SNMPWalk
SNMPWalk is a powerful network management tool that allows users to quickly and easily access and monitor information from network devices such as routers, switches, and servers. It allows users to view the SNMP tree of managed devices and then walk through the MIBs to retrieve detailed information about the device.
SnmpWalk allows for convenient and efficient retrieval of multiple pieces of data from SNMP-enabled devices.
Features:
• Support for SNMPv1/v2c/v3: SNMPWalk is compatible with all versions of SNMP and allows users to easily access and monitor information from network devices.
• Comprehensive MIB Viewer: SNMPWalk provides a comprehensive view of all MIBs on the network, making it easy to find the information needed.
• Advanced Filtering: SNMPWalk supports advanced filtering options, which allow users to easily filter out unnecessary information when walking the MIBs.
• Intelligent MIB Navigation: SNMPWalk provides an intelligent navigation system, which allows users to quickly and easily traverse the MIBs and find the desired information.
• Graphical Representation: SNMPWalk provides a graphical representation of the MIBs, which allows users to easily visualize the data and quickly identify relationships between different elements of the network.
• Automated Monitoring: SNMPWalk allows users to automate the monitoring process, so the user can set up periodic scans of the network for any changes or anomalies.
• Flexible Configuration: SNMPWalk provides a flexible configuration system, which allows users to customize the way the tool works to fit their network and their needs.
• Support for Multiple Platforms: SNMPWalk is compatible with multiple platforms and operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X.
• Easy-to-Use Interface: SNMPWalk has an easy-to-use interface, which allows users to quickly and easily access all the features of the tool.
• Comprehensive Reporting: SNMPWalk provides comprehensive reports on the status of the network, making it easy to identify any issues and take action.
• Scalable Solution: SNMPWalk is a scalable solution, which allows users to easily increase or decrease the number of devices monitored.
• Security: SNMPWalk provides secure access to the network, so users can be sure their data and information is kept safe.
Conclusion
SNMPWalk is a powerful network management tool that allows users to quickly and easily access and monitor information from network devices. It provides a comprehensive view of all MIBs on the network, advanced filtering options, an intelligent navigation system, graphical representations of the MIBs, automated monitoring, flexible configuration, support for multiple platforms, an easy-to-use interface, comprehensive reports, and secure access. SNMPWalk is a scalable solution, which allows users to easily increase or decrease the number of devices monitored.
1. A computer with an operating system that supports SNMP
2. SNMP protocol support and access to an SNMP-enabled device
3. An SNMP-compliant management application
4. An SNMP agent that supports the SNMP protocol and is installed on the device being monitored
5. An SNMP manager with the ability to walk the SNMP MIB tree
6. A network connection between the device and the manager
7. The correct SNMP community string for the device
8. A compatible version of the SNMP protocol
==============================================================================
SnmpWalk v1.02 - Lists existing SNMP variables on any network device.
==============================================================================
Copyright (C) 2009-2010 SnmpSoft Company. All Rights Reserved.
Contents
--------
1. Overview
2. Features
3. Usage & Parameters
4. Examples
5. License & Disclaimer
6. Version History
1. Overview
------------
SNMP is a unified protocol of network monitoring and network device
management. All active network devices support SNMP. Besides that,
SNMP is supported by major operational systems and a large number of
network applications.
SnmpWalk allows you to detect a set of variables that are available for
reading on a certain device. You can obtain a full list or just part.
By analyzing the results of a network device scan obtained with
SnmpWalk you can develop a list of supported MIBs and, in this way,
obtain full descriptions of variables and possible values. Besides that,
MIB documents contain information about SNMP variables that are
available only for writing. After analyzing information retrieved with
SnmpWalk from hardware or software SNMP sources, you can use SnmpSet
and SnmpGet tools to change and obtain values.
The value of SnmpWalk is not limited to only the SNMP analysis of
supported features. This tool can effectively obtain SNMP tables and
read whole sections of variables. This particularly refers to tables
that are often used for presenting statistical and status information.
SnmpWalk is a command-line tool, which makes possible its use in
scripts. This tool supports modern IPv6 in addition to the standard
IPv4. Moreover, SnmpWalk allows you to use a simple version of
SNMPv1/SNMPv2c and also supports a safe version of SNMPv3.
