Добавил(а) microsin
Иногда по неизвестным причинам некоторые команды русскоязычной версии Windows выводят русский текст в нечитаемой кодировке, кракозябрами.
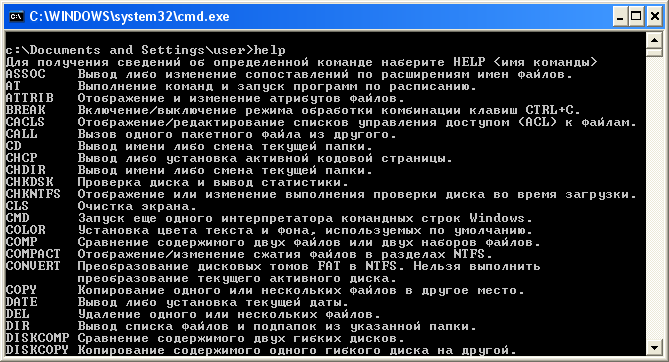
Например, команда help выводит нормальный текст:
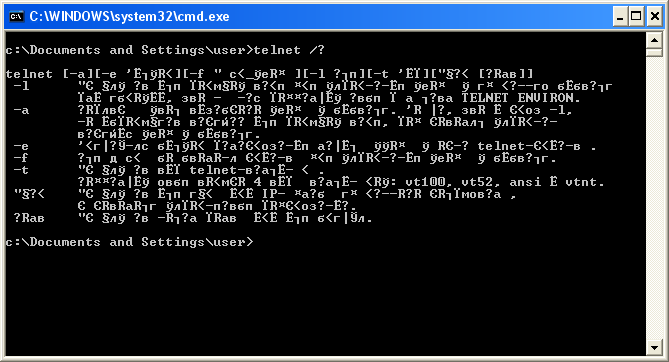
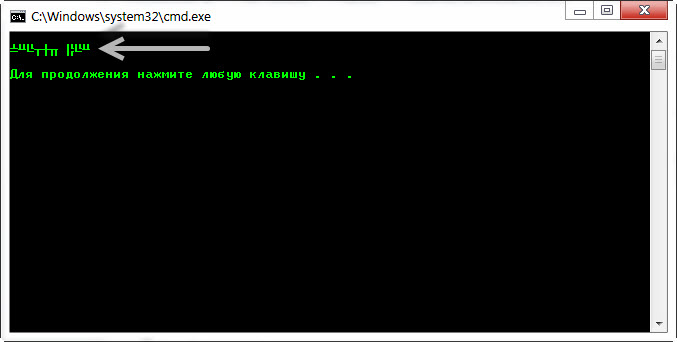
Но при этом подсказка telnet выводит в ответ кракозябры.
Так может происходить, к примеру, если текущая кодировка консоли 866, а утилита telnet.exe почему-то выводит текст в кодировке 1251. Вывести текст в нужной кодировке поможет команда chcp, которая устанавливает нужную кодировку.
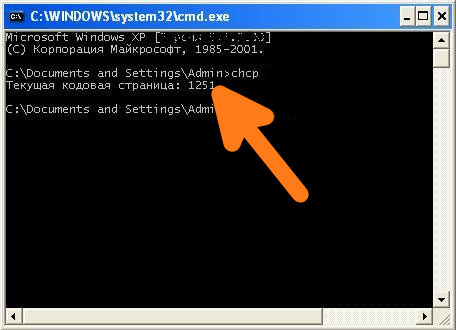
Вот так можно посмотреть текущую кодировку консоли:
c:\Documents and Settings\user>chcp Текущая кодовая страница: 866 c:\Documents and Settings\user>
А вот так можно поменять кодировку на 1251, после чего вывод подсказки telnet будет отображаться нормально:
c:\Documents and Settings\user>chcp 1251 Текущая кодовая страница: 1251 c:\Documents and Settings\user>
К сожалению, заранее угадать, в какой кодировке выводится текст, невозможно, поэтому проще попробовать установить командой chcp разные кодировки, чтобы добиться правильного отображения русского текста. Обычно используются кодировки 866 (кодировка русского текста DOS), 1251 (кодировка русского текста Windows), 65001 (UTF-8).
