How can I remove the current process/application which is already assigned to a port?
For example: localhost:8080
asked Sep 22, 2016 at 7:19
4
Step 1:
Open up cmd.exe (note: you may need to run it as an administrator, but this isn’t always necessary), then run the below command:
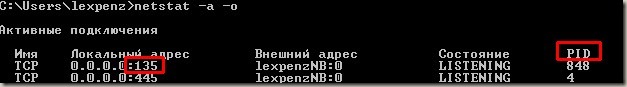
netstat -ano | findstr :<PORT>
(Replace <PORT> with the port number you want, but keep the colon)
The area circled in red shows the PID (process identifier). Locate the PID of the process that’s using the port you want.
Step 2:
Next, run the following command:
taskkill /PID <PID> /F
(No colon this time)
Lastly, you can check whether the operation succeeded or not by re-running the command in «Step 1». If it was successful you shouldn’t see any more search results for that port number.
Mujeeb
1,0551 gold badge9 silver badges18 bronze badges
answered Sep 22, 2016 at 7:59
KavinduWijeKavinduWije
39.8k4 gold badges14 silver badges17 bronze badges
15
I know that is really old question, but found pretty easy to remember, fast command to kill apps that are using port.
Requirements: [email protected]^ version
npx kill-port 8080
You can also read more about kill-port here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/kill-port
answered Jun 16, 2020 at 10:32
Rafał FiguraRafał Figura
5,5461 gold badge15 silver badges20 bronze badges
3
There are two ways to kill the processes
Option 01 — Simplest and easiest
Requirement : [email protected]^ version
Open the Command prompt as Administrator and give the following command with the port (Here the port is 8080)
npx kill-port 8080
Option 02 — Most commonly used
- Step 01
Open Windows command prompt as Administrator
- Step 02
Find the PID of the port you want to kill with the below command: Here port is 8080
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :8080"
TCP 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 18264
- Step 03
Kill the PID you received above with the below command (In my case PID is 18264)
taskkill /PID 18264 /f
answered Jul 21, 2020 at 4:16
1
Step 1 (same is in accepted answer written by KavinduWije):
netstat -ano | findstr :yourPortNumber
Change in Step 2 to:
tskill typeyourPIDhere
Note: taskkill is not working in some git bash terminal
answered Sep 21, 2017 at 11:20
afsarkhan10182afsarkhan10182
2,1821 gold badge13 silver badges17 bronze badges
1
With Windows 10/11 default tools:
✔ Step one:
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator
✔ Step two:
Find the ProcessID for the port you need to kill (e.g. 3000)
netstat -aon | findstr 3000
TCP 0.0.0.0:3000 LISTEN 1234
✔ Step three:
Kill the zombie process:
taskkill /f /pid 1234
where «1234» is your ProcessID (aka PID)
*Extra tip if you use Windows Subsystem for Linux (Ubuntu WSL):
✔ Step one:
sudo lsof -t -i:3000
✔ Step two:
sudo kill -9 1234
answered Mar 18, 2019 at 10:01
Java wanna beeJava wanna bee
2,6021 gold badge12 silver badges25 bronze badges
4
If you are using GitBash
Step one:
netstat -ano | findstr :8080
Step two:
taskkill /PID typeyourPIDhere /F
(/F forcefully terminates the process)
answered Sep 17, 2017 at 19:55
Ara YaghsizianAra Yaghsizian
1,2891 gold badge8 silver badges10 bronze badges
1
The simplest solution — the only one I can ever remember:
In Windows Powershell
Say we want to stop a process on port 8080
- Get the process:
netstat -ano | findstr :8080
- Stop the process
stop-process 82932
answered Sep 3, 2021 at 15:38
Luke GarriganLuke Garrigan
4,6111 gold badge21 silver badges31 bronze badges
2
If you already know the port number, it will probably suffice to send a software termination signal to the process (SIGTERM):
kill $(lsof -t -i :PORT_NUMBER)
answered Dec 19, 2018 at 7:43
Fellow StrangerFellow Stranger
32.3k35 gold badges170 silver badges233 bronze badges
4
For use in command line:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| find ":8080" ^| find "LISTENING"') do taskkill /f /pid %a
For use in bat-file:
for /f "tokens=5" %%a in ('netstat -aon ^| find ":8080" ^| find "LISTENING"') do taskkill /f /pid %%a
answered Jun 29, 2018 at 10:10
4
Simple CMD is working me. Easy to remember
find the port number which you want kill and run the below cmd
npx kill-port 8080
After complete the Port get stopped and getting this message
npx: installed 3 in 13.796s
Process on port 8080 killed
ux.engineer
10.3k14 gold badges67 silver badges112 bronze badges
answered Apr 28, 2021 at 7:45
DeepakDeepak
5717 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
In Windows PowerShell version 1 or later to stop a process on port 3000 type:
Stop-Process (,(netstat -ano | findstr :3000).split() | foreach {$[$.length-1]}) -Force
As suggested by @morganpdx here`s a more PowerShell-ish, better version:
Stop-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 3000).OwningProcess -Force
answered Dec 8, 2017 at 15:54
todormtodorm
4744 silver badges6 bronze badges
3
Open command prompt and issue below command
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :8888"
Output will show the process id occupying the port
Issue below command to kill the PID
taskkill /pid 8912 /f
You will receive the output as below
SUCCESS: The process with PID 8860 has been terminated.
answered Mar 31, 2021 at 13:08
Waqas AhmedWaqas Ahmed
4,8313 gold badges37 silver badges45 bronze badges
1
If you can use PowerShell on Windows you just need :
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort "8080").OwningProcess | Stop-Process
answered Oct 27, 2020 at 10:20
2
For Windows users, you can use the CurrPorts tool to kill ports under usage easily:
answered Oct 3, 2018 at 11:43
Zuhair TahaZuhair Taha
2,8382 gold badges35 silver badges33 bronze badges
1
I was running zookeeper on Windows and wasn’t able to stop ZooKeeper running at 2181 port using zookeeper-stop.sh, so tried this double slash «//» method to taskkill. It worked
1. netstat -ano | findstr :2181
TCP 0.0.0.0:2181 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 8876
TCP [::]:2181 [::]:0 LISTENING 8876
2.taskkill //PID 8876 //F
SUCCESS: The process with PID 8876 has been terminated.
answered Dec 6, 2018 at 4:29
Let’s Automate!
If you fall into this issue much often like me, make an .bat file and run it to end process.
create a bat file «killport.bat»
set /P port="Enter port : "
echo showing process running with port %port%
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :%port%"
set /P pid="Enter PID to kill : "
taskkill /pid %pid% /f
set /P exit="Press any key to exit..."
Run this file by double clicking and
- Enter port number (then it will list process with PID)
- Enter PID to kill
Done
(Optional)
Set to path environment so that you can access this file from anywhere.
Most probably you will know how to add an new path to env. But here’s how if you don’t
Step 1 of 4
Search ENV on start menu
Step 2 of 4
Select Environment Variables
Step 3 of 4
Select ‘path’ and click Edit button
Step 4 of 4
Click ‘New’ add the path where .bat file is stored. Since I saved it on ‘../Documents/bats’ folder I am adding this path. Your path will depend on where you save this file.
Open CMD and test. Remember you filename will the word to run this file. Since I saved the .bat file as ‘killport.bat’ => ‘killport’ is the word to run it.
if do enjoy!
else share how you done it here
Dharman♦
31.1k25 gold badges87 silver badges138 bronze badges
answered May 10, 2021 at 10:46
Run cmd as administrator. Then type this code in there.
netstat -ano | findstr :<8080>
Then you can see the PID run on your port. Then copy that PID number. ( PID is a unique number that helps identify a hardware product or a registered software product.) And type below code line and press enter.
taskkill /PID <Enter the copied PID Number> /F
answered Jun 10, 2021 at 18:13
If you’re using Windows Terminal then the killing process might be little less tedious.
I’ve been using windows terminal and kill PID works fine for me to kill processes on the port as the new Windows Terminal supports certain bash commands. For example: kill 13300
So, the complete process will look like this-
- Open Windows Terminal
- Type the following command to show processes running on the port you’re looking to kill processes.
netstat -ano | findstr :PORT - Type following to kill the process.
kill PID
For Example:
PS C:\Users\username> netstat -ano | findstr :4445
TCP 0.0.0.0:4445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 7368
TCP [::]:4445 [::]:0 LISTENING 7368
PS C:\Users\username> kill 7368
PS C:\Users\username> netstat -ano | findstr :4445
PS C:\Users\username>
See when I typed the first command to list processes on the port it returned empty. That means all processes are killed now.
Update: kill is an alias for Stop-Process. Thanks, @FSCKur for letting us know.
answered May 21, 2020 at 9:55
lazycipherlazycipher
3403 silver badges14 bronze badges
7
If you use powershell 7+ this worked for me. Just add this function in your $PROFILE file.
function killport([parameter(mandatory)] [string] $uport){
if($upid = (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort $uport -ErrorAction Ignore).OwningProcess){kill $upid}
}
then simply use killport 8080
or if you prefer just the command you can try this:
kill $(Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 8761 -ErrorAction Ignore).OwningProcess
answered Feb 1, 2022 at 19:19
Deekshith AnandDeekshith Anand
2,2431 gold badge22 silver badges24 bronze badges
4
You can do by run a bat file:
@ECHO OFF
FOR /F "tokens=5" %%T IN ('netstat -a -n -o ^| findstr "9797" ') DO (
SET /A ProcessId=%%T) &GOTO SkipLine
:SkipLine
echo ProcessId to kill = %ProcessId%
taskkill /f /pid %ProcessId%
PAUSE
answered Dec 5, 2018 at 7:53
flopcoderflopcoder
1,19512 silver badges26 bronze badges
the first step
netstat -vanp tcp | grep 8888
example
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.8888 *.* LISTEN 131072 131072 76061 0
tcp46 0 0 *.8888 *.* LISTEN 131072 131072 50523 0
the second step: find your PIDs and kill them
in my case
sudo kill -9 76061 50523
answered Aug 25, 2020 at 19:35
rusconruscon
772 silver badges9 bronze badges
1
netstat -ano | findstr :PORT
kill PI
answered Oct 30, 2020 at 11:31
harun ugurharun ugur
1,72620 silver badges19 bronze badges
One line solution using GitBash:
tskill `netstat -ano | grep LISTENING | findstr :8080 | sed -r 's/(\s+[^\s]+){4}(.*)/\1/'`
Replace 8080 with the port your server is listening to.
If you need to use it often, try adding to your ~/.bashrc the function:
function killport() {
tskill `netstat -ano | findstr LISTENING | findstr :$1 | sed -r 's/^(\s+[^\s]+){4}(\d*)$/\1/'`
}
and simply run
killport 8080
answered May 20, 2020 at 21:04
Italo BorssattoItalo Borssatto
15.1k7 gold badges63 silver badges88 bronze badges
2
I wrote a tiny node js script for this. Just run it like this:
node killPort.js 8080 or whatever port you need to kill. Save the following to a killPort.js file:
const { exec } = require('child_process');
const fs = require(`fs`);
const port = process.argv.length > 2 ? process.argv[2] : ``;
if (!port || isNaN(port)) console.log(`port is required as an argument and has to be a number`);
else {
exec(`netstat -ano | findstr :${port}`, (err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (!stdout) console.log(`nobody listens on port ${port}`);
else {
const res = stdout.split(`\n`).map(s => s.trim());
const pid = res.map(s => s.split(` `).pop()).filter(s => s).pop();
console.log(`Listener of ${port} is found, its pid is ${pid}, killing it...`);
exec(`taskkill /PID ${pid} /F`, (err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (!stdout) console.log(`we tried to kill it, but not sure about the result, please run me again`);
else console.log(stdout);
})
}
});
}
answered Aug 31, 2021 at 9:11
shalshal
2,8544 gold badges20 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
I am using GitBash and I error like below when ran
taskkill //PID XXXX
ERROR: The process with PID 7420 could not be terminated. Reason: This
process can only be terminated forcefully (with /F option).
So used //F like below and worked fine
taskkill //F //PID XXXX
answered Dec 25, 2021 at 11:29
Vatsal ShahVatsal Shah
1,33418 silver badges21 bronze badges
Here is a script to do it in WSL2
PIDS=$(cmd.exe /c netstat -ano | cmd.exe /c findstr :$1 | awk '{print $5}')
for pid in $PIDS
do
cmd.exe /c taskkill /PID $pid /F
done
answered Aug 14, 2020 at 9:59
MyrionSC2MyrionSC2
1,2481 gold badge14 silver badges24 bronze badges
We can avoid this by simple restarting IIS, using the below command:
IISRESET
answered Aug 21, 2018 at 12:31
0
How can I remove the current process/application which is already assigned to a port?
For example: localhost:8080
asked Sep 22, 2016 at 7:19
4
Step 1:
Open up cmd.exe (note: you may need to run it as an administrator, but this isn’t always necessary), then run the below command:
netstat -ano | findstr :<PORT>
(Replace <PORT> with the port number you want, but keep the colon)
The area circled in red shows the PID (process identifier). Locate the PID of the process that’s using the port you want.
Step 2:
Next, run the following command:
taskkill /PID <PID> /F
(No colon this time)
Lastly, you can check whether the operation succeeded or not by re-running the command in «Step 1». If it was successful you shouldn’t see any more search results for that port number.
Mujeeb
1,0551 gold badge9 silver badges18 bronze badges
answered Sep 22, 2016 at 7:59
KavinduWijeKavinduWije
39.8k4 gold badges14 silver badges17 bronze badges
15
I know that is really old question, but found pretty easy to remember, fast command to kill apps that are using port.
Requirements: [email protected]^ version
npx kill-port 8080
You can also read more about kill-port here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/kill-port
answered Jun 16, 2020 at 10:32
Rafał FiguraRafał Figura
5,5461 gold badge15 silver badges20 bronze badges
3
There are two ways to kill the processes
Option 01 — Simplest and easiest
Requirement : [email protected]^ version
Open the Command prompt as Administrator and give the following command with the port (Here the port is 8080)
npx kill-port 8080
Option 02 — Most commonly used
- Step 01
Open Windows command prompt as Administrator
- Step 02
Find the PID of the port you want to kill with the below command: Here port is 8080
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :8080"
TCP 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 18264
- Step 03
Kill the PID you received above with the below command (In my case PID is 18264)
taskkill /PID 18264 /f
answered Jul 21, 2020 at 4:16
1
Step 1 (same is in accepted answer written by KavinduWije):
netstat -ano | findstr :yourPortNumber
Change in Step 2 to:
tskill typeyourPIDhere
Note: taskkill is not working in some git bash terminal
answered Sep 21, 2017 at 11:20
afsarkhan10182afsarkhan10182
2,1821 gold badge13 silver badges17 bronze badges
1
With Windows 10/11 default tools:
✔ Step one:
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator
✔ Step two:
Find the ProcessID for the port you need to kill (e.g. 3000)
netstat -aon | findstr 3000
TCP 0.0.0.0:3000 LISTEN 1234
✔ Step three:
Kill the zombie process:
taskkill /f /pid 1234
where «1234» is your ProcessID (aka PID)
*Extra tip if you use Windows Subsystem for Linux (Ubuntu WSL):
✔ Step one:
sudo lsof -t -i:3000
✔ Step two:
sudo kill -9 1234
answered Mar 18, 2019 at 10:01
Java wanna beeJava wanna bee
2,6021 gold badge12 silver badges25 bronze badges
4
If you are using GitBash
Step one:
netstat -ano | findstr :8080
Step two:
taskkill /PID typeyourPIDhere /F
(/F forcefully terminates the process)
answered Sep 17, 2017 at 19:55
Ara YaghsizianAra Yaghsizian
1,2891 gold badge8 silver badges10 bronze badges
1
The simplest solution — the only one I can ever remember:
In Windows Powershell
Say we want to stop a process on port 8080
- Get the process:
netstat -ano | findstr :8080
- Stop the process
stop-process 82932
answered Sep 3, 2021 at 15:38
Luke GarriganLuke Garrigan
4,6111 gold badge21 silver badges31 bronze badges
2
If you already know the port number, it will probably suffice to send a software termination signal to the process (SIGTERM):
kill $(lsof -t -i :PORT_NUMBER)
answered Dec 19, 2018 at 7:43
Fellow StrangerFellow Stranger
32.3k35 gold badges170 silver badges233 bronze badges
4
For use in command line:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| find ":8080" ^| find "LISTENING"') do taskkill /f /pid %a
For use in bat-file:
for /f "tokens=5" %%a in ('netstat -aon ^| find ":8080" ^| find "LISTENING"') do taskkill /f /pid %%a
answered Jun 29, 2018 at 10:10
4
Simple CMD is working me. Easy to remember
find the port number which you want kill and run the below cmd
npx kill-port 8080
After complete the Port get stopped and getting this message
npx: installed 3 in 13.796s
Process on port 8080 killed
ux.engineer
10.3k14 gold badges67 silver badges112 bronze badges
answered Apr 28, 2021 at 7:45
DeepakDeepak
5717 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
In Windows PowerShell version 1 or later to stop a process on port 3000 type:
Stop-Process (,(netstat -ano | findstr :3000).split() | foreach {$[$.length-1]}) -Force
As suggested by @morganpdx here`s a more PowerShell-ish, better version:
Stop-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 3000).OwningProcess -Force
answered Dec 8, 2017 at 15:54
todormtodorm
4744 silver badges6 bronze badges
3
Open command prompt and issue below command
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :8888"
Output will show the process id occupying the port
Issue below command to kill the PID
taskkill /pid 8912 /f
You will receive the output as below
SUCCESS: The process with PID 8860 has been terminated.
answered Mar 31, 2021 at 13:08
Waqas AhmedWaqas Ahmed
4,8313 gold badges37 silver badges45 bronze badges
1
If you can use PowerShell on Windows you just need :
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort "8080").OwningProcess | Stop-Process
answered Oct 27, 2020 at 10:20
2
For Windows users, you can use the CurrPorts tool to kill ports under usage easily:
answered Oct 3, 2018 at 11:43
Zuhair TahaZuhair Taha
2,8382 gold badges35 silver badges33 bronze badges
1
I was running zookeeper on Windows and wasn’t able to stop ZooKeeper running at 2181 port using zookeeper-stop.sh, so tried this double slash «//» method to taskkill. It worked
1. netstat -ano | findstr :2181
TCP 0.0.0.0:2181 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 8876
TCP [::]:2181 [::]:0 LISTENING 8876
2.taskkill //PID 8876 //F
SUCCESS: The process with PID 8876 has been terminated.
answered Dec 6, 2018 at 4:29
Let’s Automate!
If you fall into this issue much often like me, make an .bat file and run it to end process.
create a bat file «killport.bat»
set /P port="Enter port : "
echo showing process running with port %port%
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :%port%"
set /P pid="Enter PID to kill : "
taskkill /pid %pid% /f
set /P exit="Press any key to exit..."
Run this file by double clicking and
- Enter port number (then it will list process with PID)
- Enter PID to kill
Done
(Optional)
Set to path environment so that you can access this file from anywhere.
Most probably you will know how to add an new path to env. But here’s how if you don’t
Step 1 of 4
Search ENV on start menu
Step 2 of 4
Select Environment Variables
Step 3 of 4
Select ‘path’ and click Edit button
Step 4 of 4
Click ‘New’ add the path where .bat file is stored. Since I saved it on ‘../Documents/bats’ folder I am adding this path. Your path will depend on where you save this file.
Open CMD and test. Remember you filename will the word to run this file. Since I saved the .bat file as ‘killport.bat’ => ‘killport’ is the word to run it.
if do enjoy!
else share how you done it here
Dharman♦
31.1k25 gold badges87 silver badges138 bronze badges
answered May 10, 2021 at 10:46
Run cmd as administrator. Then type this code in there.
netstat -ano | findstr :<8080>
Then you can see the PID run on your port. Then copy that PID number. ( PID is a unique number that helps identify a hardware product or a registered software product.) And type below code line and press enter.
taskkill /PID <Enter the copied PID Number> /F
answered Jun 10, 2021 at 18:13
If you’re using Windows Terminal then the killing process might be little less tedious.
I’ve been using windows terminal and kill PID works fine for me to kill processes on the port as the new Windows Terminal supports certain bash commands. For example: kill 13300
So, the complete process will look like this-
- Open Windows Terminal
- Type the following command to show processes running on the port you’re looking to kill processes.
netstat -ano | findstr :PORT - Type following to kill the process.
kill PID
For Example:
PS C:\Users\username> netstat -ano | findstr :4445
TCP 0.0.0.0:4445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 7368
TCP [::]:4445 [::]:0 LISTENING 7368
PS C:\Users\username> kill 7368
PS C:\Users\username> netstat -ano | findstr :4445
PS C:\Users\username>
See when I typed the first command to list processes on the port it returned empty. That means all processes are killed now.
Update: kill is an alias for Stop-Process. Thanks, @FSCKur for letting us know.
answered May 21, 2020 at 9:55
lazycipherlazycipher
3403 silver badges14 bronze badges
7
If you use powershell 7+ this worked for me. Just add this function in your $PROFILE file.
function killport([parameter(mandatory)] [string] $uport){
if($upid = (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort $uport -ErrorAction Ignore).OwningProcess){kill $upid}
}
then simply use killport 8080
or if you prefer just the command you can try this:
kill $(Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 8761 -ErrorAction Ignore).OwningProcess
answered Feb 1, 2022 at 19:19
Deekshith AnandDeekshith Anand
2,2431 gold badge22 silver badges24 bronze badges
4
You can do by run a bat file:
@ECHO OFF
FOR /F "tokens=5" %%T IN ('netstat -a -n -o ^| findstr "9797" ') DO (
SET /A ProcessId=%%T) &GOTO SkipLine
:SkipLine
echo ProcessId to kill = %ProcessId%
taskkill /f /pid %ProcessId%
PAUSE
answered Dec 5, 2018 at 7:53
flopcoderflopcoder
1,19512 silver badges26 bronze badges
the first step
netstat -vanp tcp | grep 8888
example
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.8888 *.* LISTEN 131072 131072 76061 0
tcp46 0 0 *.8888 *.* LISTEN 131072 131072 50523 0
the second step: find your PIDs and kill them
in my case
sudo kill -9 76061 50523
answered Aug 25, 2020 at 19:35
rusconruscon
772 silver badges9 bronze badges
1
netstat -ano | findstr :PORT
kill PI
answered Oct 30, 2020 at 11:31
harun ugurharun ugur
1,72620 silver badges19 bronze badges
One line solution using GitBash:
tskill `netstat -ano | grep LISTENING | findstr :8080 | sed -r 's/(\s+[^\s]+){4}(.*)/\1/'`
Replace 8080 with the port your server is listening to.
If you need to use it often, try adding to your ~/.bashrc the function:
function killport() {
tskill `netstat -ano | findstr LISTENING | findstr :$1 | sed -r 's/^(\s+[^\s]+){4}(\d*)$/\1/'`
}
and simply run
killport 8080
answered May 20, 2020 at 21:04
Italo BorssattoItalo Borssatto
15.1k7 gold badges63 silver badges88 bronze badges
2
I wrote a tiny node js script for this. Just run it like this:
node killPort.js 8080 or whatever port you need to kill. Save the following to a killPort.js file:
const { exec } = require('child_process');
const fs = require(`fs`);
const port = process.argv.length > 2 ? process.argv[2] : ``;
if (!port || isNaN(port)) console.log(`port is required as an argument and has to be a number`);
else {
exec(`netstat -ano | findstr :${port}`, (err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (!stdout) console.log(`nobody listens on port ${port}`);
else {
const res = stdout.split(`\n`).map(s => s.trim());
const pid = res.map(s => s.split(` `).pop()).filter(s => s).pop();
console.log(`Listener of ${port} is found, its pid is ${pid}, killing it...`);
exec(`taskkill /PID ${pid} /F`, (err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (!stdout) console.log(`we tried to kill it, but not sure about the result, please run me again`);
else console.log(stdout);
})
}
});
}
answered Aug 31, 2021 at 9:11
shalshal
2,8544 gold badges20 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
I am using GitBash and I error like below when ran
taskkill //PID XXXX
ERROR: The process with PID 7420 could not be terminated. Reason: This
process can only be terminated forcefully (with /F option).
So used //F like below and worked fine
taskkill //F //PID XXXX
answered Dec 25, 2021 at 11:29
Vatsal ShahVatsal Shah
1,33418 silver badges21 bronze badges
Here is a script to do it in WSL2
PIDS=$(cmd.exe /c netstat -ano | cmd.exe /c findstr :$1 | awk '{print $5}')
for pid in $PIDS
do
cmd.exe /c taskkill /PID $pid /F
done
answered Aug 14, 2020 at 9:59
MyrionSC2MyrionSC2
1,2481 gold badge14 silver badges24 bronze badges
We can avoid this by simple restarting IIS, using the below command:
IISRESET
answered Aug 21, 2018 at 12:31
0
{lang: ‘ru’}
Я уже писал о том, что можно предпринять, если не запускается Denwer. В том посте я осветил «перманентные» решения. Но что делать, если они не помогают, а работающий Denwer нужен уже сейчас?
Скажу сразу, что приведённый ниже способ сработает, только если проблема кроется в использовании порта 443 другой программой. Если 443 уже занят, Apache не сможет начать работу, а без него Денвер бесполезен. Но выход есть.
Способ решения проблемы очень прост и радикален: убить процесс, который занимает нужный порт.
Для этого, его нужно сначала найти. В этом нам поможет следующая команда командной строки (command promt)
Она выдаст список активных сетевых подключений с указанием используемых портов, а также ID процесса, который их занимает.
Ключ -a указывает, что нас интересуют все активные подключения, -o — что для каждого из них нужно отобразить PID (идентификатор процесса)
Если подключений слишком много и вам трудно найти в них висящее на 443 порту, то можно немного модернизировать команду:
|
netstat —a —o | findstr :443 |
В этом случае на экране должны появиться только строчки, содержащие строку «:443». Если же на экране ничего не появится, значит, не повезло. И причина не работы Денвера кроется в чём-то другом. Если же строка с портом появилась, то запомните PID процесса.
Нажните CTRL+C, чтобы выйти из режима отображения подключений.
Следующая команда должна убить процесс с указанным PID:
Если она не поможет, можно попробовать убить этот же процесс форсировано (-F):
Убедиться, что никто больше не занимает порт 443 можно все той же командой
P.S.: Для успешного убийства процесса может потребоваться запустить командную строку от имени администратора.
Приятного использования Denwer 
Полезная статья? Их будет больше, если вы поддержите меня!
Каждый процесс, запущенный в Windows, использует другой порт. Итак, предположим, вы пытаетесь запустить приложение, которому необходимо использовать определенный порт, который уже используется. В этом случае вы можете получить сообщение об ошибке, которое выглядит примерно так: «Порт 8080 используется» или «Указанный вами номер порта уже используется».
Единственный способ обойти эту ошибку — вручную убить процесс, который в данный момент занимает указанный порт. В приведенной ниже статье показано, как определить, какой порт используется каким процессом, и различные методы, которые позволят вам убить его, чтобы вы могли освободить этот порт.
Как узнать, используется ли порт (и связанный с ним процесс)
Прежде всего, откройте командную строку. Нажмите «Пуск», введите cmd, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши «Командная строка» и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
Введите следующую команду, чтобы получить список всех используемых портов.
netstat -ано
Нажмите Ввод.
Теперь вы получите список всех активных портов в вашей системе. Последние несколько цифр адреса (после последнего двоеточия) составляют номер порта. В то время как его соответствующий PID является уникальным идентификационным номером процесса, который связан с ним.
Чтобы узнать, используется ли конкретный порт, введите следующую команду:
netstat -ано | findstr : номер порта
Замените «номер порта» фактическим номером порта и нажмите Enter.
Если он используется, справа вы увидите PID вместе со словами Listening или Established.
Чтобы найти процесс, откройте диспетчер задач, нажав Ctrl+Shitf+Esc. Затем найдите процесс с этим PID.
Если вы не видите столбец PID, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши один из столбцов и выберите PID.
Кроме того, вы можете использовать монитор ресурсов, чтобы найти процесс. Нажмите Пуск, введите монитор ресурсов и откройте его.
Разверните Network и найдите процесс с PID.
Как убить процесс в порту
Вот несколько способов, которые позволят вам определить, какой процесс использует какой порт и как его убить.
Способ №1: через командную строку
После командной строки (как показано ранее) и введите следующую команду:
Чтобы освободить порт и убить связанный с ним процесс, введите следующую команду:
taskkill /PID <введите здесь PID> /f
Затем нажмите Enter. Теперь вы должны получить сообщение о том, что процесс завершен.
Этот метод является наиболее часто используемым методом для поиска и уничтожения процессов, которые находятся на спорных портах, таких как порт 8080 или 3000, доступ к которым может потребоваться нескольким процессам и программам.
Способ №2: через PowerShell
Завершить процесс, связанный с портом, также можно с помощью PowerShell. Вот как:
Нажмите «Пуск», введите Powershell, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши результат и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
Аналогично командной строке введите в PowerShell следующую команду:
netstat -ано
Затем нажмите Enter. Вы получите список всех активных подключений.
Когда у вас есть порт и соответствующий ему PID, вы можете узнать, какой процесс связан с ним (показано ранее). Обратите внимание на PID, который использует определенный порт.
Чтобы убить процесс, введите следующую команду:
taskkill /PID <введите здесь PID> /f
Нажмите Ввод. Теперь вы получите сообщение о том, что процесс завершен.
Способ №3: через диспетчер задач
Этот метод работает только в том случае, если вы знаете PID, связанный с портом, для чего вам неизменно придется обращаться к командной строке или Powershell. Но как только вы найдете порт и связанный с ним PID, вы также можете завершить связанный с ним процесс через диспетчер задач. Вот как это сделать.
Нажмите Ctrl+Shift+Esc, чтобы открыть диспетчер задач. Здесь, если вы еще не видите вкладку PID, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши одну из вкладок и выберите PID.
Теперь найдите процесс, связанный с PID, который вы хотите убить. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши процесс и выберите «Завершить задачу».
Вот и все. Теперь вы освободили порт, который был связан с этим процессом/PID.
Способ №4: через CurrPorts (стороннее ПО)
Есть несколько сторонних приложений, которые позволяют убить процесс, связанный с портом, одним щелчком мыши. Одним из них является CurrPorts, бесплатное программное обеспечение, которое выполняет работу в один миг.
Скачать: CurrPorts
По вышеупомянутой ссылке прокрутите вниз и нажмите «Загрузить CurrPorts». После загрузки файла извлеките его содержимое, а затем запустите файл cports.exe.
Главная страница CurrPorts предоставит вам всю информацию, связанную с данным процессом, включая его PID и используемый порт. Просто щелкните правой кнопкой мыши процесс, который вы хотите убить, и выберите «Убить процессы выбранных портов».
Теперь ваш порт свободен.
Хотя сторонних приложений предостаточно, командная строка и PowerShell по-прежнему являются одним из наиболее часто используемых методов для уничтожения процесса на порту, поскольку они помогают идентифицировать и выполнять процесс без каких-либо посторонних загрузок. Мы надеемся, что приведенные выше методы позволили вам завершить процессы на любом заданном порту в Windows 11.
Windows uses the built-in TCP and UDP protocols to run different processes on different ports on localhost. If a port is in use and you execute a process that requires that same port, you will end up with an error warning you that the port is in use. This means that you either use an alternative port or kill the process on the port that you need to use on localhost.
You might also find yourself in a situation where the process on a specific port on localhost becomes unresponsive and needs to be terminated. If you find yourself in similar situations or you just want to free up system resources and resolve conflicts, this article is for you.
We will show you different methods to kill a process that is using a port on Localhost in Windows.
Let’s get started.
Killing Processes Using CMD
To kill a process using the CMD, you need to know the Process ID (PID) then use the ID to kill that task. Let’s see how to do that step by step.
- Open the Command Prompt by searching for it at the start menu.
-
Once open, find the process ID (PID) using the
netstatcommand as shown below:>netstat -ano | findstr :<port_number>In place of
port_number, use the port number that you want to free. For this demonstration, I want to free port 3000 as seen below.>netstat -ano | findstr :3000Output:
From the command, we get our PID to be
3772as seen on the right side of the image above. Your PID is likely to be different. -
Now that we have the PID, we can kill that process using the
taskkillcommand. Here is the syntax.>taskkill /PID "Enter_PID" /FReplace
Enter_PIDwith the process ID you got from thenetstatcommand.>taskkill /PID 3772 /FOutput:
As you can see the process was terminated successfully.
-
You can confirm this by running the
netstatcommand again.>netstat -ano | findstr :3000You will notice that no processes are running on that port on localhost.
Kill Process Using Localhost Port Number
Instead of using the netstat command to find the PID then use the taskkill command, you can just specify the port number by using the npx kill-port command. Here is the syntax.
>npx kill-port <port_number>
Replace port_number with the port you want to free on localhost as shown below.
>npx kill-port 8000
NOTE: To use this command, you need to have the
kill-portpackage installed. Otherwise, you will be prompted to install it as shown below.
Once the kill-port package is installed, the command will execute successfully.
Output:
Kill Process Using Powershell
Similar to Using the command prompt, you can use the Stop-Process and Get-Process commands to kill the process on localhost. Let’s see it in action.
We first take note of the PID. We can get this with the netstat command.
> netstat -ano | findstr :3000
Output:
To kill the process, we use the stop-process command as shown below.
stop-process 38428
This command should kill the process running on port 3000 on the localhost.
Specifying the Port Number on Powershell
You can also specify the port number to avoid having to know the PID. To do this, we use the Get-Process command in conjunction with the stop-process command as shown below.
> Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort "3000").OwningProcess | Stop-Process
The Get-Process command gets the port number which is then piped using the pipe operator | to the stop-process command to kill the process.
Killing the process using the Task Manager.
As usual, we must know the process ID before we can kill the tasks.
Use the netstat command to get the PID of the port running on localhost.
> netstat -ano | findstr :3000
Output:
Now that we have the PID, we can open up the task manager by pressing ctrl + shift + Esc keys. This will launch the task manager.
The next thing is to find the PID column if it is not visible. You can do this by clicking on the Details Tab.
This will add another column for PID as shown below.
Your work is to find the PID we got from the netstat command and kill the process.
To kill the process, scroll through the list of processes until you find the PID you are looking for. Once you find it, right-click on the process and select End task.
Conclusion
To sum up, we can use the npx kill-port command on cmd to kill a process that is using a port on localhost. A similar command for PowerShell is the Get-Process command piped with the stop-process command. This article shows how to use these commands in detail. These commands are very helpful especially when you need to use a specific port but the port is busy with another process. If you found the article helpful, check out our other tutorial on what is localhost. Thank you for reading : )
What is Localhost or 127.0.0.1?
In this tutorial, we will learn what the term localhost means, how it entails to the functionality of your devices, and some major uses of it.
GeekBits
Published by
Just a guy behind the Screen who lacks knowledge about what the future holds. Join me on my Journey.