I am currently trying to install and update a few packages on a Windows OS. The only matter is that I am using Cygwin in order to type the commands through a terminal (as I’m aware, I can type in Linux type commands such as cd, ls etc. on Cygwin — I may be wrong). However, when I try to install a package like:
sudo apt-get install paparazzi-dev
I get the reply:
-sh: sudo: command not found.
Does anyone have an idea as to how I can fix this problem?
asked Mar 20, 2014 at 8:47
1
Run cygwin as administrator.. then you wouldn’t need any sudo command.
answered Aug 18, 2014 at 5:48
AimalAimal
6211 gold badge7 silver badges13 bronze badges
3
Cygwin is not a full Linux distribution. Therefore you don’t have sudo or the Debian/Ubuntu package manager apt-get. There is a number of packages available from the Cygwin repository: http://cygwin.com/packages/
You have to chose these packages during setup.
answered Mar 20, 2014 at 8:52
CalebCaleb
3434 silver badges7 bronze badges
3
Windows does not have sudo, apt, or almost any Linux commands to be exact. Cygwin may allow some, but as programs are not installed on Windows as packages apt-get will not work. Windows programs have installers as .exe or .msi instead.
The Windows version of sudo is called runas in case you need to run something as another user. Or, you can run Cygwin as administrator.
If you have to use the packages you need Linux. You can install it directly to replace Windows, dual-boot or use a virtualization software like VMware VirtualBox.
answered Mar 20, 2014 at 8:53
PurkkaKoodariPurkkaKoodari
6,7136 gold badges37 silver badges58 bronze badges
3
Making out an explanatory answer from answer here by @Aimal as it worked for me.
Cygwin may not get permissions to create folders and files when run by clicking Cygwin icon that’s in normal mode.
Cygwin gets the right authorization only when right click -> "run as adminitrator" on cygwin icon because of that it gets permissions to create folders and files.
answered Apr 9, 2016 at 19:07
veer7veer7
20.2k9 gold badges46 silver badges75 bronze badges
Cygwin lets you run certain commands, such as cd, ls, or mv; but it doesn’t let you run other commands, such as sudo or apt-get.
-
If you’re trying to add a package to your Cygwin installation, rerun Cygwin Setup. It may still be in your «Downloads» folder. Go through all the steps again. The Cygwin installer will automatically download and install the package you want, and add it to your Cygwin installation. (I think it will probably also upgrade all your other installed Cygwin packages to the latest available versions.)
-
If your desired package isn’t on the Cygwin package list but is on the Cygwin Ports package list, follow the Cygwin Ports installation instructions. Note that Cygwin Ports is separate from Cygwin. Please do not send messages about Cygwin Ports packages to the cygwin.com mailing lists.
-
If you have years of Linux experience, you may be able to compile the software you want inside Cygwin. This can be challenging.
-
Perhaps an option simpler than «compile it yourself» is this: You can install VirtualBox, then install your favorite Linux distribution inside the virtual machine, then install your desired package inside Linux. (I like Ubuntu Linux, which has more than 27,000 packages in its «Universe» repository.) Now you can run Linux and Windows at the same time.
answered Mar 20, 2017 at 3:25
I think I tried steps below after doing some research & succeeded (on windows)
1.Install scoop using powershell 3 (iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring(‘https://get.scoop.sh’))
2. do scoop install —global sudo
3. make sure paths (C:\Users\\scoop\shims & C:\ProgramData\scoop\shims) added in environmental path variable.
answered Jul 9, 2017 at 11:38
In my case, I wanted to install curl, but could not create directory /usr/local/curl/lib when running command «make install», because of permission deny. so i need to change /usr/local permission. when i run sudo chmod 755 /usr/local, sudo command not found.
after searching a few solution, found that sudo is not installed by default in Cygwin. But I tried the solution that Aimal gave which is to run Cygwin as administrator. I finally can change the folder permission. Thanks Aimal.
answered Nov 24, 2015 at 16:05
Leung Ying YingLeung Ying Ying
8461 gold badge7 silver badges5 bronze badges
1
I am currently trying to install and update a few packages on a Windows OS. The only matter is that I am using Cygwin in order to type the commands through a terminal (as I’m aware, I can type in Linux type commands such as cd, ls etc. on Cygwin — I may be wrong). However, when I try to install a package like:
sudo apt-get install paparazzi-dev
I get the reply:
-sh: sudo: command not found.
