На одном из серверов (под управлением Windows Server 2016) столкнулся с исчерпанием места на системном диске C:\. После очистки основных мест, в которых обычно скапливается разный мусор (WinSxS, каталог TEMP, профили неактивных пользователей и устаревшие обновления и пр.), но заметного эффекта это не дало. Места на диске все также не хватало. В результате нашел, что большую часть системного диска занимала папка System Volume Information. В этой статье я попробую рассказать, зачем нужен каталог System Volume Information в Windows, что в нем хранится, и как его корректно очистить.
Примечание. Инструкции, приведенные в этой статье применимы ко всем поддерживаемым Windows: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019/2016/2012 R2.
Содержание:
- Просмотр содержимого каталога System Volume Information
- Что хранится в каталоге System Volume Information?
- Как очистить системные файлы в каталоге System Volume Information?
- Очистка System Volume Information после удаления файлов на томе с дедупликацией
Просмотр содержимого каталога System Volume Information
Каталог System Volume Information автоматически создается в корне каждого диска (будь то локальный HDD, SSD диск, съемный USB накопитель, SD карта). В нем хранятся системные данные, относящиеся к службе восстановления системы, индексирования, истории файлов и т.д.
По умолчанию папка System Volume Information скрыта и доступ к ней есть только у системы (учетная запись
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
).
Чтобы показать этот каталог, нужно отключить скрытие защищенных системных файлов в File Explorer (Hide protected operating system files) или выполнить PowerShell скрипт:
$key = 'HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced'
Set-ItemProperty $key Hidden 1
Set-ItemProperty $key HideFileExt 0
Set-ItemProperty $key ShowSuperHidden 1
Stop-Process -processname explorer
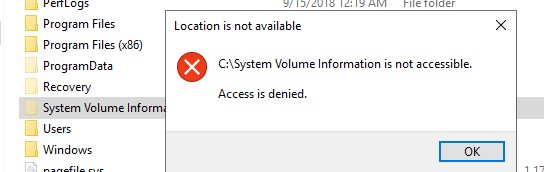
Даже администратор не может открыть его и просмотреть содержимое папки. Если попробовать открыть папку System Volume Information в проводнике, под любым пользователем (даже под встроенным администратором), появится ошибка доступа:
Расположение недоступно Нет доступа к C:\System Volume Information Отказано в доступе
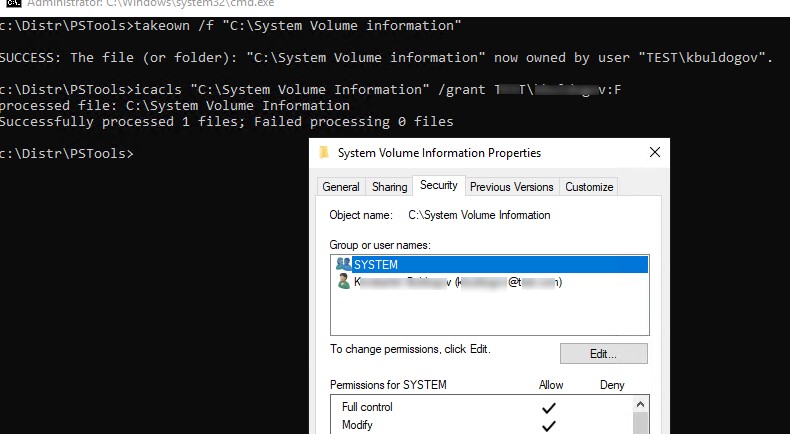
Чтобы просмотреть содержимое каталога, придется сначала назначить себя владельцем каталога и предоставить своей учетной записи права доступа на него на уровне файловой системы NTFS (это можно сделать через в свойствах папки на вкладке Безопасность). Но гораздо быстрее назначить себя владельцем и предоставить доступ к каталогу из комнадной строки:
takeown /f "C:\System Volume information"
icacls "C:\System Volume Information" /grant Corp\kbuldogov:F
Проверьте в свойствах папки на вкладке Безопасность, что у вашей учетки появились полные права доступа к папке.
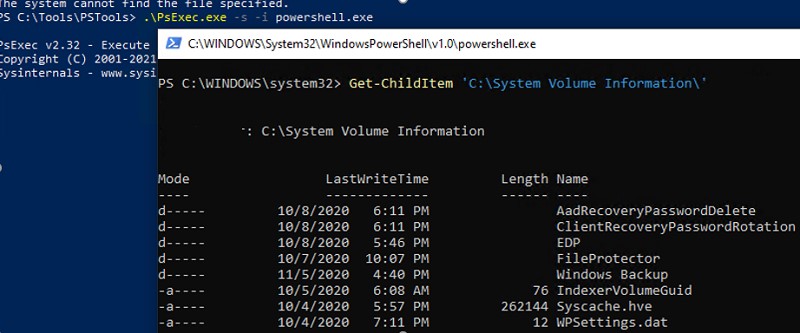
Также можно получить просмотреть содержимое каталога System Volume Information, запустив консоль PowerShell с правами SYSTEM;
PsExec.exe -i -s powershell.exe
Чтобы вывести содержимое каталога, выполните команду:
Get-ChildItem 'C:\System Volume Information\'
Размер каталога можно узнать такой командой PowerShell:
(Get-ChildItem 'C:\System Volume Information\' | measure Length -s).sum / 1Gb
Чтобы восстановить исходные права доступа на каталоге System Volume Information, выполните:
icacls "C:\System Volume Information" /setowner "NT Authority\System"
icacls "C:\System Volume Information" /remove corp\kbuldogov
Что хранится в каталоге System Volume Information?
