cmd2 : immersive interactive command line applications
Develper’s Toolbox •
Philosophy •
Installation •
Documentation •
Tutorials •
Hello World •
Projects using cmd2 •
cmd2 is a tool for building interactive command line applications in Python. Its goal is to make it
quick and easy for developers to build feature-rich and user-friendly interactive command line
applications. It provides a simple API which is an extension of Python’s built-in
cmd module. cmd2 provides a wealth of features on top
of cmd to make your life easier and eliminates much of the boilerplate code which would be necessary
when using cmd.
The developers toolbox
When creating solutions developers have no shortage of tools to create rich and smart user interfaces.
System administrators have long been duct taping together brittle workflows based on a menagerie of simple command line tools created by strangers on github and the guy down the hall.
Unfortunately, when CLIs become significantly complex the ease of command discoverability tends to fade quickly.
On the other hand, Web and traditional desktop GUIs are first in class when it comes to easily discovering functionality.
The price we pay for beautifully colored displays is complexity required to aggregate disperate applications into larger systems.
cmd2 fills the niche between high ease of command discovery applications and smart workflow automation systems.
The cmd2 framework provides a great mixture of both worlds. Application designers can easily create complex applications and rely on the cmd2 library to offer effortless user facing help and extensive tab completion.
When users become comfortable with functionality, cmd2 turns into a feature rich library enabling a smooth transition to full automation. If designed with enough forethought, a well implemented cmd2 application can serve as a boutique workflow tool. cmd2 pulls off this flexibility based on two pillars of philosophy:
- Tab Completion
- Automation Transition
Philosophy
Deep extensive tab completion and help text generation based on the argparse library create the first pillar of ‘ease of command discovery’. The following is a list of features in this category.
- Great tab completion of commands, subcommands, file system paths, and shell commands.
- Custom tab completion for user designed commands via simple function overloading.
- Tab completion from
persistent_history_filesources added with very little friction. - Automatic tab completion of
argparseflags and optional arguments. - Path completion easily enabled.
- When all else fails, custom tab completion based on
choices_providercan fill any gaps.
cmd2 creates the second pillar of ‘ease of transition to automation’ through alias/macro creation, command line argument parsing and execution of cmd2 scripting.
- Flexible alias and macro creation for quick abstraction of commands.
- Text file scripting of your application with
run_script(@) and_relative_run_script(@@) - Powerful and flexible built-in Python scripting of your application using the
run_pyscriptcommand - Transcripts for use with built-in regression can be automatically generated from
history -torrun_script -t
Installation
On all operating systems, the latest stable version of cmd2 can be installed using pip:
pip install -U cmd2
cmd2 works with Python 3.6+ on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It is pure Python code with few 3rd-party dependencies.
For information on other installation options, see
Installation Instructions in the cmd2
documentation.
Documentation
The latest documentation for cmd2 can be read online here: https://cmd2.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
It is available in HTML, PDF, and ePub formats.
The best way to learn the cmd2 api is to delve into the example applications located in source under examples.
Tutorials
- PyOhio 2019 presentation:
- video
- slides
- example code
- Cookiecutter Templates from community
- Basic cookiecutter template for cmd2 application : https://github.com/jayrod/cookiecutter-python-cmd2
- Advanced cookiecutter template with external plugin support : https://github.com/jayrod/cookiecutter-python-cmd2-ext-plug
- Example Applications
Hello World
#!/usr/bin/env python """A simple cmd2 application.""" import cmd2 class FirstApp(cmd2.Cmd): """A simple cmd2 application.""" def do_hello_world(self, _: cmd2.Statement): self.poutput('Hello World') if __name__ == '__main__': import sys c = FirstApp() sys.exit(c.cmdloop())
Found a bug?
