The clear command in Linux is used to clear the terminal’s screen.
You can also use the clear command in a Windows PowerShell where it is an alias of the Clear-Host command, that does pretty match the same – removes all text from the current display, including commands and output that might have accumulated.
But if you try to execute the clear command in a Windows command-line prompt (CMD), expecting it to clear the screen, you will get an error as follows:
‘clear’ is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.
Below you will find how to clear the command prompt in Windows.
To clear the screen in the Windows command-line prompt (CMD), use the cls command:
C:\> cls
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
In the Microsoft Windows command prompt (cmd) you can use cls command to clear screen of cmd. This equal to clear Command on Unix Like Operating Systems.
cls

Keyboard Shortcut to cls Command
Well, I do not think there is a keyboard shortcut to cls command(clear cmd) in windows, at least not by default. But that as for my knowledge (I even search in the Google).
Anyway, If any one of you know the shortcut just drop me an email message @ [email protected], SO I can update this tutorial.
The Windows command line is one of the most powerful utilities on a Windows PC. With it, you can interact with the OS directly and do a lot of things not available in the graphical user interface (GUI).
In this article, I’ll show you 40 commands you can use on the Windows command line that can boost your confidence as a Windows user.
N.B.: You have to be careful while using the commands I’ll show you. This is because some commands can have a lasting negative or positive effect on your Windows PC until you reset it.
In addition, some of these commands require you to open the command prompt as an admin.
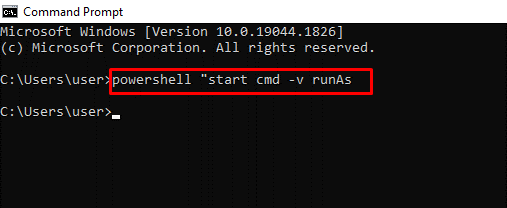
powershell start cmd -v runAs – Run the Command Prompt as an Administrator
Entering this command opens another command prompt window as an administrator:
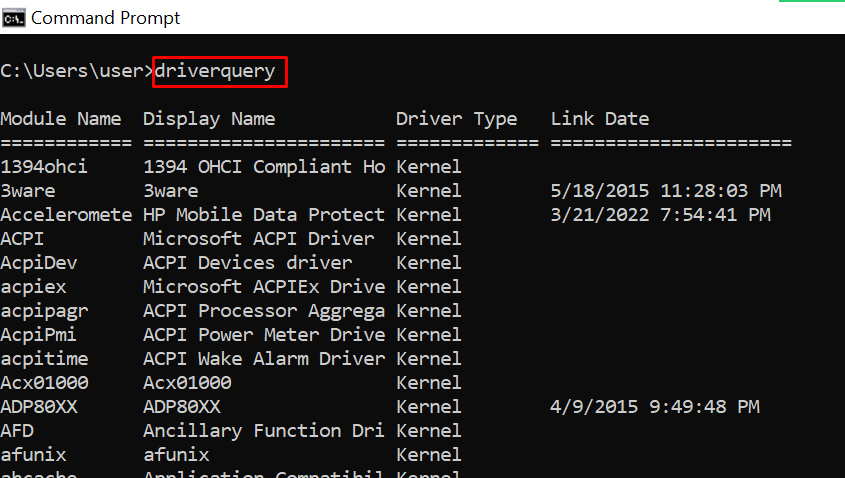
driverquery – Lists All Installed Drivers
It is important to have access to all drivers because they often cause problems.
That’s what this command does – it shows you even the drivers you won’t find in the device manager.
chdir or cd – Changes the Current Working Directory to the Specified Directory
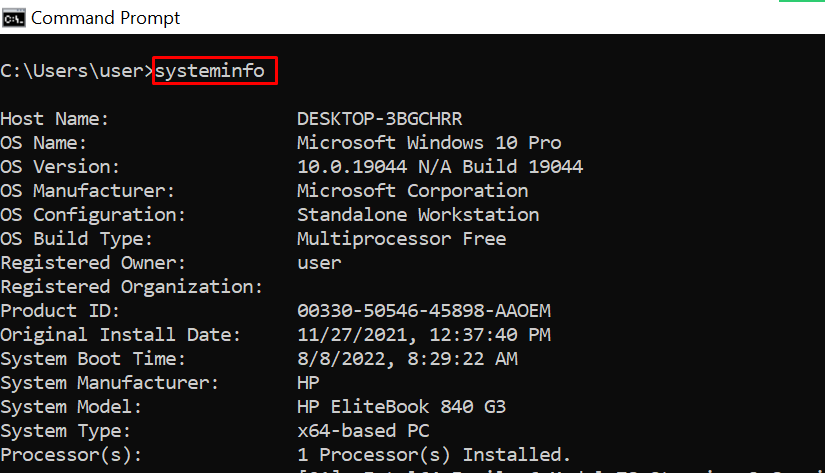
systeminfo – Shows Your PC’s Details
If you want to see more detailed information about your system you won’t see in the GUI, this is the command for you.