2. Features
------------
+ Support of SNMP v1/v2c and SNMPv3
+ Support of IPv4 and IPv6
+ Command line interface (CLI)
+ Full or partial SNMP variables tree
+ Allows for any type of SNMP variable
+ Various Auth. & Privacy protocols
+ Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/Vista/2008
3. Usage & Parameters
----------------------
SnmpWalk.exe [-q] -r:host [-p:port] [-t:timeout] [-v:version] [-c:community]
[-ei:engine_id] [-sn:sec_name] [-ap:auth_proto] [-aw:auth_passwd]
[-pp:priv_proto] [-pw:priv_passwd] [-ce:cont_engine] [-cn:cont_name]
[-os:start_oid] [-op:stop_oid] [-csv]
-q Quiet mode (suppress header; print variable values only).
-r:host Name or network address (IPv4/IPv6) of remote host.
-p:port SNMP port number on remote host. Default: 161
-t:timeout SNMP timeout in seconds (1-600). Default: 5
-v:version SNMP version. Supported version: 1, 2c or 3. Default: 1
-c:community SNMP community string for SNMP v1/v2c. Default: public
-ei:engine_id Engine ID. Format: hexadecimal string. (SNMPv3).
-sn:sec_name SNMP security name for SNMPv3.
-ap:auth_proto Authentication protocol. Supported: MD5, SHA (SNMPv3).
-aw:auth_passwd Authentication password (SNMPv3).
-pp:priv_proto Privacy protocol. Supported: DES, IDEA, AES128, AES192,
AES256, 3DES (SNMPv3).
-pw:priv_passwd Privacy password (SNMPv3).
-cn:cont_name Context name. (SNMPv3)
-ce:cont_engine Context engine. Format: hexadecimal string. (SNMPv3)
-os:start_oid Object ID (OID) of first SNMP variable to walk. Default:.1
-op:stop_oid Object ID (OID) of last SNMP variable to walk.
Default: walk to the very last variable.
-csv Output in CSV (Comma Separated Values) format.
4. Examples
------------
SnmpWalk.exe -r:MainRouter -csv
SnmpWalk.exe -r:10.0.0.1 -t:10 -c:"admin_rw" -os:.1.3.6.1.2.1.1
SnmpWalk.exe -r:"::1" -v:3 -sn:SomeName -ap:MD5 -aw:SomeAuthPass -pp:DES
-pw:SomePrivPass -os:.1.3.6.1.2.1 -op:.1.3.6.1.2.65535 -q
5. License & Disclaimer
------------------------
FREE USE LICENSE. You may install and use any number of copies
of this SOFTWARE on your devices free of charge. You must
distribute a copy of this license within ReadMe.txt file with
any copy of the SOFTWARE and anyone to whom you distribute the
SOFTWARE is subject to this license.
RESTRICTIONS. You may not reduce the SOFTWARE to human readable
form, reverse engineer, de-compile, disassemble, merge, adapt,
or modify the SOFTWARE, except and only to the extent that such
activity is expressly permitted by applicable law notwithstanding
this limitation. You may not rent, lease, or lend the SOFTWARE.
You may not use the SOFTWARE to perform any unauthorized transfer
of information, such as copying or transferring a file in
violation of a copyright, or for any illegal purpose.
NO WARRANTIES. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law,
SnmpSoft Company expressly disclaims any warranty for this
SOFTWARE. The SOFTWARE and any related documentation are provided
"as is" without warranty of any kind, either express or implied,
including, without limitation, the implied warranties of
merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. The entire
risk arising out of use or performance of the SOFTWARE remains
with you.
6. Version History
-------------------
1.02 - FIXED: CSV format output
1.01 - FIXED: Redirecting the output to a file
1.0 - Initial release
SnmpSoft Company
================
Simple Network Monitoring Programs
http://www.snmpsoft.com
FreeTools for Network Administrators
http://www.snmpsoft.com/freetools/
======================================EOF=====================================
Рекламные ссылки:
Скриншот программы:

Детали программы:
Версия: 1.02
Дата загрузки: 15 Apr 15
Тип распространения: Бесплатная
Популярность: 1450
Размер: 178 Kb
- Currently 5.00/5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Rating: 5.0/5 (Total Votes: 1)
Рекламные ссылки:
SnmpWalk позволяет обнаружить набор переменных, которые доступны для чтения на определенном устройстве. Вы можете получить полный список или только часть. Анализируя результаты сканирования сетевого устройства, полученного с SnmpWalk вы можете составить список поддерживаемых баз MIB и таким образом, получить полные описания переменных и их возможных значений. Кроме того, документы MIB содержит информацию о SNMP переменных, которые доступны только для записи. После анализа данные, полученные с SnmpWalk от аппаратных или программное обеспечение SNMP источников, вы можете использовать SNMPSET и SnmpGet инструменты, чтобы изменить и получить значения.