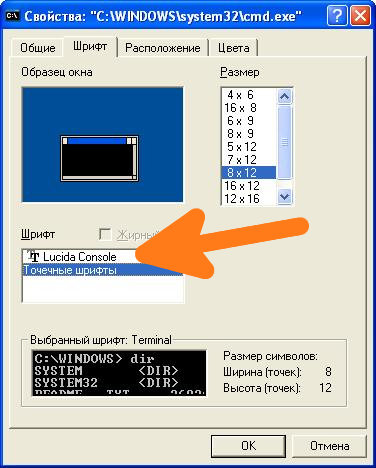
[Шрифт cmd.exe]
Иногда кракозябры можно убрать, если выбрать в свойствах окна cmd.exe шрифт Lucida Console (по умолчанию там стоит «Точечные шрифты»).
[Ссылки]
1. Универсальный декодер — конвертер кириллицы.
Windows
- 09.06.2020
- 85 128
- 6
- 195
- 191
- 4
- Содержание статьи
- Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены шрифта
- Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены кодировки
- Комментарии к статье ( 6 шт )
- Добавить комментарий
В некоторых случаях, когда используется неверная кодировка, могут возникать так называемые кракозябры или иероглифы, т.е. не читаемые символы, которые невозможно разобрать при работе с командной строкой. Эти проблемы могут также возникать и при запуске различных BAT-файлов. В данной статье мы расскажем о том, как можно сменить шрифт или кодировку, чтобы избавиться от этой проблемы. Пример таких не читаемых символов можно видеть на картинке ниже:
Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены шрифта
Первым делом нужно зайти в свойства окна: Правой кнопкой щелкнуть по верхней части окна -> Свойства -> в открывшемся окне в поле Шрифт выбрать Lucida Console и нажать кнопку ОК.
После этого не читаемые символы должны исчезнуть, а текст должен выводиться на русском языке.
Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены кодировки
Вместо смены шрифта, можно сменить кодировку, которая используется при работе cmd.exe.
Узнать текущую кодировку можно введя в командной строке команду chcp, после ввода данной команды необходимо нажать Enter.
Как видно на скриншоте, текущая используемая кодировка Windows-1251
Для изменения кодировки нам необходимо воспользоваться командой chcp <код_новой_кодировки>, где <код_новой_кодировки> — это сам код кодировки, на которую мы хотим переключиться. Возможные значения:
- 1251 — Windows-кодировка (Кириллица);
- 866 — DOS-кодировка;
- 65001 — Кодировка UTF-8;
Т.е. для смены кодировки на DOS, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 866Для смены кодировки на UTF-8, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 65001Для смены кодировки на Windows-1251, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 1251We have a project in Team Foundation Server (TFS) that has a non-English character (š) in it. When trying to script a few build-related things, we’ve stumbled upon a problem; we can’t pass the š letter to the command-line tools. The command prompt or what not else messes it up, and the tf.exe utility can’t find the specified project.
I’ve tried different formats for the .bat file (ANSI, UTF-8 with and without BOM) as well as scripting it in JavaScript (which is Unicode inherently), but no luck. How do I execute a program and pass it a Unicode command line?
asked Dec 23, 2008 at 9:30
6
Try:
chcp 65001
which will change the code page to UTF-8. Also, you need to use Lucida console fonts.
answered Dec 23, 2008 at 9:39
kgiannakakiskgiannakakis
103k27 gold badges159 silver badges194 bronze badges
9
My background: I have used Unicode input/output in a console for years (and do it a lot daily. Moreover, I develop support tools for exactly this task). There are very few problems, as far as you understand the following facts/limitations:
CMDand “console” are unrelated factors.CMD.exeis a just one of programs which are ready to “work inside” a console (“console applications”).- AFAIK,
CMDhas perfect support for Unicode; you can enter/output all Unicode chars when any code page is active. - Windows’ console has a lot of support for Unicode — but it is not perfect (just “good enough”; see below).
chcp 65001is very dangerous. Unless a program was specially designed to work around defects in the Windows’ API (or uses a C runtime library which has these workarounds), it would not work reliably. Windows 8 fixes ½ of these problems withcp65001, but the rest is still applicable to Windows 10.- I work in Windows-1252. As I already said: To input/output Unicode in a console, one does not need to set the code page.
