Please try the following commands
List all files in the current directory & subdirectories
dir /b/s *.txt
The above command searches for all txt file in the directory tree.
But as windows is started naming directories as
.nuget,.vscodeit also comes with the command above.
In order to avoid this and have a clean list use /a:-d filter as
dir /a:-d /b/s
Before using it just change the directory to root using
cd/
There is one more hacky command to do the same
for /r %f in (*) do @echo %f
Note: If you miss the
@echopart in the command above it will try to execute all the files in the directories, and the/ris what making it recursive to look deep down to subdirectories.
Export result to text file
you can also export the list to a text file using
dir /b/s *.exe >> filelist.txt
and search within using
type filelist.txt | find /n "filename"
If you are looking for files with special attributes, you can try
List all Hidden Files
dir /a:h-d /b/s
List all System Files
dir /a:s-d /b/s
List all ReadOnly Files
dir /a:r-d /b/s
List all Non Indexed Files
dir /a:i-d /b/s
If you remove the -d from all commands above it will list directories too.
Using where in windows7+:
Although this dir command works since the old dos days but Win7 added something new called Where
where /r c:\Windows *.exe *.dll
will search for exe & dll in the drive c:\Windows as suggested by @SPottuit you can also copy the output to the clipboard with
where /r c:\Windows *.exe |clip
just wait for the prompt to return and don’t copy anything until then.
Page break with more
If you are searching recursively and the output is big you can always use more to enable paging, it will show -- More -- at the bottom and will scroll to the next page once you press SPACE or moves line by line on pressing ENTER
where /r c:\Windows *.exe |more
For more help try
where/?
Please try the following commands
List all files in the current directory & subdirectories
dir /b/s *.txt
The above command searches for all txt file in the directory tree.
But as windows is started naming directories as
.nuget,.vscodeit also comes with the command above.
In order to avoid this and have a clean list use /a:-d filter as
dir /a:-d /b/s
Before using it just change the directory to root using
cd/
There is one more hacky command to do the same
for /r %f in (*) do @echo %f
Note: If you miss the
@echopart in the command above it will try to execute all the files in the directories, and the/ris what making it recursive to look deep down to subdirectories.
Export result to text file
you can also export the list to a text file using
dir /b/s *.exe >> filelist.txt
and search within using
type filelist.txt | find /n "filename"
If you are looking for files with special attributes, you can try
List all Hidden Files
dir /a:h-d /b/s
List all System Files
dir /a:s-d /b/s
List all ReadOnly Files
dir /a:r-d /b/s
List all Non Indexed Files
dir /a:i-d /b/s
If you remove the -d from all commands above it will list directories too.
Using where in windows7+:
Although this dir command works since the old dos days but Win7 added something new called Where
where /r c:\Windows *.exe *.dll
will search for exe & dll in the drive c:\Windows as suggested by @SPottuit you can also copy the output to the clipboard with
where /r c:\Windows *.exe |clip
just wait for the prompt to return and don’t copy anything until then.
Page break with more
If you are searching recursively and the output is big you can always use more to enable paging, it will show -- More -- at the bottom and will scroll to the next page once you press SPACE or moves line by line on pressing ENTER
where /r c:\Windows *.exe |more
For more help try
where/?
Is Windows search too slow for you? Learn how to speed up your search using the find command in the Command Prompt window.
Windows has some built-in search capabilities, but they may not be to your liking. Cortana or the standard Search box on the Taskbar and the Search box in File Explorer in Windows 10 allow you to search through file contents, but they can be slow, especially the File Explorer search.
There’s a faster way to search the contents of files on your hard drive using the command line. The find command searches for text strings in files and returns the lines of text from the files in which the text string was found.
NOTE: The find command is not suitable for large files or large numbers of files.
Today we’ll cover how to use the find command and we’ll provide some examples.
