How can I script a bat or cmd to stop and start a service reliably with error checking (or let me know that it wasn’t successful for whatever reason)?
mmcdole
91.6k60 gold badges186 silver badges222 bronze badges
asked Sep 25, 2008 at 15:09
0
Use the SC (service control) command, it gives you a lot more options than just start & stop.
DESCRIPTION:
SC is a command line program used for communicating with the
NT Service Controller and services.
USAGE:
sc <server> [command] [service name] ...
The option <server> has the form "\\ServerName"
Further help on commands can be obtained by typing: "sc [command]"
Commands:
query-----------Queries the status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
queryex---------Queries the extended status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
start-----------Starts a service.
pause-----------Sends a PAUSE control request to a service.
interrogate-----Sends an INTERROGATE control request to a service.
continue--------Sends a CONTINUE control request to a service.
stop------------Sends a STOP request to a service.
config----------Changes the configuration of a service (persistant).
description-----Changes the description of a service.
failure---------Changes the actions taken by a service upon failure.
qc--------------Queries the configuration information for a service.
qdescription----Queries the description for a service.
qfailure--------Queries the actions taken by a service upon failure.
delete----------Deletes a service (from the registry).
create----------Creates a service. (adds it to the registry).
control---------Sends a control to a service.
sdshow----------Displays a service's security descriptor.
sdset-----------Sets a service's security descriptor.
GetDisplayName--Gets the DisplayName for a service.
GetKeyName------Gets the ServiceKeyName for a service.
EnumDepend------Enumerates Service Dependencies.
The following commands don't require a service name:
sc <server> <command> <option>
boot------------(ok | bad) Indicates whether the last boot should
be saved as the last-known-good boot configuration
Lock------------Locks the Service Database
QueryLock-------Queries the LockStatus for the SCManager Database
EXAMPLE:
sc start MyService
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:15
FerruccioFerruccio
99k38 gold badges226 silver badges299 bronze badges
4
net start [serviceName]
and
net stop [serviceName]
tell you whether they have succeeded or failed pretty clearly. For example
U:\>net stop alerter
The Alerter service is not started.
More help is available by typing NET HELPMSG 3521.
If running from a batch file, you have access to the ERRORLEVEL of the return code. 0 indicates success. Anything higher indicates failure.
As a bat file, error.bat:
@echo off
net stop alerter
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto error
exit
:error
echo There was a problem
pause
The output looks like this:
U:\>error.bat
The Alerter service is not started.
More help is available by typing NET HELPMSG 3521.
There was a problem
Press any key to continue . . .
Return Codes
- 0 = Success
- 1 = Not Supported
- 2 = Access Denied
- 3 = Dependent Services Running
- 4 = Invalid Service Control
- 5 = Service Cannot Accept Control
- 6 = Service Not Active
- 7 = Service Request Timeout
- 8 = Unknown Failure
- 9 = Path Not Found
- 10 = Service Already Running
- 11 = Service Database Locked
- 12 = Service Dependency Deleted
- 13 = Service Dependency Failure
- 14 = Service Disabled
- 15 = Service Logon Failure
- 16 = Service Marked For Deletion
- 17 = Service No Thread
- 18 = Status Circular Dependency
- 19 = Status Duplicate Name
- 20 = Status Invalid Name
- 21 = Status Invalid Parameter
- 22 = Status Invalid Service Account
- 23 = Status Service Exists
- 24 = Service Already Paused
Edit 20.04.2015
Return Codes:
The NET command does not return the documented Win32_Service class return codes (Service Not Active,Service Request Timeout, etc) and for many errors will simply return Errorlevel 2.
Look here: http://ss64.com/nt/net_service.html
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:13
Bill MichellBill Michell
8,2703 gold badges29 silver badges33 bronze badges
3
You can use the NET START command and then check the ERRORLEVEL environment variable, e.g.
net start [your service]
if %errorlevel% == 2 echo Could not start service.
if %errorlevel% == 0 echo Service started successfully.
echo Errorlevel: %errorlevel%
Disclaimer: I’ve written this from the top of my head, but I think it’ll work.
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:15
Jonas EngströmJonas Engström
5,0153 gold badges38 silver badges36 bronze badges
0
Instead of checking codes, this works too
net start "Apache tomcat" || goto ExitError
:End
exit 0
:ExitError
echo An error has occurred while starting the tomcat services
exit 1
Mr_Green
40.8k45 gold badges160 silver badges271 bronze badges
answered Dec 7, 2013 at 16:45
vanvalvanval
9971 gold badge9 silver badges19 bronze badges
I have created my personal batch file for this, mine is a little different but feel free to modify as you see fit.
I created this a little while ago because I was bored and wanted to make a simple way for people to be able to input ending, starting, stopping, or setting to auto. This BAT file simply requests that you input the service name and it will do the rest for you. I didn’t realize that he was looking for something that stated any error, I must have misread that part. Though typically this can be done by inputting >> output.txt on the end of the line.
The %var% is just a way for the user to be able to input their own service into this, instead of having to go modify the bat file every time that you want to start/stop a different service.
If I am wrong, anyone can feel free to correct me on this.