15 Apr 15
Поддерживаемые операционные системы
Другие программы разработчика SnmpSoft
Комментарии к SnmpWalk
Популярные программы
What is SNMP?
SNMP also known as “Simple Network Management Protocol” is an application-layer protocol used to measure and monitor the performance of the devices within a network. It helps the system administrator to ensure that networks stay up and running. Today, SNMP is one of the most popular networking protocols in the world. All modern manufacturers create SNMP-enabled devices that enterprises can use to obtain performance data from the devices.
How SNMP Works?
SNMP uses the device’s Management Information Database (MIB) to collect the performance data. The MIB is a database that records information about the hardware and contains MIB files. The MIB resides within the SNMP manager designed to collect information and organize it into a hierarchical format. SNMP uses this information from the MIB to interpret messages before sending them onwards to the end-user.
There are different types of queries managers used to poll the information from the SNMP agent including, GET or GET-NEXT commands. The GET command uses the agent’s hostname and Object Identifiers (OID) to obtain the information from the MIB. The GET-NEXT command obtains the data from the next OID.
What is SNMPWALK?
SNMPWALK is a command-line utility used to collect the information from remote SNMP-enabled devices including, routers and switches. It allows you to see all the OID variables available on remote devices. It sends multiple GET-NEXT commands to OIDs then the manager collects the data from all OIDs. SNMPWALK is a command-line utility that can be installed on Linux and Windows operating systems.
In this guide, we will show you how to install SNMPWALK on Windows and Linux. We will also explain how to use it to get the information from the remote devices.
Install SNMP and SNMPWALK on Linux
In this section, we will show you how to install SNMP and SNMPWALK on Debian and RPM-based Linux operating systems.
For RPM-based operating system including, RHEL/CentOS/Fedora, install the SNMP and SNMPWALK using the following command:
yum install net-snmp net-snmp-libs net-snmp-utils -y
For Debian based operating system including, Debian/Ubuntu, install the SNMP and SNMPWALK using the following command:
apt-get install snmpd snmp libsnmp-dev -y
Once the installation has been finished, start the SNMP service and enable it to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl start snmpd
systemctl enable snmpd
You can check the status of the SNMP with the following command:
systemctl status snmpd
You should get the following output:
● snmpd.service - Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon.
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/snmpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2021-05-14 06:36:48 UTC; 3min 22s ago
Main PID: 36724 (snmpd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4691)
Memory: 8.7M
CGroup: /system.slice/snmpd.service
└─36724 /usr/sbin/snmpd -LOw -u Debian-snmp -g Debian-snmp -I -smux mteTrigger mteTriggerConf -f -p /run/snmpd.pid
May 14 06:36:48 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Starting Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon....
May 14 06:36:48 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Started Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon..By default, SNMP does not allow retrieving all available SNMP information. So you will need to edit the SNMP default configuration file and make some changes so we can retrieve all information using the SNMPWALK command.
nano /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
Find the following lines:
rocommunity public default -V systemonly
rocommunity6 public default -V systemonly
And, replace them with the following lines:
rocommunity public default
rocommunity6 public default
Save and close the file then restart the SNMP service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart snmpd
Now, open your command-line interface and print help information of SNMPWALK command as shown below:
snmpwalk -h
You should get the following output:
USAGE: snmpwalk [OPTIONS] AGENT [OID]
Version: 5.8
Web: http://www.net-snmp.org/
Email: net-snmp-coders@lists.sourceforge.net
OPTIONS:
-h, --help display this help message
-H display configuration file directives understood
-v 1|2c|3 specifies SNMP version to use
-V, --version display package version number
SNMP Version 1 or 2c specific
-c COMMUNITY set the community string
SNMP Version 3 specific
-a PROTOCOL set authentication protocol (MD5|SHA|SHA-224|SHA-256|SHA-384|SHA-512)
-A PASSPHRASE set authentication protocol pass phrase
-e ENGINE-ID set security engine ID (e.g. 800000020109840301)
-E ENGINE-ID set context engine ID (e.g. 800000020109840301)
-l LEVEL set security level (noAuthNoPriv|authNoPriv|authPriv)
-n CONTEXT set context name (e.g. bridge1)
-u USER-NAME set security name (e.g. bert)
-x PROTOCOL set privacy protocol (DES|AES)
-X PASSPHRASE set privacy protocol pass phrase
-Z BOOTS,TIME set destination engine boots/time
General communication options
-r RETRIES set the number of retries
-t TIMEOUT set the request timeout (in seconds)
Debugging
-d dump input/output packets in hexadecimal
-D[TOKEN[,...]] turn on debugging output for the specified TOKENs
(ALL gives extremely verbose debugging output)
Install SNMP and SNMPWALK on Windows 10 Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019
In this section, we will show you how to install SNMP and SNMPWALK on the Windows operating system.
