Mega Collection of PowerShell Scripts
It includes 500+ useful cross-platform PowerShell scripts located in the 📂Scripts subfolder — for the command-line interface (CLI), for remote control via SSH, for automation (e.g. AutoHotkey or Jenkins), for context menus, for voice commands (e.g. talk2windows), automatically on startup/login/logoff/daily/shutdown/etc., or simply to learn PowerShell.
Download | Table of Scripts | FAQ | Note: the scripts support Unicode — a modern console is recommended (e.g. Windows Terminal)
🔊 Scripts for Audio & Voice
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| list-voices.ps1 | Lists the installed text-to-speech voices. Read more… |
| play-beep-sound.ps1 | Plays a short beep sound. Read more… |
| play-files.ps1 | Plays the given audio files. Read more… |
| play-happy-birthday.ps1 | Plays the Happy Birthday song. Read more… |
| play-imperial-march.ps1 | Plays the Imperial March (Star Wars). Read more… |
| play-jingle-bells.ps1 | Plays Jingle Bells. Read more… |
| play-mission-impossible.ps1 | Plays the Mission Impossible theme. Read more… |
| play-m3u.ps1 | Plays the given playlist (M3U file format). Read more… |
| play-mp3.ps1 | Plays the given sound file (MP3 file format). Read more… |
| play-super-mario.ps1 | Plays the Super Mario intro. Read more… |
| play-tetris-melody.ps1 | Plays the Tetris melody. Read more… |
| speak-checklist.ps1 | Speaks the given checklist by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| speak-countdown.ps1 | Starts a countdown by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| speak-english.ps1 | Speaks text with an English text-to-speech voice. Read more… |
| speak-epub.ps1 | Speaks the content of the given Epub file by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| speak-file.ps1 | Speaks the content of the given text file by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| speak-french.ps1 | Speaks text with a French text-to-speech voice. Read more… |
| speak-german.ps1 | Speaks text with a German text-to-speech voice. Read more… |
| speak-italian.ps1 | Speaks text with an Italian text-to-speech voice. Read more… |
| speak-spanish.ps1 | Speaks text with a Spanish text-to-speech voice. Read more… |
| speak-test.ps1 | Performs a speak test by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| speak-text.ps1 | Speaks the given text by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| tell-joke.ps1 | Tells a random joke by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| tell-quote.ps1 | Tells a random quote by text-to-speech. Read more… |
| turn-volume-down.ps1 | Turns the audio volume down. Read more… |
| turn-volume-fully-up.ps1 | Turns the audio volume fully up. Read more… |
| turn-volume-off.ps1 | Turns audio off. Read more… |
| turn-volume-on.ps1 | Turns audio on. Read more… |
| turn-volume-up.ps1 | Turns the audio volume up. Read more… |
⚙️ Scripts to Manage Computers
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| add-firewall-rules.ps1 | Adds firewall rules for executables, needs admin rights. Read more… |
| check-cpu.ps1 | Checks the CPU temperature. Read more… |
| check-dns.ps1 | Checks the DNS resolution. Read more… |
| check-drive-space.ps1 | Checks a drive for free space left. Read more… |
| check-file-system.ps1 | Checks the file system of a drive (needs admin rights). Read more… |
| check-health.ps1 | Checks the system health. Read more… |
| check-ping.ps1 | Checks the ping latency to the internet. Read more… |
| check-swap-space.ps1 | Checks the swap space for free space left. Read more… |
| check-windows-system-files.ps1 | Checks the validity of the Windows system files (needs admin rights). Read more… |
| enable-crash-dumps.ps1 | Enables the writing of crash dumps. Read more… |
| hibernate.ps1 | Hibernates the local computer immediately. Read more… |
| install-github-cli.ps1 | Installs GitHub CLI. Read more… |
| install-chrome-browser.ps1 | Installs the Google Chrome browser. Read more… |
| firefox-installer.ps1 | Installs the firefox browser. Read more… |
| install-knot-resolver.ps1 | Installs the Knot Resolver (needs admin rights). Read more… |
| install-ssh-client.ps1 | Installs a SSH client (needs admin rights). Read more… |
| install-ssh-server.ps1 | Installs a SSH server (needs admin rights). Read more… |
| install-signal-cli.ps1 | Installs signal-cli from github.com/AsamK/signal-cli. Read more… |
| install-updates.ps1 | Installs updates (need admin rights). Read more… |
| install-wsl.ps1 | Installs Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), needs admin rights. Read more… |
| list-apps.ps1 | Lists the installed applications. Read more… |
| list-cli-tools.ps1 | Lists installed command-line interface (CLI) tools. Read more… |
| list-dns-servers.ps1 | Lists public DNS servers. Read more… |
| list-drives.ps1 | Lists all drives. Read more… |
| list-network-shares.ps1 | Lists all network shares of the local computer. Read more… |
| list-installed-software.ps1 | Lists the installed software. Read more… |
| list-printers.ps1 | Lists all printer known to the computer. Read more… |
| list-print-jobs.ps1 | Lists all jobs of all printers. Read more… |
| list-processes.ps1 | Lists the local computer processes. Read more… |
| list-services.ps1 | Lists the services on the local computer. Read more… |
| list-system-info.ps1 | Lists system information on the local computer. Read more… |
| list-tasks.ps1 | Lists all Windows scheduler tasks. Read more… |
| list-timezone.ps1 | Lists the current time zone details. Read more… |
| list-timezones.ps1 | Lists all time zones available. Read more… |
| list-user-groups.ps1 | Lists the user groups on the local computer. Read more… |
| poweroff.ps1 | Halts the local computer (needs admin rights). Read more… |
| query-smart-data.ps1 | Queries the S.M.A.R.T. data of your HDD/SSD’s. Read more… |
| reboot.ps1 | Reboots the local computer (needs admin rights). Read more… |
| remove-print-jobs.ps1 | Removes all jobs from all printers. Read more… |
| restart-network-adapters.ps1 | Restarts all local network adapters. Read more… |
| upgrade-ubuntu.ps1 | Upgrades Ubuntu Linux to the latest (LTS) release. Read more… |
| wake-up.ps1 | Wakes up a computer using Wake-on-LAN. Read more… |
| WinDefender.ps1 | Turn off/on and check for real time monitoring of Windwos Defender. Read more… |
💻 Scripts for the Desktop
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| close-calculator.ps1 | Closes the calculator application. Read more… |
| close-cortana.ps1 | Closes Cortana. Read more… |
| close-chrome.ps1 | Closes the Google Chrome browser. Read more… |
| close-program.ps1 | Closes the given program gracefully. Read more… |
| close-edge.ps1 | Closes the Edge browser. Read more… |
| close-file-explorer.ps1 | Closes Microsoft File Explorer. Read more… |
| close-firefox.ps1 | Closes the Firefox browser. Read more… |
| close-microsoft-store.ps1 | Closes the Microsoft Store app. Read more… |
| close-netflix.ps1 | Closes the Netflix app. Read more… |
| close-onedrive.ps1 | Closes Microsoft OneDrive. Read more… |
| close-serenade.ps1 | Closes the Serenade application. Read more… |
| close-snipping-tool.ps1 | Closes the Snipping Tool application. Read more… |
| close-spotify.ps1 | Closes Spotify. Read more… |
| close-system-settings.ps1 | Closes the System Settings window. Read more… |
| close-task-manager.ps1 | Closes the Task Manager. Read more… |
| close-thunderbird.ps1 | Closes Mozilla Thunderbird. Read more… |
| close-vlc.ps1 | Closes the VLC media player application. Read more… |
| close-windows-terminal.ps1 | Closes the Windows Terminal application. Read more… |
| enable-god-mode.ps1 | Enables the god mode (adds a new icon to the desktop). Read more… |
| install-chrome.ps1 | Installs the Google Chrome browser. Read more… |
| install-firefox.ps1 | Installs the Firefox browser. Read more… |
| list-clipboard.ps1 | Lists the contents of the clipboard. Read more… |
| new-email.ps1 | Starts the default email client to write a new email. Read more… |
| open-amazon-website.ps1 | Opens Amazon’s website. Read more… |
| open-default-browser.ps1 | Launches the default Web browser. Read more… |
| open-calculator.ps1 | Starts the calculator program. Read more… |
| open-c-drive.ps1 | Opens the C: drive folder. Read more… |
| open-downloads-folders.ps1 | Opens the user’s downloads folder. Read more… |
| open-dropbox-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s Dropbox folder. Read more… |
| open-edge.ps1 | Launches the Edge browser. Read more… |
| open-email-client.ps1 | Starts the default email client. Read more… |
| open-facebook-website.ps1 | Opens Facebook’s website. Read more… |
| open-file-explorer.ps1 | Opens the File Explorer. Read more… |
| open-firefox.ps1 | Launches the Firefox browser. Read more… |
| open-fritz-box.ps1 | Opens FRITZ!Box’s web interface. Read more… |
| open-github.ps1 | Opens GitHub’s website. Read more… |
| open-google-contacts.ps1 | Opens Google Contacts. Read more… |
| open-google-earth.ps1 | Opens Google Earth. Read more… |
| open-google-mail.ps1 | Opens Google Mail. Read more… |
| open-google-maps.ps1 | Opens Google Maps. Read more… |
| open-google-news.ps1 | Opens Google News. Read more… |
| open-google-play.ps1 | Opens Google Play. Read more… |
| open-google-search.ps1 | Opens Google Search. Read more… |
| open-google-translate.ps1 | Opens Google Translate. Read more… |
| open-home-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s home folder. Read more… |
| open-music-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s music folder. Read more… |
| open-netflix.ps1 | Starts the Netflix app. Read more… |
| open-microsoft-store.ps1 | Launches the Microsoft Store app. Read more… |
| open-notepad.ps1 | Starts the Notepad app. Read more… |
| open-onedrive-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s OneDrive folder. Read more… |
| open-pictures-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s pictures folder. Read more… |
| open-recycle-bin.ps1 | Opens the user’s recycle bin folder. Read more… |
| open-repos-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s Git repositories folder. Read more… |
| open-snipping-tool.ps1 | Starts the Snipping Tool. Read more… |
| open-speed-test.ps1 | Opens Cloudflare’s speed test. Read more… |
| open-spotify.ps1 | Opens Spotify. Read more… |
| open-system-settings.ps1 | Opens the system settings of Windows. Read more… |
| open-task-manager.ps1 | Starts the Task Manager. Read more… |
| open-videos-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s videos folder. Read more… |
| open-windows-terminal.ps1 | Launches Windows Terminal. Read more… |
| open-wikipedia-website.ps1 | Opens Wikipedia’s website. Read more… |
| open-youtube-website.ps1 | Opens YouTube’s website. Read more… |
| remind-me.ps1 | Creates a scheduled task that will display a popup message. Read more… |
| save-screenshot.ps1 | Saves a single screenshot. Read more… |
| set-wallpaper.ps1 | Sets the given image as wallpaper. Read more… |
📁 Scripts for Files & Folders
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| cd-autostart.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s autostart folder. Read more… |
| cd-desktop.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s desktop folder. Read more… |
| cd-docs.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s documents folder. Read more… |
| cd-downloads.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s downloads folder. Read more… |
| cd-dropbox.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s Dropbox folder. Read more… |
| cd-home.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s home folder. Read more… |
| cd-music.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s music folder. Read more… |
| cd-onedrive.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s OneDrive folder. Read more… |
| cd-pics.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s pictures folder. Read more… |
| cd-recycle-bin.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s recycle bin folder. Read more… |
| cd-repos.ps1 | Change the working directory to the user’s Git repositories folder. Read more… |
| cd-root.ps1 | Set the working directory to the root directory. Read more… |
| cd-scripts.ps1 | Set the working directory to the PowerShell Scripts folder. Read more… |
| cd-ssh.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s SSH folder. Read more… |
| cd-up.ps1 | Set the working directory to one directory level up. Read more… |
| cd-up2.ps1 | Set the working directory to two directory levels up. Read more… |
| cd-up3.ps1 | Set the working directory to three directory levels up. Read more… |
| cd-up4.ps1 | Set the working directory to four directory levels up. Read more… |
| cd-videos.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s videos folder. Read more… |
| check-symlinks.ps1 | Checks every symlink in a directory tree. Read more… |
| check-xml-file.ps1 | Checks the given XML file for validity. Read more… |
| clear-recycle-bin.ps1 | Removes the content of the recycle bin folder (can not be undo!). Read more… |
| copy-photos-sorted.ps1 | Copy image files sorted by year and month. Read more… |
| decrypt-file.ps1 | Decrypts the given file. Read more… |
| download-dir.ps1 | Downloads a directory tree from the given URL. Read more… |
| download-file.ps1 | Downloads a file from the given URL. Read more… |
| edit.ps1 | Edits the given file with the built-in text editor. Read more… |
| encrypt-file.ps1 | Encrypts the given file. Read more… |
| get-md5.ps1 | Prints the MD5 checksum of the given file. Read more… |
| get-sha1.ps1 | Prints the SHA1 checksum of the given file. Read more… |
| get-sha256.ps1 | Prints the SHA256 checksum of the given file. Read more… |
| inspect-exe.ps1 | Prints basic information of the given executable file. Read more… |
| list-dir-tree.ps1 | Lists the directory tree content. Read more… |
| list-empty-dirs.ps1 | Lists empty subfolders within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| list-empty-files.ps1 | Lists empty files within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| list-files.ps1 | Lists all files in the given folder and also in every subfolder. Read more… |
| list-folder.ps1 | Lists the folder content. Read more… |
| list-hidden-files.ps1 | Lists hidden files within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| list-recycle-bin.ps1 | Lists the content of the recycle bin folder. Read more… |
| list-unused-files.ps1 | Lists unused files in a directory tree. Read more… |
| list-workdir.ps1 | Lists the current working directory. Read more… |
