Windows 10 Home, Pro, Enterprise, Education, S или IoT Core — выберите вариант, соответствующий вашим задачам.
Независимо от того, хотите вы обновиться до Windows 10, приобрести новый компьютер или просто переустановить систему, вам понадобится выбрать редакцию. У этой ОС есть четыре главные редакции и ещё пара побочных. Разбираемся, чем они отличаются и кому подходят.
Выбор разрядности системы
Прежде чем выбирать редакцию Windows, нужно определить разрядность системы. Microsoft предоставляет 32-разрядную версию Windows 10 для старых процессоров и 64-разрядную — для новых.
Грубо говоря, если ваш компьютер был создан после 2007 года, он скорее всего оснащён 64-разрядным процессором. Полное руководство по определению разрядности процессора вы можете посмотреть здесь.
Выбор подходящей редакции
Windows 10 Home
Начальная редакция Windows 10, предустановленная на большинстве компьютеров и ноутбуков, которые можно найти в продаже. Эта версия не имеет продвинутых инструментов для обеспечения безопасности бизнес-данных, как в старших редакциях, но они не особенно-то и нужны домашним пользователям.
В Home Edition есть все универсальные приложения от Microsoft, такие как «Календарь», «Почта», «Карты», «Фильмы» и «Фотографии».
Основной недостаток Windows 10 Home Edition — наличие рекламных приложений, которые время от времени автоматически устанавливаются в ваше меню «Пуск». Впрочем, при желании их можно удалить.
Лицензия на Домашнюю версию Windows 10 стоит 9 499 рублей.
Кому выбрать: Windows 10 Home Edition подойдёт большинству обычных пользователей. Да, в ней нет встроенных инструментов для шифрования, но при желании вы можете установить самостоятельно сторонние программы.
Windows 10 Home в Microsoft Store →
Windows 10 Pro
Windows 10 Pro — более продвинутая редакция ОС от Microsoft. Она содержит все те же инструменты и приложения, что и Home Edition, плюс несколько дополнительных функций:
- Инструмент Microsoft Hyper-V. Используется для запуска операционных систем семейств Windows и Linux в виртуальных машинах. Полезен для разработчиков и системных администраторов, которые занимаются тестированием ПО. Обычные пользователи предпочтут применять для экспериментов более понятный VirtualBox.
- Центр обновления Windows Update for Business. Предоставляет некоторые дополнительные обновления вдобавок к тем, что доступны в редакции Home. Кроме того, позволяет откладывать установку обновлений.
- Средства безопасности Device Guard и Secure Boot. Device Guard предназначен для защиты от атак нулевого дня и полиморфных вирусов. Secure Boot защищает от буткитов, которые могут запуститься вместе с системой во время включения компьютера.
- BitLocker. Инструмент для шифрования данных. При желании можно зашифровать хоть всю систему целиком. Полезно для тех, кто хранит на компьютере важные рабочие файлы и опасается, что они окажутся не в тех руках.
- Управление групповыми политиками. Используется для работы с настройками множества компьютеров через локальную сеть. Необходимо системным администраторам.
Лицензия на Профессиональную версию Windows 10 стоит 14 199 рублей.
Кому выбрать: Windows 10 Pro ориентирована на малые предприятия. Но и обычные пользователи могут приобрести эту редакцию, если нуждаются в продвинутых инструментах безопасности и шифрования.
Windows 10 Pro в Microsoft Store →
Windows 10 Enterprise
Windows 10 Enterprise рассчитана на корпоративное применение. Она включает в себя тот же набор инструментов, что и Windows Pro. Но, помимо этого, редакция Enterprise предоставляет доступ к обновлениям Long-Term Service Branch (LTSB). Это означает, что на ваш компьютер будут устанавливаться только проверенные и самые стабильные обновления, к тому же вы сможете откладывать их получение.
В Windows 10 Enterprise отсутствуют универсальные приложения вроде «Почты», «Календаря», «Карт» и других. Кроме того, на устройства с такой операционной системой не устанавливаются рекламные приложения.
Цена на Windows 10 Enterprise зависит от количества копий, которые вы желаете приобрести. Сначала вам придётся установить на свои компьютеры Windows 10 Pro, а уж потом обновить её до Windows 10 Enterprise. Найти сертифицированных поставщиков и уточнить цены можно на сайте Microsoft или по телефону в Центре лицензирования Microsoft.
Кому выбрать: Windows 10 Enterprise разработана специально для средних и крупных предприятий и организаций. Для обычных пользователей её возможностей будет многовато.
Windows 10 Enterprise на сайте Microsoft →
Windows 10 Education
Это редакция Windows 10 для образовательных учреждений. В общем и целом она похожа на Windows 10 Enterprise, но в ней отсутствует возможность присоединиться к каналу обновлений LTSB. Упор в этой редакции Windows делается на предоставление инструментов для студентов и преподавателей.
Здесь есть приложение для настройки учебных компьютеров и инструмент для проведения тестов и экзаменов. Кроме того, пользователи Windows 10 Education получают доступ к образовательному разделу магазина Microsoft Store.
Версия доступна только через академическое лицензирование. Вам придётся сначала установить Windows 10 Home или Pro, а затем обновиться до Education.
Кому выбрать: владельцам академических учреждений. Ориентация на образовательные приложения обычным пользователям точно ни к чему.
Windows 10 Education на сайте Microsoft →
Windows 10 S
Строго говоря, Windows 10 S — это не редакция, а особый режим для Windows 10 Home или Pro, который вы можете включить, если у вас вдруг возникнет такое желание. Он доступен также в редакциях Enterprise и Education.
В Windows 10 S ограничен набор доступных приложений. Вы можете использовать только те варианты, которые устанавливаются из Microsoft Store. Просматривать страницы в интернете здесь можно только через браузер Edge. Благодаря таким ограничениям Windows 10 S значительно легче и быстрее полноценных версий ОС, но вам придётся работать только с теми инструментами, что предлагает в своём магазине Microsoft.
Этот режим чаще всего применяется на планшетах и ноутбуках-трансформерах.