If you think you’ve found a bug, please first read through the open Issues. If you’re confident it’s a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so we can reproduce the bug. At a minimum, please state the following:
cmd2version- Python version
- OS name and version
- What you did to cause the bug to occur
- Include any traceback or error message associated with the bug
Projects using cmd2
| Application Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Jok3r | Network & Web Pentest Automation Framework | |
| CephFS Shell | Ceph is a distributed object, block, and file storage platform | |
| psiTurk | An open platform for science on Amazon Mechanical Turk | |
| Poseidon | Leverages software-defined networks (SDNs) to acquire and then feed network traffic to a number of machine learning techniques. | |
| Unipacker | Automatic and platform-independent unpacker for Windows binaries based on emulation | |
| tomcatmanager | A command line tool and python library for managing a tomcat server | |
| Expliot | Internet of Things (IoT) exploitation framework | |
| mptcpanalyzer | Tool to help analyze mptcp pcaps | |
| clanvas | Command-line client for Canvas by Instructure |
Possibly defunct but still good examples
- JSShell
- FLASHMINGO
IMPORTANT NOTE: The PyCmd project has moved to GitHub: https://github.com/horeah/PyCmd
PyCmd is a smart command prompt extension for Windows’ cmd.exe; its purpose is to emulate a few power features of UNIX shells (decent Tab-completion, persistent history, etc.)
Features
- Smart Tab-completion (similar to e.g. bash)
- Searchable, persistent command history
- Enhanced editing (copy/paste, undo, emacs key bindings)
- History of recently visited directories
License
GNU Library or Lesser General Public License version 2.0 (LGPLv2)
Fraud.net delivers the world’s most advanced infrastructure for fraud management – powered by a sophisticated collective intelligence network, world class artificial intelligence, and a modern, cloud-based platform that helps you.
User Ratings
4.7
out of 5 stars
★★★★★
★★★★
★★★
★★
★
ease
1 of 5
2 of 5
3 of 5
4 of 5
5 of 5
4 / 5
features
1 of 5
2 of 5
3 of 5
4 of 5
5 of 5
3 / 5
design
1 of 5
2 of 5
3 of 5
4 of 5
5 of 5
4 / 5
support
1 of 5
2 of 5
3 of 5
4 of 5
5 of 5
3 / 5
User Reviews
- All
- ★★★★★
- ★★★★
- ★★★
- ★★
- ★
-
Very nice enhancement to CMD.EXE for the command history, the TAB completion mechanism and the trailing backslash. Really add comfort and rapidity to console usage.
One small flaw however, that caused me not to give the full 5 stars: it does not «transmit» the error code received from a program to the errorlevel environment variable. Example: lets say that I write a program and my exit code is 1244 (under Windows it means «The operation being requested was not performed because the user has not been authenticated») ; well when I check the errorlevel by $ echo %errorlevel%, I get ‘0’… while when under regular CMD.EXE I get 1244.
You may well think it’s a small detail, but for me it’s important that is why I did not give it 5 stars. But still it’s my everyday-usage console CMD extension.
Thank you for the very good work.
Gilles -
Simply awesome! Been using it daily since years. And useful and _intuitive_ features still get added sometimes, like the ALT-UP thingy in the last version. Keep it up!
-
Works well but do not provide a real «plus» to windows cmd
Read more reviews >
Additional Project Details
Operating Systems
Windows
Intended Audience
Advanced End Users
User Interface
Console/Terminal
Programming Language
Python
Related Categories
Python System Shells
2.4.3 (January 27, 2023)
- Bug Fixes
- Fixed ValueError caused when passing
Cmd.columnize()strings wider thandisplay_width.
- Fixed ValueError caused when passing
- Enhancements
- Renamed
utils.str_to_bool()->utils.to_bool(). - Enhanced
utils.to_bool()so that it accepts and convertsbool,int, andfloatin addition tostr.
- Renamed
2.4.2 (July 13, 2022)
- Enhancements
- Updated argparse decorator to remove annotations when the docstring is used for a command’s help text.
- Updated unit test to be Python 3.11 compliant.
2.4.1 (April 13, 2022)
- Bug Fixes
- Fixed value for
ansi.Bg.YELLOW. - Fixed unit tests for
ansi.allow_style.
- Fixed value for
- Enhancements
async_alert()raises aRuntimeErrorif called from the main thread.
2.4.0 (February 22, 2022)
- Bug Fixes
- Fixed issue in
ansi.async_alert_str()which would raiseIndexErrorif prompt was blank. - Fixed issue where tab completion was quoting argparse flags in some cases.
