По-умолчанию настройки Windows запрещают запуск скриптов PowerShell. Это необходимо для предотвращения запуска вредоносного кода на PowerShell. Настройки политик запуска PowerShell скриптов определяются в Execution Policy. В этой статье мы рассмотрим доступные политики запуска PS скриптов, как изменить Execution Policy и настроить политики использования PowerShell скриптов на компьютерах в домене.
Содержание:
- Выполнение PowerShell скриптов запрещено для данной системы
- Как разрешить запуск скриптов PowerShell с помощью Execution Policy?
- Настройка PowerShell Execution Policy с помощью групповых политик
- Способы обхода политики PowerShell Execution
Выполнение PowerShell скриптов запрещено для данной системы
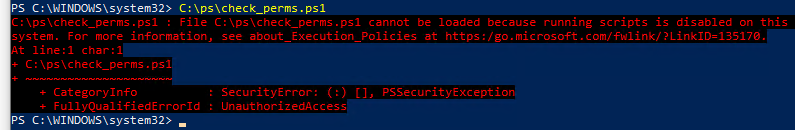
При попытке выполнить PowerShell скрипт (файл с расширением PS1) на чистой Windows 10, появляется ошибка:
File C:\ps\.ps1 cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system. For more information, see about_Execution_Policies at https:/go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170. + CategoryInfo : SecurityError: (:) [], PSSecurityException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnauthorizedAccess
Не удается загрузить файл.ps1, так как выполнение скриптов запрещено для данной системы.
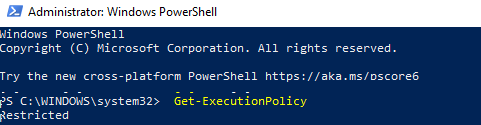
Текущее значение политики выполнения скриптов PowerShell на компьютере можно получить командой:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
Доступны следующие значения PowerShell Execution Policy:
- Restricted – запрещен запуск скриптов PowerShell, можно выполнять только интерактивные команды в консоли;
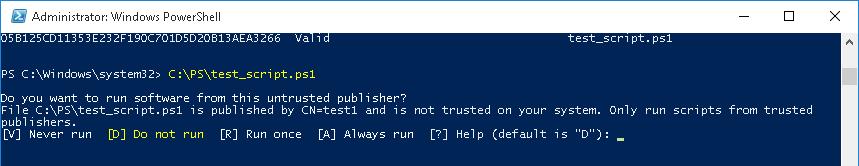
- AllSigned – разрешено выполнять только подписанные PS скрипты с цифровой подписью от доверенного издателя (можно подписать скрипт самоподписанным сертификатом и добавить его в доверенные). При запуске недоверенных скриптов появляется предупреждение:
Do you want to run software from this untrusted publisher? File .ps1 is published by CN=test1 and is not trusted on your system. Only run scripts from trusted publishers
- RemoteSigned – можно запускать локальные PowerShell скрипты без ограничения. Можно запускать удаленные PS файлы с цифровой подписью (нельзя запустить PS1 файлы, скачанные из Интернета, запущенные из сетевой папки по UNC пути и т.д.);
- Unrestricted – разрешен запуск всех PowerShell скриптов;
При запуске сторонних PowerShell скриптов может появляется предупреждение с подтверждением запуска, см. ниже.
- Bypass – разрешён запуск любых PS файлов (предупреждения не выводятся) – эта политика обычно используется для автоматического запуска PS скриптов без вывода каких-либо уведомлений (например при запуске через GPO, SCCM, планировщик и т.д.) и не рекомендуется для постоянного использования;
- Default – сброс настроек выполнения скриптов на стандартную;
В Windows 10 значение политики выполнения PowerShell по-умолчанию Restricted, а в Windows Server 2016 — RemoteSigned.
- Undefined – не задано. Применяется политика Restricted для десктопных ОС и RemoteSigned для серверных.
Как разрешить запуск скриптов PowerShell с помощью Execution Policy?
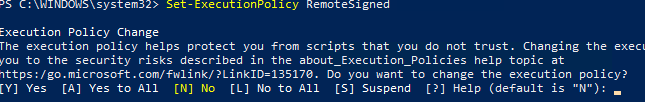
Чтобы изменить текущее значение политики запуска PowerShell скриптов, используется командлет Set-ExecutionPolicy.
Например, разрешим запуск локальных скриптов:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Подтвердите изменение политики запуска PS1 скриптов, нажав Y или A.