Кому выбрать: Windows 10 S используют те, на чьих устройствах она уже установлена. Конечно, вы можете установить её где захотите, но приготовьтесь столкнуться с рядом ограничений.
Windows 10 S на сайте Microsoft →
Windows 10 IoT Core
Windows 10 IoT Core (IoT означает Internet of Things, «Интернет вещей») предназначена для установки на разнообразные устройства и гаджеты. Хотите запрограммировать какого-нибудь робота, собранного вами, переоборудовать своё старое радио, обеспечив ему доступ в интернет, установить Windows на свой медиацентр или собственноручно создать устройство на базе Arduino? Воспользуйтесь Windows 10 IoT Core. Версия подходит и для различных однопалатных компьютеров, таких как Arrow DragonBoard 410c и Raspberry Pi 3.
Кому выбрать: Windows 10 IoT Core предназначена для опытных пользователей, которые увлекаются электроникой. Кроме того, она пригодится, если вы создаёте какой-нибудь высокотехнологичный стартап.
Windows 10 IoT Core на сайте Microsoft →
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Windows 10 has several editions, all with varying feature sets, use cases, or intended devices. Certain editions are distributed only on devices directly from an original equipment manufacturer (OEM), while editions such as Enterprise and Education are only available through volume licensing channels. Microsoft also makes editions of Windows 10 available to device manufacturers for use on specific classes of devices, including IoT devices and previously marketed Windows 10 Mobile for smartphones.
Baseline editions[edit]
Baseline editions are the only editions available as standalone purchases in retail outlets. PCs often come pre-installed with one of these editions.
- Home
- Windows 10 Home is designed for use in PCs, tablets and 2-in-1 PCs. It includes all features directed at consumers.[1][2][3]
- Pro
- Windows 10 Pro includes all features of Windows 10 Home, with additional capabilities that are oriented towards professionals and business environments, such as Active Directory, Remote Desktop, BitLocker, Hyper-V, and Windows Defender Device Guard.[1][2][3]
- Pro for Workstations
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations is designed for high-end hardware for intensive computing tasks and supports Intel Xeon, AMD Opteron and the latest AMD Epyc processors; up to 4 CPUs; up to 256 cores; up to 6 TB RAM; the ReFS file system; Non-Volatile Dual In-line Memory Module (NVDIMM); and remote direct memory access (RDMA).[4][5][6]
Organizational editions[edit]
These editions add features to facilitate centralized control of many installations of the OS within an organization. The main avenue of acquiring them is a volume licensing contract with Microsoft.
- Education
- Windows 10 Education is distributed through Academic Volume Licensing. It was based on Windows 10 Enterprise and initially reported to have the same feature set.[1][2][3] As of version 1709, however, this edition has fewer features. See § Comparison chart for details.
- Pro Education
- This edition was introduced in July 2016 for hardware partners on new devices purchased with the discounted K–12 academic license. It was based on the Pro edition of Windows 10 and contains mostly the same features as Windows 10 Pro with different options disabled by default, and adds options for setup and deployment in an education environment. It also features a «Set Up School PCs» app that allows provisioning of settings using a USB flash drive, and does not include Cortana, Microsoft Store suggestions, Windows Sandbox, or Windows Spotlight.[7][8][9]
- Enterprise
- Windows 10 Enterprise provides all the features of Windows 10 Pro for Workstations, with additional features to assist with IT-based organizations.[1][2][3] Windows 10 Enterprise is configurable on two servicing channels, Semi-Annual Channel and Windows Insider Program.[10]
- Enterprise LTSC
- Enterprise LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel) is a long-term support variant of Windows 10 Enterprise released every 2 to 3 years. Each release is supported with security updates for either 5 or 10 years after its release, and intentionally receive no feature updates.[11] Some features, including the Microsoft Store and bundled apps, are not included in this edition.[12][1][3] This edition was first released as Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB (Long-Term Servicing Branch).[13] There are currently 4 releases of LTSC: one in 2015 (version 1507), one in 2016 (version 1607), one in 2018 (labeled as 2019, version 1809), and one in 2021 (version 21H2).[14][15]
S mode[edit]
Since 2018, OEMs can ship Windows 10 Home and Pro in a feature-limited variation named S mode which evolved from the discontinued Windows 10 S. Organizations employing Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education can make use of S mode too.[16] S mode is a feature-limited edition of Windows 10 designed primarily for low-end devices in the education market. It has a faster initial setup and login process, and allows devices to be provisioned using a USB drive with the «Set Up School PCs» app.