- Fixed issue in
- Enhancements
- Added broader exception handling when enabling clipboard functionality via
pyperclip. - Added
PassThroughExceptionto__init__.pyimports. - cmd2 now uses pyreadline3 when running any version of Python on Windows
- Improved memory usage in certain use cases of tables (e.g. nested colored tables)
- Added broader exception handling when enabling clipboard functionality via
- Deletions (potentially breaking changes)
- Deleted
cmd2.fgandcmd2.bgwhich were deprecated in 2.3.0. Usecmd2.Fgandcmd2.Bginstead.
- Deleted
2.3.3 (November 29, 2021)
- Enhancements
- Added clearer exception handling to
BorderedTableandSimpleTable.
- Added clearer exception handling to
2.3.2 (November 22, 2021)
- Bug Fixes
- Fixed issue where a
ns_providercould be passedNoneinstead of its correctcmd2.CmdorCommandSetvalue.
- Fixed issue where a
2.3.1 (November 18, 2021)
- Bug Fixes
- Fixed issue introduced in 2.3.0 with
AlternatingTable,BorderedTable, andSimpleTablethat caused
header alignment settings to be overridden by data alignment settings.
- Fixed issue introduced in 2.3.0 with
- Enhancements
CompletionItemsnow saves the original object from which it creates a string.- Using
CompletionItemsas argparse choices is fully supported.cmd2patchedargparseto compare input to
the original value instead of theCompletionItemsinstance. ArgparseCompleternow does the following if a list ofCompletionItemswas created with numerical types:- Sorts completion hints numerically
- Right-aligns the left-most column in completion hint table
2.3.0 (November 11, 2021)
- Bug Fixes
- Fixed
AttributeErrorinrl_get_prompt()when prompt isNone. - Fixed bug where using choices on a Settable didn’t verify that a valid choice had been entered.
- Fixed bug introduced in cmd2 2.0.0 in which
select()converts return values to strings. It should never
have converted return values.
- Fixed
- Enhancements
- Added settings to Column class which prevent a table from overriding existing styles in header
and/or data text. This allows for things like nesting an AlternatingTable in another AlternatingTable. - AlternatingTable no longer automatically applies background color to borders. This was done to improve
appearance since the background color extended beyond the borders of the table. - Added ability to colorize all aspects of
AlternatingTables,BorderedTables, andSimpleTables. - Added support for 8-bit/256-colors with the
cmd2.EightBitFgandcmd2.EightBitBgclasses. - Added support for 24-bit/RGB colors with the
cmd2.RgbFgandcmd2.RgbBgclasses. - Removed dependency on colorama.
- Changed type of
ansi.allow_stylefrom a string to anansi.AllowStyleEnum class.
- Added settings to Column class which prevent a table from overriding existing styles in header
- Deprecations
- Deprecated
cmd2.fg. Usecmd2.Fginstead. - Deprecated
cmd2.bg. Usecmd2.Bginstead.
- Deprecated
- Breaking Changes
- To support the color upgrade, all cmd2 colors now inherit from either
ansi.FgColororansi.BgColor.
Therefore,ansi.style()no longer accepts colors as strings.
- To support the color upgrade, all cmd2 colors now inherit from either
2.2.0 (September 14, 2021)
- Bug Fixes
- Fixed extra space appended to each alias by «alias list» command
- Enhancements
- New function
set_default_ap_completer_type()allows developer to extend and modify the
behavior ofArgparseCompleter. - Added
ArgumentParser.get_ap_completer_type()andArgumentParser.set_ap_completer_type(). These
methods allow developers to enable custom tab completion behavior for a given parser by using a custom
ArgparseCompleter-based class. - Added
ap_completer_typekeyword arg toCmd2ArgumentParser.__init__()which saves a call
toset_ap_completer_type(). This keyword will also work withadd_parser()when creating subcommands
if the base command’s parser is aCmd2ArgumentParser. - New function
register_argparse_argument_parameter()allows developers to specify custom
parameters to be passed to the argparse parser’sadd_argument()method. These parameters will
become accessible in the resulting argparse Action object when modifyingArgparseCompleterbehavior. - Using
SimpleTablein the output for the following commands to improve appearance.- help
- set (command and tab completion of Settables)
- alias tab completion
- macro tab completion
- Tab completion of
CompletionItemsnow includes divider row comprised ofCmd.rulercharacter. - Removed
--verboseflag from set command since descriptions always show now. - All cmd2 built-in commands now populate
self.last_result. - Argparse tab completer will complete remaining flag names if there are no more positionals to complete.
