3 Answers
Sometimes this type of error is showing while installing a certain application
(like Python) in the windows 7 platform.
For Solution, you have to install service pack 1 to your os. You can also install the service pack for windows manually as described below.
- Open regedit (By clicking windows+R key, type regedit and then click enter)
- Go to HKEY-LOCALMACHINE->SYSTEM->Control->Windows.
- open CSDVersion
- Set the value as you want(Like 100 for servicepack 1, 200 for servicepack 2)
and then click ‘Ok’. - Restart your PC
Now you can install application
answered Jan 31, 2020 at 13:17
2
-
Thanks so much! we are looking for this for weeks.
Apr 30, 2020 at 21:20
-
I had to look up for the
CSDVersionkey because it wasn’t where you pointed it, the right key name isHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Windows. The instruction works for the 3.6.8 release (but not for 3.8.3), but the installation stops before finish with an «unspecified error» 0x80240017. The installation log says:Error 0x80240017: Failed to execute MSU package.andError 0x80240017: Failed to configure per-machine MSU package.among other messages.Jul 12, 2020 at 1:53
Try to install Python 3.7.5 in Windows 7 service pack 1. It doesn’t require windows updates.
answered Jul 14, 2022 at 10:32
1
-
Time and money saving solution (+1)!
Aug 10, 2022 at 8:31
with windows 7 sp1 python 3.5.2 got successfully installed. Pls also chk if windows visual c++ 2015 redistributable is properly installed..
answered Jun 19, 2017 at 5:24
sabrangsabrang
191 gold badge1 silver badge3 bronze badges
Python is widely used programming language for beginners and experienced coders. In Python higher version got some extra features for implementing a new concept. When installing python in windows 7, occur some error windows 7 service pack is required and all applicable required updates in python. I search lot of websites links are not downloading windows 7 service pack 1. Finally, I found a solutionlog file in python so windows build versions has not an option for service pack 1. I uploaded the video and provided link for windows 7 service pack 1.
for for python 3.7 and above please watch this video
Download For 32 Bit
Download For 32 Bit
Download For 32 Bit LINK2
Download For 32 Bit Link 2
Download For 64 Bit
Download For 64 Bit
Download For 64 Bit Link2
Download For 64 Bit Link 2
Official Site
Official Site
Tutorial Video
Video Link
November 06, 2018
This page will walk through getting started with Python. Python is an easy-to-learn object-oriented programming language. Python is an interpreted language with elegant syntax and dynamic typing. Python codes are written in .py file extension. We can install Python in our system downloading directly from Python website or we can use python installers such as Anaconda, Enthought Canopy, Python(x,y), WinPython etc. To develop Python projects we can use Python IDEs such as Thonny, Komodo, LiClipse, NetBeans, Spyder, LiClipse etc. To work with Python web project we can use Python web frameworks such as Django, Pyramid, TurboGears, Flask, Bottle, CherryPy, Sanic, Tornado etc. In our demo we will install Python 3 using Anaconda that will install Python in our system and many tools for Python development such as Spyder, Jupyter Notebook etc. To create Python web project we will use Django web framework which is bundled with its own lightweight and standalone server. Now we will get started with Python step-by-step.
Contents
- Technologies Used
- Python Installation
- Install Anaconda
- Working with Anaconda Prompt
- Working with Jupyter Notebook
- Working with Spyder IDE
- Python Web Development using Django
- References
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.
1. Python 3.7.0
2. Anaconda 5.3
3. Django 2.1.2
Python Installation
To install Python, visit the link.
1. Installing Python on Windows 7 may pop up message as «Windows 7 service pack 1 and all applicable updates are required to install python». So before installing Python on Windows 7, we need to install service pack 1.
2. We can also use Anaconda Distribution that will install Python in our system and other required libraries. To install Python using Anaconda Distribution on Windows 7, it does not require service pack 1. In our tutorial we will install Anaconda Distribution for Python.
Install Anaconda
To install Anaconda, visit the link. In our demo we are installing Anaconda 5.3 that will install Python 3.7.0 in our system. After Anaconda installation, we can see following items in our programs.
1. Anaconda Navigator
Anaconda Navigator provides application links such as Jupyter Lab, Jupyter Notebook, Qt Console, Spyder, VS code etc. It also provides Anaconda environment information and links for leaning and community.