Changes[edit]
With the exception of the Microsoft Teams desktop client which was made available for S mode in April 2019,[citation needed] the installation of software (both Universal Windows Platform (UWP) and Windows API apps) is only possible through the Microsoft Store, and built-in and Microsoft Store-obtained command line programs or shells cannot be run in this mode.[17][18][19][20] System settings are locked to allow only Microsoft Edge as the default web browser with Bing as its search engine.[21] The operating system may be switched out of S mode using the Microsoft Store for free. However, once S Mode is turned off, it cannot be re-enabled.[22][23] All Windows 10 devices in S mode include a free one-year subscription to Minecraft: Education Edition.[citation needed] Critics have compared the edition to Windows RT, and have considered it to be an alternative to ChromeOS.[22][24][25][26][27]
Device-specific editions[edit]
These editions are licensed to OEMs only, and are primarily obtained via the purchase of hardware that includes it:
- Holographic
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s HoloLens mixed reality smartglasses.[28][29]
- IoT Enterprise
- A rebranded variant of Microsoft’s earlier embedded operating systems, Windows Embedded. Designed specifically for use in small footprint, low-cost devices and IoT scenarios.[30][31] IoT Core was discontinued on 10 November 2020,[32][33] while IoT Core LTSC is supported up through 9 January 2029.[34]
- Team
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s Surface Hub interactive whiteboard.[35]
Discontinued editions[edit]
The following editions of Windows 10 were discontinued (as of Windows 10 version 21H2). For both Mobile and Mobile Enterprise, Microsoft confirmed it was exiting the consumer mobile devices market, so no successor product is available.[36]
- Mobile
- Windows 10 Mobile was designed for smartphones and small tablets. It included all basic consumer features, including Continuum capability. It was the de facto successor of Windows Phone 8.1 and Windows RT.[1][2]
- Mobile Enterprise
- Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise provided all of the features in Windows 10 Mobile, with additional features to assist IT-based organizations, in a manner similar to Windows 10 Enterprise, but optimized for mobile devices.[1][2]
- IoT Mobile
- A binary equivalent of Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise licensed for IoT applications. Also known as IoT Mobile Enterprise.[37][38]
- S
- Windows 10 S was an edition released in 2017 which ultimately evolved into the so-called S mode of Windows 10. In March 2018, Microsoft announced that it would be phasing out Windows 10 S, citing confusion among manufacturers and end-users.[39][40]
- 10X
- Originally announced for use on dual-screen devices such as the Surface Neo and other potential form factors, 10X featured a modified user interface designed around context specific interactions or «postures» on such devices, including a redesigned Start menu with no tiles, and use of container technology to run Win32 software.[41][42] The platform was described as a more direct competitor to ChromeOS.[43][44] On May 4, 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would first be used on single-screen devices, and that they would «continue to look for the right moment, in conjunction with our OEM partners, to bring dual-screen devices to market».[45] Microsoft also added anti-theft protection to Windows 10X, just like how Apple’s Activation Lock and anti-theft protection on Android devices and Chromebooks work.[46] On May 18, 2021, Head of Windows Servicing and Delivery John Cable stated that Windows 10X had been cancelled, and that its foundational technologies would be leveraged for future Microsoft products.[47] Several design changes in 10X, notably the centered taskbar and redesigned start menu, would be later introduced in Windows 11.[48]
Regional variations[edit]
- N/KN
- As with previous versions of Windows since Windows XP, all Windows 10 editions for PC hardware have «N» and «KN» variations in Europe and South Korea that exclude multimedia functionality, in compliance with antitrust rulings.[49] According to details that Microsoft has published, any app that relies on Microsoft multimedia technologies experiences impaired functionality on these editions, unable to even play audio notification tones.[50] Restoring the missing functionality to these editions entails installing the «Media Feature Pack», followed by Skype, Movies & TV, Windows Media Player, Xbox Game Bar, Windows Voice Recorder, and four codecs.[50] The variation cannot be changed without a clean install, and keys for one variation will not work on other variations.
- Home with Bing
- As with Windows 8.1, a reduced-price «Windows 10 with Bing» SKU is available to OEMs; it is subsidized by having Microsoft’s Bing search engine set as default, which cannot be changed to a different search engine by OEMs. It is intended primarily for low-cost devices, and is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home.[51]
- Home Single Language
- In some emerging markets,[citation needed] OEMs preinstall a variation of Windows 10 Home called Single Language without the ability to switch the display language. It is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home. To change display language, the user will need to upgrade to Windows 10 Home or Windows 10 Pro.
- China Government Edition
- In May 2017, it was reported that Microsoft, as part of its partnership with China Electronics Technology Group, created a specially-modified variant of Windows 10 Enterprise («G») designed for use within branches of the Chinese government. This variant is pre-configured to «remove features that are not needed by Chinese government employees», and allow the use of its internal encryption algorithms.[52][53]
Comparison chart[edit]
| Item | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Yes | Feature is present in the given edition |
| Yes, since [update] | Feature is present in the given edition after installing a certain update |
| No | Feature is absent from the given edition |
| No, since [update] | Feature is absent from the given edition after installing a certain update (It might have been fully or partly present prior to that update) |
| [Explanation] | Feature is partly present in the given edition |
| [Explanation], since [update] | Feature is partly present in the given edition, after installing a certain update (It might have been fully present prior to that update, or not present at all) |
Microsoft OEM licensing formula takes display size, RAM capacity and storage capacity into account. In mid-2015, devices with 4 GB RAM were expected to be $20 more expensive than devices with 2 GB RAM.[75]
Upgrade path[edit]
Free upgrade[edit]
At the time of launch, Microsoft deemed Windows 7 (with Service Pack 1) and Windows 8.1 users eligible to upgrade to Windows 10 free of charge, so long as the upgrade took place within one year of Windows 10’s initial release date. Windows RT and the respective Enterprise editions of Windows 7, 8, and 8.1 were excluded from this offer.[76]
| Windows version and edition | Windows 10 edition |
|---|---|
| Windows 7 Starter SP1 | Home |
| Windows 7 Home Basic SP1 | |
| Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 with Bing | |
| Windows 8.1 | |
| Windows 7 Professional SP1 | Pro |
| Windows 7 Ultimate SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 Pro | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Mobile |
Transition paths[edit]
The following table summarizes possible transition paths (upgrade, downgrade, or migration) that can be taken, provided that proper licenses are purchased.
Windows RT does not appear in this table because it cannot be upgraded to Windows 10.
On September 28, 2023, Microsoft disabled the free upgrade path to Windows 10 from Windows 7 or 8.x, although upgrades from Windows 10 to 11 are still supported.[77][78]
| Transition path | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Upgrade | Constitutes replacing the OS while preserving apps, their settings, and user data |
| Repair | Constitutes fixing a damaged OS by «upgrading» from one edition to the same |
| Downgrade | Similar to upgrade, but deliberately removes some features |
| Migration | Constitutes replacing the operating system, reinstalling the apps, restoring their settings via backup, and safeguarding user data against accidental deletion. |
| None | It is impossible to replace the OS with the intended target because of platform incompatibility |
| Windows version |
Windows edition |
Transition target | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Home |
Windows 10 Pro |
Windows 10 Pro for Workstations |
Windows 10 Pro (Education) |
Windows 10 Education |
Windows 10 Enterprise |
Windows 10 Mobile |
||
| Windows 7 | Starter | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None |
| Home Basic | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Home Premium | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Professional | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Ultimate | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | Migration | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Windows 8.1 | (Core) | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None |
| with Bing | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Pro | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro for Students | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro with Media Center | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Embedded Industry | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | None | |
| Phone 8.1 | None | None | None | None | None | None | Upgrade | |
| Windows 10 | Home | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None |
| Pro | Downgrade | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro for Workstations | Downgrade | Downgrade | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro Education | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Repair | Migration | Migration | None | |
| Education | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Repair | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Downgrade | Repair | None | |
| Mobile | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
Release channels[edit]
Microsoft releases minor versions of Windows 10 through the free feature updates.[12] Originally, Microsoft released feature updates semiannually. They contained new features as well as changes.[80] With the release of Windows 11, however, Microsoft has changed the release schedule to annual. These feature updates do not contain any noticeable changes.