Follow the below steps to install SNMP on Windows:
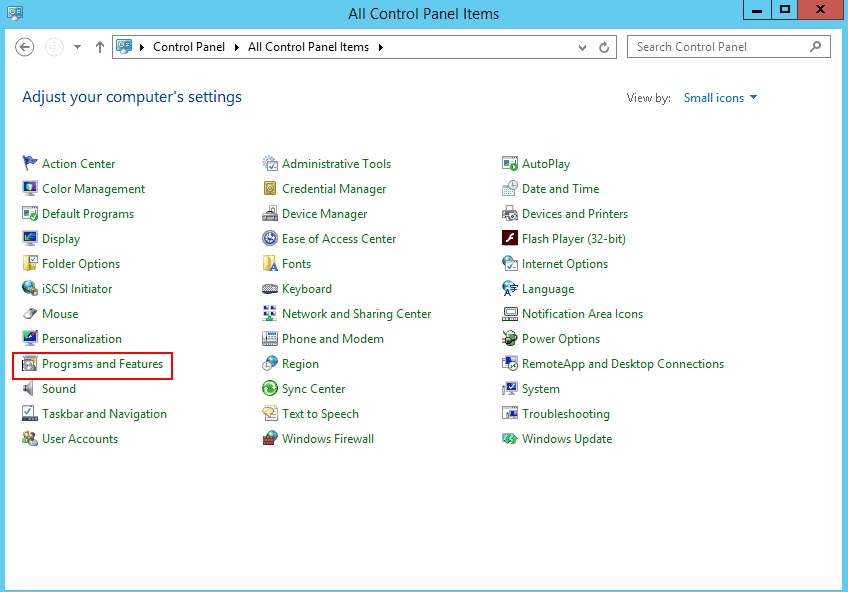
Step 1 – Open the Control Panel as shown below:
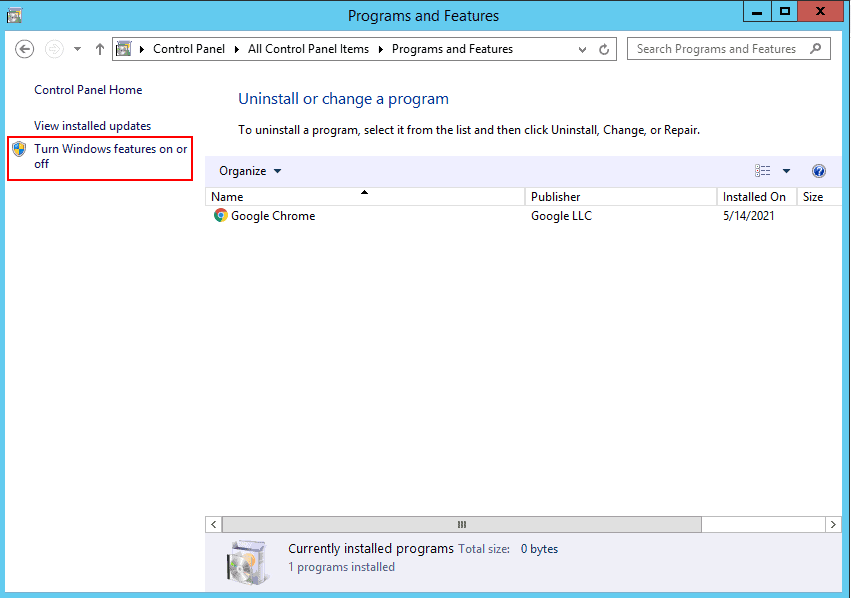
Step 2 – Click on the Programs and Features you should see in the page below:
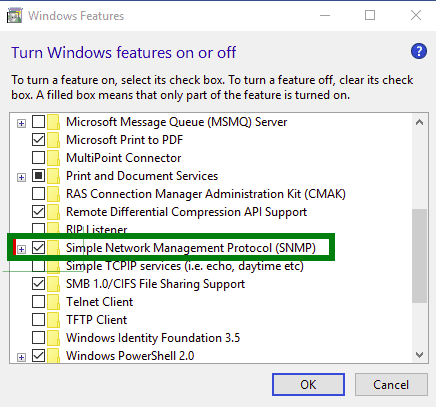
Step 3 – Click on the Turn Windows features on or off.