Чтобы запрос не появлялся, можно использовать параметр Force.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned –Force
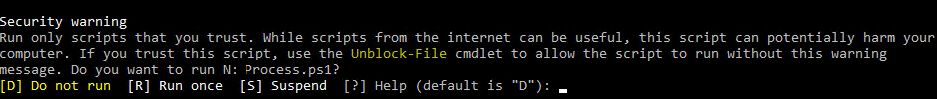
Если вы установили значение политики PowerShell Execution Policy в Unrestricted, то при запуске удаленных скриптов из сетевых каталогов по UNC пути, скачанных из интернета файлов, все равно будет появляться предупреждение:
Security warning Run only scripts that you trust. While scripts from the internet can be useful, this script can potentially harm your computer. If you trust this script, use the Unblock-File cmdlet to allow the script to run without this warning message. Do you want to run? [D] Do not run [R] Run once [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "D")
Как PowerShell различает локальные и удаленные скрипты? Все дело в идентификаторе зоны ZoneId, которую выставляет браузер в альтернативном потоке при загрузке файла (см. статью “Как Windows определяет, что файл скачан из Интернета?”). Вы можете разблокировать такой файл, поставив галку “Разблокирвать” в его свойствах или очиститься метку зоны с помощью комадлета Unblock-File.
Также следует различать различные области действия политик выполнения скриптов PowerShell (scopes):
- MachinePolicy – действует для всех пользователей компьютера, настраивается через GPO;
- UserPolicy – действует на пользователей компьютера, также настраивается через GPO;
- Process — настройки ExecutionPolicy действует только для текущего сеанса PowerShell.exe (сбрасываются при закрытии процесса);
- CurrentUser – политика ExecutionPolicy применяется только к текущему пользователю (параметр из ветки реестра HKEY_CURRENT_USER);
- LocalMachine – политика для всех пользователей компьютера (параметр из ветки реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE);
Область применения политики можно указать с помощью параметр Scope командлета Set-ExecutionPolicy. Например:
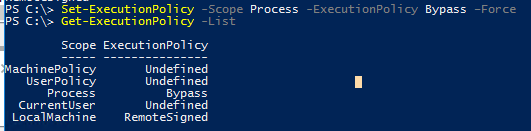
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy Bypass –Force
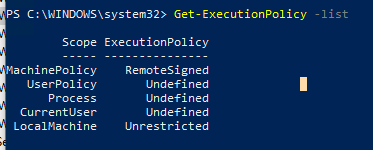
Проверим текущие настройки ExecutionPolicy для всех областей:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
Scope ExecutionPolicy ----- --------------- MachinePolicy Undefined UserPolicy Undefined Process Bypass CurrentUser Undefined LocalMachine RemoteSigned
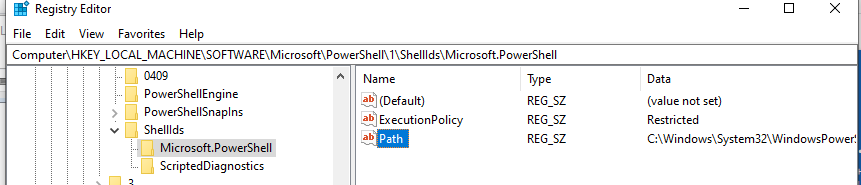
Значение политики выполнения, которые вы задаете с помощью командлета Set-ExecutionPolicy для областей CurrentUser и LocalMachine, хранятся в реестре. Например, выполните командлет:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy Restricted –Force
Откройте ветку реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PowerShell\1\ShellIds\Microsoft.PowerShell и проверьте значение REG_SZ параметра ExecutionPolicy. Оно изменилось на Restricted (допустимые значения параметра Restricted, AllSigned, RemoteSigned, Bypass, Unrestricted и Undefined).
Аналогичные настройки для области CurrentUser находятся в разделе реестра пользователя HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PowerShell\1\ShellIds\Microsoft.PowerShell.
Отметим, что чаще всего в корпоративной среде используется ExecutionPolicy со значением AllSigned на уровне LocalMachine. Это обеспечивает максимальный баланс между безопасностью и удобством. Для личного пользования на компьютере можно использовать RemoteSigned. Ну а Bypass политику лучше использовать только для запуска отдельных задач (например для запуска скриптов через GPO или заданий планировщика).
Настройка PowerShell Execution Policy с помощью групповых политик
Вы можете настроить политику выполнения PowerShel скриптов на серверах или компьютерах домена с помощью групповых политик.