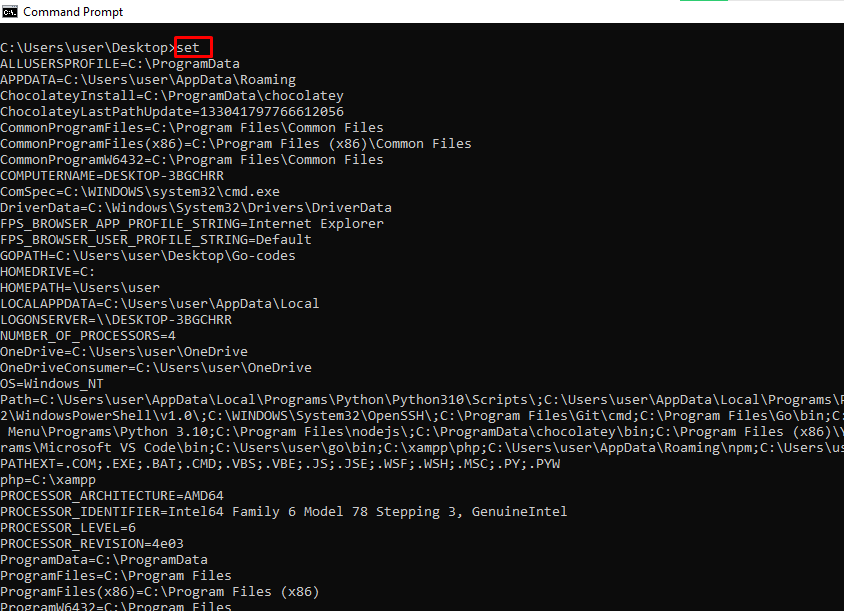
set – Shows your PC’s Environment Variables
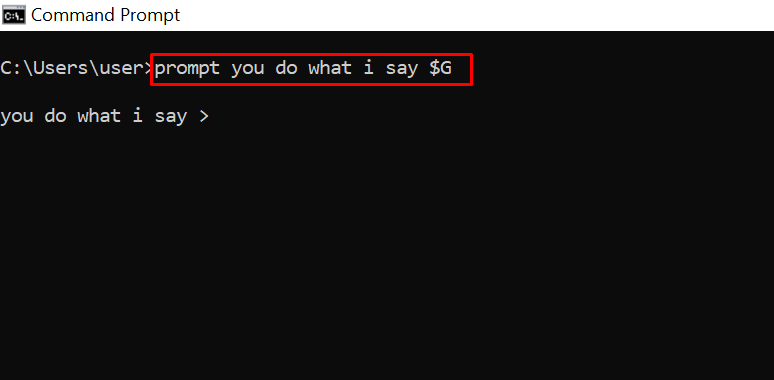
prompt – Changes the Default Text Shown before Entering Commands
By default, the command prompt shows the C drive path to your user account.
You can use the prompt command to change that default text with the syntax prompt prompt_name $G:
N.B: If you don’t append $G to the command, you won’t get the greater than symbol in front of the text.
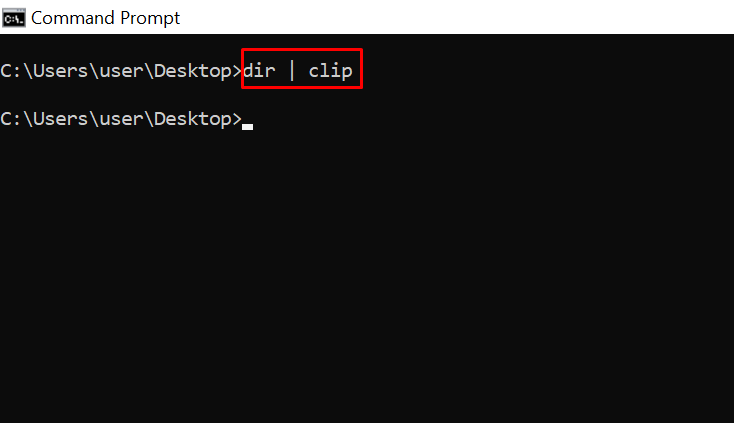
clip – Copies an Item to the Clipboard
For example, dir | clip copies all the content of the present working directory to the clipboard.
You can type clip /? and hit ENTER to see how to use it.
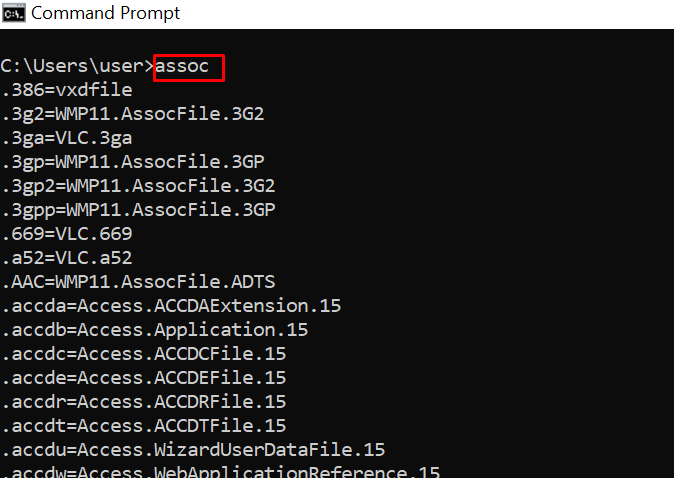
assoc – Lists Programs and the Extensions They are Associated With
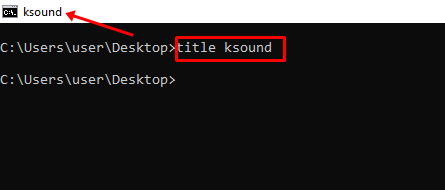
title – Changes the Command Prompt Window Title Using the Format title window-title-name
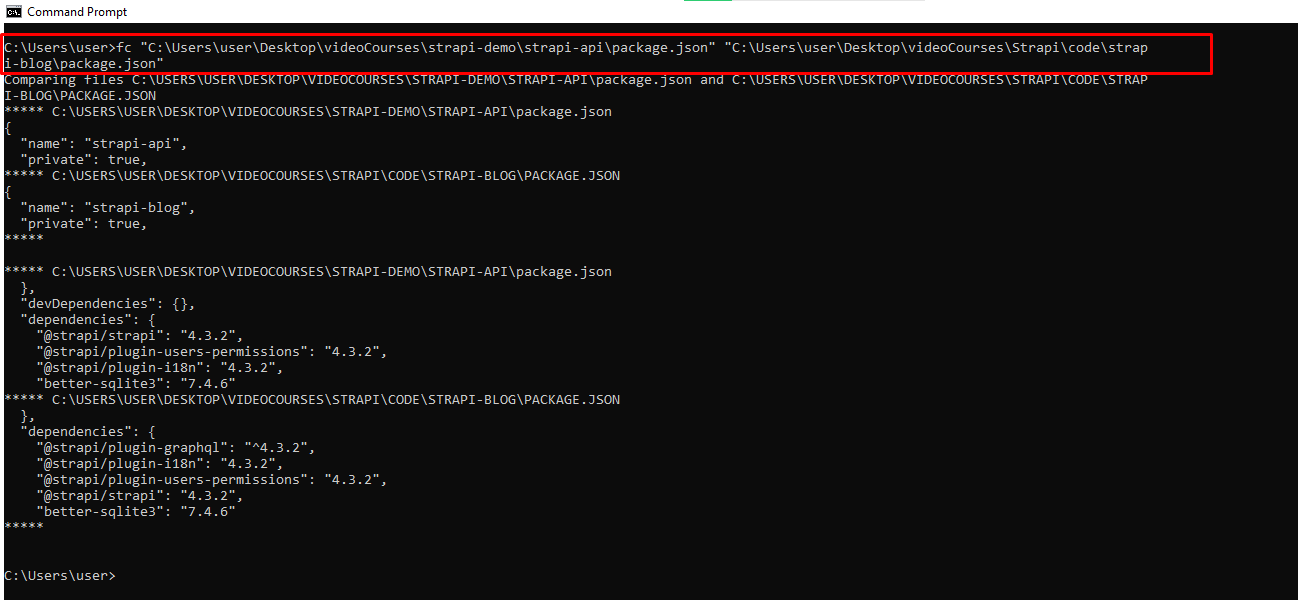
fc – Compares Two Similar Files
If you are a programmer or writer and you want to quickly see what differs between two files, you can enter this command and then the full path to the two files. For example fc “file-1-path” “file-2-path”.