- Updated
async_alert()to account forself.promptnot matching Readline’s current prompt.
- New function
- Deletions (potentially breaking changes)
- Deleted
set_choices_provider()andset_completer()which were deprecated in 2.1.2
- Deleted
- Breaking Changes
- Renamed
set_default_argument_parser()toset_default_argument_parser_type()
- Renamed
2.1.2 (July 5, 2021)
- Enhancements
- Added the following accessor methods for cmd2-specific attributes to the
argparse.Actionclassget_choices_callable()set_choices_provider()set_completer()get_descriptive_header()set_descriptive_header()get_nargs_range()set_nargs_range()get_suppress_tab_hint()set_suppress_tab_hint()
- Added the following accessor methods for cmd2-specific attributes to the
- Deprecations
- Now that
set_choices_provider()andset_completer()have been added as methods to the
argparse.Actionclass, the standalone functions of the same name will be removed in version
2.2.0. To update to the new convention, do the following:- Change
set_choices_provider(action, provider)toaction.set_choices_provider(provider) - Change
set_completer(action, completer)toaction.set_completer(completer)
- Change
- Now that
cmd2 works on Linux, macOS, and Windows. It requires Python 3.7 or
higher, pip, and setuptools. If you’ve got all that, then you can just:
Note
Depending on how and where you have installed Python on your system and on
what OS you are using, you may need to have administrator or root privileges
to install Python packages. If this is the case, take the necessary steps
required to run the commands in this section as root/admin, e.g.: on most
Linux or Mac systems, you can precede them with sudo:
$ sudo pip install <package_name>
Prerequisites¶
If you have Python 3 >=3.7 installed from python.org, you will already have pip and setuptools, but may
need to upgrade to the latest versions:
On Linux or OS X:
$ pip install -U pip setuptoolsOn Windows:
> python -m pip install -U pip setuptools
Install from PyPI¶
pip is the recommended installer. Installing packages from PyPI with pip is
easy:
This will install the required 3rd-party dependencies, if necessary.
Install from GitHub¶
The latest version of cmd2 can be installed directly from the master branch
on GitHub using pip:
$ pip install -U git+git://github.com/python-cmd2/cmd2.git
Install from Debian or Ubuntu repos¶
We recommend installing from pip, but if you wish to install from Debian or
Ubuntu repos this can be done with apt-get.
For Python 3:
$ sudo apt-get install python3-cmd2
This will also install the required 3rd-party dependencies.
Warning
Versions of cmd2 before 0.8.9 should be considered to be of unstable
“beta” quality and should not be relied upon for production use. If you
cannot get a version >= 0.8.9 from your OS repository, then we recommend
installing from either pip or GitHub — see Install from PyPI or
Install from GitHub.
Upgrading cmd2¶
Upgrade an already installed cmd2 to the latest version from PyPI:
This will upgrade to the newest stable version of cmd2 and will also
upgrade any dependencies if necessary.
Uninstalling cmd2¶
If you wish to permanently uninstall cmd2, this can also easily be done with pip:
macOS Considerations¶
macOS comes with the libedit library which is
similar, but not identical, to GNU Readline. Tab completion for cmd2
applications is only tested against GNU Readline.
There are several ways GNU Readline can be installed within a Python
environment on a Mac, detailed in the following subsections.
gnureadline Python module¶
Install the gnureadline Python module which is statically linked against a specific compatible version of GNU Readline:
$ pip install -U gnureadline
readline via conda¶
Install the readline package using the conda package manager included
with the Anaconda Python distribution:
readline via brew¶
Install the readline package using the Homebrew package manager (compiles
from source):
$ brew install openssl $ brew install pyenv $ brew install readline
Then use pyenv to compile Python and link against the installed readline
We all know that nowadays Python is one of the most popular coding languages among all. While installing Python, one IDE named IDLE is also installed. Using the IDLE we can write and also run our programs. But we can also run python programs on CMD or command prompt as CMD is the default command-line interpreter on Windows.
