Аннотация
|
Сводка статьи: |
Этот документ предоставляет:
|
Восстановление системы
«Восстановление системы» — это средство ® Windows® предназначенное для защиты и восстановления программного обеспечения компьютера. Восстановление системы делает «моментальный снимок» некоторых системных файлов и реестра Windows и сохраняет их в качестве точек восстановления. При сбое установки или повреждения данных восстановление системы может вернуть систему в рабочее состояние без необходимости переустановки операционной системы. Оно восстанавливает среду Windows, возвращаясь к файлам и настройкам, сохраненным в точке восстановления.

|
Примечание. |
Программа по умолчанию создает точки восстановления один раз в день. Она постоянно отслеживает действия в системе и создает точку восстановления при определенных действиях. К типам действий, которые запускают автоматическое создание точек восстановления, относятся:
-
установка программного обеспечения
-
обновление драйверов оборудования
-
установка новых драйверов оборудования
-
Ручное создание точек восстановления
Восстановление системы доступно в следующих операционных системах:
-
Microsoft Windows Edition (ME)
-
Microsoft Windows XP
-
Microsoft Windows Vista
Дополнительные сведения
-
«Вопросы и ответы о восстановлении системы» для Windows Vista
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Нужны дополнительные параметры?
Изучите преимущества подписки, просмотрите учебные курсы, узнайте, как защитить свое устройство и т. д.
В сообществах можно задавать вопросы и отвечать на них, отправлять отзывы и консультироваться с экспертами разных профилей.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The System Restore wizard in Windows 10 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Included with |
|
| Type | System recovery |
| Website | support |
System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows the user to revert their computer’s state (including system files, installed applications, Windows Registry, and system settings) to that of a previous point in time, which can be used to recover from system malfunctions or other problems. First included in Windows Me, it has been included in all following desktop versions of Windows released since, excluding Windows Server.[1] In Windows 10, System Restore is turned off by default and must be enabled by users in order to function.[2] This does not affect personal files such as documents, music, pictures, and videos.
In prior Windows versions it was based on a file filter that watched changes for a certain set of file extensions, and then copied files before they were overwritten.[3][4] An updated version of System Restore introduced by Windows Vista uses the Shadow Copy service as a backend (allowing block-level changes in files located in any directory on the volume to be monitored and backed up regardless of their location) and allows System Restore to be used from the Windows Recovery Environment in case the Windows installation no longer boots at all.[5]
Overview[edit]
In System Restore, the user may create a new restore point manually (as opposed to the system creating one automatically), roll back to an existing restore point, or change the System Restore configuration. Moreover, the restore itself can be undone. Old restore points are discarded in order to keep the volume’s usage within the specified amount. For many users, this can provide restore points covering the past several weeks. Users concerned with performance or space usage may also opt to disable System Restore entirely. Files stored on volumes not monitored by System Restore are never backed up or restored.
System Restore backs up system files of certain extensions (.exe, .dll, etc.) and saves them for later recovery and use.[6] It also backs up the registry and most drivers.
Resources monitored[edit]
Starting with Windows Vista, System Restore takes a snapshot of all volumes it is monitoring. However, on Windows XP, it only monitors the following:[7][8]
- Windows Registry
- Files in the Windows File Protection folder (
Dllcache) - Local user profiles
- COM+ and WMI databases
- IIS metabase
- Specific file types monitored[6]
The list of file types and directories to be included or excluded from monitoring by System Restore can be customized on Windows Me and Windows XP by editing %windir%\system32\restore\Filelist.xml.[9]
Disk space consumption[edit]
The amount of disk space System Restore consumes can be configured. Starting with Windows XP, the disk space allotted is configurable per volume and the data stores are also stored per volume. Files are stored using NTFS compression and a Disk Cleanup handler allows deleting all but the most recent Restore Points. System Restore can be disabled completely to regain disk space. It automatically disables itself if the volume’s free space is too low for it to operate.