| make-install.ps1 | Installs built executables and libs to the installation directory. Read more… |
| new-shortcut.ps1 | Creates a new shortcut file. Read more… |
| new-symlink.ps1 | Creates a new symbolic link file. Read more… |
| new-zipfile.ps1 | Creates a new .zip file from a directory. Read more… |
| publish-to-ipfs.ps1 | Publishes the given files or directory to IPFS. Read more… |
| remove-empty-dirs.ps1 | Removes empty subfolders within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| replace-in-files.ps1 | Search and replace a pattern in the given files by the replacement. Read more… |
| search-filename.ps1 | Searches the directory tree for filenames by given pattern. Read more… |
| search-files.ps1 | Searches the given pattern in the given files. Read more… |
| upload-file.ps1 | Uploads the local file to the given FTP server. Read more… |
♻️ Scripts to Convert Files
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| convert-csv2txt.ps1 | Converts a .CSV file to a text file. Read more… |
| convert-mysql2csv.ps1 | Converts a MySQL database table to a .CSV file. Read more… |
| convert-ps2bat.ps1 | Converts a PowerShell script to a Batch script. Read more… |
| convert-ps2md.ps1 | Converts the comment-based help of a PowerShell script to Markdown. Read more… |
| convert-sql2csv.ps1 | Converts a SQL database table to a .CSV file. Read more… |
| convert-txt2wav.ps1 | Converts text to a .WAV audio file. Read more… |
| export-to-manuals.ps1 | Exports all scripts as manuals. Read more… |
📝 Scripts for Git
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| build-repo.ps1 | Builds a Git repository. Read more… |
| build-repos.ps1 | Builds all Git repositories in a folder. Read more… |
| check-repo.ps1 | Checks a Git repository. Read more… |
| clean-repo.ps1 | Cleans a Git repository from untracked files. Read more… |
| clean-repos.ps1 | Cleans all Git repositories in a folder from untracked files. Read more… |
| clone-repos.ps1 | Clones well-known Git repositories. Read more… |
| configure-git.ps1 | Sets up the Git user configuration. Read more… |
| fetch-repo.ps1 | Fetches updates for a Git repository. Read more… |
| fetch-repos.ps1 | Fetches updates for all Git repositories in a folder. Read more… |
| list-branches.ps1 | Lists all branches in a Git repository. Read more… |
| list-commits.ps1 | Lists all commits in a Git repository. Read more… |
| list-latest-tag.ps1 | Lists the latest tag on the current branch in a Git repository. Read more… |
| list-latest-tags.ps1 | Lists the latests tags in all Git repositories under a directory. Read more… |
| list-repos.ps1 | Lists the Git repositories in a folder. Read more… |
| list-submodules.ps1 | Lists the submodules in a Git repository. Read more… |
| list-tags.ps1 | Lists all tags in a Git repository. Read more… |
| new-branch.ps1 | Creates a new branch in a Git repository. Read more… |
| new-tag.ps1 | Creates a new tag in a Git repository. Read more… |
| pick-commit.ps1 | Cherry-picks a Git commit into multiple branches. Read more… |
| pull-repo.ps1 | Pulls updates for a Git repository. Read more… |
| pull-repos.ps1 | Pulls updates for all Git repositories in a folder. Read more… |
| remove-tag.ps1 | Removes a tag in a Git repository. Read more… |
| switch-branch.ps1 | Switches the branch in a Git repository. Read more… |
| sync-repo.ps1 | Synchronizes a Git repository by pull & push. Read more… |
🔎 Scripts for PowerShell
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| daily-tasks.sh | Execute PowerShell scripts automatically as daily tasks (Linux only). Read more… |
| introduce-powershell.ps1 | Introduces PowerShell to new users. Read more… |
| list-aliases.ps1 | Lists all PowerShell aliases. Read more… |
| list-automatic-variables.ps1 | Lists the automatic variables of PowerShell. Read more… |
| list-cheat-sheet.ps1 | Lists the PowerShell cheat sheet. Read more… |
| list-cmdlets.ps1 | Lists the PowerShell cmdlets. Read more… |
| list-console-colors.ps1 | Lists all console colors. Read more… |
| list-modules.ps1 | Lists the PowerShell modules. Read more… |
| list-profiles.ps1 | Lists your PowerShell profiles. Read more… |
| list-scripts.ps1 | Lists all PowerShell scripts in this repository. Read more… |
| new-script.ps1 | Creates a new PowerShell script. Read more… |
| set-profile.ps1 | Updates your PowerShell user profile. Read more… |
🛒 Various PowerShell Scripts
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| add-memo.ps1 | Adds the given memo text to $HOME/Memos.csv. Read more… |
| check-ipv4-address.ps1 | Checks the given IPv4 address for validity. Read more… |
| check-ipv6-address.ps1 | Checks the given IPv6 address for validity. Read more… |
| check-mac-address.ps1 | Checks the given MAC address for validity. Read more… |
| check-subnet-mask.ps1 | Checks the given subnet mask for validity. Read more… |
| check-weather.ps1 | Checks the current weather for critical values. Read more… |
| display-time.ps1 | Displays the current time for 10 seconds by default. Read more… |
| list-anagrams.ps1 | Lists all anagrams of the given word. Read more… |
| list-city-weather.ps1 | Lists the current weather of cities worldwide (west to east). Read more… |
| list-countries.ps1 | Lists details of all countries. Read more… |
| list-credits.ps1 | Shows the credits. Read more… |
| list-crypto-rates.ps1 | Lists the current crypto exchange rates. Read more… |
| list-environment-variables.ps1 | Lists all environment variables. Read more… |
| list-emojis.ps1 | Lists the emojis of Unicode 13.0. Read more… |
| list-fritzbox-calls.ps1 | Lists the FRITZ!Box calls. Read more… |
| list-fritzbox-devices.ps1 | Lists FRITZ!Box’s known devices. Read more… |
| list-earthquakes.ps1 | Lists earthquakes with magnitude >= 6.0 for the last 30 days. Read more… |
| list-exchange-rates.ps1 | Lists the current exchange rates for the given currency. Read more… |
| list-memos.ps1 | Lists the memos at $HOME/Memos.csv. Read more… |
| list-mysql-tables.ps1 | Lists the MySQL server tables. Read more… |
| list-news.ps1 | Lists the latest news. Read more… |
| list-os-releases.ps1 | Lists operating system releases and download URL. Read more… |
| list-os-updates.ps1 | Lists operating system updates. Read more… |
| list-passwords.ps1 | Prints a list of random passwords. Read more… |
| list-pins.ps1 | Prints a list of random PIN’s. Read more… |
| list-sql-tables.ps1 | Lists the SQL server tables. Read more… |
| list-tiobe-index.ps1 | Lists the TIOBE index of top programming languages. Read more… |
| list-weather.ps1 | Lists the hourly weather. Read more… |
| locate-city.ps1 | Prints the geographic location of the given city. Read more… |
| locate-ipaddress.ps1 | Prints the geographic location of the given IP address. Read more… |
| locate-zip-code.ps1 | Prints the geographic location of the given zip-code. Read more… |
| moon.ps1 | Prints the current moon phase. Read more… |
| new-qrcode.ps1 | Generates a new QR code image file. Read more… |
| reboot-fritzbox.ps1 | Reboots the FRITZ!box device. Read more… |
| scan-ports.ps1 | Scans the network for open/closed ports. Read more… |
| send-email.ps1 | Sends an email message. Read more… |
| send-tcp.ps1 | Sends a TCP message to the given IP address and port. Read more… |
| send-udp.ps1 | Sends a UDP datagram message to the given IP address and port. Read more… |
| set-timer.ps1 | Sets a timer for a countdown. Read more… |
| simulate-presence.ps1 | Simulates the human presence against burglars. Read more… |
| start-calibre-server.ps1 | Starts a local Calibre server. Read more… |
| start-ipfs-server.ps1 | Starts a local IPFS server. Read more… |
| switch-shelly1.ps1 | Switches a Shelly1 device in the local network. Read more… |
| translate-file.ps1 | Translates the given text file into other languages. Read more… |
| translate-files.ps1 | Translates the given text files into any supported language. Read more… |
| translate-text.ps1 | Translates the given text in English into other languages. Read more… |
| weather.ps1 | Prints the current weather forecast. Read more… |
| weather-report.ps1 | Prints the local weather report. Read more… |
| what-is.ps1 | Prints a description of the given abbreviation. Read more… |
| write-animated.ps1 | Writes animated text. Read more… |
| write-big.ps1 | Writes the given text in big letters. Read more… |
| write-blue.ps1 | Writes the given text in a blue foreground color. Read more… |
| write-braille.ps1 | Writes the given text in Braille. Read more… |
| write-calendar.ps1 | Writes the calendar (month of year). Read more… |
| write-green.ps1 | Writes the given text in a green foreground color. Read more… |
| write-joke.ps1 | Writes a random Juck Norris joke. Read more… |
| write-lowercase.ps1 | Writes the given text in lowercase letters. Read more… |
| write-marquee.ps1 | Writes the given text as marquee. Read more… |
| write-morse-code.ps1 | Writes the given text in Morse code. Read more… |
| write-motd.ps1 | Writes the message of the day (MOTD). Read more… |
| write-quote.ps1 | Writes a random quote. Read more… |
| write-red.ps1 | Writes the given text in a red foreground color. Read more… |
| write-rot13.ps1 | Encodes or decodes the given text with ROT13. Read more… |
| write-typewriter.ps1 | Writes the given text with the typewriter effect. Read more… |
| write-uppercase.ps1 | Writes the given text in uppercase letters. Read more… |
| write-vertical.ps1 | Writes the given text in vertical direction. Read more… |
📧 Feedback
Send your email feedback to: markus.fleschutz [at] gmail.com
🤝 License & Copyright
This open source project is licensed under the CC0-1.0 license. All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Ниже я собрал некоторые из лучших скриптов Active directory Powershell, которые, несомненно, сэкономят ваше время. Управление доменом – это работа Active Directory, и понимание каждого компонента является обязательным. Active Directory состоит из пользователей, групп, которые можно проверить в Active directory users and computers (ADUC). Создание пользователя в домене или сохранение пользователя в домене – это работа системного администратора windows.
Работая много лет, я столкнулся со многими проблемами в качестве системного администратора windows. Иногда создание пользователей или групп в домене занимает значительное время. Это процесс можно автоматизировать, чтобы сэкономить время. В данной статье есть скрипты DNS powershell, скрипты DHCP powershell.
Полезные команды Powershell для Active Directory
Получить всех пользователей AD в домене
Get-aduser -properties * -filter *
Модуль импорта Active Directory
Import-module activedirectory
Получить все компьютеры из домена
Get-adcomputer -properties * -filter *
Отключить пользователя AD по имени учетной записи SAM
Disable-ADaccount -identity "Name"
Экспорт данных в формат CSV
Get-adcomputer -properties * -filter * |export-csv "give path"
Получить имя учетной записи AD Groups SAM
Get-ADgroup -identity "provide group name"
Выбрать конкретный атрибут пользователя
Get-aduser -properties * -filter *
Получить информацию о домене
Get-ADdomain
Установите роль Active Directory
Install-windowsfeature AD-Domain-Services
Получить список контроллеров домена
Get-ADDomainController
Восстановление пользователей AD
Восстановление удаленного пользователя из контроллера домена. Иногда мы сталкиваемся со многими проблемами при очистке AD, иногда мы удаляем пользователей AD, и это создает хаос среди наших пользователей. Вот решение этой проблемы.
Как это работает
Предоставляем решение этой проблемы в виде скриптов Active Directory Powershell.
Вероятный результат
После запуска этого скрипта выполните поиск пользователя в dsa.msc, он должен вернуться без потери информации. Этот скрипт очень удобно использовать, и я предпочитаю использовать его вместо GUI.
AD-User Recover Powershell Scripts
###### Make sure the AD recyclebin is enabled ###### $Name=read-host "Enter the deleted user" Get-ADObject -Filter 'samaccountname -eq $name' -IncludeDeletedObjects | Restore-ADObject write-host "User $Name is recovered" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen
Добавление сервера в домен
Добавление сервера в домен, смена IP – это большая задача, которая иногда становится утомительной, так почему бы не автоматизировать ее. Скрипт работает безупречно и без каких-либо заминок. Это отличный вариант в категории скриптов Active Directory Powershell.
Как это работает
Обычно скрипт просит предоставить IP контроллера домена, что является главным требованием при добавлении сервера в домен. После этого он обычно просит указать имя домена, например xyz.com, и перезагружает сервер без предварительного запроса.
Вероятный результат
После запуска этого скрипта первым делом войдите в систему с доменными учетными данными, чтобы проверить, можете ли вы войти в систему или нет.
Adding Servers into Domain Powershell Scripts
## Pre-requisite:-
#1). Update the Primary DNS IP in the Network adapter before joining server\machine to domain by running below cmd.
## For single server\machine to be added to domain.
set-DnsClientServerAddress-InterfaceIndex 2 -ServerAddresses ("Primary DNS IP address")
set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias Ethernet -AddressFamily IPv4 |Select-Object ServerAddresses
#Once DNS IP is updated, then execute below cmd.
Add-Computer -ComputerName $computers -Domain "YourDomainName" -Restart
#Give your domain credentials in the credential request window.
***************************************************************************************************************************************
## For multiple server\machine to be added to domain.
set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceIndex 2 -ServerAddresses ("Primary DNS IP address")
set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias Ethernet -AddressFamily IPv4 |Select-Object ServerAddresses
#Once DNS IP is updated on machines, then execute below cmd.
$computers = Get-Content -Path c:\test\desktop\computers.txt
Add-Computer -ComputerName $computers -Domain "YourDomainName" -Restart
#Give your domain credentials in the credential request window.
Передача роли FSMO
Cкрипт просит указать предпочтение от 1 до 5, какую роль вы хотите назначить другому DC. Аналогично, если мы делаем это с помощью GUI, это долго, а через powershell это быстро и просто. В этом скрипте при успешной передаче вы получите сообщение об успешной передаче роли.
Вероятный результат
После запуска этого скрипта вы сможете перенести роли с одного DC на другой. Роли FSMO очень важны, поэтому делайте это очень осторожно.
