The Net User command is a Windows command-line utility that allows you to manage Windows server local user accounts or on a remote computer.
The command Net User allow you to create, delete, enable, or disable users on the system and set passwords for the net user accounts.
Windows administrators can perform add or modifications in domain user accounts using the net user command-line tool.
You can get net user account information, enable or disable a user account, sets the home directory path, set account expiration, and so on.
In this article, we will discuss how to use the net user command-line tool with examples to get user account information, domain account status, and password expiry date.
Net User Command Syntax
The basic syntax for the net user command is as follows:
net user [<UserName> {<Password> | *} [<Options>]] [/domain]
net user [<UserName> {<Password> | *} /add [<Options>] [/domain]]
net user [<UserName> [/delete] [/domain]]
Refer to the below most important net user command parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Username | Enable or disable the user account |
| Password | It specifies the user account name to add, modify, or display user account information |
| /domain | Perform the operation on the domain controller |
| /active:{no | yes} | Enable or disable user account |
| /comment | Provide descriptive comments for the user account |
| /expires | Specify the date to expire user account |
| net help | Display help for the net user command |
| <Options> | Specify command-line options |
Refer to the following table to know more about options used in net user command.
| Command-line option syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| /active:{no | yes} | Use this option to enable or disable a user account. The default value is yes (active). |
| /comment:”<Text>” | Use this to provide comments for the user account, max 48 characters, and should be enclosed in quotation marks. |
| /countrycode:<NNN> | /countrycode option is used to set the country code for the user account to display help or error messages in their language. The default value is 0, which means the computer’s default country/region code. |
| /expires:{{<MM/DD/YYYY> | <DD/MM/YYYY> | <mmm,dd,YYYY>} | never} | Use this option to specify the date for the user account to expire. If the expiration date is not specified, it will assume never expires. |
| /fullname:”<Name>” | Specify the user’s full name instead of username. |
| /homedir:<Path> | Use this option to set the path for the user’s home directory. |
| /passwordchg:{yes | no} | Use this to specify if the user can change their own password. The default value is yes. |
| /passwordreq:{yes | no} | It specifies if the user must have a password or not. The default is yes. |
| /profilepath:[<Path>] | Use this option to sets a path for the user’s logon profile. This path points to a registry profile. |
| /scriptpath:<Path> | Use this to set a path for the user’s logon script. <Path> should be relative. |
| /times:{<Day>[<-Day>][,<Day>[-<Day>]],<Time>[-<Time>][,<Time>[-<Time>]][;] | all} | It specifies the times that users are allowed to use the computer. |
| /usercomment:”<Text>” | It specifies that an administrator can add or change the “User comment” for the account. |
| /workstations:{<ComputerName>[,…] | *} | It lists as many as eight workstations from which a user can log on to the network. |
Net User – List All User Accounts
Use the Net User command and run it on the Windows command prompt without any parameter to list all user accounts on the local user account.
Open a command prompt to run the net user command below
net user
The above Windows net user command returns the list of all user accounts on the local computer.
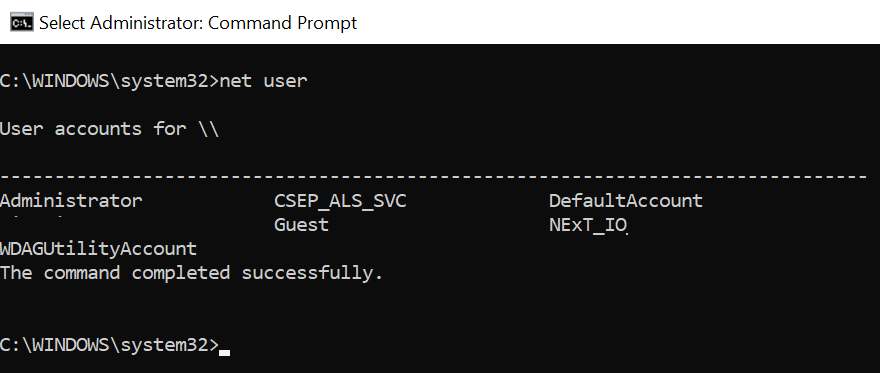
You can also use the net users command without any parameters on the cmd to retrieve a list of all user accounts on your computer.
Run the command net user on the domain controller to get a list of all users on the domain.
net user
The output of the above command net user gets the domain username accounts.