@echo off
set /p c= Would you like to start a service [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :1
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :2
:1
set /p var= Service name:
:2
set /p c= Would you like to stop a service [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :3
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :4
:3
set /p var1= Service name:
:4
set /p c= Would you like to disable a service [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :5
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :6
:5
set /p var2= Service name:
:6
set /p c= Would you like to set a service to auto [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :7
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :10
:7
set /p var3= Service name:
:10
sc start %var%
sc stop %var1%
sc config %var2% start=disabled
sc config %var3% start=auto
answered Jun 13, 2015 at 1:31
2
Using the return codes from net start and net stop seems like the best method to me. Try a look at this: Net Start return codes.
bluish
26.4k28 gold badges122 silver badges181 bronze badges
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:12
ZombieSheepZombieSheep
29.6k12 gold badges67 silver badges114 bronze badges
1
Syntax always gets me…. so…
Here is explicitly how to add a line to a batch file that will kill a remote service (on another machine) if you are an admin on both machines, run the .bat as an administrator, and the machines are on the same domain. The machine name follows the UNC format \myserver
sc \\ip.ip.ip.ip stop p4_1
In this case… p4_1 was both the Service Name and the Display Name, when you view the Properties for the service in Service Manager. You must use the Service Name.
For your Service Ops junkies… be sure to append your reason code and comment! i.e. ‘4’ which equals ‘Planned’ and comment ‘Stopping server for maintenance’
sc \\ip.ip.ip.ip stop p4_1 4 Stopping server for maintenance
answered Jan 28, 2014 at 20:52
ATSiemATSiem
1,19412 silver badges19 bronze badges
2
We’d like to think that «net stop » will stop the service. Sadly, reality isn’t that black and white. If the service takes a long time to stop, the command will return before the service has stopped. You won’t know, though, unless you check errorlevel.
The solution seems to be to loop round looking for the state of the service until it is stopped, with a pause each time round the loop.
But then again…
I’m seeing the first service take a long time to stop, then the «net stop» for a subsequent service just appears to do nothing. Look at the service in the services manager, and its state is still «Started» — no change to «Stopping». Yet I can stop this second service manually using the SCM, and it stops in 3 or 4 seconds.
answered Feb 10, 2014 at 17:04
DaveHDaveH
511 silver badge1 bronze badge
or you can start remote service with this cmd : sc \\<computer> start <service>
answered Jan 27, 2012 at 8:56
onionpsyonionpsy
1,50211 silver badges15 bronze badges
I just used Jonas’ example above and created full list of 0 to 24 errorlevels. Other post is correct that net start and net stop only use errorlevel 0 for success and 2 for failure.
But this is what worked for me:
net stop postgresql-9.1
if %errorlevel% == 2 echo Access Denied - Could not stop service
if %errorlevel% == 0 echo Service stopped successfully
echo Errorlevel: %errorlevel%
Change stop to start and works in reverse.
answered Feb 12, 2016 at 16:33
Manual service restart is ok — services.msc has «Restart» button, but in command line both sc and net commands lacks a «restart» switch and if restart is scheduled in cmd/bat file, service is stopped and started immediately, sometimes it gets an error because service is not stopped yet, it needs some time to shut things down.
This may generate an error:
sc stop
sc start
It is a good idea to insert timeout, I use ping (it pings every 1 second):
sc stop
ping localhost -n 60
sc start
answered May 24, 2016 at 8:55
KulerisKuleris
1011 silver badge3 bronze badges
Here is the Windows 10 command to start System Restore using batch :
sc config swprv start= Auto
You may also like those commands :
-
Change registry value to auto start System restore
REG ADD «HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore» /v DisableSR /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
-
Create a system restore point
Wmic.exe /Namespace:\root\default Path SystemRestore Call CreateRestorePoint «djibe saved your PC», 100, 12
-
Change System Restore disk usage
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=C: /on=C: /maxsize=10%
Enjoy
answered Nov 26, 2018 at 19:53
djibedjibe
2,7732 gold badges17 silver badges26 bronze badges
- SC
- NET STOP/START
- PsService
- WMIC
- Powershell is also easy for use option
SC and NET are already given as an anwests. PsService add some neat features but requires a download from Microsoft.
But my favorite way is with WMIC as the WQL syntax gives a powerful way to manage more than one service with one line (WMI objects can be also used through powershell/vbscript/jscript/c#).
The easiest way to use it:
wmic service MyService call StartService
wmic service MyService call StopService
And example with WQL
wmic service where "name like '%%32Time%%' and ErrorControl='Normal'" call StartService
This will start all services that have a name containing 32Time and have normal error control.
Here are the methods you can use.
With :
wmic service get /FORMAT:VALUE
you can see the available information about the services.
answered Nov 5, 2020 at 16:15
npocmakanpocmaka
55.6k18 gold badges148 silver badges188 bronze badges
SC can do everything with services… start, stop, check, configure, and more…
bluish
26.4k28 gold badges122 silver badges181 bronze badges
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:26
AxemanAxeman
3491 silver badge7 bronze badges
Sometimes you can find the stop does not work..
My SQlServer sometimes does this. Using the following commandline kills it. If you really really need your script to kill stuff that doesn’t stop. I would have it do this as a last resort
taskkill /pid [pid number] /f
answered May 9, 2018 at 9:52
andrew pateandrew pate
3,85336 silver badges28 bronze badges
I am writing a windows service in C#, the stop/uninstall/build/install/start loop got too tiring. Wrote a mini script, called it reploy.bat and dropped in my Visual Studio output directory (one that has the built service executable) to automate the loop.
Just set these 3 vars
servicename : this shows up on the Windows Service control panel (services.msc)
slndir : folder (not the full path) containing your solution (.sln) file
binpath : full path (not the folder path) to the service executable from the build
NOTE: This needs to be run from the Visual Studio Developer Command Line for the msbuild command to work.
