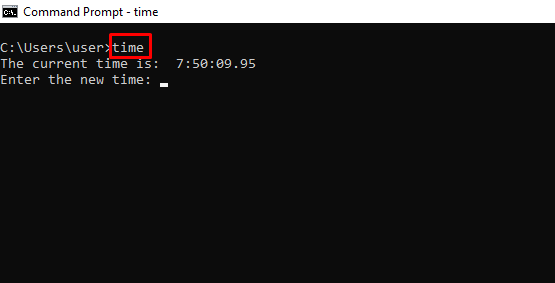
time – Shows and Changes the Current Time
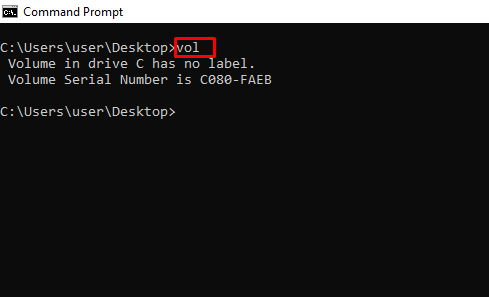
vol – Shows the Serial Number and Label Info of the Current Drive
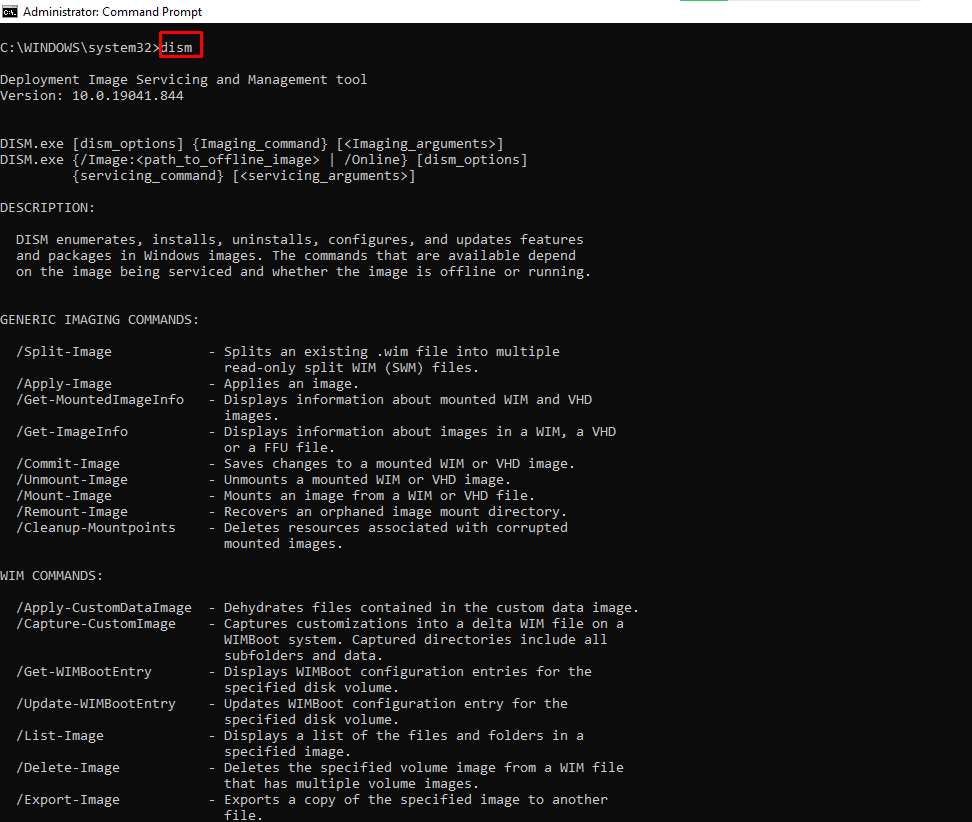
dism – Runs the Deployment Image Service Management Tool
CTRL + C – Stops the Execution of a Command
-help – Provides a Guide to other Commands
For example, powercfg -help shows how to use the powercfg command
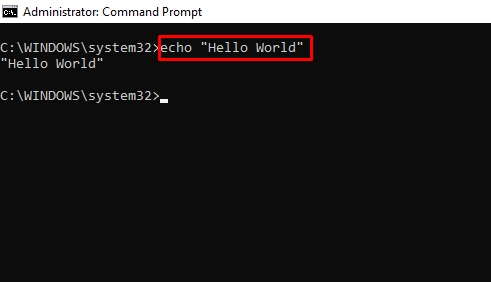
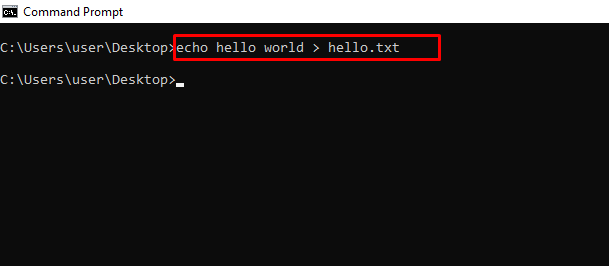
echo – Shows Custom Messages or Messages from a Script or File
You can also use the echo command to create a file with this syntax echo file-content > filename.extension.
mkdir – Creates a Folder
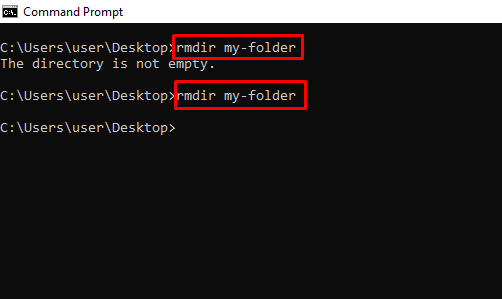
rmdir – Deletes a Folder
N.B.: The folder must be empty for this command to work.
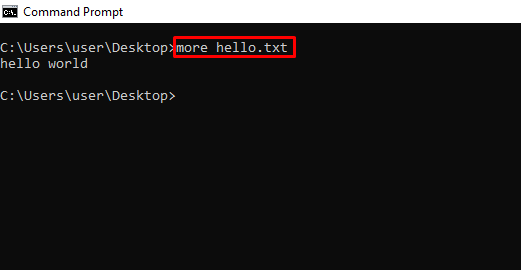
more – Shows More Information or the Content of a File
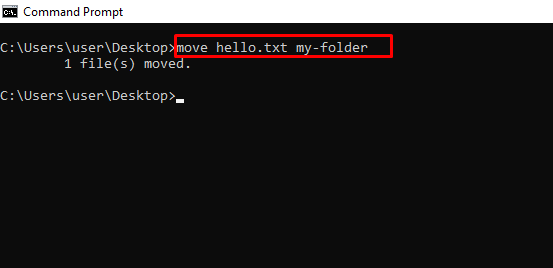
move – Moves a File or Folder to a Specified Folder
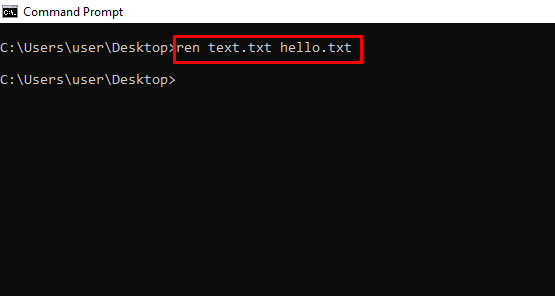
ren – Renames a File with the Syntax ren filename.extension new-name.extension
cls – Clears the Command Line
In case you enter several commands and the command line gets clogged up, you can use cls to clear all entries and their outputs.
exit – Closes the Command Line
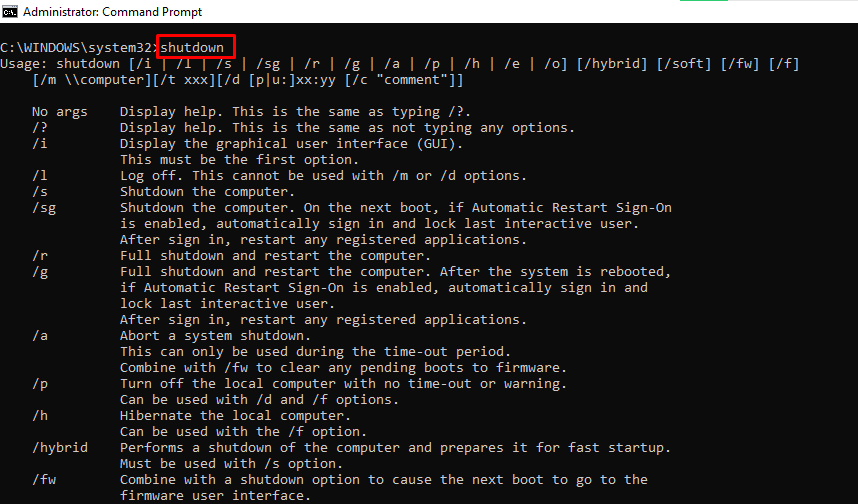
shutdown – Shuts down, Restarts, Hibernates, Sleeps the Computer
You can shut down, restart, hibernate, and sleep your PC from the command line.
Enter shutdown in the command line so you can see the extensions you can use to perform the actions. For example, shutdown /r will restart your computer.
Conclusion
This article showed you several “unknown-to-many” commands you can use to get access to hidden functionalities on your Windows PC.
Again, you should be careful while working with these commands because they can have a lasting effect on your OS.
If you find the commands helpful, share the article with your friends and family.
In case you know another useful command I did not list, tell me about it on Twitter. I will add it and mention you as the source.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Бывает, что некоторые команды Windows cmd сложно вспомнить, и сохранение их на компьютере или на бумаге в качестве шпаргалки является хорошей практикой. Этот список не является полным, но он содержит наиболее часто используемые команды. Не стесняйтесь добавить свои наиболее часто используемые команды в комментариях ниже, а так же поделиться этим списком.
Управление файлами и папками
- COPY – Копирование файлов в другое место
- DIR – Отображение файлов и папок в текущем каталоге
- DEL или ERASE – Удаление файлов
- EDIT – Запуск редактора файлов
- CD – Изменить каталог
- EXPAND – Распаковать сжатые файлы
- FC – Сравнивает файлы и показывает различия между ними
- FIND – Найти текстовую строку в файле
- MD или MAKEDIR – Создать папку
- MOVE – Переместить файлы из одной папки в другую
- PRINT – отобразить содержимое текстового файла
- RD или RMDIR – удалить папку
- REN или RENAME – переименовать файл или папку
- REPLACE – Замена файлов в одном каталоге на файлы с тем же именем в другом каталоге
- ROBOCOPY – Использует программу «Робокопи» для копирования файлов и каталогов
- TREE – Показывает структуру каталогов диска или папки
- TYPE – Отображает содержимое текстовых файлов
- OPENFILES – Управление открытыми локальными или сетевыми файлами
- XCOPY – Копирование файлов и деревьев каталогов
Приложения и процессы
- SCHTASKS – Запланированный запуск приложения приложения (планировщик задач)
- SHUTDOWN – Выключение или перезагрузка компьютера
- TASKLIST – Список выполняемых задач
- TASKKILL – Остановить или прекратить выполнение задачи (для остановки задачи используется PID, который можно узнать из TASKLIST).
- REG – Запустить редактор реестра
- RUNAS – Запуск задачи от имени другого пользователя
Управление дисками
- CHKDISK – Проверяет диск и показывает статистику
- DEFRAG – Запуск дефрагментации диска
- CHKNTFS – Отображает или изменяет выполнение проверки диска при загрузке
- COMPACT – Отображает и изменяет сжатие файлов в разделах NTFS
- CONVERT – преобразование дискового тома FAT в NTFS
- DISKPART – Отображение и настройка свойств разделов диска
- FORMAT – Форматирование диска
- FSUTIL – Отображение и настройка свойств файловой системы
- LABEL – Создание, изменение или удаление метки тома диска
- RECOVER – Восстановление данных с поврежденного или испорченного диска
- VOL – Отображение метки тома и серийного номера диска
Системная информация
- DATE – Выводит или устанавливает текущую дату
- TIME – Выводит или устанавливает системное время
- DRIVERQUERY – Отображает текущее состояние и свойства драйвера устройства
- HOSTNAME – Отображает имя компьютера
- SYSTEMINFO – Отображает информацию о конфигурации компьютера
- VER – Позволяет просмотреть версию Windows
- GPRESULT – Отображает текущие примененные групповые политики (RSoP)
- GPUPDATE – Обновление групповых политик
Сеть
- IPCONFIG – Отображает информацию о сетевых интерфейсах
- PING – Отправляет ICMP-запросы на целевой хост, проверяет его доступность
- TRACERT – Отображение пути пакетов в сети
- NSLOOKUP – Поиск IP-адреса по имени ресурса
- ROUTE – Отображает таблицы сетевых маршрутов
- ARP – Показывает таблицу с IP-адресами, преобразованными в физические адреса
- NETSH – Запускает программу управления сетевыми настройками
- GETMAC – Показывает MAC-адрес сетевого адаптера
- TFTP – Запускает TFTP-клиент в консоли
Настройка командной строки
- CLS – Очистить экран
- CMD – Отображает другую командную строку
- COLOR – Устанавливает цвет текста и фона в консоли
- PROMPT – Изменение начального текста командной строки
- TITLE – Присвоение заголовка для текущего сеанса
- HELP – Запуск справки CMD
- EXIT – Выход из командной строки
Аverage rating : 4.9
Оценок: 12
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
700
300
You can do almost anything via graphical user interfaces in Windows. However, if you are a Mac OS X user then you want to check how to automate things using the lists of commands for Mac OS X.