The pace at which a system receives feature updates depends on the «release channel» (originally, «release branch») from which the system downloads its updates.[12]
Insider Channel[edit]
Windows Insider is a beta testing program that allows access to pre-release builds of Windows 10, enabling power users, developers, and vendors to test and provide feedback on future feature updates to Windows 10 as they are developed. Windows Insider itself consists of four «rings.»
- The «Fast» ring distributes new builds as they are released
- The «Slow» ring distributes new builds with a delay following their availability on the Fast ring
- The «Release Preview» ring distributes release candidate
- The «Skip Ahead» ring distributes builds of the next feature update while a current release is being finished
General Availability Channel[edit]
Since 2022, the General Availability Channel (GAC) distributes feature updates annually. To receive these updates, users must either request them manually or wait for their version of Windows 10 to go out of support.
Originally, however, Microsoft distributed feature updates through two distinct channels, the «Current Branch» (CB) an the «Current Branch for Business» (CBB).
- The «Current Branch» (CB) distributed all feature updates as they graduated from the Windows Insider program. Microsoft only supported the latest build. Windows would automatically install the latest feature update from CB. Users could defer the CB feature update for up to 365 days.[81][82][83][84] Microsoft renamed CB to «Semi-Annual Channel (Targeted)» in version 1709.
- The «Current Branch for Business» (CBB), which was not available in the Home edition, distributed feature updates with a four-month delay. This allowed customers and vendors to evaluate and perform additional testing on new builds before broader deployments. Devices could be switched back to the Current Branch at any time.[12][85] Microsoft renamed CBB to «Semi-Annual Channel» in version 1709.
Since version 1903, Microsoft dismantled the two-channel scheme in favor of a unified «Semi-Annual Channel» (SAC). Microsoft supports each SAC version of Windows for 30 months. Windows no longer installs new feature updates automatically before the expiry of the 30-months support period. With the release of Windows 11, Microsoft changed the release schedule to annual, and change the channel’s name to «General Availability Channel» (GAC).
Long-Term Servicing Channel[edit]
LTSC exclusively distributes the «Enterprise LTSC», «IoT Core», and «IoT Enterprise LTSC» editions of Windows 10. Microsoft releases a new minor version of these editions every 2–3 years. LTSC builds adhere to Microsoft’s traditional support policy which was in effect before Windows 10, including:
- Five years of mainstream support
- Critical and security updates for ten years after their release
- No feature updates from Windows Update
Microsoft discourages the use of LTSC editions outside of «special-purpose devices» that perform a fixed function and thus do not require new user experience features. As a result, these editions do not come with Microsoft Store, most Cortana features, and most bundled apps.[12][1][3] LTSC was originally called the «Long-Term Servicing Branch» (LTSB) until 2016.[13]
See also[edit]
- Windows Server 2016, based on Windows 10 version 1607[86]
- Windows Server 2019, based on Windows 10 version 1809
- Xbox system software, an operating system now based on the Windows 10 core, designed to run on consoles
- Windows 10 version history
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b c 32-bit architectures like IA-32 and ARM32 have a memory addressing limitation of four gigabytes. In practice, less than 4 GB of memory is addressable as the 4 GB space also includes the memory mapped peripherals.
- ^ Windows 10 utilises processor groups on x86-64 to manage processor affinity and scheduling. The Windows 10 kernel has a hard-coded limit of 20 processor groups, and each processor group can contain up to 64 logical processors. A logical processor is either a physical or SMT core. Processor groups are allocated based on the NUMA topology of the system. One processor group cannot span multiple sockets or NUMA nodes. Processor groups are not available on IA-32; 32-bit builds instead use an older affinity mask implementation with a limit of 32 logical processors. The limit of 20 processor groups does not change between Windows 10 editions. There is no specific limit on the number of physical cores that can be used on Windows 10, unlike Windows Server where physical cores must be additionally licensed.[58][60][61][62]
- ^ There are three (previously four) telemetry levels, in the order of magnitude: Diagnostic data off (Security), Required (Basic), and Optional (Full). The higher the level, the more information that is sent to Microsoft. Previous Windows 10 versions had a level between Required and Optional, and the older names for the levels are shown in the parenthesis.
- ^ Cortana is available only in certain markets. Experience may vary by region and device.
- ^ a b This feature was missing from Windows 10 version 1803, but not the prior or next versions.
- ^ Windows Hello requires specialized hardware, such as a fingerprint reader, illuminated IR sensor or other biometric sensor.
- ^ On Windows 10 Pro, a Control Panel applet corresponding to this feature appears, but a Windows 10 Enterprise or Education image is still needed.[73][74]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Prophet, Tony (May 13, 2015). «Introducing Windows 10 Editions». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ a b c d e f Bott, Ed (May 14, 2015). «Windows 10 editions: Everything you need to know». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b c d e f Foley, Mary Jo (July 2, 2015). «Which Windows 10 editions get which features?». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Diaconu, Klaus (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft announces Windows 10 Pro for Workstations». Windows For Your Business. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft confirms new Windows 10 Pro for Workstations edition». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Warren, Tom (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft reveals new Windows 10 Workstations edition for power users». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 27, 2016). «Microsoft to add new Windows 10 Pro Education edition to its line-up». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 editions for education customers». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ a b «Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, «fun facts», and suggestions». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ DaniHalfin. «Assign devices to servicing branches for Windows 10 updates (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ «The next Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) release». Microsoft. February 18, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Overview of Windows as a service». Microsoft. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ a b Brinkmann, Martin (July 28, 2017). «Windows 10 LTSB becomes Windows 10 LTSC». gHacks Technology News.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg. «FAQ: Windows 10 LTSB explained». Computerworld. Retrieved October 3, 2018.
- ^ greg-lindsay. «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021 — What’s new in Windows». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved November 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 in S mode FAQ». Windows.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Turner, Rich (May 18, 2017). «Will Linux distros run on Windows 10 S?». Microsoft. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Gartenberg, Chaim (May 19, 2017). «Linux distros won’t run on Windows 10 S after all». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Smith, Sharon. «Get clients for Microsoft Teams — Microsoft Teams». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ «Update get-clients.md · MicrosoftDocs/OfficeDocs-SkypeForBusiness@5c2ca5a». GitHub. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 2, 2017). «Windows 10 S won’t let you change the default browser or switch to Google search». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ a b Chacos, Brad. «Meet Windows 10 S, a streamlined, simplified, Microsoft Store-only OS for schools». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Warren, Tom (June 19, 2017). «Microsoft now lets Surface Laptop owners revert back to Windows 10 S». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «Windows 10 S is Microsoft’s answer to Chrome OS». The Verge. Vox Media. May 2, 2017. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (September 14, 2016). «Desktop apps make their way into the Microsoft Store». Ars Technica. Condé Nast.
- ^ «Windows 10 Cloud looks just like Windows 10 in leaked screenshots». The Verge. Vox Media. February 3, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ «Leaked Microsoft document confirms Windows 10 Cloud and a Chromebook competitor». PC World. IDG. Retrieved April 23, 2017.
- ^ «Unlock Windows Holographic for Business features». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft pushes Windows 10 Holographic as the one-stop option for VR and AR». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT for your business». Windows for Business. Microsoft. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise». MS Embedded. Silica. August 14, 2015. Archived from the original on May 8, 2017. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft to combine Windows 10 IoT Core and IoT Enterprise in 2021». ZDNet. Mary Jo Foley. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ «Windows 10 Team Anniversary Update now available for Microsoft Surface Hub». Neowin. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ Patrizio, Andy (September 29, 2016). «Microsoft is leaving the consumer mobile market». Network World. IDG Publishing. Retrieved August 30, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 on Thin Clients: Deliver Best Results with Scout Agents (Part 1 of 2)». Fujitsu. Archived from the original on January 23, 2021. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Supported operating systems and browsers in Intune». Microsoft. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft admits Windows 10 S was confusing, new ‘S Mode’ upgrades will be free». The Verge. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Tung, Liam. «Windows 10 to permit block on apps installing if they’re not from Microsoft Store». ZDNet. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 2, 2019). «Microsoft Surface Neo first look: the future of Windows 10X is dual-screen». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Hollister, Sean (October 2, 2019). «Windows 10X is Microsoft’s latest stab at a ‘Lite’ operating system, exclusively for dual-screens». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft reportedly shelves Windows 10X, its Chrome OS competitor». The Verge. May 7, 2021. Retrieved May 7, 2021.
- ^ Salter, Jim (May 13, 2021). «Microsoft puts Windows 10X variant on the back burner». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 4, 2020). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is coming to laptops amid big jump in Windows usage». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Ballard, Barclay (January 25, 2021). «This clever Windows 10X feature will prevent thieves from resetting stolen devices». TechRadar. Retrieved January 21, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 11 Leaks Indicate a Dramatic New Look Is Coming Soon». Gizmodo. Archived from the original on June 16, 2021. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ Ron (August 2, 2015). «Grab the Media Feature Pack for Windows 10 N and Windows 10 KN editions». OnMSFT.com. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ a b «Media Feature Pack for Windows 10/11 N (February 2023)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ^ Slater-Robins, Max. «Microsoft is helping manufacturers make cheap tablets that can run Windows as well as Android». Business Insider UK. Retrieved April 23, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft made a version of Windows 10 for the Chinese government». Engadget. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Myerson, Terry (May 23, 2017). «Announcing Windows 10 China Government Edition and the new Surface Pro». Windows Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ Dudau, Vlad (June 10, 2015). «Microsoft shows OEMs how to market Windows 10; talks features and SKUs». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved June 19, 2015.
- ^ «Compare Windows 10 Pro & Enterprise (E3 & E5) Commercial Editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2015.
- ^ «Compare Windows 10 Editions & Versions | Home & Pro». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ^ Howse, Brett (July 2, 2015). «Windows 10 Editions Compared». AnandTech. Purch.
- ^ a b Graham Sutherland (April 7, 2022). «CPU Socket and Core Count Limits in Windows 10 (And How To Remove Them)». Codeinsecurity. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Andre Da Costa (September 15, 2015). «Understanding Windows 10 Editions, Architectures and Builds». groovyPost. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- ^ «Processor Groups — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. December 30, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «NUMA Support — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. August 19, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Geoff Chappell (December 17, 2019). «KAFFINITY_EX». Geoff Chappell, Software Analyst. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «Configure Windows telemetry in your organization». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. August 10, 2020.
- ^ «Continuum on Windows 10». July 27, 2015.
- ^ Confirmed by @MicrosoftHelps (Verified) on Twitter
- ^ «Features that are removed or deprecated in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update». Support (28 ed.). Microsoft. October 17, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ shortpatti. «DirectAccess». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ «DirectAccess and Windows 10 in Education». August 4, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 10, 2017). «Ask Paul: Is Windows To Go Coming to Windows 10 Pro?». thurrott.com. BWW Media Group.
- ^ Niehaus, Michael; Lich, Brian. «Windows To Go frequently asked questions (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 30, 2017.
How can Windows To Go be deployed in an organization? [~snip~] A Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education image
- ^ «TrendForce Adjusts Notebooks’ Unit Memory Capacity for 2015 Down by 3~5% due to Microsoft’s New License Fee Arrangement for Windows 10». DRAMeXchange. TrendForce Corp. July 27, 2015. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ Trent, Rod (June 9, 2015). «Windows 10 Upgrade Paths». SuperSite for Windows. Penton.