Step 4 – On Windows 10, select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and install it.
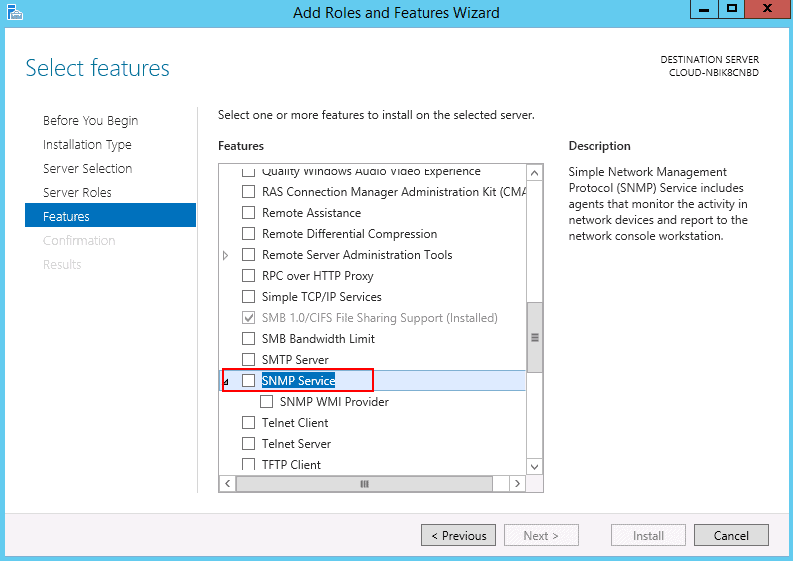
Step 5 – On Windows Server 2016 and 2019, click on the Add Roles and Features Wizard until you reach the Features section then select SNMP service.
Step 6 – Install SNMP Service.
This will automatically install the SNMP service on your Windows system.
After installing SNMP, you will need to configure it.
Follow the below steps to configure the SNMP service:
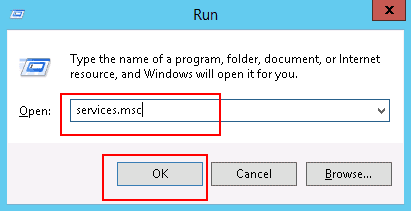
Step 1 – Press Windows + R and type services.msc as shown below:
Step 2 – Press OK to open the Windows service configuration wizard.
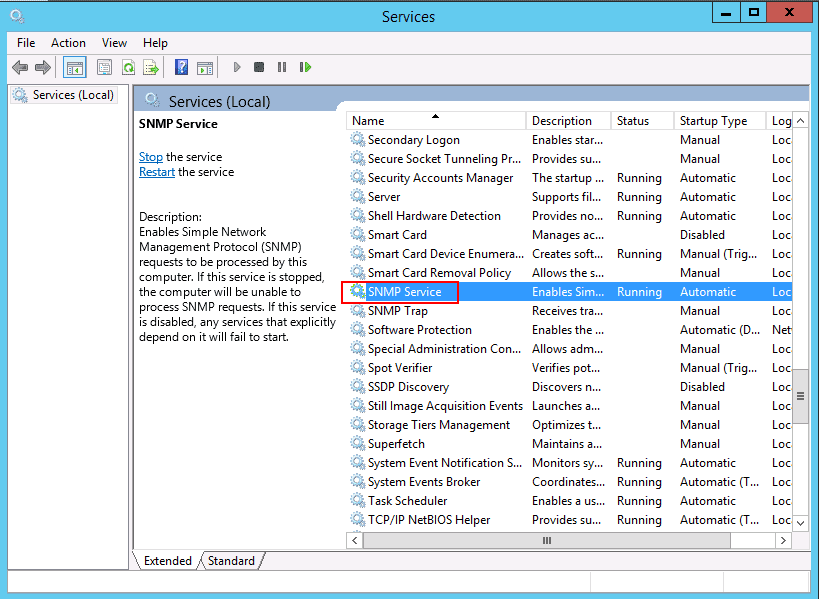
Step 3 – Select the SNMP service, right-click and click on the properties as shown below:
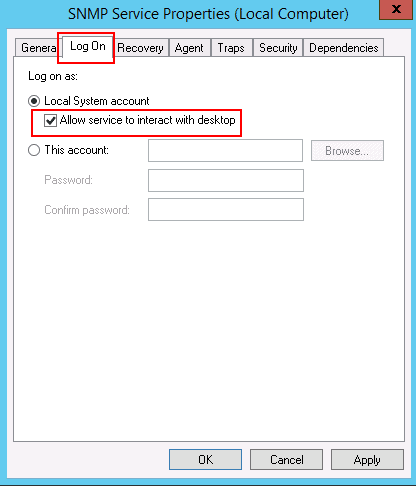
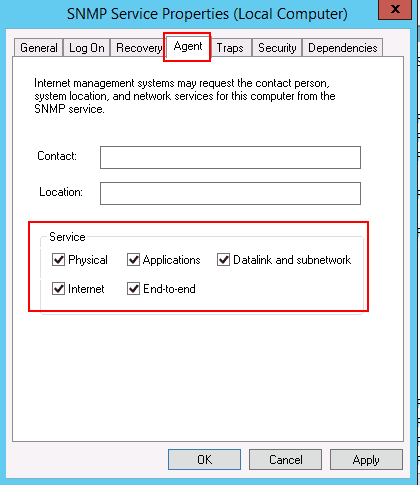
Step 4 – In the Log On tab, select “Allow service to interact with desktop”. Then click on the Agent tab as shown below:
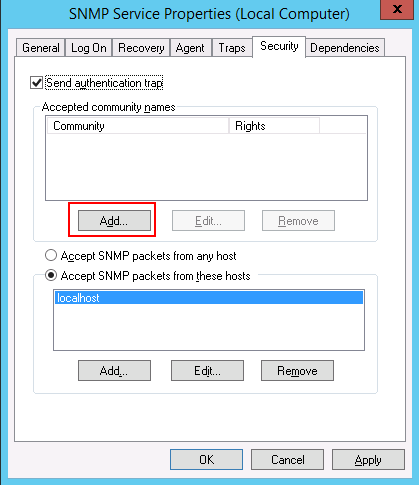
Step 5 – Select all services and click on the Security tab as shown below:
Step 6 – Click on the Add button. You should see the following screen:
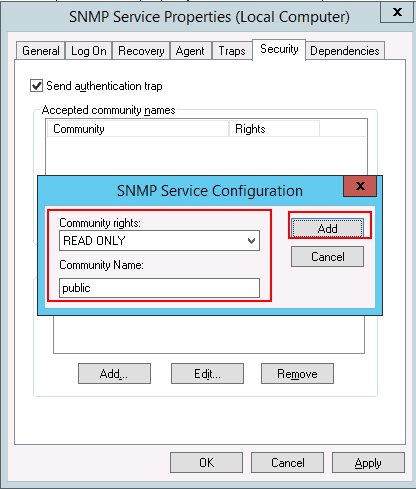
Step 7 – Provide community rights and community name then click on the Add button. You should see the following page:
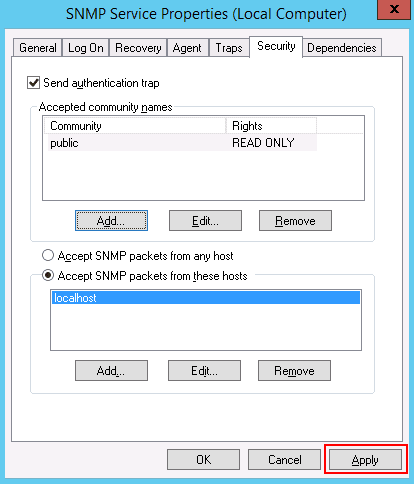
Step 8 – Click on the Apply button to apply the changes.
For full SNMP functionality, you will need to download the SolarWinds MIB Walk module from their Engineer’s Toolset to your windows system. However, you can download the free snmpwalk files from the SourceForge website and follow along with this post.
Once SNMPWALK is downloaded, extract it to the download folder. You can now use snmpwalk.exe to launch and use the SNMPWALK.
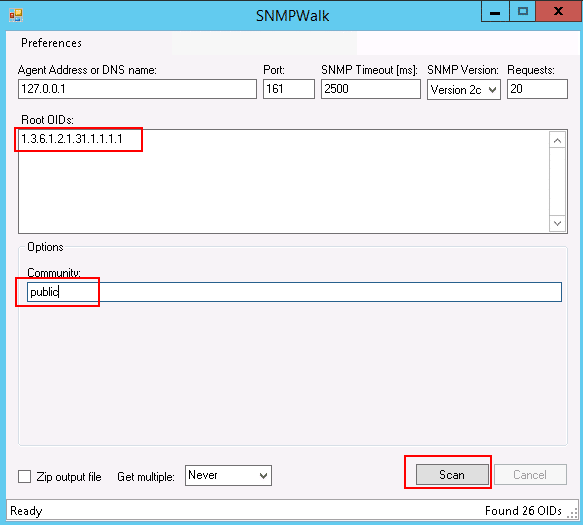
Provide your agent address, OID, community, and click the Scan button. This will generate a complete system information report based on the OID.