The details
- To read/write Unicode to a console, an application (or its C runtime library) should be smart enough to use not the
File-I/OAPI, but theConsole-I/OAPI. (For an example, see how Python does it.) - Likewise, to read Unicode command-line arguments, an application (or its C runtime library) should be smart enough to use the corresponding API.
- Console font rendering supports only Unicode characters in BMP (in other words: below
U+10000). Only simple text rendering is supported (so European — and some East Asian — languages should work fine — as far as one uses precomposed forms). There is a [minor] fine print here for East Asian and for characters U+0000, U+0001, U+30FB.]
Practical considerations
-
The defaults on Window are not very helpful. For best experience, one should tune up three pieces of configuration:
- For output: a comprehensive console font. For best results, I recommend my builds. (The installation instructions are present there — and also listed in other answers on this page.)
- For input: a capable keyboard layout. For best results, I recommend my layouts.
- For input: allow hexadecimal input of Unicode.
-
One more gotcha with “Pasting” into a console application (very technical):
- Hexadecimal input delivers a character on KeyUp of Alt; all the other ways to deliver a character happen on KeyDown; so many applications are not ready to see a character on KeyUp. (Only applicable to applications using the Console-I/O API.)
- Conclusion: many applications would not react on hexadecimal input events.
- Moreover, what happens with a “Pasted” character depends on the current keyboard layout: if the character can be typed without using prefix keys (but with arbitrary complicated combination of modifiers, as in Ctrl + Alt + AltGr + Kana + Shift + Gray) then it is delivered on an emulated key press. This is what any application expects — so pasting anything which contains only such characters is fine.
- However, the “other” characters are delivered by emulating hexadecimal input.
Conclusion: unless your keyboard layout supports input of a lot of characters without prefix keys, some buggy applications may skip characters when you
Pastevia Console’s UI: Alt + Space, E + P. (This is why I recommend using my keyboard layouts!)
One should also keep in mind that the “alternative, ‘more capable’ consoles” for Windows are not consoles at all. They do not support Console-I/O APIs, so the programs which rely on these APIs to work would not function. (The programs which use only “File-I/O APIs to the console file handles” would work fine, though.)
One example of such non-console is a part of Microsoft’s PowerShell. I do not use it; to experiment, press and release the Windows key, and then type powershell.
(On the other hand, there are programs such as ConEmu or ANSICON which try to do more: they “attempt” to intercept the Console-I/O APIs to make “true console applications” work too. This definitely works for toy example programs; in real life, this may or may not solve your particular problems. Experiment.)
Summary
-
set font, keyboard layout (and optionally, allow hexadecimal input).
-
use only programs which go through the Console-I/O APIs, and accept Unicode command-line arguments. For example, any Cygwin-compiled program should be fine. As I already said, CMD is fine too.
Update: Initially, for a bug in cp65001, I was mixing up Kernel and CRTL layers (Update 2: and Windows user-mode API!). Also: Windows 8 fixes one half of this bug; I clarified the section about “better console” application, and added a reference to how Python does it.
Glorfindel
22k13 gold badges81 silver badges109 bronze badges
answered Dec 16, 2017 at 7:29
0
I had same problem (I’m from the Czech Republic). I have an English installation of Windows, and I have to work with files on a shared drive. Paths to the files include Czech-specific characters.
The solution that works for me is:
In the batch file, change the charset page
My batch file:
chcp 1250
copy "O:\VEŘEJNÉ\ŽŽŽŽŽŽ\Ž.xls" c:\temp
The batch file has to be saved in CP 1250.
Note that the console will not show characters correctly, but it will understand them…
answered Aug 24, 2010 at 12:31
vannavanna
4094 silver badges2 bronze badges
0
Check the language for non-Unicode programs. If you have problems with Russian in the Windows console, then you should set Russian here:
answered Apr 7, 2013 at 4:18
Maxim YefremovMaxim Yefremov
13.7k27 gold badges118 silver badges166 bronze badges
1
It’s is quite difficult to change the default Codepage of Windows console. When you search the web you find different proposals, however some of them may break your Windows entirely, i.e. your PC does not boot anymore.
The most secure solution is this one:
Go to your Registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor and add String value Autorun = chcp 65001.
Or you can use this small Batch-Script for the most common code pages.