FSMO Role Transfer Powershell Scripts
#Provide the destination DC in which you want to transfer the fsmo role
$destinationdc= Read-Host "Provide the Destination domain controller"
#Choose the role you want to transfer
$role=read-host "Choose the role"
Switch($role)
{
1 { $result = 'DomainNamingMaster'}
2 { $result = 'PDCEmulator'}
3 { $result = 'RIDMaster'}
4 { $result = 'SchemaMaster'}
5 { $result = 'InfrastructureMaster'}
6 {$result = 'All'}
}
if($role -gt 6)
{
Write-host "Choose correct option" -ForegroundColor Cyan
}
#This will transfer DomainNamingMaster role to destination server
if ($role -eq 1)
{
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole -OperationMasterRole DomainNamingMaster -Identity $destinationDc -confirm:$false
Write-host "$result is transferred successfully to $destinationDc" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor Cyan
netdom query fsmo |Select-String "Domain Naming Master"
}
#This will transfer PDCEmulator role to destination server
if ($role -eq 2)
{
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole -OperationMasterRole PDCEmulator -Identity $destinationDc -confirm:$false
Write-host "$result is transferred successfully to $destinationDc" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor Cyan
netdom query fsmo |Select-String "PDC"
}
#This will transfer RID pool manager role to destination server
if ($role -eq 3)
{
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole -OperationMasterRole RIDMaster -Identity $destinationDc -confirm:$false
Write-host "$result is transferred successfully to $destinationDc" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor Cyan
netdom query fsmo |Select-String "RID pool manager"
}
#This will transfer Schema Master role to destination server
if ($role -eq 4)
{
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole -OperationMasterRole SchemaMaster -Identity $destinationDc -confirm:$false
Write-host "$result is transferred successfully to $destinationDc" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor Cyan
netdom query fsmo |Select-String "Schema Master"
}
#This will transfer Infrastructure Master role to destination server
if ($role -eq 5)
{
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole -OperationMasterRole InfrastructureMaster -Identity $destinationDc -Credential -confirm:$false
Write-host "$result is transferred successfully to $destinationDc" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor Cyan
netdom query fsmo |Select-String "Infrastructure Master"
}
#This will transfer All roles to destination server
if ($role -eq 6)
{
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole -OperationMasterRole DomainNamingMaster,PDCEmulator,RIDMaster,SchemaMaster,InfrastructureMaster -Identity $destinationDc -confirm:$false
Write-host "$result roles are transferred successfully to $destinationDc" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor Cyan
netdom query fsmo
}
Отключение неактивных пользователей в AD
Отключение пользователей AD – это ежемесячная работа, и ее может быть трудно выполнить через графический интерфейс, если пользователей много. Я предлагаю вам сценарий, в котором вы можете отключить большое количество пользователей с помощью Powershell.
Как это работает
Скрипт запросит идентификатор пользователя, которого вы хотите отключить, а для массового отключения потребуется список пользователей, и он будет идентифицировать, используя учетную запись Sam. Выглядит просто, если использовать powershell, то да, это очень просто.
Disable Active directory User Powershell Scripts
#Wintel-AD-Disable Active Directory User:
#for single:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
Disable-ADAccount -Identity user1
#for bulk:
#imports active directory module to only corrent session as it is related to AD
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
#Takes input from users.csv file into this script
Import-Csv "C:\Users.csv" | ForEach-Object {
#assign input value to variable-samAccountName
$samAccountName = $_."samAccountName"
#get-aduser will retrieve samAccountName from domain users. if we found it will disable else it will go to catch
try { Get-ADUser -Identity $samAccountName |
Disable-ADAccount
}
#It will run when we can't find user
catch {
#it will display the message
Write-Host "user:"$samAccountname "is not present in AD"
}
}
Отчет по неактивным пользователям
Во время аудита вам будет предложено предоставить список пользователей, которые не используют свои компьютеры или не заходят в систему в течение определенного периода времени, так вот, этот скрипт делает то же самое и значительно упрощает задачу.
Как это работает
Скрипт собирает данные о тех, кто не заходил в систему в течение определенного времени, например, 90 дней, и отправляет нам почту. Убедитесь, что у вас указан правильный SMTP, чтобы вы могли получать почту.
Вероятный результат
Скрипт покажет вам результаты неактивных пользователей, которые не заходили в систему в течение указанного периода времени.
AD-InActive Users Report-90 Days Powershell Scripts
#Imports active directory module to only current session
Import-Module activedirectory
#Get-Date gives the present date in the server and is assigned to the variable presentdate
$presentdate= Get-Date
#User names whose lastlogondate is less than the presentdate-90days and those usernames are given to the variable output
$output=Get-ADUser -Filter * -Properties lastlogondate | Where-Object {$_.lastlogondate -lt $presentdate.adddays(-90)} | select name
#This output is exported to a .csv file
$output | Export-Csv C:\inactiveusers.csv -NoTypeInformation
#This prints the users who are inactive by taking from the output
Write-Host "The following users are inactive : " -ForegroundColor DarkYellow
$output
Как это работает
Скрипт получает список компьютеров в окружении и экспортирует его в csv.
Вероятный результат
Мы можем получить файл csv со списком компьютеров.
AD computers to csv Powershell Scripts
get-adcomputer -properties* -filter * | export-csv "provide path"
Включение recyclebin в AD является обязательным условием, если вы не хотите потерять информацию об удаленном пользователе. Преимущество включения этой функции в том, что мы можем легко восстановить любого пользователя в несколько кликов или с помощью скрипта.
Как это работает
Это просто набор команд для включения корзины, не используя настройки Windows. Скрипт прост и может быть выполнен без каких-либо проблем.
Вероятный результат
После выполнения скрипта вы можете проверить в ADUC, включен ли он, а также проверить, что показывает вывод после выполнения сценария.
Enable Recycle bin Powershell Scripts
$domain= read-host "Provide the domain name" $DCserver = read-host "Provide DC server name" Enable-ADOptionalFeature -Identity 'Recycle Bin Feature' -Scope ForestOrConfigurationSet -Target $domain -Server $DCserver -Confirm:$false
Удаление объектов AD
Объектом AD может быть компьютер или пользователь, и этот скрипт предоставляет вам возможность удалить пользователя и его машину из окружения. Больше не нужно идти и удалять пользователя/компьютер из GUI.
Как это работает
Этот скрипт использует переключатель, чтобы вы могли выбрать правильный вариант между удалением пользователя или компьютера, удаляет выбранный вариант и показывает результат на экране.
Вероятный результат
Пользователь или компьютер будет удален из домена AD.
AD-object-deletion Powershell Scripts
#Provide the input to choose to delete either User and Computer
$input = read-host "Enter your choice"
Switch($input)
{
0 { $result = 'User Deletion'}
1 { $result = 'Computer Deletion'}
}
#If input is greater than 1 it will throw error.
if ($input -gt 1)
{
Write-host "$input is not mentioned in the provided choices" -ForegroundColor Cyan
}
#If 0 is selected then provide the user name that needs to deleted.
if($input -eq 0)
{
$user = Read-host "Provide user Name"
Try{
Remove-aduser $user -confirm:$false
Write-host "User $user is deleted" -foregroundcolor DarkGreen}
Catch{
Write-host "$user is not present in AD or the Username is incorrect" -Foregroundcolor DarkRed
}
}
#If 1 is selected then provide the computer name that needs to deleted.
if ($input -eq 1)
{
$computer = Read-host "Provide Computer Name"
Try{
Remove-ADComputer $computer -confirm:$false
Write-host "User $computer is deleted" -BackgroundColor DarkGreen}
Catch{
Write-host "$Computer is not present in AD or the Computer name is incorrect" -BackgroundColor DarkRed
}
}
Создайте несколько групп AD за один запуск. Просто укажите данные из CSV, скрипт получит результаты и создаст необходимые группы AD. Один из самых популярных скриптов, на который стоит обратить внимание.
Как это работает
Сценарий получает данные из CSV-файла и создает необходимую группу под определенным OU.
Вероятный результат
Группы AD будут созданы автоматически без каких-либо ручных операций по проверке. Просто предоставьте необходимые данные.
Create Multiple AD Groups Powershell Scripts
#\\\\\\\Create multiple AD Groups///////#
$csv = Import-csv -Path "C:\Users\test\Desktop\groups.csv"
$name=$item.GroupName
Foreach ($item in $csv)
{
try
{
New-ADGroup -Name $item.GroupName -GroupCategory $item.GroupCategory -groupScope $item.groupScope -Path $item.OU
Write-Host -ForeGroundColor Green "Group $($item.GroupName) created!"
}
catch
{
Write-Host "Group already exists $name"
}
}
Сбор данных о пользователях AD – это ежемесячный процесс, который используется при проведении аудита. Получение информации о пользователях AD – это то, к чему стремится каждая организация. Это простой скрипт для получения всех данных о пользователях.
Как это работает
После запуска скрипта он сохранит все данные о пользователях в файл формата csv.
Вероятный результат
Вы можете определить, требуется ли какая-либо выборка по дате последнего входа в систему и другие атрибуты.
AD user to csv Powershell Scripts
get-aduser -properties* -filter * | export-csv "provide path"
ADuser – Memberof – WhenCreated
Как это работает
Этот скрипт проверяет пользователя и членство, которое он имеет, а также получает дату создания учетной записи пользователя.
Вероятный результат
Вы получите представление о том, в какой группе состоит пользователь и когда он был создан в домене.
AD-when-created-memberof Powershell Scripts
$a=(Get-aduser -filter * -properties *).Name
foreach($b in $a){
$c=(Get-aduser -identity $b -properties *).Whencreated
$d=((Get-aduser -identity $b -properties *).memberof|Get-Adgroup).Name -join ','
write-host "$b | $c | $d "
}
Дата последней установки пароля
Дата последней установки пароля не может быть получена непосредственно из powershell, нам необходимо несколько изменить скрипт. Если вы попытаетесь получить дату последней установки пароля, она покажет дату в 1601 году. Поэтому я создал скрипт для получения даты последнего пароля заданного samaccount.
Как это работает
Сценарий получает атрибут последнего установленного пароля пользователя и изменяет его на правильную дату. Список пользователей может быть предоставлен с помощью файла txt.
Вероятный результат
Скрипт получит атрибут последнего установленного пароля пользователя и изменяет его на правильную дату. Список пользователей может быть предоставлен с помощью txt-документа.
Last password set Powershell Scripts
$a="Provide path for list of user in txt doc"
foreach($b in $a){
$g=get-aduser -Identity $b -Properties Name,pwdlastset
$date=[datetime]$g.pwdLastSet
$pwdlast =$date.AddYears(1600).ToLocalTime()
"$b,$pwdlast"}
Создание OU Разовое и массовое
Для создания OU без каких-либо дополнительных шагов, я подготовил скрипт. Он создает одну OU или в нужном количестве.
Как это работает
Создание OU – это одна команда в Powershell, но массовое создание требует данных, которые могут быть представлены в CSV или текстовом файле, что и делается в этом скрипте.
Вероятный результат
Если вы все сделаете правильно, вы сможете увидеть созданные OU в dsa.msc.
Create OU Powershell Scripts
create active directory OU.txt
#Wintel-AD-Create Active Directory OU:
for single:
-----------
New-ADOrganizationalUnit -Name abc -Path "OU=Employees,DC=contoso,DC=com" -Description "if any" -PassThru
For Bulk:
---------
#Take input from ou_names file
import-csv c:\ou_names.csv | ForEach-Object {
#Assign input values to variable-ouname
$ouname = $_."ouname"
#It will search for given OU already exists in AD
$ADOU=get-ADOrganizationalunit -Filter 'Name -like $ouname'
try{
#It will compare given OU and AD searched OU
if($ouname -eq $ADOU){
#If it already in AD, it will go to caught statement
write-host "given OU-" $ouname "is already there in AD"}
#It will create OU if not exits
else
{
New-ADOrganizationalUnit -Name $ouname -path "DC=contoso,DC=com" -PassThru
}
}
#It will show the path of OU which already exists
catch{
write-host $ouname "is exists in AD"
write-host $ADOU
}
}
ou_names.csv
ouname ou1 ou2 ou3 ou4 ou5
readme.txt
This script will create OU's in AD. Prerequisites: 1.We should provide the OU names which needs to created in AD. Steps to run the script: 1.Provide OU names in csv file to script. 2.It will check for OU in AD whether it already exists. 3.If it doesn't exist in AD, it will create else it will provide path od OU.
Разовое удаление пользователей AD или массовое
Нужно удалить пользователя без каких-либо дополнительных кликов, данный скрипт именно для этого. Вы можете удалить одного пользователя или удалить пользователей в массовом порядке.
Как это работает
Удаление пользователя – это отдельная команда в Powershell, но для массового удаления требуются данные, которые могут быть получены их CSV или текстового файла, что и делается в этом скрипте.
Вероятный результат
Если вы все сделаете правильно, то удаленные пользователи не будут видны в dsa.msc.
Delete-user-account Powershell Scripts
Delete Active Directory User.txt
#Wintel-AD-Disable Active Directory User:
#for single:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
Remove-ADAccount -Identity user1
###################for bulk################################
#imports active directory module to only corrent session as it is related to AD
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
#Takes input from users.csv file into this script
Import-Csv "C:\Users.csv" | ForEach-Object {
#assign input value to variable-samAccountName
$samAccountName = $_."samAccountName"
#get-aduser will retrieve samAccountName from domain users. if we found it will disable else it will go to catch
try { Get-ADUser -Identity $samAccountName |
Remove-ADAccount
}
#It will run when we can't find user
catch {
#it will display the message
Write-Host "user:"$samAccountname "is not present in AD"
}
}
users.csv
samAccountName akhila user1
readme.txt
This script will disable particularly given user accounts in AD. Prerequisites: 1.We should provide the user accounts which are in AD. Steps to run the script: 1.Provide user names in csv file to script. 2.It will check for user in AD. 3.if it is there, it will disable else it will provide a message like user is not present in AD.
Статус репликации AD
Если вы хотите узнать статус репликации AD в вашем домене, этот скрипт является наиболее подходящим для этого. Он предоставляет статус репликации и, если есть какая-либо ошибка, показывает ее.
Как это работает
Он похож на repadmin/replsum и выдает тот же результат в формате html.
Вероятный результат
Вы можете запланировать выполнение этого скрипта на регулярной основе, если возникнут ошибки, вы сможете проверить и устранить их.