Does anyone have an idea as to how I can fix this problem?
asked Mar 20, 2014 at 8:47
1
Run cygwin as administrator.. then you wouldn’t need any sudo command.
answered Aug 18, 2014 at 5:48
AimalAimal
6211 gold badge7 silver badges13 bronze badges
3
Cygwin is not a full Linux distribution. Therefore you don’t have sudo or the Debian/Ubuntu package manager apt-get. There is a number of packages available from the Cygwin repository: http://cygwin.com/packages/
You have to chose these packages during setup.
answered Mar 20, 2014 at 8:52
CalebCaleb
3434 silver badges7 bronze badges
3
Windows does not have sudo, apt, or almost any Linux commands to be exact. Cygwin may allow some, but as programs are not installed on Windows as packages apt-get will not work. Windows programs have installers as .exe or .msi instead.
The Windows version of sudo is called runas in case you need to run something as another user. Or, you can run Cygwin as administrator.
If you have to use the packages you need Linux. You can install it directly to replace Windows, dual-boot or use a virtualization software like VMware VirtualBox.
answered Mar 20, 2014 at 8:53
PurkkaKoodariPurkkaKoodari
6,7136 gold badges37 silver badges58 bronze badges
3
Making out an explanatory answer from answer here by @Aimal as it worked for me.
Cygwin may not get permissions to create folders and files when run by clicking Cygwin icon that’s in normal mode.
Cygwin gets the right authorization only when right click -> "run as adminitrator" on cygwin icon because of that it gets permissions to create folders and files.
answered Apr 9, 2016 at 19:07
veer7veer7
20.2k9 gold badges46 silver badges75 bronze badges
Cygwin lets you run certain commands, such as cd, ls, or mv; but it doesn’t let you run other commands, such as sudo or apt-get.
-
If you’re trying to add a package to your Cygwin installation, rerun Cygwin Setup. It may still be in your «Downloads» folder. Go through all the steps again. The Cygwin installer will automatically download and install the package you want, and add it to your Cygwin installation. (I think it will probably also upgrade all your other installed Cygwin packages to the latest available versions.)
-
If your desired package isn’t on the Cygwin package list but is on the Cygwin Ports package list, follow the Cygwin Ports installation instructions. Note that Cygwin Ports is separate from Cygwin. Please do not send messages about Cygwin Ports packages to the cygwin.com mailing lists.
-
If you have years of Linux experience, you may be able to compile the software you want inside Cygwin. This can be challenging.
-
Perhaps an option simpler than «compile it yourself» is this: You can install VirtualBox, then install your favorite Linux distribution inside the virtual machine, then install your desired package inside Linux. (I like Ubuntu Linux, which has more than 27,000 packages in its «Universe» repository.) Now you can run Linux and Windows at the same time.
answered Mar 20, 2017 at 3:25
I think I tried steps below after doing some research & succeeded (on windows)
1.Install scoop using powershell 3 (iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring(‘https://get.scoop.sh’))
2. do scoop install —global sudo
3. make sure paths (C:\Users\\scoop\shims & C:\ProgramData\scoop\shims) added in environmental path variable.
answered Jul 9, 2017 at 11:38
In my case, I wanted to install curl, but could not create directory /usr/local/curl/lib when running command «make install», because of permission deny. so i need to change /usr/local permission. when i run sudo chmod 755 /usr/local, sudo command not found.
after searching a few solution, found that sudo is not installed by default in Cygwin. But I tried the solution that Aimal gave which is to run Cygwin as administrator. I finally can change the folder permission. Thanks Aimal.
answered Nov 24, 2015 at 16:05
Leung Ying YingLeung Ying Ying
8461 gold badge7 silver badges5 bronze badges
1
Sudo (Elevate) for Windows™
I do a lot of work on the command line in Windows™.
In Cygwin itself I believe you can run a root command with su -c /the/cmd as for sudo itself within Windows™ file-system elevating the user’s permissions from the command line, If you are an administrator, this will work great for you. Otherwise, use runas and get admin’s pass ;).
Now I cannot remember where we got this code but here it is. I hope it helps.