@ECHO off
SET ROOT_KEY="HKEY_CURRENT_USER"
FOR /f "skip=2 tokens=3" %%i in ('reg query HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Nls\CodePage /v OEMCP') do set OEMCP=%%i
ECHO System default values:
ECHO.
ECHO ...............................................
ECHO Select Codepage
ECHO ...............................................
ECHO.
ECHO 1 - CP1252
ECHO 2 - UTF-8
ECHO 3 - CP850
ECHO 4 - ISO-8859-1
ECHO 5 - ISO-8859-15
ECHO 6 - US-ASCII
ECHO.
ECHO 9 - Reset to System Default (CP%OEMCP%)
ECHO 0 - EXIT
ECHO.
SET /P CP="Select a Codepage: "
if %CP%==1 (
echo Set default Codepage to CP1252
reg add "%ROOT_KEY%\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor" /v Autorun /t REG_SZ /d "@chcp 1252>nul" /f
) else if %CP%==2 (
echo Set default Codepage to UTF-8
reg add "%ROOT_KEY%\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor" /v Autorun /t REG_SZ /d "@chcp 65001>nul" /f
) else if %CP%==3 (
echo Set default Codepage to CP850
reg add "%ROOT_KEY%\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor" /v Autorun /t REG_SZ /d "@chcp 850>nul" /f
) else if %CP%==4 (
echo Set default Codepage to ISO-8859-1
add "%ROOT_KEY%\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor" /v Autorun /t REG_SZ /d "@chcp 28591>nul" /f
) else if %CP%==5 (
echo Set default Codepage to ISO-8859-15
add "%ROOT_KEY%\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor" /v Autorun /t REG_SZ /d "@chcp 28605>nul" /f
) else if %CP%==6 (
echo Set default Codepage to ASCII
add "%ROOT_KEY%\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor" /v Autorun /t REG_SZ /d "@chcp 20127>nul" /f
) else if %CP%==9 (
echo Reset Codepage to System Default
reg delete "%ROOT_KEY%\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor" /v AutoRun /f
) else if %CP%==0 (
echo Bye
) else (
echo Invalid choice
pause
)
Using @chcp 65001>nul instead of chcp 65001 suppresses the output «Active code page: 65001» you would get every time you start a new command line windows.
A full list of all available number you can get from Code Page Identifiers
Note, the settings will apply only for the current user. If you like to set it for all users, replace line SET ROOT_KEY="HKEY_CURRENT_USER" by SET ROOT_KEY="HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE"
answered Nov 2, 2015 at 10:23
0
On a Windows 10 x64 machine, I made the command prompt display non-English characters by:
Open an elevated command prompt (run CMD.EXE as administrator). Query your registry for available TrueType fonts to the console by:
REG query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Console\TrueTypeFont"
You’ll see an output like:
0 REG_SZ Lucida Console
00 REG_SZ Consolas
936 REG_SZ *新宋体
932 REG_SZ *MS ゴシック
Now we need to add a TrueType font that supports the characters you need like Courier New. We do this by adding zeros to the string name, so in this case the next one would be «000»:
REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Console\TrueTypeFont" /v 000 /t REG_SZ /d "Courier New"
Now we implement UTF-8 support:
REG ADD HKCU\Console /v CodePage /t REG_DWORD /d 65001 /f
Set default font to «Courier New»:
REG ADD HKCU\Console /v FaceName /t REG_SZ /d "Courier New" /f
Set font size to 20:
REG ADD HKCU\Console /v FontSize /t REG_DWORD /d 20 /f
Enable quick edit if you like:
REG ADD HKCU\Console /v QuickEdit /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
answered Aug 1, 2016 at 9:07
Alon OrAlon Or
7987 silver badges7 bronze badges
2
Actually, the trick is that the command prompt actually understands these non-English characters, just can’t display them correctly.
When I enter a path in the command prompt that contains some non-English characters it is displayed as «?? ?????? ?????». When you submit your command (cd «??? ?????? ?????» in my case), everything is working as expected.
answered Apr 14, 2009 at 13:03
UserUser
30.5k22 gold badges79 silver badges107 bronze badges
0
One really simple option is to install a Windows bash shell such as MinGW and use that:
There is a little bit of a learning curve as you will need to use Unix command line functionality, but you will love the power of it and you can set the console character set to UTF-8.