SET servicename="My Amazing Service"
SET slndir="C:dir\that\contains\sln\file"
SET binpath="C:path\to\service.exe"
SET currdir=%cd%
call net stop %servicename%
call sc delete %servicename%
cd %slndir%
call msbuild
cd %bindir%
call sc create %servicename% binpath=%binpath%
call net start %servicename%
cd %currdir%
Maybe this helps someone 
answered Oct 5, 2018 at 18:53
sh87sh87
1,06310 silver badges12 bronze badges
1
I didn’t find any of the answers above to offer a satisfactory solution so I wrote the following batch script…
:loop
net stop tomcat8
sc query tomcat8 | find "STOPPED"
if errorlevel 1 (
timeout 1
goto loop
)
:loop2
net start tomcat8
sc query tomcat8 | find "RUNNING"
if errorlevel 1 (
timeout 1
goto loop2
)
It keeps running net stop until the service status is STOPPED, only after the status is stopped does it run net start. If a service takes a long time to stop, net stop can terminate unsuccessfully. If for some reason the service does not start successfully, it will keep attempting to start the service until the state is RUNNING.
answered Nov 25, 2021 at 2:59
MickMick
6,5774 gold badges52 silver badges68 bronze badges
With this can start a service or program that need a service
@echo
taskkill /im service.exe /f
taskkill /im service.exe /f
set "reply=y"
set /p "reply=Restart service? [y|n]: "
if /i not "%reply%" == "y" goto :eof
cd "C:\Users\user\Desktop"
start service.lnk
sc start service
eof
exit
answered Mar 10, 2022 at 17:46
Время на прочтение
8 мин
Количество просмотров 111K
Продолжаем знакомиться с тем, как осуществлять управление службами Windows с использованием PowerShell. В предыдущем посте мы рассмотрели, как получить статус службы на локальном и удаленном компьютере, произвести фильтрацию служб (например, найти только остановленные службы) и определить зависимые службы. В этом посте будут рассмотрены такие достаточно тривиальные вещи, как:
- Остановка службы
- Запуск службы
- Перезапуск службы
- Приостановка и возобновление работы
- Управление удаленными службами
- Настраиваем автозагрузку службы
Мы уделим большее внимание разбору команд в PowerShell для осуществления выше перечисленного на локальном компьютере. В разделе “управление службами удаленных компьютерах” мы рассмотрим, ограничения работы в PowerShell v2 и v3. Подробности под катом.
Предыдущая статья:
Управляем службами Windows с помощью PowerShell. Часть 1. Получаем статус служб
PS C:\> get-service bits
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
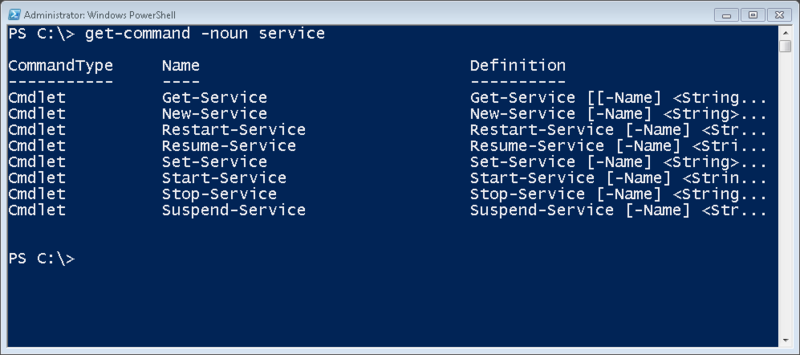
Так как команда для получения статуса службы называется Get-Service, догадаться о том, как пишутся другие команды не составит труда. На худой конец мы можем спросить у PowerShell обо всех командах, так или иначе относящихся к работе со службами. Обратите внимание, что мы использовали параметр –noun для получения всех команд, связанных со службами.
Взглянем на эти команды внимательнее.
STOP-SERVICE
Чтобы остановить службу, мы должны уточнить ее имя.
PS C:\> stop-service wuauserv
Однако в конвейер ничего не будет передано. Некоторые командлеты, такие как Stop-Service, созданы таким образом, что по умолчанию они не записывают объект в конвейер. Мы же заставим это сделать, использовав параметр –Passthru.
PS C:\> stop-service bits -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Если служба не запущена, то командлет ничего не выведет, равно как и не выдаст никакой ошибки. Поэтому иногда лучше передать объект в Stop-Service (естественно использовав при этом параметр –whatif).
PS C:\> get-service browser | stop-service -WhatIf
What if: Performing operation “Stop-Service” on Target “Computer Browser (browser)”.
Параметр –WhatIf был добавлен для того, чтобы мы посмотрели, что будет, если командлет будет запущен. Когда я удостоверюсь, что это именно та служба, которая меня интересует, я просто удалю -Whatif и остановлю службу.
PS C:\> get-service browser | stop-service
Как я уже упомянул выше, если служба уже остановлена, то командлет ничего не сделает. И использование Stop-Service в этом случае никому не навредит. Однако я все же предпочитают более цивилизованный подход, а именно:
PS C:\> get-service bits | where {$_.status -eq 'running'} | stop-service -pass
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Если служба запущена, то объект передается в конвейер и отправляется в Stop-Service. Ниже приведен вариант с остановкой нескольких служб.