BTW, the package we use to compile this was gcc-mingw32.
$ i586-mingw32msvc-gcc sudo.c -o sudo.exe
# Put sudo.exe in /usr/bin or in your windows path (%homedrive%\windows)
#example:
$ sudo vi /cygdrive/c/windows/system32/drivers/etc/hosts
/**
* (sudo for Windows™)
* @filename sudo.c
*/
#ifndef UNICODE
#define UNICODE
#endif
#include <windows.h>
#include <shellapi.h>
#include <wchar.h>
LPWSTR *mergestrings(LPWSTR *left, LPCWSTR right)
{
size_t size = ( 1 + lstrlen(*left) + lstrlen(right) ) * sizeof(LPWSTR*);
if ( *left ) {
LPWSTR leftcopy = _wcsdup(*left);
*left = (LPWSTR)realloc(*left, size);
*left = lstrcpy(*left, leftcopy);
*left = lstrcat(*left, right);
free( leftcopy );
}
else
*left = _wcsdup(right);
return left;
}
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE prevInstance, LPSTR lpcommand, int nShowCmd)
{
DWORD result = 0x2a;
LPWSTR *argv = NULL;
int argc = 0;
if ( argv = CommandLineToArgvW(GetCommandLineW(), &argc) ) {
if ( argc < 2 ) {
LPWSTR usagemsg = NULL;
usagemsg = *mergestrings(&usagemsg, argv[0]);
usagemsg = *mergestrings(&usagemsg, TEXT(" <command_to_run> [arguments]"));
MessageBox(NULL, usagemsg, TEXT("Usage:"), MB_OK | MB_ICONEXCLAMATION );
LocalFree( argv );
free( usagemsg );
return ERROR_BAD_ARGUMENTS;
}
else {
LPWSTR command = argv[1];
LPWSTR arguments = NULL;
int c;
for ( c = 2; c < argc; c++ ) {
arguments = *mergestrings(&arguments, argv[c]);
arguments = *mergestrings(&arguments, TEXT(" "));
}
result = (DWORD)ShellExecute(NULL, TEXT("runas"), command, arguments, NULL, SW_SHOWNORMAL);
LocalFree( argv );
if ( arguments )
free( arguments );
switch ( result )
{
case 0:
result = ERROR_OUTOFMEMORY;
break;
case 27:
case 31:
result = ERROR_NO_ASSOCIATION;
break;
case 28:
case 29:
case 30:
result = ERROR_DDE_FAIL;
break;
case 32:
result = ERROR_DLL_NOT_FOUND;
break;
default:
if ( result > 32 )
result = 0x2a;
}
}
}
else
result = GetLastError();
if (result != 0x2a) {
LPWSTR errormsg = NULL;
FormatMessage(FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER,
NULL, result, 0, (LPWSTR)&errormsg, 0, NULL);
MessageBox(NULL, errormsg, TEXT("Error:"), MB_OK | MB_ICONERROR);
LocalFree( errormsg );
return result;
}
else
return NO_ERROR;
}
В Windows нет sudo, apt или, если быть точным, почти любых команд Linux. Cygwin может разрешить некоторые из них, но поскольку программы не установлены в Windows, пакеты apt-get работать не будут. Программы для Windows имеют установочные файлы в формате .exe или .msi.
Версия sudo для Windows называется runas на тот случай, если вам нужно запустить что-то от имени другого пользователя. Или вы можете запустить Cygwin от имени администратора.
Если вам нужно использовать пакеты, вам понадобится Linux. Вы можете установить его напрямую, чтобы заменить Windows, с двойной загрузкой или использовать программное обеспечение виртуализации, такое как VMware VirtualBox.
person
PurkkaKoodari
schedule
20.03.2014
comment
Как вы думаете, можно ли установить пакеты через Cygwin, используя runas, а затем скопировать их на машину с Linux? Проблема в том, что у моей Linux-машины нет подключения к Интернету, и у меня больше нет административных прав для этой машины.
— person Adam; 20.03.2014
comment
@Mahmoud Нет, поскольку в Windows нет команд для установки пакетов. Кроме того, установка пакетов на компьютер A и копирование полученных файлов на компьютер B часто может привести к неправильной настройке.