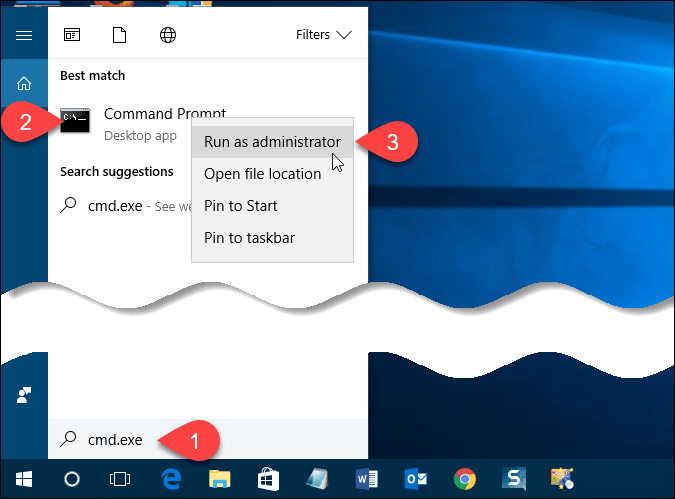
Open the Command Prompt Window with Administrative Privileges
Opening the Command Prompt window as administrator is not necessary. However, it does help you avoid annoying confirmation dialog boxes. Just be careful what commands you run as administrator on the command line. Using the find command as administrator is safe as it doesn’t change or delete any files.
Enter cmd.exe in the Search box on the Taskbar. Then, right-click on the Command Prompt item under Best match and select Run as administrator from the popup menu.
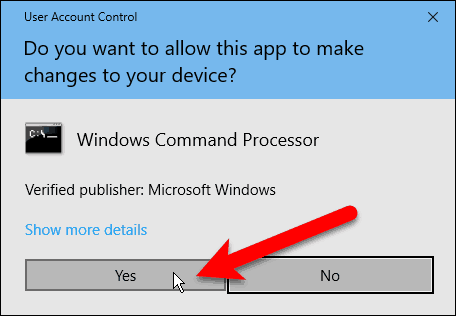
If the User Account Control dialog box displays, click Yes to continue.
NOTE: You may not see this dialog box, depending on your User Account Control settings. We don’t recommend disabling UAC entirely.
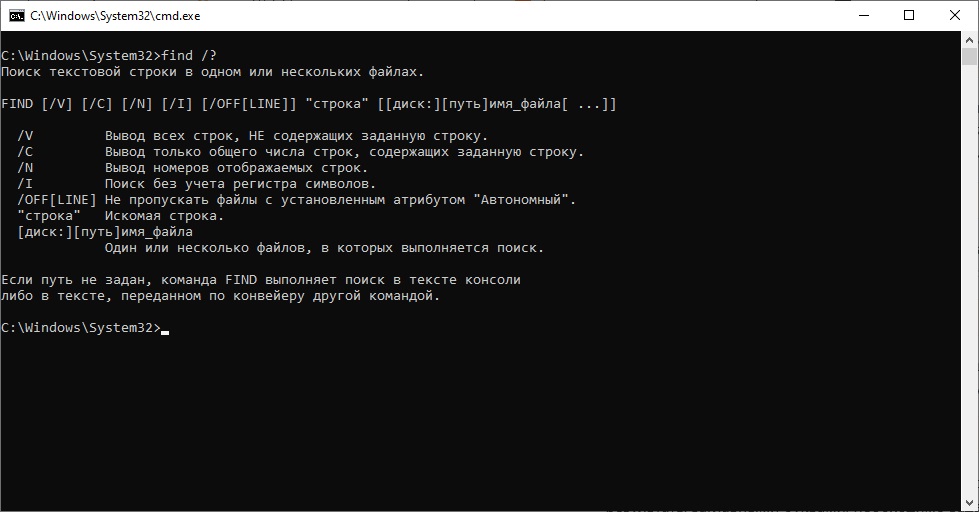
Switches and Parameters for the find Command
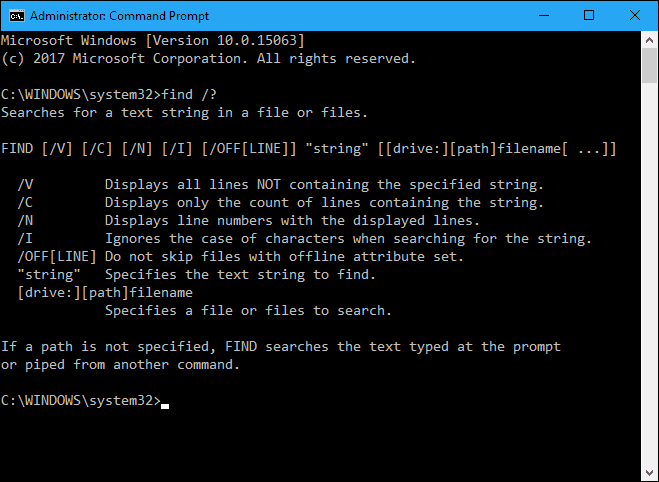
Most commands have optional switches that modify the default operation of the command. You can get help to see all the available switches for the find command by typing the following line at the prompt and pressing Enter.
find /?