cipher – Wipes Free Space and Encrypts Data
On a PC, deleted files remain accessible to you and other users. So, technically, they are not deleted under the hood.
You can use the cipher command to wipe the drive clean and encrypt such files.
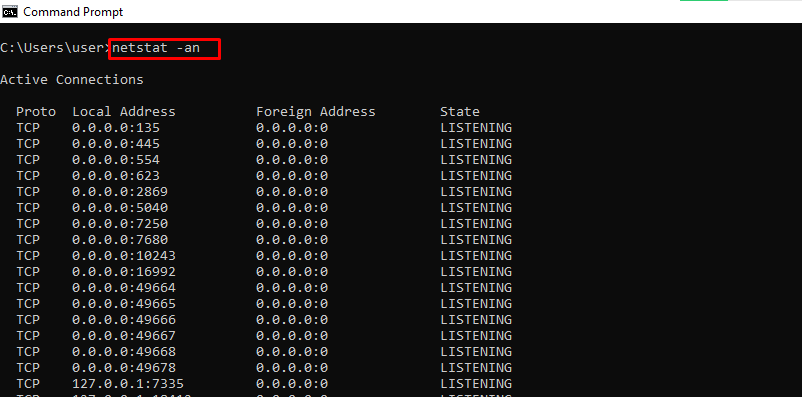
netstat -an – Shows Open Ports, their IP Addresses and States
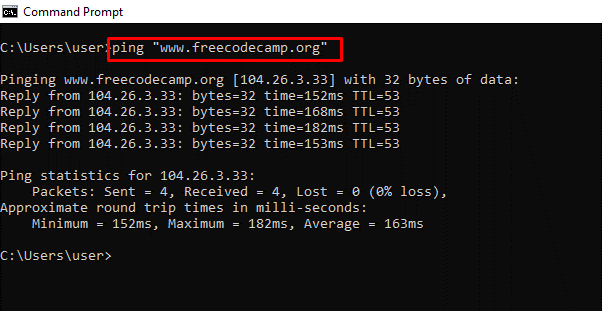
ping – Shows a Website IP Address, Lets you Know How Long it Takes to Transmit Data and a Get Response
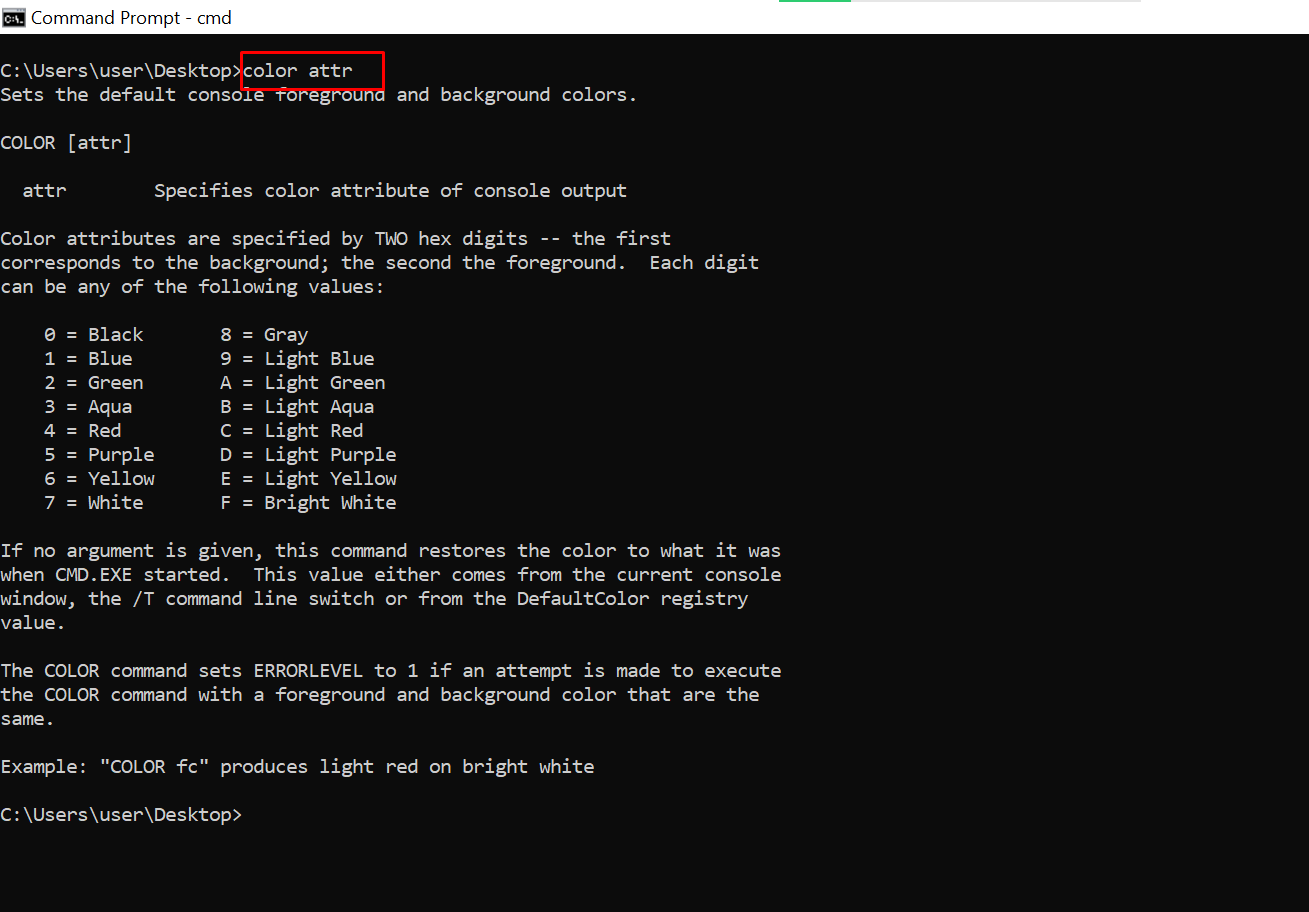
color – Changes the Text Color of the Command Prompt
Enter color attr to see the colors you can change to:
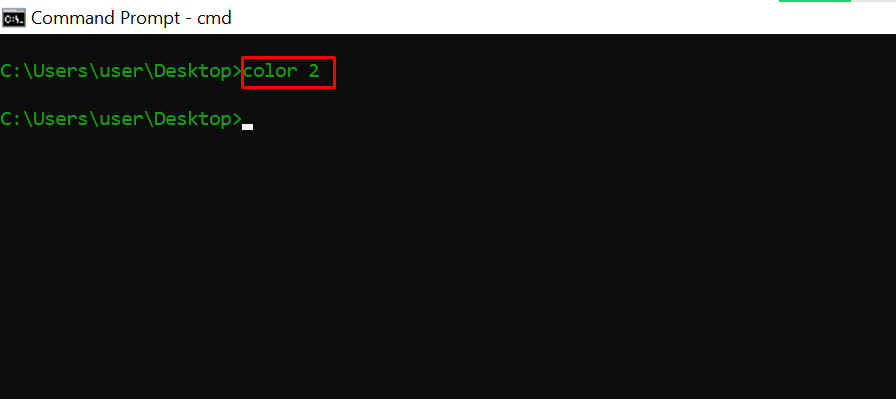
Entering color 2 changes the color of the terminal to green:
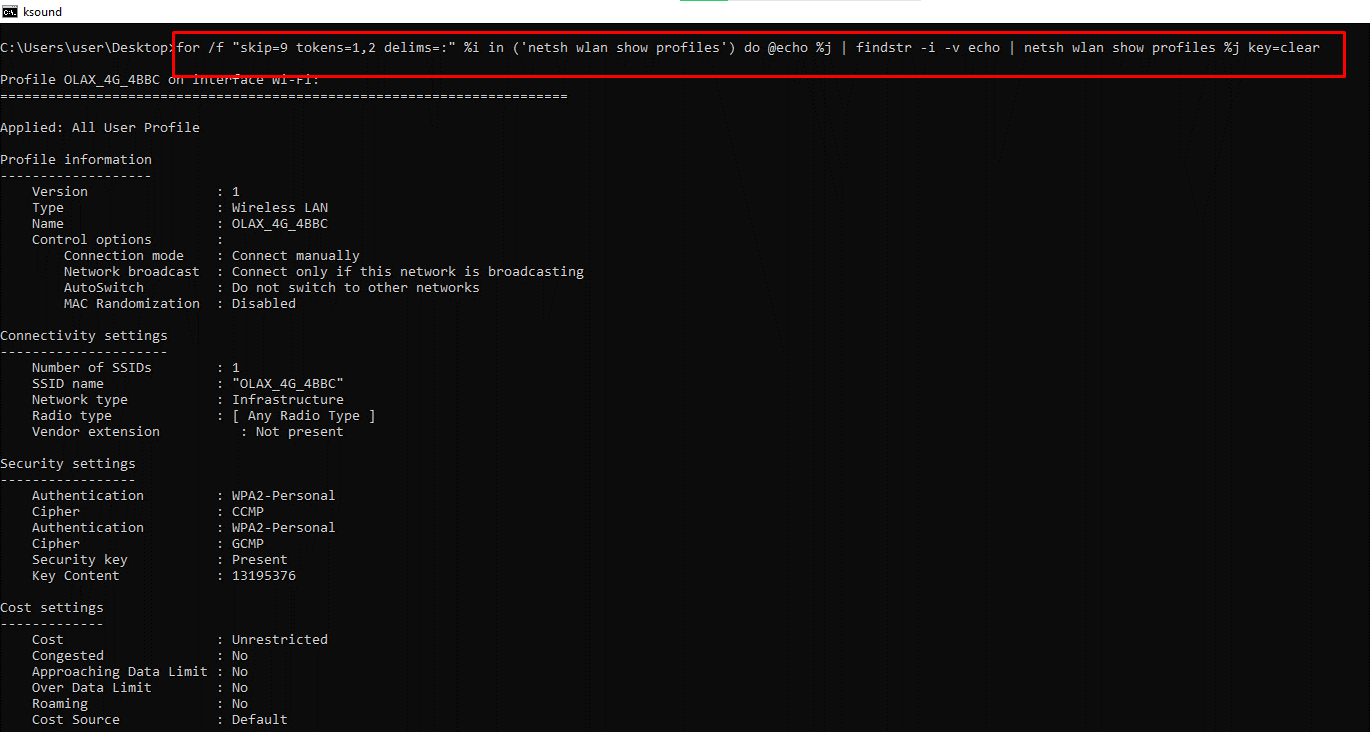
for /f "skip=9 tokens=1,2 delims=:" %i in ('netsh wlan show profiles') do @echo %j | findstr -i -v echo | netsh wlan show profiles %j key=clear – Shows All Wi-Fi Passwords
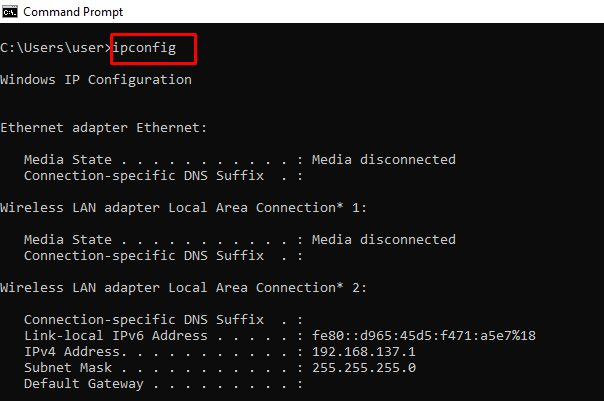
ipconfig – Shows Information about PC IP Addresses and Connections
This command also has extensions such as ipconfig /release, ipconfig /renew, and ipconfig /flushdns which you can use to troubleshoot issues with internet connections.