2. Anaconda Prompt
Using Anaconda prompt we can run python command and write python scripts. Anaconda prompt also runs conda and pip command that can be used to manage python packages and install required plugin or tools.
3. Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook is a web application that is used to create and share documents containing live code, text etc.
4. Spyder
Spyder is an IDE for Python development. We can run and debug Python code and can launch IPython console.
5. Reset Spyder settings
It resets Spyder IDE settings.
Working with Anaconda Prompt
Using Anaconda prompt we can run python command and write python scripts and can run conda and pip command. Here we will create a sample Python code and run it using Anaconda Prompt.
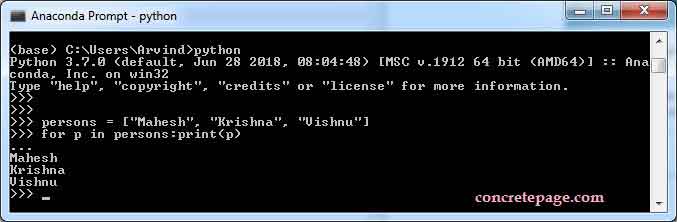
Go to the Anaconda prompt and type python command. We will see following message.
(base) C:\Users\Arvind>python Python 3.7.0 (default, Jun 28 2018, 08:04:48) [MSC v.1912 64 bit (AMD64)] :: Anaconda, Inc. on win32 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
To know Python version, we can use following command from Anaconda prompt.
Now write a sample Python code. Here we are using for loop to print array elements. Find the code
>>> persons = ["Mahesh", "Krishna", "Vishnu"] >>> for p in persons:print(p)
Output will be as following.
Find the print screen.
To exit from Python console, use exit() command. Now we will write code in in a file. File extension should be .py . Suppose we have following file.
person_details.py
persons = ["Mahesh", "Krishna", "Vishnu"]
for p in persons:
print(p)
Open the Anaconda Prompt and navigate to the person_details.py file location and run following command.
Working with Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook is a web application that is used to create and share documents containing live code, text etc. Here we will write and run sample Python code using Jupyter Notebook.
Go to the Jupyter Notebook and we will see a message in command prompt as following.
Copy/paste this URL into your browser when you connect for the first time,
to login with a token:
http://localhost:8888/?token=68acf093500c313791571a8cc009e645bda53a3b83bfa9f5
Access the above URL in web browser. Click on the New button on the right side and select Python 3. We will reach to a URL as following.
http://localhost:8888/notebooks/Untitled1.ipynb?kernel_name=python3
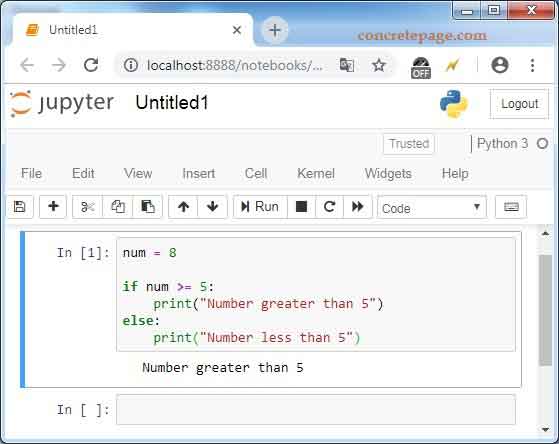
This URL (not localhost) can be used from anywhere to write, edit and run the code. Write a sample code as following.
num = 8
if num >= 5:
print("Number greater than 5")
else:
print("Number less than 5")
Code is saved automatically. Now run the program using Run button given on the header. Output will be as following.
Find the print screen.
Working with Spyder IDE
Spyder is an IDE for Python development. We can run and debug Python code using Spyder.
Note: If Spyder is opening black screen, it is the pyqt issue. Run the conda install pyqt=5.6 command from Anaconda Prompt and after installing pyqt, rerun the Spyder.