Restore points[edit]
Windows creates restore points:
- When software is installed using Windows Installer or other installers that are aware of System Restore[10]
- When Windows Update installs new updates
- When the user installs a driver that is not digitally signed by Windows Hardware Quality Labs
- Periodically. By default:
- Windows XP creates a restore point every 24 hours[11]
- Windows Vista creates a restore point if none is created within the last 24 hours[11]
- Windows 7 creates a restore point if none has been created within the last seven days[11]
- On user’s command
Windows XP stores restore point files in a hidden folder named «System Volume Information» on the root of every drive, partition or volume, including most external drives and some USB flash drives.[3]
The operating system deletes older restore points per the configured space constraint on a first in, first out basis.
Implementation differences[edit]
There are considerable differences between how System Restore works under Windows XP and later Windows versions.
- Configuration user interface – In Windows XP, there is a graphical slider to configure the amount of disk space allotted to System Restore. In Windows Vista, the slider to configure the disk space is not available. Using the command-line tool Vssadmin.exe or by editing the appropriate registry key,[12][13] the space reserved can be adjusted. Starting with Windows 7, the slider is available once again.
- Maximum space – In Windows XP, System Restore can be configured to use up to a maximum of 12% of the volume’s space for most disk sizes;[8] however, this may be less depending on the volume’s size. Restore points over 90 days old are automatically deleted, as specified by the registry value RPLifeInterval (Time to Live – TTL) default value of 7776000 seconds. In Windows Vista and later, System Restore is designed for larger volumes.[14] By default, it uses 15% of the volume’s space.[10]
- File paths monitored – Up to Windows XP, files are backed up only from certain directories. On Windows Vista and later, this set of files is defined by monitored extensions outside of the Windows folder, and everything under the Windows folder.[15]
- File types monitored – Up to Windows XP, it excludes any file types that are considered «personal» to the user, such as documents, digital photographs, media files, e-mail, etc. It also excludes the monitored set of file types (.DLL, .EXE etc.) from folders such as My Documents. Microsoft recommends that if a user is unsure as to whether certain files will be modified by a rollback, they should keep those files under My Documents.[8] When a rollback is performed, the files that were being monitored by System Restore are restored and newly created folders are removed. However, on Windows Vista and later, it excludes only document file types; it does not exclude any monitored system file type regardless of its location.
- Configuring advanced System Restore settings – Windows XP supports customizing System Restore settings via Windows Registry and a file at
%windir%\system32\restore\Filelist.xml.[9][16] Windows Vista and later no longer support this.[17] - FAT32 volume support – On Windows Vista and later, System Restore no longer works on FAT32 disks and cannot be enabled on disks smaller than 1 GB.[14]
Restoring the system[edit]
Up to Windows XP, the system can be restored as long as it is in an online state, that is, as long as Windows boots normally or from Safe mode. It is not possible to restore the system if Windows is unbootable without using 3rd-party bootable recovery media such as ERD Commander. Under Windows Vista and later, the Windows Recovery Environment can be used to launch System Restore and restore a system in an offline state, that is, in case the Windows installation is unbootable.[5] Since the advent of Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack, Diagnostics and Recovery Toolset from it can be used to create a bootable recovery disc that can log on to an unbootable Windows installation and start System Restore. The toolset includes ERD Commander for Windows XP that was previously a 3rd-party product by Winternals.
Limitations and complications[edit]
A limitation which applies to System Restore in Windows versions prior to Windows Vista is that only certain file types and files in certain locations on the volume are monitored, therefore unwanted software installations and especially in-place software upgrades may be incompletely reverted by System Restore.[18] Consequently, there may be little or no practical beneficial impact. Certain issues may also arise when attempting to run or completely uninstall that application. In contrast, various other utilities have been designed to provide much more complete reversal of system changes including software upgrades. However, beginning with Windows Vista, System Restore monitors all system file types on all file paths on a given volume, so there is no issue of incomplete restoration.