Also, there are many tasks that are repeatable and you can simply write the set of commands (into a so-called batchfile on Windows, script on Mac OS X and Ubuntu) that will do the same thing, the same scenario but much faster and you don’t need to click buttons and sit at the computer all the time.
That is why Windows has CMD commands supported. In fact, these commands, in general, are a mix between a programming language and actions. You can make many things via the command line that you can do through the user interface.
If you prefer a video instead of reading an article, please check the video below:
The purpose of the batch file is to type a sequence of special commands that explain to the computer what you want to do. The added benefits compared to using UIs with a mouse and keyboard are that in a single click you can launch from dozens to a hundred (!) of commands you previously prepared in a text file. Even better, you can schedule to run these commands to be launched at a specific time. It is easier than regular programming.
That’s why the Command Prompt is so popular in the developer’s community. So if you want to benefit, it’s time to get to know the most useful Command Prompt commands!
- Starting Point: Basic Windows CMD commands
- Make commands more powerful: pipes and tips
- Chaining Windows commands safely
- 1. Deltree command
- 2. Driverquery
- 3. Ping
- 4. Pathping
- 5. Tasklist
- 6. Taskkill
- 7. System File Checker
- 8. Repair-bde
- 9. NetDiag
- 10. Tracert
- 11. CIPHER
- 12. Finger
- 13. Comp
- 14. Clip
- 15. Color
- 16. Append
- 17. Getmac
- 18. Label
- 19. Logman
- 20. Ftype
- 21. BCDBOOT
- 22. CERTREQ
- 23. Delprof
- 24. DIRUSE
- 25. DSMGMT
- 26. Fsutil
- 27. Dnscmd
- 28. Klist
- 29. mqsvc
- 30. mstsc
- Conclusion
Starting Point: Basic Windows CMD Commands
What you can do in a command line depends on the program’s understanding of your commands. In Windows, it’s either cmd.exe or PowerShell. They are interpreting your commands. PowerShell is nice but it requires a .NET framework and you may not have access to it in Windows Recovery or Windows Safe Mode.
On the other side, cmd.exe represents the shell that you can use in Windows Recovery or Windows Safe Mode too. Also, .bat files (shortened from “batch“, these are the files where commands are stored) are used by cmd.exe by default. It is still the most common way to distribute shell batch files for Windows. So learning cmd.exe commands and how it works means that you will be able to read and understand .bat files.
In order to launch Win 10 Command Prompt, click on the Windows menu, then go to the Windows System folder and open Command Prompt. Please note that if you run the Command Prompt without administration rights, all Windows CMD commands typed inside it will be without rights as well. That’s nice to avoid problems while learning.
Let’s start by displaying text with echo:
echo Hello World!
This will display the text in the console. Congratulations on your first command! Displaying things is very helpful in scripts and in loops, in order to show helpful comments on what is going on or simply to indicate progress.
In order to display two lines, you can use & command like this
echo Hello World! & echo Hello Again!
The & operator allows executing two commands in one line. It’s useful in commands you directly type. That is important especially if something must launch quickly after another task.
In the command line, you often work with files. You may want to know what are current files in the folder you’re in. Right, you can use Windows Explorer too in another window but when you just can’t, the Windows Command Prompt list directory method is the way to go. Also, you can ignore or show hidden files more easily.
So:
dir
Now, you may be looking for a specific file. You have a starting point but you don’t know the exact folder. In dir you can show all files in current directories, but also files in subdirectories in one command:
dir /S
But when you know a little more about dir command, let’s learn a bit more. Dir command also allows you to do searches. It has a way different behavior than Windows Explorer search but it’s useful. Let’s say you need to find a file with the word SQL in the filename:
dir /S *sql*
Please note that if you search the word put, it will match also the filenames like input or output because both words contain put. The search is case-insensitive by default because Windows generally ignores cases when it’s about files and directories.
Now you may want to display the content of a file using the type command. Don’t do so with too big files because your Command Prompt will be filled out with too many lines. But it is still useful for relatively small files like configurations.
type "filename"
That’s the right time to tell you something you should do in all Command Prompt commands: always put double quotes (like this: “filename.txt“) around all filenames. Yes, it’s tempting to skip a few keystrokes but if you speak double quotes around filenames or folders then it may cause you a serious problem someday. You don’t want to have your filename interpreted as a shell command that can happen if your filename or folder name suddenly uses spaces inside.
Make CMD Commands More Powerful: Pipes and Tips
Important: you can halt and cancel any running command by pressing CTLR+C on the keyboard at any time.
When some command outputs too much content to fit on the screen, you will need to use more commands. This is one of the simple CMD commands that you will need in many circumstances since the Command Prompt on Windows 10 can’t contain much text. more command works like this: it prints one screen of text and you press the spacebar to show the next screen of text until you’ve read it all.
However, unlike other commands we’ve seen so far, the more command takes the text as input. A lot of text. So you need to redirect the text from the type command to move, otherwise, it won’t work out. You can do so using the pipe | operator. On the left side of pipe |, you put a command to produce output. On the right side, you write a command that will receive the output and do something with it. So for example when trying to look at a long text file:
type "filename" | more
We use this technique here with type and more, but it can work in other cases too. For example, you may combine more with the help command to display the documentation page by page:
help | more
Note that if you no longer need to show the next screen and you want to leave more command, just press the Q key on your keyboard. You can also press an equal sign “=” to display the current line number. And even better: you can skip a few lines at the beginning of the output. For example when you want to list a directory but you don’t want to see the header and you want to skip the first 7 lines:
dir | more +7
The “+7” means seven lines you want to skip. By the way, you don’t need to use type to display a file using more. It supports directly file display by putting the filename at the end of the command:
more "filename"
It has an added benefit: more command tells your current viewing position in the file with a percentage of the progress. In general, if you have some command that also provides an additional feature it is better to use this command and its feature instead of two separate commands. You will often find the benefits of using commands with additional parameters because it makes the script shorter.
But the best views of the world don’t replace a good text editor. Sometimes you really want to have the output of the command inside a new file instead. Good news: there’s another cmd.exe command for that and it is represented by the simple “>” symbol (without quotes). You can use it like this:
tree /F > "files.txt"
You may think of it as showing the direction of the output: take everything from the console and save it into “files.txt” filename.
As you can see, first the command is written normally, as you would if you wanted to see the result in that dark Windows 10 Command Prompt console window. Then you have “the greater than” symbol > operator and after that operator, we have the output filename where the output from the console will be direct to instead of the visible window. Much like when you do “File > Save” in an application, you will generally put the name of a new, non-existent file.
Well, if you really want, you can put the name of an existing file. Be careful though, this operator will replace the actually existing file, effectively deleting all its contents, much like with “File > Save”.
Even better, there’s a second operator that is represented by double greater than “>>” symbols. Instead of writing into a file and erasing the content, this one can use the existing file and write the output at the end of this existing file. This is really convenient when you need to compare multiple commands output but also you can literally write files with echo commands used in the Command Prompt, much like this:
echo "Hello World" > "Command log.txt" copy "Big Archive.zip" "Backup Big Archive.zip"
IMPORTANT: use @echo instead of echo to output the result of the command only. Otherwise, you will see duplicated lines: original command and its result.
Using >> command is also a good and practical way to concatenate two existing text files. Yes, using the double greater than operator and type program, you can suddenly concatenate two files. Combining good features from different programs is an important aspect of the command line scripts. Type command alone might not look useful, but that’s for this kind of combination that exists. So for example, concatenating files is useful to combine your monthly reports in CSV:
type "September report.csv" >> "Combined report.csv" type "October report.csv" >> "Combined report.csv"
Note that you need to use the “double greater than“ >> operator to add the content to an existing file. If you use > (single “greater than“) then it will overwrite any existing file content or will create a new file.
There’s a bonus: all cmd prompt commands support these two operators: “>” and “>>” !
Chaining Windows CMD Commands Safely
Now, we’ve seen earlier how to chain two commands with & operator. The thing is that, when you chain two commands, it’s usually because they’re related and you only want to execute the second command only if the first one worked out.
For example, you want to create a new directory and copy a file in this new directory. Now, if the directory creation failed somehow, are you really sure you want to continue and copy that file? The copy might fail in the cascade because the directory doesn’t exist because of the previous error as the directory creation may have failed because the folder already existed and so coping new file may also erase an existing file you didn’t intend to. That’s exactly where you start to wonder if you really want to run that copy command without checking.
By using the double ampersand && operator, the second command will execute only if the first one worked correctly. Here’s an example of creating a new directory and then copying a file:
mkdir "v2" && copy "index.html" "v2"
If you run this command once, assuming you have an index.html file already, you will get a new directory. In this directory, there will be a copy of the index.html file. However, if you delete the index.html file in the new v2 directory via Windows Explorer and then you run the command chain again, you will see that index.html doesn’t get copied. That proves that the && operator works out and didn’t run the “copy” command because mkdir command failed.
But how does it know that? There’s a thing called exit code. When an application exits, it always returns an exit code to the operating system in order to indicate if all has gone right or not. This way various apps can launch other applications and have a simple way to know how the task launched finished its job. Generally, an exit code of 0 (zero) is considered as “everything went fine!”. If the application returns something that is not a zero, a parent app understands the application had an error. Also, the non-zero number is the error code returned and can explain the reason.
Exit code is the basic Windows commands concept or even, we can say a core concept. Hence why it’s integrated straight into the syntax of CMD line commands. Exit codes aren’t just dark numbers that are only accessible to Windows command line operators. The exit code of the last command is always stored in the global %ERRORLEVEL% command variable that any app can read.
In the command line, we often want to extract data and sometimes we need only one line or just one special file. It may be simpler for you to tell the computer to find a specific date in your log file instead of scrolling through yourself and looking for it. That’s the purpose of the find command. It searches a string in a text and outputs any line that contains that search string to allow easy filtering. Let’s get back to the log file filter example, the command would look like this:
find "[07/Oct" "Connections Log.txt"
See how it helps to see more clearly what’s happening? But find does not only work with files! Thanks to the so-called “pipe” operator represented by “|” symbol (no quotes). find operator combined with | operator can be to filter lines you really want to look for, such as your IP address using ipconfig, which is one of the Windows System commands:
ipconfig | find "IPv"
See how it’s convenient? Instead of a whole screen, you get only a few lines with exactly what you want. Maybe you would want to keep it in Windows 10 Command Prompt list!
Take a look at a few more Windows Prompt commands:
1. Deltree Command
Important: This command is not supported on Windows 10 Home and Pro.
This is one of the most important commands prompt Windows commands. It is a short form of delete tree. Deltree is a command utilized to delete files and directories forever from the computer or laptop. Be very very careful with this command because it removes data permanently.
Syntax
This command removes a directory and all the subdirectories and files in it.
To delete more than one file and directory the syntax is as shown below:
DELTREE [/Y] [drive:]path [[drive:]path[...]]
Where
/Y: Crushes assisting to validate if the user wants to delete the subdirectory.
[drive:]path: This defines the name of the directory user wants to remove.
Example
deltree c:\MyFile
When the user fires the above command in the Command Prompt Windows 10 then it deletes the MyFile directory and everything present in that directory.
2. Driverquery
This is one of the most important Windows commands. Wrong device drivers can point to any quantity of system dilemmas. If users want to view which drivers are placed on a Windows operating system, they can achieve this by executing the driver query Windows command-line tool. This command comes under basic CMD prompt commands which give data about each driver that is being utilized.