- С помощью редактора доменных GPO (gpmc.msc) создайте новую GPO (или отредактируйте) существующую и назначьте ее на OU с компьютерами, к которым нужно применить политику запуска PowerShell скриптов;
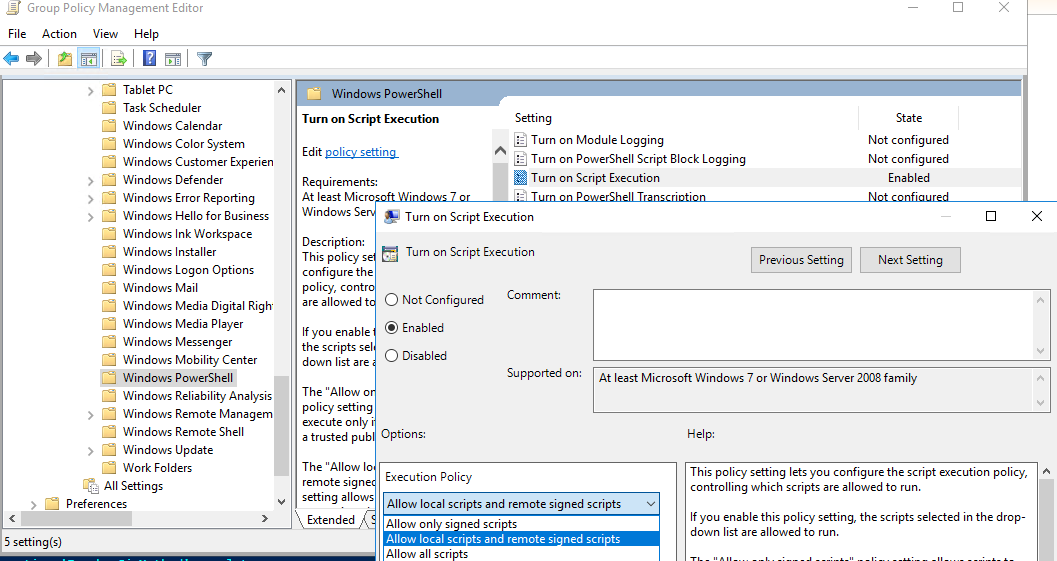
- В редакторе политики перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows PowerShell и найдите политику Turn on Script Execution (Включить выполнение сценариев);
Аналогичная политика есть в пользовательском разделе GPO — User Configuration, но политика компьютера имеет приоритет.
- Для политики доступны три значения:
- Allow only signed scripts (Разрешать только подписанные сценарии) — соответствует политике AllSigned;
- Allow local scripts and remote signed scripts (Разрешать локальные и удаленные подписанные сценарии) — соответствует политике PS RemoteSigned;
- Allow all scripts (Разрешать все сценарии) — политика Unrestricted.
- Выберите необходимое значение политики, сохраните GPO и обновите политики на компьютере.
- Проверьте, что для области MachinePolicy теперь действуют новые настройки выполнения.
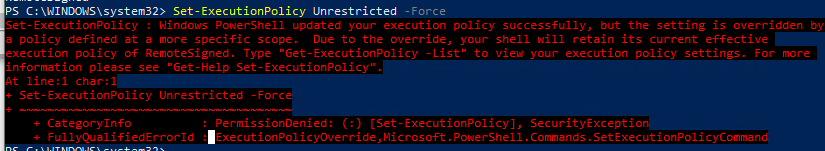
После настройки политики выполнения через GPO вы не сможете изменить настройки политики выполнения скриптов вручную. При попытке изменить настройки Execution Policy на компьютере, на который применяется такая GPO, появится ошибка:
Set-ExecutionPolicy : Windows PowerShell updated your execution policy successfully, but the setting is overridden by a policy defined at a more specific scope. Due to the override, your shell will retain its current effective execution policy of RemoteSigned. Type "Get-ExecutionPolicy -List" to view your execution policy settings.
Способы обхода политики PowerShell Execution
Есть несколько трюков, которые могут помочь вам, когда нужно запустить на компьютере PowerShell скрипт, не изменяя настройки политики выполнения. Например, я хочу запустить простой PS1 скрипт, который поверяет, что запущен с правами администратора.