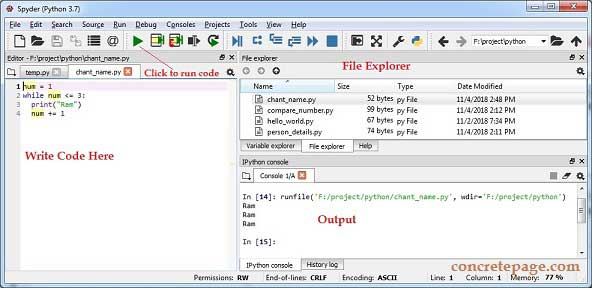
On the left side, by default, we will see a temp.py file where we can write Python code and run using run button in the header. On the bottom we will see IPython Console where we will get output. On the right side and at the top we can see the file explorer using which we can open the directory that contains our Python files and access the file that will open on left side. Suppose we access following file in Spyder IDE and run it.
chant_name.py
num = 1
while num <= 3:
print("Ram")
num += 1
Output in IPython console.
Find the print screen.
Python Web Development using Django
For the Python web development, there are many frameworks such as Django, Pyramid, TurboGears, Flask, Bottle, CherryPy, Sanic, Tornado etc. Here in our demo we will create Python web project using Django framework. Django web framework is bundled with its own lightweight and standalone server for development and testing.
1. Install Django
To install Django, open the Anaconda Prompt and run the following command.
conda install -c anaconda django
To confirm the Django installation, run the command.
2. Create Virtual Environment
To work with Django project, first we need to create virtual environment. Open the Anaconda Prompt and run the following command.
conda create -n myDjangoEnv python=3.7 anaconda
The above command will create virtual environment within the envs directory inside the anaconda installation directory. We can also assign the desired path for virtual environment using following command.
conda create -n F:\project\python\myDjangoEnv python=3.7 anaconda
3. Create Project
Now we will create our Django project. Navigate to the required location using Anaconda Prompt where we want to create our Django project and run the following command.
django-admin startproject myDjangoProject
We will get following directory and file structure.
myDjangoProject
|
|--manage.py
|--myDjangoProject
| |
| |--__init__.py
| |--settings.py
| |--urls.py
| |--wsgi.py
Now navigate to myDjangoProject root directory using Anaconda Prompt and run following command.
python manage.py runserver
The above command will start the project at following URL.
Access the above URL on browser and we will see Django success message. To change the IP and port, we can use following command.
python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8282
This will start project at 8282 port.
4. Create web page with «Hello World!» message
Look into the urls.py file.
urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]
The /admin/ URL is created by default. Now we will create our own URL that will display «Hello World!» message.
First import HttpResponse as following.
from django.http import HttpResponse
Now define the view.
def helloWorld(request):
return HttpResponse(
'<h1>Hello World!</h1>'
)
Configure URL pattern.
urlpatterns = [
path('hello/', helloWorld),
------
]
Complete urls.py file will look as following.
urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.http import HttpResponse
def helloWorld(request):
return HttpResponse(
'<h1>Hello World!</h1>'
)
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('hello/', helloWorld),
]
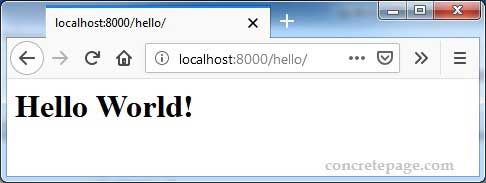
Now access the below URL.
http://localhost:8000/hello/
Find the print screen.
5. Using variables in HTML template
First we need to import engines as following.
from django.template import engines
Now create the definition for address that has name and city as variable.
def personAddress(request):
address_template = '''<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Address</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Name: {{ name }}</p>
<p>City: {{ city }}</p>
<p><a href="{% url 'helloPage' %}">Return to the Hello Page</a>.</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
name = 'Mahesh'
city = 'Varanasi'
django_engine = engines['django']
template = django_engine.from_string(address_template)
html = template.render({'name': name, 'city': city})
return HttpResponse(html)
In our HTML template we are also adding a link to navigate to hello page. Now find the URL pattern.
urlpatterns = [
path('hello/', helloWorld, name="helloPage"),
path('address/', personAddress),
------
]
Find the complete urls.py file.
urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.template import engines
# Hello world
def helloWorld(request):
return HttpResponse(
'<h1>Hello World!</h1>'
)
# Using variable in HTML template
def personAddress(request):
address_template = '''<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Address</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Name: {{ name }}</p>
<p>City: {{ city }}</p>
<p><a href="{% url 'helloPage' %}">Return to the Hello Page</a>.</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
name = 'Mahesh'
city = 'Varanasi'
django_engine = engines['django']
template = django_engine.from_string(address_template)
html = template.render({'name': name, 'city': city})
return HttpResponse(html)
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('hello/', helloWorld, name="helloPage"),
path('address/', personAddress),
]
Access the URL as following.