— person PurkkaKoodari; 20.03.2014
comment
Спасибо. Это то, о чем я думал.
— person Adam; 20.03.2014
There are many scenarios when you get “sudo command not found error” and you keep looking for solutions on the internet to fix it. One of the common examples, when you have installed Debian with a minimal package and trying to run sudo. For me whenever I try to ssh into any of the remote servers and run sudo, I get this “bash: sudo commands not found error”. So I decided to write a post, which covers all the scenarios of this famous error.
Below mentioned errors will be covered in this post. so if you are getting any of the following errors, this post will definitely solve your error –
- sudo command not found mac
- sudo command not found ubuntu
- sudo command not found debian
- zsh sudo command not found
- sudo command not found windows
- sudo command not found centos
- bash: /usr/bin/sudo: No such file or directory
These are the common scenarios that result in this error –
- You have installed a linux distribution with minimal package like Debian
- Sudo is not installed
- Path is not setup for sudo command
- You are trying to ssh a remote server first time and sudo is not working
Before getting into the solutions, if you are a newbie let’s understand why sudo is used?
Why sudo is used in Linux before every command?
Sudo is one of the famous prefixes to any command you run in the Linux world. It allows running any Linux command with elevated privileges to run administrative tasks. Also, the operations which are only permitted by a root user can be done using a normal user with sudo rights. The “sudoers” file controls, who can use the sudo command to gain elevated access and location is /etc/sudoers in all Linux distributions.
How to fix sudo command not found error in Debian/Ubuntu like Distros
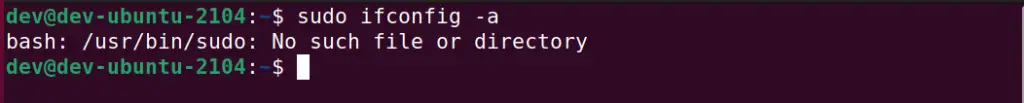
As we discussed already, there may be many reasons to encounter this error. As you will see in the image, running the “sudo ifconfig -a” command results in “bash: /usr/bin/sudo: No such file or directory error“. I am running this command in Ubuntu 21.04 installed as VM.
Let’s deep dive and find the fixes for different scenarios –
Solution-1 Check and install sudo package
This is very uncommon when sudo is not installed by default with Linux installation. Still, you may get this situation when you have installed the Debian Linux with the minimal package. Follow these steps to fix it –
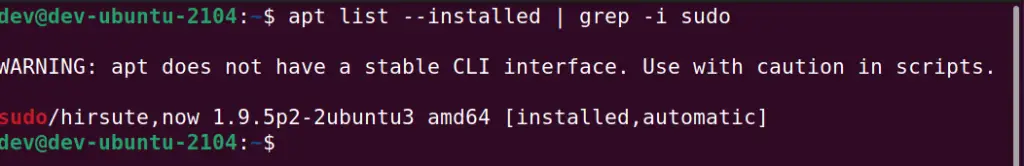
Step1.1 List installed packages in Ubuntu and look for the “sudo” package
$ apt list --installed | grep -i sudo
If you can find package name sudo with “installed” status as shown in the image. Then you can directly move to solution-2 to fix the “sudo: command not found error“.
If you don’t have the sudo package installed, run the following command to install it in Ubuntu or Debian based distros. You would need root access to achieve this.