It is not possible to create a permanent restore point. All restore points will eventually be deleted after the time specified in the RPLifeInterval registry setting is reached or earlier if allotted disk space is insufficient. Even if no user or software triggered restore points are generated, allotted disk space is consumed by automatic restore points.[8] Consequently, in systems with little space allocated, if a user does not notice a new problem within a few days, it may be too late to restore to a configuration from before the problem arose.
For data integrity purposes, System Restore does not allow other applications or users to modify or delete files in the directory where the restore points are saved. On NTFS volumes, the restore points are protected using ACLs. Since its method of backup is fairly simplistic, it may end up archiving malware such as viruses, for example in a restore point created before using antivirus software to clean an infection. Antivirus software is usually unable to remove infected files from System Restore;[19] the only way actually to delete the infected files is to disable System Restore, which will result in losing all saved restore points; otherwise they will remain until Windows deletes the affected restore points. However stored infected files in themselves are harmless unless executed; they will only pose a threat if the affected restore point is reinstated. Windows System Restore is not compatible with restore points made by third party applications.
Changes made to a volume from another operating system (in case of multi-booting scenarios) cannot be monitored. In addition, multi-booting different versions of Windows can disrupt the operation of System Restore. Specifically, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 delete the checkpoints created by Windows Vista and later.[20] Also, checkpoints created by Windows 8 may be destroyed by previous versions of Windows.[21]
See also[edit]
- Backup
References[edit]
- ^ «No Restore Point For You». Cnet. December 28, 2007. Archived from the original on January 19, 2013. Retrieved February 27, 2020.
- ^ Jim Tanous, «Why and How to Enable System Restore in Windows 10» Archived December 21, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Tekrevue, July 28, 2015
- ^ a b Russinovich, Mark E.; Solomon, David A. (2005). Microsoft Windows Internals: Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, and Windows 2000 (4 ed.). Redmond, WA: Microsoft Press. pp. 706–711. ISBN 0-7356-1917-4.
- ^ «Windows Backup». Windows Vista portal. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 10, 2007. Retrieved January 11, 2014.
- ^ a b Fok, Christine (September 2007). «A Guide to Windows Vista Backup Technologies». TechNet Magazine. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved January 11, 2014.
- ^ a b «MSDN System Restore Reference: Monitored File Extensions». Archived from the original on October 20, 2017. Retrieved May 22, 2008.
- ^ «Monitoring the System». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 6, 2012. Retrieved May 10, 2014.
- ^ a b c d «Frequently Asked Questions Regarding System Restore in Windows XP». TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 24, 2008.
- ^ a b «System Restore: Monitored File Name Extensions». Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved May 4, 2017.
- ^ a b «Selected Scenarios for Maintaining Data Integrity with Windows Vista». TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved May 10, 2014.
- ^ a b c «About System Restore». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 6, 2012. Retrieved May 10, 2014.
- ^ «MSFN’s Unattended Windows : Reduce Disk Space Used By System Restore». Archived from the original on July 6, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2009.
- ^ «The Registry Keys and Values for the System Restore Utility». September 15, 2006. Archived from the original on October 31, 2009. Retrieved November 3, 2009.
- ^ a b «Windows Vista Help: System Restore FAQs». Archived from the original on May 22, 2008. Retrieved May 22, 2008.
- ^ Windows Vista System Restore FAQs: Bert Kinney — System Restore MVP Archived March 27, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «The Registry Keys and Values for the System Restore Utility». Archived from the original on October 31, 2009. Retrieved November 5, 2009.
- ^ «Vista System Restore Q&A — System Restore MVP Bert Kinney». Archived from the original on March 27, 2008. Retrieved May 22, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Server Hacks: Hacking System Restore — O’Reilly Media». Archived from the original on August 28, 2008. Retrieved September 19, 2008.
- ^ «Antivirus Tools Cannot Clean Infected Files in the _Restore Folder». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on January 4, 2007. Retrieved September 19, 2007.