How to Use SNMPWALK to Retrieve the System Information
In this section, we will show you how to use the SNMPWALK command in Linux to retrieve the system information.
You can use the following options with the SNMPWALK command to retrieve the system information:
- -v: Specify the SNMP version.
- -c: Specify the community string which you have configured on the SNMP.
- hostname: Specify the hostname or IP address of the system where the SNMP agent is installed.
- OID: Specify the OID to return all SNMP objects.
Now, open your command-line interface and run the following command to list all existing OIDs on the network..
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public localhost
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: "Linux ubuntu2004 5.4.0-29-generic #33-Ubuntu SMP Wed Apr 29 14:32:27 UTC 2020 x86_64"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 = OID: iso.3.6.1.4.1.8072.3.2.10
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (19907) 0:03:19.07
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0 = STRING: "Me <me@example.org>"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: "ubuntu2004"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0 = STRING: "Sitting on the Dock of the Bay"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.7.0 = INTEGER: 72
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.8.0 = Timeticks: (3) 0:00:00.03
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.1 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.10.3.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.2 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.11.3.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.3 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.15.2.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.4 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.5 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.16.2.2.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.6 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.49
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.7 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.4
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.8 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.50
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.9 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.13.3.1.3
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.10 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.92
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.1 = STRING: "The SNMP Management Architecture MIB."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.2 = STRING: "The MIB for Message Processing and Dispatching."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.3 = STRING: "The management information definitions for the SNMP User-based Security Model."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.4 = STRING: "The MIB module for SNMPv2 entities"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.5 = STRING: "View-based Access Control Model for SNMP."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.6 = STRING: "The MIB module for managing TCP implementations"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.7 = STRING: "The MIB module for managing IP and ICMP implementations"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.8 = STRING: "The MIB module for managing UDP implementations"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.9 = STRING: "The MIB modules for managing SNMP Notification, plus filtering."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.10 = STRING: "The MIB module for logging SNMP Notifications."
You can see the different OIDs in the above output. The typical format of an OID is shown below:
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1
A brief explanation of the most commonly used OIDs are shown below:
- 1 – ISO – International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- 3 – org – Organizations according to ISO/IEC 6523-2
- 6 – dod – US Department of Defense (DOD)
- 1 – Internet protocol
- 4 – Private – Device manufactured by a private company
- 2021 – It is the particular device manufacturer number.
To get the hostname of the system, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: "ubuntu2004"
To get the hostname and kernel information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: "Linux ubuntu2004 5.4.0-29-generic #33-Ubuntu SMP Wed Apr 29 14:32:27 UTC 2020 x86_64"
To get the network interface information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c 127.0.0.1 -c public .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.1 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.2 = INTEGER: 2
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.3 = INTEGER: 3
To get the MAC address information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c 127.0.0.1 -c public .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6.1 = ""
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6.2 = Hex-STRING: 00 00 2D 3A 26 A4
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6.3 = Hex-STRING: 00 00 0A 3A 26 A4
To get a list of all network interface, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1.1 = STRING: "lo"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1.2 = STRING: "eth0"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1.3 = STRING: "eth1"
To get an IP address of the system, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1.45.58.38.164 = IpAddress: 45.58.38.164
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1.127.0.0.1 = IpAddress: 127.0.0.1
To get the Subnet Mask of the system, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3.45.58.38.164 = IpAddress: 255.255.255.0
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3.127.0.0.1 = IpAddress: 255.0.0.0
To get the CPU information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.3 |grep -i cpu
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.3.196608 = STRING: "GenuineIntel: QEMU Virtual CPU version 2.5+"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.3.196609 = STRING: "GenuineIntel: QEMU Virtual CPU version 2.5+"
To get the system load information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.1.1 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.1.2 = INTEGER: 2
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.1.3 = INTEGER: 3
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.2.1 = STRING: "Load-1"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.2.2 = STRING: "Load-5"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.2.3 = STRING: "Load-15"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.1 = STRING: "0.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.2 = STRING: "0.01"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.3 = STRING: "0.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.4.1 = STRING: "12.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.4.2 = STRING: "12.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.4.3 = STRING: "12.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.5.1 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.5.2 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.5.3 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.6.1 = Opaque: Float: 0.000000
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.6.2 = Opaque: Float: 0.010000
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.6.3 = Opaque: Float: 0.000000
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.100.1 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.100.2 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.100.3 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.101.1 = ""
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.101.2 = ""
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.101.3 = ""
To get the system uptime information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (66282) 0:11:02.82
Conclusion
In the above post, you learned how to install and use SNMP and SNMPWALK on Windows and Linux to get the system information across the connected devices. I hope this will help you to monitor the network devices.