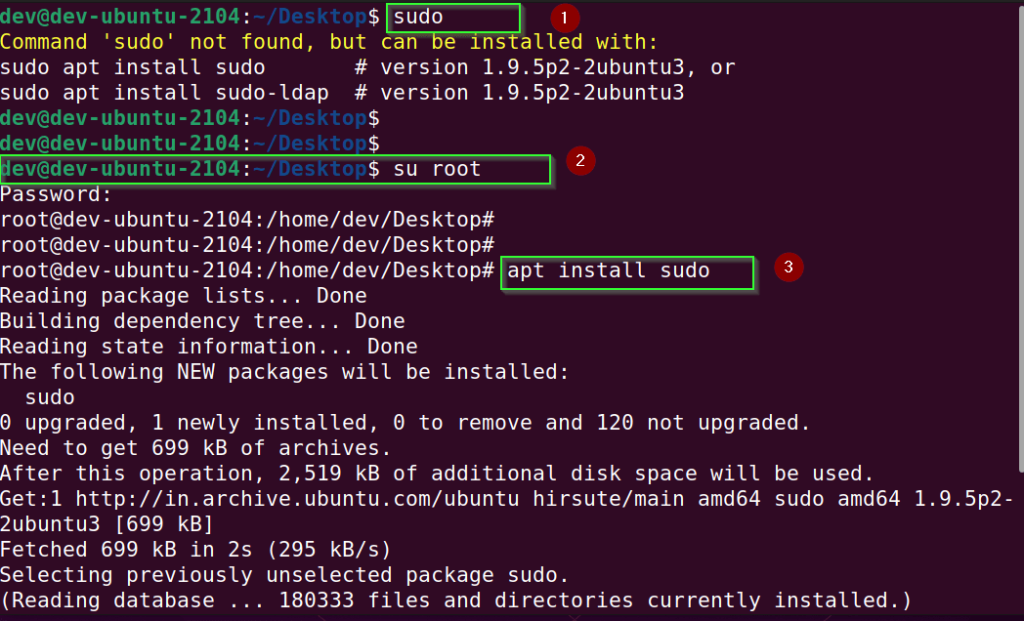
Step1.2 Switch to root user
$ su root
Enter “root” password, when prompted.
If you don’t have a root password, then follow this link to reset your root password.
Step1.3 Run apt command to install sudo package in Ubuntu/Debian
# apt install sudo
Refer to the following image for reference.
Step1.4 Give sudo rights to your own user by adding it to the sudo group
# usermod -aG sudo yourusername
For example, I will add my user “dev” to sudo group –
# usermode -aG sudo dev
Step1.5 Verify your user is added to the sudo group
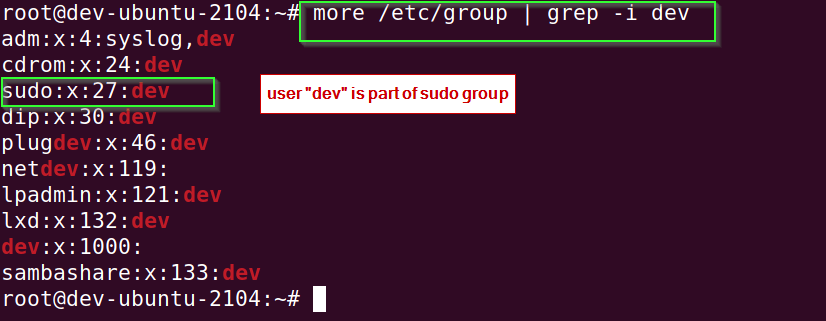
Open /etc/passwd file and check whether your user is added to the sudo group or not.
# cat /etc/group | grep -i username
I will check for my user “dev” in this example.
# more /etc/group | grep -i username
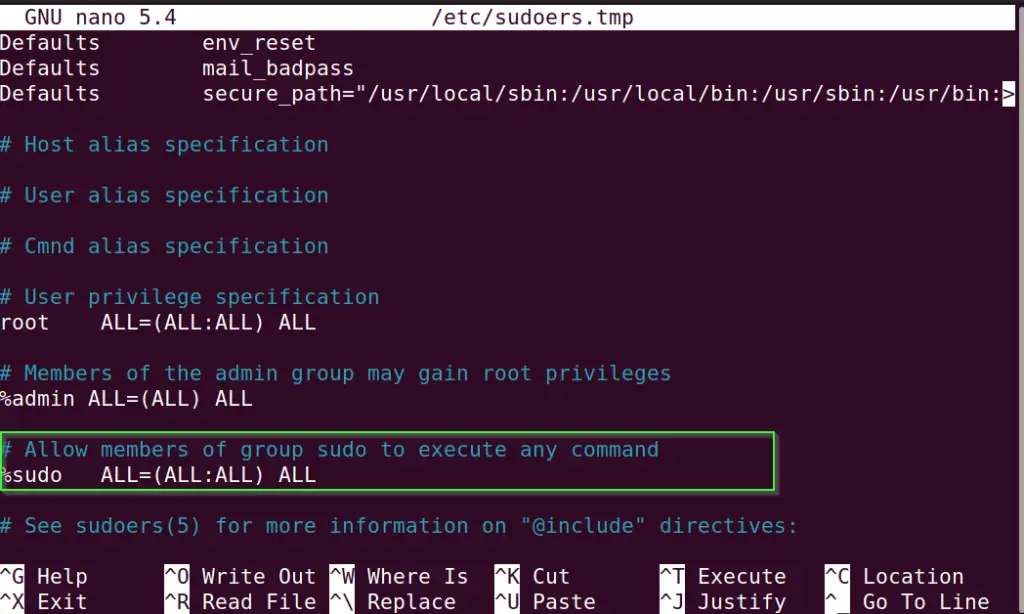
Step1.6 Make sure your sudoers file have sudo group added
- Run
visudocommand to modify sudoers file and add the following line into it (if it is missing):
# Allow members of group sudo to execute any command
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALLPress Ctrl + X and press “Y” to save the file and exit from the nano editor.