Of course you also get all the usual *nix goodies like grep, find, less, etc.
answered Jan 2, 2016 at 9:15
Steve BarnesSteve Barnes
27.7k6 gold badges64 silver badges73 bronze badges
0
I found this method as useful in new versions of Windows 10:
Turn on this feature: «Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support»
Control panel -> Regional settings -> Administrative tab-> Change
system locale…
answered Apr 14, 2019 at 11:28
zvizvi
3,8372 gold badges30 silver badges48 bronze badges
1
Starting June 2019, with Windows 10, you won’t have to change the codepage.
See «Introducing Windows Terminal» (from Kayla Cinnamon) and the Microsoft/Terminal.
Through the use of the Consolas font, partial Unicode support will be provided.
As documented in Microsoft/Terminal issue 387:
There are 87,887 ideographs currently in Unicode. You need all of them too?
We need a boundary, and characters beyond that boundary should be handled by font fallback / font linking / whatever.What Consolas should cover:
- Characters that used as symbols that used by modern OSS programs in CLI.
- These characters should follow Consolas’ design and metrics, and properly aligned with existing Consolas characters.
What Consolas should NOT cover:
- Characters and punctuation of scripts that beyond Latin, Greek and Cyrillic, especially characters need complex shaping (like Arabic).
- These characters should be handled with font fallback.
answered May 6, 2019 at 20:36
VonCVonC
1.3m530 gold badges4436 silver badges5277 bronze badges
As I haven’t seen any full answers for Python 2.7, I’ll outline the two important steps and an optional step that is quite useful.
- You need a font with Unicode support. Windows comes with Lucida Console which may be selected by right-clicking the title bar of command prompt and clicking the
Defaultsoption. This also gives access to colours. Note that you can also change settings for command windows invoked in certain ways (e.g, open here, Visual Studio) by choosingPropertiesinstead. - You need to set the code page to
cp65001, which appears to be Microsoft’s attempt to offer UTF-7 and UTF-8 support to command prompt. Do this by runningchcp 65001in command prompt. Once set, it remains this way until the window is closed. You’ll need to redo this every time you launch cmd.exe.
For a more permanent solution, refer to this answer on Super User. In short, create a REG_SZ (String) entry using regedit at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor and name it AutoRun. Change the value of it to chcp 65001. If you don’t want to see the output message from the command, use @chcp 65001>nul instead.
Some programs have trouble interacting with this encoding, MinGW being a notable one that fails while compiling with a nonsensical error message. Nonetheless, this works very well and doesn’t cause bugs with the majority of programs.
answered Apr 7, 2016 at 1:49
Aaron3468Aaron3468
1,74416 silver badges29 bronze badges
This problem is quite annoying. I usually have Chinese character in my filename and file content. Please note that I am using Windows 10, here is my solution:
To display the file name, such as dir or ls if you installed Ubuntu bash on Windows 10
-
Set the region to support non-utf 8 character.
-
After that, console’s font will be changed to the font of that locale, and it also changes the encoding of the console.
After you have done previous steps, in order to display the file content of a UTF-8 file using command line tool
- Change the page to utf-8 by
chcp 65001 - Change to the font that supports utf-8, such as Lucida Console
- Use
typecommand to peek the file content, orcatif you installed Ubuntu bash on Windows 10 - Please note that, after setting the encoding of the console to utf-8, I can’t type Chinese character in the cmd using Chinese input method.
The laziest solution: Just use a console emulator such as http://cmder.net/
answered Jan 22, 2017 at 6:02
code4jcode4j
4,2385 gold badges34 silver badges51 bronze badges
0
A quick decision for .bat files if you computer displays your path/file name correct when you typing it in DOS-window:
- copy con temp.txt [press Enter]
- Type the path/file name [press Enter]
- Press Ctrl-Z [press Enter]
This way you create a .txt file — temp.txt. Open it in Notepad, copy the text (don’t worry it will look unreadable) and paste it in your .bat file.
Executing the .bat created this way in DOS-window worked for mе (Cyrillic, Bulgarian).
answered Apr 9, 2015 at 8:52
For a similar problem, (my problem was to show UTF-8 characters from MySQL on a command prompt),
I solved it like this:
-
I changed the font of command prompt to Lucida Console. (This step must be irrelevant for your situation. It has to do only with what you see on the screen and not with what is really the character).