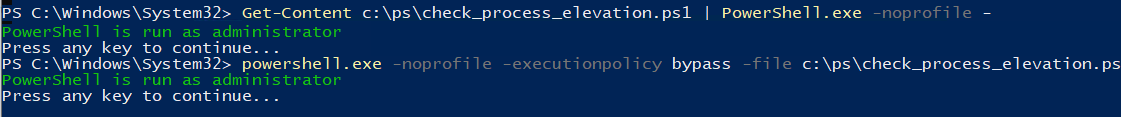
Можно с помощью Get-Content получить содержимое скрипта и перенаправить его в стандартныq поток ввода консоли PS.
Get-Content c:\ps\check_process_elevation.ps1 | PowerShell.exe -noprofile –
Либо можно запустить новый процесс powershell.exe с политикой выполнения Bypass:
powershell.exe -noprofile -executionpolicy bypass -file c:\ps\check_process_elevation.ps1
Представьте себе ситуацию: вы скачиваете из Интернета скрипт и пытаетесь его запустить. Но если вы ранее не настроили PowerShell, то вместо работы скрипта вы видите раздражающее сообщение об ошибке, написанное красным шрифтом. Эту проблему можно легко решить.
PowerShell обладает рядом режимов исполнения, которые определяют, какой тип кода разрешается выполнять. Все это управляется ключом реестра, живущим в HKLM. Существует 4 различных режима исполнения:
Ограниченный (Restricted): Политика исполнения по умолчанию, не допускает работу скриптов и разрешает работу лишь интерактивных команд.
Все подписанные (All Signed): Допускает работу всех скриптов. Правда, все скрипты и файлы конфигурации должны быть подписаны издателем, которому вы доверяете; данный режим подвергает вас риску работы подписанных (но вредоносных) скриптов, после получения подтверждения доверия издателю.
Удаленные подписанные (Remote Signed): Локальные скрипты работают без подписи. Все скачанные скрипты должны иметь цифровую подпись.
Неограниченный (Unrestricted): Все скрипты и файлы конфигурации, полученные из коммуникационных приложений, вроде Microsoft Outlook, Internet Explorer, Outlook Express и Windows Messenger работают после подтверждения, что вы понимаете, что файл исходит из Интернета; никакие цифровые подписи не требуются; данный режим подвергает вас риску работу неподписанных, вредоносных скриптов.
По умолчанию для PowerShell используется режим «Ограниченный». В этом режиме, PowerShell работает лишь как интерактивная оболочка. Он не допускает работу скриптов, и загружает лишь те файлы конфигурации, которые подписаны издателем, которому вы доверяете.
Если вы получаете раздражающую красную ошибку, то, в большинстве случаев, ее появление связано именно с тем, что вы пытаетесь запустить неподписанный скрипт. Самым безопасным способом решения этой проблемы является – изменение политики исполнения на неограниченную, запуск скрипта, и затем обратный возврат к ограниченной политике.
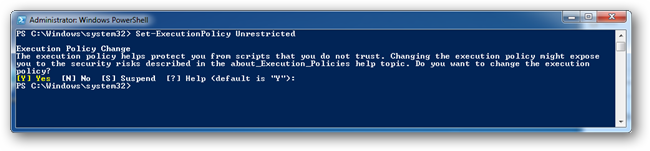
Для изменения политики исполнения на неограниченную, запустите нижеследующую команду в административном PowerShell:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
Вы увидите запрос подтверждения. Нажмите Enter.
Теперь вы можете запустить скачанный скрипт. Однако, вы подвергаете себя серьезному риску, так что по окончании работы скрипта, не забудьте вернуть политику исполнения назад в ограниченный режим. Сделать это можно с помощью следующей команды:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Restricted
И снова вы увидите запрос подтверждения. Нажмите Enter.
Вот и все! Удачи вам!
PowerShell — это новая командная оболочка для Windows, которая по задумкам Microsoft должна вытеснить и заменить cmd. По-умолчанию, эта оболочка уже идет в составе Windows 7 и выше. Если у вас более старая операционная система или вы просто хотите скачать более свежую версию PowerShell, сделать это можно здесь: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/scriptcenter/dd742419.aspx
Как запустить скрипт PowerShell?
Есть несколько различных способов запуска скрипта, ниже приведены основные:
- Запустить оболочку PowerShell и в ней запустить скрипт (ввести путь до файла и имя файла, например, так: C:\Scripts\test.ps1, или перейти в папку скрипта командой cd C:\Scripts и запустить его командой .\test.ps1)Оболочку можно найти и запустить множеством способов. Один из способов — через меню «Пуск». Для Windows 7 — нужно зайти во «Все программы» — «Стандартные» — «Windows PowerShell» и запустить оболочку «Windows PowerShell». Для Windows 10 — нужно найти группу на букву «W» и в ней вы найдете «Windows PowerShell».
- Запустить «Интегрированную среду сценариев Windows PowerShell ISE» — это программа — среда разработки, позволяющая редактировать и отлаживать скрипты PowerShell, которая так же есть по-умолчанию вместе с самим PowerShell. Запустив ее, нужно просто нажать кнопку «Открыть» или зайти в меню Файл — Открыть и выбрать нужный скрипт, затем нажать F5 или кнопку «Выполнить скрипт».Найти Windows PowerShell ISE можно там же, где и оболочку PowerShell — в меню «Пуск».
- Запустить стандартную коммандную строку и в ней написать:
powershell -file <имя_скрипта> (пример: powershell -file myscript.ps1)
Если вы раньше не запускали скрипты PowerShell, то скорее всего, вы получите сообщение: Не удается загрузить файл <имя_скрипта>, так как выполнение скриптов запрещено для данной системы. Введите «get-help about_signing» для получения дополнительных сведений. Связано это с тем, что из соображений безопасности и недопущения случайного выполнения вредоносного кода, все скрипты должны быть подписаны цифровой подписью.
Как разрешить выполнение неподписанного скрипта PowerShell?
1. В оболочке PowerShell, перед тем как запускать скрипт, выполнить команду, разрешающую выполнение неподписанных скриптов для текущего сеанса оболочки:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
2. При запуске из стандартной коммандной строки использовать параметр -executionpolicy, т.е. запускать скрипт так:
powershell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -file <имя_скрипта>
Оба способа устанавливают политику только для текущего сеанса, при этом, политика безопасности выполнения скриптов PowerShell, прописанная в реестре, не будет изменена и останется прежней. Если вы хотите поменять политику безопасности выполнения скриптов «на постоянно», то используйте такой способ:
3. Разрешить запуск навсегда: запустить оболочку PowerShell от имени «Администратора», затем выполните команду:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Однако, я бы не рекомендовал такой способ, чтобы не подвергать ваш компьютер возможным угрозам, т.к. так вы разрешаете выполнение скриптов всем и всегда.
Примечание: Если скрипт был загружен из интернета, то чтобы избежать запроса на подтверждение запуска, нужно вместо RemoteSigned использовать Bypass — полное отключение любых запросов и предупреждений.
Как запустить скрипт PowerShell в фоновом режиме?
Для этого достаточно использовать параметр запуска -WindowStyle, который может принимать значения: Normal, Minimized, Maximized и Hidden. Таким образом, чтобы запустить неподписанный скрипт в фоновом режиме, нужно выполнить команду:
powershell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -WindowStyle Hidden -file <имя_скрипта>
Так же можно еще при желании добавить -NonInteractive, чтобы скрипт не задавал никаких вопросов. Таким образом, скрипт выполнится незаметно для пользователя. Будmте внимательны, используя такой способ.
Запуск скрипта PowerShell c параметрами
Собственно запуск нужно делать как если бы вы запускали обычную программу или bat-файл с параметрами. Например, для запуска скрипта с параметрами из командной, можно написать такую команду:
powershell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -file <имя_скрипта> param1 param2 «еще один текстовый параметр»
В самом скрипте вы можете получить эти параметры так:
param ($var1, $var2, $var3) echo $var1, $var2, $var3
В интегрированной среде PowerShell ISE запустить скрипт с параметрами можно аналогично, используя область команд.
Как запустить скрипт PowerShell с помощью ярлыка?
Осуществить такую задачу можно двумя способами:
- Создать bat/cmd файл, в котором прописать команду для запуска скрипта (с параметрами вы ознакомились выше)
- Создать ярлык на PowerShell, который можно найти в папке c:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v<версия>\ и в свойствах ярлыка в поле «Объект» дописать необходимые параметры.
Таким образом, например, чтобы запустить скрипт powershell при входе пользователя, можно просто создать ярлык, как описано во 2-м пункте и поместить его в автозагрузку. Так же, создание ярлыка одним из способов выше позволит легко запустить скрипт от имени администратора или от имени любого другого пользователя как обычную программу.
Скриптовый язык PowerShell — довольно мощный инструмент для решения различных задач, но его можно использовать не только для хороших вещей, но и во вред, поэтому, пользуйтесь им с умом 
When I try to execute my PowerShell script I get this error:
File C:\Common\Scripts\hello.ps1 cannot be loaded because the execution of scripts is disabled on this system. Please see «get-help about_signing» for more details.
At line:1 char:13
+ .\hello.ps1 <<<<
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [], PSSecurityException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : RuntimeException
asked Feb 8, 2010 at 18:41
Pavel ChuchuvaPavel Chuchuva
11.9k5 gold badges22 silver badges24 bronze badges
1
-
Start Windows PowerShell with the «Run as Administrator» option. Only members of the Administrators group on the computer can change the execution policy.
-
Enable running unsigned scripts by entering:
set-executionpolicy remotesigned
This will allow running unsigned scripts that you write on your local computer and signed
scripts from Internet.
See also Running Scripts at Microsoft TechNet Library.
answered Feb 8, 2010 at 18:44
Pavel ChuchuvaPavel Chuchuva
11.9k5 gold badges22 silver badges24 bronze badges
9
On my machine that I use to dev scripts, I will use -unrestricted as above. When deploying my scripts however, to an end user machine, I will just call powershell with the -executionpolicy switch:
powershell.exe -noprofile -executionpolicy bypass -file .\script.ps1
answered Jan 14, 2013 at 0:46
3
We can get the status of current ExecutionPolicy by the command below:
Get-ExecutionPolicy;
By default it is Restricted. To allow the execution of PowerShell Scripts we need to set this ExecutionPolicy either as Bypass or Unrestricted.
We can set the policy for Current User as Bypass or Unrestricted by using any of the below PowerShell command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Force;
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -Force;
Unrestricted policy loads all configuration files and runs all scripts. If you run an unsigned script that was downloaded from the Internet, you are prompted for permission before it runs.
Whereas in Bypass policy, nothing is blocked and there are no warnings or prompts during script execution. Bypass ExecutionPolicy is more relaxed than Unrestricted.
answered Sep 7, 2016 at 7:06
Depending on the Windows version and configuration, you may have the following warning, even in Unrestricted mode:
Security warning Run only scripts that you trust. While scripts from the internet can be useful, this script can potentially harm your computer. If you trust this script, use the Unblock-File cmdlet to allow the script to run without this warning message. Do you want to run? [D] Do not run [R] Run once [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "D")
The solution is to use the «bypass» policy, enabled with the following command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass
From the documentation:
Bypass: Nothing is blocked and there are no warnings or prompts.
This is obviously insecure, please understand the risks involved.
answered Jan 21, 2016 at 10:01
8
A .reg file with:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell]
"EnableScripts"=dword:00000001 "ExecutionPolicy"="Bypass"
and:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell]
"EnableScripts"=dword:00000001 "ExecutionPolicy"="Unrestricted"
works indeed too.
answered Nov 29, 2017 at 10:10
1
For some reason the PowerShell cmdlet did not enable local execution globally, just for the local user context. If I tried to start a Powershell script from inside CygWin’s bash prompt, for example, which runs under its own user context, it would not run, giving the «is not digitally signed» error. The answer was to go into the Local Group Policy Editor -> Local Computer Policy -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows PowerShell and double-click on ‘Turn on Script Execution’. This then let me change it to ‘Enabled’ and then execution policy of «Allow local scripts and remote signed scripts» and have it work globally regardless of user context.
answered Dec 4, 2018 at 22:06
The accepted answer is right, but the policy modification is only available for the currently running instance of the Powershell, meaning once the instance of the Powershell is shut down. The policy will be reset. If a user reopens another instance of Powershell, the default policy will be applied which is Restricted
For me, I need to use the VisualStudio Code console and g++ from cygwin to build things. The console is using Powershell, with the default policy, nothing can be done. One solution is changing the policy everytime the console is fired in VisualStudio Code console, maybe a script of changing the policy.
I am lazy, so another solution is when I run the Powershell in admin mode, similar to what the accepted answer does. but with an extra parameter which changes values in the Registry table. Once it been done. Other instances of Powershell will use the RemoteSigned policy by default.
set-executionpolicy remotesigned -Scope CurrentUser
answered Dec 15, 2018 at 1:09
r0ngr0ng
8252 gold badges7 silver badges12 bronze badges
Setting the policy (correctly) is the best choice but on my managed systems I do not have the ability to change that policy.
For me, the simplest work-around to changing the policy is to open the script in the
«PowerShell ISE», highlight the code (or part of the code) to execute and then click the «Run Selection» button (or use the F8 shortcut).
This is not the best solution & does little for automating tasks, but it does allow me the use & utility of PowerShell while not running afoul of my IS department.
answered Apr 24, 2019 at 14:47
DBADonDBADon
4734 silver badges11 bronze badges
-
Open Start.
-
Search for PowerShell, right-click the top-result and click the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to allow scripts to run and press Enter:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -
Type A and press Enter (if applicable).
-
Type the following command to run the script and press Enter:
& "C:\PATH\TO\SCRIPT\first_script.ps1"In the above command, make sure to change «PATH\TO\SCRIPT» to the location of your script.
After you complete the steps, the script will run, and if it was crafted correctly, you should see its output without issues.
phuclv
26.7k15 gold badges115 silver badges235 bronze badges
answered Apr 9, 2020 at 4:33
Just one note:
Do not use PowerShell ISE to run set-executionpolicy remotesigned command as a script.
It doesn’t work in my case.
Run it in elevated PowerShell — Please follow step-by-step recommendation provided by Pavel Chuchuva.
answered Jul 29, 2020 at 14:38
If you downloaded the .ps1 from the internet right click properties might have an unblock button on it, just click that.
answered Sep 23, 2020 at 18:50
colin lamarrecolin lamarre
2571 gold badge3 silver badges8 bronze badges
On my local machine, I solved by setting the execution policy to Bypass.
-
Start Windows PowerShell with the «Run as Administrator» option. Only members of the Administrators group on the computer can change the execution policy.
-
Enable running unsigned scripts by entering:
set-executionpolicy Bypass(type A and press Enter to accept all questions).
answered Nov 25, 2020 at 12:07
2
I don’t know if anyone has carefully tried and tested this or not, but even in latest updates of Windows 10 (11 could be too, but not tried), if you run these lines in the exact given order then you can easily set the ExecutionPolicy to your liking.
Open Powershell with Admin elevation(Run As Administrator) and run these lines one by one but all 3 in the exact given order is must:
powershell "Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Force"
powershell "Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Force"
powershell "Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Force"
And after that, not only the current Powershell Window, but even newly opened Powershell windows by any User would be able to run .ps1 scripts.
Let me know in comments if any issues.
answered Feb 28, 2022 at 18:33
Vicky DevVicky Dev
4421 gold badge6 silver badges23 bronze badges
The reason that the reg key works, is because it is doing exactly what the PS commands do. The commands write the changes to the reg keys. Commands are much quicker and easier than creating a reg key or digging into the registry.
answered Apr 5, 2018 at 13:49
1
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Windows PowerShell is a powerful tool that can be used by system administrators and power users to perform administrative tasks, including task automation, managing user accounts and groups, etc. Despite this, PowerShell does not allow you to run scripts by default.
Instead, Microsoft pre-installed PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) in Windows 10 and 11, specifically used to run scripts. But what if you need to run scripts and cmdlets simultaneously in PowerShell?
If you try running a script in PowerShell, you will get see the following error message:
In that case, you need to explicitly allow PowerShell to run scripts. Not only that, but you can also define policies used to execute the script, as well as its scope.
Let us now dig into the details of the execution policy and its scope, and then show you how to enable script execution in Windows PowerShell.
Table of contents
- What is a Script?
- PowerShell Execution Policies and Scopes
- How to Allow Scripts to Run in PowerShell
- Set Script Execution Policy to RemoteSigned
- Through Settings App
- From PowerShell
- How to Change Script Execution Policy for Specific Scope
- Set Script Execution Policy to RemoteSigned
- Set Script Execution Policy to Default
- How to Check PowerShell Execution Policy
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How do we allow PowerShell script only this once?
- How do we revert all script execution policies to default?
- How do we allow PowerShell scripts for current user account only?
What is a Script?
A script is a piece of code, in any programming language, which performs a specific function or a task. A script can be as short as a single expression, or as long as running a complex algorithm.
Scripts can be run directly in a scripting environment – an application designed for coding – or saved in a file, such as a batch file.
In the case of PowerShell scripts, we run the code directly inside the PowerShell window or run a PowerShell file with the extension “.PS1” which contains the script.
Before we discuss how to allow script execution in PowerShell, here is some information we think you ought to know beforehand.
PowerShell Execution Policies and Scopes
As we mentioned earlier, you can optionally choose from the different script execution policies that can be configured for PowerShell. Each of these policies is designed to distinguish between the different types of scripts, and which to allow and which to block. The table below lists the policies you can choose from and what each of them allows.
| Execution Policy | Description |
| Default | Sets Windows to the default execution policy (Restricted for Windows and RemoteSigned for Servers). |
| Restricted | This is the default execution policy for Windows 10 and 11. You can’t run any PowerShell scripts and PowerShell is set to interactive mode so that you can only run individual commands. |
| RemoteSignedThis is the default execution policy for Windows Servers. You can run downloaded PowerShell scripts, but they must be signed by a trusted publisher. Self-written (non-downloaded) PowerShell scripts can run without a signature. | |
| AllSigned | You can only run PowerShell scripts from a trusted publisher, regardless of where they come from. |
| Unrestricted | You can run unsigned scripts, but you’ll get a warning before trying to run ones that come from the internet. |
| Bypass | This is the least strict setting. Run any script with no warnings or prompts. Not recommended for anything other than test machines. |
| Undefined | No policy has been implemented, which automatically applies to the Restricted policy. |
Furthermore, each of these policies can be defined for a different scope. By scope, we mean where the policy will be applied. The table below lists the different scopes.
| Scope | Description |
| Process | Set the execution policy for the current Windows PowerShell instance. This will discontinue once PowerShell is closed. |
| CurrentUser | The execution policy is set for the current user only and stored in the HKEY_CURRENT_USER registry key. |
| LocalMachine | Sets the policy for everyone on the machine via a HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE key. |
| MachinePolicy | Configured using Group Policy for all user accounts on the computer. |
| UserPolicy | Configured using Group Policy for the current user account. |
You can use these execution policies and scopes to manage how to execute scripts in Windows PowerShell.
How to Allow Scripts to Run in PowerShell
You can now use a combination of execution policies and scopes to configure how you want to run your scripts. Each of the sections below gives a different example of how to set a policy.
Set Script Execution Policy to RemoteSigned
Users usually prefer setting the script execution policy for Windows PowerShell to RemoteSigned, as it keeps their system safe by preventing unauthorized scripts from running. There are 2 ways in Windows to configure this policy.
Through Settings App
The Settings app in Windows allows you to manage how, whether you wish to allow scripts to run in PowerShell or not. Here’s how to enable it:
- Navigate to the following:
- Windows 11:
Settings app >> Privacy & security >> For developers - Windows 10:
Settings app >> Update & security >> For developers
- Windows 11:
- Now scroll down to the bottom of the page and check the box next to “Change execution policy to allow local PowerShell scripts to run without signing. Require signing for remote scripts” under the PowerShell section. Then click Apply.
Note that this will only allow scripts from trusted online and local sources in the “CurrentUser” scope.
From PowerShell
If you’d prefer only the Command Line Interface (CLI), here is how to configure the RemoteSigned Execution Policy directly from PowerShell:
- Launch PowerShell with administrative rights.
- Now paste the following command and hit Enter.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned - Now enter A to confirm.
The command above will set the RemoteSigned execution policy for all users on the computer (scope: LocalMachine). If you want to change the scope of the policy, use the -Scope parameter followed by the scope name. Here is an example:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUserYou will then need to confirm this change as well.
How to Change Script Execution Policy for Specific Scope
You can now use this method to configure any one of the above-discussed policies to any scope using the cmdlet below. Simply replace NewPolicy with the Execution Policy and NewScope with the Scope where you want to define it.
Set-ExecutionPolicy NewPolicy -Scope NewScopeSet Script Execution Policy to Default
If you no longer wish to allow scripts to run in PowerShell, you can always change their value to default, which is Undefined or Restricted. However, if a policy has been applied to a specific scope, then you need to update the policy for that particular scope again.
In the command below, we are going to restore the script execution policy for the LocalMachine scope to its default setting:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Undefined -Scope LocalMachineYou can now run the script again with a different scope to change all scopes to their default (restricted) policy.
How to Check PowerShell Execution Policy
To check your current script execution policy in PowerShell, run the following command in PowerShell:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -ListYou can then use this information to change your script execution policy using the guide given above.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do we allow PowerShell script only this once?
You can use the Process scope to restrict the execution policy to one-time only. The execution policy will then revert once the PowerShell window is closed. Here is an example code to set the execution policy to RemoteSigned for this instance of PowerShell only:Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process -Force
How do we revert all script execution policies to default?
If you have defined the execution policies scope-wise, then you must revert them scope-wise as well. However, in case you did not define a scope ( where the policy is automatically configured for LocalMachine), use the following cmdlet to change it back to default:Set-ExecutionPolicy Undefined
How do we allow PowerShell scripts for current user account only?
You can define a script execution policy on your current account only by defining the scope to “CurrentUser.” Here is an example:Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
This will prevent all other users from running a script in Windows PowerShell.