О LENOVO
+
О LENOVO
-
Наша компания
-
Новости
-
Контакт
-
Соответствие продукта
-
Работа в Lenovo
-
Общедоступное программное обеспечение Lenovo
КУПИТЬ
+
КУПИТЬ
-
Где купить
-
Рекомендованные магазины
-
Стать партнером
Поддержка
+
Поддержка
-
Драйверы и Программное обеспечение
-
Инструкция
-
Инструкция
-
Поиск гарантии
-
Свяжитесь с нами
-
Поддержка хранилища
РЕСУРСЫ
+
РЕСУРСЫ
-
Тренинги
-
Спецификации продуктов ((PSREF)
-
Доступность продукта
-
Информация об окружающей среде
©
Lenovo.
|
|
|
|
In this article, I’ll show you how to use the SCCM feature update option to perform a Windows 10 22H2 upgrade. We will use Windows Servicing in SCCM to upgrade Windows 10 devices to version 22H2 via the enablement package.
Windows 10, version 22H2, also known as the Windows 10 2022 Update, is available for eligible devices running Windows 10, versions 20H2 and newer. Microsoft released Windows 10, version 22H2 (KB5015684) on 18th October 2022, and it is an enablement package.
For home users running Windows 10 version 20H2 and later, the recommended way to get the Windows 10 22H2 is via Windows Update. Go to Start > Settings > Windows Update and run Check for Updates. Select the Feature update to Windows 10, version 22H2 and install it.
When you want to upgrade multiple Windows 10 devices to version 22H2, Configuration Manager is the best tool. It simplifies the way you deploy and manage updates and saves a lot of time. With Configuration Manager, you can select the “Feature Update to Windows 10 Version 22H2 via Enablement Package” and deploy it to a set of devices.
Ways to upgrade to Windows 10 22H2
There are multiple ways that you can use to upgrade to Windows 10 version 22H2.
- Get the Windows 10 22H2 update via Windows Update.
- Use Servicing Plans to upgrade eligible Windows 10 devices to version 22H2.
- Upgrade Windows 10 21H2 to Windows 10 22H2 using ConfigMgr Windows Servicing feature.
- Deploy the Windows 10 22H2 update using the SCCM task sequence.
- Using the Intune to upgrade to Windows 10 22H2 upgrade for WUfB managed devices.
We will use the Configuration Manager feature update option to deploy the Windows 10 22H2 enablement package out of all the above methods. This is the easiest and quickest way I can think of to update Windows 10 to version 22H2.
Recommended: Upgrade to Windows 10 21H2 using SCCM | ConfigMgr
Can I use SCCM Servicing Plans to Upgrade to Windows 10 version 22H2?
Yes, you can use the Servicing Plans in SCCM to upgrade the computers running Windows 10 to version 22H2. With Configuration manager servicing plans you can ensure that all the Windows 10 systems are kept up-to-date when new builds are released. Servicing plans are ADR that can help you to upgrade Windows 10 to version 22H2. Take a look at detailed guide on Windows 10 Servicing Plans in SCCM.
If you are unsure whether to upgrade to Windows 10 22H2 using a Servicing Plan or a feature update deployment, I would advise choosing the latter. There are only a few steps involved in deploying a Windows 10 22H2 feature update, making it much simpler than a servicing plan. You get to make the final decision.
Related Article: Windows 11 22H2 upgrade using SCCM | ConfigMgr
About Windows 10 version 22H2
Windows 10 22H2 is an enablement package and this is good news for admins. The enablement package is a great option for installing a scoped feature update like Windows 10, version 22H2. You can upgrade from version 2004, 20H2, 21H1, or 21H2 to version 22H2 with a single restart, reducing update downtime. Since Windows 10 22H2 is an enablement package, the devices currently on Windows 10, version 20H2 or newer will have a fast installation experience because the update will install like a monthly update.
Prerequisites
With Configuration Manager, you need few things to be configured before you deploy the feature updates to computers. If you have deployed the feature updates before, it means most of the prerequisites are already taken care of. If your SCCM setup is new, you may have to configure them once before deploying the upgrades.
Listed below are all the prerequisites required for Windows 10 22H2 upgrade using SCCM.