But there’s a need to set up the environment variable in windows to use python on the command-line. Following are the steps to add Python Environment to Windows path:
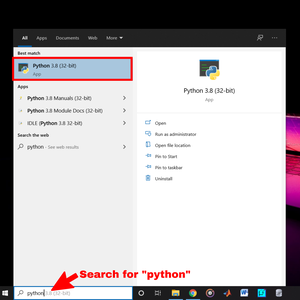
Step 1: For setting up Python on CMD we must check whether Python is installed on your machine or not. For doing this go to the Windows search bar and search for python. If you find python in the result then you are good to go.
You can see Python3 is installed on my computer
If python is not installed on your computer, then it can be installed with How to install Python on Windows?.
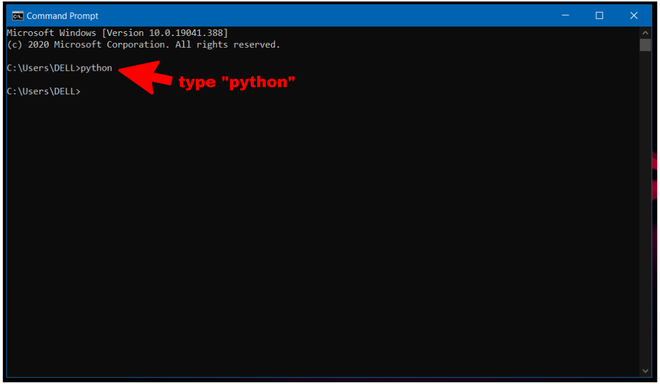
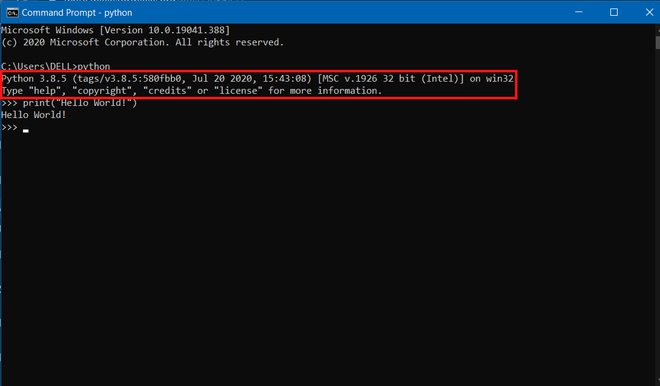
Step 2: Now check whether python is already set up in Command Prompt or not. For doing this just open cmd and type python. If you see any python version then it is already setup.
You can see after typing python nothing happened. So, python is not set up on cmd yet.
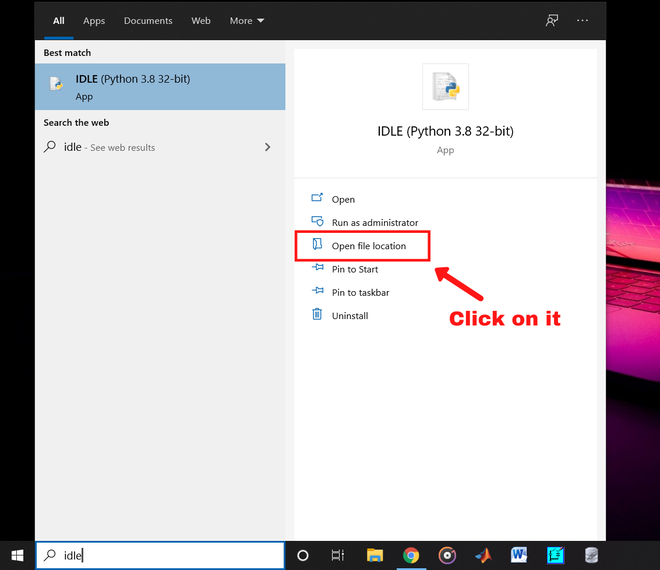
Step 3: Now open the Windows search bar and search for “idle”. Without opening the app click on “Open file location”. If you didn’t get the option right click on the app and you will get it.