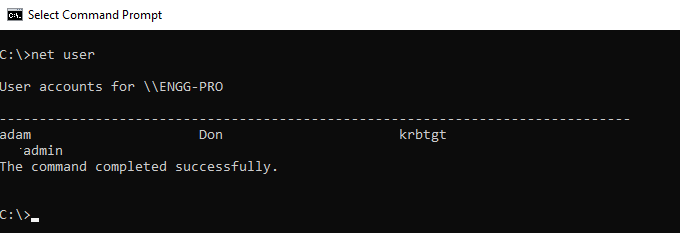
You can also use the net user command-line tool to get user account information, modify a user account, and check when the password was last set.
Net User Account – Display User Account Information
Run the net user command in the command line to get user account information.
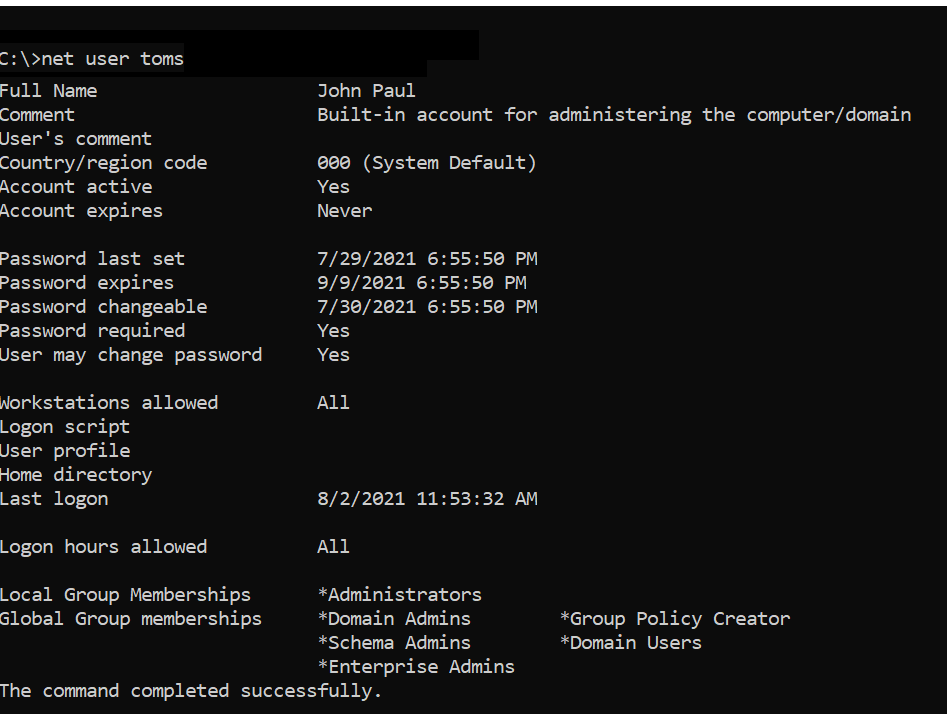
# Get the user account information for Toms user. net user Toms
The above net user command uses the username to retrieve user details and display net user account information below
C:\>net user Toms
User name Toms
Full Name John Paul
Comment Built-in account for administering the computer/domain
User's comment
Country/region code 000 (System Default)
Account active Yes
Account expires Never
Password last set 7/29/2021 6:55:50 PM
Password expires 9/9/2021 6:55:50 PM
Password changeable 7/30/2021 6:55:50 PM
Password required Yes
User may change password Yes
Workstations allowed All
Logon script
User profile
Home directory
Last logon 8/2/2021 11:53:32 AM
Logon hours allowed All
Local Group Memberships *Administrators
Global Group memberships *Domain Admins *Group Policy Creator
*Schema Admins *Domain Users
*Enterprise Admins
The command completed successfully.