AD-Replication-status Powershell Scripts
$myRepInfo = @(repadmin /replsum * /bysrc /bydest /sort:delta)
# Initialize our array.
$cleanRepInfo = @()
# Start @ #10 because all the previous lines are junk formatting
# and strip off the last 4 lines because they are not needed.
for ($i=10; $i -lt ($myRepInfo.Count-4); $i++) {
if($myRepInfo[$i] -ne ""){
# Remove empty lines from our array.
$myRepInfo[$i] -replace '\s+', " "
$cleanRepInfo += $myRepInfo[$i]
}
}
$finalRepInfo = @()
foreach ($line in $cleanRepInfo) {
$splitRepInfo = $line -split '\s+',8
if ($splitRepInfo[0] -eq "Source") { $repType = "Source" }
if ($splitRepInfo[0] -eq "Destination") { $repType = "Destination" }
if ($splitRepInfo[1] -notmatch "DSA") {
# Create an Object and populate it with our values.
$objRepValues = New-Object System.Object
$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name DSAType -value $repType # Source or Destination DSA
$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name Hostname -value $splitRepInfo[1] # Hostname
$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name Delta -value $splitRepInfo[2] # Largest Delta
$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name Fails -value $splitRepInfo[3] # Failures
#$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name Slash -value $splitRepInfo[4] # Slash char
$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name Total -value $splitRepInfo[5] # Totals
$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name "% Error" -value $splitRepInfo[6] # % errors
$objRepValues | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name ErrorMsg -value $splitRepInfo[7] # Error code
# Add the Object as a row to our array
$finalRepInfo += $objRepValues
}
}
$html = $finalRepInfo|ConvertTo-Html -Fragment
$xml = [xml]$html
$attr = $xml.CreateAttribute("id")
$attr.Value='diskTbl'
$xml.table.Attributes.Append($attr)
$rows=$xml.table.selectNodes('//tr')
for($i=1;$i -lt $rows.count; $i++){
$value=$rows.Item($i).LastChild.'#text'
if($value -ne $null){
$attr=$xml.CreateAttribute('style')
$attr.Value='background-color: red;'
[void]$rows.Item($i).Attributes.Append($attr)
}
else {
$value
$attr=$xml.CreateAttribute('style')
$attr.Value='background-color: green;'
[void]$rows.Item($i).Attributes.Append($attr)
}
}
#embed a CSS stylesheet in the html header
$html=$xml.OuterXml|Out-String
$style='<style type=text/css>#diskTbl { background-color:black ; }
td, th { border:1px solid black; border-collapse:collapse; }
th { color:black; background-color:yellow; }
table, tr, td, th { padding: 2px; margin: 0px } table { margin-left:50px; }</style>'
ConvertTo-Html -head $style -body $html -Title " AD Replication Report"|Out-File C:\Scripts_new\Replication\ReplicationReport.htm
$html1=get-content C:\Scripts_new\Replication\ReplicationReport.htm
$smtpServer = ""
$smtpFrom = ""
$smtpTo = ""
$messageSubject = ""
$message = New-Object System.Net.Mail.MailMessage $smtpfrom, $smtpto
$message.Subject = $messageSubject
$message.IsBodyHTML = $true
$message.Body =$html1
$smtp = New-Object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smtpServer)
$smtp.Send($message)
#send-MailMessage -From "Replication@lycra.mail.onmicrosoft.com" -to "dhrub.bharali@capgemini.com" -Subject "Lycra AD Replication Report(Do not reply)" -SmtpServer "lycra-com.mail.protection.outlook.com" -body -BodyAsHtml
Отчет об устаревших объектах
Хотите узнать, какие объекты еще присутствуют в вашем домене, тогда это отличный скрипт, который найдет их и поможет вам полностью создать объекты. Это самый интересный скрипт в категории скриптов Active Directory Powershell.
Как он работает
С помощью этого скрипта можно найти неиспользуемые объекты в течение определенного промежутка времени.
Вероятный результат
Вы можете удалить неиспользуемые объекты, если они соответствуют вашим критериям поиска.
Stale comp reports Powershell Scripts
###############################################
#Description:
#This script will fetch stale computer objects beyond 90 days . And should run in any of the AD servers.
################################################################################################
#FIND INACTIVE COMPUTERS
#-------------------------------
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
#Get AD Computers that haven't logged on in xx days
$DaysInactive = 90
$InactiveDate = (Get-Date).Adddays(-($DaysInactive))
$Computers = Get-ADComputer -Filter { LastLogonDate -lt $InactiveDate -and Enabled -eq $true } -Properties LastLogonDate | Select-Object Name, LastLogonDate, DistinguishedName
# REPORTING
#-------------------------------
# Export results to CSV
$Computers | Export-Csv C:\Users\test\Desktop\InactiveComputers.csv -NoTypeInformation
Добавление или удаление нескольких пользователей из нескольких групп
Как это работает
Скрипт использует файл csv для получения входных данных и выполняет их в вашей среде.
Вероятный результат
После выполнения скрипта вероятным результатом будет удаление пользователя или добавление его в необходимую группу безопасности.
Multiple user remove from groups Powershell Scripts
{<######### CSV format ########## >
user,group
test1,"domain admins"
test2,Administrators #>}
Import-CSV c:\users\dbharali\desktop\list.csv | % {
$check1= Get-ADGroupMember -Identity ($_.group) | select -ExpandProperty Name
if ($check1 -contains $_.user){
write-host "$($_.User) is a member of $($_.Group) !" -ForegroundColor DarkYellow
try{
remove-ADGroupMember -Identity $_.group -Member $_.User -Confirm:$false
Write-host "Removing $($_.User) from $($_.Group).......... " -ForegroundColor cyan
$check2 = Get-ADGroupMember -Identity ($_.group) | select -ExpandProperty Name
if ($check2 -notcontains $_.user){
write-host "$($_.User) is successfully removed from $($_.Group) !" -ForegroundColor green
}
}
catch{
Write-Warning "Exception String: $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
}
else {
Write-host $($_.user) is not a member of $($_.group) -ForegroundColor red
}
}
Add multiple user to multiple groups Powershell Scripts
{<######### CSV format ########## >
user,group
test1,"domain admins"
test2,Administrators #>}
$ErrorActionPreference = "SilentlyContinue"
Import-CSV c:\users\dbharali\desktop\list.csv | % {
$check1= Get-ADGroupMember -Identity ($_.group) | select -ExpandProperty Name
if ($check1 -contains $_.user){
write-host "$($_.User) is already a member of $($_.Group) !" -ForegroundColor red
}
else
{
Try{
Write-host "Checking $($_.Users) in $($_.Group).......... " -ForegroundColor cyan
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity $_.group -Member $_.User -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$check2 = Get-ADGroupMember -Identity ($_.group) | select -ExpandProperty Name
if ($check2 -contains $_.user){
write-host "$($_.User) is successfully added to $($_.Group) !" -ForegroundColor green
}
}
catch{
Write-Warning "Exception String: $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
}
}
Получение источника NTP из нескольких серверов
Когда мы сталкиваемся с проблемой синхронизации времени, лучше проверить источник, из которого сервер получает время.
Как он работает
Он считывает введенный список серверов и пытается найти источник NTP из предоставленного списка.
Вероятный результат
Считывает входные данные списка серверов и пытается найти источник NTP из предоставленного списка.
NTP Source Powershell Scripts
$Inventory = New-Object System.Collections.ArrayList
$AllComputers = gc C:\users\admin\desktop\server.txt
foreach($computers in $allcomputers){
$Computers
$ComputerInfo = New-Object System.Object
$ntp = w32tm /query /computer:$computers /source
$ComputerInfo |Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name "ServerName" -Value "$Computers"
$ComputerInfo |Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name "NTP Source" -Value "$Ntp"
$Inventory.Add($ComputerInfo) | Out-Null
}
$Inventory | Export-Csv C:\users\admin\desktop\NTP.csv -NoTypeInformation
Сравнение групп AD
Иногда это превращается в сложную задачу, когда вам нужно сравнить две группы AD и найти ту, в которой отсутствует один пользователь из-за того, что несколько пользователей добавлены в определенные группы. Я создал простой скрипт, чтобы сэкономить время, поэтому делюсь им с вами.
Как это работает
Сценарий сравнивает 2 предоставленные группы и показывает, чего не хватает в этих двух группах. Если значение показывает “==”, значит пользователь есть в обеих группах, если “=>” или “<=”, значит некоторые пользователи отсутствуют в одной из групп.
Вероятный результат
С помощью скрипта вы узнаете, какой пользователь отсутствует или какая группа безопасности отсутствует.
Compare ad groups Powershell Scripts
$group1 = read-host "Enter group 1" $group2 = read-host "Enter group 2" $a= get-adgroupmember -identity $group1 |select -expandproperty Name $b= get-adgroupmember -identity $group2 |select -expandproperty Name compare $b $a -includeequal
Зеркальные группы AD
Вы когда-нибудь думали о том, как добавить похожих пользователей в разные группы, чтобы они были зеркальным отражением друг друга? Этого можно легко добиться с помощью Powershell и сэкономить массу драгоценного времени.
Как это работает
Сценарий получает список пользователей из обеих групп AD, и если в целевой группе AD отсутствует член эталонной группы AD, то пользователь будет добавлен в целевую группу.
Вероятный результат
Обе группы AD – эталонная и целевая – будут иметь одинаковых членов.
Add missing AD group members Powershell Scripts
$group1 = read-host "Enter group 1"
$group2 = read-host "Enter group 2"
$a= get-adgroupmember -identity $group1 |select -expandproperty Name
write-host "$group1 members are $a"
$b= get-adgroupmember -identity $group2 |select -expandproperty Name
write-host "$group2 members are $b"
Foreach($c in $a)
{
Foreach($d in $b)
{
if ($c -notcontains $d)
{
write-host "adding $c to $group2"
add-adgroupmember -members $c -identity $group2
write-host "$c is added to $group2"
}
else
{write-host "$c is not copied"}
}
}
write-host "$group2 members are"
get-adgroupmember -identity $group2 |select -expandproperty Name
Доброго времени суток дорогие читатели. В данной статье мы познакомимся с основами Powershell. Данный язык программирования используется во всех ОС Microsoft начиная с Windows XP SP3. Писать Powershell скрипты должен уметь каждый уважающий себя системный администратор windows.
Все команды в Powershell как правило используются в форме командлетов. Все командлеты это специализированные классы .NET Framework и .NET Core (используется в PowerShell Core 6 и выше).
Powershell класса .NET Framework это версии с 1 по 5.1 а Powershell .NET Core это версия 6 и выше (на данный момент 7.0). По заявлению Microsoft новых функций в Powershell 5.1 (.NET Framework) вносить уже не будут. Однако 7 версия еще не полностью поддерживает все модули предыдущих версий. Но судя по всему Microsoft стремится к этому и скоро версия Core будет единственной. В общем cmd отходит в прошлое и теперь без Powershell никуда. Давайте приступим к практике. Так всегда лучше запоминается материал.
Запуск Powershell
На примере Windows 10 Powershell можно запустить просто нажав правой кнопкой мыши на меню пуск.
Также нижняя строчка позволяет запустить Powershell с повышенными правами администратора.
Еще можно воспользоваться поиском в WIndows 10 и ввести название powershell
Как видно на картинке выше нашелся не только Powershell но и Powershell ISE. Консоль powershell удобна если требуется запустить последовательно не больше одной команды. Либо несколько команд в конвейере. Однако в случае написания полноценных скриптов лучше использовать Powershell ISE. Это бесплатная среда разработки сценариев на языке Powershell поставляется вместе с ОС Windows.
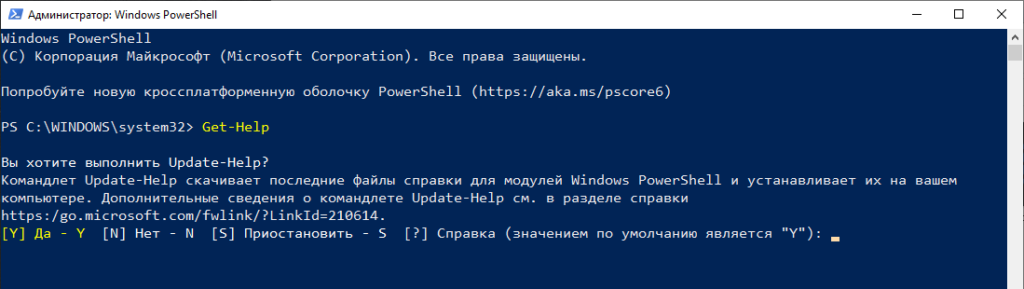
Сразу после запуска консоли рекомендую запустить командлет Get-Help — встроенная справка по всем командлетам, аналог man в Linux.
Видим что консоль предлагает обновить встроенную помощь. Нажимаем Y и соглашаемся.
Командлеты
Командлеты — это название команд в Powershell. Каждый командлет реализует заложенную в него функциональность. Как правило наименование командлета состоит из пары: глагол-существительное. Например: Get-Help — получить помощь. Обычно Get используется чтобы получить информация, Set — внести изменение, New — создать новый объект, политику и т.п. и Remove -удалить объект, политику и т.п.
Командлеты не чувствительны к регистру. Написать Get или get не важно, powershell воспримет эти команды одинаково.