Syntax
driverqueryIf a user wants a bit extra report, you can affix the -v switch. Another alternative is to affix the -si switch, which makes the tool demonstrate signature data for the drivers. Here’s how they seem:
driverquery -vdriverquery -si
3. Ping
Ping is presumably the easiest of all distinguishing Command Prompt Windows 10 commands. It is utilized to check fundamental TCP/IP connectivity to a web host. To apply it, just enter the command, accompanied by the alias or IP address of the host you need to examine.
Syntax
ping 192.168.1.1
Always remember that this command will operate only if the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) movement is permitted to move between the two computers. If at any time a firewall is preventing ICMP traffic, the ping will break.
4. Pathping CMD Command
Ping does an excellent duty of informing users whether two computers can interact with each other over TCP/IP, but if ping does break then users will not give any data regarding the characteristics of the collapse. This is where the Windows Command Prompt commands like pathping are handy.
Syntax
The command is given below.
pathping 192.168.1.1Pathping is intended for circumstances in which one or more routers live between hosts. It conveys a sequence of packets to each router that’s on the route to the target host in an attempt to discover whether the router is operating moderately or filtering packets. At its purest, the syntax for pathping is the same as that of the ping command.
5. Tasklist
This is one of the best Windows Command Prompt codes. The tasklist command is created to give data about the tasks that are operating on a Windows operating system.
Syntax
Users can put the following command.
tasklistThe tasklist command has many arbitrary switches. The -m switch, which makes the tasklist to illustrate all the DLL modules connected with a job. The next is the -svc switch, which places the settings that back each job. Here’s how they work:
tasklist -mtasklist -svc
6. Taskkill
This is one of the basic CMD commands. The taskkill command eliminates a task, either by title or by process ID. The arrangement for this command is manageable. Users must fire the taskkill command with -pid (process ID) or -im (image name) and the title or process ID of the job that they need to stop.
Syntax
Here are two samples of how this command operates.
taskkill -pid 3125taskkill -im chrome.exe
7. System File Checker
One can say that this command comes under the most important Windows commands. Wicked apps will regularly strive to substitute kernel system files with altered variants in an attempt to gain control of the system. The System File Checker can be utilized to check the probity of the Windows system registers. If any of the folders are discovered to be lost or nefarious, they will be repaired.
Syntax
Users can execute the System File Checker by utilizing this command.
sfc /scannowThe sfc /scannow command examines all secured system files, and substitute damaged files with a cached model that is placed in a compressed enclosure at %WinDir%\System32\dllcache.
8. Repair-bde Windows command
This is one of the most amazing Windows command line commands. If a drive that is secured is facing some problems then users can seldom retrieve the data utilizing a service named repair-bde.
Syntax
To apply this command, users require a target drive to which the retrieved data can be recorded, as well as the BitLocker retrieval key or restoration password. The primary syntax for this command is:
repair-bde <root> <target> -rk | rp <root>Users should define the root drive, the target drive, and both the rk (recovery key) or the rp (recovery password) switch, along with the route to the restoration key or the restoration password. Following is the example:
repair-bde c: d: -rk e:\restore.bek9. NetDiag
Conceivably the most valuable of the CMD prompt commands that are developed into Windows is NetDiag. The NetDiag command is outlined to operate a series of analyses on the computer in order to assist the professional sketch out why the computer is encountering networking difficulties.
Syntax
The command is shown below:
NetdiagImportant: This command is not supported on Windows 10 Home and Pro.
Listing the NetDiag command by itself will make all of the possible analyses to be covered. Netdiag can assist users to interpret any amount of network problems such as Monitoring Virtual Private Networks.
10. Tracert CMD command
The tracert command tracks the path it exercises for a packet to touch a target and displays users an erudition about each jaunt along that path. For example, if users run tracert abc.com, they’ll notice information about each link the packet communicates with on its route to touch the server.
Syntax
If users are having concerns comparing to a website, tracert can explicate where the enigma is transpiring.
tracert abc.comThe above command is one of the most crucial Command Prompt Windows 10 commands.
11. CIPHER
The cipher comes under the encryption Windows Command Prompt Commands. This reveals or changes the encryption of records and files on NTFS volumes. If employed without parameters, cipher reveals the encryption status of the prevailing directory and any records it holds.
Syntax
For example, the following command enables the encryption of the Private directory.
cipher /e private 12. Finger
The Command Prompt Windows 10 also has one important command known as finger. It displays information about a user or users on a particular remote computer.
Syntax
For example, finger user1@users.abc.com
13. Comp
This Windows Command Line command is used to compare the contents of two files byte-by-byte. If applied without parameters, it allows users to enter the files to compare.
Syntax
For example,
comp c:\annualreports \\sales\myfile\march 14. Clip
The clip comes under the redirecting Windows Commands. It redirects command output from the command line. Users can also paste the output into other programs and files.
Syntax
For example,
clip < myfile.txt 15. Color
The color is one of the featuring CMD Prompt Commands. It develops the font and background colors in the Command Prompt pane for the running session. If applied without parameters, color alters the default view and sets colors.
Syntax
For example,
color 84 16. Append
Important: This command is not supported on Windows 10 Home and Pro.
The append comes under the directories Command Prompt Commands Windows 10. This allows programs to open files in particular folders or directories. If applied without parameters, the append command reveals the appended directory index.
Syntax
For example,
append /eThe above command will store a copy of the appended directory list.
17. Getmac
The getmac command comes under the most important Windows CMD Commands. This command gives the media access control (MAC) address. It also gives the record of network rules connected with each address for all network cards locally or over a network. getmac can be beneficial if you want to use the MAC address into a network analyzer or when you want to understand what rules are running on a specific network adapter.
Syntax
For example,
getmac /fo table /nh /v 18. Label
The label commands are basic CMD Line Commands. It forms, switches, or removes the name of a disk. If applied without parameters, the label command modifies the prevailing volume label or eliminates the current label. An NTFS volume label is 32 characters in length. It can retain and disclose the fact that was applied when the label was formed.
Syntax
For example,
label a:reports-december 19. Logman
The logman commands are used in the Windows server Command Prompt Windows 10. The logman command builds and maintains Performance logs and Event Trace Session. This command also backs many roles of Performance Monitor from the command line.
Syntax
For example,
logman query "perf_log" 20. Ftype
The ftype commands are Windows System Commands. It represents or changes filetypes that are applied in file name extension assistance. If applied without an operator(=), ftype shows the prevailing open command string for the designated filetype. If applied without parameters, ftype shows the filetypes that have open strings specified.
Syntax
For example,
ftype txtfile21. BCDBOOT
BCDBOOT is a command-line utility. It is applied to install the bootmgr bootloader and to set and configure its boot configuration data (BCD). BCD is a binary file that represents all installed Windows applications. bcdboot images the primary boot files from a separated Windows on the disk to the custom boot distribution, and combines that with a proper admission to the boot configuration data. In other words, bcdboot is used to build and repair a system partition.
Syntax
For example, the following command is displaying the use of bcdboot command.
bcdboot C:\Windows 22. CERTREQ
The CERTREQ command can be utilized to get certificates from a certification authority (CA), to regain a reply to a prior request from a CA, to build a new request. The .cer file users get from the Certificate Authority can simply be fixed by keeping the file on the server they created the CSR on, for example as cert.cer, and by performing the subsequent command at the prompt:
Syntax
certreq –submit certrequest.req certnew.cer certnew.pfxC:\>certreq -accept cert.cer
This is the default certreq.exe option. If no alternative is defined at the CMD, certreq.exe tries to give a certificate call to a certificate authority. Users must define a certificate request when utilizing the –submit method. If this parameter is discarded, a standard File Open window surfaces, allowing users to pick the suitable certificate call file.
23. Delprof
Important: This command is not supported on Windows 10 Home and Pro.
Delprof is a CMD utility that one can apply to delete user profiles on local or remote machines running various Windows OS. User profiles can take up significant disk space, particularly if various users are utilizing one machine. In such cases, Delprof.exe can be used to restore disk space by removing profiles that are no longer needed. But, because each profile on the machine is shown in sequence when users run the utility, they may require to use the graphical interface.
Syntax
Delprof2 /c:mymachineThe above command deletes inactive profiles on ‘mymachine’.
24. DIRUSE
Important: This command is not supported on Windows 10 Home and Pro.
The Windows NT Resource Kit comprises DIRUSE which provides disk usage by drive, folder, or sub-folders. The command reveals the total folders, files, and space utilized by the machine. Users can apply DIRUSE to mark folders eating more than a specific setpoint. The following command is used to display the disk usage by the drive and many important parameters.
Syntax
DIRUSE [/S | /V] [/M | /K | /B] [/C] [/,] [/Q:# [/L] [/A] [/D] [/O]] [/*] DIRSExample:
diruse /, /* c:\
25. DSMGMT
DSMGMT command is utilized for maintaining active directory lightweight directory assistance partitions. It is used for managing and regulating single compliant operations and picking up metadata that is moved by broken active directory domain controllers. This command is convenient if the AD LDS server role is installed. To apply dsmgmt, users first must run the dsmgmt command from an advanced command prompt. For most of the dsmgmt commands, users are only required to type the initial few characters than the entire command.
Syntax
For instance, users can type either of the following commands to execute configurable settings:
configurable settingsco s
26. Fsutil
The fsutil is one of the administrative commands. It is used to accomplish jobs that are linked to the file allocation table (FAT) and NTFS file systems. For example, this command is used for handling reparse points, sparse files, or decreasing a volume. It can also be used with various parameters and if it is used without parameters then it displays a list of supported sub-commands. To use this command, one must be an administrator.
Syntax
For example,
fsutil file findbysid myfile d:\helloThe above command will find ‘myfile’ from the hello folder.
27. Dnscmd
Important: This command is not supported on Windows 10 Home and Pro.
The dns is the phonebook of the system. The dnscmd command is a command-line interface for handling DNS servers. This command or utility is beneficial in scripting batch files. The scripted batch files are used to automate regular DNS management tasks. This command can also be used to perform a single abandoned structure and configuration of different DNS servers on the network. This command can also be used to get the zone information and it is also used to clear cache and with many useful parameters.
Syntax
For example,
dnscmd/zoneinfoThe above command is used to get the current zone information.
28. klist
This command is used to display a list of cached Kerberos tickets. This notice refers to Windows Server 2012. In Kerberos, the client sends a request for a ticket to the key distribution center. It is the process of authentication. The klist command is used to list cached tickets. This command is also used with various parameters and if parameters are not provided then the klist command will give all the tickets to currently logged-in users.
Syntax
For example,
klist sessionsThe above command is used when you want to diagnose a logon session for a user or a service. This command is used to find the LogonID from the klist.
29. mqsvc
Important: This command is not supported on Windows 10 Home and Pro.
Message Queuing allows different applications working at various times to reach across varied networks and operations that may be momentarily offline. Message Queuing gives confirmed message delivery, dynamic routing, safety. This command can be used to complete solutions asynchronous and synchronous messaging situations. This is one of the most important windows commands.
Syntax
For example,
Mqsvc.exeThe above command is used for the confirmed message delivery and can be used for various versions of Windows such as windows 10, windows 7, windows 8/8.1, and also different windows servers.
30. mstsc
This command is used to create a remote desktop connection to Remote Desktop Session Host (rd Session Host) servers or other remote machines. This command is also used to edit the current remote Desktop Connection (.rdp) configuration file. It is also used to transfer old connection files that were designed with the Client Connection Manager to new .rdp connection files. This windows command is used on a Windows Server and many other versions of the Windows operating system. It can be used with different parameters and it can also be used to start a remote desktop connection in a full-screen mode. In other words, this command is mainly used for remote desktop connections.
Syntax
For example,
mstsc/fThe above command is used to connect to a screen in a full-screen mode.
Conclusion
You should now have more knowledge to use the line commands effectively. With all these tips and commands and operators we have discussed, you should be able to create new command-line batch files and update existing batch files that you already have.
Now it’s time to practice! Create a sample folder and try these CMD commands inside the sample folder. Try to do tests, copy new files, and see what you can do. It is always good to verify your command line scripts inside sample testing folders instead of testing them on new files. And don’t forget to do backups first especially if you are going to modify, replace, or delete content, or files!
About the Author
ByteScout Team of Writers
ByteScout has a team of professional writers proficient in different technical topics. We select the best writers to cover interesting and trending topics for our readers. We love developers and we hope our articles help you learn about programming and programmers.
Introduction
The Windows operating system features over 280 commands for CMD (Command Prompt). Some commands are specific to Windows servers, while others are available for desktop versions. In both cases, CMD commands communicate directly with the OS and allow to perform various IT automation tasks.
This guide showcases important Windows CMD commands and provides hands-on examples.

Prerequisites
- Access to the command prompt (CMD).
- Administrator privileges (for some commands).