PS C:\> get-service bits,wsearch,winrm,spooler | where {$_.status -eq 'running'} | stop-service -whatif
What if: Performing operation "Stop-Service" on Target "Print Spooler (spooler)".
What if: Performing operation "Stop-Service" on Target "Windows Remote Management (WS-Management) (winrm)".
What if: Performing operation "Stop-Service" on Target "Windows Search (wsearch)".
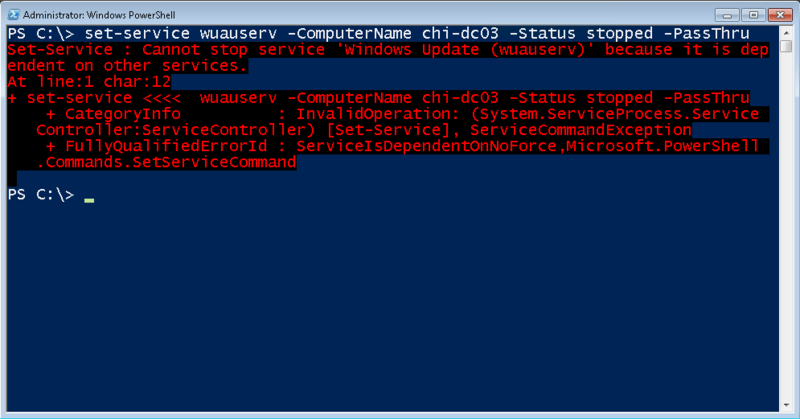
Некоторые службы не захотят останавливаться – в силу наличия зависимых служб – что мы и видим на скриншоте ниже.
В таком случае используем параметр –Force. В большинстве случаев это работает, но без “защиты от дурака”. Помните, что команда также остановит зависимые службы.
PS C:\> stop-service lanmanserver -force –PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped Browser Computer Browser
Stopped lanmanserver Server
START-SERVICE
Запуск службы осуществляется аналогичным образом. Он поддерживает параметр –Whatif, и вам придется использовать –Passthru, чтобы увидеть объекты.
PS C:\> start-service wuauserv -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running wuauserv Windows Update
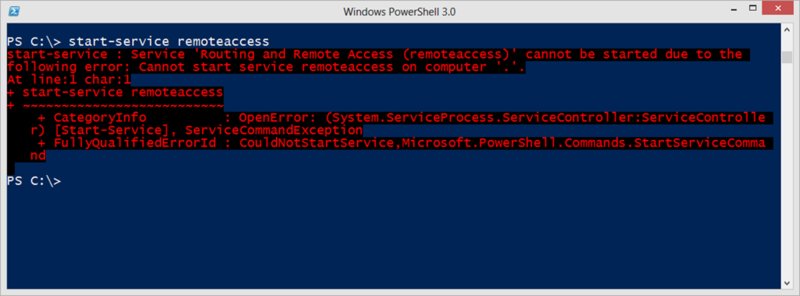
И снова: если служба уже запущена, командлет ничего не сделает. Однако вы можете попытаться запустить службу и получите такую ошибку.
Причиной тому в большинстве случаев является выключенные службы. Как конфигурировать настройки службы, я расскажу в следующей статье.
Если вы хотите запустить службы и все службы, зависимые от нее, используйте следующее выражение:
PS C:\> get-service lanmanserver | Foreach { start-service $_.name -passthru; start-service $_.DependentServices -passthru}
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running lanmanserver Server
Running Browser Computer Browser
Мы должны явно получить зависимые службы, потому что Start-Service не запустит автоматически их.
RESTART-SERVICE
Вы удивитесь, но перезапуск службы работает также как два предыдущих примера. Используйте –Passthru, если хотите убедиться, что служба запущена.
PS C:\> restart-service spooler -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running spooler Print Spooler
Так как мы осуществляем остановку службы, нам может понадобиться параметр –Force.
ПРИОСТАНОВКА И ВОЗОБНОВЛЕНИЕ РАБОТЫ
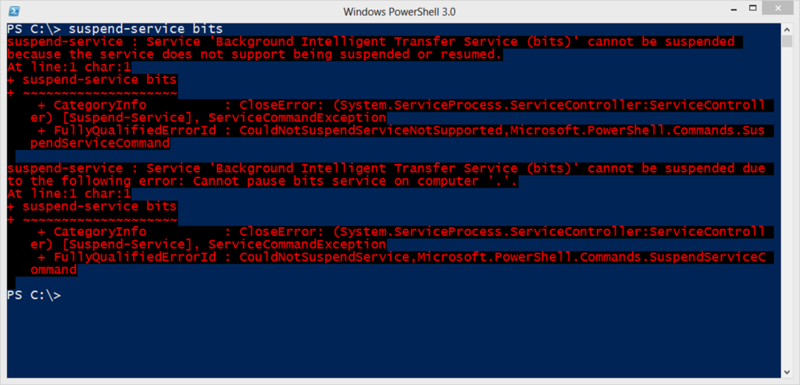
Работа некоторых служб может быть приостановлена на некоторое время, а затем возобновлена, и мы можем это сделать через PowerShell. Однако если служба не удовлетворяет требованиям, мы получим такие ошибки. (на примере показано, что мы пытались приостановить службу bits)
В чем же проблема? Смотрим на объект (используя Get-Service).