-
I changed the codepage to Windows-1253. You do this on the command prompt by «chcp 1253». It worked for my case where I wanted to see UTF-8.
answered Dec 2, 2012 at 12:41
1
I see several answers here, but they don’t seem to address the question—the user wants to get Unicode input from the command line.
Windows uses UTF-16 for encoding in two byte strings, so you need to get these from the OS in your program. There are two ways to do this—
-
Microsoft has an extension that allows main to take a wide character array:
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t *argv[]);
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/6wd819wh.aspx -
Call the Windows API to get the Unicode version of the command line
wchar_t win_argv = (wchar_t)CommandLineToArgvW(GetCommandLineW(), &nargs);
CommandLineToArgvW function (shellapi.h)
Read UTF-8 Everywhere for detailed information, particularly if you are supporting other operating systems.
answered Aug 31, 2018 at 14:53
1
A better cleaner thing to do: Just install the available, free, Microsoft Japanese language pack. (Other oriental language packs will also work, but I have tested the Japanese one.)
This gives you the fonts with the larger sets of glyphs, makes them the default behavior, changes the various Windows tools like cmd, WordPad, etc.
answered May 31, 2013 at 12:19
0
Changing code page to 1252 is working for me. The problem for me is the symbol double doller § is converting to another symbol by DOS on Windows Server 2008.
I have used CHCP 1252 and a cap before it in my BCP statement ^§.
answered Feb 12, 2015 at 7:18
0
I got around a similar issue deleting Unicode-named files by referring to them in the batch file by their short (8 dot 3) names.
The short names can be viewed by doing dir /x. Obviously, this only works with Unicode file names that are already known.
answered Dec 2, 2015 at 13:39
0
Mind for those using WSL who also do not want the extra packages from Cygwin or Git, wsltty is available which provides just the terminal with UTF-8 support.
answered Jun 6, 2022 at 7:35
Время чтение: 4 минуты
2014-01-19
Как корректно отобразить Русский текст в CMD. Проблемы с кодировкой могут возникнуть, например, при выполнении Bat файла, когда нужно вывести в консоль русский текст и при других обстоятельствах, о которых речь пойдёт далее.
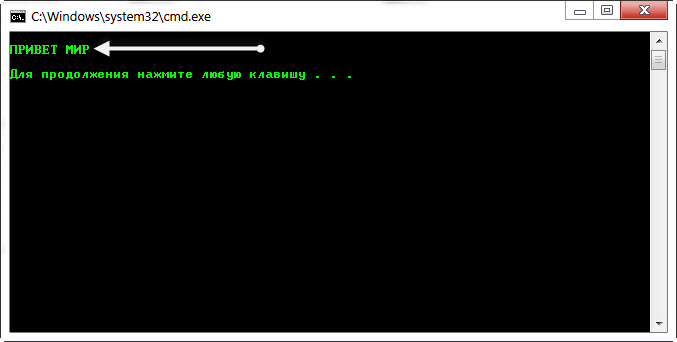
Рассмотрим пример: когда нужно вывести в консоль Русский текст, скажем «Примет мир». Для этого создадим Bat файл с именем «1.bat». Используйте для этого обычный Блокнот Windows (Notepad.exe) Запишем в него следующие строки!
|
@Echo off echo. echo ПРИВЕТ МИР echo. Pause |
Для тех, кто не понял или не в курсе, строчки «echo.» я добавил специально, что бы были отступы, от строки «Примет мир»
Теперь запускаем файл 1.bat и результат будет такого вида.
Как видим проблема с кодировкой в cmd на лицо. И произошло это по следующей причине.
Стандартный блокнот Windows сохранил Bat файл в кодировке «1251» а консоль вывела его в кодировки «866». Вот от сюда все проблемы!
Решения проблемы с кодировкой в CMD. 1 Способ.