- Configure Software Update Point by enabling the upgrades for Windows 10 and Windows 11.
- Ensure the service connection point is online.
- Enable dynamic update for feature updates in Configuration Manager Client Settings.
- Windows 10 1903, and later product must be enabled under Software Update Point > Products.
Download Windows 10 22H2 Enablement Package
Let’s look at steps for downloading Windows 10 22H2 enablement package using SCCM. First of all ensure you have synchronized the updates in Configuration Manager. You can either download the feature first and deploy or directly deploy the feature update. I prefer to download it first, let the content get distributed to distribution points and then deploy it.
Go to Software Library > Overview > Windows 10 Servicing > All Windows 10 Updates. Look for the update “Feature Update to Windows 10 Version 22H2 x64-based systems 2022-10 via Enablement Package“. You can also search the updates with article ID 5015684.
If you have got both x64-based systems and x86-based systems, you must download Feature Update to Windows 10 Version 22H2 x64-based and x86-based. In my lab, all my Windows 10 VMs are running Windows 10 64-bit OS, and therefore I am going to download only Feature Update to Windows 10 Version 22H2 x64-based systems 2022-10 via Enablement Package.
Create Deployment Package
On the Deployment package window, specify the deployment package for Windows 10 22H2 upgrade files. This deployment package that you create will contain the software update files that will be deployed to the clients.
Select Create a new deployment package and specify the package name as “Windows 10 22H2 Deployment Package.” Add a brief description and specify the package source – a shared folder where you want to download the updates. Enabling the binary differential replication is optional. Click Next.
Click on Add button and select the distribution point servers to which you would like to distribute the Windows 10 22H2 upgrade files. Click Next.
On the Distribution Settings page, you can specify the general distribution settings for the deployment package. Click Next.
The download location lets you select an option to download the updates from. For example, you can download the software updates directly from internet or choose to download the software updates from the location on network. Select the option “Download software updates from the internet“. Click Next.
Specify the update language for the products. The default language is English US. Click Next.
Review the Windows 10 22H2 deployment package settings and close the Download software updates wizard.
Note: In case you encounter issues while downloading the Windows 10 22H2 enablement package update, review the PatchDownloader.log located in the %temp% folder. This log file will log all the errors that occur during the download of Windows 10 feature updates.
In the above step, the files required to upgrade Windows 10 to version 22H2 are downloaded to the specified location. If you browse to the downloaded location, you will notice that Windows 10 22H2 enablement package contains only one update which is Windows10.0-KB5015684-x64. The size of the Windows 10 22H2 enablement package is 32 KB. This one file is sufficient to upgrade Windows 10 computers to version 22H2.
In this step, using the Windows Servicing, we will perform the Windows 10 22H2 feature update deployment using Configuration Manager. You can deploy the feature update to a single client or to multiple devices using device collection.
If you are deploying the Windows 10 22H2 update for the first time, I suggest testing the upgrade on a Pilot device collection. A few devices that are intended to test the upgrade to 22H2 should be included in this device collection. Use the following guide to create a device collection for Windows 10 computers in SCCM.
Recommended Article: Upgrade Windows 10 21H1 using SCCM | ConfigMgr
Use the following steps to deploy the Windows 10 22H2 feature update using SCCM:
- In the ConfigMgr console, navigate to Software Library\Overview\Windows Servicing\All Windows Feature Updates.
- Right-click Feature Update to Windows 10 Version 22H2 x64-based systems 2022-10 via Enablement Package update, and select Deploy.
On the General page, enter the details for Windows 10 22H2 feature update deployment.
- Deployment Name: Enter a suitable name such as Deploy Windows 10 22H2 Enablement Package.
- Description: Although it’s optional, you may add a brief description.
- Software Update Group: This is created automatically and is visible under Software Update Groups in Configuration Manager console.
- Collection: Click Browse and select a device collection consisting of few pilot devices selected for testing Windows 10 2022 upgrade.
Click the Next button to continue.
On the Deployment Settings page, specify the type of deployment. Choose whether you want to make the Windows 10 22H2 upgrade available for users in the Software Center or deploy it as required. Read more about SCCM Available vs. Required to know the differences. Click Next.
