| Автор | Сообщение |
|---|---|
|
Заголовок сообщения: Что такое IGMP Fast Leave и RTSP ALG?
|
|
|
|
Что такое и для чего нужно IGMP Fast Leave и RTSP ALG? Цитата: Доступна новая версия прошивки (RU_1.55) для устройства DSL-2500U/BRU/D (H/W: D1, D2, D3, D4). Список изменений: Ссылка для загрузки: ftp://ftp.dlink.ru/pub/ADSL/DSL-2500U_B … 062010.zip размер: 1,9 Мб |
| Вернуться наверх | |
|
Alexander Gorelik |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: Что такое IGMP Fast Leave и RTSP ALG?
|
|
|
nickm33 писал(а): Что такое и для чего нужно IGMP Fast Leave и RTSP ALG? Цитата: Доступна новая версия прошивки (RU_1.55) для устройства DSL-2500U/BRU/D (H/W: D1, D2, D3, D4). Список изменений: Ссылка для загрузки: ftp://ftp.dlink.ru/pub/ADSL/DSL-2500U_B … 062010.zip размер: 1,9 Мб
RTSP (TCP/UDP:554) — протокол передачи мультимедийных потоков, обеспечивает удаленное управление потоками аудио/видео данных в сети Интернет. Применяется операторами для предоставления услуги видео по запросу (VoD). IGMP Fast Leave относится к функционалу IGMP Snooping и обеспечивает незамедлительную передачу запросов на отключение клиента от IGMP группы из LAN сети в WAN сеть. Другими словами, сообщения IGMP leave во внешнюю сеть передаются в приоритетном порядке. |
| Вернуться наверх |
|
|
Halk |
Заголовок сообщения:
|
|
|
Эти функции нужно где-то включать или они работают по умолчанию ? _________________ |
| Вернуться наверх |
|
|
Alexander Gorelik |
Заголовок сообщения:
|
|
|
Halk писал(а): Эти функции нужно где-то включать или они работают по умолчанию ? Они работают по умолчанию, включать не нужно. |
| Вернуться наверх |
|
|
Halk |
Заголовок сообщения:
|
|
|
всё понятно. спасибо. _________________ |
| Вернуться наверх |
|
Toggle table of contents sidebar
ALG is a feature that allows several applications to work correctly when they pass through the NAT. When an application client sends a private IP address and port in its message, ALG allocates a public IP address and port and translates them in the message. Simply put, ALG does the same thing with application messages as NAT does with the regular IP header. This translation is necessary so that the application server can send a response to a correct public IP address and port.
NAT supports ALG for FTP, TFTP, PPTP, SIP, RTSP, and DNS.
9.13.1. FTP ALG¶
When using NAT44, the subscriber can use the passive FTP mode to work through the NAT with ALG disabled. Otherwise, if the subscriber uses the active FTP mode, ALG needs to be enabled. In this case, ALG translates the IP address and port in the PORT message.
When using NAT64, ALG must be enabled to allow subscribers to use FTP. In this case, ALG translates the IP address and port in the following messages:
-
EPRT. In addition to address and port translation, the command itself is changed toPORT. -
EPSV. The command is changed toPASV. -
227(response toPASV). The command is changed to229(response toEPSV).
Commands
- <nat|nat64> inspection ftp enable [{control-port (1-65535)|vrf NAME}]¶
-
FTP ALG is disabled by default. This command enables it.
- show <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg ftp¶
-
Display FTP ALG counters information.
Counter
Description
FTP translationsTranslation of internal ip:port to external ip:port and vice
versaFTP packets droppedThe number of FTP packets that were dropped
FTP session entriesThe number of the sessions established at the moment
FTP session creationsThe number of the sessions established over a whole period
of the operation
- clear <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg ftp¶
-
Clear FTP ALG counters.
9.13.2. TFTP ALG¶
TFTP does not send IP addresses in its messages, but it is incompatible with Address-and-Port-Dependent Filtering behavior. If this mode is used, TFTP ALG must be enabled to allow users to use TFTP.
Commands
- <nat|nat64> inspection tftp enable [{control-port (1-65535)|vrf NAME}]¶
-
TFTP ALG is disabled by default. This command enables it.
- show <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg tftp¶
-
Display TFTP ALG counters information.
Counter
Description
TFTP translationsTranslation of internal ip:port to external ip:port and vice
versaTFTP session entriesThe number of the sessions established at the moment
TFTP session creationsThe number of the sessions established over a whole period
of the operation
- clear <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg tftp¶
-
Clear TFTP ALG counters.