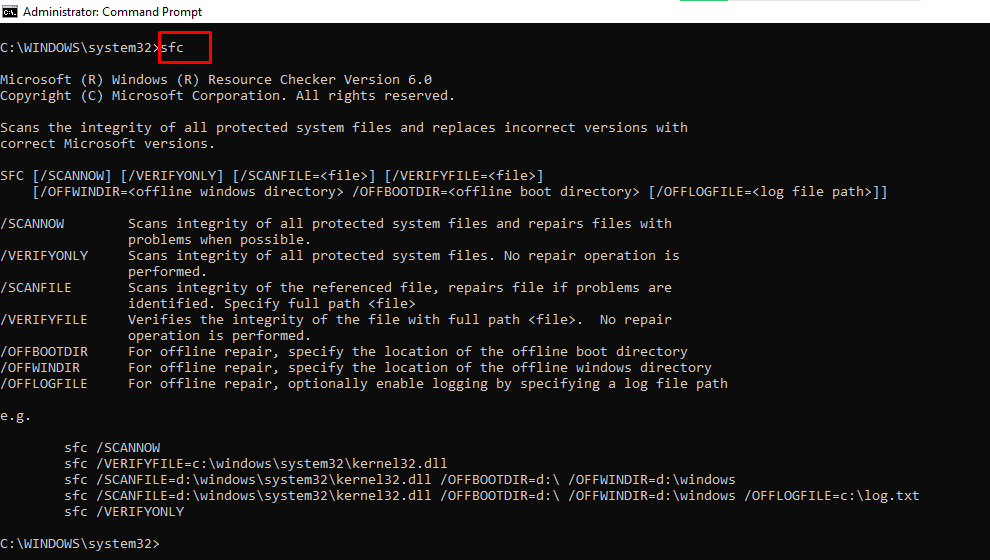
sfc – System File Checker
This command scans your computer for corrupt files and repairs them. The extension of the command you can use to run a scan is /scannow.
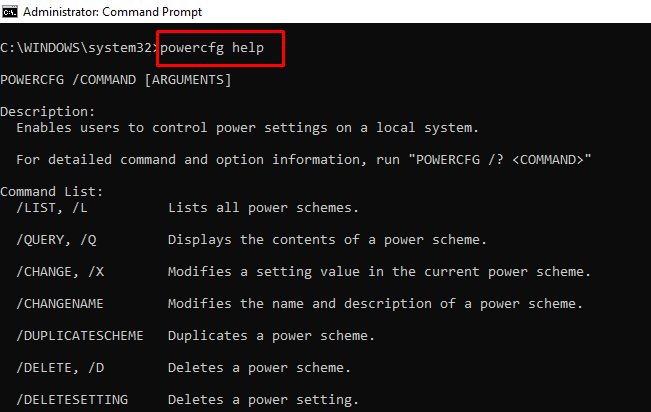
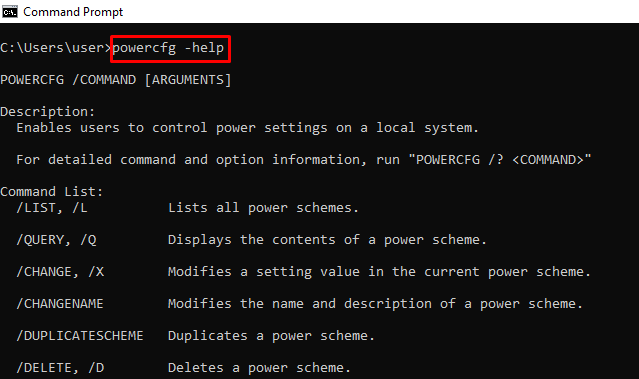
powercfg – Controls Configurable Power Settings
You can use this command with its several extensions to show information about the power state of your PC.
You can enter powercfg help to show those extensions.
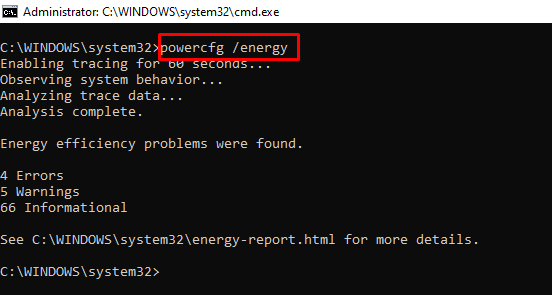
For example, you can use powercfg /energy to generate a battery health report.
The powercfg /energy command will generate an HTML file containing the report. You can find the HTML file in C:\Windows\system32\energy-report.html.
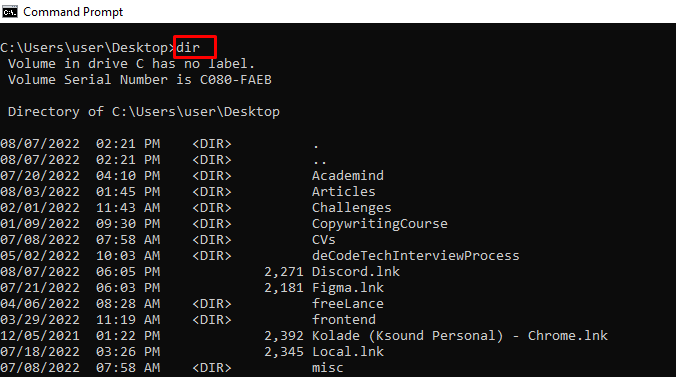
dir – Lists Items in a Directory
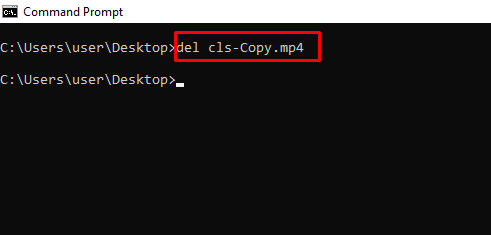
del – Deletes a File
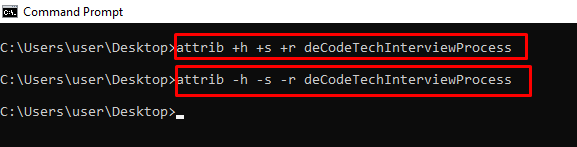
attrib +h +s +r folder_name – Hides a Folder
You can hide a folder right from the command line by typing in attrib +h +s +r folder_name and then pressing ENTER.