http://localhost:8000/address/
6. Access URL query parameters
Find the definition for welcome page by name. We will pass name as query parameter in URL.
def welcome(request):
name = request.GET.get('name', '')
return HttpResponse(
'<h1>Welcome '+ name +'!</h1>'
)
Add the URL pattern as following.
urlpatterns = [
path('welcome/', welcome),
------
]
Find the complete urls.py file.
urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.template import engines
# Hello world
def helloWorld(request):
return HttpResponse(
'<h1>Hello World!</h1>'
)
# Using variable in HTML template
def personAddress(request):
address_template = '''<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Address</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Name: {{ name }}</p>
<p>City: {{ city }}</p>
<p><a href="{% url 'helloPage' %}">Return to the Hello Page</a>.</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
name = 'Mahesh'
city = 'Varanasi'
django_engine = engines['django']
template = django_engine.from_string(address_template)
html = template.render({'name': name, 'city': city})
return HttpResponse(html)
# Access URL query parameters
def welcome(request):
name = request.GET.get('name', '')
return HttpResponse(
'<h1>Welcome '+ name +'!</h1>'
)
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('hello/', helloWorld, name="helloPage"),
path('address/', personAddress),
path('welcome/', welcome),
]
Access the URL as following.
http://localhost:8000/welcome/?name=Mahesh
References
Home — Python Programming Language
The Python Tutorial
Home — Anaconda
Django
The computer was broken by installing RHEL yesterday. After reinstalling the system, download and install python3, and the result is a problem
One or more issues caused the setup to fail.Please fix the issues and then retry setup.For more information see the log file.
Windows 7 Service Pack 1 and all applicable updates are required to install Python 3.6.4(64-bit).
Please update your machine and then restart the installation.
It can’t be installed. It turns out to be a problem of my Windows system. I need to install the SP1 package upgrade package. The download address of the upgrade package is: https://www.microsoft.com/zh-CN/download/details.aspx?id=5842
Download instructions: According to my system version selection, my system is 64-bit, I chose Windows_Win7SP1.7601.17514.101119-1850.AMD64CHK.Symbols.msi (independent debugging symbols for 64-bit computers (verified version) ) This contains debugging symbols for Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1)

After the download is complete, the installation is basically all the way to the next step.
After downloading and installing, I restarted the system and installed python3.6 again, but it did not succeed, the same problem. So I started Windows Update and updated the package, but sp1 always failed to update
Then I went back to the beginning
https://www.microsoft.com/zh-CN/download/details.aspx?id=5842
Chose another version After the installation is complete, you can install python3.6
After the installation is complete, you can install python3.6 , Here I have another problem after installing python.
, Here I have another problem after installing python.
Unable to start the program because api-ms-win-crt-runtime- | 1-1-0.dll is missing from the computer. Try to reinstall the program to resolve this issue
Solution: download and install vc_redist.x64.exe, download address
Link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1kXb1nLl Password: p84n
Restart the system after downloading and installing, and it will be OK after restarting! So far the problem is solved perfectly.
After the installation is complete, if you need to activate the windows system, the activation tool Baidu network disk address link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jJbSYLS password: 17ii There are several activation tools, always one option fit for you.
Posted on Thursday, August 31, 2017 by admin
with windows 7 sp1 python 3.5.2 got successfully installed. Pls also chk if windows visual c++ 2015 redistributable is properly installed..
Sometimes this type of error is showing while installing a certain application
(like Python) in the windows 7 platform.
For Solution, you have to install service pack 1 to your os. You can also install the service pack for windows manually as described below.
- Open regedit (By clicking windows+R key, type regedit and then click enter)
- Go to HKEY-LOCALMACHINE->SYSTEM->Control->Windows.
- open CSDVersion
- Set the value as you want(Like 100 for servicepack 1, 200 for servicepack 2)
and then click ‘Ok’. - Restart your PC
Now you can install application
Tags:
python
windows






 After the installation is complete, you can install python3.6
After the installation is complete, you can install python3.6 , Here I have another problem after installing python.
, Here I have another problem after installing python.