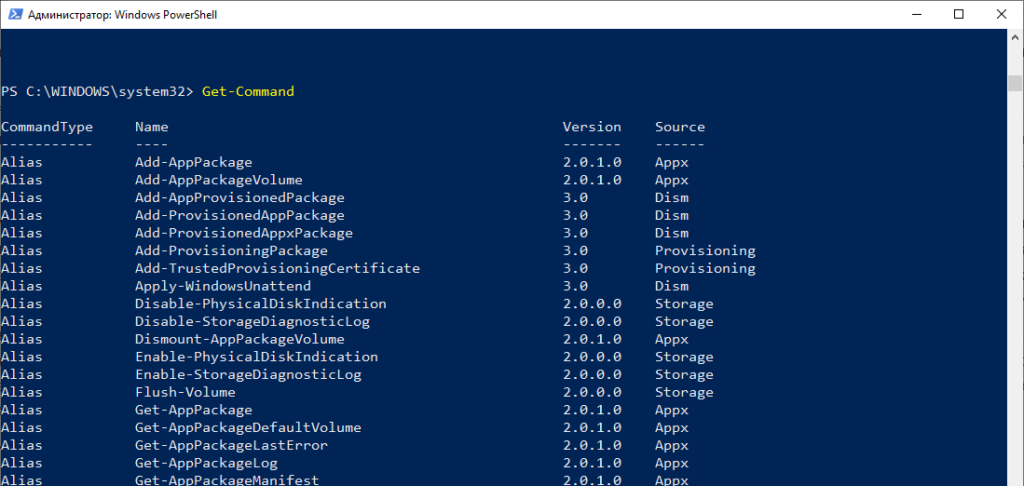
Чтобы получить список всех доступных командлетов необходимо использовать Get-Command
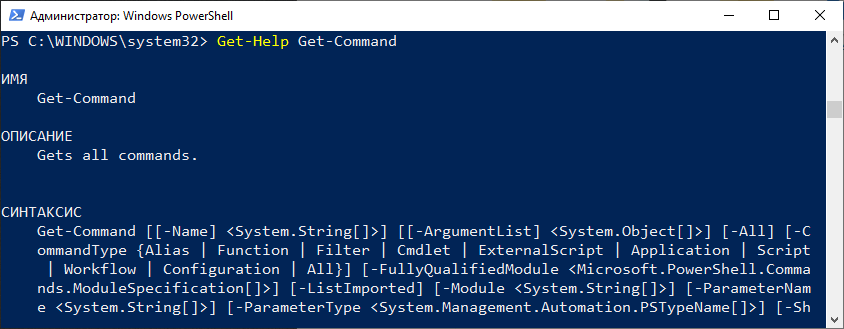
Для получения справки по любому командлету напишите Get-Help имя-комндлета. Например
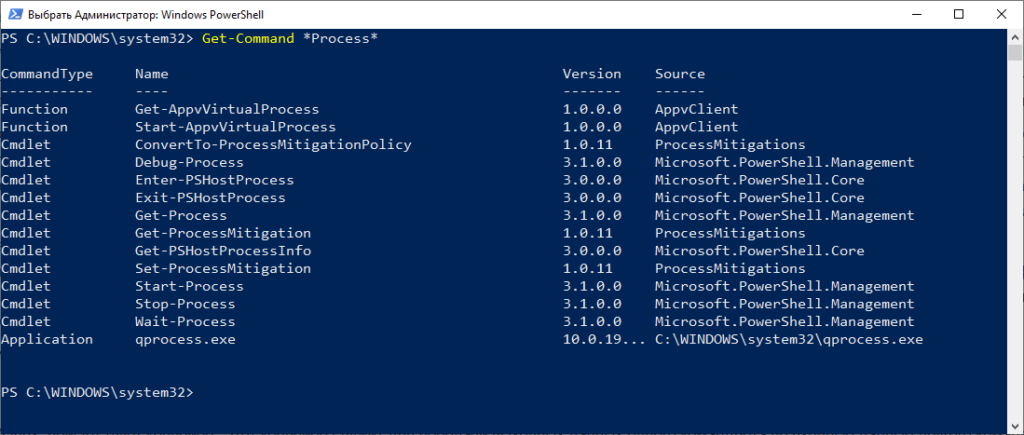
Давайте представим что нам необходимо вывести список командлетов для управления процессами. Воспользуемся Get-Command и укажем ему параметры для более точного поиска.
И вот мы видим список командлетов позволяющих управлять процессами: Get-Process — список всех запущенных процессов, Start-Process — запустить указанный процесс, Stop-Process— остановить указанный процесс, Wait-Process — ожидать указанный процесс. Как видно из названий командлетов можно легко понять для чего каждый служит.
Используя командлет Get-Help можно получить справку по любому командлету.
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Help Get-Process
ИМЯ
Get-Process
ОПИСАНИЕ
Gets the processes that are running on the local computer or a remote computer.
СИНТАКСИС
Get-Process [[-Name] <System.String[]>] [-ComputerName <System.String[]>] [-FileVersionInfo] [-Module] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-Process [-ComputerName <System.String[]>] [-FileVersionInfo] -Id <System.Int32[]> [-Module] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-Process [-ComputerName <System.String[]>] [-FileVersionInfo] -InputObject <System.Diagnostics.Process[]> [-Module] [<Com
monParameters>]
Get-Process -Id <System.Int32[]> -IncludeUserName [<CommonParameters>]
Get-Process [[-Name] <System.String[]>] -IncludeUserName [<CommonParameters>]
Get-Process -IncludeUserName -InputObject <System.Diagnostics.Process[]> [<CommonParameters>]
ОПИСАНИЕ
The `Get-Process` cmdlet gets the processes on a local or remote computer.
Without parameters, this cmdlet gets all of the processes on the local computer. You can also specify a particular process b
y process name or process ID (PID) or pass a process object through the pipeline to this cmdlet.
By default, this cmdlet returns a process object that has detailed information about the process and supports methods that l
et you start and stop the process. You can also use the parameters of the `Get-Process` cmdlet to get file version informati
on for the program that runs in the process and to get the modules that the process loaded.
ССЫЛКИ ПО ТЕМЕ
Online Version: https://docs.microsoft.com/powershell/module/microsoft.powershell.management/get-process?view=powershell-5.1
&WT.mc_id=ps-gethelp
Debug-Process
Get-Process
Start-Process
Stop-Process
Wait-Process
ЗАМЕЧАНИЯ
Для просмотра примеров введите: "get-help Get-Process -examples".
Для получения дополнительных сведений введите: "get-help Get-Process -detailed".
Для получения технических сведений введите: "get-help Get-Process -full".
Для получения справки в Интернете введите: "get-help Get-Process -online"
При использовании командлета есть возможность указать несколько параметров при запуске. Первый параметр можно не называть. Выше я писал Get-Command *Process* где указал поиск командлетов со словом Process. Однако я не написал параметр -Name, хотя именно его и указал. Если полностью то поиск по имени выглядит так: Get-Command -Name *Process* . В случае отсутствия непосредственного указания -Name Powershell принимает в качестве имени введенное слово *Process*.
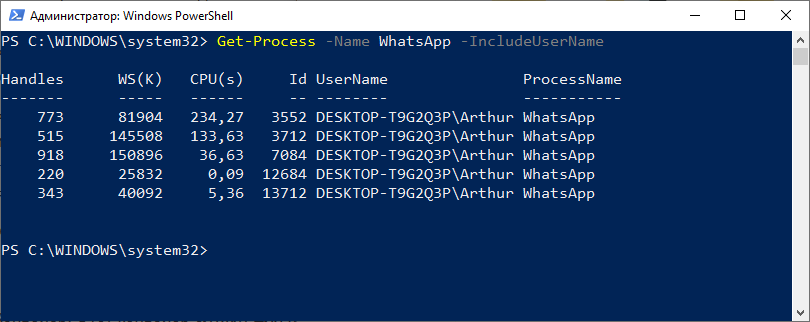
Давайте выведем список процессов с именем WhatsApp
Get-Process -Name WhatsApp -IncludeUserName
Мы вывели все процессы с именем WhatsApp и добавили в вывод дополнительный параметр -IncludeUserName, что позволило нам увидеть кем запущен процесс.
Алиасы
Алиасы в Powershell это по сути более короткие названия командлетов. Т.е. любому командлету можно присвоить свое короткое имя (alias). Например алиасом для командлета Get-Process является gps. Согласитесь куда проще и быстрее написать gps чем Get-Process.
Список всех alias можно получить используя командлет Get-Alias
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> get-alias CommandType Name Version Source ----------- ---- ------- ------ Alias % -> ForEach-Object Alias ? -> Where-Object Alias ac -> Add-Content Alias asnp -> Add-PSSnapin Alias cat -> Get-Content Alias cd -> Set-Location Alias CFS -> ConvertFrom-String 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility Alias chdir -> Set-Location Alias clc -> Clear-Content Alias clear -> Clear-Host Alias clhy -> Clear-History Alias cli -> Clear-Item Alias clp -> Clear-ItemProperty Alias cls -> Clear-Host Alias clv -> Clear-Variable Alias cnsn -> Connect-PSSession Alias compare -> Compare-Object Alias copy -> Copy-Item Alias cp -> Copy-Item Alias cpi -> Copy-Item Alias cpp -> Copy-ItemProperty Alias curl -> Invoke-WebRequest Alias cvpa -> Convert-Path Alias dbp -> Disable-PSBreakpoint Alias del -> Remove-Item Alias diff -> Compare-Object Alias dir -> Get-ChildItem Alias dnsn -> Disconnect-PSSession Alias ebp -> Enable-PSBreakpoint Alias echo -> Write-Output Alias epal -> Export-Alias Alias epcsv -> Export-Csv Alias epsn -> Export-PSSession Alias erase -> Remove-Item Alias etsn -> Enter-PSSession Alias exsn -> Exit-PSSession Alias fc -> Format-Custom Alias fhx -> Format-Hex 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility Alias fl -> Format-List Alias foreach -> ForEach-Object Alias ft -> Format-Table Alias fw -> Format-Wide Alias gal -> Get-Alias Alias gbp -> Get-PSBreakpoint Alias gc -> Get-Content Alias gcb -> Get-Clipboard 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Alias gci -> Get-ChildItem Alias gcm -> Get-Command Alias gcs -> Get-PSCallStack Alias gdr -> Get-PSDrive Alias ghy -> Get-History Alias gi -> Get-Item Alias gin -> Get-ComputerInfo 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Alias gjb -> Get-Job Alias gl -> Get-Location Alias gm -> Get-Member Alias gmo -> Get-Module Alias gp -> Get-ItemProperty Alias gps -> Get-Process Alias gpv -> Get-ItemPropertyValue Alias group -> Group-Object Alias gsn -> Get-PSSession Alias gsnp -> Get-PSSnapin Alias gsv -> Get-Service Alias gtz -> Get-TimeZone 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Alias gu -> Get-Unique Alias gv -> Get-Variable Alias gwmi -> Get-WmiObject Alias h -> Get-History Alias history -> Get-History Alias icm -> Invoke-Command Alias iex -> Invoke-Expression Alias ihy -> Invoke-History Alias ii -> Invoke-Item Alias ipal -> Import-Alias Alias ipcsv -> Import-Csv Alias ipmo -> Import-Module Alias ipsn -> Import-PSSession Alias irm -> Invoke-RestMethod Alias ise -> powershell_ise.exe Alias iwmi -> Invoke-WmiMethod Alias iwr -> Invoke-WebRequest Alias kill -> Stop-Process Alias lp -> Out-Printer Alias ls -> Get-ChildItem Alias man -> help Alias md -> mkdir Alias measure -> Measure-Object Alias mi -> Move-Item Alias mount -> New-PSDrive Alias move -> Move-Item Alias mp -> Move-ItemProperty Alias mv -> Move-Item Alias nal -> New-Alias Alias ndr -> New-PSDrive Alias ni -> New-Item Alias nmo -> New-Module Alias npssc -> New-PSSessionConfigurationFile Alias nsn -> New-PSSession Alias nv -> New-Variable Alias ogv -> Out-GridView Alias oh -> Out-Host Alias popd -> Pop-Location Alias ps -> Get-Process Alias pushd -> Push-Location Alias pwd -> Get-Location Alias r -> Invoke-History Alias rbp -> Remove-PSBreakpoint Alias rcjb -> Receive-Job Alias rcsn -> Receive-PSSession Alias rd -> Remove-Item Alias rdr -> Remove-PSDrive Alias ren -> Rename-Item Alias ri -> Remove-Item Alias rjb -> Remove-Job Alias rm -> Remove-Item Alias rmdir -> Remove-Item Alias rmo -> Remove-Module Alias rni -> Rename-Item Alias rnp -> Rename-ItemProperty Alias rp -> Remove-ItemProperty Alias rsn -> Remove-PSSession Alias rsnp -> Remove-PSSnapin Alias rujb -> Resume-Job Alias rv -> Remove-Variable Alias rvpa -> Resolve-Path Alias rwmi -> Remove-WmiObject Alias sajb -> Start-Job Alias sal -> Set-Alias Alias saps -> Start-Process Alias sasv -> Start-Service Alias sbp -> Set-PSBreakpoint Alias sc -> Set-Content Alias scb -> Set-Clipboard 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Alias select -> Select-Object Alias set -> Set-Variable Alias shcm -> Show-Command Alias si -> Set-Item Alias sl -> Set-Location Alias sleep -> Start-Sleep Alias sls -> Select-String Alias sort -> Sort-Object Alias sp -> Set-ItemProperty Alias spjb -> Stop-Job Alias spps -> Stop-Process Alias spsv -> Stop-Service Alias start -> Start-Process Alias stz -> Set-TimeZone 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Alias sujb -> Suspend-Job Alias sv -> Set-Variable Alias swmi -> Set-WmiInstance Alias tee -> Tee-Object Alias trcm -> Trace-Command Alias type -> Get-Content Alias wget -> Invoke-WebRequest Alias where -> Where-Object Alias wjb -> Wait-Job Alias write -> Write-Output
Как видно из списка для alias использованы аналогичные по значению команды из Linux: ls, man, mount, md, kill и т.п. Видимо чтобы линуксоиду было по привычнее 🙂 Можно создать свой alias используя командлет New-Alias
Конвейер
Конвейер используется для передачи выходных данных командлета идущего вначале во входные данные командлета следующего за ним. Ничего непонятно? 🙂 Давайте на примерах, так всегда яснее.
Возьмем уже известный нам командлет Get-Process, посмотрим на его вывод
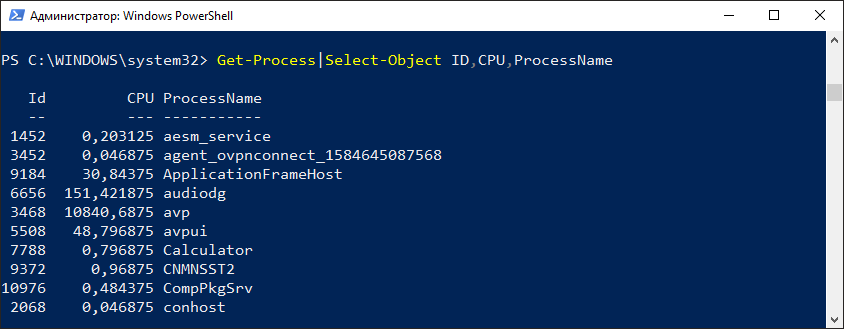
Как по мне многовато лишних столбцов. Мне эта информация не нужна, поэтому я выберу только нужные данные. Для таких целей служит командлет Select-Object. Давайте используем его в конвейере.