Commands are built-in programs that run through the Command Prompt program. The main use for commands is to automate various tasks, such as user provisioning and other routine actions.
Below is an overview of some common Windows CMD (Command Prompt) commands. Every command has a brief explanation and an example use case.
Note: All commands were tested on a Windows 10 machine in Command Prompt.
1. arp Command
The arp (address resolution protocol) command shows and modifies entries in the ARP cache. The cache contains one or multiple tables that map IP addresses to resolved physical addresses.
The syntax for the command is:
arp <options> <address>Without any parameters, the arp command shows the help window.
To show the ARP cache table, run the following command:
arp -a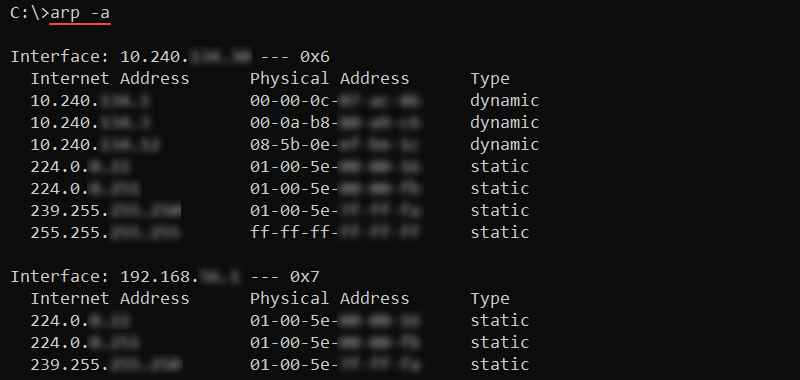
The output lists all the current ARP entries grouped by the interface.
2. assoc Command
The assoc (association) command lists and modifies file extension associations on the system. The syntax for the command is:
assoc .<extension>=<filetype>Without any parameters, the command prints the current file extension associations.
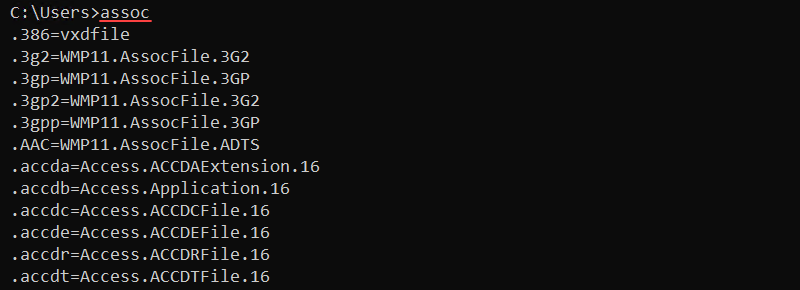
Use the assoc command to view, change, or remove file associations. For example, to view the .log file associations, run:
assoc .log
Change the file association with:
assoc .log=txtfileAlternatively, remove all file associations for files with the .log extension by running:
assoc .log= The command requires adding a space after the equals sign to remove the association.
3. attrib Command
The attrib (attribute) command shows or changes file attributes. The possible attributes are:
- R — Read-only.
- H — Hidden.
- S — System file.
The syntax for the attrib command is:
attrib <+ or -> <attribute>The plus sign (+) sets an attribute, while the minus sign (-) removes an attribute from a file. Without any options, the command shows the file attributes in the current directory.
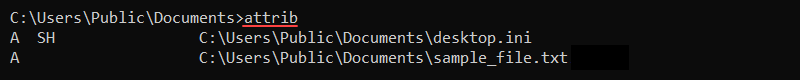
To set a file to have the read-only (R) and hidden (H) attributes, use the following command:
attrib +R +H sample_file.txt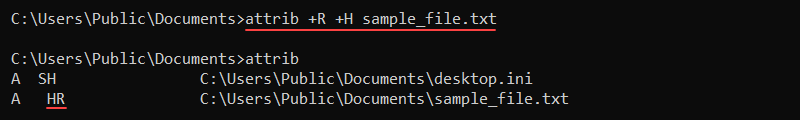
To make a file visible, remove the hidden (H) attribute:
attrib -H sample_file.txt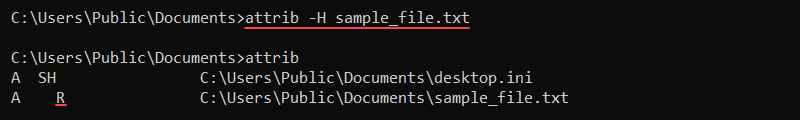
The minus removes the attribute from the file and returns the file to the default visible state.
4. bcdboot Command
The bcdboot (boot configuration data boot) command sets up a system partition by copying BCD files into an empty partition.
The syntax for the command is:
bcdboot <path>For example, to copy the BCD files into C:\Windows, use:
bcdboot C:\Windows
The output prints a confirmation message about file creation.
5. cd Command
The cd (change directory) command shows or changes the current location. The syntax for the command is:
cd <directory>The directory parameter is optional, and without it, the command prints the current working directory.
For example, to change the location to a directory named Public, add the directory name after the command:
cd Public
The prompt reflects the change and shows the new location.
To change the location to a different disk, add the /d option before the path. For example, to change to disk S:\ use:
cd /d S:
Without the option, the command prints the path without changing to the provided location.
To change to the parent directory, use the following shortcut:
cd ..
The current directory changes to one directory above the current location.
6. chkdsk Command
The chkdsk command scans the local file system and metadata for errors. The syntax for checking a disk is:
chkdsk <volume> <options>Without additional parameters, the chkdsk command shows the current disk state without fixing any errors.
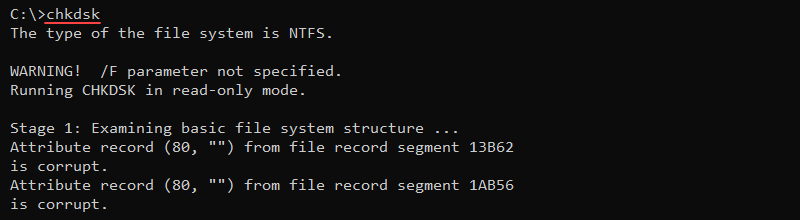
Additional parameters enable fixing errors on a disk, such as the /f option:
chkdsk <volume> /f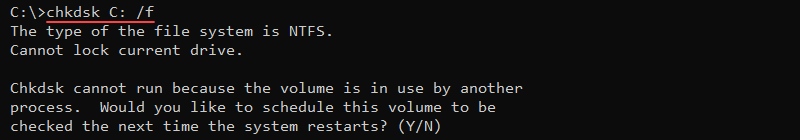
The command attempts to fix errors on the disk. If the disk is in use, run the check on the next system restart. Stopping the command does not affect the system, but ensure to run the scan later to fix any potential data corruption.
7. choice Command
The choice command prompts a user to choose an answer from a list of options. Without any parameters, the command prompts the user to choose between Y and N options.
Additional options control the number of choices and the prompt text. For example, to add a third choice, use the /c parameter and list the three option names:
choice /c ync
Insert additional text to explain the available options with the /m parameter. For example:
choice /c ync /m "Yes, No, Continue"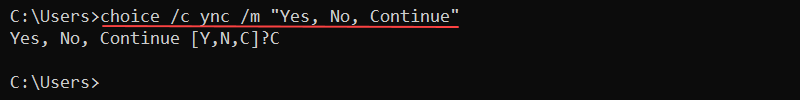
In all cases, the command returns the choice index and exits.
8. cipher Command
The cipher command shows and modifies the encryption for files or directories. The command syntax is:
cipher <option> <file or directory>Without any options, the cipher command shows the encryption state for all files and directories in the current location. The U represents «unencrypted,» whereas E is «encrypted.»
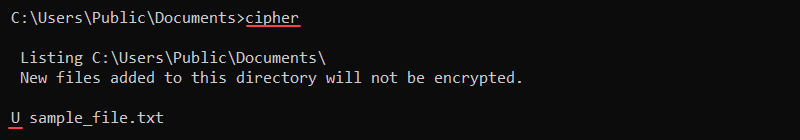
To encrypt a file in the current directory, use the /e parameter:
cipher /e <file name>The file’s indicator changes from U to E, which marks the file as encrypted.
Note: The encrypting and unencrypting files and directories feature is available for Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions.
9. clip Command
The clip command copies a command output or file contents to the clipboard. The syntax for copying a command’s output in CMD is:
<command> | clipFor example, to copy the current directory path, pipe the cd command to clip:
cd | clipPaste the contents anywhere in the window using CTRL+V (or right-click in CMD).
To copy the contents of a file, use redirection:
clip < <filename>For example, to copy the contents of a sample.txt file to the clipboard, run:
clip < sample.txtThe file’s contents are saved to the clipboard and can you can paste them anywhere.
10. cls Command
The cls command clears the text in a command prompt window and returns a blank surface. Use the command to clear the screen contents.
Note that the previous contents and output do not return to the screen.
11. cmd Command
The cmd command starts a new instance of the command interpreter. Use the following syntax to run the command:
cmd <options> <command>Without additional parameters, the cmd command shows the current cmd.exe program version.
Use cmd to run commands without affecting the current session. For example, to test a command and return to the current command interpreter session, use the /c parameter:
cmd /c cd ..The new interpreter changes the directory. However, the /c tag ensures the interpreter returns to the original session, and the directory stays unchanged.
To run a command and stay in the new session, use the /k parameter:
cmd /k cd ..
The /k parameter switches to the new session and runs the cd command to switch to the parent directory.
12. color Command
The color command changes the default console background and text colors. The command syntax is:
color <background><font>The color attributes are hexadecimal numbers from 0 to f. The help window displays all the possible color options:
help color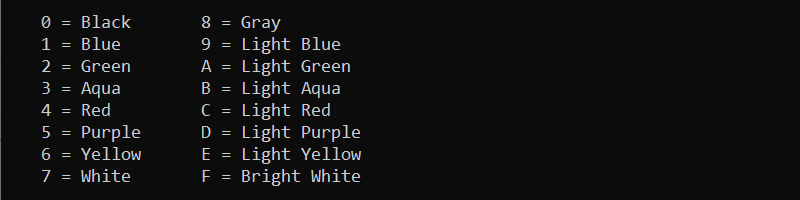
For example, to change the background to blue (1) and the font to light aqua (b), run:
color 1b
To return to the default console colors, run the color command without options.
13. comp Command
The comp command compares the contents of two files. The comparator program inspects file bytes and outputs characters where the two files differ.
The syntax for the command is:
comp <file 1> <file 2> <options>Without any options, the comp command starts an interactive prompt to enter file names and additional options.
To demonstrate how the command works, compare two text files with the following contents:
- sample_file_1.txt contains «test»
- sample_file_2.txt contains «text»
Run the comp command and provide the two file names:
comp sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt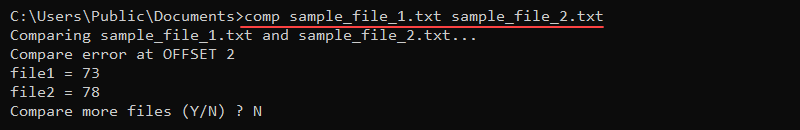
The output prints the comparison error as characters in hexadecimal format and asks to compare more files (enter N to exit).
To print the comp results in human-readable format, use the /a parameter:
comp /a sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt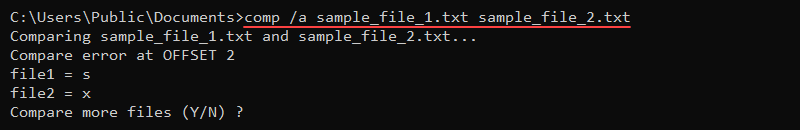
The comparison fails at character «s» in the first file and character «x» in the second file.
14. compact Command
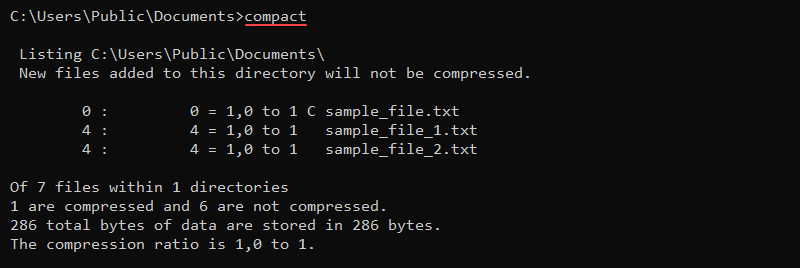
The compact command is a built-in feature for compressing files and folders. The syntax for the command is:
compact <options> <file>Without any options or parameters, the compact command prints the compression state in the current directory.