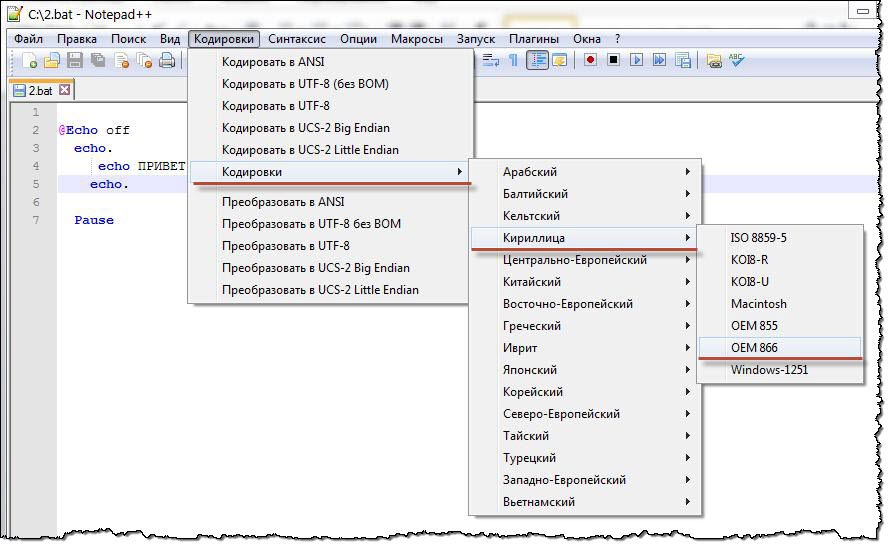
Для решения проблемы нужно просто использовать текстовой редактор, с помощью которого можно сохранить текст в кодировке «866». Для этих целей прекрасно подходит «Notepad++» (Ссылку для загрузки Вы можете найти в моём Twitter-e).
Скачиваем и устанавливаем на свой компьютер «Notepad++».
После запуска «Notepad++» запишете в документ те же строки, которые мы уже ранние записывали в стандартный блокнот.
|
@Echo off echo. echo ПРИВЕТ МИР echo. Pause |
Теперь осталось сохранить документ с именем «2.bat» в правильной кодировке. Для этого идём в меню «Кодировки > Кодировки > Кириллица > OEM-866»
и теперь сохраняем файл с именем «2.bat» и запускаем его! Поле запуска результат на лицо.
Как видим, текст на Русском в CMD отобразился, как положено.
Решения проблемы с кодировкой в CMD. 2 Способ.
Теперь рассмотрим ещё одну ситуацию, когда могут возникнуть проблемы с кодировкой в CMD.
Допустим, ситуация требует сохранить результат выполнения той или иной команды в обычный «TXT» файл. В приделах этого поста возьмём для примера команду «HELP».
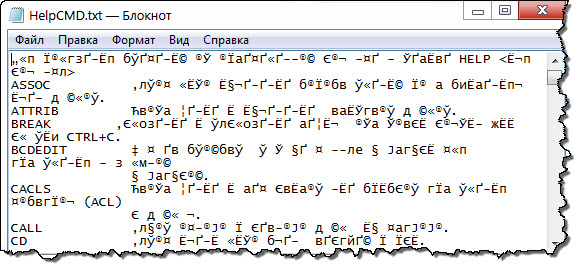
Задача: Сохранить справку CMD в файл «HelpCMD.txt. Для этого создайте Bat файл и запишите в него следующие строки.
|
@Echo off Help > C:\HelpCMD.txt Pause |
После выполнения Bat файла в корне диска «C:\» появится файл «HelpCMD.txt» и вместо справки получится вот что:
Естественно, такой вариант не кому не понравится и что бы сохранить справку в понятном для человека виде, допишите в Bat файл строку.
Теперь содержимое кода будет такое.
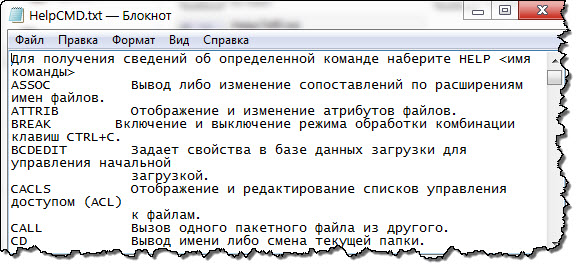
|
@Echo off chcp 1251 >nul Help > C:\HelpCMD.txt Pause |
После выполнения «Батника» результат будет такой:
Вот так на много лучше, правда?
Пожалуй, на этом я закончу пост. Добавить больше нечего. Если у Вас имеются какие-то соображения по данной теме, буду рад Вашему комментарию к посту.