9.13.3. PPTP ALG¶
For both NAT44 and NAT64, PPTP ALG must be enabled to allow subscribers to use PPTP. PPTP ALG translates IP address and port in the following messages:
-
Outgoing-Call-Request
-
Outgoing-Call-Reply
-
Call-Clear-Request
-
Call-Disconnect-Notify
-
WAN-Error-Notify
-
Set-Link-Info
Commands
- <nat|nat64> inspection pptp enable [{control-port (1-65535)|vrf NAME}]¶
-
PPTP ALG is disabled by default. This command enables it.
- show <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg pptp¶
-
Display counters for PPTP ALG.
Counter
Description
PPTP translationsTranslation of internal ip:port to external ip:port and vice
versaPPTP packets droppedThe number of PPTP packets that were dropped
PPTP outgoing call
requestsThese requests are PPTP control messages sent by the PNS
(refers to the remote client) to the PAC (refers to the server)
to indicate that an outbound call from the PAC is to be
established. See RFC 2637#section-2.7PPTP call clear requestsControl message indicates that a particular call is to be
disconnected. See RFC 2637#section-2.12 for referencePPTP outgoing call
repliesControl messages from the PAC to the PNS in response to a
received Outgoing-Call-Request message.
See RFC 2637#section-2.8 for referencePPTP call disconnect
notifiesControl message from the PAC to the PNS is issued whenever a
call is disconnected. See RFC 2637#section-2.13 for referencePPTP session entriesThe number of the sessions established at the moment
PPTP session creationsThe number of the sessions established over a whole period
of the operation
- clear <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg pptp¶
-
Clear PPTP ALG counters.
9.13.4. SIP ALG¶
Warning
The vast majority of SIP clients support NAT-traversal techniques described in RFC 6314, so SIP ALG is not necessary for them. Furthermore, you SHOULD NOT enable SIP ALG unless you have a specific reason to do that because SIP ALG may interfere with NAT traversal techniques.
For both NAT44 and NAT64, SIP ALG translates IP address and port in the following messages:
-
REGISTER
-
INVITE
-
UPDATE
-
ACK
-
PRACK
-
BYE
Commands
- <nat|nat64> inspection sip enable [{control-port (1-65535)|vrf NAME}]¶
-
SIP ALG is disabled by default. This command enables it.
- show <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg sip¶
-
Display SIP ALG counters information.
Counter
Description
SIP translationsTranslation of internal ip:port to external ip:port and vice
versaSIP packets droppedThe number of SIP packets that were dropped
SIP session entriesThe number of the sessions established at the moment
SIP session creationsThe number of the sessions established over a whole period
of the operation
- clear <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg sip¶
-
Clear SIP ALG counters.
9.13.5. RTSP ALG¶
Warning
The vast majority of RTSP clients support NAT-traversal techniques described in RFC 7604 and RFC 7825, so RTSP ALG is not necessary for them. Furthermore, you SHOULD NOT enable RTSP ALG unless you have a specific reason to do that because RTSP ALG may interfere with NAT traversal techniques.
For both NAT44 and NAT64, RTSP ALG translates the IP address and port in SETUP messages.
Commands
- <nat|nat64> inspection rtsp enable [{control-port (1-65535)|vrf NAME}]¶
-
RTSP ALG is disabled by default. This command enables it.
- show <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg rtsp¶
-
Display RTSP ALG counters information.
Counter
Description
RTSP translationsTranslation of internal ip:port to external ip:port and vice
versaRTSP packets droppedThe number of RTSP packets that were dropped
RTSP setup messagesThese messages are used to specify the transport mechanism
for the streamed media. See RFC 2326#section-10.4 for
referenceRTSP session entriesThe number of the sessions established at the moment
RTSP session creationsThe number of the sessions established over a whole period
of the operation
- clear <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg rtsp¶
-
Clear RTSP ALG counters.
9.13.6. DNS ALG¶
When using NAT44, DNS ALG is not necessary for the correct work of DNS protocol because it does not use private IP addresses in its messages. However, when you enable DNS ALG, it tracks DNS requests sent by subscribers and immediately deletes the session when the corresponding DNS response is received. This allows to significantly reduce the number of concurrent sessions in the NAT session table.
When using NAT64, DNS ALG is necessary to process DNS requests sent by subscribers through the NAT. It translates AAAA requests into A requests and A responses into AAAA responses.
Warning
The correct network architecture for NAT64 involves using a separate DNS64 network element that processes all DNS requests from subscribers. In this case, no DNS requests pass through the NAT, and DNS ALG is not necessary.
Commands
- <nat|nat64> inspection dns enable [{control-port (1-65535)|vrf NAME}]¶
-
DNS ALG is disabled by default. This command enables it.
- show <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg dns¶
-
Display DNS ALG counters information.