The switches can be lowercase or uppercase.
For the “string” parameter, you must surround the string with double quotes, otherwise the find command will not work and will return an error.
The [drive:][path]filename parameter can be anything from a drive letter to a single file or multiple files.
Syntax for the find Command
A command’s syntax is a specific way to organize the command and its switches and parameters. The following is the general syntax for the find command.
find [switches] "string" [pathname/s]
The switches can be in any order as long as they’re before the “string” parameter. The brackets [] indicate that the switch or parameter is optional.
Search a Single Document for a Text String
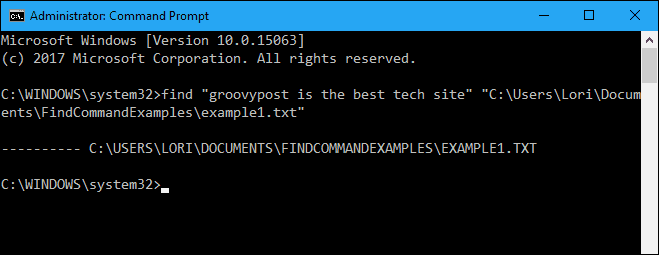
First, we’ll show you how to search one document for all occurrences of a text string. The following command searches the example1.txt file for the phrase “groovypost is the best tech site”.
find "groovypost is the best tech site" "C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples\example1.txt"
NOTE: If there are spaces in any part of the path or file name, you must put quotes around the entire path, like we did in the above command. The quotes are not really needed in this case, but it doesn’t hurt to have them.
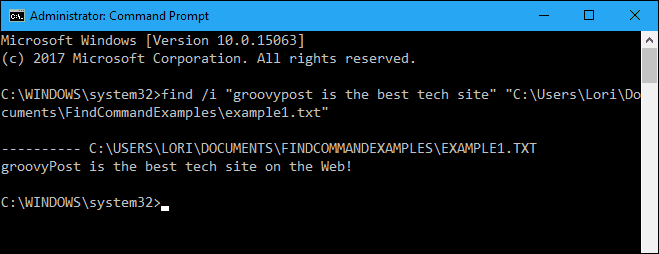
Notice that the phrase was not found in the above example (nothing is listed below the path to the file), even though it is in the file. That’s because the case in “groovypost” did not match what was in the file, which is “groovyPost”. Add the “/i” (lowercase or uppercase letter “i”) switch right after the find command (before the phrase) to ignore the case when looking for the text phrase.
find /i "groovypost is the best tech site" "C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples\example1.txt"
Now, the phrase was found and the entire line containing the phrase prints to the screen below the path to the file being searched.
Search Multiple Documents for the Same Text String
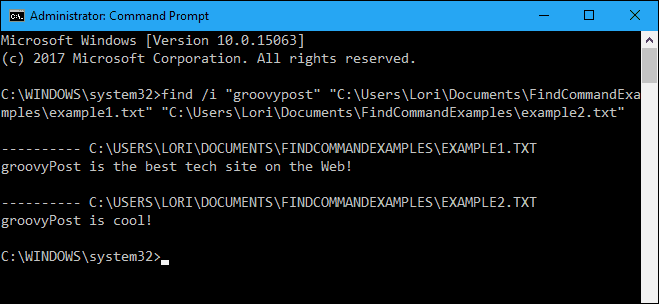
Now that you can search one file for a text string, let’s search multiple files for the same text string.
You can specify multiple files to search in the find command by putting the path to each file in quotes separated by a space.
find /i "groovypost" "C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples\example1.txt" "C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples\example2.txt"
You could also search all text files in a directory using the wildcard character, which is an asterisk (*), as shown in the following command.
find /i "groovypost" "C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples\*.txt"
The search term was found in both documents and the sentences in which they were found are listed under the full path to each file.