Дополнительно из комментариев то Garric
Автор очень хорошо описал принцип. ! Но это неудобно.
Нужно бы добавить. Если автор добавит это в статью то это будет Good.
Создаём файл .reg следующего содержания:
——
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.bat\ShellNew]
«FileName»=»BATНастроенная кодировка.bat»
——
Выполняем.
——
Топаем в %SystemRoot%\SHELLNEW
Создаём там файл «BATНастроенная кодировка.bat»
Открываем в Notepad++
Вводим любой текст. (нужно!) Сохраняемся.
Удаляем текст. Меняем кодировку как сказано в статье. Сохраняемся.
———-
Щёлкаем правой кнопкой мыши по Рабочему столу. Нажимаем «Создать» — «Пакетный файл Windows».
Переименовываем. Открываем в Notepad++. Пишем батник.
В дальнейшем при работе с файлом не нажимаем ничего кроме как просто «Сохранить». Никаких «Сохранить как».
На чтение 3 мин Опубликовано Обновлено
Командная строка Windows 10 — это мощное средство для работы с системой операционной Windows. Однако, иногда пользователь может столкнуться с проблемой кодировки символов, когда некорректно отображаются некоторые символы или текст на другом языке.
Изменение кодировки символов в командной строке Windows 10 может позволить исправить проблему и корректно отображать текст на любом языке. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, как изменить кодировку символов в командной строке Windows 10, чтобы вы смогли успешно работать с командами и отображать текст на нужных языках.
Чтобы изменить кодировку символов в командной строке Windows 10, необходимо воспользоваться командой chcp (change code page). Эта команда позволяет задать нужную кодировку символов, которая будет использоваться в командной строке Windows 10.
Примечание: Перед выполнением любых действий в командной строке Windows 10, рекомендуется создать точку восстановления системы или сделать резервную копию важных данных.
Как изменить кодировку в командной строке Windows 10
Кодировка текста играет важную роль при работе с командной строкой Windows 10. Правильная кодировка обеспечивает корректное отображение текста и предотвращает возникновение ошибок. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как изменить кодировку в командной строке Windows 10.
Для изменения кодировки в командной строке Windows 10 следуйте приведенным ниже шагам:
| Шаг | Действие |
|---|---|
| Шаг 1 | Откройте командную строку Windows 10, нажав клавишу Win + R, введите cmd и нажмите клавишу Enter. |
| Шаг 2 | Введите команду chcp и нажмите клавишу Enter, чтобы узнать текущую кодировку. |
| Шаг 3 | Введите команду chcp {кодировка} и нажмите клавишу Enter, чтобы изменить кодировку. Например, для установки кодировки UTF-8, введите chcp 65001. |
После выполнения этих шагов кодировка в командной строке Windows 10 будет изменена на указанную. Пожалуйста, обратите внимание, что не все кодировки могут быть поддерживаемыми и корректно отображаться в командной строке Windows 10.
Изменение кодировки в командной строке Windows 10 может быть полезно при работе с файлами и программами, которые используют определенную кодировку. Убедитесь, что выбрана правильная кодировка, чтобы избежать проблем со считыванием и отображением текста в командной строке Windows 10.
Подробная инструкция
Изменение кодировки в командной строке Windows 10 может понадобиться, если вы столкнулись с проблемой отображения некорректных символов или текста на другом языке.
Для изменения кодировки в командной строке Windows 10 выполните следующие шаги:
| Шаг | Описание |
| 1 | Откройте командную строку. Для этого нажмите клавиши Win + R, введите команду «cmd» в поле «Выполнить» и нажмите Enter. |
| 2 | Введите команду «chcp» (change code page), чтобы узнать текущую кодировку командной строки. |
| 3 | Введите команду «chcp номер_кодировки», где «номер_кодировки» — это кодировка, которую вы хотите установить. Например, если вы хотите установить кодировку UTF-8, введите команду «chcp 65001». |
| 4 | Нажмите Enter, чтобы выполнить команду. |
| 5 | Проверьте, что кодировка успешно изменена, введя команду «chcp» еще раз. Кодировка командной строки должна соответствовать выбранной вами кодировке. |
После выполнения этих шагов кодировка в командной строке Windows 10 будет изменена на выбранную вами. Теперь вы сможете правильно отображать текст и символы на других языках.