The Scheduling page lets you configure schedule details for the deployment. Configure the following settings:
- Schedule Evaluation | Time Based on: Select Client Local Time.
- Software Available Time: As soon as possible.
If you want to make the Windows 10 22H2 upgrade available at a specific date and time, select Specific time and define them. Define the deadline installation to ensure the upgrade happens in the defined period.
Click Next to continue.
Specify the following user experience settings for the deployment.
- User Notifications: Display in Software Center and show all notifications
- Commit changes at the deadline or during a maintenance window (requires restarts): Yes
- If any update in this deployment requires a system restart, run updates deployment evaluation cycle after restart: No.
Click Next.
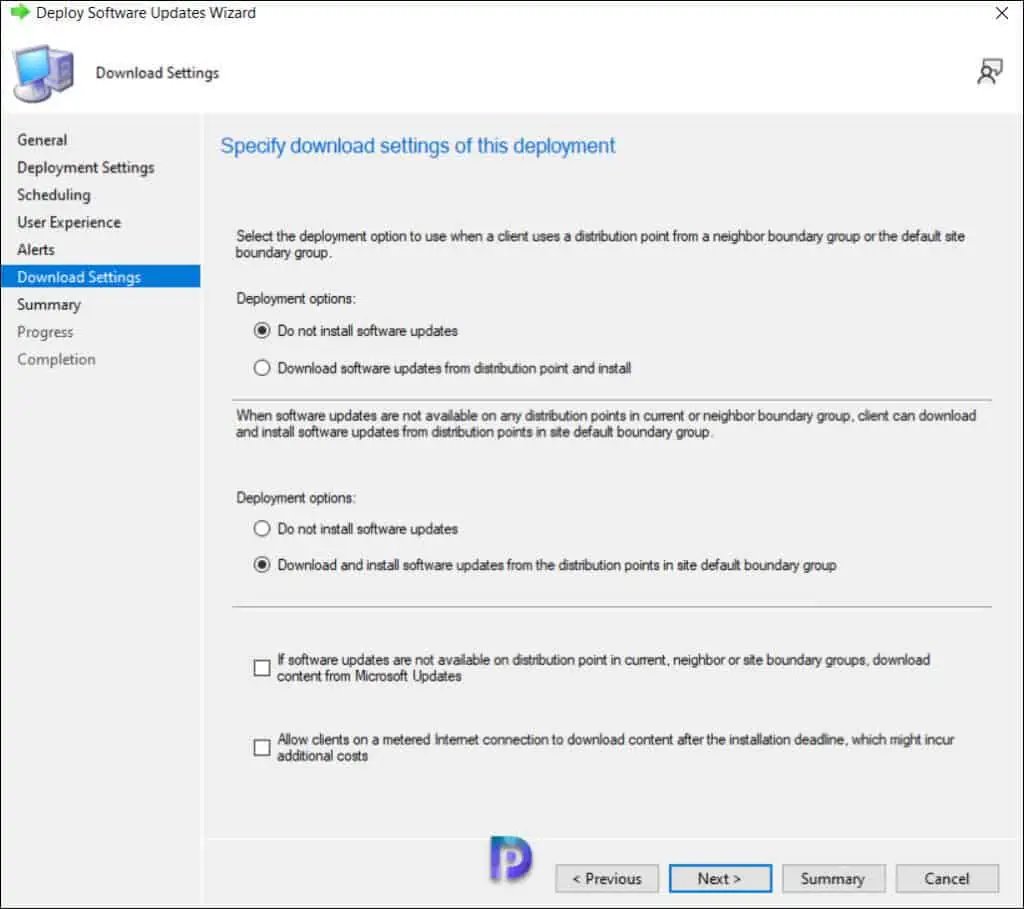
On the Download settings page, specify the download settings for the current deployment:
- Client Computers can use distribution points from neighbor boundary: No
- Download and install software updates from the fallback content source location: Yes
Click Next to continue.
Review the deployment settings of Windows 10 22H2 on Summary page and click Next. On the Completion window, click Close.
Windows 10 22H2 Servicing: End-User Experience for Upgrade
After you have deployed Windows 10 22H2 enablement package update using Windows Servicing, it’s time to test the upgrade installation on end computers. The end-user experience is similar to other feature upgrades.