For example, to compress a file, use the /c parameter and provide the file name:
compact /c sample_file.txt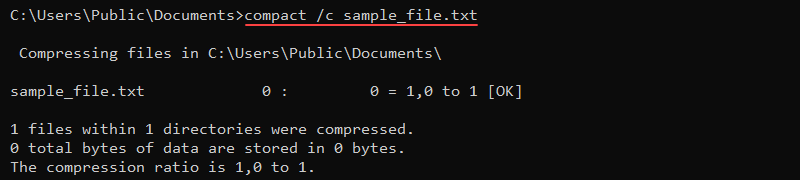
To uncompress a file, use the /u parameter:
compact /u sample_file_1.txt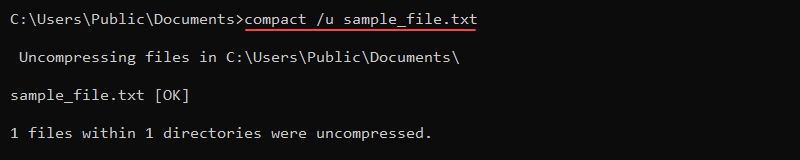
Use the compact command to save disk space and compress large files and directories.
15. copy Command
The copy command copies one or multiple files from one location to another. The command syntax is:
copy <options> <source> <destination>For example, to copy a file’s contents into a new file in the same location, use:
copy sample_file.txt sample_file_copy.txtThe command creates the new file and copies all the contents from the source file.
16. date Command
The date command shows and modifies the current date on the system. Without any parameters, the command prints the current date and requests to enter a new date:
date
Enter the date as mm-dd-yyyy to change the current date on the system or exit with CTRL+C.
Use the /t parameter to avoid modifying the system state and only print the current date:
date /t
The command shows the day of the week and the current date.
17. defrag Command
The defrag (defragmentation) command finds and aggregates fragmented files on the system. The command reduces unnecessary empty data blocks and improves system performance.
The syntax for the defrag command is:
defrag <volumes> <options>For example, to defragment the C:\ drive, run:
defrag C:\ /u /v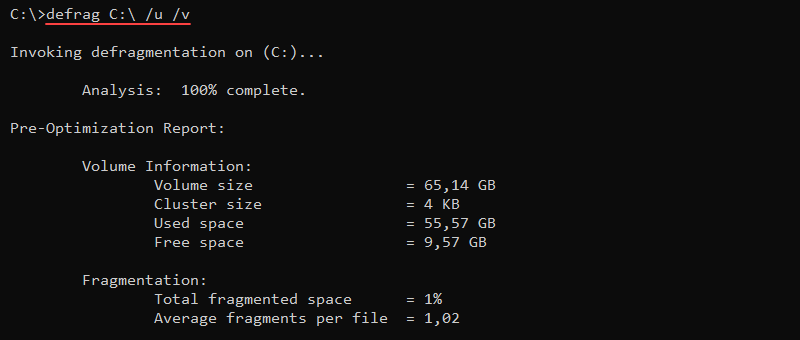
The /u parameter prints the progress, while /v shows a verbose output. These parameters are optional.
18. del and erase Commands
The del and erase commands delete one or more files. The syntax for the commands is:
del <options> <file(s)>erase <options> <files(s)>Both commands permanently delete the specified file or files from a disk and are irretrievable.
For example, to delete a file with the name sample.txt, run:
del sample.txtOr alternatively:
erase sample.txtTo avoid accidental deletion, use the /p parameter:
del /p sample.txt
The output shows a prompt with the file name and requires confirmation before deleting the file.
19. dir Command
The dir (directory) command lists directory contents, including files and subdirectories. The syntax for the command is:
dir <drive><path><filename> <options>The dir command without options shows information for the current directory.
To show the C:\ drive contents, run:
dir C:\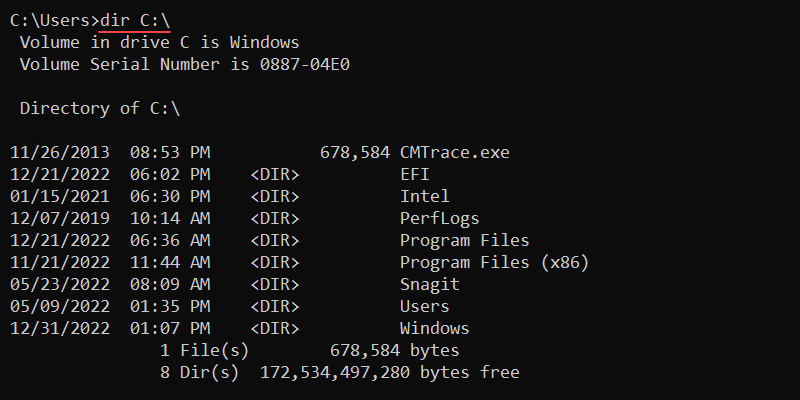
The output shows the following information:
- Volume drive.
- Volume serial number.
- Directory contents with modification time.
- File and directory count.
20. doskey Command
The doskey command starts the Doskey.exe program for the previously entered commands. The command helps recall command history and create macros.
For example, to see the command history from the current command prompt session, run:
doskey /history
The output shows all the commands from the CMD session from oldest to newest.
21. driverquery Command
The driverquery command is a command for admins to display the installed device drivers and their information. The command works for both local and remote access machines.
The syntax for the command is:
driverquery <options>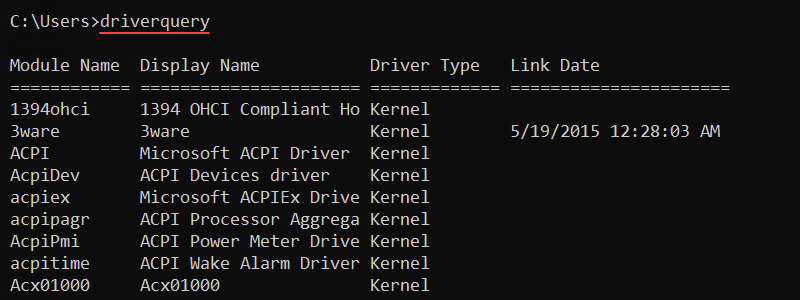
Without any options, the driverquery command shows device drivers on the local machine. Additional options control the output format or allow querying remote machine drivers.
22. echo Command
The echo command prints a message to the console and controls the settings for the command. The syntax for the command is:
echo <message>Without any parameters, the command shows the current settings.
To use the command and show a «Hello, world!» message to the screen, run:
echo "Hello, world!"
The echo command often appears in scripts to print useful information while the script runs.
23. exit Command
The exit command ends the current batch script or the command interpreter session. To exit a batch script, add the /b parameter:
exit /bWithout the /b option, the exit command closes the command interpreter.
24. fc Command
The fc (file compare) command compares two or more files. The output prints the contents to the console if there is a difference between the files.
The syntax for fc is the following:
fc <options> <file 1> <file 2> For example, to compare two sample files, sample_file_1.txt and sample_file_2.txt, run:
fc sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt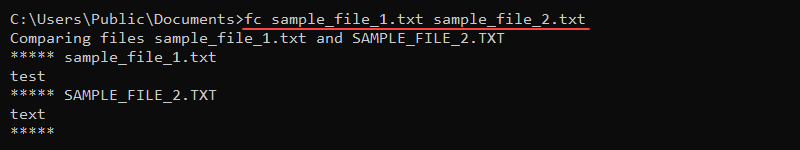
The command prints the file contents, indicating there is a difference between the two files.
25. find Command
The find command searches for a string in a file and prints the line of text when there is a result. The command syntax is:
find <string> <file>For example, to search for the string «text» in a file, use:
find "text" <file>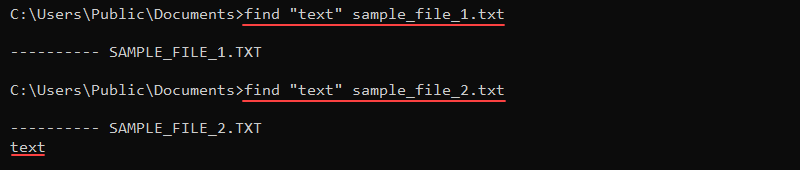
The command looks for an exact match and returns the file name along with the line of text that contains the string. If a file does not contain the text, the command returns the file name without the text.
26. findstr Command
The findstr (find string) command performs a similar task to the find command. The command returns the whole line where the text is located without the file name. This feature makes it more convenient for use in scripts.
The command syntax is:
findstr <string> <file>For example, to find a string «text» in a file, run:
findstr "text" <file>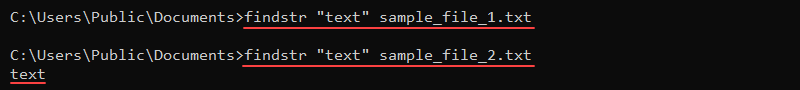
If the command does not return a result, the string is not in the file.
27. ftype Command
The ftype (file type) command shows and changes a file type and extension association. The command syntax is:
ftype <file type>=<open command>The file type parameter is the file to show or modify (such as txtfile), while the open command option is a string that calls a program to read the file type. The open command string substitutes the file name into the open command to run a file in the provided program.
Without any options, ftype prints all file types and extension associations.
To show the current file type and extension association for text files, enter:
ftype txtfile
To remove file type association, append an (=) sign:
ftype txtfile=The command omits the program for opening files and removes the program association.
28. getmac Command
The getmac command fetches the MAC addresses for all network cards on the computer or in the network. The command also shows the protocols associated with each address.
The syntax is:
getmac <options>Additional options provide detailed information about a remote computer or control the output display. For example, to show the MAC addresses in the CSV format, use:
getmac /fo csv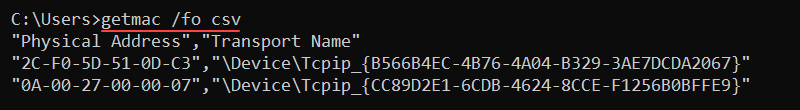
Use the command to parse the MAC address to a network monitoring tool or to check the protocols on network adapters.
29. help Command
The help command shows detailed information for a specific command. Without any parameters, the help command lists all available system commands.
The syntax for the command is:
help <command>For example, to view the help menu for the cd command, run:
help cd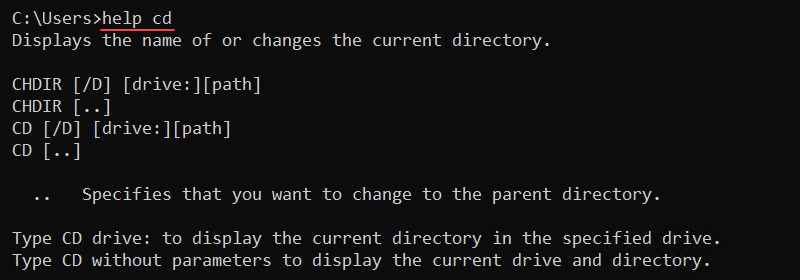
Use any key to go through the pages if the help page is larger than the command line. Alternatively, press CTRL+C to exit.
Note: For non-system commands, use the following format to see the help window:
<command> /?
30. hostname Command
The hostname command is a simple command to display a machine’s host name. Run the command to see the name of the computer:
hostname
The command does not have options, and providing any additional parameters throws an error. The hostname command is available for systems with TCP/IP installed on a network adapter.
31. ipconfig Command
The ipconfig (IP configuration) command is a networking CMD tool that shows all current TCP/IP network configuration information. The command also refreshes DHCP and DNS settings.
The syntax for the command is:
ipconfig <options>Omitting options shows the basic TCP/IP configuration for all adapters:
ipconfig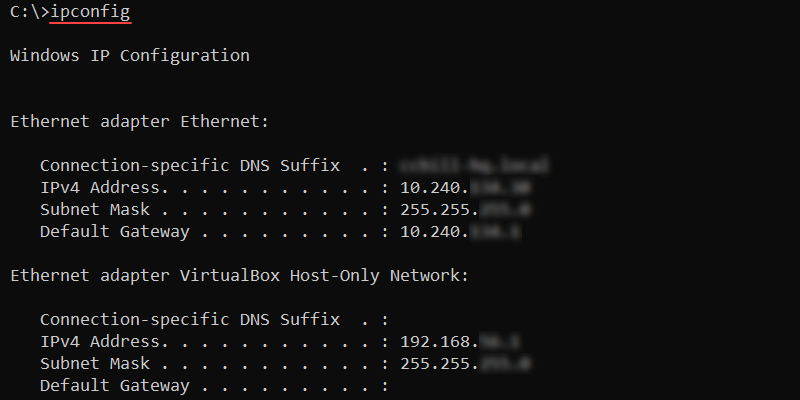
To show the full TCP/IP configuration for all adapters, run:
ipconfig /allRenew the DHCP IP address for the local area connection with:
ipconfig /renew Local Area ConnectionTo flush the DNS cache, use:
ipconfig /flushdnsUse the command when troubleshooting DNS issues.