C:\>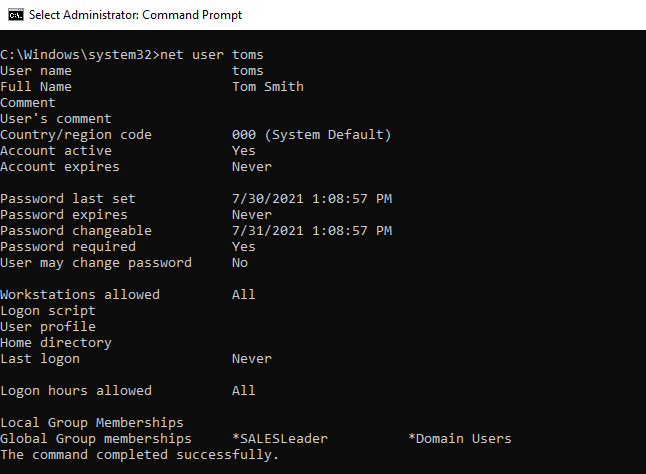
Cool Tip: How to get-aduser in the active directory using PowerShell!
Net User Add Account
To create a new local user account, use the /Add parameter and specify the desired username:
# Create a new user account on local computer with login name Teresa net user /Add Teresa
To create a domain user account, add the /domain parameter and specify the username and password:
# Create a new user account on domain with login name Peter and password Shell@123 net user /Add /domain Peter Shell@123
The above command creates a user account on the domain with a username Peter and password as Shell@123 as plain text in the command line.
Another option to specify the password is using the * in the command after the username, it will show a prompt to enter the password.
net user /Add /domain Peter *
Net User Delete User Account
To delete a local user account, use the /delete parameter and specify the username, it will delete the user account. It doesn’t ask for confirmation before deleting a user account.
# Delete the user on the local computer net user /delete Teresa
To delete a domain user account, add the /domain parameter and specify the username.
# Delete the domain user account net user /delete /domain Peter
Net User Password Change for User Account
If you want to change a user password using the command line, use the net user command-line tool to set the password.
The syntax for the command net user to set a password for a user account is given below:
net user userid password
Let’s consider an example to reset the password for user account GaryW on the local computer, run the below command
net user garyw Test@123
In the above net user command, garyw is a user account id and Test@123 is a password that is used with the command to set the password for the user account on the local computer.
The output of the above command as below
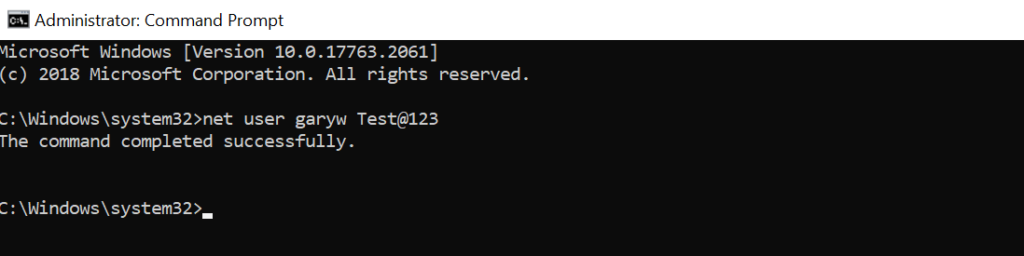
Note: Run Windows command prompt using administrator account privileges else it will display “System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied“
There is an alternative and secure way to change the user password using the net user cmd tool as below
C:\>net user garyw * Type a password for the user: Retype the password to confirm: The command completed successfully.
In the command, use * after the user name and hit enter.
It will prompt you to type the password for the user: and retype the password to confirm.
While typing a password, it won’t display password text on the command line.
Cool Tip: How to get-aduser password expiration date in PowerShell!
Net User /domain – change domain user account password
Using the net user Windows command-line tool, you can set the password for the domain user account.
The syntax for the command net user to set the password for the domain user account is:
net user username /domainRun the following command to reset the domain user account password
net user garyw * /domain
In the above command, the net user command takes the user id as input, * indicates to prompt for the password. /domain specifies to perform domain account password change operation.
The output of the above net user /domain password change as below
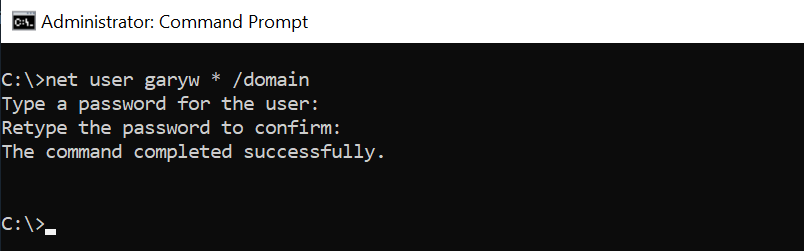
Cool Tip: How to use the Get-AdUser cmdlet to manage Active Directory Use Account!