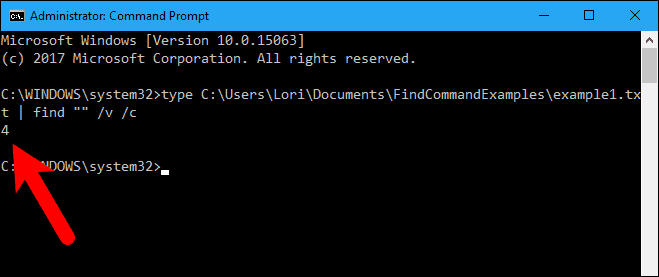
Count the Number of Lines in a File
If you want to know how many lines there are in a file, you can use a combination of the type and find commands. The type command displays the contents of one or more text files.
We piped the results of the type command into the find command using the vertical bar (|). We used the “/v” switch to display all lines NOT containing the “” string, so every line with text will be counted. To display only the number of lines in the text file (not the lines themselves), we use the “/c” switch.
type C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples\example1.txt | find "" /v /c
Send the Output of Another Command to the Find Command
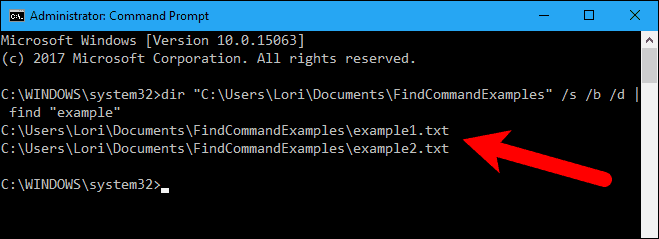
You can also search all file names in a directory for a certain string by piping the output of the dir command to the find command.
For example, we got the directory listing of the C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples directory and any subdirectories in that directory (“/s” switch). We also specified to use the bare format with no heading information or summary (“/b” switch) and to display the listing in the same format as the wide list format (“/w” switch) but sorted by column (“/d” switch).
Then, we pipe (|) the output of the dir command into the find command, only adding “example” as the parameter. We didn’t add any switches to the find command. The file names to search come from the output of the dir command.
dir "C:\Users\Lori\Documents\FindCommandExamples" /s /b /d | find "example"
Do you prefer using the find command or the Search box in File Explorer? How have you used the find command? Share your ideas and examples with us in the comments below.
- 01.02.2020
- 12 249
- 0
- 04.08.2021
- 10
- 10
- 0
- Содержание статьи
- Описание
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Примечания
- Примеры
- Справочная информация
- Добавить комментарий
FIND — Поиск заданной строки текста в файле или нескольких файлах.
Описание
После поиска в заданных файлах команда find выведет на экран все строки из этих файлов, содержащие заданный образец.
Синтаксис
find [/v] [/c] [/n] [/i] "строка" [[диск:][путь]ИмяФайла[...]]Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| /v | Выводит все строки, не содержащие строку, заданную параметром строка |
| /c | Подсчет строк, содержащих строку, указанную параметром строка, и отображение общего количества |
| /n | Выводит номера строк перед самими строками |
| /i | Задает поиск без различия строчных и заглавных букв |
| «строка_поиска» | Обязательный параметр. Указывает группу символов, поиск которой будет производиться. Необходимо заключить параметр строка в кавычки («строка») |
| [диск:][путь] ИмяФайла | Задает местоположение и имя файла, в котором будет производиться поиск заданной строки символов |
| /? | Отображение справки в командной строке |
Примечания
- Если ключ /i не указан, команда find ищет именно то, что указано в параметре строка. Например, для команды find символы «a» и «A» являются различными. Если используется ключ /i, команда find не различает строчные и прописные буквы, и символы «a» и «A» являются одинаковыми.
- Если строка поиска содержит кавычки, при вызове команды каждая кавычка в строке поиска должна быть заменена двумя символами кавычек («СтрокаСодержания»»Кавычки»).
- Если имя файла пропущено, find действует как фильтр, получая ввод из стандартного источника вывода (обычно клавиатура, канал или файл перенаправления), и выводит все строки, содержащие параметр строка.
- Параметры и ключи команды find могут быть заданы в произвольном порядке.