- ^ «How restore points and other recovery features in Windows Vista are affected when you dual-boot with Windows XP». File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. July 14, 2006. Archived from the original on July 18, 2006. Retrieved March 21, 2007.
- ^ «Calling SRSetRestorePoint». MSDN Library. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved February 1, 2015.
Snapshots of the boot volume created by System Restore running on Windows 8 may be deleted if the snapshot is subsequently exposed by an earlier version of Windows.
Further reading[edit]
- «Use System Restore to Undo Changes if Problems Occur». Windows XP Help. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 15, 2008.
- «Windows XP System Restore». MSDN. Microsoft. April 2001. Archived from the original on September 1, 2008.
- «Checkpoints that you create after September 8, 2001 do not restore your computer». Support (3.8 ed.). Microsoft. October 26, 2007. Archived from the original on November 5, 2004. Retrieved May 9, 2014.
- «The Registry Keys and Values for the System Restore Utility». Support (1.3 ed.). Microsoft. January 15, 2006. Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved May 9, 2014.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Support article
Окно восстановления системы в Windows XP
Восстановление системы (англ. System restore) — компонент операционной системы Windows (процесс rstrui.exe), предназначенный для восстановления работоспособности ОС путем отката (восстановления предыдущего состояния ПК) системных файлов, ключей реестра, инсталлированных программ и т.д. System restore присутствует в системах Windows ME и Windows XP, а также новой системе Windows Vista.
Семейство Windows Server не включает в себя функцию System Restore. Восстановление системы, встроенное в Windows XP, может быть инсталлировано на устройстве, работающем под Windows Server 2003, хотя эта операция не поддерживается Windows Vista данный компонент обладает улучшенным интерфейсом и построен на технологии Shadow Copy, в отличие от предыдущих версий, построеных на файловом фильтре, который отслеживал изменения в определённом наборе расширений файлов и затем копировал файлы, прежде чем они перезаписывались. Преимущество использования технологии Shadow Copy в том, что блок-уровневые изменения в файлах, находящихся в любой папке на диске, могут быть отслежены и резервные копии созданы независимо от местонахождения файлов.
Содержание
- 1 Обзор
- 2 Точки восстановления
- 3 Различия в Операционных Системах
- 4 Запуск и управление программой
- 5 Техническая реализация
- 6 Ограничения и сложности
Обзор
Пользователь может создавать новую точку восстановления вручную, производить откат к уже существующей точке или изменять конфигурацию System Restore. Более того, восстановление само по себе может быть обратимым. Старые точки восстановления сбрасываются для того, чтобы поддерживать использование объёма диска в точно определённом размере. Для многих пользователей это может обеспечить точки восстановления, покрывающие несколько прошедших недель. Пользователи, для которых важны производительность или используемый объём диска, могут также выбрать полное отключение System Restore. Для файлов, хранящихся на дисках, но которые служба восстановления не отследила, не будут созданы резервные копии и такие файлы никогда не будут восстановлены. System Restore создаёт резервные копии системных файлов определённых расширений (.exe, .dll и т.д.) и сохраняет их для дальнейшего восстановления и использования. Также создаются резервные копии Реестра и большинства драйверов.
Точки восстановления
Точки восстановления создаются:
- когда программа инсталлируется с помощью Windows Installer, Package Installer или других Установщиков, знающих о существовании System Restore;
- когда Windows Update инсталлирует новые обновления;
- когда пользователь устанавливает драйвер без цифровой подписи Windows Hardware Quality Labs;
- каждые 24 часа пользования компьютером (10 часов в Windows Me), или каждые 24 часа календарного времени, в зависимости от того, что истечёт раньше. Эту установку можно конфигурировать через реестр. Подобные точки восстановления известны как Точки Проверки Системы. Для создания таких точек Восстановлению Системы требуется Task Scheduler. Более того, точки проверки системы создаются лишь тогда, когда система находится в бездействии в течение некоторого времени;
- когда система запускается, будучи отключенной более 24 часов;
- по требованию пользователя.