Net User Disable Account
To disable or lock a domain account using the net user command-line tool, use the /Active:No and /domain parameters and specify the username:
# Disable the user account on domain net user garyw /Active:No /domain
The above net user command disables the user account or locks the domain user account specified using the user name and /Active set to No in the net user /domain command.
Run the command net user garyw /domain to check the user’s account status, it displays Account active : No
C:\>net user garyw /domain
User name garyw
Full Name Gary Willy
Comment
User's comment
Country/region code 000 (System Default)
Account active No
Account expires NeverTo disable a local user account, use the /Active:No parameter:
# Disable local user account net user testadmin /Active:No
Cool Tip: How to find a disabled aduser using PowerShell!
Net User to Enable Domain Account
To enable or unlock the domain user account using the net user command, use the /Active:Yes and /domain parameters and specify the username:
# Enables domain user account net user garyw /Active:Yes /domain
net user /domain command using /Active option set to Yes enables user account.
To enable a local user account, use the /Active:Yes parameter and specify the username:
net user testadmin /Active:Yes
Net User User Password Policy
If you want users to restrict them to change their domain account password or allow domain account user to change their password, use the /Passwordchg:No parameter and specify the username:
net user garyw /Passwordchg:No
In the above net user command, /Passwordchg:No prevents the user from changing the password.
To allow users to change the password, use the /Passwordchg:Yes and specify the username:
net user garyw /Passwordchg:Yes
The above command, /Passwordchg:Yes allows the user to change their password.
Cool Tip: How to find active directory groups I m in using PowerShell!
Net User to Find User Full Name
You can use the net user command-line tool to find the user’s full name in the domain using the Find /i parameter and specify the “full name” :
net user garyw /domain | Find /i "full name"
The above command finds the full name of the user in the domain, it uses the username /domain to find the user account in the domain and pipes the result to get the full name.
C:\Windows\system32>net user garyw /domain | Find /i "full name"
Full Name Gary WillySet Home Directory Path For User
Use the net user command-line tool to set a home directory path for a new user or existing user using the homedir option as below
Set the home directory path for the new user:
# Set the home directory path for user adams net user adams /domain /add /homedir:C:\users\adams
In the above command, the net user creates a new user with the name adams in the domain and set up the home directory path for the user to C:\users\adams
You can set up a home directory for the existing user as below
# Set the home directory path for existing user garyw net user garyw /domain /homedir:C:\users\garyw
In the above command, it set up the home directory path for the existing user in the domain using the net user command and homdir option.
Cool Tip: How to unlock the ad account in the active directory using PowerShell!
Set Expiry date for User Account on Local and Domain
The expiration date for the user account has been good practice for organizations to manage security and resource management.
Using the net user command, you can easily set an expiry date for the user account on the local computer or domain user account.
To set up an expiry date for user accounts on the local computer or a Windows 11 user account, use the /expires parameter and specify the date in MM/DD/YYYY format:
# Set expire date for local user account Net User devadmin /expires:03/05/2023
In the above command, the net user command takes the username as the input parameter and uses /expires option to set up the expiry date for the user account on the local computer.
If you want to set up an expiry date for the user account on the domain controller, run the following command.
# Set expire date for domain user account Net User Toms /domain /expires:09/20/2022
In the above command, the net user takes the user name and uses /domain to set up an expiry date in the domain using /expires option.
Set Login Times for User Account
Using the net user command, you can set log in times for the user account to allow them to be used within specific hours only. Use the /time parameter followed by the allowed login times.
Run the following command to set login times for the user account on the local computer.
# Set login time to allow user login in specific duration Net User Toms /time:M-F,07:00-16:00
In the above command, the net user command takes the user name to set up login time for the account to allow login between 7 am to 4 pm on Monday-Friday only.
For domain user accounts, add the /domain parameter:
# Set login time to allow user login in specific duration on the domain Net User garyw /time:M-F,07:00-16:00 /domain
Net User Command Examples and FAQ
How to reset the user password using the net user command?
Open the Windows command prompt with Administrator privileges and run the following command to reset the password for a user account.
net user userid newpassword
How to use the net user command?