Get-Process|Select-Object ID,CPU,ProcessName
Как вы уже наверно догадались конвейер обозначается знаком | и идет сразу следом за командлетом. И так данные по конвейеру можно передавать и дальше другим командлетам. Итак я передал выходные данные (список запущенных процессов) на вход командлета Select-Object. Который в свою очередь выбрал данные по 3 столбцам ID, CPU, ProcessName. Теперь можно передать эти данные дальше. Например выгрузить в текстовый файл
Get-Process|Select-Object ID,CPU,ProcessName|Out-File C:\TMP\out.txt
Просто не правда ли? У нас конвейер из трех командлетов, на выходе которого получаем текстовый файл со списком запущенных процессов и необходимой информацией по ним.
Структура объектов
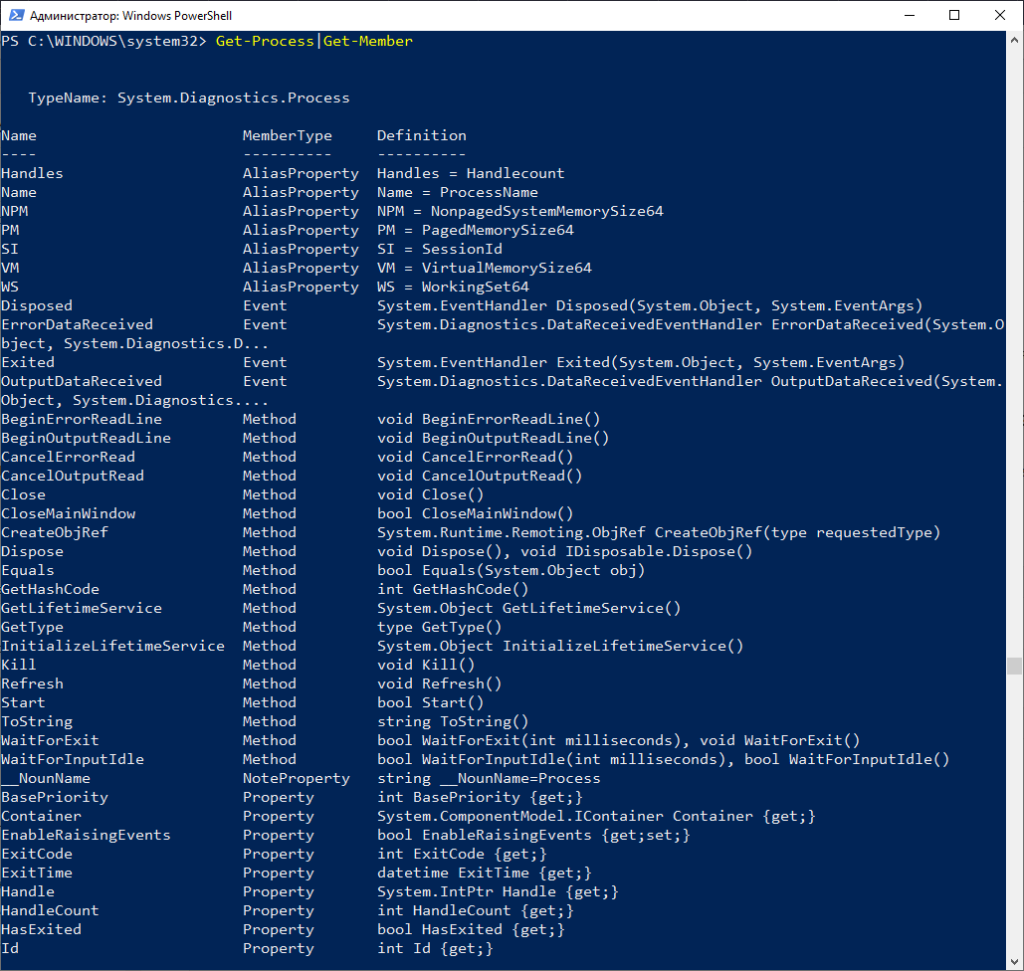
В Powershell объекты играют самую важную роль. От типа объекта зависит что именно с ним можно сделать. Узнать тип объекта и вывести список всех его элементов позволяет команда Get-Member
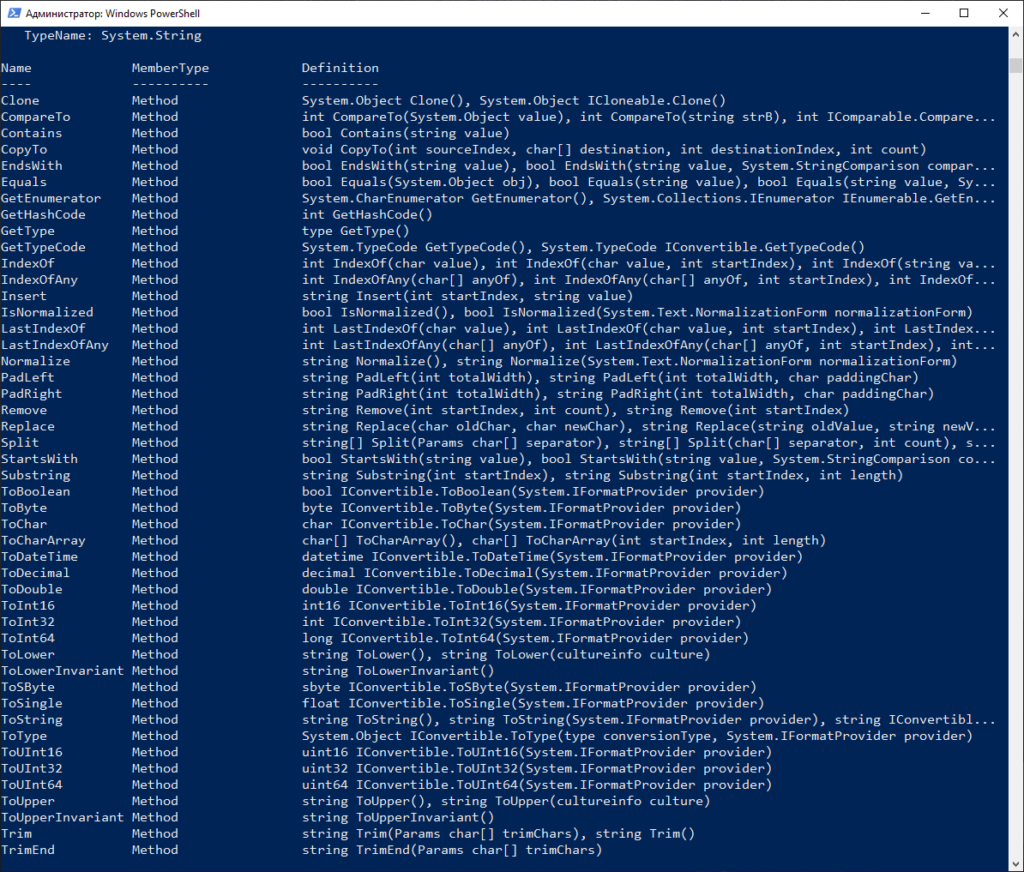
Вот далеко не полный список элементов командлета Get-Process. В данному случае тип данных это System.Diagnostics.Process
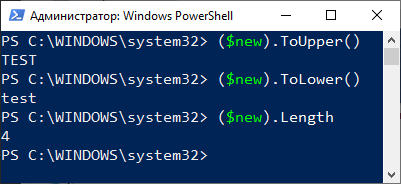
Давайте посмотрим тип данных у новой переменной
$new="Test" $new|Get-Member
В данном случае тип данных System.String т.е. строка. Что вполне логично. А теперь посмотрите что можно сделать с этой строкой с учетом указанных выше параметров.
Как видно на картинке выше мы заключаем нашу тестовую переменную $new в скобки и после них пишем точку и указываем метод. В примере я использовал три метода:
- ToUpper — перевод всех букв в строке в верхний регистр
- ToLower — перевод всех букв в строке в нижний регистр
- Length — подсчитать количество символов в строке
Это всего лишь небольшой пример что можно сделать с параметрами объекта. Чаще используйте Get-Member и вы откроете для себя безграничные возможности манипуляции над объектами.
Скрипты Powershell
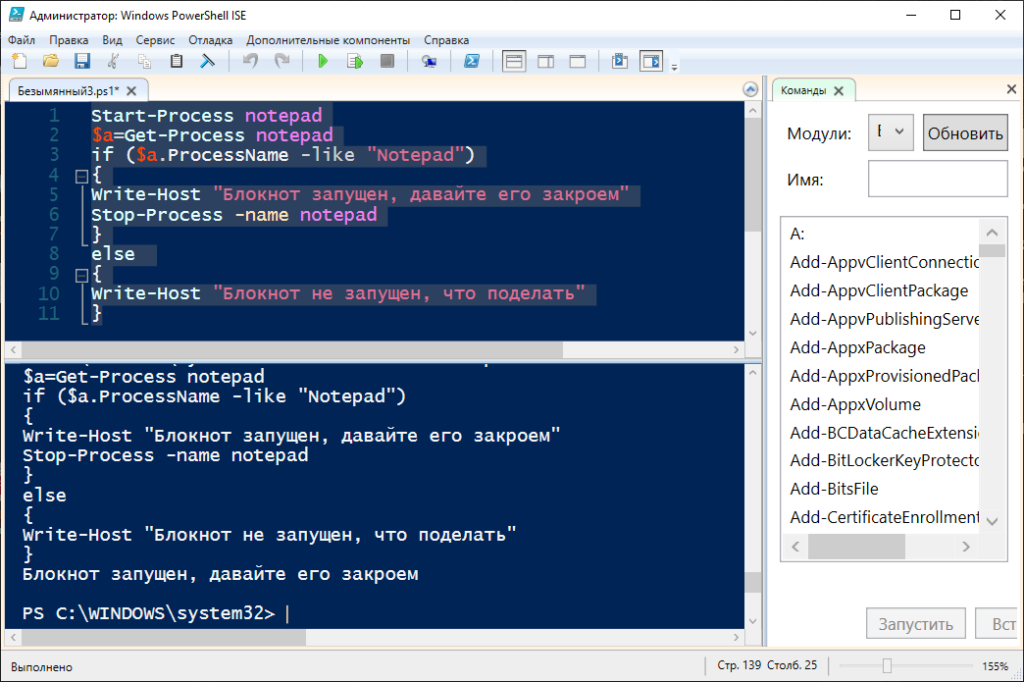
В самом начале статьи указал на встроенный инструмент Powershell ISE. Давайте запустим его и создадим свой первый скрипт. Кстати скрипты сохраняются в файлах с расширением ps1
Скрипт будет запускать блокнот, далее выполняется проверка если блокнот запущен выводится сообщение об этом и после блокнот закрывается. Если блокнот не запущен то выводится соответствующее сообщение об этом. На самом деле блокнот будет всегда запущен, т.к. мы вначале скрипта написали Start-Process notepad
Start-Process notepad
$a=Get-Process notepad
if ($a.ProcessName -like "Notepad")
{
Write-Host "Блокнот запущен, давайте его закроем"
Stop-Process -name notepad
}
else
{
Write-Host "Блокнот не запущен, что поделать"
}
В этом скрипте я использовал цикл if else. О циклах будет подробнее в следующей статье. Итак давайте сохраним скрипт и выполним его.
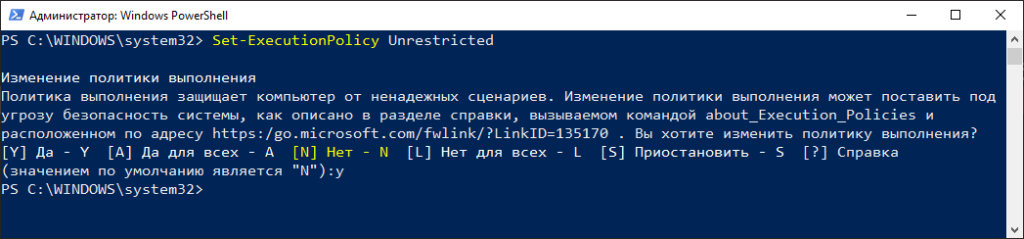
В ответ мы получим такую ошибку:
Невозможно загрузить файл, так как выполнение сценариев отключено в этой системе. Для получения дополнительных сведений см.
about_Execution_Policies по адресу https:/go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=1351
70.
+ CategoryInfo : Ошибка безопасности: (:) [], ParentContainsError
RecordException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnauthorizedAccess
Все верно, изначально в WIndows запрещено выполнять скрипты Powershell. Это сделано для повышения безопасности системы. Для включения возможности запуска скриптов Powershell необходимо запустить Powershell от Администратора и ввести командлет Set-ExecutionPolicy с одним из параметров:
- Restricted — политика по умолчанию. Выполнение всех скриптов запрещено
- RemoteSigned — разрешено запускать собственные скрипты и подписанные доверенным разработчиком
- AllSigned — разрешено запускать скрипты, подписанные доверенным разработчиком. Каждый раз перед запуском такого скрипта PowerShell будет запрашивать подтверждение
- Unrestricted — в системе разрешается запускать любые скрипты
Если вы полностью уверены в запускаемых скриптах можете поставить Unrestricted. Давайте так и сделаем
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Unrestricted
Будет предупреждение по безопасности, соглашаемся нажав Y
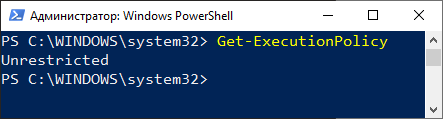
Можем посмотреть текущую настройку политики безопасности при помощи командлета Get-ExecutionPolicy
В данной статье мы рассмотрели основы чтобы подготовиться писать скрипты Powershell. В следующих статьях мы более подробно изучим циклы, массивы, функции, работу со строками и много другое. Кстати вот раздел посвященный Powershell. Там много всего интересного 😉
Рекомендую к прочтению:
- Переменные
- Операторы сравнения
- Операторы условий
- Циклы
Содержание
Управление дисками и файлами
Получение текущего расположения (Get-Location)
Чтобы определить путь к текущему каталогу, введите команду Get-Location.
PS> Get-Location Path ---- C:\Documents and Settings\PowerUser
Примечание
Командлет Get-Location аналогичен команде pwd в оболочке BASH. Командлет Set-Location аналогичен команде cd в Cmd.exe.