На Windows Vista теневые копии, создаваемые во время процедуры File Backup и Complete PC Backup, могут также использоваться как точки восстановления.
Различия в Операционных Системах
Существует значительное различие, как System Restore работает под Windows XP и Windows Vista. В Windows XP можно конфигурировать используемый размер до 12% объёма диска. В Windows Vista служба восстановления разработана для бо́льших объёмов и не может быть запущено на дисках, меньших чем 1 ГБ (по умолчанию используется 15% объёма диска). Используя командную строку Vssadmin.exe, можно установить требуемый объём. Вплоть до Windows XP файлы резервировались только из определённых папок. На Windows Vista этот набор файлов обозначен отслеженными расширениями вне пределов папки Windows, и ВСЕМИ файлами папки Windows. Вплоть до Windows XP исключались все типы файлов, используемых для личных файлов данных пользователя, таких как документы, цифровые фото, медиа-файлы, e-mail и т.д. Также исключался отслеженный набор типов файлов (.exe, .dll) из таких папок, как Мои Документы. Windows Vista исключения касаются только файлов типа «документ», и при откате ни один отслеженный файл другого типа не исключается (независимо от своего местонахождения) и Восстановление Системы производится по всему объёму.
Вплоть до Windows XP система может быть восстановлена, пока Windows загружается в Нормальном или Безопасном режиме. Если Windows не запускается, восстановление невозможно. Под Windows Vista в этом случае может быть использован Windows Recovery Environment для запуска System Restore.
Запуск и управление программой
Для запуска программы можно использовать один из способов:
- Выберите Пуск => (Все) программы => Стандартные => Служебные => Восстановление системы
- Выберите Пуск => Справка и поддержка и щелкните «Отмена изменений с помощью Восстановления системы»
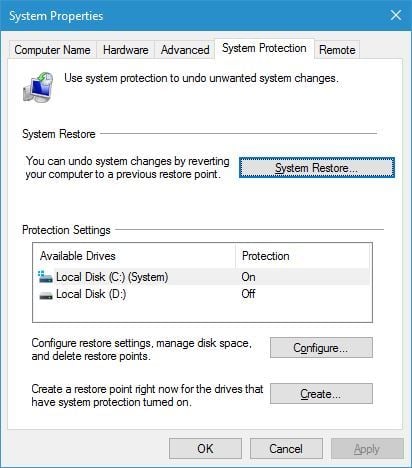
Для задания параметров программы необходимо нажать в ее главном окне ссылку «Параметры восстановления системы» или открыть свойства значка Мой компьютер (или апплет панели управления «Система») и перейти на вкладку «Восстановление системы».
Техническая реализация
System Restore сохраняет точки восстановления в папку System Volume Information. По умолчанию (при установке на диск с файловой системой Windows XP запрещает доступ пользователей к папке System Volume Information, разрешая доступ лишь системе (пользователю SYSTEM).
Ограничения и сложности
Ограничения, с которыми приходится сталкиваться при Восстановлении Системы в версиях Windows до Windows Vista состоит в том, что только отслеженные типы файлов и только файлы из определённых папок (System Restore резервирует целиком только Реестр Windows) могут быть отслежены, следовательно, нежелательные установки программ и приложений и особенно обновления программ, могут быть не полностью возвращены в первоначальное состояние. В результате воздействие может быть незначительным или практически отсутствовать (не считая использованного места на диске). Могут возникнуть нежелательные моменты при попытке запустить или удалить такие приложения. Для сравнения, различные другие утилиты разработаны для обеспечения намного более полного возврата изменений системы, включая обновления программ. Например, при отслеживании всех изменений, GoBack от Norton или Rollback Rx от Horizon DataSys позволяют полное восстановление файловой системы к прежнему состоянию от любой из сотен ежедневных точек восстановления. Однако, частое или непрерывное отслеживание может также влиять на производительность системы, в то время как точки System Restore обычно создаются быстро и экономно. При отсутствии адекватного свободного места на диске (точки восстановления в папке System Volume Information занимают относительно большой объём) System Restore будет не способно создать точку восстановления, так что пользователь при попытке восстановить Систему может обнаружить, что не существует ни одной точки восстановления.