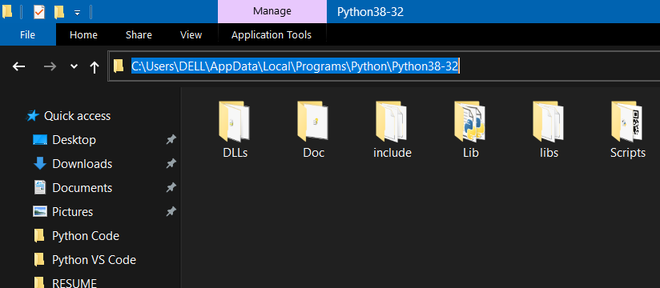
Now a file location will be opened on Windows explorer.
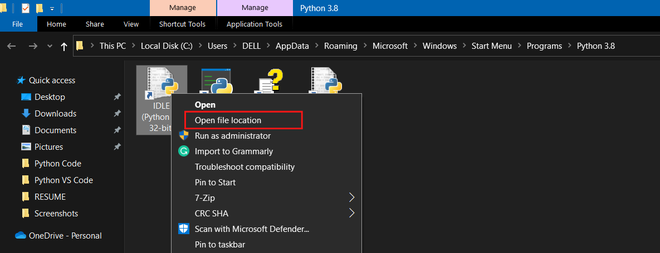
Step 4: Now right-click on “IDLE” and click on “open file location”
Click on “Open file location”
After opening the file location copy the path.
Copy the location
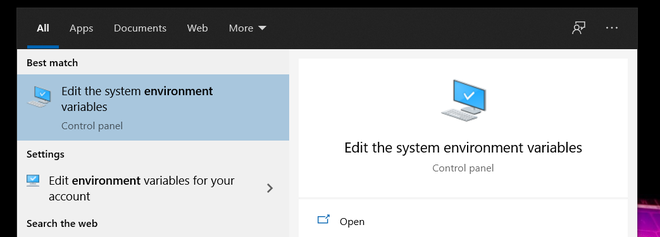
Step 5: Now go to the windows search bar and search for “Environment variables” and open it.
Open this
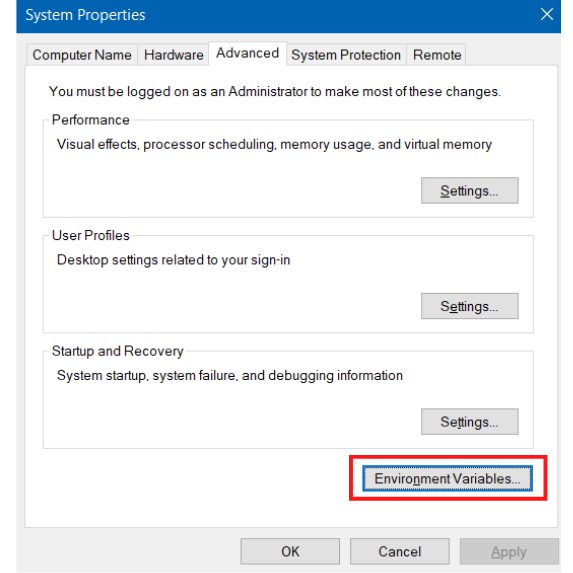
After opening the menu click on “Environment Variables”
Click on the “Environment Variables”
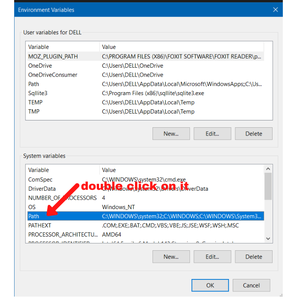
Now double click on the “path” in the “System Variables”
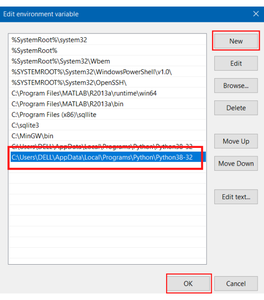
In the “Edit System Variable” menu click on “new”, then paste the file location you copied and click ok.
Now close the Environment menus by clicking ok and congratulation, we have set up the Command Prompt for python.
Step 6: Now check whether it works. Open Command Prompt and type “python” and hit enter. You will see a python version and now you can run your program there.
Last Updated :
28 Jul, 2020
Like Article
Save Article