Настройка текущего расположения (Set-Location)
Команда Get-Location используется с командой Set-Location. Команда Set-Location позволяет вам указать расположение текущего каталога.
Set-Location -Path C:\Windows
Обратите внимание, что после ввода команды вы не получите прямого отклика о действии команды. Большинство команд Windows PowerShell, выполняющих действия, практически не создают выходных данных, так как выходные данные не всегда полезны. Чтобы проверить успешность внесения изменения в каталог при вводе команды Set-Location, укажите параметр -PassThru при вводе команды Set-Location.
PS> Set-Location -Path C:\Windows -PassThru Path ---- C:\WINDOWS
Параметр -PassThru можно использовать с некоторыми командами Set в Windows PowerShell для возврата сведений о результате, когда отсутствуют выходные данные по умолчанию.
Вы можете указать пути относительно текущего расположения так же, как и в большинстве командных оболочек UNIX и Windows. В стандартной нотации для относительных путей точка ( . ) представляет текущую папку, а две точки ( .. ) — родительский каталог текущего расположения.
Например, если вы находитесь в папке C:\Windows, точка ( . ) представляет C:\Windows, а две точки ( .. ) представляют C: . Текущее расположение можно изменить на корень диска C: путем ввода следующей команды:
PS> Set-Location -Path .. -PassThru Path ---- C:\
Тот же метод работает для дисков Windows PowerShell, которые не являются дисками файловой системы, например HKLM: . В реестре в качестве расположения можно задать раздел HKLM\Software путем ввода следующего кода:
PS> Set-Location -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE -PassThru Path ---- HKLM:\SOFTWARE
После этого можно изменить расположение каталога на родительский каталог, который является корнем диска Windows PowerShell HKLM: с помощью относительного пути:
PS> Set-Location -Path .. -PassThru Path ---- HKLM:\
Вы можете ввести Set-Location или использовать любой из встроенных псевдонимов Windows PowerShell для Set-Location (cd, chdir, sl). Пример:
cd -Path C:\Windows
chdir -Path .. -PassThru
sl -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE -PassThru
Сохранение и отзыв последних расположений (Push-Location и Pop-Location)
При изменении расположения полезно отслеживать свое предыдущее расположение и иметь возможность вернуться к нему. Командлет Push-Location в Windows PowerShell создает упорядоченный журнал («стек») путей к каталогам, которые вы открывали, чтобы можно было вернуться по нему на шаг назад, используя дополнительный командлет Pop-Location.
Например, Windows PowerShell обычно запускается в корневом каталоге пользователя.
PS> Get-Location Path ---- C:\Documents and Settings\PowerUser
Чтобы передать текущее расположение в стек, а затем переместить его в папку локальных параметров, введите:
Push-Location -Path "Local Settings"
После этого можно передать расположение локальных параметров в стек и переместить его в папку Temp, введя следующее:
Push-Location -Path Temp
Чтобы убедиться, что каталоги изменены, введите команду Get-Location.
PS> Get-Location Path ---- C:\Documents and Settings\PowerUser\Local Settings\Temp
После этого можно перейти в последний открытый каталог, введя команду Pop-Location, и проверить изменение, введя команду Get-Location.
PS> Pop-Location PS> Get-Location Path ---- C:\Documents and Settings\me\Local Settings
Как и в случае с командлетом Set-Location, можно включить параметр -PassThru при вводе командлета Pop-Location, чтобы открыть указанный каталог.
PS> Pop-Location -PassThru Path ---- C:\Documents and Settings\PowerUser
Кроме того, можно использовать командлеты расположения с сетевыми путями. Если у вас есть сервер FS01 с общей папкой Public, можно изменить расположение, введя
Set-Location \\FS01\Public
или диспетчер конфигурации служб
Push-Location \\FS01\Public
Чтобы изменить расположение на любой доступный диск, можно использовать команды Push-Location и Set-Location. Например, если у вас есть локальный дисковод компакт-дисков с буквой диска D, содержащий компакт-диск с данными, вы можете изменить расположение на него, введя команду Set-Location D: .
Если дисковод пуст, вы получите следующее сообщение об ошибке:
PS> Set-Location D: Set-Location : Cannot find path 'D:\' because it does not exist.
Работа с файлами и папками. Получение списка файлов и папок, содержащихся в папке.
Извлечь все элементы непосредственно из папки можно с помощью командлета Get-ChildItem. Для отображения скрытых и системных элементов добавьте необязательный параметр Force. Например, эта команда отображает непосредственное содержимое диска C Windows PowerShell (которое совпадает с содержимым физического диска C Windows):
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Force
Эта команда выводит только элементы, содержащиеся на диске непосредственно, так же как и команда DIR оболочки Cmd.exe или команда ls оболочки UNIX. Для показа вложенных элементов необходимо также указать параметр -Recurse. (Время выполнения этой операции будет очень велико.) Для вывода всего содержимого диска C введите:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Force -Recurse
Командлет Get-ChildItem позволяет отфильтровать элементы с помощью параметров Path, Filter, Include и Exclude, но обычно осуществляется лишь фильтрация по имени. Сложную фильтрацию на основе других свойств элементов можно выполнить с помощью Where-Object.
Следующая команда находит все исполняемые файлы в папке Program Files, которые были в последний раз изменены после 1 октября 2005 г. и размер которых не менее одного мегабайта и не более десяти мегабайт:
Get-ChildItem -Path $env:ProgramFiles -Recurse -Include *.exe | Where-Object -FilterScript {($_.LastWriteTime -gt '2005-10-01') -and ($_.Length -ge 1mb) -and ($_.Length -le 10mb)}
Копирование файлов и папок
Копирование выполняется с помощью командлета Copy-Item. Следующая команда создает резервную копию C:\boot.ini в C:\boot.bak:
Copy-Item -Path C:\boot.ini -Destination C:\boot.bak
Если целевой файл уже существует, то попытка копирования завершается неудачей. Чтобы перезаписать имеющийся целевой файл, используйте параметр Force.
Copy-Item -Path C:\boot.ini -Destination C:\boot.bak -Force
Эта команда работает, даже если целевой объект доступен только для чтения.
Так же выполняется и копирование папок. Эта команда копирует папку C:\temp\test1 в новую папку C:\temp\DeleteMe рекурсивно.
Copy-Item C:\temp\test1 -Recurse C:\temp\DeleteMe
Можно также скопировать избранные элементы. Следующая команда копирует все файлы TXT, содержащиеся в папке C:\data, в папку C:\temp\text:
Copy-Item -Filter *.txt -Path c:\data -Recurse -Destination C:\temp\text
Для копирования элементов файловой системы можно использовать и другие средства. В Windows PowerShell по-прежнему работают команды XCOPY, ROBOCOPY и такие COM-объекты, как Scripting.FileSystemObject. Например, можно воспользоваться COM-классом Scripting.FileSystem сервера сценариев Windows для создания резервной копии файла C:\boot.ini в файле C:\boot.bak:
(New-Object -ComObject Scripting.FileSystemObject).CopyFile('C:\boot.ini', 'C:\boot.bak')
Создание файлов и папок
Создание новых элементов осуществляется одинаковым образом всеми поставщиками Windows PowerShell. Если поставщик Windows PowerShell поддерживает более одного типа элементов (например, поставщик Windows PowerShell FileSystem различает каталоги и файлы), необходимо указать тип элемента.
Эта команда создает папку C:\temp\New Folder:
New-Item -Path 'C:\temp\New Folder' -ItemType Directory
Эта команда создает пустой файл C:\temp\New Folder\file.txt.
New-Item -Path 'C:\temp\New Folder\file.txt' -ItemType File
Важно!
При использовании параметра Force с командой New-Item для создания папки, которая уже существует, она не перезапишет и не заменит папку. Будет просто возвращен имеющийся объект папки. Однако, если использовать New-Item -Force в уже имеющимся файле, файл будет полностью перезаписан.
Удаление всех файлов и папок, содержащихся в папке
Удалить вложенные элементы можно с помощью командлета Remove-Item, однако он потребует подтверждения удаления, если элемент сам что-нибудь содержит. Например, при попытке удаления папки C:\temp\DeleteMe, которая содержит другие элементы, Windows PowerShell предварительно предложит подтвердить удаление этой папки:
Remove-Item -Path C:\temp\DeleteMe Confirm The item at C:\temp\DeleteMe has children and the Recurse parameter was not specified. If you continue, all children will be removed with the item. Are you sure you want to continue? [Y] Yes [A] Yes to All [N] No [L] No to All [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "Y"):
Если подтверждение для каждого вложенного элемента нежелательно, задайте параметр Recurse:
Remove-Item -Path C:\temp\DeleteMe -Recurse
Подключение локальной папки как диска
Отобразить локальную папку можно с помощью команды New-PSDrive. Следующая команда создает локальный диск P:, корневым каталогом которого является локальный каталог Program Files, отображающийся только в сеансе PowerShell:
New-PSDrive -Name P -Root $env:ProgramFiles -PSProvider FileSystem
Как и при использовании сетевых дисков, диски, отображенные в Windows PowerShell, немедленно становятся доступными оболочке Windows PowerShell. Чтобы создать подключенный диск, отображающийся в проводнике, нужен параметр -Persist. Но с этим параметром можно использовать только удаленные пути.
Чтение текстового файла в массив
Одним из наиболее общих форматов хранения текстовых данных является файл, отдельные строки которого рассматриваются как отдельные элементы. Командлет Get-Content используется для чтения всего файла за один шаг, как показано далее:
PS> Get-Content -Path C:\boot.ini [boot loader] timeout=5 default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS [operating systems] multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS="Microsoft Windows XP Professional" /noexecute=AlwaysOff /fastdetect multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS=" Microsoft Windows XP Professional with Data Execution Prevention" /noexecute=optin /fastdetect
Командлет Get-Content сразу рассматривает данные, считанные из файла, как массив с одним элементом на строку содержимого файла. Убедиться в этом можно, проверив свойство Length полученного содержимого:
PS> (Get-Content -Path C:\boot.ini).Length 6
Эта команда наиболее полезна для непосредственного ввода в Windows PowerShell информационных списков. Например, можно хранить в файле C:\temp\domainMembers.txt список имен компьютеров или IP-адресов по одному имени на каждую строку файла. Вы можете использовать командлет Get-Content, чтобы извлечь содержимое файла и поместить его в переменную $Computers:
$Computers = Get-Content -Path C:\temp\DomainMembers.txt
Теперь переменная $Computers представляет собой массив, содержащий в каждом элементе имя компьютера.
Работа с файлами, папками и разделами реестра
Перечисление файлов, папок и разделов реестра (Get-ChildItem)
Так как получение коллекции элементов из определенного расположения является обычной задачей, командлет Get-ChildItem разработан специально для возврата всех элементов, найденных в контейнере, например в папке.
Если необходимо вернуть все файлы и папки, которые находятся непосредственно в папке C:\Windows, введите:
PS> Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows
Directory: Microsoft.Windows PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::C:\Windows
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a--- 2006-05-16 8:10 AM 0 0.log
-a--- 2005-11-29 3:16 PM 97 acc1.txt
-a--- 2005-10-23 11:21 PM 3848 actsetup.log
...
Списки выглядят аналогично тем спискам, которые появляются при вводе команды dir в Cmd.exe или команды ls в командной оболочке UNIX.
С помощью параметров командлета Get-ChildItem можно создавать очень сложные списки. Далее рассмотрим несколько сценариев. Синтаксис командлета Get-ChildItem можно увидеть, введя:
Get-Command -Name Get-ChildItem -Syntax
Эти параметры можно скомбинировать и сопоставить для получения настраиваемых выходных данных.
Перечисление всех элементов в контейнере (-Recurse)
Чтобы увидеть оба элемента в папке Windows и все элементы во вложенных папках, используйте параметр Recurse для Get-ChildItem. В списке отображается все, что находится в папке Windows, а также элементы в ее вложенных папках. Пример:
PS> Get-ChildItem -Path C:\WINDOWS -Name addins AppPatch assembly ...
Принудительное перечисление скрытых элементов (-Force)
В выходных данных команды Get-ChildItem не отображаются элементы, которые обычно невидимы в проводнике или Cmd.exe. Чтобы показать скрытые элементы, используйте параметр Force для Get-ChildItem. Пример:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows -Force
Этот параметр называется Force, так как позволяет принудительно переопределить обычное поведение команды Get-ChildItem. Параметр Force широко используется для принудительного выполнения действия командлетом. Тем не менее, он не будет выполнять действия, компрометирующие систему безопасности.
Сопоставление имен элементов с подстановочными знаками
Команда Get-ChildItem допускает подстановочные знаки в пути к перечисляемым элементам.
Так как сопоставление с подстановочными знаками обрабатывается подсистемой Windows PowerShell, все командлеты, которые принимают подстановочные знаки, используют одну нотацию и имеют одно поведение сопоставления. В нотацию подстановочных знаков Windows PowerShell входит:
- Звездочка (*) — соответствует нулю или большему количеству вхождений любого символа.
- знак вопроса (?) — соответствует ровно одному символу;
- Открывающая квадратная скобка ([) и закрывающая квадратная скобка (]) — заключают в себя набор символов для сопоставления.
Далее приводится несколько примеров работы спецификации из подстановочных знаков.
Чтобы найти в каталоге Windows все файлы, имеющие суффикс .log и ровно пять символов в основном имени, введите следующую команду:
PS> Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows\?????.log
Directory: Microsoft.Windows PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::C:\Windows
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
...
-a--- 2006-05-11 6:31 PM 204276 ocgen.log
-a--- 2006-05-11 6:31 PM 22365 ocmsn.log
...
-a--- 2005-11-11 4:55 AM 64 setup.log
-a--- 2005-12-15 2:24 PM 17719 VxSDM.log
...
Чтобы найти в каталоге Windows все файлы с именами, начинающимися на букву x, введите:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows\x*
Чтобы найти все файлы с именами, начинающимися на x или z, введите:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows\[xz]*
Исключение элементов (-Exclude)
Вы можете исключить определенные элементы с помощью параметра Exclude для Get-ChildItem. Это позволит вам выполнить сложную фильтрацию в одном операторе.
Например, предположим, что вы пытаетесь найти библиотеку службы времени Windows в папке System32 и все, что вам известно об имени библиотеки, — то, что оно начинается на W и содержит «32».