To show the folder again, execute the command – attrib -h -s -r folder_name.
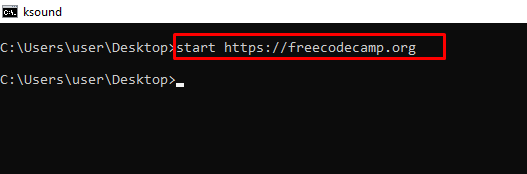
start website-address – Logs on to a Website from the Command Line
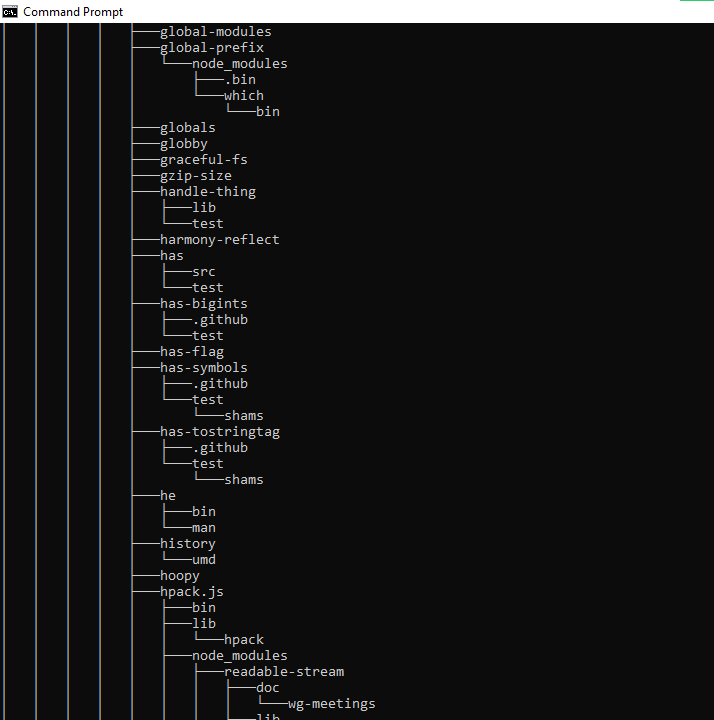
tree – Shows the Tree of the Current Directory or Specified Drive
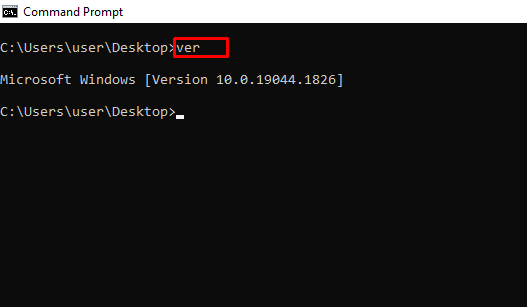
ver – Shows the Version of the OS
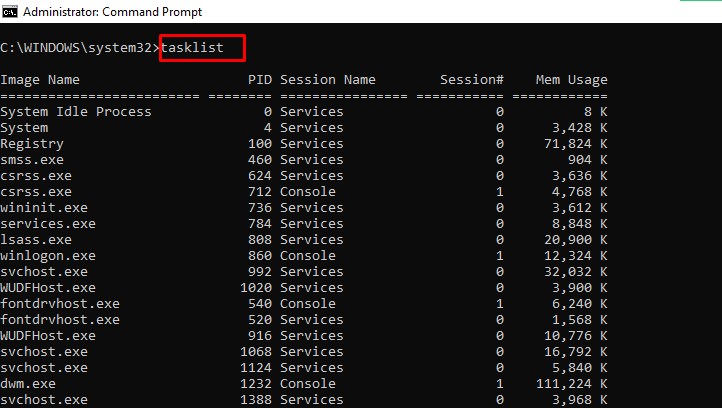
tasklist – Shows Open Programs
You can do the same thing you do with the task manager with this command:
The next command shows you how to close an open task.