On the client computer, first launch the Software Center. Once the Software Center has been opened, select Feature Update to Windows 10 Version 22H2 x64-based systems 2022-10 via Enablement Package update by clicking the Updates tab. Click on the Install button.
Confirm you want to upgrade the operating system on this computer. It will take only few minutes to upgrade the operating system as this is an enablement package. Note that this is an in-place upgrade to version 22H2, and the setup automatically migrates your apps, data, and settings. Click on the Install button to begin the Windows 10 22H2 upgrade.
The Feature Update to Windows 10 Version 22H2 x64-based systems 2022-10 via Enablement Package is installed in less than 2 minutes. Click on Restart.
On the confirmation box, click Restart.
The Windows 10 22H2 upgrade is complete. Log in to the Windows 10 computers and click Start > About My PC. Under Windows Specifications, you will find the build number and version of Windows 10. In the below screenshot, we see the Windows version is “22H2” and the OS build number is 19045.2006.
After you have upgraded multiple Windows 10 computers to version 22H2, you can create a device collection in SCCM. Refer to this article to learn how to create Windows 10 22H2 device collection using WQL Query. If you want to get to Windows 11, you can upgrade to Windows 11 using different methods.

Prajwal Desai is a Microsoft MVP in Intune and SCCM. He writes articles on SCCM, Intune, Windows 365, Azure, Windows Server, Windows 11, WordPress and other topics, with the goal of providing people with useful information.
Microsoft Configuration Manager helps IT manage PCs and servers, keeping software up-to-date, setting configuration and security policies, and monitoring system status while giving employees access to corporate applications on the devices that they choose. When Configuration Manager is integrated with Microsoft Intune, you can manage corporate-connected PCs and Macs along with cloud-based mobile devices running Windows, iOS, and Android, all from a single management console.
New features of Configuration Manager, such as the support of Windows 10 in-place upgrade, co-management with Microsoft Intune, Windows 10 and Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise Servicing Dashboard, integration with Windows Update for Business, and more make deploying and managing Windows easier than ever before.
- Need more technical information about Microsoft Configuration Manager? Checkout product documentation.
- To include Microsoft Intune in your evaluation for a unified management of PCs and servers, as well as, cloud-based mobile devices, sign up for a free evaluation.
Languages
- English
Editions
- Microsoft Configuration Manager (Current Branch- version 2303) | 32-bit and 64-bit
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) is a systems management tool. Learn everything you need to know about it in this article.
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) is a systems management tool designed for monitoring network devices that was recently updated by a new tool called Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM)
The decision to redesign SCCM surprised many given the number of enterprises that relied on the program.
In this article, our main goal is to look at what SCCM is, and while we’ll briefly take a look at the Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager rebrand, the main focus will be on the original SCCM most enterprises are familiar with.
What is SCCM?
Before SCCM was rebranded as Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager, it was an application designed for managing Windows and Mac OS computers, Linux/Unix servers, and mobile devices using Windows/iOS/Android.
Some of the features SCCM could be used for include:
- OS deployment Create images of operating systems and deploy them.
- Remote Control An administrator can take control of a remote device to troubleshoot if a device experiences performance issues.
- Maintenance Windows A user can define a time when configuration management can be completed on a collection of devices (i.e. carry out updates when they won’t affect productivity).
- Integration with Microsoft Intune Manage mobile devices for iOS, Android, and Windows with Microsoft Intune.
- Scheduling Schedule updates to make sure that your network infrastructure is periodically updated (useful for minimizing vulnerabilities).
- Reporting Create reports on systems for further information on patch status. For example, you can create a report on systems that have missed patches.
- Endpoint protection Manage anti malware policies and firewall security from one location to protect computers.
For example, you could distribute updates to Windows 10 devices throughout your entire network. SCCM is a staple for many enterprises because it offers an efficient means of updating multiple devices.