The net user is a command-line tool to manage user accounts on local and domain controllers. To use the net user command, open the command prompt and type the net user command, it will list all user accounts.
net user
How to check domain user details in cmd?
Use the net user command to view the user account details on the domain. The syntax to check user account information is:
net user userid
How to use the net user command to see when the password expires?
If you run net user userid on cmd terminal, it retrieves user information that includes the property “Password expires“. Use this property to see the user account password expiry date.
How to use the net user command to check the last login of the user?
To check the last login of the user on the domain using the net user command, run the command prompt and run the below command.
net user Toms /domain | Findstr "Last"
It returns the Last Login date for the user account on the domain.
How to use the net user command to set a password never expires using the command line?
To set the password never expires on the user account using the net user command in the cmd terminal, run the following command.
WMIC useraccount where Name='username' set PasswordExpires=FALSE
For example, to set the administrator password never expires using the net user command,
net user administrator |findstr /C:expires
Returns the output as
Account expires Never
Password expires 2/26/2023 4:10:20 PM
Run the WMIC command to set the PasswordExpires property for the administrator account to false.
WMIC useraccount where Name='administrator' SET PasswordExpires=FALSE
The above command line tool set up the administrator password never set to expire.
Conclusion
I hope the above article on the net user command line tool in the Windows system helps you to understand how to manage net user accounts using the command line.
net user without any option gets all the user accounts on the computer. You can also use the net users command to manage the user accounts on the local and domain controller.
You can find more topics about PowerShell Active Directory commands and PowerShell basics on the ShellGeek home page.
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
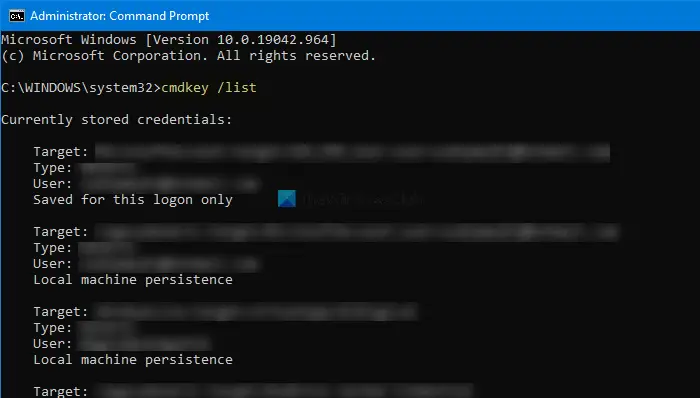
Windows Credential Manager stores all the saved passwords automatically, and it is possible to manage them from the given interface. We have already seen how to add, remove or manage Credentials from Credential Manager using the interface – not let us see how to do it using the Command Prompt. You can execute all the commands in the Command Prompt or Windows Terminal.
To view Credentials from Credential Manager using Command Prompt, follow these steps-
- Search for cmd in the Taskbar search box.
- Click on the Run as administrator option.
- Click the Yes button.
- Type cmdkey /list command.
- Press the Enter button.
Whether you want to view, add, or delete credentials from the Credential Manager, you must open the Command Prompt with administrator permission. For that, search for cmd in the Taskbar search box, and click on the Run as administrator option.
Next, select the Yes option. Once the Command Prompt is opened, you can type the following command-
cmdkey /list
It displays the following information immediately-
- Target
- Type
- User
- Saved for
By default, it shows all the saved credentials at once. However, if you want to filter these entries and find credentials from a particular networked computer, the following command works-
cmdkey /list:your-computer-name
Don’t forget to replace your-computer-name with the original name of the computer.
Add Windows Credentials in Credential Manager using Command Prompt
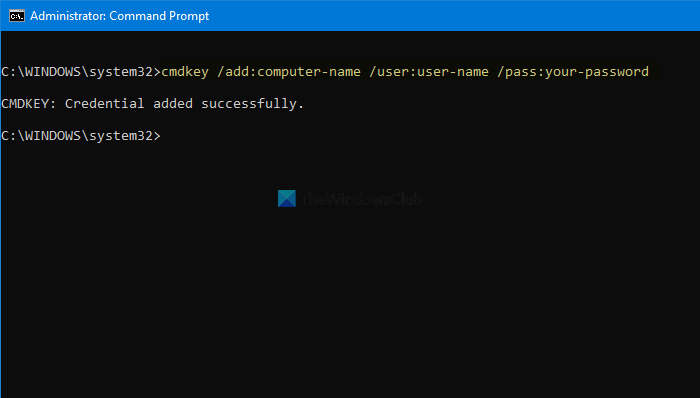
It is possible to add an entry in the Windows Credentials section in Credential Manager using the Command Prompt. It is possible to add an Internet or network address, user name, password, etc.
For that, open an elevated Command Prompt window, and enter this command-
cmdkey /add:computer-name /user:user-name /pass:your-password
Before pressing the Enter button, you need to change a few things in the above command. For example, replace the computer-name, user-name, and your-password.
Once done, you can open the Credential Manager and find the entry under Windows Credentials section.
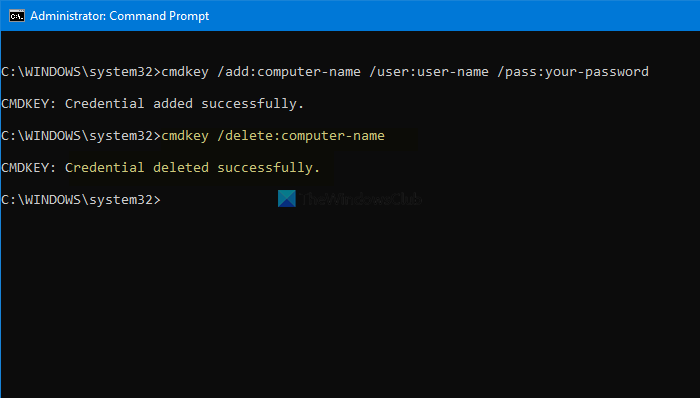
Delete credentials from Credential Manager using Command Prompt
It is possible to delete or remove saved credentials from the Credential Manager using Command Prompt like viewing and adding. For that, you need to follow the following steps.
Open the Command Prompt with administrator privilege, and enter the same command you used to view all entries. In other words, you have to enter this command-
cmdkey /list
It helps you note the Target, which is required to delete the credential entry from the Credential Manager. Next, enter this command-
cmdkey /delete:target-name
Don’t forget to replace the target-name with the original name that you copied earlier.
Once done, you can find a message saying Credential deleted successfully.
It is possible to repeat these commands to add or remove credentials from the Credential Manager using Command Prompt.
Read: How to clear all Credentials from Credential Manager.
When he is not writing about Microsoft Windows or Office, Sudip likes to work with Photoshop. He has managed the front end and back end of many websites over the years. He is currently pursuing his Bachelor’s degree.
Для просмотра и управления учетными записями через командную строку используется команда NET USER.
Если ввести команду net user без параметров, то она покажет список пользователей Windows. Для просмотра справки по команде необходимо указать параметр net user /?
Список основных команд для работы с учетными записями через командную строку:
| Добавить пользователя | net user /add имя_пользователя пароль |
| Включить учетную запись пользователя | net user /active:yes имя_пользователя |
| Отключить учетную запись пользователя | net user /active:no имя_пользователя |
| Удалить пользователя | net user /delete имя_пользователя |
Для добавления пользователя в группу в командной строке используется команда управления локальными группами net localgroup
| Добавить пользователя в группу | net localgroup имя_группы имя_пользователя /add |
| Удалить пользователя из группы | net localgroup имя_группы имя_пользователя /delete |
Например, необходимо создать учетную запись пользователя «Root» с правами администратора и паролем 12345.
Создаем учетную запись:
net user /add root 12345Добавляем созданного пользователя в группу администраторов:
net localgroup Администраторы rooton March 29, 2011
Using Net user command, administrators can manage user accounts from windows command prompt. Below are some examples on how to use this command.
Add a domain user account:
Net user /add username newuserPassword /domain
Add new user on local computer:
Net user /add username newuserPassword
Advanced options to add new user account can be read in the below article.
Add new user from windows command line.