32. label Command
The label command shows, changes, or removes the volume label (name) of a disk. The command requires administrator privileges to perform any changes.
Without any options, the label command shows the label for the C:\ drive and starts a prompt to change the name:
label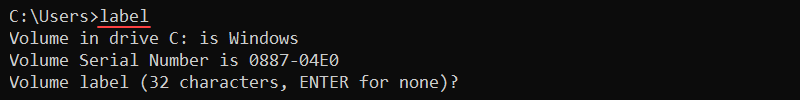
Press Enter to remove the label, or enter a new name to change the current label name. Confirm the change with Y or press N to keep the existing name.
33. makecab Command
The makecab command creates a cabinet (.cab) file. Cabinet files are an archive format specific to Windows systems with support for lossless data compression and archive integrity.
Use the following syntax to create .cab files with the makecab command:
makecab <options> <source> <destination>For example, to create a sample_cab.cab file in the current directory and add a sample_file.txt file to the archive, use:
makecab sample_file.txt sample_cab.cab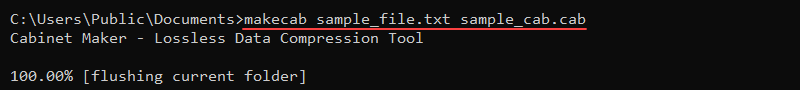
The output prints the compression progress and exits when done.
34. md and mkdir Commands
The md and mkdir (make directory) commands create a new directory or subdirectory. The command syntax is:
md <path>mkdir <path>For example, to make a new subdirectory called Subdir in the current location, run:
mkdir SubdirThe command extensions enable md and mkdir to create a directory tree:
md Subdir\Subsubdir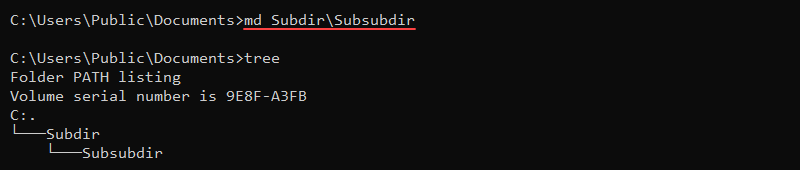
The command immediately creates all intermediate subdirectories.
35. mklink Command
The mklink (make link) command creates a hard or symbolic link to a file or directory. The command requires administrator privileges to run and uses the following syntax:
mklink <options> <link> <target>Without any additional options, the mlink command creates a symbolic link to a file. For example:
mklink my_link sample_file.txt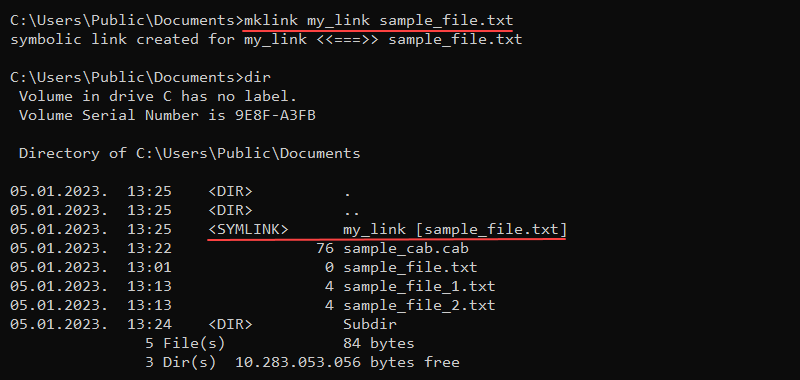
To create a hard link instead of a symbolic link, use the /h parameter:
mklink /h my_link sample_file.txtCreate a directory link with the /d parameter:
mklink /d \Docs \Users\milicad\DocumentsThe dir command shows the links in the directory listing. To enter the directory, use the cd command and treat the link as a regular directory (cd Docs).
36. more Command
The more command is a Windows CMD utility for displaying long documents or outputs one screen at a time. To use more with a command, use the pipe character:
<command> | more <options>Alternatively, use the command to display long files page by page:
more <path>For example, run the help cd command and pipe the more command to truncate the output:
help cd | more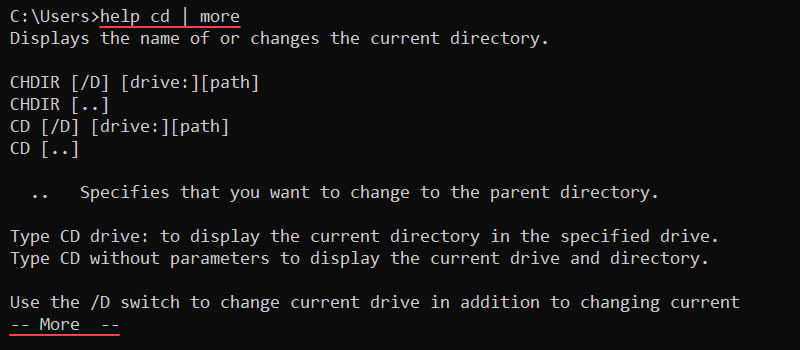
Press Enter to go to the following line and Space to go to the next page. To exit, press q.
37. mountvol Command
The mountvol command creates, removes, or shows a volume mount point. Mounting a volume makes data on a storage device available for local users through the file system.
The command syntax is:
mountvol <path> <volume name>The command does not require a drive letter to link a volume. Without any parameters, the mountvol command shows the help menu, mount points, and possible volume names.
For example, to list the volume name and current mount point for the C:\ drive, run:
mountvol C:\ /l
The output shows the GUID for the volume, which is a unique unchanging identifier.
38. move Command
The move command is a CMD shell command for moving files from one location to another. The syntax for the command is:
move <options> <source> <destination>The source and destination are either a folder or a file. The move command renames a file if the source and destination locations are the same but have different file names.
For example, the following command renames a file named sample_file.txt to file.txt:
move sample_file.txt file.txt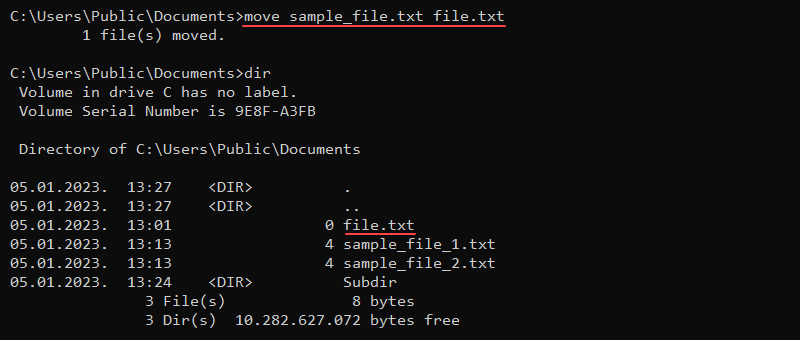
Provide the full path to move a file to another location:
move C:\Users\Public\Downloads\my_file.txt C:\Users\Public\Desktop\my_file.txt If overwriting an existing file, the command prompts to confirm, unless the command runs as part of a batch script.
39. msiexec Command
The msiexec program runs the Windows Installer program for installing, managing, and removing .msi software packages. The command syntax is:
msiexec <options> <path to package>The program features various install, display, update, and repair options. Without any options, the msiexec command opens a window to show the command information.
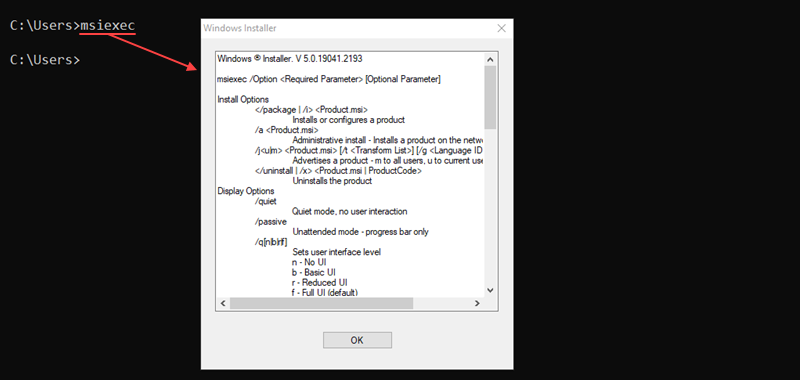
For example, to perform a normal installation of a .msi package, run:
msiexec /i "C:\example.msi"The /i option indicates a normal installation of the .msi package located at the provided path.
40. msinfo32 Command
The msinfo32 command opens the System Information window, which has details about the system.
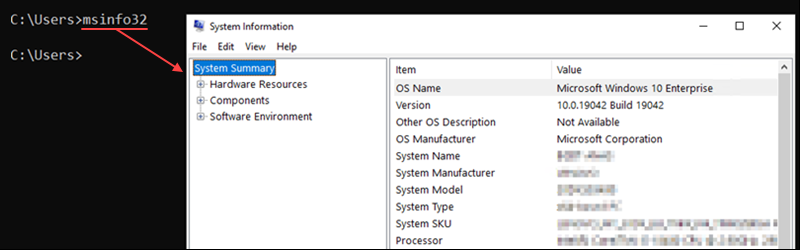
The command syntax is:
msinfo32 <options>Additional options filter the information or export the data into specific file formats. For example, to export all system information into an.nfo file, use:
msinfo /nfo sysinfo.nfoThe command automatically appends the .nfo extension if omitted.
41. mstsc Command
The mstsc command starts the Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) program to connect to a remote machine. Use the command for remote connection or to alter an existing .rdp file.
The command syntax is:
mstsc <options> <file>For example, to start an RDC session in full-screen mode, use this command:
mstsc /f
To edit an existing connection, use the /edit parameter and provide the file name:
mstsc /edit example.rdpUser-created .rdp files are in the Documents folder by default.
42. net Commands
net commands are a set of commands for managing various network aspects, such as users and network services.
The command syntax is:
net <subcommand> <options>Without additional parameters, the net command shows all available subcommands with a short description.
Use the net start command to list all running Windows services:
net start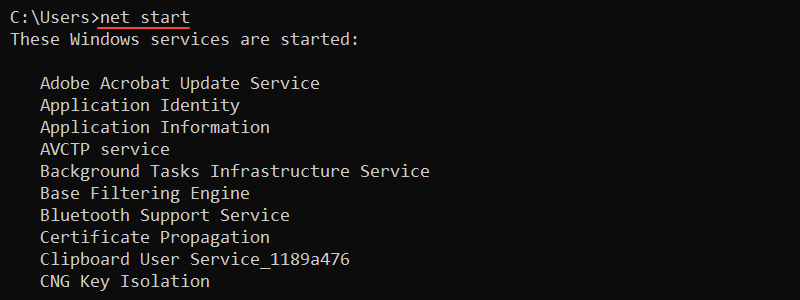
To stop a service, use the following command:
net stop <service>View the login and password requirements for a user with the following:
net accounts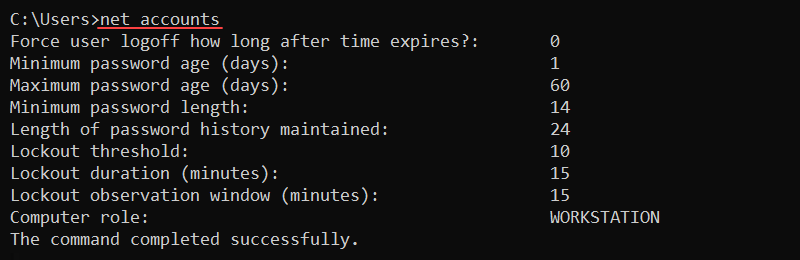
Display additional help for a subcommand using the following syntax:
net help <command>The output shows a detailed help window for any provided command.
43. netstat Command
The netstat (network statistics) command is a crucial command for network administrators. The command lets you view various network statistics.
The basic syntax for the command is:
netstat <options>The command displays active TCP connections when used without options. The output shows the protocol, local and foreign addresses, and the TCP connection state.