PS C:\> get-service bits | select *
Name : bits
RequiredServices : {RpcSs, EventSystem}
CanPauseAndContinue : False
CanShutdown : False
CanStop : True
DisplayName : Background Intelligent Transfer Service
DependentServices : {}
MachineName : .
ServiceName : bits
ServicesDependedOn : {RpcSs, EventSystem}
ServiceHandle : SafeServiceHandle
Status : Running
ServiceType : Win32ShareProcess
Site :
Container :
Если значение свойства CanPauseAndContinue равно True, значит мы можем приостанавливать и возобновлять работу службы. Найдем такие службы:
PS C:\> get-service | where {$_.CanPauseandContinue}
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running LanmanServer Server
Running LanmanWorkstation Workstation
Running MSSQLSERVER SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER)
Running O2FLASH O2FLASH
Running stisvc Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)
Running Winmgmt Windows Management Instrumentation
Как мы видим, не так много служб удовлетворяют этому требованию.
PS C:\> suspend-service o2flash -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Paused O2FLASH o2flash
Готовы возобновить работу службы? Используйте следующее выражение:
PS C:\> resume-service o2flash -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running O2FLASH o2flash
Оба командлета также поддерживают –Whatif.
УДАЛЕННЫЕ СЛУЖБЫ
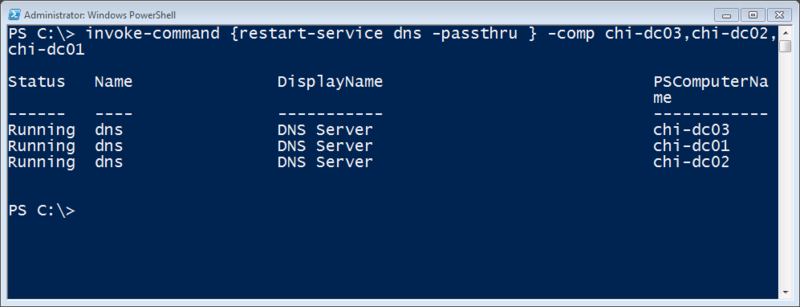
Как вы могли обратить внимание, все примере выше мы демонстрировали на локальном машине. И это неслучайно. К сожалению даже в PowerShell v3, ни у одного из этих командлетов нет параметра, который позволял бы управлять службой на удаленном компьютере. Get-Service, конечно, поддерживает параметр –Computername, но не более. Службу лицезреть вы сможете, а что-либо с ней сделать не получится. Нет, можно, конечно, если удаленный компьютер работает с PS v2 и включен PowerShell Remoting. Тогда мы можете использовать все выше приведенные команды, используя Invoke-Command для удаленного компьютера или PSSession. С другой стороны, проще управлять одной службой на нескольких серверах.
PS C:\> Invoke-Command {restart-service dns –passthru} –comp chi-dc03,chi-dc02,chi-dc01
Управление службами на удаленных компьютерах не ограничивается вышеперечисленным, но это уже будет предмет рассмотрения последующих статей.
Все эти командлеты могут быть использованы в конвейерном выражении и зачастую это лучший вариант. Использование Get-Service для получения объектов и последующая передача их в подходящий командлет.
УСТАНАВЛИВАЕМ УДАЛЕННЫЙ СТАТУС
Итак, мы выяснили, что у командлета Stop-Service отсутствует такой полезный параметр как –Computername. Мы можете использовать эти команды в удаленной сессии, обратившись к командлету Invoke-Command, что уже само по себе продуктивно, если вы работаете со службой на нескольких компьютерах. Одно можно запускать, останавливать, перезапускать, ставить на паузу и запускать заново, используя Set-Service.
PS C:\> set-service wuauserv -ComputerName chi-dc03 -Status stopped -WhatIf
What if: Performing operation "Set-Service" on Target "Windows Update (wuauserv)".
Эта команда поддерживает параметр –WhatIf. Вы также должны использовать –Passthru для передачи объектов в конвейер.
PS C:\> set-service bits -ComputerName chi-dc03 -Status running -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Валидными значениям для параметра –Status являются “запущена” (running), “остановлена” (stopped) и “на паузе” (paused). Помните, что у службы есть зависимые службы, мы не сможете изменять ее, что и продемонстрировано на скриншоте ниже.
К сожалению, у Set-Service отсутствует параметр –Force, поэтому придется вернуться к использованию PowerShell remoting и Invoke-Command. Если вы хотите перезапустить удаленную службу, используйте следующую команду:
PS C:\> set-service w32time -ComputerName chi-dc03 -Status Stopped -PassThru | set-service -PassThru -Status Running
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running w32time Windows Time
Не забудьте использовать –Passthru, в противном случае вторая команда Set-Service ничего не осуществит.
Что по мне, так я предпочитаю работать сразу с несколькими службами, которые я не могу удаленно остановить, используя Set-Service, хотя их запуск проблем составляет. Я использую Invoke-Command. Но помните, что используя параметр –Computername PowerShell осуществляет подключение, используя RPC и DCOM, что может привести к проблемам с файрволом. Invoke-Command использует PowerShell remoting, который мы может быть еще не настроили или не включили.
УСТАНАВЛИВАЕМ ТИП АВТОЗАПУСКА СЛУЖБЫ
Set-Service полезнен, когда вы хотите включить или отключить службу, используя параметр –StartupType. Если Вы настроили службу, используя значения Automatic, Manual or Disabled. К сожалению, не существует варианта для Automatic (Delayed).
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Manual -WhatIf
What if: Performing operation "Set-Service" on Target "Remote Registry (remoteregistry)".