Disable/Lock a domain user account:
Net user username /ACTIVE:NO /domain
To enable/unlock a domain user account:
Net user loginid /ACTIVE:YES /domain
Prevent users from changing their account password:
Net user username /Passwordchg:No
To allow users to change their password:
Net user username /Passwordchg:Yes
To retrieve the settings of a user:
Net user username
Example:
C:\>net user techblogger User name techblogger Full Name Comment User's comment Country code 000 (System Default) Account active Yes Account expires Never Password last set 4/21/2011 10:10 PM Password expires 8/19/2011 10:10 PM Password changeable 4/21/2011 10:10 PM Password required Yes User may change password Yes Workstations allowed All Logon script User profile Home directory Last logon Never Logon hours allowed All Local Group Memberships *Users Global Group memberships *None The command completed successfully.
CMD Управление пользователями в Windows. Команда NET USER, WHOAMI
Управление пользователями в Windows, помимо графической оснастки «Учетные данные пользователей», расположенной в панели управления, можно производить с помощью командной строки.
Команда NET USER
Команда NET USER предназначена для просмотра, добавления или редактирования учетных записей пользователей на компьютерах. При выполнении команды в командной строке без параметров отображается список учетных записей пользователей Windows, присутствующих на компьютере(локальные УЗ). Информация об учетных записях пользователей хранится в базе данных Windows.
Синтаксис команды NET USER
net user [имя_пользователя [пароль | *] [параметры]] [/domain]
net user имя_пользователя {пароль | *} /add [параметры] [/domain]
net user имя_пользователя [/delete] [/domain], где
- имя_пользователя — Указывает имя учётной записи пользователя, которую можно добавить, удалить, отредактировать или просмотреть. Имя может иметь длину до 20 символов.
- пароль — Присваивает или изменяет пароль пользователя. Введите звездочку (*) для вывода приглашения на ввод пароля. При вводе с клавиатуры символы пароля не выводятся на экран.
- /domain — Выполняет операцию на контроллере основного для данного компьютера домена.
- параметры — Задает параметр командной строки для команды.
- net help команда — Отображение справки для указанной команды net.
- /delete — Удаление учетной записи пользователя.
Дополнительные параметры команды NET USER:
- /active:{yes | no} — Активирует или деактивирует учетную запись. Если учетная запись не активирована, пользователь не может получить доступ к серверу. По умолчанию учетная запись активирована.
- /comment:»текст» — Позволяет добавить описание учетной записи пользователя (максимум 48 символов). Текст описания заключается в кавычки.
- /countrycode:nnn — Использует код страны, указанный для операционной системы, для реализации соответствующих языковых файлов при отображении пользовательской справки и сообщений об ошибках. Значение 0 соответствует коду страны, используемому по умолчанию.
- /expires:{дата | never} — Дата истечения срока действия учетной записи. Значение never соответствует неограниченному сроку действия. Дата указывается в формате мм/дд/гг или дд/мм/гг в зависимости от кода страны. Месяц может указываться цифрами, полностью или в сокращенном виде (тремя буквами). Год может указываться двумя ли четырьмя цифрами. Элементы даты разделяются слэшем (/) без пробелов.
- /fullname:»имя» — Полное имя пользователя (в отличии от имени учетной записи пользователя). Имя указывается в кавычках.
- /homedir:путь — Указывает путь к домашнему каталогу пользователя. Указанное место должно существовать.
- /passwordchg:{yes | no} — Указывает, может ли пользователь изменять свой пароль (по умолчанию yes).
- /passwordreq:{yes | no} — Указывает, должна ли учетная запись пользователя иметь пароль (по умолчанию yes).
- /profilepath[:путь] — Указывает путь к профилю входа в систему пользователя.
- /scriptpath:путь — Путь к сценарию, используемому пользователем для входа в систему.
- /times:{время | all} — Время для входа в систему. Параметр время указывается в формате день[-день][,день[-день]],час [-час][,час [-час]], причем приращение равняется 1 часу. Название дней недели могут указываться полностью или в сокращенном виде. Часы могут указываться в 12- или 24-часовом представлении. Для 12-часового представления используются обозначения am, pm, a.m. или p.m. Значение all соответствует отсутствию ограничений на время входа в систему, а пустое значение обозначает полный запрет на вход в систему. Значения дней недели и времени разделяются запятой; несколько записей для значений дней недели и времени разделяются точкой с запятой.
- /usercomment:»текст» — Позволяет администратору добавить или изменить комментарий к учетной записи.
- /workstations:{имя_компьютера[,…] | *} — Позволяет указать до 8 компьютеров, с которых пользователь может войти в сеть. Если для параметра/workstations не указан список компьютеров или указано значение *, пользователь может войти в сеть с любого компьютера.
Примеры команды NET USER
- Для вывода списка всех пользователей данного компьютера служит команда:
- Для вывода информации о пользователе «petr» служит следующая команда:
- Для добавления учетной записи пользователя Petr с полным именем пользователя и правом на подключение с 8 до 17 часов с понедельника по пятницу используется следующая команда:
net user petr /add /times:Пн—Пт,08:00—17:00/fullname:«Petr»
- Для удаления учетной записи необходимо ввести команду:
- Для отключения учетной записи необходимо ввести команду:
Для просмотра членов локальной группы можно использовать команду net localgroup <«имя группы»>
|
net localgroup «Администраторы» |
Команда WHOAMI
Есть еще одна команда для определения свойств УЗ текущего пользователя, это команда WHOAMI
Три способа выполнения WhoAmI:
Синтаксис 1:
WHOAMI [/UPN | /FQDN | /LOGONID]
Синтаксис 2:
WHOAMI { [/USER] [/GROUPS] [/CLAIMS] [/PRIV] } [/FO <формат>] [/NH]
Синтаксис 3:
WHOAMI /ALL [/FO <формат>] [/NH]
Описание:
Эту программу можно использовать для получения сведений об имени
пользователя и группе, а также о соответствующих идентификаторах
безопасности (SID), утверждениях, привилегиях, идентификаторе входа
текущего пользователя на локальном компьютере, т. е. для
определения текущего пользователя. Если параметр не указан, имя
пользователя отображается в формате NTLM (домен\пользователь).
Параметры:
/UPN Отображение имени пользователя в формате
имени участника-пользователя (UPN).
/FQDN Отображение имени пользователя в формате
полного доменного имени (FQDN).
/USER Отображение сведений о текущем пользователе
вместе с идентификатором безопасности (SID).
/GROUPS Отображение для текущего пользователя членства
в группах, типа учетной записи, идентификаторов
безопасности (SID) и атрибутов.
/CLAIMS Отображение требований для текущего пользователя,
включая имя требования, флаги, тип и значения.
/PRIV Отображение привилегий безопасности текущего
пользователя.
/LOGONID Отображение идентификатора входа текущего
пользователя.
/ALL Отображение имени пользователя, членства
в группах, идентификаторов безопасности
(SID), утверждений и привилегий для
маркера входа текущего пользователя.
/FO <формат> Формат вывода.
Допустимые значения: TABLE, LIST, CSV.
Заголовки столбцов в формате CSV
не отображаются. Формат по умолчанию: TABLE.
/NH Строка заголовков столбцов
не отображается при выводе. Действительно
только для форматов TABLE и CSV.
/? Вывод справки по использованию.
Примеры использования WHOAMI:
WHOAMI — отобразить имя текущего пользователя в формате «домен\имя»
WHOAMI /UPN — отобразить имя текущего пользователя в формате «имя@домен»
WHOAMI /FQDN — отобразить имя текущего пользователя в формате полного доменного имени (FQDN).
WHOAMI /LOGONID — отобразить идентификатор текущего пользователя.
WHOAMI /USER — отобразить имя и SID текущего пользователя.
WHOAMI /USER /FO LIST — то же, что и в предыдущем случае, но с выводом данных в виде списка.
WHOAMI /GROUPS — отобразить список групп, членом которых является текущий пользователь.
WHOAMI /GROUPS /FO CSV — то же, что и в предыдущем случае, но с выводом результатов в виде полей, разделяемых запятой.
WHOAMI /GROUPS /FO CSV > C:\MyGroups.csv — то же, что и в предыдущем примере, но с выводом результатов в файл C:\MyGroups.csv.
WHOAMI /PRIV — отобразить список привилегий текущего пользователя.
WHOAMI /PRIV /FO TABLE — то же, что и в предыдущем примере, но с отображением результатов в виде таблицы.
WHOAMI /ALL — отобразить информацию о SID текущего пользователя, принадлежности к группам и перечень привилегий.
При подготовке этой шпаргалки использовались материалы:
http://cmd4win.ru/administrirovanie-computera/administrirovanie-polzovatelej/43-netuser
https://ab57.ru/cmdlist/whoami.html
Читайте также: Linux. Пользователи и группы.