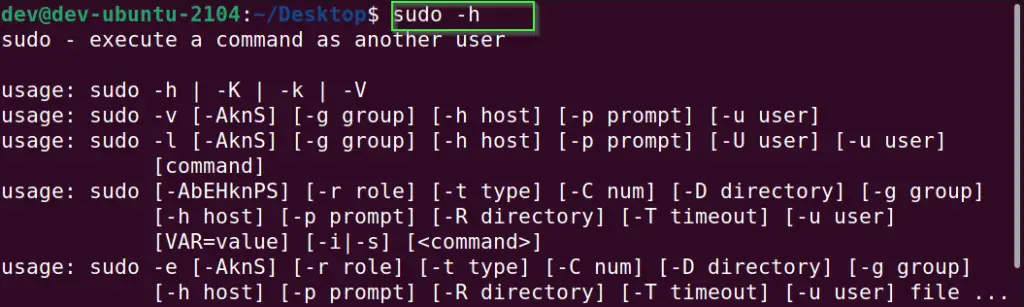
Exit from the root shell and check the sudo command functionality.
- Run sudo -h command. Now you will not get any “sudo command not found error” as it’s fixed now.
Solution2 – Setup path variable to fix sudo command not found errors
If you have a sudo package installed as explained in Step 1.1 and still you are getting sudo command not found error. It means you don’t have “/usr/bin/” setup in the PATH variable or your /etc/environment file got messed up.
To add sudo in your Path variable, add /usr/bin/ directory by following the method.
Step2.1 Switch to root user
$ su root
Enter root user password, when asked.
Step2.2 Run /usr/bin/sudo command to check whether it’s working or not
# /usr/bin/sudo -h
Step2.3 Edit /etc/environment file and add “/usr/bin" directory in PATH
# vi /etc/environment
Alternatively, you can also run export command to set up the path variable
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/binIn case you are getting visudo and usermod command not found errors also. Make sure you add /usr/sbin in the PATH variable as shown in the last step.
Fix “sudo command not found error” in Fedora/AlmaLinux/Rocky Linux Distros
This section covers sudo error for all the Linux distros based on RedHat like Fedora, AlmaLinux, CentOS and Rocky Linux. I have Rocky Linux Installed as a virtual machine. The procedure is the same as explained earlier, Look for the package, install it and set the path variable, if required. But the commands will differ now.
Solution3- Install sudo and add user to “Wheel” group to fix sudo errors
You have the option to set up sudo during installation in RedHat based Linux distros. But if you forgot to do that, You must have access to the root user to set up sudo for your user.
Step3.1 – Login with root user and check for sudo package installation
Follow this link to reset your root password, in case you forgot or don’t have it.
Once you are done with login as root, open Terminal and type
# yum list installed | grep -i sudo
If you get the sudo package installed already skip to the next step3.3.