Add the -a option to display all active TCP connections and listening TCP and UDP ports:
netstat -a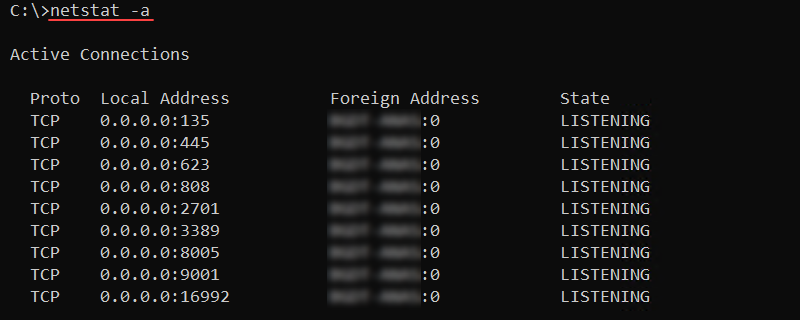
Use the command to scan for open ports or to check the port protocol type.
44. nslookup Command
The nslookup command is a DNS infrastructure diagnostics tool for web servers. The command features a non-interactive mode for looking up a single piece of information and an interactive mode for looking up additional data.
The syntax for nslookup is:
nslookup <host> <command> <options>Without any options, nslookup enters interactive mode. To find DNS records for a specific domain name, use:
nslookup <domain>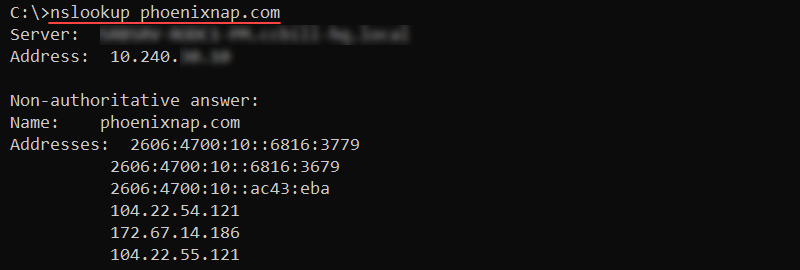
The output prints the A records for the provided domain.
45. path Command
The path command helps add directories to the PATH environment variable. The variable contains a set of directories that point to executable files.
The command syntax looks like the following:
path <location>Without any parameters, path shows the current state of the PATH variable.
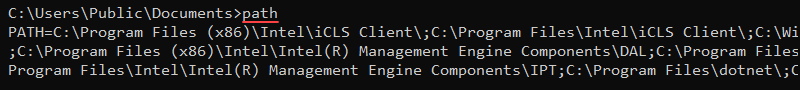
To add multiple locations to PATH, separate each location with a semicolon (;) as in the following example:
path <location 1>; <location 2>Both locations append to the variable.
46. ping Command
The ping command is another essential network troubleshooting tool. The command checks the connectivity with another machine by sending ICMP request messages.
The syntax for the command is:
ping <options> <host>For example, to check connectivity to the phoenixNAP website, use:
ping phoenixnap.com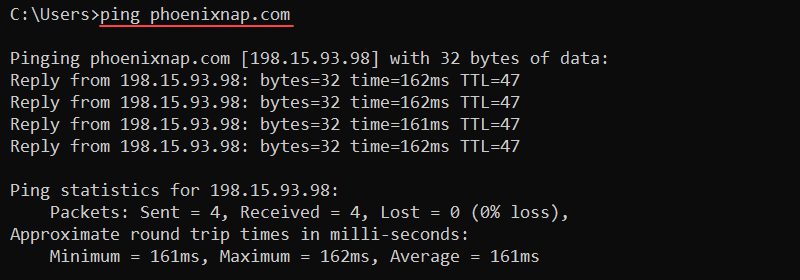
The output prints corresponding reply messages and round-trip times. Use the command to check for connectivity and name resolution issues.
47. powercfg Command
The powercfg (power configure) command runs the powercfg.exe program for controlling the system’s power plans. The monitoring tool also helps troubleshoot battery life and energy efficiency problems on a device.
The command syntax is:
powercfg <options> <arguments>To list the current power plan setup on a device, use:
powercfg /list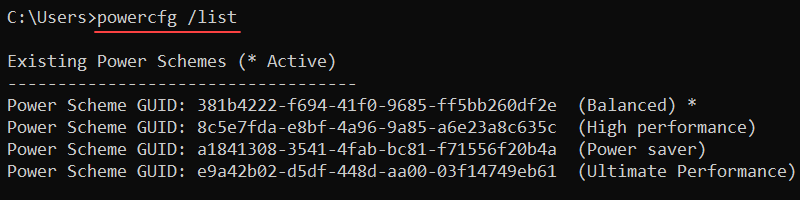
The output lists all power schemes on the system. The active power scheme has an asterisk (*).
48. prompt Command
The prompt command allows changing the CMD prompt display to the specified string. By default, the prompt shows the current location and the greater-than sign (>).
The command syntax is:
prompt <string and variables>The prompt command offers various variables to add special characters or additional features to the prompt. For example, to change the prompt to an arrow, use:
prompt --$g
The $g variable represents the greater-than sign (>) and the prompt stays during the command-line session.
49. rd and rmdir Commands
The rd and rmdir commands remove an empty directory from the system. The syntax for the commands is:
rd <path>rmdir <path>Attempting to delete a directory with files results in an error message. Add the /s parameter to delete a directory with subdirectories and files to avoid the error message:
rd /s <path>The command deletes the complete subdirectory tree and all files.
50. ren and rename Commands
The ren and rename commands rename files or directories. The syntax for the two commands is:
ren <path><old name> <new name>rename <path><old name> <new name>The commands do not allow moving the files to a different location. Wildcard characters work for multiple files. For example, to change all .txt files to .c files, use:
ren *.txt *.c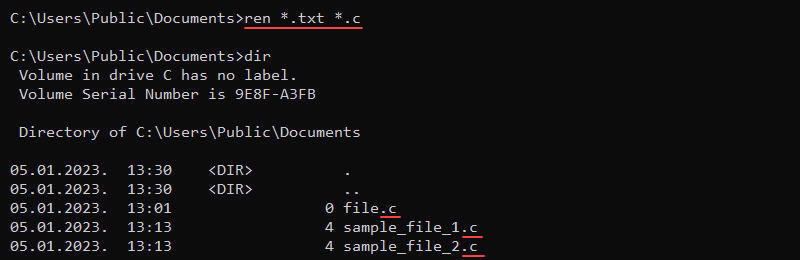
The asterisk (*) character helps discover all file names in the current directory with the .txt extension and renames the files to have the .c extension.
51. robocopy Command
The robocopy command is a robust command for copying files and directories. The syntax for the command is:
robocopy <source> <destination> <file> <options>The main benefit when using robocopy is the /mt parameter for higher-performance multithreading. Additionally, the /z parameter lets you restart a transfer in case of interruptions.
An example transfer looks like the following:
robocopy C:\Users\user\Downloads C:\Users\user\Documents database.db /mt /z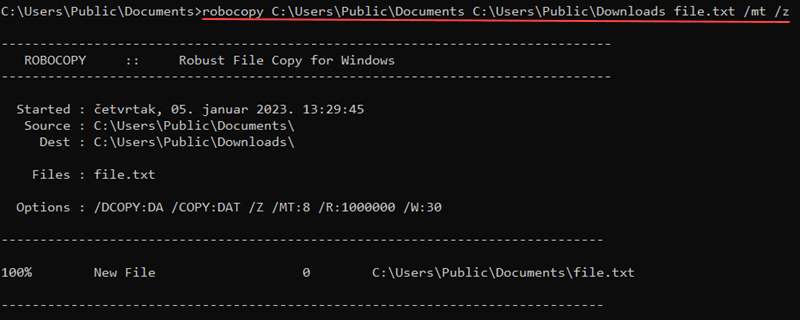
Use the command for large file transfers that are sensitive to interruptions.
52. route Command
The route command shows and alters entries in the local routing table. The command syntax is:
route <options> <command> <value>The different available commands are:
add— Adds a route entry to the table.change— Modifies an entry in the table.delete— Removes a route from the table.print— Displays a route or routes.
For example, to print all routes from the table, use:
route print 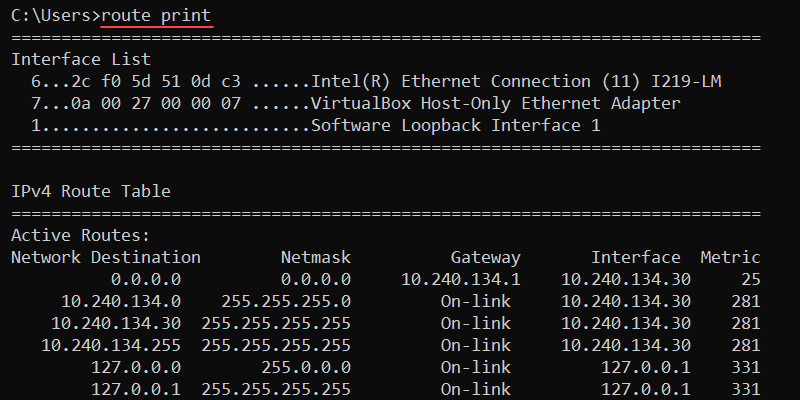
The output prints the interface list, and IPv4 and IPv6 routing tables.
53. schtasks Commands
The schtasks command helps schedule commands or programs to run on the system. The tasks run at specified times or periodically. The syntax for the commands is:
schtasks /<subcommand>The following subcommands are available:
change— Modifies existing properties of a task.create— Creates a new task.delete— Removes a task.end— Stops a program started by a task.query— Prints scheduled tasks on the machine.run— Starts a scheduled task.
For example, to show currently scheduled tasks on the system, use:
schtasks /query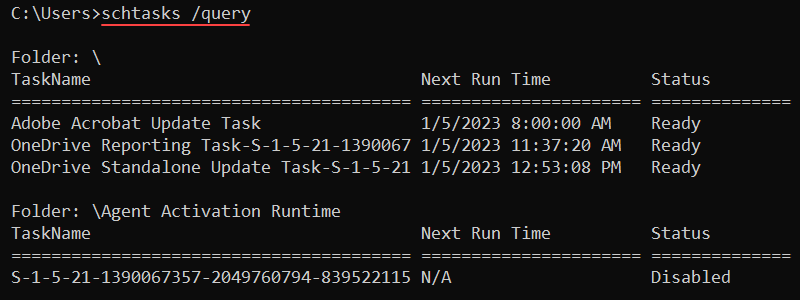
The output displays task names, next run times, and task statuses.
54. set Command
The set command shows, sets, and removes environment variables in the CMD. The syntax for the command is:
set <variable>=<value>Without additional parameters, the set command shows all environment variables.
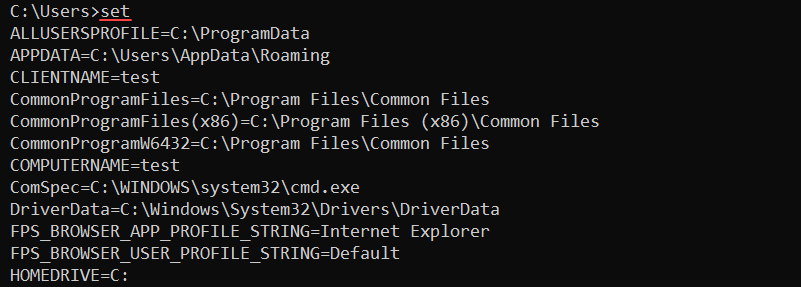
The variables are available to use with any command. For example, to create a new CMD variable called message, use:
set message="Hello, world!"Reference the variable using the following syntax:
echo %message%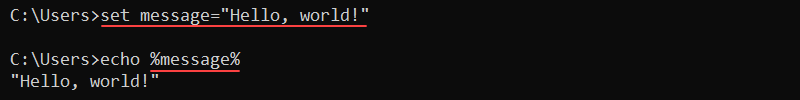
Encasing the variable in the percent signs (%) reads the value and outputs it to the screen.
Note: The variables do not persist and are only valid for the current command-prompt session.
55. sfc Command
The sfc (system file checker) is an administrator command for checking protected file version integrity. The command also replaces incorrect overwritten protected files with the correct file version.
The syntax for the command is:
sfc <options> <files or directories>For example, to scan the system and repair all files, use the following command:
sfc /scannow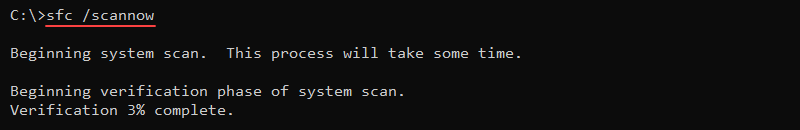
The command scans all protected system files and repairs problematic files when possible.
56. shutdown Command
The shutdown command restarts or shuts down a local or remote computer. The command syntax is:
shutdown <options>Without any arguments, the shutdown command opens the help menu.