Нет возможности создавать постоянную точку, которая не будет удалена спустя несколько дней, когда автоматическим точкам потребуется место на диске. Так что если проблема не была обнаружена в течение нескольких дней, в момент, когда она всё-таки будет обнаружена, может быть уже поздно для восстановления того состояния системы, которое было до появления проблемы.
По умолчанию System Restore не позволяет другим приложениям или пользователям изменять или удалять файлы из директорий, где сохраняются точки восстановления в целях неприкосновенности. Поскольку этот метод резервирования довольно упрощённый, результатом может быть архивирование вредоносных программ, таких как компьютерные черви и вирусы. В этом случае антивирусная программа будет неспособна удалить заражённый файл. Единственный способ удаления инфекции состоит в отключении System Restore, что приведёт к потере всех сохранённых точек, или просто ждать, когда Windows удалит (старые)точки для освобождения места под новые. Более того, если заражённый набор файлов восстановлен, результатом может быть также восстановление вируса.
Под Windows Vista System Restore не работает на дисках
Изменения, произведённые на диске с другой ОС ( в случае, если на диске установлены две и более ОС) не могут быть отслежены. Также возникают вопросы совместимости во время Восстановления Системы при нахождении на одном загрузочном диске Windows XP (или Windows Server) и Windows Vista (или более поздней ОС). Теневые точки на диске удаляются, когда более старые ОС получают доступ к этому диску
Распространенная проблема, что при откате CS файлы удаляются, так как не считаются файлами данных. То есть, выполнив откат, вы потеряете всю работу в Visual Studio с C# файлами, и вам придется отменить откат. Однако, если вы выполняли откат из защищенного режима, то отмена отката невозможна, что потенциально может привести к потере важных данных.
|
Компоненты Microsoft Windows |
||
|---|---|---|
| Основные |
Aero • Desktop Window Manager • Проводник (Explorer) • Панель задач • Меню «Пуск» • Shell (namespace • Special Folders • File associations) • Search (Saved search • iFilters) • Graphics Device Interface • WIM • Next Generation TCP/IP stack () • .NET Framework • Audio • Printing (XML Paper Specification) • Active Scripting (WSH • VBScript • COM (OLE • OLE Automation • DCOM • ActiveX • ActiveX Document • Structured storage • Transaction Server) • Previous Versions • WDDM • UAA • Win32 console |
|
| Службы управления |
Backup and Restore Center • Панель управления (Applets) • Диспетчер устройств • Очистка диска • Дефрагментация диска • Event Viewer • Management Console • Problem Reports and Solutions • Sysprep • • Диспетчер задач • System File Checker • Восстановление системы • Windows Installer • Windows PowerShell • Windows Update • WinSAT • Windows Easy Transfer |
|
| Приложения |
Калькулятор • Calendar • Таблица символов • Contacts • DVD Maker • Fax and Scan • Internet Explorer • Journal • Outlook Express • Почта Windows • Magnifier • Media Center • Meeting Space • Mobile Device Center • Mobility Center • Movie Maker • Narrator • Notepad • Paint • Фотоальбом • Private Character Editor • Remote Assistance • Sidebar • Snipping Tool • Звукозапись • Windows Media Player • Windows Speech Recognition • Игры |
Chess Titans • Hold ‘Em • InkBall • Mahjong Titans • Purble Place • Пасьянс «Косынка» • Пасьянс «Паук» • Сапёр • Пасьянс «Свободная ячейка» • Пинбол • Червы |