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Manual -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped remoteregistry Remote Registry
Однако, просто взглянув на объект, мы не сможем сказать, к какому типу автозагрузки он относится.
PS C:\> get-service remoteregistry | select *
Name : remoteregistry
RequiredServices : {RPCSS}
CanPauseAndContinue : False
CanShutdown : False
CanStop : False
DisplayName : Remote Registry
DependentServices : {}
MachineName : .
ServiceName : remoteregistry
ServicesDependedOn : {RPCSS}
ServiceHandle : SafeServiceHandle
Status : Stopped
ServiceType : Win32ShareProcess
Site :
Container :
Как это сделать – одна из тем следующей статьи.
Помните, что изменение типа автозагрузки не повлияет на текущий статус службы.
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Disabled -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running remoteregistry Remote Registry
Так что если вы хотите выключить и остановить (или включить и запустить) службу, передайте объект в подходящий командлет.
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Disabled -PassThru | Stop-Service -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped remoteregistry Remote Registry
Технически, Set-Service позволяет вам изменить отображаемое имя службы и описание, но лично мне никогда не приходилось использовать в своей работе. Я использую Set-Service для включения и выключения служб. Если необходимо управлять службами удаленно, то я использую Invoke-Command.
Все, что я продемонстрировал в последних статьях, было связано с использованием специфических типов объектов службы, которые, как вы могли заметить, имеют некоторые ограничения. В следующей статье мы рассмотрим другие возможности по управлению службами, которые призваны обойти эти ограничения.
Upd:
В посте приведены переводы статей с портала 4sysops.com
Managing Services the PowerShell way – Part 3
Managing Services the PowerShell way – Part 4
I have a batch script that looks like:
sc stop myservice
sc start myservice
it errors out because sc doesn’t wait till the service is stopped. How do I restart a service with a script?
splattne
28.5k20 gold badges98 silver badges148 bronze badges
asked Jun 12, 2009 at 22:48
1
The poster wants to ensure the service is stopped before trying to restart it. You can use a loop on the output of «sc query» doing something like this:
:stop
sc stop myservice
rem cause a ~10 second sleep before checking the service state
ping 127.0.0.1 -n 10 -w 1000 > nul
sc query myservice | find /I "STATE" | find "STOPPED"
if errorlevel 1 goto :stop
goto :start
:start
net start | find /i "My Service">nul && goto :start
sc start myservice
answered Jun 12, 2009 at 22:54
crbcrb
7,9981 gold badge38 silver badges53 bronze badges
11
May be missing something, but I use this all the time:
net stop «myservice»
net start «myservice»
or shorter:
net stop «myservice» && net start «myservice»
answered Jun 13, 2009 at 0:23
SkawtSkawt
6984 silver badges9 bronze badges
Dead simple with powershell:
PS >Restart-Service MySrvcHere
Even better, using display names:
PS >Restart-Service -displayname "My Service Name Here"
Get-Help Restart-Service for more
answered Jun 13, 2009 at 8:50
Factor MysticFactor Mystic
4631 gold badge10 silver badges15 bronze badges
If it is purely for restarting the service, you can use
Net stop myservice
Net start myservice
However, if you want access to the options of sc, you can use the start /wait command
start /B /WAIT CMD /C "sc stop myservice"
start /B /WAIT CMD /C "sc start myservice"
this technique is a more general solution that can be applied to any command.
answered Jun 13, 2009 at 9:29
Peter StuerPeter Stuer
1,4739 silver badges11 bronze badges
1
To have quiet restart of some service, which asks confirmations to be stopped (as Server service, for example), You could add /y to the end of stop command.
net stop Server /y
net start Server
It would be helpful for automatic script execution.
answered May 20, 2011 at 14:55
Fedir RYKHTIKFedir RYKHTIK
5971 gold badge9 silver badges18 bronze badges
If you want to restart a failed service you do not need to run a script. In the services MMC snapin right click on a service, select properties, click the recovery tab. Here you can set what actions you want taken should the service stop. There is alot of flexibility available. You will need a script if y ou are trying to stop the service , do something then start the script, preface the batch file with net stop "myserviceshortname" and end with net start "myserviceshortname"
In vbscipt it’s a little more code to stop a service and its’ dependants:
strComputer = "."
Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:" _
& "{impersonationLevel=impersonate}!\\" & strComputer & "\root\cimv2")
Set colServiceList = objWMIService.ExecQuery("Associators of " _
& "{Win32_Service.Name='myservice'} Where " _
& "AssocClass=Win32_DependentService " & "Role=Antecedent" )
For each objService in colServiceList
objService.StopService()
Next
Wscript.Sleep 20000
Set colServiceList = objWMIService.ExecQuery _
("Select * from Win32_Service where Name='myservice'")
For each objService in colServiceList
errReturn = objService.StopService()
Next
Here’s starting a service and anything it depends on (this should be familiar)
strComputer = "."
Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:" _
& "{impersonationLevel=impersonate}!\\" & strComputer & "\root\cimv2")
Set colServiceList = objWMIService.ExecQuery _
("Select * from Win32_Service where Name='Myservice'")
For each objService in colServiceList
errReturn = objService.StartService()
Next
Wscript.Sleep 20000
Set colServiceList = objWMIService.ExecQuery("Associators of " _
& "{Win32_Service.Name='myservice'} Where " _
& "AssocClass=Win32_DependentService " & "Role=Dependent" )
For each objService in colServiceList
objService.StartService()
Next
answered Jun 13, 2009 at 3:22
Jim BJim B
24.1k4 gold badges36 silver badges60 bronze badges
You may use the following commands:
@echo off
sc Stop <Name of Agentry Service Here>
timeout 30
sc start <Name of Agentry Service Here>
PeterJ
1354 gold badges4 silver badges15 bronze badges
answered Feb 26, 2016 at 6:59
I made a hybrid: in *.cmd file:
powershell -Command "& {Restart-Service MyService;}"
answered Oct 15, 2020 at 5:54
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
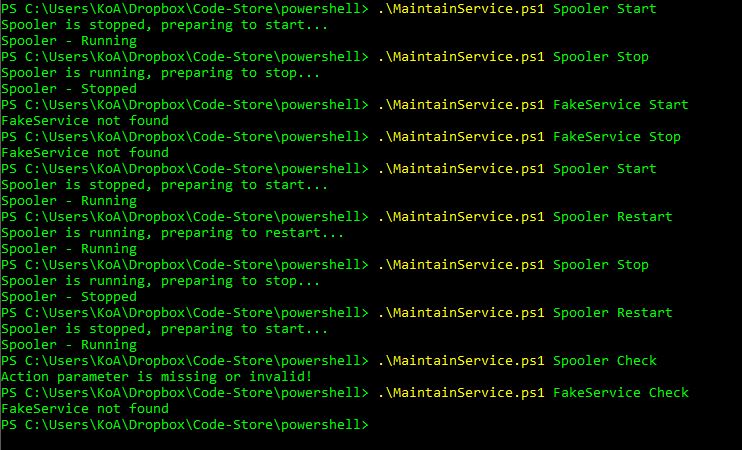
- Copy and save the below script as MaintainService.ps1
- Open Powershell and navigate to the path where the script is saved
- Simply type part of the script name and then press tab for auto-complete
- You have to provide a service name and action (stop, start, restart) as part of the script parameters.
<#
Author: Khoa Nguyen
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> $PSVersionTable.PSVersion
Major Minor Build Revision
----- ----- ----- --------
5 1 15063 608
This is a quick script to start, stop and restart a service. The script will validate that
the service exists and the required action parameter (stop, start, restart) is valid prior
to executing the script.
Sample Executions:
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 Spooler Start
Spooler is stopped, preparing to start...
Spooler - Running
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 Spooler Stop
Spooler is running, preparing to stop...
Spooler - Stopped
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 FakeService Start
FakeService not found
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 FakeService Stop
FakeService not found
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 Spooler Start
Spooler is stopped, preparing to start...
Spooler - Running
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 Spooler Restart
Spooler is running, preparing to restart...
Spooler - Running
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 Spooler Stop
Spooler is running, preparing to stop...
Spooler - Stopped
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 Spooler Restart
Spooler is stopped, preparing to start...
Spooler - Running
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 Spooler Check
Action parameter is missing or invalid!
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell> .\MaintainService.ps1 FakeService Check
FakeService not found
PS C:\Users\KoA\Dropbox\Code-Store\powershell>
#>
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string] $ServiceName,
[string] $Action
)
#Checks if ServiceName exists and provides ServiceStatus
function CheckMyService ($ServiceName)
{
if (Get-Service $ServiceName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
{
$ServiceStatus = (Get-Service -Name $ServiceName).Status
Write-Host $ServiceName "-" $ServiceStatus
}
else
{
Write-Host "$ServiceName not found"
}
}
#Checks if service exists
if (Get-Service $ServiceName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
{ #Condition if user wants to stop a service
if ($Action -eq 'Stop')
{
if ((Get-Service -Name $ServiceName).Status -eq 'Running')
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "is running, preparing to stop..."
Get-Service -Name $ServiceName | Stop-Service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
CheckMyService $ServiceName
}
elseif ((Get-Service -Name $ServiceName).Status -eq 'Stopped')
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "already stopped!"
}
else
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "-" $ServiceStatus
}
}
#Condition if user wants to start a service
elseif ($Action -eq 'Start')
{
if ((Get-Service -Name $ServiceName).Status -eq 'Running')
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "already running!"
}
elseif ((Get-Service -Name $ServiceName).Status -eq 'Stopped')
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "is stopped, preparing to start..."
Get-Service -Name $ServiceName | Start-Service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
CheckMyService $ServiceName
}
else
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "-" $ServiceStatus
}
}
#Condition if user wants to restart a service
elseif ($Action -eq 'Restart')
{
if ((Get-Service -Name $ServiceName).Status -eq 'Running')
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "is running, preparing to restart..."
Get-Service -Name $ServiceName | Stop-Service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-Service -Name $ServiceName | Start-Service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
CheckMyService $ServiceName
}
elseif ((Get-Service -Name $ServiceName).Status -eq 'Stopped')
{
Write-Host $ServiceName "is stopped, preparing to start..."
Get-Service -Name $ServiceName | Start-Service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
CheckMyService $ServiceName
}
}
#Condition if action is anything other than stop, start, restart
else
{
Write-Host "Action parameter is missing or invalid!"
}
}
#Condition if provided ServiceName is invalid
else
{
Write-Host "$ServiceName not found"
}
Is there a way to restart a Windows service from the command prompt?
asked Jun 24, 2011 at 17:54
You can use net stop [service name] to stop it and net start [service name] to start it up again basically restarting the service.