SNMPWALK FAQs
What is a snmpwalk tool?
SNMPWALK is a process of exploring the Management Information Base (MIB) structure of an SNMP report. The MIB has a tree structure that is denoted by a dot-notation number and the “walk” crawls through these numbers, recreating the tree. An SNMPWALK tool can construct a MIB tree by mapping the relationship between the values in a MIB. Each number that identifies a node on the MIB tree will have a label and a value. The OID (Object ID) is a reference code for the label.
Is SNMP v3 TCP or UDP?
All versions of SNMP use the same ports – there are two and they are both UDP. Regular SNMP transactions involve the SNMP Manager sending out a broadcasted request, to which the SNMP device agents reply with a MIB. This communication occurs on UDP port 161. The SNMP agent can send out a warning message without waiting for a request. This is called a Trap and it goes to UDP port 162.
What is OID in Linux?
OID is short for Object ID. It is the level code that identifies a node in a tree structure that is used for reporting in SNMP. An SNMP report is called a Management Information Base (MIB). It has a set number of fields that are identified by OIDs. The OID uses a dot-notation format to indicate the inheritance of a node on the tree.
SNMPWalk
SNMPWalk is a powerful network management tool that allows s to quickly and easily access and monitor information from network devices such as routers, switches, and servers. It allows s to view the SNMP tree of managed devices and then walk through the MIBs to retrieve detailed information about the device.
SnmpWalk allows for convenient and efficient retrieval of multiple pieces of data from SNMP-enabled devices.
Features:
• for SNMPv1/v2c/v3: SNMPWalk is compatible with all versions of SNMP and allows s to easily access and monitor information from network devices.
• Comprehensive MIB Viewer: SNMPWalk provides a comprehensive view of all MIBs on the network, making it easy to find the information needed.
• Advanced Filtering: SNMPWalk s advanced filtering options, which allow s to easily filter out unnecessary information when walking the MIBs.
• Intelligent MIB Navigation: SNMPWalk provides an intelligent navigation system, which allows s to quickly and easily traverse the MIBs and find the desired information.
• Graphical Representation: SNMPWalk provides a graphical representation of the MIBs, which allows s to easily visualize the data and quickly identify relationships between different elements of the network.
• Automated Monitoring: SNMPWalk allows s to automate the monitoring process, so the can set up periodic scans of the network for any changes or anomalies.
• Flexible Configuration: SNMPWalk provides a flexible configuration system, which allows s to customize the way the tool works to fit their network and their needs.
• for Multiple Platforms: SNMPWalk is compatible with multiple platforms and operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X.
• Easy-to-Use Interface: SNMPWalk has an easy-to-use interface, which allows s to quickly and easily access all the features of the tool.
• Comprehensive Reporting: SNMPWalk provides comprehensive reports on the status of the network, making it easy to identify any issues and take action.
• Scalable Solution: SNMPWalk is a scalable solution, which allows s to easily increase or decrease the number of devices monitored.
• Security: SNMPWalk provides secure access to the network, so s can be sure their data and information is kept safe.
Conclusion
SNMPWalk is a powerful network management tool that allows s to quickly and easily access and monitor information from network devices. It provides a comprehensive view of all MIBs on the network, advanced filtering options, an intelligent navigation system, graphical representations of the MIBs, automated monitoring, flexible configuration, for multiple platforms, an easy-to-use interface, comprehensive reports, and secure access. SNMPWalk is a scalable solution, which allows s to easily increase or decrease the number of devices monitored.
1. A computer with an operating system that s SNMP
2. SNMP protocol and access to an SNMP-enabled device
3. An SNMP-compliant management application
4. An SNMP agent that s the SNMP protocol and is installed on the device being monitored
5. An SNMP manager with the ability to walk the SNMP MIB tree
6. A network connection between the device and the manager
7. The correct SNMP community string for the device
8. A compatible version of the SNMP protocol