Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests…
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Are you looking for a step-by-step guide on how to configure a syslog server in Windows? If yes, you have come to the right place! In this article, we will walk you through the process of configuring a syslog server in Windows. We will discuss the benefits of using a syslog server, how to set up the server and the configuration settings that are needed for successful deployment. By the end of this article, you will be able to set up and configure your own syslog server in Windows with ease. So let’s get started!
Steps to Configure Syslog Server in Windows:
- Open the Start Menu and search for Event Viewer. In the search results, click on the Event Viewer result.
- In the Event Viewer, expand the Windows Logs option on the left side.
- Right-click on the Application option and select Properties.
- In the Application Properties window, select the General tab.
- In the General tab, under the Logging option, select the Syslog option.
- Now, enter the Syslog server details like IP Address and Port Number.
- After entering all the details, click on the OK button.
Your Syslog Server has been successfully configured in Windows.
Configuring a Syslog Server in Windows
Syslog is a protocol used to send log messages across the network to a centralized server. Configuring a syslog server in Windows can be done using either a third-party syslog agent or the built-in Windows Event Collector service. In this article, we will discuss how to configure a syslog server in Windows using both methods.
Using a Third-Party Syslog Agent
The first step in configuring a syslog server in Windows is to install a third-party syslog agent. There are a number of different syslog agents available, but the most popular ones are syslog-ng and rsyslog. After installing the syslog agent, you need to configure it to listen for incoming syslog messages. This can be done by editing the configuration file for the syslog agent.
Once the syslog agent is configured to listen for incoming messages, you can start sending syslog messages from other devices on the network. To do this, you will need to configure the devices to send their log messages to the IP address of the syslog server.
Finally, you can configure the syslog agent to forward the messages it receives to an external log server, such as Splunk or Loggly. This allows you to aggregate all of your log data in one place, making it easier to analyze and troubleshoot.
Using the Windows Event Collector Service
Another way to configure a syslog server in Windows is to use the built-in Windows Event Collector service. This service is included in Windows Server and allows you to collect log messages from other devices on the network and forward them to an external log server.
The first step in configuring the Windows Event Collector service is to enable it on the server. This can be done by using the Services applet in the Control Panel. Once the service is enabled, you can configure it to listen for incoming syslog messages.
Setting Up the Listener
Next, you will need to set up the listener to receive the messages. This can be done by creating a new event subscription in the Windows Event Collector console. Once the subscription is created, you can configure it to specify what types of messages you want to receive and which log server you want to forward them to.
Configuring the Network Devices
Finally, you will need to configure the network devices to send their log messages to the Windows Event Collector service. This can be done by editing the configuration file for each device and specifying the IP address of the Windows Event Collector service as the destination for log messages.
Conclusion
Configuring a syslog server in Windows can be done using either a third-party syslog agent or the built-in Windows Event Collector service. By using either of these methods, you can easily centralize your log data and make it easier to analyze and troubleshoot.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Syslog Server?
A syslog server is a type of logging server used to collect and store logging information from multiple sources. It is typically used to collect system logs from computers, routers and other network devices, as well as from applications and services running on the network. The syslog server then stores the log data in a central location for easy access and analysis.
What are the Benefits of Configuring a Syslog Server in Windows?
The main benefit of configuring a syslog server in Windows is to centralize log data from multiple sources into one place. This makes it easier to monitor and troubleshoot issues that may arise. In addition, syslog data can be used to generate reports and dashboards, which can provide valuable insight into system performance and security.
How to Configure a Syslog Server in Windows?
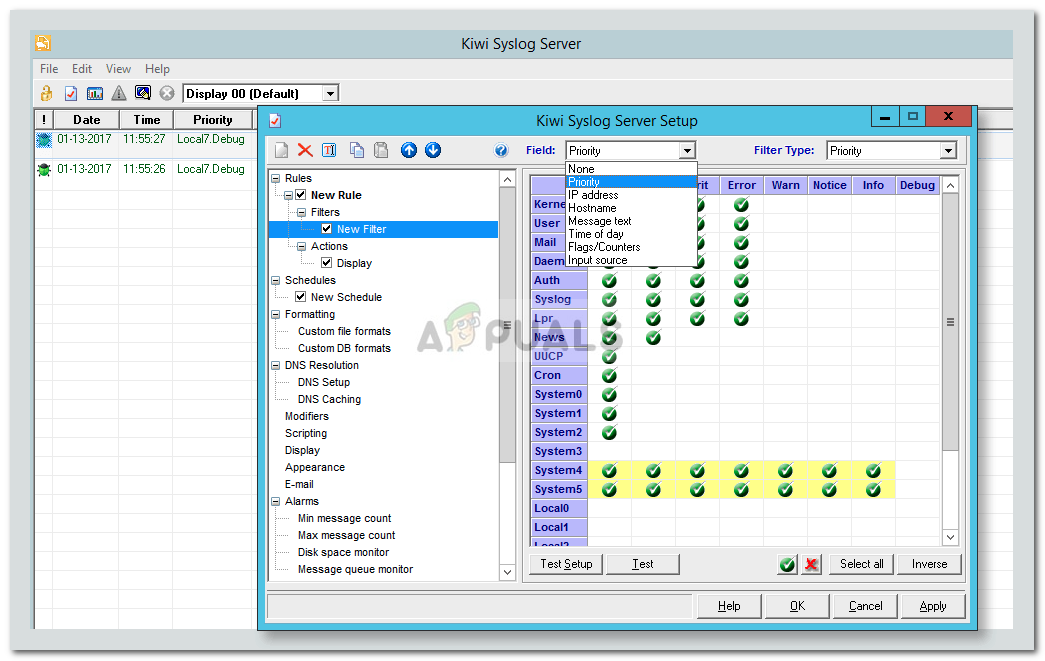
Configuring a syslog server in Windows involves installing a syslog server program, configuring the server and then configuring the various network devices and applications to log to the server. First, you need to install a syslog server program such as SolarWinds Log & Event Manager, Syslog-ng, or Kiwi Syslog Server. Once these are installed, you can configure the server, including setting up the logging parameters, security settings, and log storage options. Finally, you will need to configure the various network devices and applications to log to the server.
What are the Common Logging Options for Syslog?
Common logging options for syslog include storing log messages in a text file, sending log messages to a remote server, and emailing log messages. Additionally, there are options to store log messages in a database, send log messages to a SIEM, and forward log messages to a syslog-ng instance.
What Security Measures Should be Taken When Configuring a Syslog Server?
When configuring a syslog server, there are several security measures that should be taken. These include enabling strong encryption for remote log messages, setting up authentication for logging connections, and configuring access control for log messages. Additionally, the system should be monitored for any suspicious activity, and all log data should be backed up regularly.
What are the Best Practices for Managing Syslog Data?
The best practices for managing syslog data include archiving log data regularly, setting up alerts for suspicious activity, and regularly monitoring the system for potential security issues. Additionally, it is important to keep the system up to date with the latest security patches, and to ensure that all log data is backed up regularly. Finally, log data should be analyzed regularly to ensure that any potential issues can be addressed promptly.
How to Configure Syslog Server and Forwarder for Windows Event Kiwi Syslog Server
Configuring a Syslog Server in Windows is a simple and straightforward process. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can quickly and easily configure a Syslog Server in Windows, allowing you to track, monitor, and analyze the data collected from your network environment. With the help of a Syslog Server, you can ensure that your network is running smoothly and efficiently, while also providing you with a valuable source of information.
Introduction
The syslog (system logging) protocol is used for monitoring network devices and sending log messages to a logging server (a syslog server).
The syslog server and syslog protocol work together to facilitate log tracking and management.
In this article, you will learn what a syslog server is, what it is used for, and see the best syslog servers available for Linux and Windows.
What Is a Syslog Server?
A syslog server collects syslog messages from all devices in a single location, whether it is a bare metal server, a virtual machine, or a software service. The syslog server usually consists of a syslog listener, which receives and interprets the incoming data, and a database for storing the data.
The server collects, filters, and displays the collected messages from all devices and operating systems. A syslog server can usually store the logs for a long time.
Advanced syslog servers provide automated notifications and tailored responses to detected issues — i.e., to run a script, filter and forward a message, create and deliver a report, etc.
With all the benefits and features of a syslog server, it is easy to optimize device performance and health after analyzing server data.
What Is a Syslog Server Used For?
A syslog server’s primary purpose is to collect log messages from the connected network devices and store them in a centralized location for monitoring purposes. The server keeps the logs in a consistent format, allowing users to spot performance irregularities easily.
Use a syslog server to improve network monitoring and management by inspecting network specifics and parameters. Automate actions by setting up automatic alerts about a variation in a device’s data log. Some syslog servers come with a message severity level indicator.
The benefits of using a syslog server and logging data are:
- Reduced number of alerts.
- Reduced downtime.
- Fewer business interruptions.
- Preventive troubleshooting.
Finally, syslog servers can store event logs for a long time, enabling access to historical events. Various syslog servers rotate logs and create new files periodically, thus keeping the data organized.
This section lists the most popular and feature-rich Linux and Windows syslog servers. For a comparison of supported platforms and free trial availability, refer to the table below:
| Syslog Server | Supported Platforms | Free Trial |
|---|---|---|
| Kiwi | Unix, Linux, Windows | 14 days |
| PRTG | Windows | 30 days |
| Syslog Watcher | Unix, Linux, Windows | Per request |
| The Dude | Linux, macOS, Windows | / |
| Visual Syslog Server | Unix, Linux | / |
| Datagram | Windows | Unlimited trial version |
| ManageEngine EventLog Analyzer | Linux, Windows | / |
| Icinga | Unix, Linux | / |
| GrayLog | Linux | / |
| WinSyslog | Windows | / |
| Nagios | Linux, Windows | 30 days |
| Splunkbase | Unix, Linux, Windows | 14 days |
| Progress WhatsUp Gold | Windows | 14 days |
| Logstash | Unix, Linux, Windows | 14 days |
| Loggly | Cloud-based | 30 days |
| Site24x7 | Cloud-based | 30 days |
Free Syslog Servers
The following section lists the best free syslog servers:
1. Kiwi Syslog Server
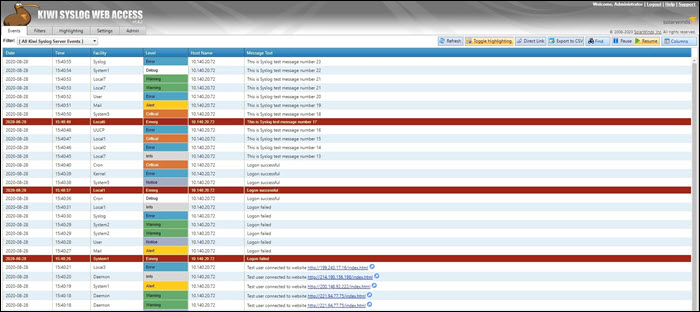
The Kiwi syslog server was created by SolarWinds. It is a comprehensive logging utility that collects syslog events and messages on Unix, Linux, and Windows and generates reports in plain text or HTML.
Kiwi’s GUI allows users to easily and efficiently manage logs in a single place. The tool can create network traffic graphics and, optionally, send daily summary emails.
The free edition collects syslog messages from up to five devices and provides an option to set up alerts for various events, including heavy traffic, login attempts, hardware failures, etc. Additionally, Kiwi offers the possibility of archiving syslog messages or forwarding them to a database. The free version comes with a trial of full functionalities lasting 14 days.
The full version costs $329 and offers automation, allowing you to set up actions that are automatically triggered by specific events and a web-based interface for remote management.
2. PRTG Syslog Server
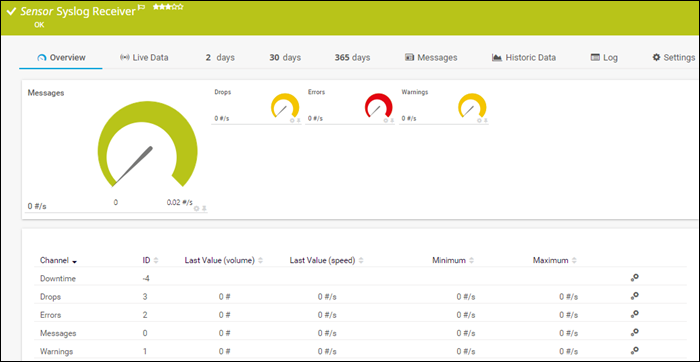
The PRTG syslog server is part of the PRTG Network Monitor application, and it is completely free for up to 100 sensors. The free trial allows users to use more sensors for 30 days but later reverts to the free version. The Syslog Receiver sensor for monitoring and analyzing network traffic doesn’t require additional software installations.
PRTG can receive and process up to 10,000 syslog messages per second from network devices and Windows environments. The number depends on the processing power, storage, and overall system configuration.
PRTG offers an intuitive web interface for viewing, analyzing, and filtering syslog messages by type, severity, etc. It also provides message categorization and further filtering to ensure only relevant messages are displayed.
The server offers automation by sending alerts triggered by errors, warnings, or a high number of messages.
3. Syslog Watcher
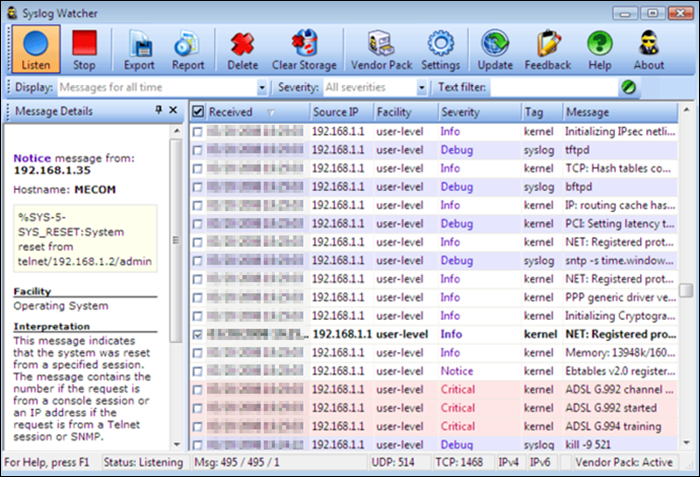
The SNMPSoft Syslog Watcher is a dedicated syslog server compatible with various devices and software that support syslog sending. The tool collects system log events from Unix, Windows or Linux servers.
The free version allows syslog message collection from five sources, while the professional version supports an unlimited number of sources. Depending on the configuration, Syslog Watcher can handle up to 5,000 syslog messages per second.
Syslog Watcher can collect messages over UDP and TCP and supports IPv4 and IPv6 networks. The utility also enables automation by sending email alerts for specific errors, events, or messages.
Message filtering, storing, and customization depend on filters, the message severity level, and the rules set by the user. Syslog Watcher also offers exporting messages to a database, manually or automatically.
4. The Dude
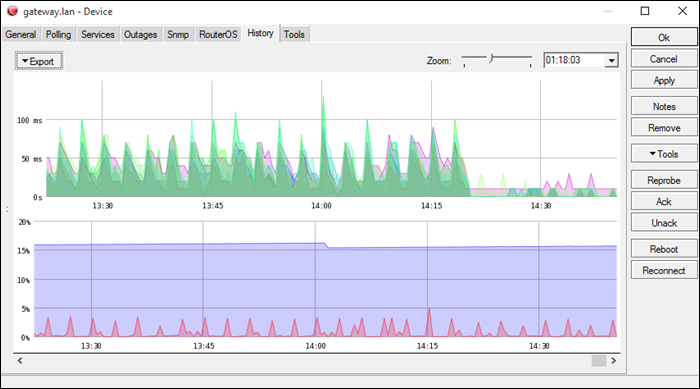
The Dude is a network management application developed by MicroTik, with a free built-in syslog server. The application offers general network management, while the syslog server captures syslog messages from your devices.
The Dude supports remote logging via RouterOS. It is compatible with Windows-based systems, while on Linux or macOS, it runs using Wine/Darwine.
The server automates maintenance by allowing users to create alerts for specific syslog events or messages and filters.
It includes an auto-discovery feature, automatically mapping nearby devices on the network, which facilitates network building.
5. Visual Syslog Server
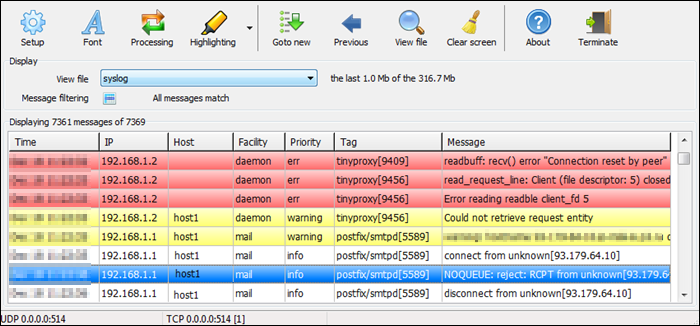
Visual Syslog Server is a free and lightweight Windows-based syslog server that monitors incoming data in real-time. It accepts messages via UDP and TCP and stores them on a disk. Previous syslog messages remain on the disk for future analysis as long as the user specifies.
Message filters include filtering based on the host, source address, priority, facility, or message content. Filtering makes it easy to find an issue when dealing with a large data volume.
Users can also configure thresholds for triggering the execution of scripts, programs, or email notifications. Thus, the tool automates problem-solving and reduces response time for pressing issues.
6. Datagram
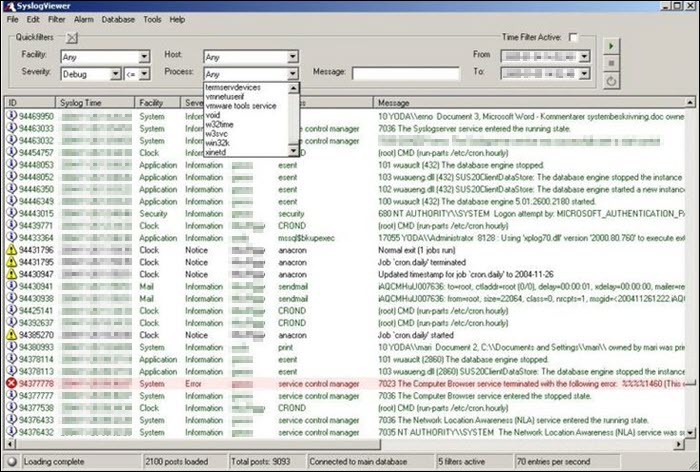
The Datagram Syslog Server is part of the Datagram SyslogServer Suite. Its Datagram SyslogAgent is installed as a service on Windows clients and servers, supporting Windows 2000 or newer systems.
The program provides enterprise-level functionality, capable of log collection, message filtering, alerts, database storage, and log viewing.
The GUI is intuitive and offers a live network view. The filters include the hostname, process, facility, issue severity, message, or even custom SQL queries.
The trial version is free, supports eight logging IP addresses, but supports the Microsoft Access database only. Entries cannot be backed up or deleted, and there are no email notifications. Users can create ten filters and set up to ten alarms.
On the other hand, the enterprise version costs $200 for 50 IP addresses, $500 for 500, and $900 for 5000 IP addresses. The enterprise version allows users to back up or delete entries, supports MSSQL databases, and sets no limit on creating filters or alarms. It also supports email notifications.
7. ManageEngine EventLog Analyzer
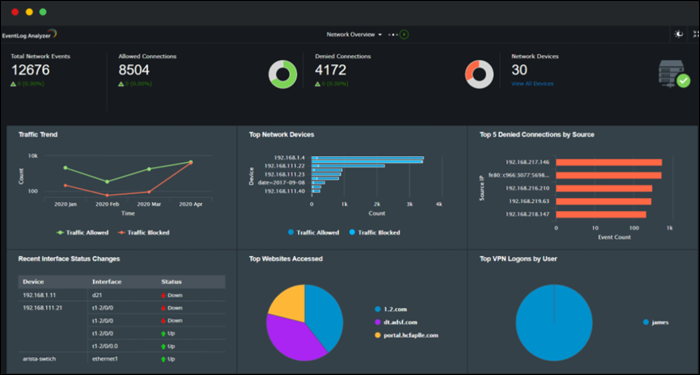
The ManageEngine EventLog Analyzer is a tool that allows the monitoring of up to five devices for free. It is compatible with Windows and Linux, while monitoring works for various devices running any operating system.
The EventLog Analyzer provides a GUI with a real-time log view and comparison, allowing for quick detection of suspicious messages and possible security threats. The functional dashboard enables users to create custom rules for alerts and notifications about security issues. There are also predefined rules for security event logs.
The auto-discovery feature finds devices on the network and facilitates log collection. Each message is labeled, making it clear which device it came from.
Compression and encryption of archived logs restrict data access to users without administrator privileges.
8. Icinga
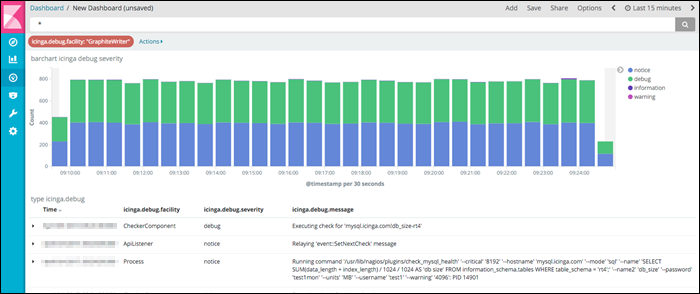
Icinga is an open-source tool that monitors and reports on device health. This syslog server accepts various modifications that enable it to fit any organization’s network monitoring needs.
The syslog tool collects, stores, and organizes data in a time-series database, showing earlier and current syslog data. It instantly notifies the user about any suspicious data, which helps prevent downtime and allows monitoring based on events.
Icinga’s web interface provides charts and graphs depicting device health and optimizing troubleshooting and debugging. Its integration with other devices facilitates real-time data collection, storage, and visualization of log metrics.
9. GrayLog
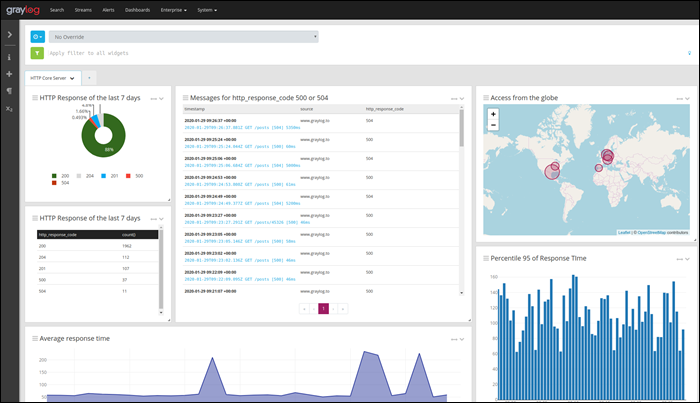
GrayLog is an open-source syslog server for Linux. The tool is free for 5 GB of data per day, making it an excellent choice for small networks, but it isn’t suitable for large organizations.
The server includes a query and search function with lots of filters that enable users to find a specific record quickly. The program interface consists of a fully customizable web GUI with graphs, charts, and changeable basic components for creating a custom day-to-day monitoring environment.
The server has prominent security features with automatic email notifications about failed logins, device faults, or security threats. With in-built automatic IP blocking, GrayLog can prevent an attack as soon as it recognizes one.
The app also offers fault tolerance features, audit logs, and role-based access control, further increasing security.
10. Windows Syslog Server
WinSyslog is a syslog server designed for Microsoft Windows. It supports syslog monitoring via UDP or TCP and it is free for displaying 60 messages at a time, with free troubleshooting support. Paid versions unlock additional features, provide greater security and unlimited device support.
WinSyslog is reliable, highly scalable, and collects syslog messages from any device compatible with the syslog protocol. It maintains device health using the Active Status Monitor feature, which pings the selected device and warns the admin if there is no response.
The server creates a daily log containing the received syslog messages, with customizable size and storage options. Store the file in a database or write it to the event log of Windows NT, 2000, or XP systems.
The program also features an automatic email notification in case of a security issue.
Paid Syslog Servers
The following is a list of the best paid syslog servers:
1. Nagios Log Server
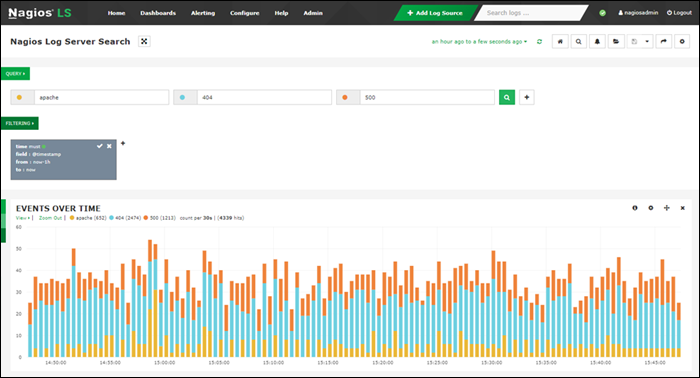
Nagios is a scalable syslog server that helps monitor systems, networks, and infrastructure. While it does offer a free plan, it is only 500 MB/day, making it unsuitable for medium and large businesses.
Other pricing plans are:
- Single Instance. For $1,995, it covers only one installation, which excludes failover. With this purchase, the data plan is unlimited.
- Two Instances. Costing $4,995, it covers two separate installations, which allow for redundant data with automatic failover.
- Four Instances. Costing $6,995, it allows four separate installations, further increasing redundancy and speeds.
- Ten Instances. At $14,995, it allows for ten installations with maximum redundancy and query speeds.
The server can receive logs from a wide variety of operating systems and devices, including Windows, Linux, mail servers, Web and application servers, SQL servers, etc. It is customizable, with configurable thresholds, email notifications, script execution, or alert forwarding.
The dashboard provides an overview of all logs over time, with customizable filters that include the timestamp, ID, host, message, severity, program, etc. The tool generates reports which are also customizable and that automatically update in real-time.
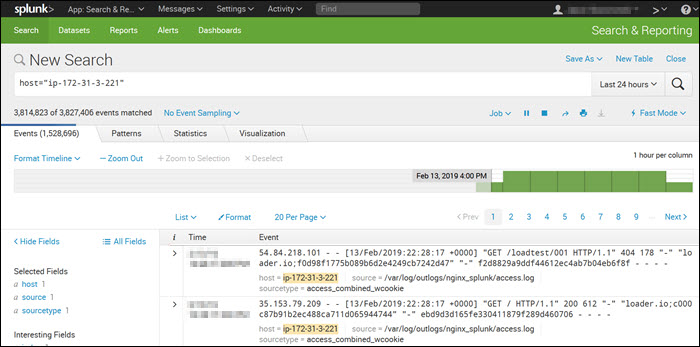
2. Splunkbase
Splunk is a syslog server used for monitoring, querying, analyzing, and visualizing log data in real-time. It is a paid tool with a 60-day free trial that includes syslog features. The server is compatible with Linux and macOS.
Splunk costs $1,150 per GB of data for a yearly 15 GB license, including maintenance.
Splunk features an intuitive and user-friendly UI with real-time statistics and a customizable dashboard.
It includes powerful search functionalities and filters that narrow every search down to the messages the user needs, such as error messages or device-specific messages. Splunk allows users to perform Boolean, quoted string, and wildcard searches in real-time, time range, or transaction level.
3. Progress WhatsUp Gold Log Management
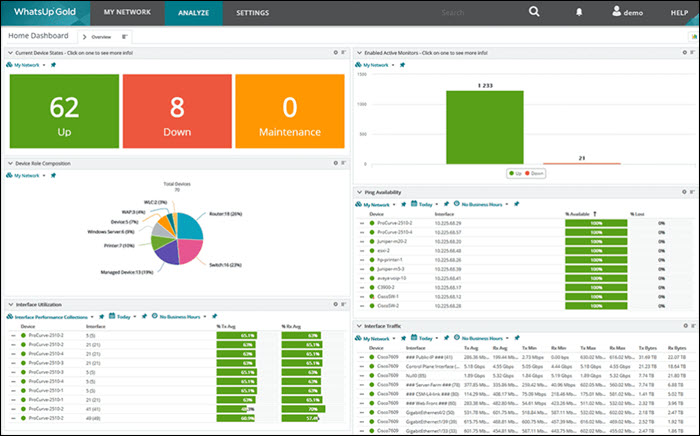
Progress WhatsUp Gold (formerly IPSwitch) is a paid syslog server that comes with a free 14-day trial. The syslog management tool is an add-on to the WhatsUp Gold monitoring tool for Windows Server, and it also receives Windows Events messages.
The price plans differ for a subscription and a perpetual license. For example, the pricing plans for a 1-year license include:
- 5 Servers — $1,325
- 10 Servers — $2,300
- 25 Servers — $5,250
The logging tool receives the log and Windows event messages and files them together. If there are sudden out-of-band increases or decreases, the tool creates an alert and notifies the user.
The customizable drag & drop dashboard shows messages in real-time as they arrive. Color-coded icons and graphs improve the visibility of each message’s severity, allowing the team to react immediately.
WhatsUp’s interactive interface shows each device’s availability and performance, both on-premise and in the cloud.
4. Logstash
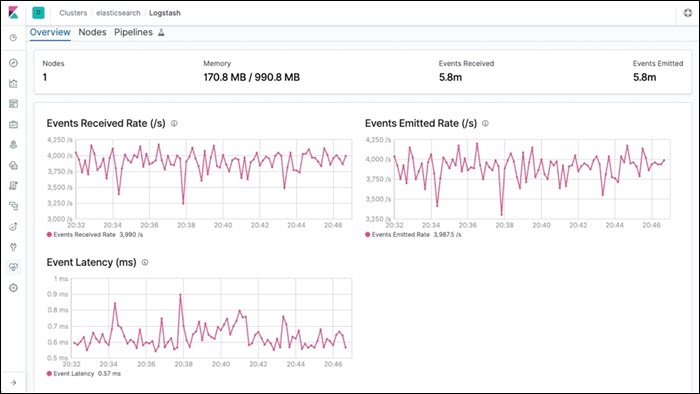
Logstash is part of a software suite called ELK stack that collects log messages. One part of the stack, Elasticsearch, sorts and filters the messages for analysis, while Kibana processes and displays the data. All technologies in the ELK stack are Linux-based, but work on macOS as well.
Logstash comes in four pricing plans:
- Standard. For $16 per month.
- Gold. Costs $19 per month.
- Platinum. Costs $22 per month.
- Enterprise. Contact the sales team for a quote.
Logstash listens on the network for messages coming from a wide variety of devices, but also supports collecting data from cloud services and applications. It collects logs via TCP or UDP, and it also supports TLS-encrypted messages.
Logstash can read messages from a file or database, get messages from mail servers, IRC or RSS feeds, and pick up SNMP messages. The filters allow users to find specific messages and quickly resolve any issues.
The front-end part of the ELK stack, Kibana, works well for any syslog server.
5. Loggly
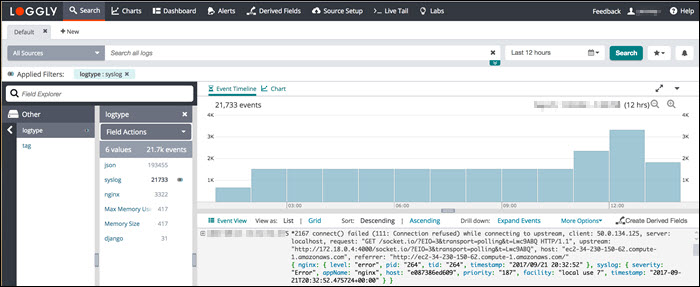
Loggly is a cloud-based syslog consolidator and analyzer. It doesn’t require software installations on-premises but requires setting up automated file transfer procedures that upload the logs to the Loggly server.
The utility comes in four pricing plans:
- Lite. Free, includes 200 MB/day, and retains data for seven days.
- Standard. Starting at $79/month, it limits data to 1 GB/day and retains data for 15 days.
- Pro. Starting at $159/month, data volume is up to 100GB/day, and retains data for up to 30 days.
- Enterprise. With a starting price of $279/month, it includes a custom data volume and retains the log data for up to 90 days.
Loggly standardizes and stores syslog messages from many sources, allowing users to access the data uniformly. Once the data is stored, it is accessible via the log analysis tools in the online service.
Loggly includes storage space with the software purchase, but since it stores data remotely and offsite, it is good to back up the log files on another site to improve system security. Data retention depends on the purchased package.
6. Site24x7 Server Monitoring
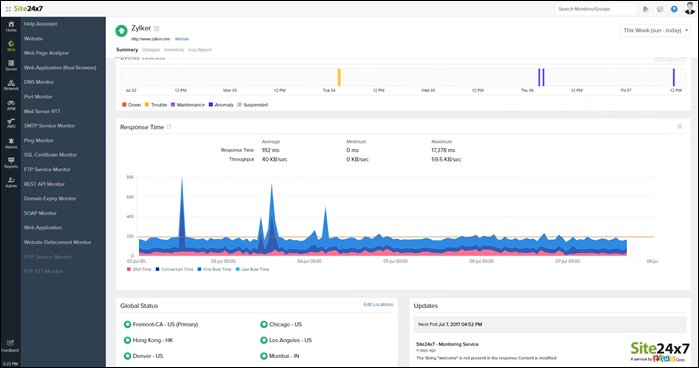
Site24x7 is a cloud-based monitoring and management software suite that includes the Log Manager. The Site 24×7 Infrastructure utilities offer a 30-day free trial. A monthly subscription comes with a 500 MB log processing allowance costing $9 with the following possible upgrades:
- 10 GB. Costs $10 per month.
- 100 GB. Costs $95 per month.
- 1 TB. Costs $900 per month.
Although the system is cloud-based, a Site24x7 agent must be installed on the monitored system for the Log Manager to work. The agent is compatible with Linux and Windows server.
When receiving syslog messages, the server standardizes them and files the messages in the same format. Message standardization allows users to analyze messages from different sources together.
The dashboard includes many data analysis options within the log file viewer tool, including log querying, sorting, filtering, and grouping messages.
How to Choose a Syslog Server?
There are several factors to consider when choosing a syslog server:
- Business Size. A paid syslog server is probably a better choice for a large enterprise due to the data volume and device number restrictions of free servers. On the other hand, a free syslog tool can provide the necessary functionalities for small businesses with low device numbers and a small data volume.
- Support. If your organization doesn’t have skilled IT staff or if you need help setting up the software, a paid tool usually includes support and troubleshooting assistance. Some free utilities also have basic documentation, but don’t offer round-the-clock support and troubleshooting.
- Storage. A better choice for businesses with their own storage capacities are syslog servers sold as a software suite, which are installed on-premises. An on-premises option improves security and lowers the chance of a data breach. On the other hand, some syslog tools are sold as a cloud-based syslog service, which is a good choice if you don’t have your own storage.
Conclusion
This article listed the 16 best syslog servers, their benefits, features, capabilities, and pricing. You should now be able to decide which syslog server is the most suitable for your organization.
Отправка логов Windows Server на syslog является важным шагом для обеспечения безопасности и мониторинга сервера. Система syslog позволяет собирать и анализировать логи с различных источников, включая Windows Server, для обнаружения проблем и атак. Это обеспечивает эффективный и централизованный способ управления логами сервисов и приложений.
В этом подробном руководстве вы узнаете, как настроить отправку логов Windows Server на syslog. Мы рассмотрим основные шаги, необходимые для установки и конфигурации syslog-сервера, а также настройки Windows Server для отправки логов. Вы сможете выбрать между локальной и удаленной отправкой логов, в зависимости от ваших потребностей.
Кроме того, мы рассмотрим различные параметры конфигурации syslog-сервера, которые позволят вам настроить уровни журналирования и фильтрацию логов, чтобы получать только необходимую информацию. Вы узнаете, как создавать правила фильтрации логов и настраивать email-уведомления для оповещения о критических событиях.
Настройка отправки логов Windows Server на syslog является мощным инструментом для обеспечения безопасности и мониторинга сервера. Следуя этому подробному руководству, вы сможете настроить syslog-сервер и Windows Server таким образом, чтобы получить полный контроль над журналированием и анализом событий, происходящих на вашем сервере.
Содержание
- Настройка отправки логов Windows Server на syslog
- Установка и настройка сервера syslog на Windows
- Настройка Windows Server для отправки логов на syslog
- Настройка фильтрации и ретрансляции логов на сервере syslog
- Проверка отправки логов с Windows Server на сервер syslog
- Настройка мониторинга логов на сервере syslog
- Применение отправки логов Windows Server на syslog в практических сценариях
Настройка отправки логов Windows Server на syslog
В данном руководстве мы рассмотрим шаги по настройке отправки логов Windows Server на syslog сервер.
1. Шаг: Установка syslog сервера.
Первым шагом необходимо установить и настроить syslog сервер на целевой машине. Вы можете выбрать один из доступных серверов, таких как Syslog-ng, rsyslog или Kiwi Syslog Server.
2. Шаг: Настройка Windows Server для отправки логов.
Далее необходимо настроить Windows Server для отправки логов на указанный syslog сервер. Для этого выполните следующие шаги:
— Откройте «Диспетчер событий» на сервере.
— Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на «Журналы Windows», затем выберите «Подписчик журнала Windows».
— В появившемся окне нажмите кнопку «Добавить».
— Укажите IP-адрес или DNS-имя вашего syslog сервера и выберите протокол syslog (обычно UDP).
— Нажмите «Далее» и установите необходимые фильтры для определения журналов, которые вы хотите отправить на syslog сервер.
— Щелкните «Далее» и укажите имя подписчика журнала.
— Завершите конфигурацию, нажав кнопку «Финиш».
3. Шаг: Проверка отправки логов.
После настройки Windows Server и syslog сервера, можно проверить, что логи успешно отправляются. Для этого выполните следующие действия:
— Откройте syslog сервер и убедитесь, что все журналы, которые вы хотите отправить, появляются на сервере.
— Проверьте соединение между Windows Server и syslog сервером, убедившись, что нет блокировок на уровне сети или брандмауэра на сервере.
— Убедитесь, что все настроенные фильтры правильно отображаются на syslog сервере и соответствуют вашим ожиданиям.
— Проверьте, что записи логов отображаются в соответствии с требуемым форматом.
В заключение, настройка отправки логов Windows Server на syslog сервер может быть выполнена с помощью указанных выше шагов. Проверьте настройки и убедитесь, что логи успешно отправляются на заданный сервер.
Установка и настройка сервера syslog на Windows
В этом разделе мы рассмотрим процесс установки и настройки сервера syslog на операционной системе Windows.
Шаг 1: Скачайте установочный пакет сервера syslog с официального сайта или из другого доверенного источника.
Шаг 2: Запустите установщик сервера syslog и следуйте инструкциям мастера установки.
Шаг 3: Во время установки выберите путь для установки сервера syslog на вашем компьютере. Рекомендуется выбрать стандартный путь, предложенный установщиком.
Шаг 4: После завершения установки, запустите сервер syslog. Обычно это делается путем запуска соответствующего ярлыка на рабочем столе или из меню «Пуск».
Шаг 5: Проверьте, что сервер syslog успешно запустился, открыв веб-интерфейс сервера в веб-браузере. Обычно адрес веб-интерфейса указан в инструкции к установке или в окне, которое открылось после запуска сервера syslog.
Шаг 6: В интерфейсе сервера syslog найдите раздел настроек и перейдите в него. Там вы найдете список доступных опций настройки сервера. Рекомендуется просмотреть каждую опцию и установить значения в соответствии с требованиями вашего окружения.
Шаг 7: Одной из наиболее важных настроек является настройка прослушиваемого порта. Убедитесь, что прослушиваемый порт сервера syslog соответствует порту, на который будут направляться логи с Windows Server.
Шаг 8: Если ваш сервер syslog предоставляет возможность аутентификации пользователей, настройте соответствующие параметры аутентификации. В этом случае вам понадобится создать учетные записи пользователей и предоставить им права доступа.
Шаг 9: После завершения настройки сервера syslog, сохраните изменения и перезапустите сервер для применения новых настроек.
Теперь ваш сервер syslog полностью настроен и готов принимать логи с Windows Server.
Настройка Windows Server для отправки логов на syslog
Системные логи Windows Server могут предоставить полезную информацию о состоянии сервера, об ошибках и событиях, происходящих в системе. Чтобы легче анализировать и управлять этой информацией, можно настроить сервер для отправки логов на syslog сервер.
Syslog — это стандартный протокол передачи лог-файлов, который широко используется в системах Unix и Linux. Если вы хотите, чтобы логи вашего Windows Server также отправлялись на syslog сервер, вам понадобится установить и настроить соответствующее программное обеспечение.
| Шаг | Описание |
|---|---|
| 1 | Установите на сервер программу для отправки логов на syslog сервер. Популярным выбором является программное обеспечение EventLog Analyzer. |
| 2 | Настройте программу, указав адрес и порт syslog сервера, на который вы хотите отправлять логи. |
| 3 | Включите функцию логирования на сервере Windows. Для этого откройте «Службы Windows» и найдите «Служба журнала событий Windows». |
| 4 | Откройте «Свойства» службы и перейдите на вкладку «Логирование». Переключите опцию «Передавать журнал событий через TCP/IP» и введите адрес и порт syslog сервера. |
| 5 | Подтвердите изменения и перезапустите службу журнала событий Windows. |
После завершения этих шагов, Windows Server будет отправлять свои логи на указанный syslog сервер. Вы можете использовать программное обеспечение для анализа и отображения этих логов, чтобы получить более удобную и наглядную информацию о работе вашего сервера.
Настройка фильтрации и ретрансляции логов на сервере syslog
После того, как вы успешно настроили отправку логов с Windows Server на сервер syslog, вы можете также настроить фильтрацию и ретрансляцию логов на самом сервере syslog. Это поможет вам создать более четкую структуру ваших логов и отправить их на нужные адреса.
Следуйте этим шагам, чтобы настроить фильтрацию и ретрансляцию логов:
- Откройте файл конфигурации сервера syslog. Обычно он находится по пути
/etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf. - Найдите секцию, которая начинается с
source s_networkи заканчивается передdestination d_default. - Чтобы настроить фильтрацию для конкретного типа логов, добавьте следующий код внутри этой секции:
- Чтобы настроить ретрансляцию для фильтрованных логов, добавьте следующий код после секции фильтров:
- Сохраните файл конфигурации и перезапустите сервер syslog, чтобы внести вступившие изменения в силу:
filter f_filtername {
facility(type);
}
Замените filtername на имя фильтра, а type на тип логов, которые вы хотите фильтровать. Например, если вы хотите фильтровать только события от системы, код может выглядеть так:
filter f_system {
facility(local0);
}
destination d_destinationname {
tcp("адрес_получателя" порт);
}
log {
source(s_network);
filter(f_filtername);
destination(d_destinationname);
}
Замените destinationname на имя вашего пункта назначения (например, d_syslog) и адрес_получателя и порт на адрес и порт сервера, куда вы хотите отправить логи.
sudo systemctl restart syslog-ng
После выполнения этих шагов ваш сервер syslog будет фильтровать и ретранслировать логи согласно вашей конфигурации. Вы можете повторить вышеприведенные шаги для каждого типа логов, чтобы создать отдельные фильтры и пункты назначения для них.
Проверка отправки логов с Windows Server на сервер syslog
После настройки отправки логов с Windows Server на сервер syslog необходимо проверить, что логи действительно отправляются и достигают целевого сервера. Для этого можно воспользоваться одним из следующих методов:
1. Проверка на сервере syslog: на сервере syslog можно проверить наличие отправленных логов при помощи соответствующих инструментов. В зависимости от используемого сервера syslog, можно использовать специальную команду или графический интерфейс для просмотра логов.
2. Проверка на Windows Server: на самом Windows Server можно использовать инструмент Event Viewer для просмотра отправленных логов. Для этого необходимо открыть Event Viewer и перейти к разделу Службы и приложения > Службы событий > Log-Summary > Microsoft. Здесь можно найти логи, которые были отправлены с помощью syslog.
3. Проверка на целевом сервере: также можно проверить наличие отправленных логов на целевом сервере, на который была настроена отправка. Для этого нужно перейти на целевой сервер и проверить наличие логов в соответствующем приложении или инструменте, который используется для просмотра логов.
Если все проверки указывают на успех, это означает, что логи Windows Server успешно отправляются на сервер syslog и могут быть использованы для анализа и мониторинга системы.
Настройка мониторинга логов на сервере syslog
Для начала настройки мониторинга логов на сервере syslog вам потребуется установить и настроить сервер syslog на вашем сервере. После установки, вам необходимо настроить Windows Server для отправки своих логов на сервер syslog.
Для настройки Windows Server для отправки логов на сервер syslog вы можете использовать дополнительное программное обеспечение, такое как NxLog или Snare, которые предоставляют гибкие инструменты для настройки и отправки логов на сервер syslog.
После установки и настройки соответствующего программного обеспечения на Windows Server, вам нужно будет указать IP-адрес и порт сервера syslog, на котором будет прослушиваться Windows Server. Эти настройки обычно указываются в конфигурационных файлах программы или через интерфейс управления.
Когда настройка Windows Server и сервера syslog выполнена, Windows Server начнет отправлять свои логи на сервер syslog. Вы сможете отслеживать и анализировать все события, происходящие на Windows Server, в реальном времени или настроить уведомления о подозрительной активности или критических событиях.
Мониторинг логов на сервере syslog позволяет вам быстро реагировать на проблемы безопасности и проблемы с производительностью вашего сервера Windows. Вы сможете анализировать логи, идентифицировать потенциальные уязвимости и предотвращать возможные атаки.
Кроме того, мониторинг логов на сервере syslog помогает собирать данные для аудита и соответствия нормам безопасности. Вы сможете отслеживать действия пользователей, обеспечивать соответствие политик безопасности и быстро реагировать на любые отклонения от установленных правил.
В целом, настройка мониторинга логов на сервере syslog является важной частью сетевой безопасности и управления сервером Windows. Она позволяет вам контролировать и анализировать все события, происходящие на вашем сервере, и предотвращать возможные угрозы безопасности и проблемы производительности.
Применение отправки логов Windows Server на syslog в практических сценариях
Отправка логов Windows Server на syslog предоставляет возможность централизованного хранения и анализа логов с различных серверов в сети. Это позволяет эффективно контролировать и отслеживать события, происходящие на серверах, а также принимать оперативные меры для решения проблем и обеспечения безопасности.
Одним из практических сценариев использования отправки логов Windows Server на syslog является мониторинг и анализ безопасности. С помощью syslog можно получать информацию о неавторизованных попытках доступа, внутренних угрозах или других потенциальных уязвимостях, что позволяет быстро реагировать на подобные инциденты и принимать меры для защиты серверов.
| Практический сценарий | Описание |
|---|---|
| Мониторинг доступа к файлам | Отправка логов Windows Server на syslog позволяет отслеживать действия пользователей, связанные с доступом к файлам и папкам. Это позволяет контролировать, кто, когда и какие файлы открывает, изменяет или удаляет, и в случае необходимости принимать соответствующие меры. |
| Регистрация событий безопасности | События безопасности, такие как неудачные попытки входа, изменения настроек безопасности или обнаружение вредоносного кода, могут быть отправлены на syslog для дальнейшего анализа. Это позволяет выявлять потенциальные угрозы и принимать меры по их нейтрализации. |
| Отслеживание событий сетевого трафика | Отправка логов событий сетевого трафика на syslog позволяет мониторить активность сети, обнаруживать аномальную активность или необычный трафик. Это помогает снизить риск кибератак и своевременно обнаруживать атаки на сервера. |
Применение отправки логов Windows Server на syslog может быть полезным в различных сценариях, в зависимости от потребностей и требований организации. Важно настроить серверы и syslog соответствующим образом, чтобы гарантировать корректную и безопасную передачу логов.
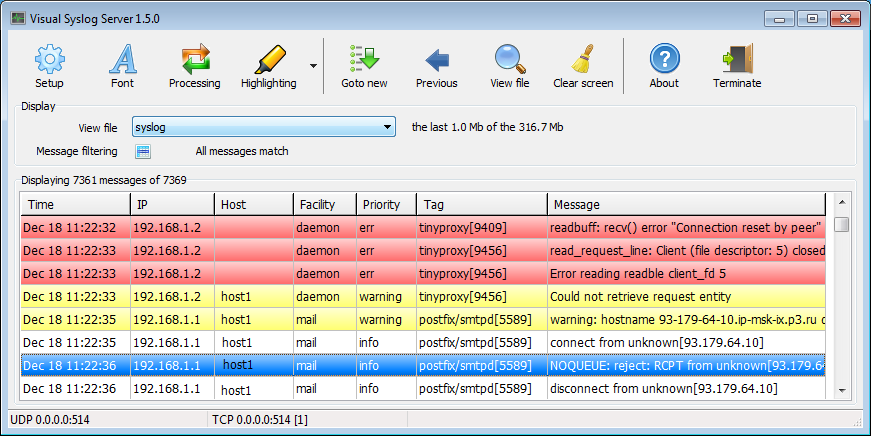
Visual Syslog Server for Windows is a free open source program to receive and view syslog messages.
Useful when setting up routers and systems based on Unix/Linux.
Visual Syslog Server for Windows has a live messages view: switches to a new received message. Helpful color highlighting.
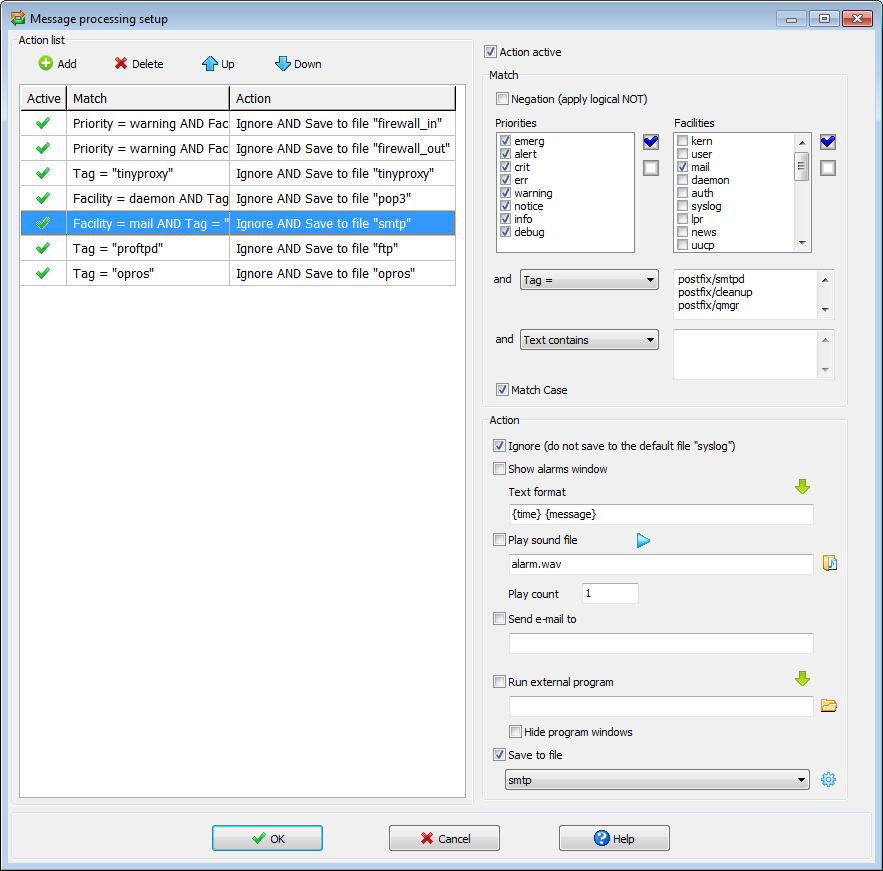
Useful message filtering. Customizable notification and actions.
Read in Russian / Читать на русском языке
Features
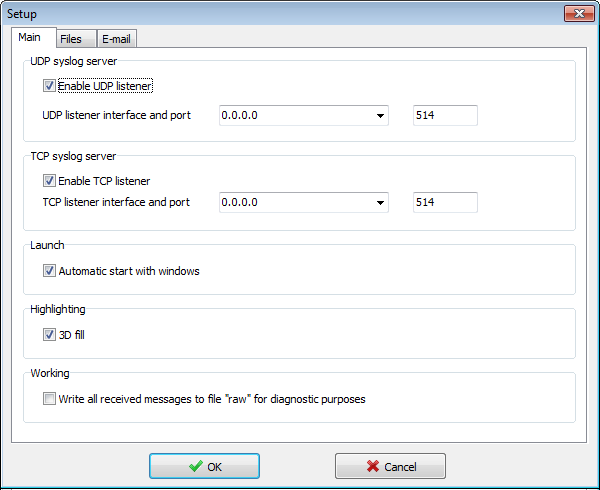
- Receive messages from various devices via UDP or TCP protocol (compliant to RFC 3164)
- Syslog messages are displayed in real-time
- Stores messages in files on disk
- Log file rotation by size or by date
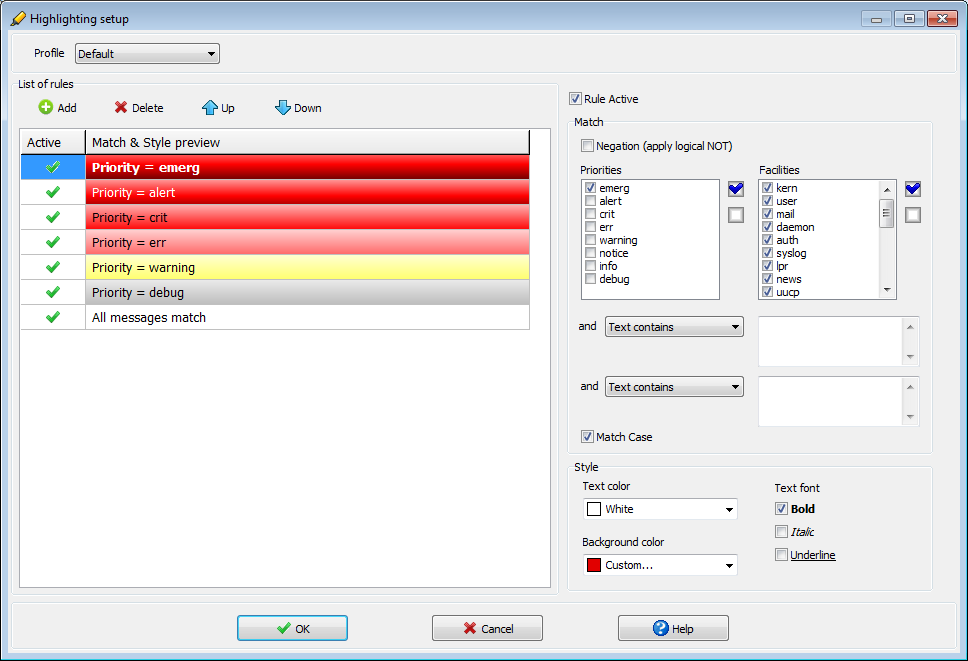
- Filter displayed syslog messages based on facility, priority, host, source address, tag or message contents
- Customizable color highlighting with nice 3D design
- Generating notifications depending on the content of the received message:
- Show alarms windows
- Play sound file
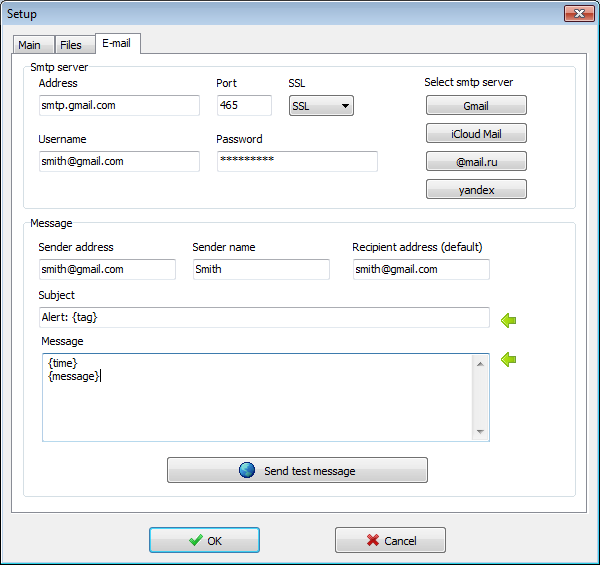
- Send e-mail notifications via smtp server
- Customizable notices format
- Performs actions depending on the content of the received message:
- Run external program with params
- Saving message to the specified file
- Support for sending mail via SMTP server with authentication SSL / TLS
(Support Gmail and iCloud mail smtp servers. You can use the push notifications on your mobile device for instant delivery of alarms.) - Lightweight and very fast
- Run as a Windows application
- Minimize to system tray
- Support Windows XP/Vista/7/8/8.1, Windows Server 2003/2008/2012
- Easy to install: adjustment is not required
- Import historical syslog messages after the start of the program
- View syslog messages from the file
- The ability to receive messages encoded in UTF8
- Free open source software, licensed under the GPL V2
Download
Visual Syslog Server for Windows download installer:
Last developper snapshot 1.6.2
Latest stable release 1.6.2
Installation
After installation Visual Syslog Server for Windows works immediately: adjustment is not required.
Waiting for messages on the UDP and TCP port 514 (default setting).
Visual Syslog Server is an Windows application (installing a system service is not required).
Installer adds firewall exception.
Building from sources
To build Windows Syslog Server from sources use CodeGear RAD Studio C++Builder 2007
Main project file visualsyslog.cbproj
Required components: Indy.Sockets (VCL) version 10
To build the installer, use Inno Setup Compiler 5.5.1(a)
Installer project file visualsyslog.iss
Support
Your questions and suggestions please send to
Future plans
- Message statistics
If you need these or other functions let me know.
Screenshots
Color highlighting setup
Message processing setup
Main setup
Files rotation setup
Smtp server setup to send e-mail messages