To combine them just do this — net stop [service name] && net start [service name].
There is also a command built specifically for messing with services: sc
DESCRIPTION:
SC is a command line program used for communicating with the
Service Control Manager and services.
USAGE:
sc [command] [service name] ...
The option has the form "\\ServerName"
Further help on commands can be obtained by typing: "sc [command]"
Commands:
query-----------Queries the status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
queryex---------Queries the extended status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
start-----------Starts a service.
pause-----------Sends a PAUSE control request to a service.
interrogate-----Sends an INTERROGATE control request to a service.
continue--------Sends a CONTINUE control request to a service.
stop------------Sends a STOP request to a service.
config----------Changes the configuration of a service (persistent).
description-----Changes the description of a service.
failure---------Changes the actions taken by a service upon failure.
failureflag-----Changes the failure actions flag of a service.
sidtype---------Changes the service SID type of a service.
privs-----------Changes the required privileges of a service.
managedaccount--Changes the service to mark the service account
password as managed by LSA.
qc--------------Queries the configuration information for a service.
qdescription----Queries the description for a service.
qfailure--------Queries the actions taken by a service upon failure.
qfailureflag----Queries the failure actions flag of a service.
qsidtype--------Queries the service SID type of a service.
qprivs----------Queries the required privileges of a service.
qtriggerinfo----Queries the trigger parameters of a service.
qpreferrednode--Queries the preferred NUMA node of a service.
qrunlevel-------Queries the run level of a service.
qmanagedaccount-Queries whether a services uses an account with a
password managed by LSA.
qprotection-----Queries the process protection level of a service.
delete----------Deletes a service (from the registry).
create----------Creates a service. (adds it to the registry).
control---------Sends a control to a service.
sdshow----------Displays a service's security descriptor.
sdset-----------Sets a service's security descriptor.
showsid---------Displays the service SID string corresponding to an arbitrary name.
triggerinfo-----Configures the trigger parameters of a service.
preferrednode---Sets the preferred NUMA node of a service.
runlevel--------Sets the run level of a service.
GetDisplayName--Gets the DisplayName for a service.
GetKeyName------Gets the ServiceKeyName for a service.
EnumDepend------Enumerates Service Dependencies.
The following commands don't require a service name:
sc
boot------------(ok | bad) Indicates whether the last boot should
be saved as the last-known-good boot configuration
Lock------------Locks the Service Database
QueryLock-------Queries the LockStatus for the SCManager Database
EXAMPLE:
sc start MyService
QUERY and QUERYEX OPTIONS:
If the query command is followed by a service name, the status
for that service is returned. Further options do not apply in
this case. If the query command is followed by nothing or one of
the options listed below, the services are enumerated.
type= Type of services to enumerate (driver, service, all)
(default = service)
state= State of services to enumerate (inactive, all)
(default = active)
bufsize= The size (in bytes) of the enumeration buffer
(default = 4096)
ri= The resume index number at which to begin the enumeration
(default = 0)
group= Service group to enumerate
(default = all groups)
SYNTAX EXAMPLES
sc query - Enumerates status for active services & drivers
sc query eventlog - Displays status for the eventlog service
sc queryex eventlog - Displays extended status for the eventlog service
sc query type= driver - Enumerates only active drivers
sc query type= service - Enumerates only Win32 services
sc query state= all - Enumerates all services & drivers
sc query bufsize= 50 - Enumerates with a 50 byte buffer
sc query ri= 14 - Enumerates with resume index = 14
sc queryex group= "" - Enumerates active services not in a group
sc query type= interact - Enumerates all interactive services
sc query type= driver group= NDIS - Enumerates all NDIS drivers
answered Jun 24, 2011 at 17:58
paradd0xparadd0x
9,1497 gold badges37 silver badges44 bronze badges
9
Please, note that if there are other services that depends on this service — usual net stop & net start will not restart them. net stop /y will stop all dependencies
Most common example — SQL Server & SQL Agent.
I do recommend PowerShell cmdlet to solve this:
powershell -command "Restart-Service MSSQLSERVER -Force"
After MSSQLSERVER starts — cmdlet starts all previously stopped dependancies.
PS: Make sure you are running command as admin
answered Mar 15, 2017 at 13:57
2
To restart a Windows service from the command prompt or scheduled tasks, use this:
cmd /c "net stop "Service Name" & sc start "Service Name""
answered Feb 12, 2013 at 7:27
KikiKiki
1311 silver badge2 bronze badges
1
You could also use PowerShell:
stop-Service
Gaff
18.6k15 gold badges57 silver badges68 bronze badges
answered Jun 24, 2011 at 18:12
devlifedevlife
2411 gold badge2 silver badges7 bronze badges
1
To solve the annoying Wacom Intuous Driver not running Error I get on every reboot.
Windows key + R, paste, Bam!
sc stop WTabletServicePro && sc start WTabletServicePro
Simon E.
3,8615 gold badges29 silver badges31 bronze badges
answered Oct 20, 2014 at 3:45
GeorgeGeorge
611 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
The PsService utility from PsTools provides a restart command for services, with additional parameters to run it on another machine.
psservice [-accepteula] [\\Computer [-u Username [-p Password]]] restart <service-name>
The -accepteula flag saves you the EULA window just in case it’s the first time you use this utility with the current user.
answered May 22, 2018 at 16:00
cdlvcdlvcdlvcdlv
1,4711 gold badge19 silver badges27 bronze badges
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.