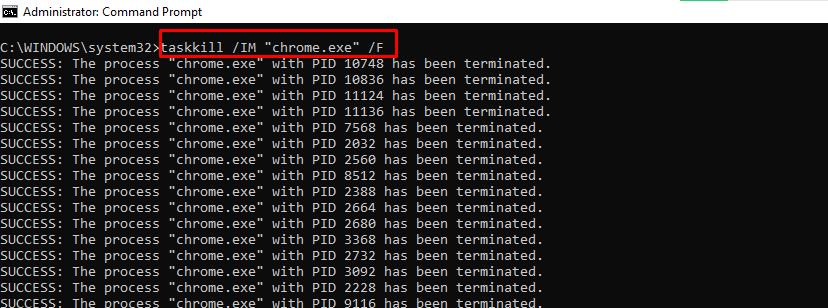
taskkill – Terminates a Running Task
To kill a task, run taskkill /IM "task.exe" /F. For example, taskkill /IM "chrome.exe" /F:
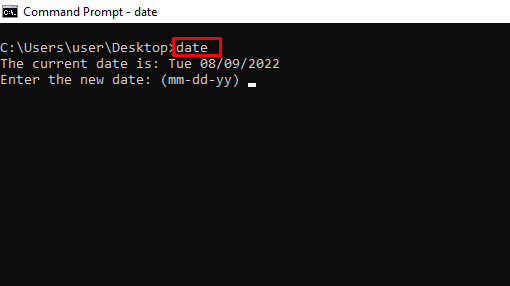
date – Shows and Changes the Current Date
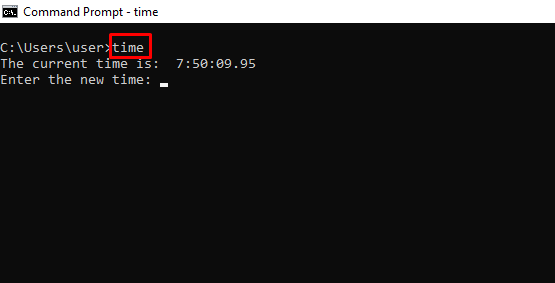
time – Shows and Changes the Current Time
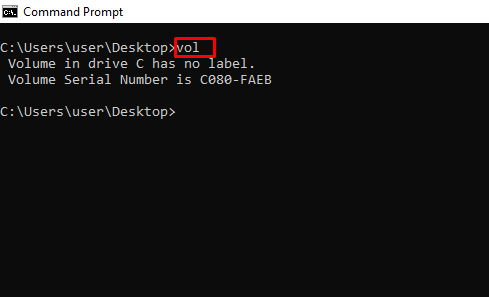
vol – Shows the Serial Number and Label Info of the Current Drive
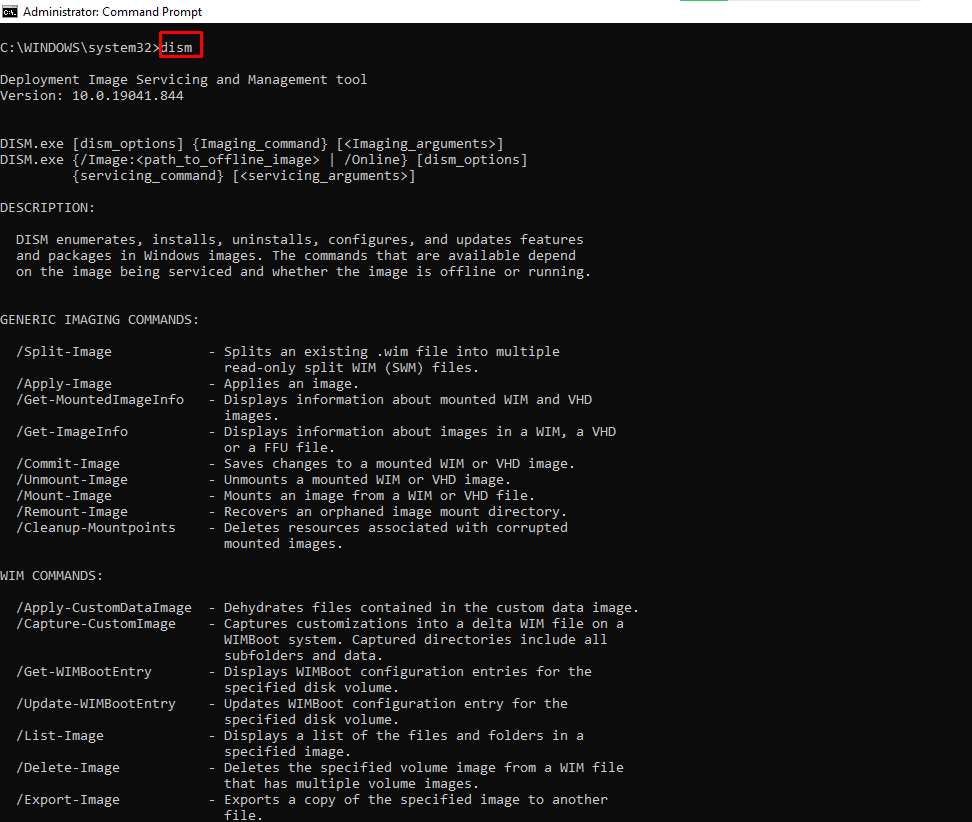
dism – Runs the Deployment Image Service Management Tool
CTRL + C – Stops the Execution of a Command
-help – Provides a Guide to other Commands
For example, powercfg -help shows how to use the powercfg command
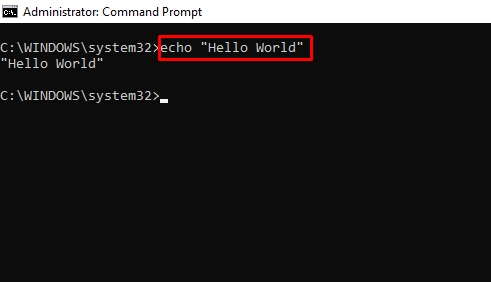
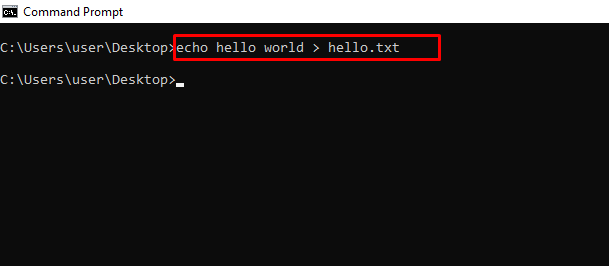
echo – Shows Custom Messages or Messages from a Script or File
You can also use the echo command to create a file with this syntax echo file-content > filename.extension.
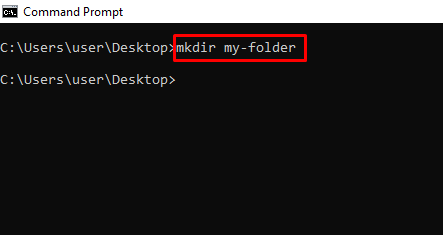
mkdir – Creates a Folder
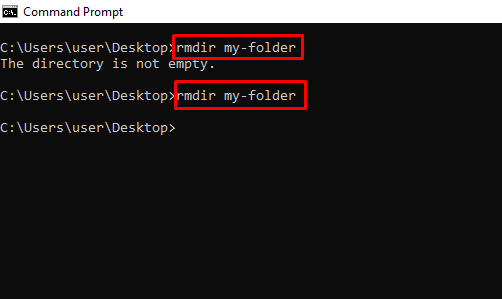
rmdir – Deletes a Folder
N.B.: The folder must be empty for this command to work.