SCCM is part of the System Center family of products, which includes tools such as:
- System Center Operations Manager
- System Center Data Protection Manager
- System Center Virtual Machine Manager
- System Center Service Manager
- System Center Capacity Planner
- System Center Mobile Device Manager
- System Center Essentials
SCCM is sometimes mistaken for Microsoft System Center Operations Manager (SCOM), a platform used for monitoring the health and performance of systems. The main difference between the two is that SCCM is used for configuration management and SCOM is used to monitor applications and services.
Why Do I Need to Use SCCM?
Using SCCM is a good idea if you’re in need of a solution for configuring and managing systems in an enterprise network environment. SCCM provides you with a single tool to deploy installations to multiple devices which streamlines the hardware management process.
Overseeing the updates and configurations of devices from a top-down viewpoint saves you from having to manage devices individually on every single device. There’s manual work to do as you can manage everything from one location.
Creating an inventory of hardware and software, updating OS’s, deploying applications, monitoring configurations, and managing endpoint protection (anti-malware) are just some of the things that you can use the software for.
Windows Management / Patch Management
Windows management or patch management is one of the main use cases offered by SCCM. With SCCM you can manage Windows devices and remotely update software. The program uses Microsoft WSUS to check for updates and deploy patches to devices.
Through one console you can maintain multiple Windows devices, and schedule/deploy patches to devices periodically. From a security standpoint, deploying patches is essential for keeping your software updated and reducing the likelihood of a cyber attacker exploiting a vulnerability.
Patches run in the background to minimize disruption. However, it is important to note that the patch management capabilities offered by SCCM do have limitations. One of the most significant is the limited support for third-party patching.
The inability to patch third-party applications leaves open vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. Issues like this can be fixed by using external tools, such as SolarWinds Patch Manager or ManageEngine Connect Plus, which extend SCCM’s patching for third-party applications.
Endpoint Protection
Endpoint protection is another main function of SCCM. SCCM enables you to configure anti-malware policies and firewall settings, set automatic deployment rules for software updates, configure Endpoint Protection client configurations, send notifications, and more.
Essentially you can create anti-malware policies and then deploy them to devices throughout your network. From then onward you can monitor endpoints with activity reports. For example, you can create an Antimalware Activity Report that tells you about the security status of your infrastructure (see the next section for more information on reports).
There are also malware alerts. Alerts notify you about the presence of malicious activity in the network and can be seen through the dashboard or sent to individual users. You can configure your own alert conditions to determine when notifications will be generated and set the severity of the alerts.
Reporting
Another key function of SCCM is report creation. SCCM comes with out-of-the-box reports for monitoring devices throughout the network. The default reports cover everything from asset management to vulnerability assessments and user data. In order to run reports, you need to have the appropriate permissions. Reports are customizable so you can pick which information to monitor.
You can edit reports with the Report Builder. The Report Builder gives you the option to add visual elements like charts, maps, sparklines, and data bars for greater clarity. It is important to note that the Report Builder must be installed from SSRS or Microsoft websites.
The reporting features offered by SCCM are extremely valuable from a regulatory compliance perspective and display that systems have been updated. Once you’ve completed a report you can export it in a PDF, CSV, or Microsoft Excel format.
Why is SCCM now Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager? And What is Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
Recently, Brad Anderson, Corporate Vice President for Microsoft 365 announced the decision to rebrand SCCM and combine it with Microsoft Intune, a mobile management solution to form Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
SCCM has now been renamed to Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager and is one of several services that make up Microsoft Endpoint Manager including Device Management Admin Center (DMAC) and Desktop Analytics.
The rebrand took place in an attempt to provide users with a complete endpoint management solution for cloud environments with intelligence features. In other words, the update was designed to give enterprises the features they need to thrive in the modern workplace with all the range of devices making their way into the workplace.
The Benefits of Using SCCM
Using SCCM brings to the table a number of benefits for enterprises managing a network full of devices:
- Unified management of Windows endpoints
- Integration with Windows systems
- Simple to administrate (compare to other tools like Chef and Puppet)
Perhaps the biggest advantage is that SCCM unifies the management of Windows endpoints. An administrator can manage dozens of devices through a single platform, push updates to devices, and update configurations remotely. Having a configuration management tool saves time that would be lost manually updating devices.
Overall administration is also much easier. An administrator has access to an inventory of IT assets without having to create one manually. Having a clear inventory enhances visibility and enables the user to keep systems compliant more easily.