Что же хранится в каталоге System Volume Information? Мне удалось найти информацию о следующих службах, хранящих свои файлы в этой папке (список не является исчерпывающим):
- WindowsImageBackup — данные точек восстановления системы на клиентских системах или резервные копии System State, сделанные через Windows Server Backup (wbadmin), на серверных ОС;
- Содержимое базы службы индексирования (Indexing Service), используемого для быстрого поиска файлов (в том числе для поиска в Outlook);
- База данных службы Distributed Link Tracking Service;
- Данные снапшотов дисков (теневых копий), создаваемых службой Volume Shadow Copy , которые можно использовать для восстановления старых версий файлов. Для каждого снапшота создается отдельный файл без расширения с длинным ID;
- Настройки дисковых квот NTFS;
- База и чанки службы дедупликации файлов;
- База репликации DFSR (dfsr.db);
- Файл WPSettings.dat — создается службой хранилища (StorSvc);
- На USB накопителях будет хранится также файл IndexerVolumeGuid, в котором хранится уникальная метка диска, используемая службой поиска Windows;
- AppxProgramDataStaging, AppxStaging – резервные копии UWP приложений Windows (можно использовать для восстановления после удаления).
Если вы используете на своем компьютере или сервере теневые копий для возможности отката к старым версиям файлов/состояниям системы, имейте в виду: каждый новый VSS снапшот (снимок) сохраняет данные в каталог System Volume Information, увеличивая его размер. Чем чаще создаются теневые копии и чем чаще изменяются файлы на диске, тем быстрее растет размер этого каталога.
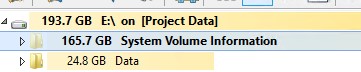
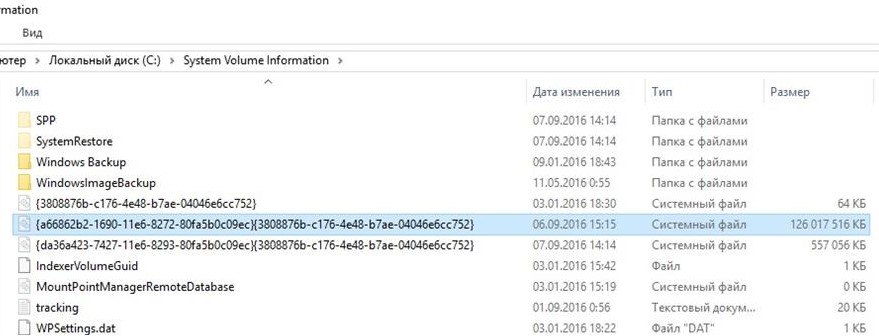
На скриншоте ниже видно, что в папке System Volume Information есть системный файл размером больше 120 Гб.
Как очистить системные файлы в каталоге System Volume Information?
Примечание. Не рекомендуется вручную удалять файлы в каталоге System Volume Information, т.к. в нем хранится важная информация, необходимая для восстановления системы и другая важная информация.
Радикально очистить каталог System Volume Information можно, отключив ведение точек восстановления системы и истории файлов. Но это не всегда допустимо.
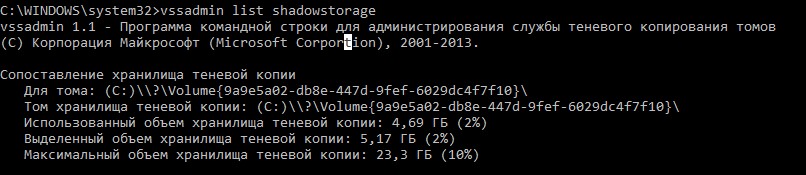
Посмотрим для начала, чем же занят каталог. Выведем статистику использования теневых копий:
vssadmin list shadowstorage
vssadmin 1.1 - Программа командной строки для администрирования службы теневого копирования томов
(C) Корпорация Майкрософт (Microsoft Corportion), 2001-2013.
Сопоставление хранилища теневой копии
Для тома: (C:)\\?\Volume{9a9e5a02-db8e-447d-9fef-6029dc4f7f10}\
Том хранилища теневой копии: (C:)\\?\Volume{9a9e5a02-db8e-447d-9fef-6029dc4f7f10}\
Использованный объем хранилища теневой копии: 4,69 ГБ (2%)
Выделенный объем хранилища теневой копии: 5,17 ГБ (2%)
Максимальный объем хранилища теневой копии: 23,3 ГБ (10%)
Как мы видим, для данных теневых снаншотов на диске C:\ выделено 10% места на диске, из которых занято 2%. Если Максимальный объем хранилища теневой копии (Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space) равен UNBOUNDED, это означает, что лимит для теневых копий не задан и они потенциально могут занять все доступное свободное место на диске. Windows по умолчанию отводит под хранение данных теневых снимков 10 % от общего размера диска.
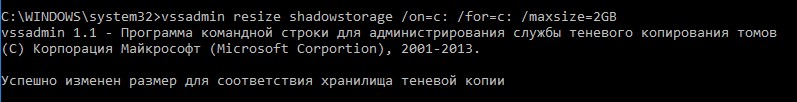
Уменьшите лимит использования дискового пространства службой VSS до 2 гб с помощью команды vssadmin. Команда имеет следующий синтаксис:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /on=[drive letter]: /For=[drive letter]: /MaxSize=[maximum size]
В нашем примере она будет выглядеть так:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /on=c: /for=c: /maxsize=2GB
vssadmin 1.1 - Программа командной строки для администрирования службы теневого копирования томов (C) Корпорация Майкрософт (Microsoft Corportion), 2001-2013. Успешно изменен размер для соответствия хранилища теневой копии
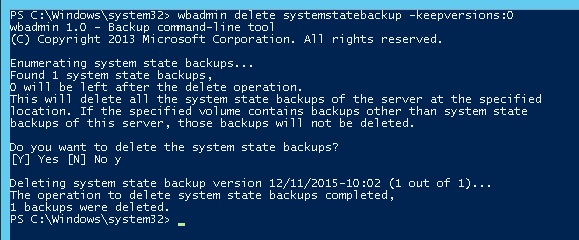
Если вы создаете резервные копии состояния системы с помощью Windows Server Backup (WSB), в Windows Server можно удалить старые версии копий system state с помощью команды:
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -keepversions:0
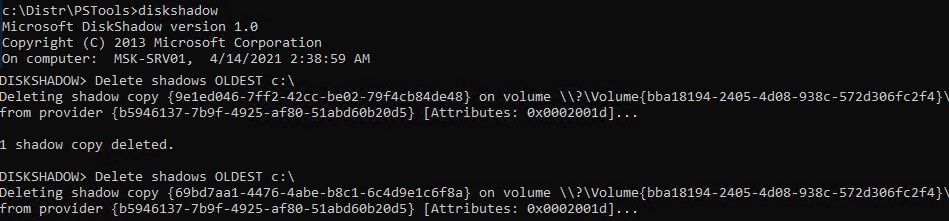
Для быстрой очистки старых версий резервных копий состояния системы (system state) и снапшотов в Windows Server используйте утилиты diskshadow:
DiskShadow
Delete shadows OLDEST c:\
При каждом запуске команды удаляется самая старая теневая копия (снапшот) диска.
При запуске команды
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup
в Windows 10 появляется ошибка – «
Команда DELETE SYSTEMSTATEBACKUP не поддерживается в этой версии ОС Windows
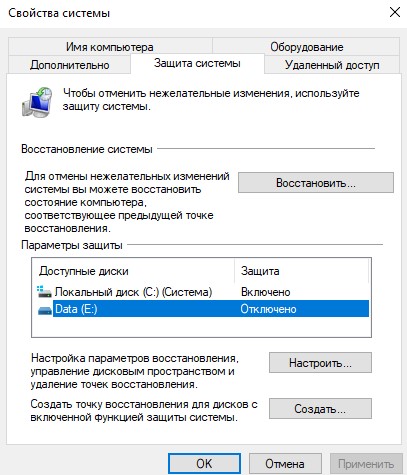
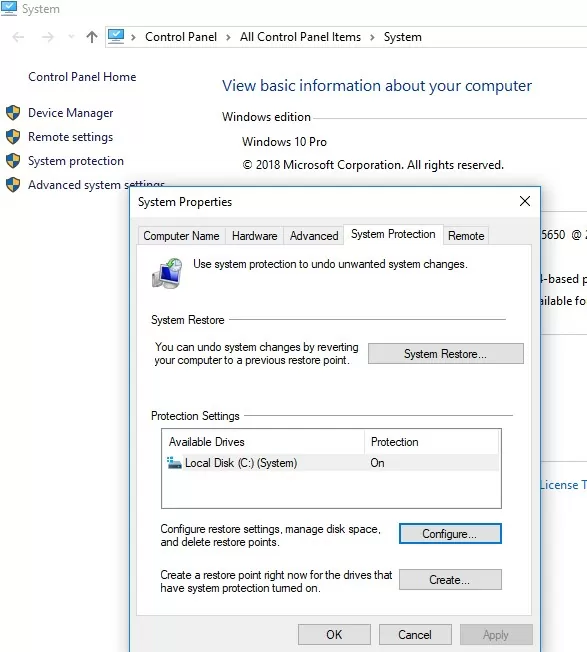
«. Дело в том, что в клиентских системах (Windows 10 / 8.1 /7) управление точками восстановления и лимитами возможно только из графического интерфейса. В свойствах системы (System) перейдите на вкладку System Protection (Защита системы).
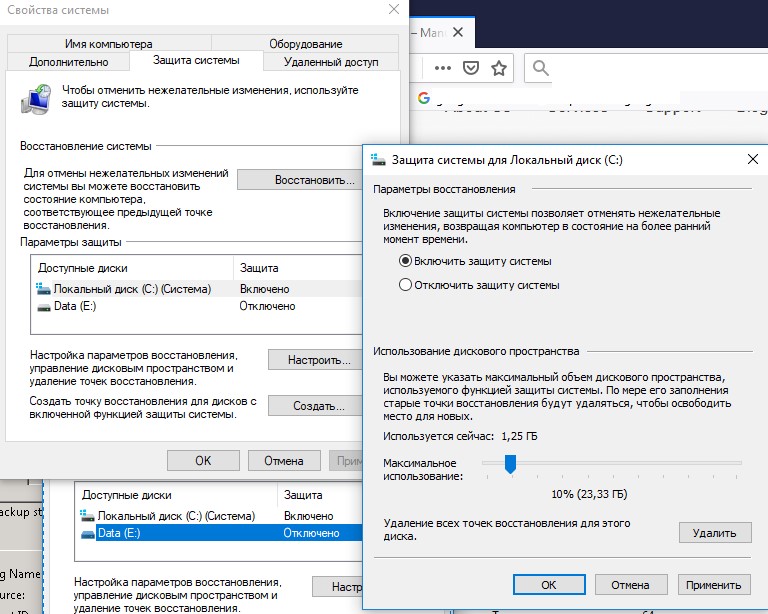
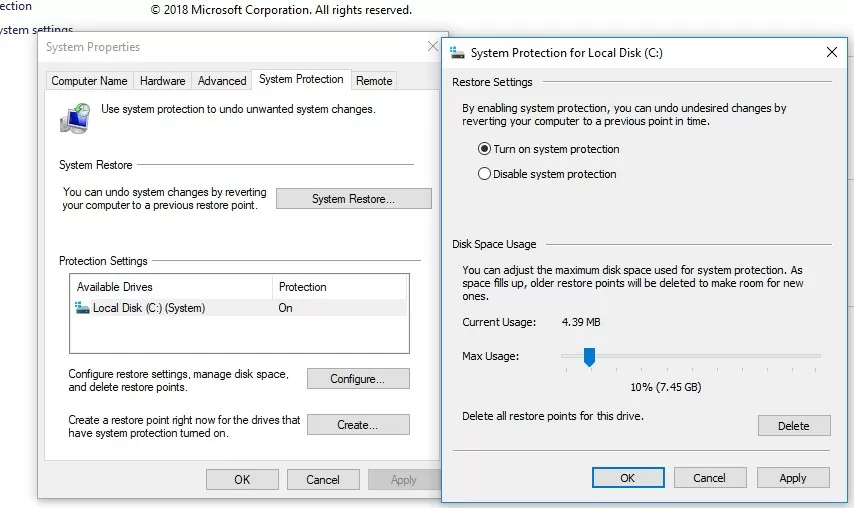
Выберите системный диск и нажмите на кнопку Configure (Настроить). Откроется диалоговое окно настройки квот для хранения точек восстановления системы. Вы можете уменьшить размер диска под хранение теневых копий. Здесь же можно удалить все имеющие точки восстановления (кнопка Удалить), либо совсем отключить создание точек восстановления, выбрав Отключить защиту системы.
Также для уменьшения размера каталога System Volume Information вы можете:
- Перенести данные VSS на другой NTFS диск (
vssadmin add shadowstorage /for=c: /on=d: /maxsize=30%
); - Отключить/перенастроить функцию История файлов Windows;
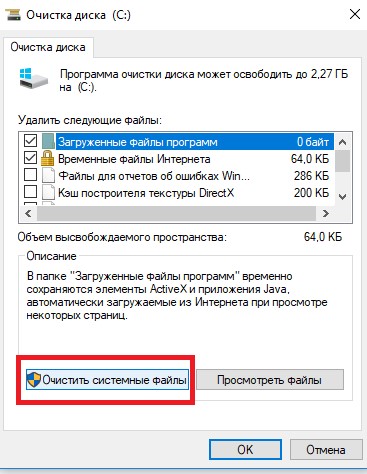
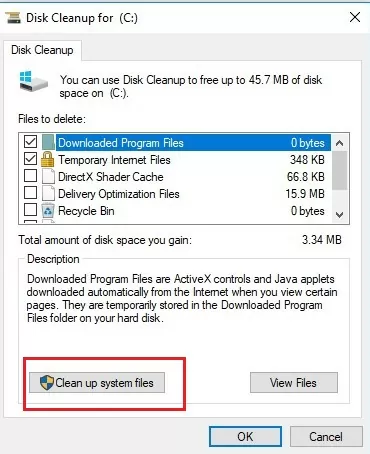
- Выполнить очистку системных файлов на диске с помощью встроенной утилиты cleanmgr.exe (свойства диска -> Очистка диска).
Очистка System Volume Information после удаления файлов на томе с дедупликацией
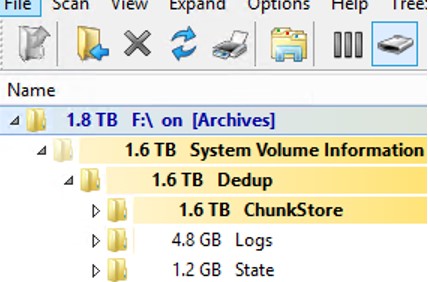
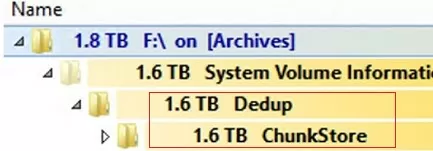
При анализе содержимого каталога System Volume Information в Windows Server вы можете заметить, что много места занимает каталог Dedup\ChunkStore. Это означает, что на диске включена дедупликация файлов.
Служба дедупликации при нахождении одинаковых чанков в файлах заменяет их на ссылку на уникальный чанк, который сохраняется в каталог System Volume Information. Если вы переместили или удалили оптимизированные файлы с дедуплицированного тома, старые чанки не удаляются немедленно. Эти блоки удаляются специальным заданием сбора мусора (GarbageCollection), которое запускается раз в неделю. Именно поэтому, место на томе с включенной дедупликацией не освобождается немедленно.
Чтобы немедленно запустить процедуру удаления неиспользуемые чанки, выполните команду PowerShell:
start-dedupjob -Volume C:-Type GarbageCollection
Следующее задание проверит целостность оставшихся чанков:
start-dedupjob -Volume C: -Type DataScrubbing
Для мониторинга этих задач используйте командлет:
Get-DedupJob
После окончания задач неиспользуемые чанки в каталоге System Volume Information будут удалены, а свободное место на диске увеличится.
Будьте внимательны при отключении дедупликацию данных для тома командой деоптимизации файлов
Start-DedupJob -Volume D: -Type Unoptimization
. Данная команда удалит все чанки в каталоге System Volume Information. Но при этом на диске де-оптимизированные файлы вернутся в исходное состояние и будут занимать на диске полное место. Поэтому перед отключением оптимизации проверьте, что на диске достаточно свободного места.
- What is system Volume information Windows Server?
- Where is system Volume information?
- What are the files in system volume information?
- Is it safe to delete Desktop ini?
- How do I fix system volume information?
- How do I copy files from system Volume information?
- Why is system volume information Access Denied?
- How do I get rid of shadow copies?
- What is recycle bin file?
- How do I delete Windows restore points?
What is system Volume information Windows Server?
The System Volume Information folder is used to store system data related to system recovery service, indexing, File History feature, etc.
Where is system Volume information?
The System Volume Information folder is a hidden and protected folder located at the root of every drive or partition. It’s even found on your SD card, USB pen drive, and external hard disk if you have connected them to your Windows computer earlier.
What are the files in system volume information?
The System Volume Information folder is automatically created at the root of each drive (be it a local HDD, SSD, removable USB flash drive, SD card). It stores system data related to System Restore, Indexing, File History, etc.
Is it safe to delete Desktop ini?
The desktop. ini file can technically be deleted from any directory, although it’s not advised. The file saves settings associated with the folder where it is contained, deleting it changes the settings back to default. … ini file, the icon would revert to what it was before.
How do I fix system volume information?
While in Command Prompt, type chkdsk /f /r and enter and let it run. It will scan and try to fix any corruption or bad sectors on your hard drive and mostly remove that as a cause.
How do I copy files from system Volume information?
Open Computer Management. In the console tree, right-click Shared Folders, select All Tasks, and click Configure Shadow Copies. Click the volume where you want to make changes (in our case, C:) and then click Settings.
Why is system volume information Access Denied?
The «Access Denied» error is occurred because the «C:\System Volume Information» is a system folder that is used from Windows to store information about the system restore points and by default this folder is not accessible by users.
How do I get rid of shadow copies?
Open File Explorer, and right-click the volume on which you want to disable Volume Shadow Copies. Select Configure Shadow Copies. 2. Select the volume and click Disable, then, click Delete Now.
What is recycle bin file?
The $recycl. bin folder is an important hidden system folder that is normally stored at the root of a specific drive of an internal or external hard drive. $recycle. bin is the link folder of the system Recycle Bin on each hard drive, which is used to save the file or folder deleted from the hard disk.
How do I delete Windows restore points?
To delete System Restore points, you need to open the System Protection window. For that, you can search for it in the Taskbar search box and click on the individual search result. After that, select the system drive from the list, and click the Configure button. Next, click the Delete button and confirm your removal.
One of the servers (running Windows Server 2016) has run out of free disk space on a system drive (C:\). I checked and cleaned all resource-consuming locations (WinSxS, TEMP folders, inactive user profiles, old update files, etc.), but it didn’t give a noticeable effect. There was still not enough disk space. At last, I have found that a large part of a system drive has been occupied by System Volume Information folder. In this article I will try to tell you how the System Volume Information folder is used on Windows, what is stored in it, and how to properly clean it up.
Contents:
- How to Access System Volume Information Folder on Windows?
- What is System Volume Information Folder in Windows?
- How to Clean Up System Volume Information Folder?
- Clean Up Dedup ChunkStore in System Volume Information
How to Access System Volume Information Folder on Windows?
The System Volume Information folder is automatically created at the root of each drive (be it a local HDD, SSD, removable USB flash drive, SD card). It stores system data related to System Restore, Indexing, File History, etc.
By default, the System Volume Information folder is hidden and only the NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM account can access it.
In order to show this folder, you need to disable the option “Hide protected operating system files” in File Explorer or run a PowerShell script:
$regkey = 'HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced'
Set-ItemProperty $regkey Hidden 1
Set-ItemProperty $regkey HideFileExt 0
Set-ItemProperty $regkey ShowSuperHidden 1
Stop-Process -ProcessName explorer
Even the administrator cannot open it and view the contents of the folder. If you try to open the System Volume Information folder in File Explorer under any user (even under the built-in administrator account), you will receive an access denied error:
Location is not available. C:\System Volume Information is not accessible. Access is denied.
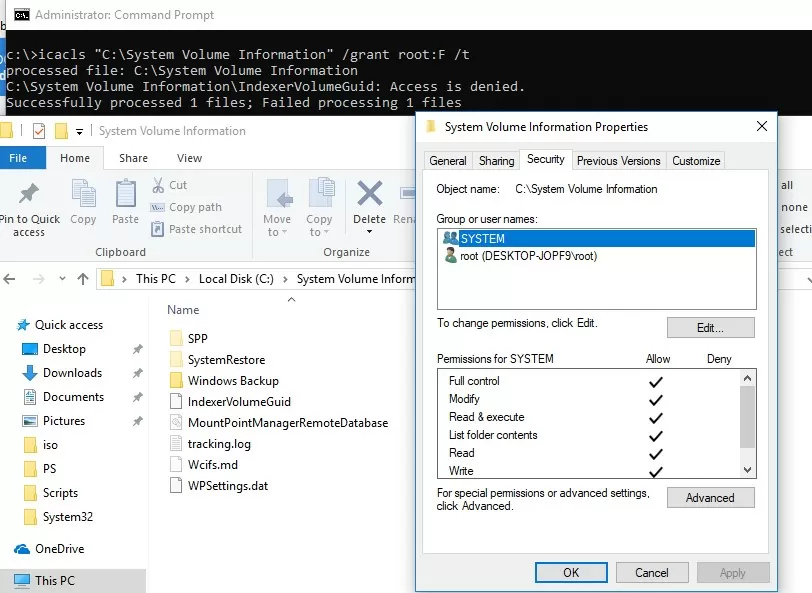
To view the contents of the folder, you have to assign yourself as the directory owner and grant your account the NTFS permissions to access it (this can be done through the Security tab in the folder properties). But it is much faster to assign yourself the owner and grant access to the directory from the command prompt:
takeown /f "C:\System Volume information"
icacls "C:\System Volume Information" /grant woshub\jwolf:F
Check in the folder properties on the Security tab that your account now has full control permissions.
You can also view the contents of the System Volume Information directory by running the PowerShell console with NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM privileges:
PsExec.exe -i -s powershell.exe
To view the contents of a folder, run the command:
Get-ChildItem 'C:\System Volume Information\'
The folder size can be found with the following PowerShell command:
(Get-ChildItem 'C:\System Volume Information\' | measure Length -s).sum / 1Gb
To restore the original permissions on the System Volume Information folder, run:
icacls "C:\System Volume Information" /setowner "NT Authority\System"
icacls "C:\System Volume Information" /remove woshub\jwolf
What is System Volume Information Folder in Windows?
What is stored in the System Volume Information folder? I found information about the following services, which store their files in this folder (the list is not exhaustive):
- WindowsImageBackup —system restore points on desktop Windows versions or System State backups made using Windows Server Backup (
wbadmin) in server OSs; - The contents of Indexing Service database used for fast file search (including Outlook search);
- Distributed Link Tracking Service database;
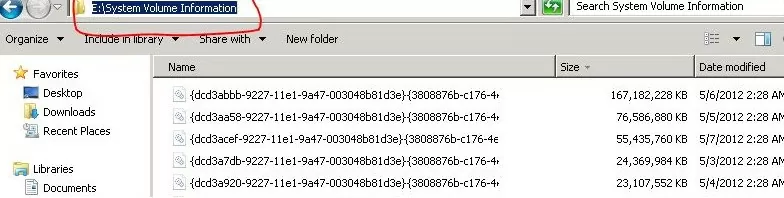
- Disk snapshots made by Volume Shadow Copy, which can be used to recover older versions of files. For each snapshot, a separate file is created with a long ID as a name;
- NTFS disk quota settings;
- Base and chunks of the Data Deduplication service;
- DFS Replication database (dfsr.db);
- WPSettings.dat file – created by the storage service (StorSvc);
- The USB drives will also store an IndexerVolumeGuid file that defines the unique disk label used by the Windows Search service;
- AppxProgramDataStaging, AppxStaging – Windows UWP app backups (it can be used for recovery after removal).
If you are using shadow copies on your computer or server to roll back to old versions of files/system states, keep in mind that each new VSS snapshot saves data to the System Volume Information directory, increasing its size. The more often shadow copies are created and the more often the files on the disk change, the faster the size of this directory grows.
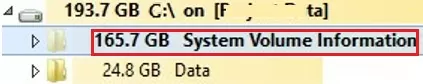
In the screenshot below, you can see that in the System Volume Information folder there is a system file larger than 160 GB.
How to Clean Up System Volume Information Folder?
Note. It is not recommended to manually delete files in System Volume Information folder, since it stores information for system recovery and data for some critical services.
You can radically clean up the System Volume Information directory by disabling the system restore points and file history. But this is not always acceptable.
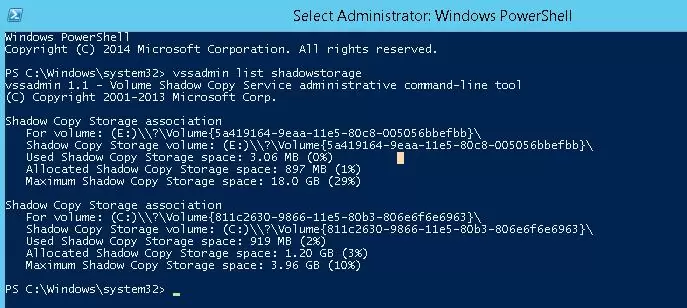
Firstly, let’s see what is stored in this directory. Display the statistics of using shadow copies:
vssadmin list shadowstorage
vssadmin 1.1 - Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command-line tool
(C) Copyright 2001-2013 Microsoft Corp.
Shadow Copy Storage association
For volume: (E:)\\?\Volume{5a419164-9eba-11e5-84c5-004046bbefbb}\
Shadow Copy Storage volume: (E:)\\?\Volume{5a419164-9eba-11e5-84c5-004046bbefbb}\
Used Shadow Copy Storage space: 3.08 MB (0%)
Allocated Shadow Copy Storage space: 896 MB (1%)
Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space: 19.0 GB (29%)
Shadow Copy Storage association
For volume: (C:)\\?\Volume{843c6330-9866-11e5-80b3-806e6f6e6942}\
Shadow Copy Storage volume: (C:)\\?\Volume{843c6330-9866-11e5-80b3-806e6f6e6942}\
Used Shadow Copy Storage space: 912 MB (2%)
Allocated Shadow Copy Storage space: 1.20 GB (3%)
Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space: 3.98 GB (10%)
As you can see, 10% of system drive (C:\) space is allocated for shadow copy files and only 2% of which is used. If the value of Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space is set to UNBOUNDED, it means that the limit for shadow copies is not set and they can potentially take up all available free disk space. Windows by default allocates 10% of the total disk size for storing shadow copies.
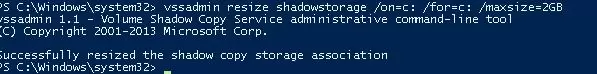
You can reduce the disk usage limit of VSS to 2 GB using the vssadmin command. The vssadmin command has the following syntax:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /on=[drive letter]: /For=[drive letter]: /MaxSize=[maximum size]
In our example it will look like this:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /on=c: /for=c: /maxsize=2GB
vssadmin 1.1 - Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command-line tool (C) Copyright 2001-2013 Microsoft Corp. Successfully resized the shadow copy storage association
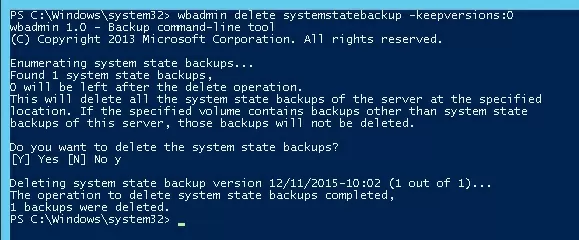
If you create system state backups using WSB (Windows Server Backup), all old system state copies can be deleted as follows (in the Windows Server editions):
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -keepversions:0
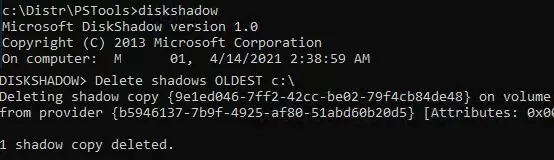
To quickly clean up old versions of VSS snapshots on Windows Server, use the diskshadow tool:
DiskShadow
Delete shadows OLDEST c:\
Each time the command is run, the oldest shadow copy (snapshot) of the volume is deleted.
When you run the wbadmin delete systemstatebackup command in Windows 10, an error appears: “The DELETE BACKUP command is not supported in this version of Windows“. The fact is that on desktop OS (Windows 10/ 8.1/ 7), restore point and limits can only be managed from the Windows GUI. Open the System properties and click on the System Protection tab.
Select the system drive and click the Configure button. The quota configuration dialog box for storing system restore points will open. You can reduce the size of the disk for storing shadow copies. Here you can either delete all existing restore points (Delete button), or completely disable the creation of restore points by selecting Disable system protection.
To reduce the size of the System Volume Information directory you can also:
- Move the VSS data to another NTFS drive (
vssadmin add shadowstorage /for=c: /on=d: /maxsize=30%); - Disable or reconfigure the Windows File History feature;
- Clean up system files using the built-in tool cleanmgr.exe (disk properties -> Disk Cleanup).
Clean Up Dedup ChunkStore in System Volume Information
When analyzing the contents of the System Volume Information folder on Windows Server, you may notice that the Dedup\ChunkStore directory is consuming a lot of space. This means that file deduplication feature is enabled for this volume.
If the Windows Data Deduplication service found identical chunks (fragments) in files on a volume, it replaces them with a link to the unique chunk, which is saved to the System Volume Information directory. If you move or delete optimized files from a deduplicated volume, old chunks are not deleted immediately. These blocks are removed by a special GarbageCollection job that runs once a week. This is why space on a deduplication-enabled volume is not immediately reclaimed.
To immediately start the process of removing unused chunks, run the PowerShell command:
start-dedupjob -Volume C: -Type GarbageCollection
The next dedup job will check the integrity of the remaining chunks:
start-dedupjob -Volume C: -Type DataScrubbing
To monitor these tasks, use the Get-DedupJob cmdlet.
After the completion of the tasks, unused chunks in the System Volume Information directory will be deleted, and additional disk space will be freed.
Be careful when disabling data deduplication for a volume with the Start-DedupJob -Volume D: -Type Unoptimization command. This command will delete all chunks in the System Volume Information directory and the unoptimized files on the volume will revert to their original size. Therefore, before disabling optimization, make sure that there is enough free disk space.
The system volume information is often kept hidden on Windows for security purposes. This folder stores system files related to restore & backups and content indexing services.
It is located at the root of the system volume and can fill up fast with backup/restore files, content index databases, and Dedup chunks(On Windows Server).
It is not recommended to delete this folder as it can prove to be vital in case the system suffers a crash. Instead, you can free up the disk by cleaning up the contents inside the System Volume Information Folder.
Table of Contents
How to Fix ‘System Volume Information Folder Too Large’ Error
Limit the Disk Usage Space for Folder
Whenever the system creates the restore points, the associated files are stored by the Windows on the System volume information folder. If the disk space usage limit is not set for such restore points, it will accumulate data in the folder over time and fill up the disk faster.
It is recommended to configure the disk usage for the system restore up to 15 percent of the total size of the volume.
- Click on the Start button, type Create a restore point and open it.
- Go to the System Protection section.
- Click on the Configure button.
- Reduce the Disk Space usage for system protection by using the Max Usage slider.
- Click on Apply to save changes.
- Finally, restart the computer and check the folder size. The System Volume Information Folder will now shred down to the configured size.
Perform Disk Cleanup
The Volume Shadow Copy Service creates a backup of the data on your computer as a shadow copy. It stores such backups in the System volume information folder. These shadow copies metadata can be cleaned by performing a disk cleanup.
- Press Windows Key + R to open Run.
- Type
C:\windows\SYSTEM32\cleanmgr.exe, and hit enter. - Select the System volume (on most devices, it’s
C:) drive and click on OK. - Click on the Cleanup system files button.
- Again, select the system volume and click on OK.
- Go to the More options tab.
- Under the System Restore and Shadow Copies section, click on the Cleanup button.
Delete the System Volume Information Folder from the USB
The system volume information folder usually does not have a huge file size on USB storage devices. However, if the device has been infected by malware and viruses, this folder will show up as a large folder. You also sometimes cannot delete this folder using the normal modus operandi.
- Connect the USB to your Windows device.
- Open the USB volume from File Explorer.
- Right-click on the empty space of the Drive window and select Open in Terminal.
- Now, run this command line in the command prompt.
rmdir "System Volume Information" /s /q
- This will delete the folder in the USB drive. However, it will be re-created once you eject and reconnect the flash drive. This only helps if the folder occupies large disk spaces in the USB.
Note: The System Volume Information is kept hidden by the system for security reasons on both the root directory and the USB storage device. You can make this folder visible and accessible from the File explorer settings.
- Open the File explorer.
- Click on the three vertical dots located at the file explorer’s Toolbar.
- Go to View tab.
- Uncheck the option Hide protected operating files and select the Show hidden files, folders and drivers.
- Click on Apply to save the changes.
Restrict the System From Creating the Folder
You can delete the system volume information with the above-suggested methods. But the system recreates this folder once you reconnect the USB device. This happens if the group policy configurations allow the locations to be indexed in the system volume information folder.
- Press Windows Key + R, type
gpedit.msc, and hit enter to open the Group policy editor. - Now, navigate to this directory from the panel on the left.
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Search - Search for a Setting Do not allow locations on removable drives to be added to libraries and open it.
- Click on Enable.
- Click on OK to save the changes.
Clean up the System Volume Information folder
On Windows Server, the Data Deduplication service compresses and stores the redundant data in the System Volume Information folder. These chunks of files accumulate and occupy heaps of disk space.
- Open PowerShell and run this command. This will start removing the unused files from the System Volume Information folder.
start-dedupjob -Volume C: -Type GarbageCollection - Now, use this command to start the data cleansing to fix the data integrity.
start-dedupjob -Volume C: -Type DataScrubbing
Nishant is an enthusiast who loves writing about technology. He also is heavily invested in keeping himself updated about the latest happenings in the tech world. At Tech News Today, he covers Operating Systems, how-to-topics, and Fixes.
System Volume Information (Информация о том, какого объема каждая система занимает на сервере) является скрытой папкой на операционной системе Windows Server 2012. В этой папке система хранит информацию о том, как управлять, а также восстанавливать системные файлы. Она играет важную роль в обеспечении стабильной работы сервера.
Папка System Volume Information располагается на каждом разделе или диске сервера. Она содержит информацию о точках восстановления системы, состоянии файловой системы, журналах событий и других системных данных. Несмотря на то, что папка скрыта для пользователя и недоступна для просмотра и изменения, некоторые пользователи могут столкнуться с необходимостью управлять ее содержимым.
Чтобы получить доступ к папке System Volume Information, необходимо быть администратором сервера. Чтобы просмотреть содержимое папки, можно использовать командную строку или специализированные программы. Однако, следует быть осторожным при изменении или удалении файлов в этой папке, так как это может привести к нарушению стабильности работы сервера.
Важно помнить, что System Volume Information является важной частью операционной системы Windows Server 2012 и содержит критическую информацию. Лучше всего обратиться к специалистам или изучить документацию, прежде чем совершать какие-либо действия с этой папкой. Неправильные манипуляции могут привести к серьезным проблемам и потере данных.
Содержание
- Определение и назначение
- Местоположение и доступ
- Функции и хранение данных
- Резервное копирование и восстановление
- Управление доступом и безопасность
- Настройки и параметры
Определение и назначение
Основное назначение папки System Volume Information заключается в хранении данных, связанных с теневыми копиями (Shadow Copies) и системными точками восстановления (System Restore) операционной системы. Она является частью функциональности системы защиты данных и позволяет восстанавливать файлы и систему к более ранним состояниям в случае ошибок или потери данных.
Папка System Volume Information недоступна для прямого доступа и нормального просмотра ее содержимого из-за своей системной природы. Для доступа к данным внутри папки требуются определенные права доступа и специальные инструменты, такие как командная строка или специализированные утилиты.
Важно отметить, что удаление или изменение содержимого папки System Volume Information может повредить работу системы и привести к потере данных. Поэтому не рекомендуется вмешиваться в работу этой папки без необходимой экспертизы или инструкций со стороны разработчиков операционной системы.
Местоположение и доступ
Папка System Volume Information находится в корневой директории каждого диска в системе Windows Server 2012. Обычно она скрыта, и для ее отображения необходимо включить опцию «Показывать скрытые файлы и папки» в настройках папки.
Доступ к папке System Volume Information имеют только системные процессы и пользователи с административными привилегиями. По умолчанию, даже администраторы не имеют полного доступа к содержимому этой папки. Это сделано для обеспечения безопасности системы и предотвращения случайного удаления или изменения важных системных файлов.
Если вам необходимо получить доступ к содержимому папки System Volume Information, вы можете воспользоваться привилегиями администратора или включить полный доступ для пользователя в настройках папки.
Обратите внимание, что удаление или изменение файлов в папке System Volume Information может привести к непредсказуемым последствиям и нарушению работы системы. Будьте осторожны при работе с этой папкой и делайте резервные копии важных файлов перед внесением изменений.
Функции и хранение данных
Папка System Volume Information выполняет несколько важных функций на операционной системе Windows Server 2012. Она предназначена для хранения системных файлов и служит для обеспечения функциональности системы и безопасности данных.
Основные функции папки System Volume Information:
- Системное восстановление: папка System Volume Information используется для хранения точек восстановления и резервных копий файлов системы. В случае проблем с операционной системой, эти точки восстановления позволяют восстановить систему в предыдущее рабочее состояние.
- Журналы системы: папка также содержит журналы, которые записывают информацию о важных событиях и изменениях в системе. Эти журналы могут быть использованы для диагностики проблем и обнаружения ошибок.
- Антивирусная защита: папка System Volume Information может быть использована антивирусными программами для сканирования и анализа файлов системы. Они проверяют изменения, происходящие в этой папке, чтобы обнаружить и предотвратить вредоносную активность.
Папка System Volume Information скрыта по умолчанию и защищена от случайного удаления. Ее местоположение зависит от раздела файловой системы: для каждого раздела на сервере будет создан свой экземпляр папки.
Резервное копирование и восстановление
System Volume Information также играет важную роль при резервном копировании и восстановлении данных на Windows Server 2012.
Директория System Volume Information содержит данные, необходимые для восстановления системы. При резервном копировании, вместе с другими системными файлами, рекомендуется также создавать резервную копию этой директории.
Для выполнения резервного копирования директории System Volume Information можно использовать утилиту Windows Server Backup, которая входит в состав операционной системы. С помощью этой утилиты можно создавать резервные копии всей системы или отдельных дисков, включая System Volume Information.
Для восстановления данных из резервной копии, в том числе и директории System Volume Information, также можно использовать утилиту Windows Server Backup. Восстановление может быть выполнено как на целый диск, так и на отдельные файлы и папки.
Важно учитывать, что для восстановления данных из директории System Volume Information требуются соответствующие права доступа. Обычно требуются административные права.
Управление доступом и безопасность
Для управления доступом к System Volume Information на Windows Server 2012, следует выполнить следующие шаги:
1. Запустите утилиту Восстановление системы (System Restore) или Восстановление файлов (File Recovery).
Чтобы получить доступ к System Volume Information, можно воспользоваться утилитой Восстановление системы или Восстановление файлов, которая предоставляет доступ к разделам диска и позволяет просмотреть содержимое System Volume Information.
2. Измените права доступа к System Volume Information.
Для изменения прав доступа к System Volume Information, нужно открыть свойства папки (кликнув правой кнопкой мыши на папке) и перейти на вкладку «Безопасность». Затем необходимо выбрать группу или пользователя, чьи права доступа вы хотите изменить, и нажать на кнопку «Изменить». В появившемся окне можно задать нужные разрешения на чтение, запись, выполнение, и т.д.
3. Позвольте доступ к System Volume Information через политики безопасности.
Для открытия доступа к System Volume Information через политики безопасности на Windows Server 2012, откройте «Локальные политики безопасности» из меню «Пуск» или введите «secpol.msc» в командной строке. Затем перейдите в раздел «Правила локальной политики» и настройте политику «Доступ к файлам System Volume Information». Установите нужные параметры, чтобы разрешить доступ.
Следуя этим шагам, можно управлять доступом и повысить безопасность System Volume Information на Windows Server 2012.
Настройки и параметры
Следующие настройки и параметры могут быть полезны при управлении System Volume Information на Windows Server 2012:
- Размер System Volume Information можно настроить с помощью команды vssadmin в командной строке.
- Вы можете изменить расположение папки System Volume Information, используя инструмент DiskPart.
- Если вы хотите предотвратить создание новых точек восстановления, вы можете отключить службу теневого копирования тома.
- Вы также можете изменить параметры сохранения точек восстановления, например, установить ограничение на их количество и продолжительность хранения.
- У вас также есть возможность удалить точки восстановления, используя операционную систему или инструменты сторонних производителей.

![] Location is not available. C:\System Volume Information is not accessible. Access is denied](https://woshub.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/System-Volume-Information-Access-is-denied.jpg.webp)

![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 1 system protection configuration](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/system-protection-configuration.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 2 Change the disk usage](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Chnage-the-disk-usage.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 3 clean up system files](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/clean-up-system-files-1.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 4 more options for clean up](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/more-options-for-clean-up.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 5 Open USB volume in terminal](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/OPen-in-terminal.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 6 rmdir command](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/rmdir-command.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 7 group policy editor](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/group-policy-editor.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 8 restrict locations on USB drives](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/restrict-locations-on-USB-drives.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 9 enable settings from gpedit](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/enable-settings-from-gpedit.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 10 garbage collection command](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/garbage-collection-command.jpg)
![[Solve] System Volume Information Folder Too Large 11 data scrubbing command](https://www.technewstoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/data-scrubbing-command.jpg)