For example, to shut down and restart the computer, use the /r option:
shutdown /r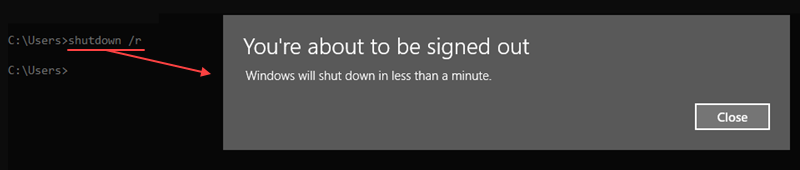
To shut down without restarting, use the /s argument:
shutdown /sIn both cases, the shutdown is not immediate. To cancel the action, use the /a option:
shutdown /aThe option ensures that a previously executed shutdown command aborts.
57. sort Command
The sort command allows sorting provided data from a file or user input. Additional options control the sorting mechanism and from which point to start sorting.
To use the command interactively, do the following:
1. Run sort without any options.
2. Enter a new word in each line.
3. Press CTRL+Z and Enter at the end of the list to sort the input values alphabetically.

Alternatively, use the sort command on files:
sort sample_file.txt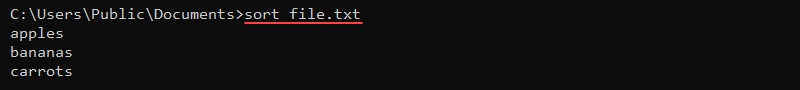
The command sorts the file contents and prints the result to the console.
58. start Command
The start command opens a new command-prompt window according to the specified options. The command syntax is:
start <title> <options>For example, to load start a new command-prompt session with the title «Hello, world!» and set the path to C:\. enter the following command:
start "Hello, world!" /d C:\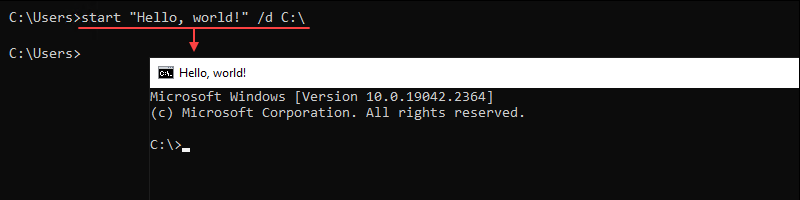
A new CMD window opens with the starting path on the C:\ drive and a custom title.
59. systeminfo Command
The systeminfo command displays detailed system information about the OS and computer, including hardware properties. The command works on both local and remote machines.
Use the command without options to show the local system information:
systeminfo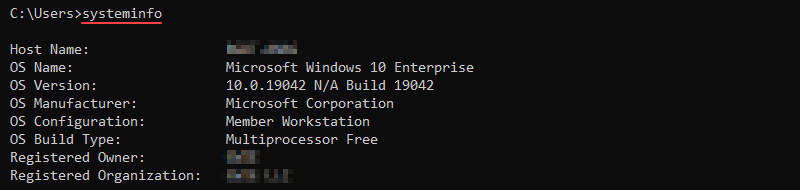
Additional options allow checking system information for remote computers or controlling the output format. For example, show the output in CSV format with:
systeminfo /fo csvDifferent formats enable parsing the information through scripts effectively.
60. takeown Command
The takeown (take ownership) command allows an administrator account to take ownership of a file. The command provides access to a file for an administrator and makes the administrator the owner.
Add the /f option and specify the file name:
takeown /f <file>
The administrator now has full permissions over the file.
61. taskkill Command
The taskkill command ends a running process or task on the Windows system through the command line. Use the command to forcefully end processes and tasks which did not end correctly.
The syntax for the command is:
taskkill <options> <task or process>A common way to end a task is to find the process ID (PID) with the tasklist command and end the process with:
taskkill /pid <Process ID>
The command finds the process by ID and kills it.
62. tasklist Command
The tasklist command shows all running processes on a local or remote computer and their memory usage. The command helps locate and reference specific processes.
The syntax for tasklist is:
tasklist <options>Without additional options, the command shows all currently running processes.
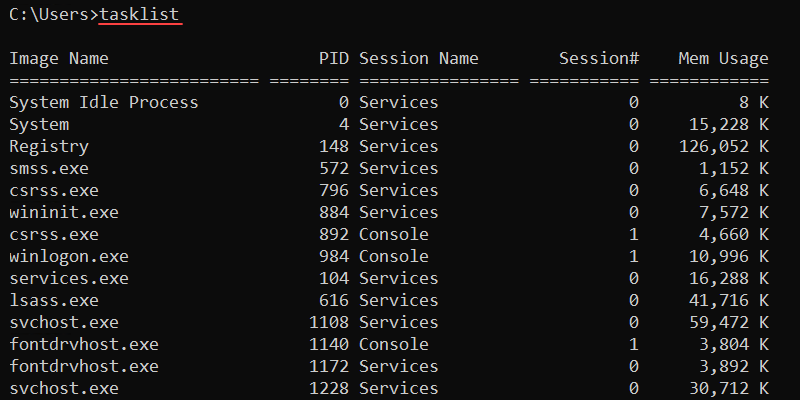
The image name and PID are unique identifiers for a process. The final column shows the memory usage for a process. This is a good indicator for identifying processes that slow down the system.
63. telnet Command
The telnet command is a Windows tool for bidirectional CLI communication. The tool uses the Telnet protocol to send messages and enable an interactive communication channel.
The syntax for the command is:
telnet <command> <options>See our detailed guide for using Telnet on Windows.
64. time Command
The time command manages and displays the current system time. Without any options, the command prints the current time and prompts to enter a new time:
time
Enter a new time to change the system time or exit the prompt using CTRL+C. Use the /t option to avoid making modifications:
time /t
The command prints the current time and returns to the command line.
65. timeout Command
The timeout command pauses the command line for a specified number of seconds. The syntax for the command is:
timeout /t <seconds>For example, to pause the interpreter for ten seconds, run:
timeout /t 10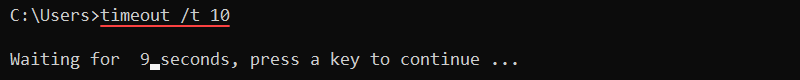
The output counts down and returns to the command line. Press any key to interrupt the timeout earlier. Use the command in scripts to wait for execution between two commands.
66. title Command
The title command is a simple utility for changing the command prompt’s title. The syntax is:
title <string>For example, to set the title to "Hello, world!", use:
title "Hello, world!"
The CMD window title changes to the provided string. Use the command when running multiple batch scripts to differentiate between different command prompts.
67. tracert Command
The tracert (traceroute) command is a networking tool for determining the path from a local computer to a destination. The command sends ICMP messages with increasing TTL values to map routers along the path.
The syntax for tracert is:
tracert <options> <destination>For example, to trace the path to phoenixnap.com, use:
tracert phoenixnap.comAlternatively, use the IP address of the destination.
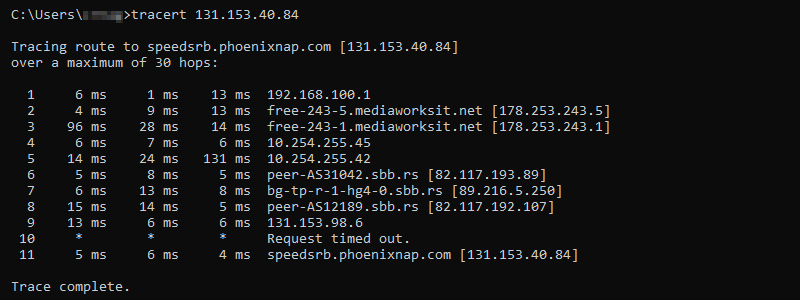
The output shows the hops between the source and destination, providing an IP address and name resolution where applicable. Use the command to discover connectivity issues to a host.
68. tree Command
The tree command displays the contents inside a drive or directory in a tree-like structure. The syntax is:
tree <options> <path>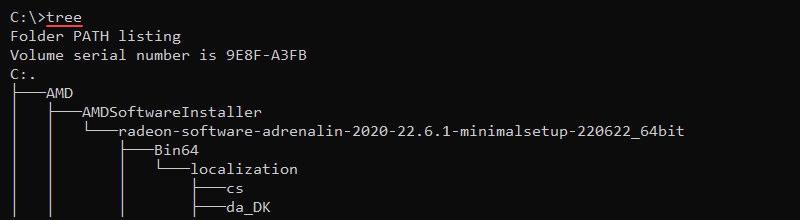
Without any options, the tree command displays the directory structure of the C:\ drive.
69. type Command
The type command is a built-in command for showing file contents. The command allows viewing a file directly in CMD without modifying the text.
The syntax for the type command is:
type <file path>For example, to show the contents of the file called sample_file.txt, run:
type sample_file.txt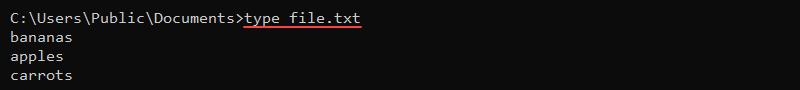
The output prints the file’s contents to the command line. Use this command to preview files directly in the command prompt.
70. tzutil Command
The tzutil (time zone utility) command helps modify and display the currently set time zone on the system. Without any options, the command shows the help window.
Display the current time zone with:
tzutil /g
The output shows the time zone ID. List all available time zone IDs with:
tzutil /l | moreThe more command helps truncate long outputs. Use the /s parameter and provide the time zone ID to change the system time zone.
71. ver Command
The ver command is a simple utility to show the operating system version. Use the command to find the exact version of the operating system:
ver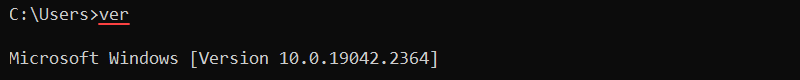
The version prints to the output and returns to the command line.
72. vol Command
The vol command prints the disk volume and label. The syntax for the command is:
vol <drive>:
Without a specified drive, the vol command shows information for the currently selected drive.
73. where Command
The where command searches for the location of a file using a search pattern and prints the location to the command line. The syntax for the command is:
where <options> <location to search> <file name>Omitting the location searches for the file in the current directory without going through subdirectories. To perform a recursive search, add the /r parameter. For example:
where /r C:\ sample_file.txt
The command searches the C:\ drive and all subdirectories. If the file is found, the command returns the location path.
74. whoami Command
The whoami command shows the current user’s domain and username. The syntax for the command is:
whoami <options>Without options, the command shows the domain and user name.

Add the /all parameter to show detailed information for the current user:
whoami /all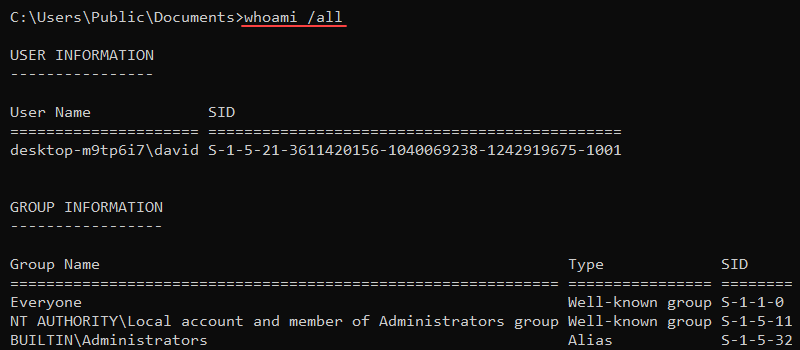
The user’s name, security ID, groups, and privileges print to the console.
75. xcopy Command
The xcopy command copies files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another. The syntax for the command is:
xcopy <source> <destination> <options>For example, use the following command to copy contents from one location to another, including subdirectories (even if empty):
xcopy <source> <destination> /s /e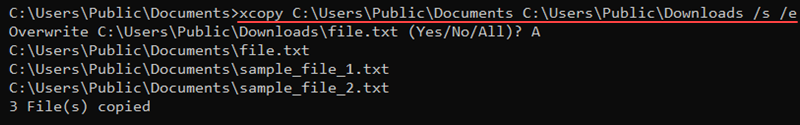
The /s parameter enables subdirectory copy, while /e includes empty directories. If any files with the same name exist in the destination, the command prompts before overwriting.
Windows CMD Commands Cheat Sheet
All the listed commands are available in a single-page cheat sheet in PDF format. Save the cheat sheet for future use and reference by clicking the Download Windows CMD Commands Cheat Sheet button below.
Conclusion
After reading and trying out the commands from this guide, you’ve familiarized yourself with the Windows Command Prompt (CMD) tool. Windows allows performing a variety of tasks through the command prompt using just commands.
Continue practicing and researching commands further to master the Command Prompt in Windows.