From a security standpoint, being able to identify and fix non-compliant systems reduces cybersecurity risks and helps to ensure compliance with industry regulations. As the WannaCry outbreak showed enterprises in 2017, unpatched devices can have a devastating impact on a company’s operations.
The Limitations of SCCM
While SCCM is a very useful tool it does have some substantial limitations:
- Support is limited for non-Windows devices
- Limited support for third-party application patches
- Pricing is complex and expensive
Given that SCCM was designed for Windows devices there is limited support for Mac and Linux tools. You must have a Windows server to run the platform, which immediately rules out many cross-platform environments. SCCM is recommended to users whose infrastructure is dominated by Windows devices unless you want to do additional manual patching.
As we noted further above, there’s also limited support for third-party application patching. SCCM is largely ineffective at patching third-party applications. This is a substantial weakness given that third-party software still needs to be secured, and can be used as an entry point to a network by cyber attackers.
Finally, the pricing of SCCM can be costly for enterprise users. Individual client licenses range from $41 (£33) for the Client ML to $430 (£353) for the Enterprise ML version. When you can consider the cost alongside the limitations in third-party patching and limited support for non-Windows devices, it’s a lot of money for incomplete coverage.
Microsoft Intune vs SCCM
One solution that’s often compared with SCCM is Microsoft Intune. Before Microsoft Intune was merged into Endpoint Manager alongside SCCM, the former was a cloud-based mobile device management and system management solution. The intention behind the program was to equip customers to manage cloud-based infrastructure.
Features include:
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
- A central admin portal
- Application Level Management
- Integration with SCCM
- Microsoft Malware Protection Engine
- Reporting
The key difference between SCCM and Intune is that the former was aimed at managing on-premises infrastructure, while the latter was aimed at cloud-based services. SCCM has some key advantages over Intune:
- You can manage systems that aren’t connected to the internet
- You don’t need to use Microsoft Cloud
- You can manage Windows Servers
In contrast, Intune has a number of advantages over SCCM:
- Mobile device management (MDM) for mobile devices
- You don’t need local infrastructure
- You don’t need to maintain the program or infrastructure
It’s important to note that you don’t need to choose between the two, even though it’s useful to have an idea of each solution’s strengths. Combining the two gives users a lot more co-management options to work with. The user can combine both to manage on-premise and cloud-based infrastructure from computers to mobile devices, and applications.
Is SCCM Dead?
SCCM has a long way to go before it’s obsolete. Microsoft still supports the software and while the rebranding to MECM may have changed the nature of endpoint management with a new cloud-based console, the SCCM capabilities enterprises are familiar with are still there. The addition of intelligent features and analytics will only serve to enhance the device management process.
For now, SCCM or MECM still has a significant role to play in managing configurations and OS deployments. As more updates roll out in the foreseeable future we can expect to see configuration management capabilities grow with the needs of enterprises.
SCCM FAQs
What is SCCM used for?
SCCM is the System Center Configuration Manager from Microsoft. It is designed to support operating systems and software packages produced by Microsoft. The system is concerned with the security and availability of software within a business. Two of the major functions of SCCM are software distribution and installation and patch management. The package also has some security management tools included.
What is SCCM called today?
In 2019, Microsoft introduced the Microsoft Endpoint Manager with version 1910 of Windows. SCCM is now part of this package and it is called Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM).
What are the SCCM services?
Microsoft Systems Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) provides the following services:
- Centralized endpoint management
- Remote control
- Operating system deployment
- Hardware inventory
- Software inventory
- Software distribution
- Patch management
- Network access protection
Обзор некоторых новых функций
Configuration Manager 2016 (Current Branch)
от версии 1511 до 1806, которые мне интересны, которые оказались долгожданными и очень полезными после перехода с SCCM 2012R2. Полный перечень новинок можно прочитать здесь [https://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/sccm/core/plan-design/changes/what-has-changed-from-configuration-manager-2012].
Высокая доступность сервера сайтаСоздан функционал высокой доступности сервера. Здесь имеется ввиду, что при “падении” основного сервера Configuration
Manager в работу вступает резервный. Резервный сервер всё основное время работает в пассивном режиме, а при крайней необходимости становится активным.