| Ядро ОС |
hal.dll • System Idle Process • Registry (реестр) • Windows service • Service Control Manager • EXE • Boot Manager • Recovery Console • I/O • WinRE • WinPE • Kernel Patch Protection |
|
| Службы |
Autorun • BITS • Task Scheduler • Wireless Zero Configuration • Shadow Copy • Windows Error Reporting • Multimedia Class Scheduler • CLFS |
|
| Файловые системы |
Hard link • Junction point • Mount Point • Reparse point • Symbolic link • TxF • FAT • CDFS • UDF • DFS • IFS |
|
| Сервер |
Domains • Active Directory • DNS • Групповая политика • Roaming user profiles • Folder redirection • Координатор распределённых транзакций • MSMQ • Windows SharePoint Services • Windows Media Services • Rights Management Services • IIS • Terminal Services • WSUS • Network Access Protection • DFS Replication • Remote Differential Compression • Print Services for UNIX • Remote Installation Services • Windows Deployment Services • Windows System Resource Manager • Hyper-V |
|
| Архитектура |
NT series architecture • Object Manager • Startup process (Vista) • I/O request packets • Kernel Transaction Manager • Logical Disk Manager • Security Accounts Manager • Windows Resource Protection • LSASS • CSRSS • SMSS |
|
| Безопасность |
UAC • BitLocker • Defender • DEP • Protected Media Path • Mandatory Integrity Control • UIPI • Windows Firewall • Security Center |
|
| Совместимость |
Unix subsystem (Interix) • Virtual DOS Machine • Windows on Windows • WOW64 |
How to use System Restore in Windows 10
by Milan Stanojevic
Milan has been enthusiastic about technology ever since his childhood days, and this led him to take interest in all PC-related technologies. He’s a PC enthusiast and he… read more
Updated on
System Restore is a recovery feature in the Windows operating system that allows you to restore your PC to an earlier state. By using System Restore, you’ll revert Windows files and settings, system files, installed programs and drivers to their previous state.
System Restore will allow you to restore your system to a working state after making changes to the system files or after installing new software. Bear in mind that System Restore won’t affect files such as your documents, pictures, etc., so you can’t use it to restore files that you’ve recently removed.
In order to restore your PC using System Restore, you need to have a restore point available. You can create restore points manually at any time, but your PC will usually create them on its own when installing new software, driver or system update.
How to create a System Restore point in Windows 10
- Press the Start button and search for system restore.
- Choose Create a restore point
- Click on the Create button to start the process.
How to do a System Restore
To use System Restore, follow these steps:
- Press Windows Key and type system restore. Choose Create a restore point option.
- Click on System Restore button.
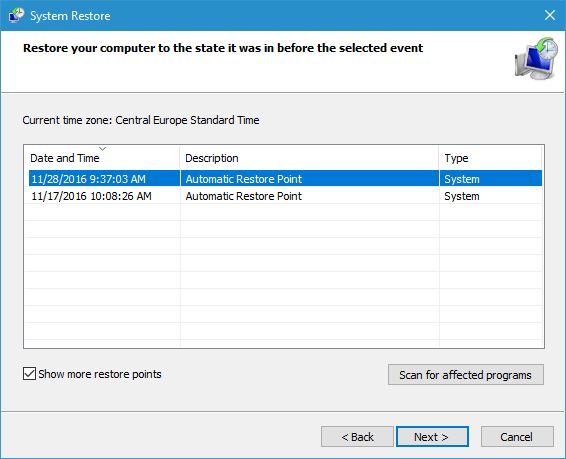
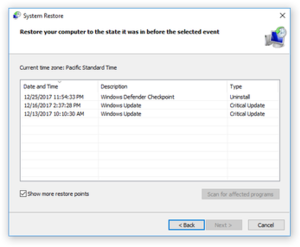
- Check Show more restore points. Select the available restore point and click Next.
- Follow the instructions to perform the restore.
Although System Restore is a great feature, sometimes issues with it can appear. If you encounter any problems with it, be sure to check our wide collection of troubleshooting guides.