- ^ «Windows Ends Installation Path for Free Windows 7/8 Upgrade». Microsoft. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Tyson, Mark (September 29, 2023). «Microsoft Says the Days of Free Windows 7 to 10 or 11 Updates Are Over». Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Lindsay, Greg; Lich, Brian (April 5, 2017). «Windows 10 upgrade paths». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 20, 2017). «Microsoft will now release major Windows 10 updates every March and September». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «How to Pause Windows 10 Automatic Updates To Avoid Critical Bugs». www.bleepingcomputer.com. Retrieved September 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 : the case of the missing update deferral options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. May 28, 2019. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (March 1, 2017). «Put Windows 10 updates on hold—now available in Creators Update build 15046». Computerworld. IDG. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ Paul, Ian (April 18, 2017). «How to defer future updates in the Windows 10 Creators Update». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (November 17, 2015). «How to defer upgrades and updates in Windows 10 Pro». Computerworld. IDG.
- ^ Woods, Rich (September 24, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809 will be generally available in October». Neowin.
Summary
Windows 10 Anniversary Update (Windows 10, version 1607) continues our commitment to productivity, security, and privacy for all customers. Windows 10 Pro and Windows 10 Enterprise offer the functionality and safety features demanded by business and education customers around the globe. Windows 10 is the most secure Windows weve ever built. All of our Windows commercial editions can be configured to support the needs of schools, through group policies, domain join, and more. To learn more about Microsofts commitment to security and privacy in Windows 10, see more on both security and privacy.
Windows 10, version 1607 offers a variety of new features and functionality, such as simplified provisioning with the Set up School PCs app or Windows Imaging and Configuration Designer (ICD), easier delivery of digital assessments with Take a Test, and faster log in performance for shared devices than ever before. These features work with all Windows for desktop editions, excluding Windows 10 Home. You can find more information about Windows 10, version 1607 on windows.com.
Windows 10, version 1607 introduces two editions designed for the unique needs of K-12 institutions: Windows 10 Pro Education and Windows 10 Education. These editions provide education-specific default settings for the evolving landscape in K-12 education IT environments.
Windows 10 Pro Education
Windows 10 Pro Education builds on the commercial version of Windows 10 Pro and provides important management controls needed in schools. Windows 10 Pro Education is effectively a variant of Windows Pro that provides education-specific default settings, including the removal of Cortana*. These default settings disable tips, tricks and suggestions & Microsoft Store suggestions. More detailed information on these default settings is available in Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, tricks, and suggestions.
Windows 10 Pro Education is available on new devices pre-installed with Windows 10, version 1607 that are purchased with discounted K-12 academic licenses through OEM partners (these discounted licenses are sometimes referred to as National Academic or Shape the Future).
Existing devices running Windows 10 Pro, currently activated with the original OEM digital product key and purchased with discounted K-12 academic licenses through OEM partners (these discounted licenses are sometimes referred to as National Academic or Shape the Future), will upgrade automatically to Windows 10 Pro Education as part of the Windows 10, version 1607 installation.
Customers with Academic Volume Licensing agreements with rights for Windows can get Windows 10 Pro Education through the Volume Licensing Service Center, available at a later date.
Customers that deploy Windows 10 Pro are able to configure the product to have similar feature settings to Windows 10 Pro Education using policies. More detailed information on these policies and the configuration steps required is available in Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, tricks, and suggestions. We recommend that K-12 customers using commercial Windows 10 Pro read the document and apply desired settings for your environment.
Windows 10 Education
Windows 10 Education builds on Windows 10 Enterprise and provides the enterprise-grade manageability and security desired by many schools. Windows 10 Education is effectively a variant of Windows 10 Enterprise that provides education-specific default settings, including the removal of Cortana*. These default settings disable tips, tricks and suggestions & Microsoft Store suggestions. More detailed information on these default settings is available in Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, tricks, and suggestions.
Windows 10 Education is available through Microsoft Volume Licensing. Customers who are already running Windows 10 Education can upgrade to Windows 10, version 1607 through Windows Update or from the Volume Licensing Service Center. We recommend Windows 10 Education to all K-12 customers as it provides the most complete and secure edition for education environments. If you do not have access to Windows 10 Education, contact your Microsoft representative or see more information here.
Customers that deploy Windows 10 Enterprise are able to configure the product to have similar UI feature settings to Windows 10 Education using policies. More detailed information on these policies and the configuration steps required is available in Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, tricks, and suggestions. We recommend that K-12 customers using commercial Windows 10 Enterprise read the document and apply desired settings for your environment.
For any other questions, contact Microsoft Customer Service and Support.
-
http://aka.ms/edudeploy
-
Windows 10 upgrade paths
-
Volume Activation for Windows 10
-
Plan for volume activation
__________________________________________________
* — Cortana available in select markets; experience may vary by region and device. Cortana is disabled in the Pro Education and Education editions.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
В мае Microsoft официально представила семь редакций Windows 10, дав нам лишь краткое описание каждой из них. Семь редакций, включая те, которые предназначены для пользователей, предприятий и образовательных учреждений, две версии для смартфонов и вариант операционной системы для «Интернета вещей» (IoT).
Поскольку до выхода настольных версий Windows 10 остается совсем немного, и такое количество редакций может создать некоторую путаницу среди неопытных пользователей, компания опубликовала сводную таблицу (в формате PDF), которая сравнивает функции, содержащиеся в Windows 10 Home, Pro, Enterprise и Education.
К счастью, ушли те времена, когда не все издания операционной системы позволяли изменить фон рабочего стола. Другими словами, все основные функции Windows 10 будут доступны в каждой из четырех версий для настольных компьютеров, в том числе Кортана (будет работать не во всех регионах), Windows Hello, Continuum, Hiberboot и InstaGo (быстрый запуск), браузер Microsoft Edge и новый интерфейс (с меню «Пуск» и виртуальными рабочими столами).
Реальные различия между ними заключаются в наличии у Enterprise и Education (которые практически не имеют отличий друг с другом) инструментов для интеграции в сетевую инфраструктуру, дополнительных функций безопасности и режимов обновления – в общем, все то, что предназначено для предприятий и организаций.
Практически все эти функции отсутствуют в версии Home, но частично их нет и в Pro.
Отличного Вам дня!
Каждая из версий Windows существует в нескольких редакциях (выпусках). У старых версий, выпускаемых в 90-е годы, их было значительно меньше. Эволюция операционной системы, адаптация компании Microsoft к современному рынку сбыта, а также прочие обстоятельства обусловили появление новых разновидностей Windows. Последняя версия 10 – лидер по их числу. Её дистрибутивов – как функциональных редакций, так и сборок, фиксирующих то или иное состояние системы – существует огромное множество. Ниже попробуем разобраться в них.
Прежде чем приступить к обзору дистрибутивов конкретно «Десятки», предлагаю для начала посмотреть на изначальную структуру разновидностей Windows. Так поймём всю грандиозность размаха основного продукта Microsoft.
Главенствующий критерий деления Windows – это семейства. Основные семейства такие:
- Windows NT – это линейка десктопных (для ПК, ноутбуков и планшетов) и линейка серверных систем, начиная с Windows NT 3.1 и заканчивая Windows 10 и серверной Windows Server 2022. Десктопные NT – это те, что используются повсеместно;
- Windows Embedded – тип системы для терминалов, банкоматов, прочих автоматов и различной аппаратуры;
- Windows 10 IoT – пришедшая на замену Embedded операционная система для производственных устройств, но уже с большим перечнем их поддержки. Среди таких устройств – системы автоматизации «Умный дом»;
- Windows Mobile, она же в более раннем релизе Windows Phone – платформа для мобильных устройств.
***
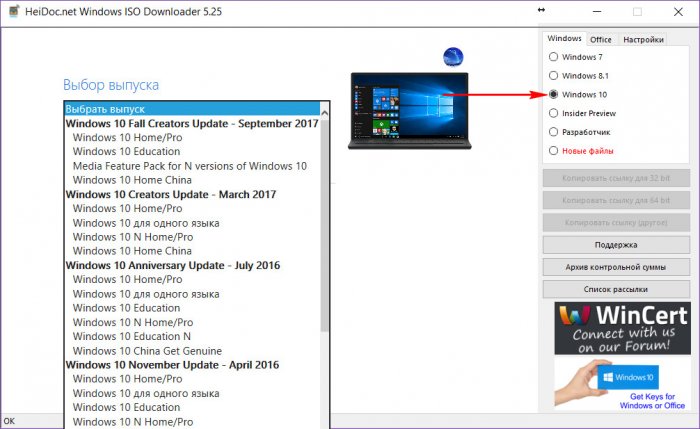
В каждом семействе могут существовать свои линейки (как в случае с NT), свои версии, свои редакции, свои подредакции и т.п. У «Десятки» же делений ещё больше. Если будем скачивать её установочный ISO-образ не с помощью официальной утилиты от Microsoft MediaCreationTool, а, например, посредством программы Windows ISO Downloader, в перечне выбора увидим массу возможных дистрибутивов.
В случае с «Десяткой» имеем не только стабильную ветвь операционной системы, но и ветвь в рамках проекта Windows Insider – программы тестирования новшеств операционной системы. Плюс к этому, поскольку Microsoft заявила, что как минимум в скором будущем не будет новых версий системы, и компания собирается работать над совершенствованием «Десятки» параллельно с её использованием массами, по итогу этой работы на сегодняшний день имеем массу сборок и версий самой версии 10. К этим всем разновидностям мы ещё вернёмся, а пока же рассмотрим, какие существуют редакции системы.
Редакции – четвёртое колено деления Windows NT. В семействе существует две линейки, в линейках есть свои версии, а у каждой из версий – свои редакции. Редакции предусматриваются прежде всего для удобства самой компании Microsoft, так ей выгоднее торговать лицензионными копиями операционной системы. Основа торговли – редакция Pro, от неё уже пляшется в ту или иную сторону. Урезая какой-то функционал, компания снижает лицензионную плату за использование операционной системы, делая её таким образом доступной по цене большему числу лиц. А, предлагая дополнительные возможности в редакциях для определённых сегментов рынка, компания умудряется торговать одним и тем же, но по принципу «Для бедных цена — рубль, для богатых — два».
В плане урезания возможностей, кстати, компании нужно отдать должное. В отличие от производителей процессоров, которые толкают на рынок модели для «днищенских» ноутбуков, заведомо понимая, что такие процессоры непригодны для использования в современных условиях, Microsoft меру знает и палку не перегибает. Базовая редакция Home любой из версий Виндовс способна в полной мере удовлетворить потребности обывателя.
Итак, какие существуют редакции Виндовс 10?
Home
Home (Домашняя) – базовый набор возможностей «Десятки» с урезанными функциями редакции Pro как то: групповая политика, BitLocker, Hyper-V, средства удалённого подключения, подключение к Azure AD и т.п. Home также ограничена в возможности отложить системные обновления на определённый срок, как это можно делать в редакциях выше. Это бюджетный вариант законного использования системы, но не самый дешёвый.
Home Single Language
Производная от Home подредакция Home Single Language (Домашняя для одного языка) ограничена использованием Windows только в рамках одного системного языка. У неё самый дешёвый лицензионный ключ.
Pro
Pro (Профессиональная) – редакция с оптимальной подборкой функционала для продвинутых пользователей.
Pro for Workstations
Pro for Workstations (Профессиональная для рабочих станций) – продвинутая подредакция для мощных компьютеров, в частности, для серверного оборудования. Появилась вместе с осенним крупным апдейтом Fall Creators Update. Её ключевой особенностью является улучшенная надёжность хранения данных, в частности, работа с файловой системой ReFS.
Enterprise
Enterprise (Корпоративная) – редакция для организаций, предусматривающая поверх возможностей Pro усиленные технологии безопасности и функционал, предназначенный для системщиков-профессионалов. У «Корпоративной» есть урезанная функционально и с долгосрочной задержкой поставки обновлений подредакция LTSB для предприятий и сервисов, коим нужна стабильная среда для функционирования техники. Microsoft не продаёт Enterprise обычным пользователям, только юридическим лицам по подписке. Компания заявляет, что покупка этой редакции частными лицами невозможна в принципе, однако в Интернете купить лицензию для Enterprise можно сплошь и рядом. И, естественно, далеко не все точки продаж цифровых ключей будут требовать от нас подтверждения о причастности к сфере хозяйствования.