Имеется возможность перенести папку SCCMContentLib, в которой находятся все файлы для развертываний программного обеспечения, обновлений, ОС. Переместить библиотеку
содержимого можно на другой диск сервера, на отдельный сервер или на внешние хранилища данных.
Появилась роль
Service Connection
Point, которая отвечает за обновления SCCM-сервера и клиентов. При наличии обновлении системному администратору об этом выдаётся
следующее сообщение: A new
update
is
available
for
Configuration
Manager. You can view and enable available updates in the Administration workspace from the Updates and Servicing node. Обновления
располагаются
в разделе Administration->Overview->Updates and Servicing. Удобство заключается в том, что теперь не надо искать хотфиксы, скачивать, добавлять их в консоль, распространять.
Выделив системное обновление, можно внизу увидеть его описание, надобность, а нажав на кнопку в виде ссылки
Show Status в правом нижнем углу, можно увидеть состояние выполнения данного обновления по шагам.
Стало возможным определить те клиентские устройства, которые требуют перезапуска, а также использовать действие уведомления клиента для их перезапуска.
В качестве ещё одного новшества отметим наличие визуального состояния компьютеров в реальном времени в виде иконок, пройдя в
Assets and Compliance->Overview->Devices.
Рядом отображается и текущий пользователь, выполнивший вход и значение для любого списка устройств в коллекции, которое соответствует статусу клиента. При выходе пользователя из системы это значение очищается. Если же в систему никто не входил, то поле со значением
будет пустым.
Чтобы связать основного пользователя с устройством, нужно в параметрах клиента в разделе User and Device Affinity
активировать параметр Automatically configure user device affinity from usage data, установив значение
Yes.
Ещё одно полезное изменение (исправление) относится к нормальному отображению рабочего стола при удалённом подключении к нему даже если у пользователя несколько мониторов. Неудобство заключалось в том, что на своем мониторе в консоли SCCM нужно было нижнюю
полосу прокрутки тянуть вправо + изображение плохо масштабировалось.
Апгрейд Windows 10
Появился раздел
Windows 10 Servicing, располагающийся в Software Library->Overview. Здесь в виде диаграмм (кольца обслуживания) можно увидеть количество ОС Windows 10 и их версии, а затем настроить скачивание и применение обновлений (апгрейдов). Диаграммы
являются “живыми” – выделенная часть остаётся яркой, а все остальные – тусклыми, то есть присутствует наглядный визуальный эффект.
Чтобы скачивать апгрейды, нужно активировать новую галочку Upgrades во вкладке
Classifications, пройдя в Administration->Overview->Site Configuration->Sites->Configure Sites Components->Software Update Point.
Применение скриптов PowerShell Ещё один новый раздел в меню —
Scripts (Softaware->Overview->Scripts), с помощью которого можно распространять скрипты PowerShell и просмотра результата в реальном времени.
Инвентаризация оборудованияДля инвентаризации оборудования стало возможным настроить длину строк, превышающую 255 символов. Но есть ограничение – такая возможность относится только к новым добавленным классам и к свойствам
инвентаризации оборудования, которые не являются ключевыми.
Для более правильного отображения целых чисел при выполнении инвентаризации оборудования установлено максимальное значение 18 446 744 073 709 551 616 (2^64).
Ранее это значение равнялось 4 294 967 296 (2^32) и могло быть достигнуто при работе с жёсткими дисками, где размер измеряется в байтах. Если значение превышало максимально допустимое, то оно в базе данных не сохранялось.
Последовательность задачК следующей новой функции отнесём возможность в основной последовательности задач создавать дочернюю. С помощью таких связей “родители–потомки” получаются модульные и многоразовые последовательности
задач. Для создания такой связки необходимо в родительской последовательности задач добавить шаг
Run Task Sequence и выбрать другую (дочернюю).
Task Squence обзавёлся поэтапным развёртыванием программного обеспечения. В этом случае сайтом постепенно предоставляется доступ к ПО с учетом всех настроек для каждого этапа, а для клиента устанавливается крайний срок выполнения (установки). У данной функции
имеется собственный интерфейс мониторинга, который расположен в Monitoring->Overview->Deployments. Тут есть одно “НО”: поэтапное развертывание не поддерживает установку с носителя или по сети и мы пока не смогли придумать, в каких случаях можно применить
данное новшество.