- Подстановочные знаки (* и ?) не могут быть использованы в именах файлов и расширениях, задаваемых в команде find. Чтобы искать строку в множестве файлов, указанных с помощью подстановочных знаков, можно использовать команду find в команде for.
- Если в одной команде заданы ключи /c и /v, команда find выведет на экран количество строк, которые не содержат заданную строку поиска. Если в одной команде указаны оба ключа: /c и /n, команда find игнорирует ключ /n.
- Команда find не распознает символ перевода строки. Когда команда find используется для поиска текста в файле, который содержит символы перевода строки, необходимо ограничить строку поиска текстом, который может быть найден между символами перевода строки (строка не может прерываться символом перевода строки). Например, find не найдет совпадение для строки «файл налогов» если перевод строки в файле стоит между словами «файл» и «налогов».
Примеры
Для вывода всех строк из файла Pencil.ad, которые содержат слова «Точилка» служит следующая команда:
find "Точилка" pencil.adДля поиска строки, содержащей текст, указанный в кавычках, необходимо сначала заключить в кавычки всю строку. Во-вторых, необходимо использовать двойные кавычки для каждых кавычек, содержащихся в строке. Для поиска фразы «Точилка» (именно с ковычками в файле Pencil.ad:
find ""Точилка"" pencil.adЕсли поиск требуется провести в нескольких файлах, следует использовать команду find с командой for. Для поиска файлов с расширением .bat, содержащих строку «PROMPT», можно использовать следующую команду:
for %f in (*.bat) do find "PROMPT" %fДля поиска на жестком диске C файлов, содержащих строку «CPU» и отображения их имен используйте символ канала (|), чтобы направить результаты команды dir в команду find:
dir c:\ /s /b | find "CPU"Так как команда find проводит поиск, различая строчные и заглавные буквы, а команда dir выводит результаты заглавными буквами, необходимо задать строку «CPU» заглавными буквами или использовать ключ /i в команде find.
Справочная информация
I want a command to search for a file in a directory and all sub directories in windows using the command line. I saw all the available commands but I couldn’t find any suitable command to do this operation.
fixer1234
27.1k61 gold badges76 silver badges117 bronze badges
asked Aug 18, 2010 at 6:52
At prompt (Command Line) type:
dir /S /P "Path\FileName"
If you want to save the results in a text file:
dir /S "Path\FileName" > "Path\ResultFilename"
answered Aug 18, 2010 at 7:14
Matan EldanMatan Eldan
2,6771 gold badge22 silver badges22 bronze badges
3
use the /b switch to dir to print full path might be helpful.
say, C:\ > dir /b /s *file*.*
still, you can filter the result with find or for, and redirect output to file with >filename
answered Aug 18, 2010 at 7:30
JokesterJokester
1,6833 gold badges14 silver badges21 bronze badges
dir was not meant for searching files but to list directories, but now there is where which can be used to search multiple file types as
where /R c:\Users *.dll *.exe *.jpg
do check the full syntax and the answer for How to do a simple file search in cmd
WHERE [/R dir] [/Q] [/F] [/T] pattern...
Description:
Displays the location of files that match the search pattern.
By default, the search is done along the current directory and
in the paths specified by the PATH environment variable.
Parameter List:
/R Recursively searches and displays the files that match the
given pattern starting from the specified directory.
/Q Returns only the exit code, without displaying the list
of matched files. (Quiet mode)
/F Displays the matched filename in double quotes.
/T Displays the file size, last modified date and time for all
matched files.
pattern Specifies the search pattern for the files to match.
Wildcards * and ? can be used in the pattern. The
"$env:pattern" and "path:pattern" formats can also be
specified, where "env" is an environment variable and
the search is done in the specified paths of the "env"
environment variable. These formats should not be used
with /R. The search is also done by appending the
extensions of the PATHEXT variable to the pattern.
/? Displays this help message.
NOTE: The tool returns an error level of 0 if the search is
successful, of 1 if the search is unsuccessful and
of 2 for failures or errors.
Examples:
WHERE /?
WHERE myfilename1 myfile????.*
WHERE $windir:*.*
WHERE /R c:\windows *.exe *.dll *.bat
WHERE /Q ??.???
WHERE "c:\windows;c:\windows\system32:*.dll"
WHERE /F /T *.dll
answered Dec 24, 2017 at 21:57
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.