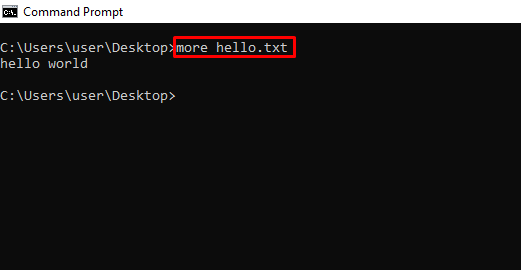
more – Shows More Information or the Content of a File
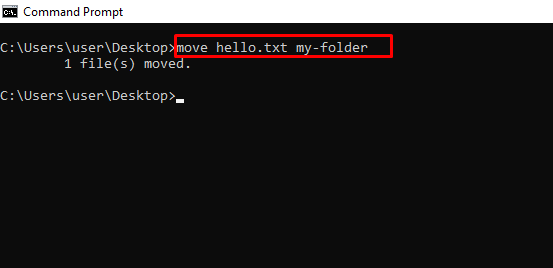
move – Moves a File or Folder to a Specified Folder
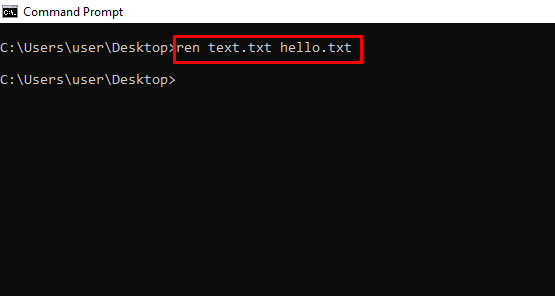
ren – Renames a File with the Syntax ren filename.extension new-name.extension
cls – Clears the Command Line
In case you enter several commands and the command line gets clogged up, you can use cls to clear all entries and their outputs.
exit – Closes the Command Line
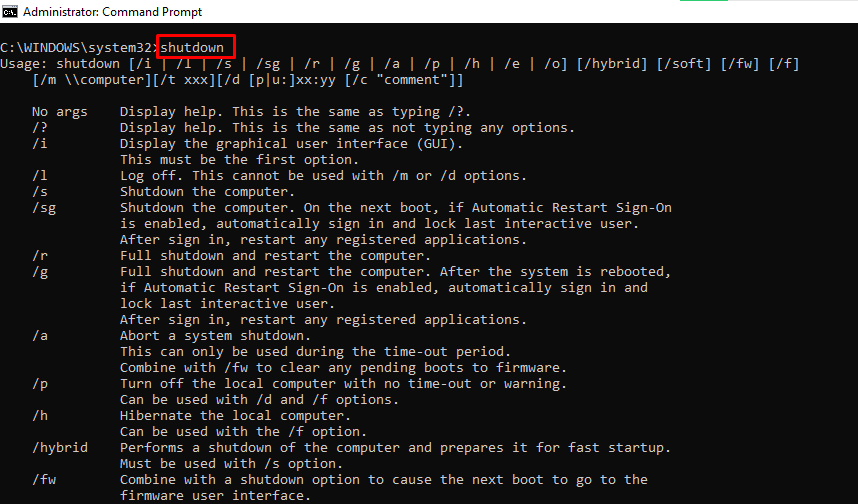
shutdown – Shuts down, Restarts, Hibernates, Sleeps the Computer
You can shut down, restart, hibernate, and sleep your PC from the command line.
Enter shutdown in the command line so you can see the extensions you can use to perform the actions. For example, shutdown /r will restart your computer.
Conclusion
This article showed you several “unknown-to-many” commands you can use to get access to hidden functionalities on your Windows PC.
Again, you should be careful while working with these commands because they can have a lasting effect on your OS.
If you find the commands helpful, share the article with your friends and family.
In case you know another useful command I did not list, tell me about it on Twitter. I will add it and mention you as the source.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
3
Problem :
When writing long commands, sometimes I want to clear the line in one shot.
I know how to do it in Windows : Hold Shift, Home key, then delete. However this doesn’t work in command prompt. How can I do this?
- windows
- command-line
Improve this question
edited Jul 6, 2015 at 20:24
Cher
asked Jul 6, 2015 at 20:19
CherCher
2,79910 gold badges37 silver badges64 bronze badges
0
Add a comment
|
1 Answer
Sorted by:
Reset to default
10
Hit Esc to clear the current command.
Improve this answer
answered Jul 6, 2015 at 20:29
glenn jackmanglenn jackman
240k38 gold badges222 silver badges354 bronze badges
Add a comment
|
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by Artificial Intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Sign up using Google
Sign up using Facebook
Sign up using Email and Password
Post as a guest
Name
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge that you have read and understand our privacy policy and code of conduct.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
- windows
- command-line
or ask your own question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
- windows
- command-line
or ask your own question.
How can I clear the current line in the command prompt? (I’m using Windows 7.)
Too often, I enter a command, execute it, get many lines of output, then wish to enter another command. But before entering the second command, I press the up arrow key to review the first command, then I find I have to hold backspace for 30-or so characters. (I can’t just press down again to get an empty line. Nor can I get it by pressing up again.)
asked Mar 5, 2012 at 18:43
2
The Escape (Esc) key will clear the input line.
In addition, pressing Ctrl+C will move the cursor to a new, blank line. This may be helpful as the input you just reviewed remains visible while you type the new command.
answered Mar 5, 2012 at 18:45
Myrddin EmrysMyrddin Emrys
2,3813 gold badges21 silver badges29 bronze badges
12
Aside from the two that Myyrddin covered — Esc and Ctrl+C — there are also two more shortcuts related to clearing the current input in CMD.
Ctrl+Home will clear all characters in the input before the cursor (equivalent to Ctrl+U in Bash)
Ctrl+End will clear all characters in the input after the cursor (equivalent to Bash’s Ctrl+K)
Both are fairly useful and, once internalised and gotten used to, could speed up editing in CMD by quite a bit.
answered Nov 22, 2016 at 23:39
Hashim AzizHashim Aziz
12.1k35 gold badges99 silver badges167 bronze badges
5
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.