Выражение w*32*.dll найдет все библиотеки DLL, удовлетворяющие условию, но может также вернуть библиотеки Windows 95 и библиотеки, совместимые с 16-разрядной версией Windows, в именах которых содержится «95» или «16». Файлы с такими числами в именах можно пропустить, используя параметр Exclude с шаблоном *[9516]* :
PS> Get-ChildItem -Path C:\WINDOWS\System32\w*32*.dll -Exclude *[9516]* Directory: Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::C:\WINDOWS\System32 Mode LastWriteTime Length Name ---- ------------- ------ ---- -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 174592 w32time.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 22016 w32topl.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 101888 win32spl.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 172032 wldap32.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 264192 wow32.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 82944 ws2_32.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 42496 wsnmp32.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 22528 wsock32.dll -a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 18432 wtsapi32.dll
Смешение параметров Get-ChildItem
В одной команде можно использовать несколько параметров Get-ChildItem. Перед тем как комбинировать параметры, убедитесь, что понимаете принципы сопоставления подстановочных знаков. Например, следующая команда не возвращает результатов:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows\*.dll -Recurse -Exclude [a-y]*.dll
Результаты отсутствуют, даже если существуют две библиотеки, которые начинаются на букву z в папке Windows.
Результаты не возвращены, так как подстановочный знак указан как часть пути. Хотя команда и была рекурсивной, командлет Get-ChildItem ограничил элементы до тех, которые находятся в папке Windows с именами, заканчивающимися на .dll.
Чтобы указать рекурсивный поиск для файлов, имена которых соответствуют специальному шаблону, используйте параметр -Include.
PS> Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows -Include *.dll -Recurse -Exclude [a-y]*.dll
Directory: Microsoft.Windows PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::C:\Windows\System32\Setup
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 8261 zoneoc.dll
Directory: Microsoft.Windows PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::C:\Windows\System32
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a--- 2004-08-04 8:00 AM 337920 zipfldr.dll
Работа с записями реестра. Создание списков записей реестра.
Существует несколько способов просмотра реестра. Самый простой — получить имена свойств, связанные с разделом. Например, чтобы просмотреть имена записей в разделе реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion, используйте Get-Item. Разделы реестра содержат свойство с универсальным именем Property, которое является списком записей реестра в разделе. Следующая команда выбирает свойство Property и расширяет элементы так, чтобы они отображались в списке:
Get-Item -Path Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Property
DevicePath MediaPathUnexpanded ProgramFilesDir CommonFilesDir ProductId
Чтобы просмотреть записи реестра в более удобочитаемой форме, используйте Get-ItemProperty.
Get-ItemProperty -Path Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SO
FTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SO
FTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
PSChildName : CurrentVersion
PSDrive : HKLM
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
DevicePath : C:\WINDOWS\inf
MediaPathUnexpanded : C:\WINDOWS\Media
ProgramFilesDir : C:\Program Files
CommonFilesDir : C:\Program Files\Common Files
ProductId : 76487-338-1167776-22465
WallPaperDir : C:\WINDOWS\Web\Wallpaper
MediaPath : C:\WINDOWS\Media
ProgramFilesPath : C:\Program Files
PF_AccessoriesName : Accessories
(default) :
Все свойства Windows PowerShell раздела имеют префиксы PS, например PSPath, PSParentPath, PSChildName и PSProvider.
Для создания ссылки на текущее расположение можно использовать нотацию *.*. Set-Location можно использовать для изменения значения на контейнер реестра CurrentVersion.
Set-Location -Path Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Кроме того, можно использовать встроенный диск HKLM PSDrive с Set-Location.
Set-Location -Path hklm:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Затем можно использовать нотацию *.* для текущего расположения, чтобы перечислить свойства без указания полного пути.
Get-ItemProperty -Path .
... DevicePath : C:\WINDOWS\inf MediaPathUnexpanded : C:\WINDOWS\Media ProgramFilesDir : C:\Program Files ...
Расширение пути работает так же, как и в файловой системе, поэтому в этом расположении можно получить перечисление ItemProperty для HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Help с помощью Get-ItemProperty -Path ..\Help.
Получение одной записи реестра
Если необходимо получить конкретную запись в разделе реестра, можно использовать один из нескольких возможных подходов. Этот пример получает значение DevicePath в HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion.
Вместе с Get-ItemProperty используйте параметр Path, чтобы указать имя раздела и параметр Name, а также имя записи DevicePath.
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name DevicePath
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\
Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\
Microsoft\Windows
PSChildName : CurrentVersion
PSDrive : HKLM
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
DevicePath : C:\WINDOWS\inf
Эта команда возвращает стандартные свойства Windows PowerShell, а также свойство DevicePath.
Примечание
Хотя Get-ItemProperty содержит параметры Filter, Include и Exclude, их нельзя использовать для фильтрации по имени свойства. Эти параметры относятся к разделам реестра (путям элементов), а не записям реестра. Записи реестра — это свойства элементов.
Другой вариант — использовать средство командной строки Reg.exe. Для получения справки по reg.exe введите reg.exe /? в командной строке. Чтобы найти запись DevicePath, используйте reg.exe, как показано в следующей команде:
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion /v DevicePath
! REG.EXE VERSION 3.0
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
DevicePath REG_EXPAND_SZ %SystemRoot%\inf
Также можно использовать объект WshShell COM, чтобы найти некоторые записи реестра, хотя этот метод не работает с большими двоичными данными или именами записей реестра, содержащими такие символы, как \. Добавьте имя свойства с разделителем «\» в путь элемента:
(New-Object -ComObject WScript.Shell).RegRead("HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\DevicePath")
%SystemRoot%\inf
Настройка одной записи реестра
Если необходимо изменить определенную запись в разделе реестра, можно использовать один из нескольких подходов. Этот пример изменяет запись Path в разделе HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment. Запись Path указывает расположение для поиска исполняемых файлов.
- Получите текущее значение записи Path с помощью
Get-ItemProperty. - Добавьте новое значение, отделив его с помощью
;. - Используйте
Set-ItemPropertyс указанным разделом, именем записи и значением, чтобы изменить запись реестра.
$value = Get-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment -Name Path $newpath = $value.Path += ";C:\src\bin\" Set-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment -Name Path -Value $newpath
Примечание
Хотя Set-ItemProperty содержит параметры Filter, Include и Exclude, их нельзя использовать для фильтрации по имени свойства. Эти параметры относятся в разделам реестра (путям элементов), а не к записям реестра (свойствам элементов).
Другой вариант — использовать средство командной строки Reg.exe. Для получения справки по reg.exe введите reg.exe /? . в командной строке.
В следующем примере запись Path изменяется за счет удаления пути, добавленного в предыдущем примере. Get-ItemProperty по-прежнему используется для получения текущего значения, исключая анализ строки, возвращаемой reg query. Методы SubString и LastIndexOf используются для получения последнего добавленного пути в запись Path.
$value = Get-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment -Name Path
$newpath = $value.Path.SubString(0, $value.Path.LastIndexOf(';'))
reg add HKCU\Environment /v Path /d $newpath /f
The operation completed successfully.
Создание новых записей реестра
Чтобы добавить новую запись реестра с именем PowerShellPath в раздел CurrentVersion, используйтеNew-ItemProperty с путем к разделу, именем записи и значением записи. В этом примере используется значение переменной Windows PowerShell $PSHome, в которой хранится путь к каталогу установки Windows PowerShell.
Вы можете добавить новую запись в раздел с помощью следующей команды, и команда также вернет сведения о новой записи:
New-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PowerShellPath -PropertyType String -Value $PSHome
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows PSChildName : CurrentVersion PSDrive : HKLM PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry PowerShellPath : C:\Program Files\Windows PowerShell\v1.0
Значение PropertyType должно быть именем элемента перечисления Microsoft.Win32.RegistryValueKind из следующей таблицы:
Примечание
Запись реестра можно добавить в несколько расположений, указав массив значений для параметра Path:
New-ItemProperty -Name PowerShellPath -PropertyType String -Value $PSHome ` -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion, HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Кроме того, можно перезаписать существующее значение записи реестра, добавив параметр Force в любую команду New-ItemProperty.
Переименование записей реестра
Чтобы переименовать запись PowerShellPath в PSHome, используйте Rename-ItemProperty.
Rename-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PowerShellPath -NewName PSHome
Чтобы отобразить переименованное значение, добавьте параметр PassThru в команду.
Rename-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PowerShellPath -NewName PSHome -passthru
Удаление записей реестра
Чтобы удалить записи реестра PSHome и PowerShellPath, используйте Remove-ItemProperty.
Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSHome Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PowerShellPath
Время на прочтение
4 мин
Количество просмотров 22K
В этой статье рассмотрим почему мы все любим Powershell на паре рабочих примеров. Все это будет полезно при инвентаризации, поиске конкретного компьютера и прочих делах. Powershell оборудован удобными и запоминающимися командлетами, автодополнение всего и интуитивные названия делают его наверное самым простым в освоении языком.
В этом руководстве рассмотрим несколько крутых по мнению автора команд и расскажем почему это круто. Начнем со снипетов.
Полезные снипеты:
Заносим компьютер в TrustedHosts
Пригодится при подключении к серверу по WinRm. Команда перезапишет предыдущее значение, будьте осторожны, добавляйте ip или имена хостов через запятую. Если все ваши хосты находятся в AD, трогать этот файл не нужно.
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value '192.168.0.1'Wildcard тоже работает, если не хотите каждый раз добавлять новый хост в TrustedHosts.
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value '*'Храним пароль в зашифрованном виде в файле:
Пригодится для автоматизации, сильно облегчает жизнь при выполнении скриптов из планировщика, но при этом пароль хранится в безопасном виде.
Если выполнять скрипты из под зашедшего пользователя, будут использоваться креды этого пользователя.
Read-Host -AsSecureString | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force | ConvertFrom-SecureString | Out-File -FilePath .\Password.txtЗабираем зашифрованный пароль из файла:
$Password = Get-Content C:\Password.txt | ConvertTo-SecureStringТоже самое можно проделать и с Credentials, заменим Read-Host на Get-Credential.
Get-Credential | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force | ConvertFrom-SecureString | Out-File -FilePath .\Credential.txtПолучаем дату последней загрузки ОС.
(gcim win32_operatingsystem).LastBootUpTimeТем же самым способом получаем еще и аптайм.
Get-CimInstance Win32_operatingsystem -ComputerName $computers |
Select-Object LastBootUpTime,
@{Name="Uptime";Expression = {(Get-Date) - $_.LastBootUptime}} Получаем список установленных программ:
Именно программ, а не компонентов:
Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, Publisher, InstallDate |
Format-Table –AutoSize
Получаем список дисков, в том числе сетевых и свободное место на них
Get-PSDrive -PSProvider filesystem | where-object {$_.used -gt 0} |
Select-Object -property Root,@{name="Size";expression={($_.used+$_.free)/1GB -as [int]}},
@{name="Used";expression={($_.used/1GB) -as [int]}},
@{name="Free";expression={($_.free/1GB) -as [int]}} Останавливаем процесс по его имени.
В этом примере останавливаем Chrome. Wildcard тоже подойдет, если хотите завершить всё.
Get-Process -Name "chrome" | Stop-ProcessКопируем настройки доступа к папкам на дочерние папки
Пригодится, если вам захочется отобрать или дать права на пользование к папке и всем подпапкам у группы пользователей или у пользователя. Команда рекурсивно, снизу вверх копирует права на чтение и запись.
Копируем ACL у папки:
$Acl = Get-Acl -Path C:\folder\Вставляем ACL на все файлы и подпапки:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Folder\ -Recurse | Set-Acl $Acl Полезные скрипты:
Вот тут начинается самое страшное веселье. Если вам нужно провести инвентаризацию, будет очень полезно глянуть. Если ваши компьютеры не в AD, то скрипт станет немного сложнее, итерировать придется по заранее составленному файлу, а пароли нужно будет брать из файла или через Get-Credential. Вся разница:
C AD:
$ADComputers = (Get-ADComputer -filter *).DNSHostNameБез AD:
$Credentials = Get-Credential
$Computers = Get-Content -Path C:\servers.txtПолучаем аптайм дату последней загрузки каждого из компьютеров в AD:
$ADComputers = (Get-ADComputer -filter *).DNSHostName
foreach ($i in $ADComputers) {
Invoke-Command $i {
Get-CimInstance Win32_operatingsystem |
Select-Object LastBootUpTime,
@{Name="Uptime";Expression = {(Get-Date) - $_.LastBootUptime}}
}
}
Получаем все установленные программы на всех компьютерах AD:
$ADComputers = (Get-ADComputer -filter *).DNSHostName
foreach ($i in $ADComputers) {
Invoke-Command -computername $i {
gcim win32_product -computername $env:computername | Sort-Object -property Vendor,Name | Select-Object -property Vendor,Name, Caption
}
}Тоже самое можно будет получить и для компонентов, подставив в Invoke-Command:
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object -Property "Installed" -EQ "Installed"Получаем компьютеры, где запущен нужный нам процесс:
Если вы забыли на каком компьютере запущена та или иная программа, можно получить её таким способом. Рассмотрим на примере браузера:
$ADComputers = (Get-ADComputer -filter *).DNSHostName
foreach ($i in $ADComputers) {
Invoke-Command -computername $i {
Get-Process -Name "Chrome" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
}Убить браузер можно будет так же легко, как и получить процесс:
$ADComputers = (Get-ADComputer -filter *).DNSHostName
foreach ($i in $ADComputers) {
Invoke-Command -computername $i {
Get-Process -Name "Chrome" | Stop-Process -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
}Получаем компьютеры, где установлена конкретная программа:
Кокретно в этом случае Java. Поможет при проведении инвентаризации можно будет посмотреть имена компьютеров где она была установлена.
$ADComputers = (Get-ADComputer -filter *).DNSHostName
foreach ($i in $ADComputers) {
Invoke-Command -computername $i {
gcim win32_product -computername $env:computername | Select-String -Pattern "Java" -AllMatches | Sort-Object -property Vendor,Name | Format-Table -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
}Если у вас возникнут предложения, будем рады добавить их в эту статью. Надеемся, эти примеры были для вас полезны.
Предлагаем обновлённый тариф UltraLite Windows VDS за 99 рублей с установленной Windows Server 2019 Core.