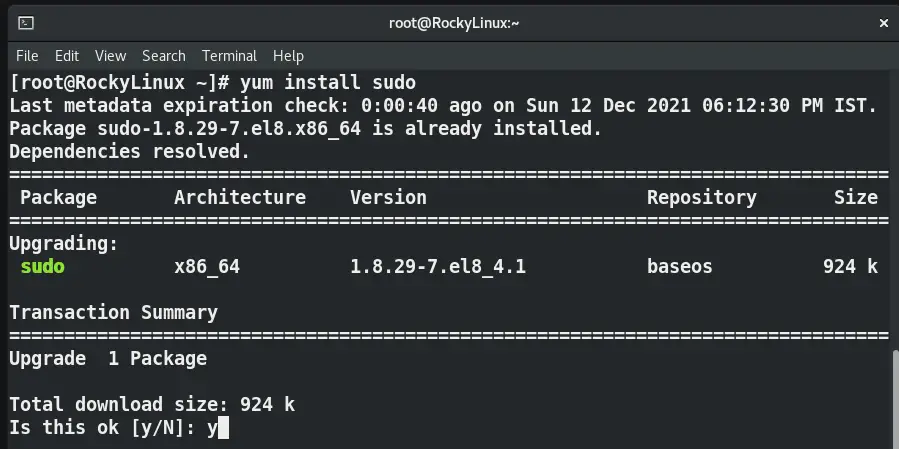
Step3.2 Install sudo package
You can use the “yum” or “dnf” command to install any package from the repository.
Update all old packages and refresh the repository.
# dnf update
Then install the sudo package using the dnf or yum command.
# yum install sudo or # dnf install sudo
Step3.3 Add user to the wheel group
The wheel group is already set to provide sudo access to run all commands. So is the quickest way is to add your user to this group. Switch to the root user first using su command
su -
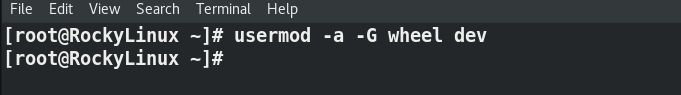
Now run usermod command to add your user in the wheel group.
# usermod -a -G wheel "username"
For example, I will add my user “dev” as an example
# usermod -a -G wheel "dev"
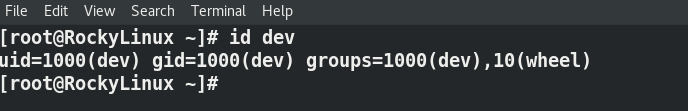
Step4.4 Check with the id command
Next, run the id command to see whether your user is part of the wheel group or not.
# id "username"
Example: My user dev is part of 10(wheel) the group.
# id dev
Congrats! you must have fixed your “sudo command not found error ” now and you can run all your privileged commands using sudo.
Frequently asked questions on sudo
Q1: Why is sudo not working?
These are many reasons when sudo may not work –
1. You don’t have a sudo package installed
2. If the sudo package is installed then the path variable is not set up correctly
3. Your system got broken and all your packages and permissions got messed up
4. Your user is not added to the sudo or wheel group based on your Linux distro.
Q2: How do I enable sudo?
If the sudo package is already installed based on your Linux distro run the following command. Replace “dev” with your username.
for Ubuntu and Debian based distros –
$ su root
Then run the usermod command to add your user to the sudo group
# usermode -aG sudo dev
For RedHat based distros –
Switch to root (superuser)
$ su -
Add to the wheel group.
# usermod -a -G wheel dev
Q3: How do I find sudo commands?
Open terminal and type sudo -h. It will show you all the sudo command options and arguments. You can also type man sudo to get the manual of the sudo command.
Q4: How do I fix sudo command not found Mac?
Run the following sequence of commands to fix the sudo command not found error in macOS.
1. Check the syntax of command and spelling of sudo, so that you are sure, you are not running the misspelt command
2. switch to root user$ su -
3. Run the following command
In the case of OS prior to Catalina
# visudo /etc/sudoers
in the case of Catalina
# visudo /private/etc/sudoers
4. Add your user as follows in sudoers file –
username ALL=(ALL) ALL
replace username with your user. e.g John
Save and exit sudoers file
5. reopen the terminal and it will fix all your zsh: sudo command not found error in macOS.
Q5: Do I need to install sudo?
By default all the Linux or Unix distros have sudo installed. But in case you don’t, then you must install sudo. it is the recommended way to use root privileged commands (only when required) and helps to avoid mistakes that can break your system.
Ending Note
I have covered all the possible solutions to fix the sudo command not found error and I hope this tutorial is helpful to you. In case, none of the solutions works for you and your system has broken severly, Either re-install your system or let me know the issue via your comments.
I will try to help you to the best of my knowledge.
Keep Learning!!