Помимо использования скриптов PowerShell из основного меню их можно ещё задействовать и в Task Sequence, добавив в нём шаг
Run PowerShell Script из пункта меню General.
Ещё через последовательность задач можно производить апгрейд операционных систем Windows 7 до Windows 10. При создании Task Sequence теперь нужно выбрать новый пункт
Upgrade an operating system from an upgrade package, а в редакторе Task Sequence появился новый шаг
Upgrade Operating System из пункта меню Images.
АналитикаАналитика управления предоставляет сведения о текущем состоянии среды. Для ее просмотра нужно зайти в
Administration->Overview->Management Insights->All Insights, будут доступны следующие категории:
- Security;
- Software Center;
- Applications;
- Windows 10;
- Simplified Management;
- Collections;
- Cloud Services;
- Proactive Maintenance.
Нажав правой кнопкой мыши на категории, а затем на меню
Show Insights, можно увидеть правила выполнения, процесс, необходимые действия.
Пакеты и приложения
На пользовательском компьютере при надобности установить несколько программ нет необходимости “выстаивать” очередь, а через Software Center можно их ставить одновременно.
Появилась поддержка новых форматов пакета приложения APPX и APPXBUNDLE, MSIX и MSIXBUNDLE (*.appx, *.appxbundle, *. msix,
*.msixbundle).
Роль Distribution Point Distribution Point расширила свой функционал за счёт возможности работать без роли Windows Deployment Services (WDS). В свойствах точки распространения на вкладке
PXE появилась новая галочка Enable a PXE responder without Windows Deployment Service. То есть сейчас в некоторых случаях можно обойтись и без WDS, а использовать ответы от клиентских ОС Windows 7/8/10 на запросы устанавливать систему.
ОтчётыНовинки в отчётах также присутствуют. Появился отчет, отображающий количество клиентов с определенным веб-браузером по умолчанию. Данный отчёт называется
Default Browser Counts, расположен в группе отчетов Software –
Companies and Products.
Отчёт Windows 10 Servicing details for a specific collection выдаёт информацию про системы c ОС Windows 10: ID ресурса, NetBIOS-имя, имя ОС, имя выпуска ОС, сборка, ветвь ОС и состояние обслуживания устройств Windows 10, и находится в разделе
Operation System.
CMPivot
Встроенная в консоль программа CMPivot предоставляется доступ к состоянию устройств в режиме реального времени. Она отправляет запрос сразу на все подключенные устройства в целевой коллекции и возвращает результат.
Для запуска программы нужно зайти в Asset and Compliance->Overview->DeviceCollection, на коллекции устройств нажать правой кнопкой мыши и в контекстном меню выбрать пункт
Start CMPivot.
Например, можно узнать количество дисков в компьютерах из коллекции, написав следующий код:
Disk | summarize dcount( Device ) by Name,
а затем нажимая на значения (они в виде ссылок), можно получить больше информации: на каком компьютере данный диск, какого он объёма и другое, причём код
будет сам изменяться в зависимости от выбора.
УтилитыСерверные и клиентские утилиты Configuration Manager стали входить в состав сервера, они находятся в директории
CD.Latest\SMSSETUP\Tools
и дополнительная их установка не требуется.
Утилита для просмотра log-файлов CMTrace уже автоматически устанавливается вместе с клиентской частью SCCM и
уже не спрашивается, использовать ли её по умолчанию.
Данная утилита располагается в
WinDir%\ccm\.
Утилита CMUpdateReset.exe позволяет удалить зависшее состояние во время установки очередного хотфикса.
SetupDiag
— это автономное средство диагностики, которое помогает узнать причину сбоя при обновлении Windows 10. Данное средство анализирует журналы установки системы. SetupDiag можно запустить на проблемном компьютере или же на другом, экспортировав с проблемного лог-файлы.
Утилита NowMicro’s RightClickTools в этой версии SCCM также работает без проблем, как и в 2012R2.