Now that you know how to perform a System Restore, let’s see some of the common questions related to this process.
How long does a system restore take?
A normal operation of restoring the system with the tools already built-in Windows takes somewhere between 15 – 35 minutes. It depends on the size of the restore point, the hardware of the device and the speed of the disk drive.
Does system restore delete files?
First, you should always make a backup copy of your files when performing any outside of the ordinary operation.
Now, are you worried that you would lose files if you do a System Restore? No need to worry – it will not delete any personal files such as documents, images, videos etc.
You will lose some of the programs that are already installed and you would need to re-install them though.
Тема: Восстановление системы
Восстановление
системы
(англ.
System restore)
— компонент операционной системы
Windows (процесс
rstrui.exe), предназначенный для восстановления
работоспособности ОС путем отката
(восстановления предыдущего состояния
ПК) системных файлов, ключей реестра,
инсталлированных программ и т.д. System
restore присутствует в системах Windows ME и
Windows XP, а
также новой системе Windows
Vista.
Семейство
Windows Server
не включает в себя функцию System Restore.
Восстановление системы, встроенное в
Windows XP,
может быть инсталлировано на устройстве,
работающем под Windows
Server 2003, хотя эта операция не поддерживается
Microsoft.
В
Windows Vista
данный компонент обладает улучшенным
интерфейсом и построен на технологии
Shadow
Copy, преимущество использования этой
технологии в том, что блок-уровневые
изменения в файлах, находящихся в любой
папке на диске, могут быть отслежены и
резервные копии созданы независимо от
местонахождения файлов.
Пользователь
может создавать новую точку восстановления
вручную, производить откат к уже
существующей точке или изменять
конфигурацию System Restore. Более того,
восстановление само по себе может быть
обратимым. Старые точки восстановления
сбрасываются для того, чтобы поддерживать
использование объёма диска в точно
определённом размере. Для многих
пользователей это может обеспечить
точки восстановления, покрывающие
несколько прошедших недель. Пользователи,
для которых важны производительность
или используемый объём диска, могут
также выбрать полное отключение System
Restore. Для файлов, хранящихся на дисках,
но которые служба восстановления не
отследила, не будут созданы резервные
копии и такие файлы никогда не будут
восстановлены. System Restore создаёт резервные
копии системных файлов определённых
расширений (.exe, .dll и т.д.) и сохраняет их
для дальнейшего восстановления и
использования. Также создаются резервные
копии Реестра и большинства драйверов.
Точки восстановления
Точки
восстановления создаются:
-
когда
программа инсталлируется с помощью
Windows
Installer, Package Installer или других Установщиков,
знающих о существовании System Restore; -
когда
Windows Update
инсталлирует новые обновления; -
когда
пользователь устанавливает драйвер
без цифровой подписи Windows
Hardware Quality Labs; -
каждые
24 часа пользования компьютером (10 часов
в Windows Me),
или каждые 24 часа календарного времени,
в зависимости от того, что истечёт
раньше. Эту установку можно конфигурировать
через реестр. Подобные точки восстановления
известны как Точки Проверки Системы.
Более того, точки проверки системы
создаются лишь тогда, когда система
находится в бездействии в течение
некоторого времени; -
когда
система запускается, будучи отключенной
более 24 часов; -
по
требованию пользователя.
На
Windows Vista
теневые копии, создаваемые во время
процедуры File Backup и Complete PC Backup, могут
также использоваться как точки
восстановления.
Запуск и управление программой
Для
запуска программы можно использовать
один из способов:
-
Выберите
Пуск => (Все) программы => Стандартные
=> Служебные => Восстановление системы
-
Выберите
Пуск => Справка и поддержка и щелкните
«Отмена изменений с помощью
Восстановления системы»
Для
задания параметров программы необходимо
нажать в ее главном окне ссылку «Параметры
восстановления системы» или открыть
свойства значка Мой компьютер (или
апплет панели управления «Система»)
и перейти на вкладку «Восстановление
системы».
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #