- anvldko
- Ветеран
- Сообщения: 947
- Зарегистрирован: 30 июн 2019, 01:30
- Откуда: Росси́йская Федера́ция
- Контактная информация:
Re: Huawei E3372 (МТС 827F/829F, МегаФон M150-2, Билайн E3372/E3370, TELE2 E3372h-153)
С включением ipv6 все ваши устройства в локальной сети становятся под угрозой, так как по спецификации в ipv6 несуществует файрволов. Каждому устройству в сети выдаётся уникальный белый ipv6 адрес. И если в смартфоне нет нормального фаервола, то практически любой им может поживится. Как и писалось выше оператор выдаёт целый пул ipv6 адресов для каждого вашего устройства. И если он видит что вы используете больше чем 1 ipv6 адрес, то считается что вы раздаёте интернет не зависимо зафиксированы хопы ттл или не зафиксированы. При фиксайии хопов будет работать ipv6 только в случае если между модемом и смартфонами существует посредник (другой роутер) который выдаёт виртуальные ipv6 адреса всем вашим устройствам, но по факту используется только один. Так же при использовании ipv6 не работает блокировщик рекламы, посему можно сделать вывод что ipv6 зло и обычному юзеру не нужно.
- anvldko
- Ветеран
- Сообщения: 947
- Зарегистрирован: 30 июн 2019, 01:30
- Откуда: Росси́йская Федера́ция
- Контактная информация:
Re: Huawei E3372 (МТС 827F/829F, МегаФон M150-2, Билайн E3372/E3370, TELE2 E3372h-153)
Сообщение: # 987Сообщение anvldko
Max77 писал(а): ↑16 фев 2020, 20:07
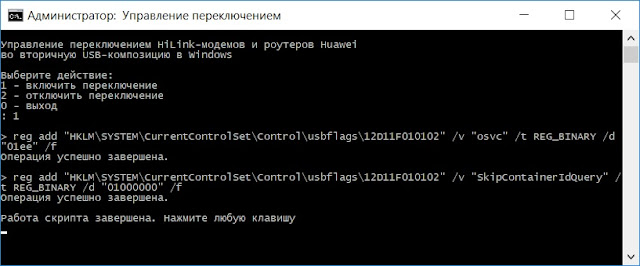
Что за скрипт лежит на виртуальном CD-ROMе после перепрошивки, который пишет какие-то ключи в реестр?
Переключение во вторичную композицию, альтернатива оригинальному драйверу переключалки , разработки rust3028 — мобилсервер, который раньше грузил систему, особенно на слабых компах под 50 и выше.
Без этих ключиков сетевая карта ни когда не появится. То-есть при их наличии , модем может работать в любом компе без дров.
Даже для перепрошивки файлом ехе дрова не нужны, так как они входят уже в файл прошивки.
Дрова нужны только для иглы.
- Max77
- Местный
- Сообщения: 9
- Зарегистрирован: 16 фев 2020, 13:29
Один и тот же модем может присутствовать на рынке как в HiLink, так и в Stick вариантах (например МТС 829F, он же Huawei E3372H поставляется с HiLink прошивкой, а точно такой же модем, который можно приобрести у оператора Tele2 — уже HiLink).
Итак, если ваш модем имеет Stick прошивку, то после того как вы его установите в ПК и установите драйвера и ПО со встроенного CDROM раздела, то в диспетчере устройств он будет определяться у вас как, собственно, модем (в разделе Телефоны и модемы), а также несколько COM портов. Плюс к этому, для того чтобы выйти в интернет, вам придется запускать специальное ПО под названием дашборд (dashboard):
На двух фото выше изображены дашборды от МТС — Коннект Менеджер и стандартный Huawei’евский дашборд от Mobile Partner. Все это справедливо если наш модем имеет stick-прошивку, т.е. здесь мы имеем дело с ПО для выхода в интернет, а само устройство у нас определяется как модем и несколько COM-портов.
Совершенно по-другому обстоят дела если мы имеем HiLink прошивку. В этом случае после установки ПО с CDROM раздела модем у нас определяется как виртуальная сетевая карта (RNDIS адаптер) и никакого ПО для соединения с интернет нет. Модем устанавливает соединение с интернет автоматически, а для управления настройками модема есть web-интерфейс. Т.е. фактически в этом случае модем представляет собой ethernet-роутер, имеющий собственный IP адрес в локальной сети (например, 192.168.8.1). Ваш ПК получает на интерфейс RNDIS адаптера (виртуальной сетевой карты) IP из подсети модема — 192.168.8.0/24, и выходит через шлюз 192.168.8.1 в интернет. Само соединение, естественно устанавливается в модеме, просто в данном случае он дополнительно выполняет функции роутера, в котором поднимается NAT и т.д.
(отсюда)
STICK
С этой прошивкой устройство ведет себя как классический USB-модем: имеется командный AT-порт, через который можно установить соединение посредством PPP-протокола. Именно так работают практически все 3G-модемы предыдущих поколений. При этом скорость ограничена — не более 20-30 Mbit на прием. Кроме PPP-режима, имеется режим NDIS. При этом модем эмулирует сетевой интерфейс, через который и передаются данные, а через AT-порт идут только управляющие команды. В этом режиме скорость не ограничена. Основная особенность stick-режима — установление соединения и поддержка работы канала производится средствами ОС компьютера, к которому подключен модем. При этом компьютер получает IP-адрес непосредственно у провайдера сотовой связи через запрос DHCP, а модем работает как сетевой мост, передавая пакеты от компьютера в сотовую сеть и обратно, никак их не изменяя.
Начальная USB-композиция stick-модема — это виртуальный CD-ROM и картридер microSD. Для того, чтобы появились модемные порты, надо сделать переключение композиции. Под windows этим занимается операторский софт, имеющийся на виртуальном CD, или фирменная программа от huawei — Mobile Partner. Под linux переключение делает программа usb-modeswitch. Имеется возможность запретить перелючение композиций. Это делается такой командой:
AT^SETPORT=»FF;10,12,16″
При этом модем сразу после включения будет выглядеть как 2 AT-порта и сетевая карта NDIS. CD и microSD будут исключены из конфигурации. Такой режим крайне удобен для использования модема в различных домашних роутерах. Вернуть обратно композицию с переключением можно командой:
AT^SETPORT=»A1,A2;10,12,16,A1,A2″
Номера версий stick-прошивки всегда начинаются на 21 — например, 21.285.01.02.143. С таким типом прошивки поставляются модемы от МТС и Мегафона.
HILINK
С прошивкой HILINK модем работает в режиме роутера, и представляется компьютеру в виде сетевого интерфейса (usb-ethernet-rndis). Компьютер получает с этого интерфейса сетевые настройки через DHCP, и далее ходит через него в интернет, как через обычную проводную локальную сеть. Всю заботу об установлении соединения и поддержании канала модем берет на себя, компьютер даже не замечает, что доступ в интернет осуществляется через сототвую сеть. В этом режиме модем имеет свой собственный локальный IP-адрес (обычно 192.168.8.1), видимый со стороны компьютера как шлюз по умолчанию (default route), а также внешний IP-адрес, получаемый из сотовой сети. Между сетью сотового провайдера и локальной сетью (модем-компьютер) осуществляется маршрутизация с использованием механизма трансляции адресов (NAT). Предусмотрен проброс портов из внешней сети (port forwarding и DMZ).
Настройка модема в этом режиме производится через WEB-интерфейс, имеющийся в модеме, и доступный через его локальный IP-адрес. Также через WEB-интерфейс доступна информация о состоянии модема и сигнале сотовой сети, управление подключением, прием-передача SMS-сообщений и USSD-команд, SIM-меню и многое другое. Это особенно ценно для пользователей Linux, а также для тех, у кого модем подключен не к компьютеру, а к домашнему роутеру. Настройка модема через AT-команды, как в stick-прошивках, в штатном режиме hilink-прошивок не производится, хотя и возможна в специальном отладочном режиме DebugMode.
Начальная USB-композиция HILINK-модема в точности такая же, как и у stick — виртуальный CD-ROM и картридер microSD. Переключение композиций под windows производится небольшой программой mbbservice, запускаемой со встроенного CD. Под linux это делает программа usb-modeswitch. Штатно разработчиками модема не предусмотрен режим без переключения композиций. Тем не менее, путем некоторой модификации прошивки такой режим сделать возможно. При этом теряется встроенный картридер SD, однако появляется возможность использовать модем с любым роутером, поддерживающим сетевые карты usb-rndis.
Номера версий hilink-прошивки всегда начинаются на 22 — например, 22.286.03.00.00. С таким типом прошивки поставляется модем от Билайна.
Прошивки HILINK состоят из двух частей — сама прошивка, и WebUI (вебинтерфейс). Первой прошивается основная прошивка, потом WebUI.
Mikrotik
Отличаться также будет и настройка в микротике: для режима Stick появится ppp-out* устройство, а для HiLink — lte* в отдельном разделе LTE.
Хотя есть мануалы, где сказано, что можно переводить модемы в stick и hilink без перепрошивки:
AT^U2DIAG=0 — в stick
AT^U2DIAG=119 — в hilink
Ну и вероятно полезная комбинация:
AT^SETPORT=»FF;10,12,16,A2″ — режим «без переключения». Т.е. в данном режиме первичная композиция модема (initial mode) отключена, т.е. задана как FF — Dummy (отсутствие переключения), а вторичная композиция (normal mode) задана как 10,12,16,A2 — т.е. 10 — модем, 12 — PC UI, 16 — RNDIS (у нас его нет), A2 — TF Card Reader.
Experienced
[offline]
Group: Friendssavagemessiahzine.com
Messages 694
Check in: 05.12.06
TurboPad 910
Reputation:
Huawei E3372h / E3372s (MTS 827F / 829F / 829FT, Megaphone M150-2, Beeline E3370)— Discussion
Attention!
The most popular questions with answers and off-topic (which will be deleted),refrain from themso as not to shower you with tomatoes!
The answers to these questions are in the topic header or in other profile topics!
- How to unlock (unlock) modem
- How to fix TTL
- How to change IMEI
- How to change the MAC address
- How to bypass the torrent
- How to make friends with the router
- How the operator distinguishes the phone from the modem
- Any question about the operators, including the tariffs Yota, Unlimited, #CanAll, All for …, MegaEz-Limit, Unlimited Black
Rules of conduct in the subject
- We read this item carefully, 90% of messages are deleted due to non-compliance with this item!First check if there is an answer to your question in the FAQ. Use the search on the topic, perhaps a similar question already understood. If you did not find the answer to your question,necessarilyattach all the information that is listed in the spoiler «Necessary information for help«, and write as fully as possible so that you do not have to clarify the details.
If you are unable to unlock or flash the modem, please read all the information in the header (the first message of the topic you are reading now), try different USB cables, operating systems and computers, and only after that if you have failed ask a question.
Remember — for all actions with your modem, you are responsible, and not someone else. Expect help in the subject, but rely only on yourself.Necessary information for help
You need a screenshot, or text in the log code tag fromDC-Unlocker. An important requirement — the serial number, firmware version and the rest not to paint over!
If the DC-Unlocker modem does not see, then you can only take a screenshot of the Device Manager.
You also need a screenshot of the Device Manager with the expanded:
- DVD and CD drives
- Disk devices
- USB controllers
- Ports (COM and LPT)
- Network adapters
For Linux users
We need results in the code tag of the following AT commands:
- ATI
- AT ^ SN
- AT ^ FHVER
- AT ^ DLOADINFO?
- AT ^ HWVER
An important requirement — IMEI, serial number, firmware version and the rest do not paint!
And we also need the results of the lsusb and ifconfig command (not ipconfig!) In the code tag.
- Please do not write messages in the style of “I’m not getting anything”, “I tried — it didn’t work”, “Throw me detailed instructions”.
Better in each message, clearly indicate what specific actions you performed, what result they received, with screenshots. - Questions about the modem with your router ask in the topic of your router. We do not know the features of your router, but they know the subject of the router. Old-timers are not millionaires, they do not have all the routers.
- Please remove the images under the spoiler. The image without a spoiler like a man without clothes — looks, to put it mildly, ugly. Anyway, unethical.
- Do not use the BMP format! Such messages will be 100% deleted.
- Write correctly!
- Be sure to read the spoiler. Important information! There really is important information, without knowing which, you can mimic the modem!
Important information!
All the manipulations with the firmware and configuration of the modem you do at your own peril and risk!
- Existstwo models of modemsE3372: E3372sand E3372h. They are built on different platforms, firmware from one will not fit the other. Model E3372hnewer and E3372salready out of production.
- There are two types of firmware:StickandHilink. With the Stick’s firmware, the modem will be seen as an AT-modem, to connect to the Internet you need to «dial». With HiLink firmware, the modem is represented by an Ethernet network card and does not require any configuration in the OS.
- For E3372h modems, the serial number starts atG4P, and at E3372s —L8f. More precisely, your modem candefine like this. You can not flash E3372h firmware from E3372s — get a brick. However, she herself will not go — will give an error. Is that under pressure …
- If you have E3372h and firmware on your modem from 2x.200.15.xx.xx to (not including!) 2x.317.xx.xx.xx, then send the command AT ^ SFM = 1 before the firmware, otherwise you will get error 19 ( Moreover, 2x.200.15.xx.xx and above can not be removed from the download mode, you will have to alter using the needle method or look for your firmware on the network and sew on it)
- If the modem has stopped seeing the network, or has become unknown or an ADB deviceit means the flash is broken. You can fix itlike this.
- The modem is not compatible with Kaspersky products!The muzzle is unavailable from it, disabling does not help,only delete! Before buying a modem, think about whether you are ready to abandon this product.
- The firmware flasher and boot loader (the one used for the needle) under macOS can be foundhere. There is no need to resort to virtualka, and it is dangerous. Also, balong_flash’em can remove the modem from boot mode (switch -r).
- Formodem works with HiLink firmware in Windows 10 Version 1709patch requiredKB4051963and update the driver through the device manager
- Change the MAC address is not possible
Beginner, if you don’t understand anything about computers and don’t know where to start, read HERE!
First you need to start by readingRules of the topic, especially the sub-spoiler «Useful info for help» — in order to know what information to provide in case of problems, to know how to ask a question, to know what you shouldn’t ask, etc.Without DC-Unlcoker log and device manager screen with expanded categories from that spoiler, messages will be deleted without warning!
Next, readImportant information- to learn about important nuances and how not to get to the elementary error.
Further, if you just need an unlock, then in this post there is a spoiler «Modem unlocking»(a little running ahead, I will say that most likely» just unlock «will not work, all current models come with strong protection, which is the easiest to defeat with firmware)
And if you need to flash / upgrade the modem, then in the Important Information there is a link to the instructions for the firmware in HiLink and Stick.
In case you need to flash the modem «under the phone» and «so that the operator does not burn the distribution», then there is a FAQdetailed instructionsI.
I would also like to note that there are no such concepts as “flash under mts”, “flash under the beeline”, etc. You will simply not be understood if you ask to flash under some kind of operator.
Also, I present to the attention of a small glossary with local slang and terms:
Glossary
Firmware— starts at 22 (HiLink) or 21 (Stick) and nothing else (for this model). Also, this can be understood not just as a version, but as a file stitched by you, since it is impossible to add modification identifiers to the version, therefore they are present only in the firmware file (For example: M_AT_05, M_01).
Dashboard— management program, or its firmware file. His version starts with 23 or whatever.
HiLink— this is router mode. The modem in this mode has a web interface, like a router (of course, Wi-Fi doesn’t have any growth at all: D), it’s very convenient when using a router, and in general you don’t need to install extra software.
Stick— this is a normal modem that connects through a control program (dashboard) or through the Windows Network Manager (which is built into Windows 7 and higher)
Modified firmware— firmware modified by the forum member. There may be many of them, so it is better to read the explanations for the identifiers that are in the post with these firmware.
Modification Identifiers— short letter designation built-in modifications.
Unlock— unlock modem to work on all SIM-cards.
Cleaning flush— an operation that almost completely clears the internal memory of the modem, clearing away the contrived damage (this modem has such a complex that over time it begins to think that all its internal memory is in error). The link to the installation is in this post, in the spoiler «Useful links ->Firmware / Recovery. «
Needle, pricking, etc.— recovery operation, at which the test point closes. This instruction is also in the FAQ, which was already mentioned above.
About modem
Photo modem
Insides
E3372h
Photo from Sou1t
E3372s
Photo from Sou1t
Specifications
Supported ranges:
GSM / EDGE / EVDO / LTE / FDD / TDD / UMTS
The speed of data reception modem up to 150 Mbps,
Data transfer rate — up to 50 Mbps
Supported frequencies
GSM / GPRS / EDGE 850/900/1800/1900
UMTS / DC-HSPA + / WCDMA 900/2100
LTE 800/900/1800/2100/2600 MHz
Additionally
MicroSD card support up to 32 GB
External antenna
The type of connector of the external antenna is CRC9, which, in the huawei terminology, is TS-5.
The modem has 2 antenna connectors (for MIMO antennas), a single antenna connects to the connector closest to USB
Operating Systems:
Support for Windows XP SP3, Windows Vista SP1 / SP2, Windows 7, Windows 8, Mac OS X 10.5, 10.6, 10.7, 10.8, Linux
Link to the product page on the manufacturer’s website
http: //consumer.huawei…s/tech-specs/e3372.htm
Types and features of modem firmware
For this modem, there are 2 fundamentally different types of firmware — STICK and HILINK. Firmware interchangeable, that is, in any modem you can flash any firmware. The following describes their features and provides links to the firmware files.
STICK
With this firmware, the device behaves like a classic USB modem: there is a command AT-port through which you can establish a connection using the PPP protocol. This is how almost all previous-generation 3G modems work. The speed is limited — no more than 20-30 Mbit at the reception. In addition to the PPP mode, there is an NDIS mode. In this case, the modem emulates a network interface through which data is transmitted, and only control commands are sent through the AT port. In this mode, the speed is not limited. The main feature of the stick mode is to establish the connection and support the operation of the channel using the OS of the computer to which the modem is connected. At the same time, the computer receives an IP address directly from the cellular provider through a DHCP request, and the modem acts as a network bridge, transmitting the packets from the computer to the cellular network and back without changing them.
The initial USB stick stick composition is a virtual CD-ROM and microSD card reader. In order for modem ports to appear, you need to switch the composition. Under windows, this is done by carrier software available on a virtual CD, or by the huawei proprietary program Mobile Partner. Under linux, switching is done by the usb-modeswitch program. It is possible to prohibit the transformation of songs. This is done with the following command:
AT ^ SETPORT = «FF; 10,12,16»
At the same time, the modem immediately after switching on will look like 2 AT ports and a NDIS network card. CD and microSD will be excluded from the configuration. This mode is extremely convenient for using the modem in various home routers. To switch back the composition with switching, use the command:
AT ^ SETPORT = «A1, A2; 10,12,16, A1, A2»
Version numbers of stick-firmware always start at 21 — for example, 21.285.01.02.143. With this type of firmware, modems from MTS and Megaphone are supplied.
Included with the Stick-firmware, a so-called Dashboard is flashed into the modem — an image of a virtual CD that appears in the system after the modem is connected. This CD contains modem drivers for various operating systems, as well as a control program that establishes a connection to the Internet, reads SMS, makes USSD requests, and so on. There is a universal version of this program from the manufacturer of the Huawei modem (Huawei Modem), as well as specialized versions from specific telecom operators.
HILINK
With HILINK firmware, the modem works in the router mode and is presented to the computer as a network interface (usb-ethernet-rndis). The computer receives network settings from this interface via DHCP, and then goes through it to the Internet, like through a regular wired LAN. The modem assumes all care for establishing a connection and maintaining the channel, the computer does not even notice that access to the Internet is through a cellular network. In this mode, the modem has its own local IP address (usually 192.168.8.1), visible from the computer as a default gateway (default route), as well as an external IP address obtained from the cellular network. Routing is performed between the network of the cellular provider and the local network (modem-computer) using the address translation mechanism (NAT). Provides port forwarding from the external network (port forwarding and DMZ).
The modem is configured in this mode via the WEB interface available in the modem and accessible via its local IP address. Also through the WEB-interface information is available on the state of the modem and the signal of the cellular network, connection management, reception and transmission of SMS messages and USSD commands, SIM menu and much more. This is especially valuable for Linux users, as well as for those who have a modem connected not to a computer, but to a home router. Modem configuration via AT commands, as in stick firmware, is not performed in the normal mode of hilink firmware, although it is possible in the special DebugMode debug mode.
The initial HILINK modem USB composition is exactly the same as that of the stick — a virtual CD-ROM and microSD card reader. Switching tracks under windows is a small program mbbservice, run from the built-in CD. Under linux, this is done by the usb-modeswitch program. Regularly modem developers do not provide a mode without switching tracks. Nevertheless, it is possible to make such a mode by some modification of the firmware. At the same time, the built-in SD card reader is lost, however, it becomes possible to use a modem with any router that supports usb-rndis network cards.
Version numbers of hilink firmware always start at 22 — for example, 22.286.03.00.00. With this type of firmware modem comes from Beeline.
HILINK firmware consists of two parts — the firmware itself, and the WebUI (web interface). The first firmware is the main firmware, then the WebUI.
The participants of this forum completed the revision of the standard firmware to extend the functionality and enable the functions initially blocked.
If the modem asks a password when flashing, then it can be calculated with the same calculator (link in the header of the header). It is called flash code there.
Inside the modem, an operating system based on Android 2.3 with a linux 3.4.5 kernel works. Modified firmware allows access to the console of the Linux-part of the modem via telnet:
And also through the Android debugging utility — ADB:
adb connect 192.168.8.1
adb shell
Useful information on the procedure for flashing the modem
When you first flash operator modems, the flash driver will request the Flash code (password).
This code can be calculated from the IMEI modem usingThis code calculator .
If during the firmware the flash program stops seeing the modem, then you need to install the mbbservice drivers.
If you are working under Linux, then you can use the modem firmwareby thisflasher.
If you forgot to flash Dashboard 3.5 before uploading HILINK firmware, then you will not be able to create and edit network connection profiles in the web interface (settings ->profile management). In this case, go to the Linux console (via telnet, adb or A-shell), and enter the commands:
umount / data
(for E3372S)busybox flash_eraseall / dev / mtd / mtd16
(for E3372H)flash_erase / dev / mtd / mtd17 0 0
And then restart the modem.
For windows users, scripts have been developed to automatically perform all actions to resolve problems with profiles. See section useful links.
Note!Each of the firmware consists of 2 components: stick-firmware and Dashboard, hilink-firmware and WebUI. Do not try to flash WebUI on stick-firmware, and Dashboard — on Hilink-firmware. You can bring the modem into a completely non-operational state!
Useful and interesting AT commands and modem configuration
The following commands mainly refer to stick modems. Hilink modems are configured via a web interface, and under normal conditions they do not have an AT command port in the configuration at all. Some commands require the release of a command lock (datalock) using the at ^ datalock comand. This will be noted in the description of specific commands.
Modem Command Help
A list of all commands supported by the modem can be obtained from the command:
at + clac
This list will list all command names that are in the internal modem command table, except for hidden commands. Hidden commands are commands marked with a special flag in the command table. You can find them only by disassembling the kernel of the Linux part of the modem. For those interested, here is a list of these commands for the E3372 modem:
+ CEER
^ CPULOAD
^ MFREELOCKSIZE
^ MEMQUERY
^ CMST
^ CMSTUB
^ CVOICE
^ DDSETEX
^ CMMI
^ ADCTEMP
^ YJCX
^ USSDMODE
^ BOOT
^ CMM
^ RSSI
^ LFROMCONNTOIDLE
^ CNMR
^ CECELLID
^ CIMEI
^ CGAUTH
^ CCIN
^ CSND
^ DWINS
^ SETPID
In general, commands have 4 forms of recording (hereinafter cmd is the name of the command):
atcmd — command without parameters
atcmd? — view the current value of the parameters controlled by the command
atcmd = X — setting parameter values
atcmd =? — request for help on the command format
Each of the commands supports one or more recording forms. For example:
at + cgdcont
+ CME ERROR: Incorrect parameters
The form without parameters is not supported by the command.
at + cgdcont?
+ CGDCONT: 0, «IP», «», «», 0,0,0,0
+ CGDCONT: 1, «IP», «internet.mts.ru», «», 0,0,0,0
The form of request for the current value of the parameters — a list of Internet connection profiles
at + cgdcont = 1, «ip», «internet.mts.ru»
Ok
Assigning a value to the parameters — profile setting 1.
at + cgdcont =?
+ CGDCONT: (0-31), «IP» , (0-2), (0-3), (0,1), (0,1)
+ CGDCONT: (0-31), «IPV6» , (0-2), (0-3), (0.1), (0.1)
+ CGDCONT: (0-31), «IPV4V6» , (0-2), (0-3), (0.1), (0.1)
+ CGDCONT: (0-31), «PPP» , (0-2), (0-3), (0,1), (0,1)
View the + CGDCONT command format and a list of valid parameters.
USB modem control
On the computer side, the USB modem looks like a collection of separate, independent USB devices. The list of devices represented in the modem can be managed using the special command ^ setport.
Initially, after connecting to a computer, the modem usually looks like a CD-ROM and microSD card reader. This is the primary composition of the modem. After a special command from the operating system, the modem switches its composition to the secondary — ports of AT commands and network interfaces appear. Such a switch is made solely because of the ideological curvature of the Windows operating systems, and in many cases it only hurts. For example, when connecting a modem to home routers. Therefore, it is possible to prohibit such switching — then the modem will immediately turn on with the secondary (working) device composition.
Command format ^ setport:
at ^ setport = «<list of primary composition>;<secondary composition list>»
Each of the lists is a comma-separated device code. A semicolon is put between the primary and secondary list. In the pre-list, only codes A1, A2 and FF are allowed, in the secondary list, all but FF. The modem understands the following codes:
FF — prohibit the primary composition
10 — AT port for establishing PPP connections (modem)
12 — AT port for setting up NDIS connections (PCUI)
16 — NDIS-network card
5 — Linux console (A-shell)
A — VxWorks console (C-shell)
A1 — CD-ROM with dashboards and drivers
A2 — microSD card reader
Letter codes can be written in both large and small letters. Changing the device list takes effect only after the modem is rebooted (using the at ^ reset command or reconnection).
Note! The command ^ setport is able to manage the composition only in stick firmwares! In hilink, the composition can be changed only by editing the record nvram 50091.
USB song setting examples:
at ^ setport = «a1, a2; 10,12,16, a1, a2» — standard factory composition. Only a CD and a card reader are visible in the primary composition, all AT ports, a network card, a CD, a card reader in the secondary composition.
at ^ setport = «ff; 10,12,16, a2» — composition without switching. Very convenient for use in home routers and computers with operating systems other than windows. After connecting, the modem immediately appears as 2 AT ports, a network card and a card reader.
at ^ setport = «FF; 10,12,16,5, A, A1, A2» — Composition with included all devices that are only in the modem. Convenient for those who need access to modem consoles.
The current usb-track used can be viewed with the ^ getportmode command. For example:
at ^ setport?
^ SETPORT: FF; 10,12,16,5, A, A1, A2
Ok
at ^ getportmode
^ GETPORTMODE: TYPE: WCDMA:, modem: 1, pcui: 2, ncm: 3, a_shell: 4, c_shell: 5, mass: 6, mass_two: 7,
The device names are listed here in the same order as they appear in the ^ setport command. Note that the ^ getportmode command shows exactly the current composition. If you changed it with the ^ setport command, but have not yet reset the modem, the changes will not be taken into account.
Network priority setting and allowed ranges
The modem allows you to explicitly specify with which types of networks (GSM / UMTS / LTE) and the ranges it should work. To do this, use the at ^ syscfgex command. The command format is:
AT ^ SYSCFGEX = «<net_order>»,<band>,<roaming>,2,<lteband>,,
<net order> — a list of preferences for network types. Valid values are:
00 — all types of networks
01 — only 2G
02 — only 3G
03 — only 4G
99 — leave the value unchanged
Codes can be combined. Naprimer “0302” — LTE preference ->3G
<band> — code of acceptable ranges for 2G / 3G networks. Possible values:
80 — GSM 1800
300 — GSM 900
80000 — GSM 850
200000 — GSM 1900
400000 — UMTS B1 (2100)
2000000000000 — UMTS B8 (900)
3FFFFFFF — all ranges
Each of the codes is a hexadecimal (HEX) number. To specify a combination of ranges, add the corresponding codes. For example, to set GSM850, GSM900, GSM1800 ranges, you need to calculate 0x80 + 0x300 + 0x0x80000 = 0x80380. This will be the resulting code range — 80380.
<roaming> — permission of the modem in roaming:
0 — ban
1 — allow
2 — leave unchanged
<lte band> — code of valid LTE bands.
1 — B1 (FDD 2100)
4 — B3 (FDD 1800)
40 — B7 (FDD 2600)
80 — B8 (FDD 900)
80000 — B20 (FDD 800)
800C5 — all ranges
As for the 2g / 3g ranges, the codes are hexadecimal numbers that can be added to specify range combinations.
Command example:
AT ^ SYSCFGEX = «00», 3FFFFFFF, 1,2,800C5 , — register in all possible networks and ranges
AT ^ SYSCFGEX = «0302», 400000,1,2,800C5 , — register on the LTE network, if LTE is not available, then on 3G (the modem will not register on 2G networks). All bands are available for LTE, for 3G — only 2100 range.
Search for cellular base stations
This modem has a unique property — it can do a search for all surrounding base stations (BS). And not only the BS of the operator of the sim card inserted in it, but in general all the BSs of all operators, the signal from which reaches the modem antenna. For each BS found, its CID and the level of signal received from it are displayed. This allows you to select the operator with the highest signal level, as well as select a specific BS for pointing an external antenna to it. The only drawback of this modem is that it can only search BS 2G and 3G. He does not know how to search for LTE cells.
Search is made with the help of the command at ^ netscan. Before searching, make sure that:
— Internet channel is disabled
— the modem does not see any LTE-cells.
If there is an LTE signal in the district, then the modem should be switched to 2G3G mode using the command AT ^ SYSCFGEX = «0201», 3FFFFFFF, 1,2,800C5 , or in the settings of the web interface.
Also note that this command can only be entered via the management port (PCUI). If you enter it through the port intended for the PPP connection (modem), the command will issue an empty response (just OK and that’s it).
Command format:
AT ^ NETSCAN = num, level, mode
num — the number of BS found, from 1 to 20. If more than num BS is found, then the stations with the weakest signal will be excluded from the list
level — the minimum level of the BS signal included in the list. Set in dB, from -110 (lowest level) to -47 (highest level). Stations with a signal level below the level will not be included in the list.
mode — BS type. 0 search 2G stations, 1 — search for 3G stations.
Command example:
at ^ netscan = 20, -108.1
^ NETSCAN: 10638 , 1e7e, 250.02.0, -78.8b77.400000
^ NETSCAN: 10687 , 1e7e, 250.02.0, -79, d5c8,400000
^ NETSCAN: 10662 , 1e7e, 250.02, -82.8ade, 400,000
^ NETSCAN: 10587 , 4cf8,250,20,0, -105, d4fc, 400000
^ NETSCAN: 10563 , 4cf8,250,20,0, -106, d4f9,400000
In this example, a 3G BS search is ordered with a signal level not lower than -108 dB. The result is given in the form of a list, sorted by signal level. The topmost BS is the most powerful, the bottom one is the weakest. List item format:
^ NETSCAN: 10638 , 1e7e, 250.02.0, -78.8b77.400000
1e7e — LAC Station
250 — MCC (Russia)
02 — MNC (in this case — MTS).
0 — I myself would like to know what it is, from the disassembled code I did not understand the meaning of this field.
-78 — signal level of a given BS
8b77 — station CID
400000 is the range in which the BS signal is received (as in the ^ syscfgex command).
According to the results of this example, we can conclude that the strongest signal in a given area is at the MTS, and the antenna should be sent to the BS with CID = 8b77 LAC = 1e7e. Coordinate BS can be viewed on the site xinit.ru.
Unlocking Extended Command Set
Some commands that are listed in the command list are initially blocked. That is, even if you enter a command in the correct format, the modem will respond ERROR. Apparently, this is done to protect against fools — in some cases, the thoughtless use of an extended command set can lead to a complete inoperability of the modem. To access this set of commands, you need to unlock it. This is done by the command:
at ^ datalock = «<password>»
The password is the same nlock-code, calculated by the algorithm 201 from the IMEI modem, which is used to remove simlock. Command example:
at ^ datalock = «13325014»
If the password is entered correctly, the modem will answer OK and release the datalock lock, otherwise ERROR will respond.
Work with NVRAM modem
The modem has a storage of various configuration information — NVRAM. It is organized as a set of variable-length records. Each record has a number — from 0 to 65535, but not all record numbers are physically present in the modem.
To find out the length of a particular entry, use the command:
at ^ nvrdlen =<item>
<item> — record number. In response, the modem gives its length:
at ^ nvrdlen = 8268
^ NVRDLEN: 12
If instead of length the modem responds with ERROR, then there is no record with that number at all in the modem.
You can view the contents of a specific entry with the command:
at ^ nvrdex =<item>,<offset>,<len>
<offset> — offset from the beginning of the recording to the fragment of interest to us (0 — from the beginning)
<len> — the length of the output fragment must be no more than the full length of the record minus the offset.
Example:
at ^ nvrdex = 8268,0,12
^ NVRD: 8268,0,12,01 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 0A 00 00 00
At the beginning of the response, the command parameters are listed separated by commas, then, by space, the bytes of the record contents.
To change the contents of the nvram command is used:
at ^ nvwrex =<item>,<offset>,<len>,<b0><b1>….<bn>
The meaning of the first three parameters is the same as in the reading command. b0 … bn — bytes written to nvram. They should be exactly len pieces, and they are listed through the space. For example:
at ^ nvwrex = 8268,0,12,1.00 00 00 02 00 00 00 0A 00 00 00
In addition to the above, there are 2 simplified commands for working with nvram — ^ nvrd and ^ nvwr. Unlike the ones discussed above, these commands require the precautionary release of the datalock lock.
at ^ nvrd =<item> — displays a full dump of the specified entry
at ^ nvwr =<item>,<b0>,…<bn> — saves the specified bytes from the beginning of the item.
Change IMEI modem
You can change IMEI with the command:
The command requires prior release of the datalock lock. IMEI change is necessary for work in the yota network — the modem needs to install an IMEI modem imei from a device of the type (smartphone, tablet) for which a sim card was purchased.
Please note that for the command to work correctly, a sim card must be inserted into it. Absolutely any. In addition, IMEI must be correct (with the correct last check digit). Incorrect IMEI modem will not accept with an error message. You can check the correctness of IMEIcalculator
Change modem ID
E3372h with megafon firmware does not work with Omni II and other new routers. The fact is that with this firmware the modem model is defined as «MegaFon M150-2», and not «E3372».
This string is stored in the cell NVRAM 53525, and you can replace it with «E3372» with the following AT commands:
AT ^ NVWREX = 53525.0,84.0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 45 33 33 37 32 48 2D 31 33 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 32 45 33 33 33 48 4D 0 0
AT ^ NVWREX = 53525,84,84,0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 50 50 31 31 73 2D 53 53 49 43 4B 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 45 33 33 37 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After that, the modem will be easily identified by kinetics and work.
In general, in ZyXEL modems are defined by vid / pid (in the config), for example, the E3272 block looks like this:
interface CdcEthernet0
description «USB MODEM»
usb device-id 12d1 14db
and for E3372s — like this:
interface CdcEthernet0
description «USB MODEM»
usb device-id 12d1 14dc
Accordingly, you can enter the necessary values manually for any modem: there are libraries for almost everyone, with very few exceptions (for example, sierra modems)
Blocks are given for modems in HiLink mode (with a CdcEthernet0 upgrade).
Manufacturer field editing
It is necessary to check what lies in the cell NVRAM 8203. In the right case, there will be this:
AT ^ NVRDEX = 8203,0,32
^ NVRDEX: 8203,0,32,68 75 61 77 65 69 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Ok
If different, write this value there.
at ^ nvwrex = 8203,0,32,68 75 61 77 65 69 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Access to modem command interfaces
The modem is built on the Hisilicon hi6930 chip (Balong v7r2). This chip has in its composition 2 processor cores ARM7. Each processor core runs on its own operating system.
Kernel 0, which starts when the modem is turned on, runs on Android 2.3 (Linux kernel v3.4.5). The system environment is a stripped down version of Android — without the Dalvik virtual machine. The linux kernel itself is almost completely consistent with the standard Android kernel, but additional proprietary modules developed by Huawei are compiled into it — for example, the AT command handler. In addition to the initial launch of the modem and the processing of AT commands, in the HILINK firmware, the linux part of the modem supports the network stack and the operation of the WEB server.
Kernel 1 is managed by the VxWorks v6.8 real-time operating system. This OS directly manages the radio module and interacts with the cellular network. VxWorks is launched using a special subsystem built into the Linux kernel.
Thus, 2 operating systems work simultaneously in the modem. They can interact with each other using the ICC subsystem, which transfers data packets from one OS to another in a special way. ICC contains debugging tools, which allows, if desired, to consider in detail the process of interaction between VxWorks and Linux. Each OS has a command processor that allows you to talk and command the OS. Further I will tell how to get access to the command line of these OS.
The easiest way to access the command line is the Linux part of the modem in HILINK firmware. To do this, it is enough to flash the modified firmware from this topic. This firmware allows access to the Linux shell via telnet and adb.
telnet:
adb:
adb connect 192.168.8.1
adb shell
Access via the Android debugger ADB also allows you to transfer and receive files from the internal file system of the modem.
If you have a modem with stick-firmware, or standard (unmodified) HILINK-firmware, then the above methods will not work. In addition, these methods do not allow access to the VxWorks console. Therefore, we consider a more universal method, originally incorporated into the modem by the manufacturer — the A-shell and C-shell ports. Both of these ports are USB-serial devices that are included in the USB-modem compression mode DebugMode. The first one is the Linux console, the second is the VxWorks console.
First you need to get access to the command AT-port of the modem. In stick firmware, this port is available immediately — this is the very first port (/ dev / ttyUSB0). In standard HILINK firmware, the AT port is not available by default. To open access to this port, you need to flash the modified web interface, and then go to the browser at this address:
[url = «http://192.168.8.1/html/switchDebugMode.html»] http://192.168.8.1/html/switchDebugMode.html [/ url]
This will switch the modem to debug mode — now, in addition to the network interface, 6 serial ports are also available. The very first of them will be the command AT-port. Now you need to enter any terminalka on this port, and enter the following AT commands:
at ^ spword = «password»
at ^ shell = 2
at ^ reset
The password in the ^ spword command is a code calculated according to the usual algorithm of v201, but from an IMEI modem deployed backwards. In the calculator for this there is a button Reverse. After entering the commands, the modem reboots.
For a HILINK modem, you should again switch to debug mode via the WEB interface, as I wrote above. As a result, the modem will have 6 serial ports:
ttyUSB0 — AT Command Port
ttyUSB1 — VxWorks console
ttyUSB2 — Linux dwarf
ttyUSB3
ttyUSB4
ttyUSB5 — DSP log
For a stick-modem, you will have to enter into the list of available ports (using the ^ setport command) two additional ports — with numbers 5 and A, for example:
at ^ setport = «FF; 10,12,16, A2,5, A»
As a result, the modem will have 4 serial ports:
ttyUSB0 — AT port for PPP connections
ttyUSB1 — AT port for NDIS connections
ttyUSB2 — Linux dwarf
ttyUSB3 — VxWorks console
The Linux console port is the primary system console (/ dev / console), for which all kernel system messages are issued. Shell there is installed the Android toolbox by default, which is extremely inconvenient in operation. To make your life easier, enter the command:
after which the shell will become busybox and a normal command line editor will appear.
VxWorks also has 2 shells — C-shell (installed by default) and CMD (set by the cmd command). Which one is more convenient is a matter of taste. In both shells there is a help command, and more detailed information on working with the VxWorks command line can be obtained from this document -http://read.pudn.com/d…ls_users_guide_6.2.pdf
Access to the modem OS consoles opens up the broadest prospects for a deep study of the modem code and its hidden capabilities. For lovers of poking around in the code, this is just a bonanza. I want to warn all the others — thoughtless input of commands in consoles can lead to negative consequences — from the hangup of the modem to the destruction of important data structures on the flush and the complete loss of performance. Be careful!
Drivers and programs
Programs
Balong USB Downloader fromDecker — Utility for emergency USB-loading modems on the Balong V7R2 and V7R11 chipset
Switch program fromrust3028
Modem unlocking
E3372h
To begin with, this modem has a v4 unlock algorithm, which means the code is not generated by IMEI.
First of all, determine the firmware version of your modem.
The easiest modem withancient firmware (2x.180) unlock AT command:
at ^ nvwrex = 8268,0,12,1,0,0,0,2,0,0,0, a, 0,0,0
You can also use specials. calculators:
Calculator for E3372h
Calculator for E3372h, showing the process, not hanging, able to take the necessary data from the modem and unlock it
Translated (Russian, English and Urdu) calculator for E3372h with a custom interface, showing a process that is not hanging, able to take the necessary data from the modem, find the COM port, save information to a file and unlock
Well, or change the code to eight zeros:Change of OEM and SIMLOCK modem codes E3372N
Next, with firmware2x.200.07 (except 21.200.07.0 0 .209) it’s getting harder.
AT commands are blocked, which means you will not change or calculate the code, and you will not remove the lock flag in NVRAM. There are two options:
- Flash on a modified firmware, or older
- Calculate code through needle method
Further — even worse! Starting with firmware2x.200.15 just do not flash it, you need to translate the modem in the Factory Mode by the AT command:
And since2x.317 — and this hole was closed! Starting from 2x.317 there are three options:
- Needle method to upgrade to a modified or old firmware
- Needle method to calculate the code
- From Huawei there was a flush of keys; in the instructions for the firmware in HiLink, you can find special firmware for flashing on “needle” firmware without pricking.If your not, write in a personal rust3028.
Fortunately, with MTS 22.323, you can roll back to MTSova 21.315, and even though Beeline made a new one, please, without this hole, although not 317, you can also roll back to the old Beeline.
E3372s
As usual, modems from cellular operators are delivered blocked — they can work only with SIM cards of this operator. The list of plmn-codes allowed for use can be found with the at ^ simlock? Command.
Of course, this situation does not suit us — we want, having bought a modem, to use it with any sim card. For this, the manufacturer laid the opportunity to unlock the modem. This is done by entering the unlock code (nlock-code), calculated by a special tricky algorithm from the IMEI modem. Calculator for calculating codescan be downloaded here (there are versions for windows and linux). To unlock, follow these steps;
— Calculate the unlock code using the above calculator. Of all the codes it calculates, the code v201 is used.
— Insert another SIM card into the modem (SIM card of another cellular provider, not the one who sold you the modem).
— Connect the modem to the computer.
Further, the control program (for stick-modems) or the web interface (for hilink-modems) will ask for the unlock code, which must be entered. All — the modem is unlocked and will work with any sim card.
In addition to entering the code through the program and the web interface, you can also enter it via the AT command. This is especially true for stick-modems under linux. The command looks like this:
at ^ cardlock = «unlock code»
The number of attempts to enter the code is limited to 10 attempts. If the wrong code was entered 10 times, the modem blocks further attempts — more, the at ^ cardlock command will not unblock it, even if you enter it with the correct code. If you still managed to exhaust all input attempts, that’s okay — they are easy to recover. This is done by the following commands:
at ^ datalock = «unlock code»
at ^ maxlcktms = 10
10 is the new number of attempts (you can enter any number from 1 to 255). Then you can enter the at ^ cardlock command with the correct code and unlock the modem. This method may work on other 4G modems from huawei.
The lock flag (simlock) is stored in the NVRAM of the modem, in record 8268. In addition, in this record is a flag that allows you to completely disable the unlock code. If your mobile operator turned out to be such a gossip that it set this flag, then all at ^ cardlock commands will be rejected by the modem.
But, as you know, there is no reception against scrap. There is a universal possibility of unlocking the modem by direct recording to nvram by executing the AT command in the Terminal program, joining the modem via the PC UI Interface port or DS Unlock:
at ^ nvwrex = 8268,0,12,1,0,0,0,2,0,0,0, a, 0,0,0
The command must be entered carefully, to the nearest comma, so as not to accidentally damage other nvram entries. This method unlocks the modem ALWAYS — with any, including the native sim card, with exhausted input attempts, with the ^ cardlock command blocked … In general, I do not imagine the condition under which the command would not work.
Firmware
Recommended firmware version for E3372h:E3372h-153_Update_22.323.01.00.143_M_AT_05.10
Recommended firmware version for E3372s:E3372s-153_Update_22.300.09.00.00_M_AT_04.10
Recommended version of the web interface: There are no friends to choose from, taste or color
ATTENTION: Here are original, modified and transitional firmware, as well as original and modified web interfaces.
The difference between the original and modified firmware is that most AT commands can be blocked, as well as the possibility of flashing.Be vigilant and sew the original only when you know what you are doing!
The difference between the original and modified interfaces in the functional, the modified ones have more.Before asking to add some function, please carefully examine all interfaces, most likely it is already implemented in one of them.
In addition, there are so-called transitional firmware, they refer to the stick,but they are not intended for everyday work and the Internet does not work for them.
Web interfaces
Original
Web Interface 17.100.11.03.161 (Beeline)
Web Interface 17.100.13.01.161 (Beeline)(In the post firmware + muzzle, I ask only for E3372h, the muzzle is placed on both E3372s and E3372h)
Web interface 17.100.17.00.143 (MTS) for 829F(In the post firmware + muzzle, I ask only for E3372h, the muzzle is placed on both E3372s and E3372h)
Web Interface 17.100.05.06.965(In the post firmware + muzzle, I ask only for E3372s, the muzzle is placed on both E3372s and E3372h)
Web interface 17.100.14.02.577 (Beeline KZ)
Web Interface 17.100.14.02.778 (Russia Open Market)
Dashboards
Dashboard Set
Dashboard Mobile Partner
Dashboard 23.015.05.11.143 (MTS) for 827F / 829F (WIN10 + MAC10.11)(In the post firmware + dashboard, please only for E3372h, dashboards are placed on both E3372s and E3372h)
Compatible with routers
The modem is not programmed for compatibility with routers, on the contrary, manufacturers of routers do this. Therefore, look for a list of compatible models with your router. If you are looking for a router to work with this modem, then create a theme inSelection and Comparison. Here all requests for help with the choice are deleted.
Further, if you need help in order to make friends with the modem router, then you need to ask for help in the subject of the router. Why? Because the routers are very different, people in this thread have no idea what needs to be done to make the modem work with it. Modems, on the contrary, are determined by everything in only a few different ways, something non-standard is rare. This modem has several different methods for determining: RAS, NDIS in Stick-firmware and RNDIS, CDC in HiLink-firmware (RNDIS for Windows, CDC for Linux, including routers. And NDIS is not RNDIS, they are different things). In other words, you need to be friends with a modem router, not a modem with a router, since drivers must be embedded in it. And what can you do with a modem? And nothing, you need to pick a router, the manufacturer did not put the driver in it.
In case you are being driven from the router’s topic here, you do not need to write about it, there are no exceptions and the post will still be deleted. It is better to skip the link to this text in the topic of the router, so that they understand that they are wrong. And if it didn’t help, well, that means no luck.
PS: the most hassle-free scheme with a router: HiLink firmware on a modem with auto-switching in CDC + Zyxel Keenetic 4G III rev.A with Padavan firmware
K
The curator is looking for a topic!
Main tasks: updating the topic header, monitoring the observance of forum rules in the topic.Requirements for candidates to the curators of the forum.
Those wishing to write in QMS moderators section or inI want to be curator.
Post has been editedRamsteiner — 20.04.19, 16:56
Для организации доступа в интернет в загородном доме, приобрел 4G-модем Huawei e3372h-153. Сигнал в моем районе достаточно сильный, чтобы смотреть видео с камер наблюдения в режиме реального времени. Прошивался для того, чтобы можно было поменять ttl, и не слететь с выгодного тарифа. Да и возможностей по-больше, чем в стоковом WEB-интерфейсе.
Заказал ещё один точно такой же 4G модем для родителей, только на 1К дешевле. На сдачу взял антенну, для усиления сигнала, на муське был неплохой обзор на неё. Буду ловить интернет на даче). Себе тоже приобрёл и протестировал антенну, не смотря на уверенный сигнал. Скорость выросла, инет стал шустрее что-ли, отзывчевее ))
За основу, был взят материал с 4pda. Собрал всё в одном архиве, на всё про всё, по пунктам, уходит 10 минут.
Итак, на руках у меня модем e3372h-153 со стоковой прошивкой 2x.3xx.xx.xx.778. Модем не привязан к оператору!
0. Если уже втыкали модем, удалите установленное ПО.
1. Установите 1_HUAWEI_DataCard_Driver_6.00.08.00_Setup
2. Установите 2_FC_Serial_Driver_Setup
3. Запустить из папки 3_set_hilink_switch/set_hilink_switch.cmd и выбрать действие «1» (!с админскими правами!)
4. Запустить из папки 4_E3372_sw\E3372_sw.cmd (!с админскими правами!) чтобы появились порты (проверить можно в диспетчере устройств, в разделе Порты (COM и LPT)
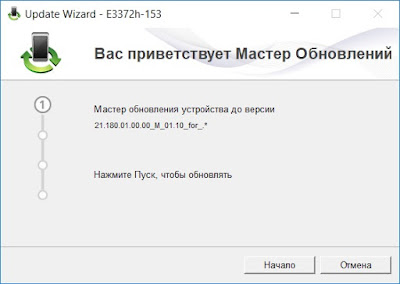
5. Ставим переходную прошивку, запускаем 5_E3372h-153_Update_21.180.01.00.00_M_01.10_for_.778\E3372h-153_Update_21.180.01.00.00_M_01.10_for_.778.exe
После окончания установки ждем минуту, пока модем перезагрузится.
6. Устанавливаем рабочую прошивку 6_E3372h-153_Update_22.329.07.00.00_M_AT_05.11\E3372h-153_Update_22.329.07.00.00_M_AT_05.11_nv.exe
После окончания установки опять ждем минуту, пока модем перезагрузится.
7. Запускаем установку модифицированной веб-морды с расширенными настройками для управления модемом 7_Update_WEBUI_17.100.13.01.03_HILINK_Mod1.11\Update_WEBUI_17.100.13.01.03_HILINK_Mod1.11.exe
Опционально.
Поменяем значение ttl. Надо отрыть cmd от имени администратора, перейти в папку 8_fix_ttl и запустить fix_ttl.cmd
Можно сделать прямо из Проводника, перейти в папку и щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши с зажатым шифтом, чтобы выбрать меню «Открыть окно PowerShell здесь»
Затем запускаем .\fix_ttl.cmd
Нажимаем «1».
Открываем 192.168.8.1 в браузере и проверяем настройки.
Теперь можно замутить отправку SMS через модем.
Check your 3G / 4G modem. If it is in stick mode then use the Huawei terminal to transfer modem into modem mode by a AT ^ SETPORT = «FF; 1″ or the command AT ^ U2DIAG = 0. Modem in HiLink mode does not respond to AT commands, no modem can be found , no SMS can be sent.
Disabling HiLink mode and transfer of 3/4G-modem to mode «modem only«.
The very first thing to do — to disable a request / check the pin code in the modem software. After that you need to get a SIM card from the modem and all subsequent actions be made without a SIM card.
-
The modem restarts and in a Device Manager, You can see two serial interfaces
-
Switch to «modem only« — run the program Huawei Modem Terminal. Later in the program, select your device from the top «HUAWEI Mobile Connect — 3G PC UI Interface» and push Connect. Then need to check whether modem is responsible . In the bottom string write command AT and push Enter. You should see something like:
Send: AT
Receive: AT
Receive: OK
If so , the modem is responsible, and we can give him commands. Switch it to the «modem only» state by command:
AT^U2DIAG=0
If it is successful, modem will answer OK.
For modern modems command is:
AT^SETPORT="FF; 1"
If it is successful, modem will answer OK.
To change HILink mode into modem mode, it is necessary to change the driver, sometimes You can Huawei modem driver, or maybe E3372s modem drivers.
The way for a more modern Huawei E3372h is here:
- Visit either one of these sites to calculate device-specific «Flash code» based on your IMEI and write it down.
- Online calculator 1
- Online calculator 2
- Download and extract this ZIP that contains required tools, drivers, and firmware images
- Install «[1] Mobile Broadband HL Service» by running mbbServiceSetup.exe
- Installs RNDIS driver
- Installs service to switch from CD emulation to RNDIS (like usb-modeswitch on Linux)
- Install «[2] Datacard Driver» by running DriverSetup.exe
- Installs serial port drivers (v5.05.01.00)
- Insert E3372h-153 with HiLink firmware to the USB port
- Preferably directly to PC, avoid cheap low-quality USB extension cables.
- Open Device Manager and verify that the RNDIS interface is present under Network adapters
- Open command prompt and «PING 192.168.8.1» to make sure HiLink firmware is running
- Run «sw_project_mode.cmd» from «[3] Switchmode E3372h» folder
- This will enable the «PC UI» serial port required for firmware upgrade
- Wait until you can see it under Ports in Device Manager
- Run «Update_WEBUI__Hilink_V7R2_9x25_CPIO.exe» from «[4] Huawei E3372h WebUI»
- This updates the user interface but does not touch the rest of the firmware.
- If you have Error Code 13 this will fix it. Code 13 («Authentication failed») is caused by failed attempt to flash firmware resulting in Error Code 19 («Download failed»).
- See HUAWEI_Module_Firmware_Upgrade_Guide_on_Windows_V100R001_01(5).pdf for complete list of error codes.
- Wait until the WebUI update is complete and you can ping 192.168.8.1 again.
- Run «sw_project_mode.cmd» from «[3] Switchmode E3372h» folder
- Run «E3372h-153_Update_.exe» from «[5] Huawei E3372h-153 HiLink FW» folder.
- This upgrades (or downgrades) your HiLink firmware version. You will need Flash code from one of those calculators to do this.
- Wait until HiLink update is complete and you can ping 192.168.8.1 again.
- Run «sw_project_mode.cmd» from «[3] Switchmode E3372h» folder
- Run «E3372h-153_Update_.exe» from «[6] Huawei_E3372h-153 Stick FW» folder.
- This finally changes firmware from the HiLink to Stick. You will need Flash code again.
- Wait until the Stick update is complete. You can no longer ping 192.168.8.1 and the RNDIS adapter has changed to «HUAWEI Mobile Connect — Network Card».
- Run «putty.exe» from «[7] Putty» folder
- Find serial port name from Device Manager, for example in the case of «HUAWEI Mobile Connect — PC UI Interface (COM15)» port name is COM15
- Click Serial on the right-hand side of the Putty screen and type COM15 or whatever your port is.
- Click Open on bottom of Putty
- Type ‘ ATE1 ‘ without quotes, you won’t see what you type, and DO NOT try to use backspace. If you did it right you got ‘ OK ‘ as a reply. Ignore ^RSSI etc. lines you might also see.
- Type following commands one per line to see info about your device and verify connection works.
- ‘ ATI ‘
- ‘ AT^FHVER ‘
- ‘ AT^VERSION? ‘
- Get the current SETPORT value by typing ‘ AT^SETPORT? ‘. You might want to write these down if you ever want to revert back to defaults. Mine was ‘ ^SETPORT:A1,A2;12,1,16,A1,A2 ‘.
- Set new SETPORT value by typing ‘ AT^SETPORT=»FF;12,16″ ‘, this disables CD emulation, disables modem emulation (PPP) and enables NCM mode.
- If you want to keep PPP support for example for the older router with a USB port using’ AT^SETPORT=»FF;12,10,16″ ‘ instead. Remember that you won’t get full speed with PPP.
- Reset the modem by typing ‘ AT^RESET ‘.
- Close Putty now.
- Done.