Enterprise multi-session
Enterprise multi-session, ранее известная как Enterprise for Virtual Desktops — подредакция Enterprise, заточенная под работу операционной системы по типу узла сеанса удалённого рабочего стола.
IoT Enterprise
IoT Enterprise — подредакция Enterprise, заточенная под работу на устройствах фиксированного назначения (терминалы, вывески, почтоматы, телекоммуникационные системы, торговое, медицинкое, бортовое, транспортное и пр. оборудование)
Education
Education (Образовательная) – это, по сути, та же редакция Enterprise, только с возможностью удаления голосового ассистента Кортаны и невозможностью перехода на LTSB. Главное отличие Education – её ориентация на рынок образовательных учреждений и в связи с этим распространение по цене, в разы меньшей, нежели Enterprise. Приобрести редакцию могут ВУЗы, ПТУ, библиотеки, музеи, благотворительные организации, преподавательский состав учебных заведений и сами студенты, если они не заочники. Условием приобретения редакции является право компании Microsoft требовать документального подтверждения соответствующего статуса покупателя.
S
S – редакция, урезанная в части недоступности десктопного функционала. Её специфика детально описывается в этой статье. Редакция более не существует.
Примечание: друзья, детальное сравнение основных редакций Windows 10 вы можете посмотреть
на сайте Майкрософт, где компания представляет подробную сравнительную таблицу с описанием доступного для редакций функционала
.
N и KN
Windows N – это не отдельная редакция, даже не подредакция, это разновидность Home и Pro без Windows Media Player и ещё некоторых компонентов. Урезанную сборку Microsoft вынуждена была создать в 2004 году в соответствии с требованием Европейской Комиссии, ставшей на защиту интересов сторонних европейских разработчиков, что выпускали свои мультимедийные продукты.
Windows KN также появилась в принудительном порядке. Через пару лет после европейского прецедента решение против Microsoft вынесла Южнокорейская Торговая комиссия, удовлетворив иск разработчика Daum Communications и обязав софтверного гиганта выпускать на южнокорейский рынок сборку операционной системы без штатного проигрывателя и Instant Messenger (мессенджера на борту Windows XP).
В версии Windows 10 сборки N и KN не предусматривают предустановленных приложений Windows Media Player, Groove Music, «Кино и ТВ», «Запись голоса» и «Скайп». Также не работают функции синхронизации системы, веб-камера, Cortana, открытие PDF-файлов в Microsoft Edge и прочие вещи. Windows 10 N и KN предназначены, соответственно, для Европы и Южной Кореи – территориальных юрисдикций органов, вынесших решения против Microsoft. И поскольку существование этих сборок носит принудительный характер, естественно, компания о них без надобности не распространяет информацию.
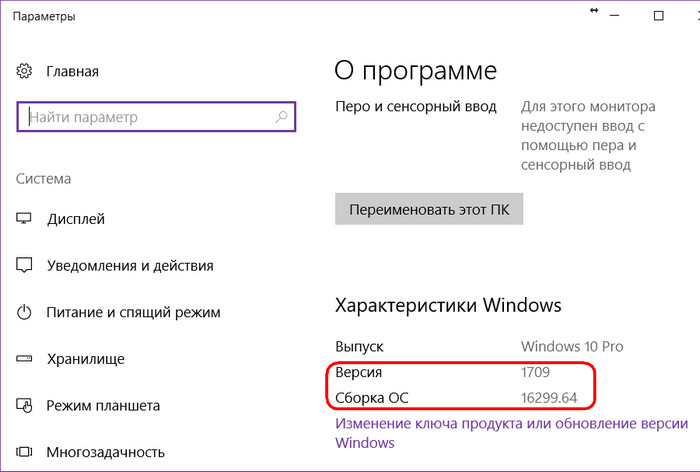
Если мы откроем свойства «Десятки», в графе характеристик увидим отметку о её версии и сборке.
Номер сборки отражает информацию об определённом наборе функционала Windows 10 и меняется часто, по мере внедрения обновлений в стабильную ветвь после их «обкатки» в рамках программы Windows Insider. Номера версий «Десятки» меняются реже, их смена приурочена к серии функциональных обновлений, выпускаемых каждые полгода. Порядковые номера версий не носят последовательный характер, в них заключена информация о месяце или полугодии и годе выпуска. Кроме номеров, у версий есть названия – технические (для разработчиков Microsoft и инсайдеров) и носящие название самих полугодичных функциональных обновлений (простые понятия для обычных пользователей). Версий Windows 10 много:
- 1507, Threshold 1 – первое обновление «Десятки», вышедшее в июле 2015 г.;
- 1511, Threshold 2, по-простому November Update – второе обновление, вышедшее в ноябре 2015 г.;
- 1607, Redstone 1, по-простому Anniversary Update – третье обновление, вышедшее в июле 2016 г.
- 1703, Redstone 2, по-простому Creators Update – четвёртое обновление, вышедшее в марте 2017 г.;
- 1709, Redstone 3, по-простому Fall Creators Update – пятое обновление, вышедшее в октябре 2017 г.;
- 1803, Redstone 4, по-простому April 2018 Update – шестое обновление, вышедшее в апреле 2018 г.;
- 1809, Redstone 5, по-простому October 2018 Update – седьмое обновление, вышедшее в октябре 2018 г.;
- 1903, 19H1, по-простому May 2019 Update – восьмое обновление, вышедшее в мае 2019 г.;
- 1909, Vanadium или 19H2, по-простому November 2019 Update – девятое обновление, вышедшее в ноябре 2019 г.;
- 2004, 20H1, по-простому May 2020 Update – десятое обновление, вышедшее в мае 2020 г.;
- 2009, 20H2, Windows 10 «Manganese» — одиннадцатое незначительное обновление, вышедшее в октябре 2020 г.
Вот сколько много щупалец у гигантского спрута под названием Windows 10.
Статьи на эту тему:
- История операционной системы Windows,
- Виды лицензий Windows,
- Windows 10 VS Windows 7: какая из операционных систем лучше.