Counter
Description
DNS translationsTranslation of internal ip:port to external ip:port and vice
versaDNS reply packetsDisplay the number of the reply packets
DNS oversized packetsDNS packets consider oversized when the TC flag (1 bit)
is set in the DNS header. This flag is set in the reply packet
if the server could not put all the necessary information in
the packet because of restrictionsDNS amplification
packetsShows how many requests related to DNS amplification were
droppedDNS invalid packetsThis counter will increment when the security appliance
detects an invalid DNS packet. For example, a DNS packet with
no DNS header, the number of DNS resource records not matching
the counter in the header, etc.DNS session entriesThe number of the sessions established at the moment
DNS session creationsThe number of the sessions established over a whole period
of the operation
- clear <nat|nat64> counters [vrf NAME] alg dns¶
-
Clear DNS ALG counters.
9.13.7. Additional Considerations¶
Subscribers behind the NAT may experience issues with their VPN connections when using IPsec. It happens because IPsec uses ESP as an underlying protocol, and its payload is encrypted, so it is not possible to implement an ALG that would translate IP/TCP headers inside the ESP header.
To solve this problem, subscribers should enable NAT-traversal in their IPsec VPN clients. The vast majority of them support this functionality as described in RFC 3715 and RFC 3947.
Chapter 11 NAT Forwarding
Modem router’s NAT (Network Address Translation) feature makes the devices in the LAN use the same public IP address to communicate in the internet, which protects the local network by hiding IP addresses of the devices. However, it also brings about the problem that external host cannot initiatively communicate with the specified device in the local network.
The modem router can use a forwarding feature to remove the isolation of NAT and allow external internet hosts to intuitively communicate with the devices in the local network, thus enabling some special features.
TP-Link modem router includes four forwarding rules. If two or more rules are set, the priority of implementation from high to low is Virtual Servers, Port Triggering, UPNP and DMZ.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•Translate Address and Port by ALG
•Share Local Resources over the Internet by Virtual Server
•Open Ports Dynamically by Port Triggering
•Make Applications Free from Port Restriction by DMZ
•Make Xbox Online Games Run Smoothly by UPnP
1. Translate Address and Port by ALG
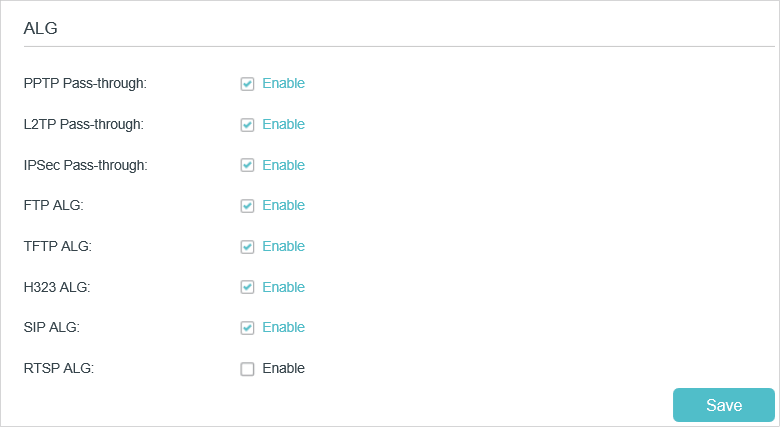
ALG (Application Layer Gateway) allows customized NAT (Network Address Translation) traversal filters to be plugged into the gateway to support address and port translation for certain application layer “control/data” protocols: FTP, TFTP, H323 etc. Enabling ALG is recommended.
Visit http://tplinkmodem.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router. Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > ALG.
•PPTP Pass-through: If enabled, it allows Point-to-Point sessions to be tunneled through an IP network and passed through the router.
•L2TP Pass-through: If enabled, it allows Layer 2 Point-to-Point sessions to be tunneled through an IP network and passed through the router.
•IPSec Pass-through: If enabled, it allows IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) to be tunneled through an IP network and passed through the router. IPSec uses cryptographic security services to ensure private and secure communications over IP networks.
•FTP ALG: If enabled, it allows FTP (File Transfer Protocol) clients and servers to transfer data via NAT.
•TFTP ALG: If enabled, it allows TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) clients and servers to transfer data via NAT.
•H323 ALG: If enabled, it allows Microsoft NetMeeting clients to communicate via NAT.
•SIP ALG: If enabled, it allows clients communicate with SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) servers via NAT.
•RTSP ALG: If enabled, it allows RTSP (Real-Time Stream Protocol) clients and servers to transfer data via NAT.
2. Share Local Resources over the Internet by Virtual Server
When you build up a server in the local network and want to share it on the internet, Virtual Server can realize the service and provide it to the internet users. At the same time virtual server can keep the local network safe as other services are still invisible from the internet.
Virtual server can be used for setting up public services in your local network, such as HTTP, FTP, DNS, POP3/SMTP and Telnet. Different service uses different service port. Port 80 is used in HTTP service, port 21 in FTP service, port 25 in SMTP service and port 110 in POP3 service. Please verify the service port number before the configuration.
I want to:
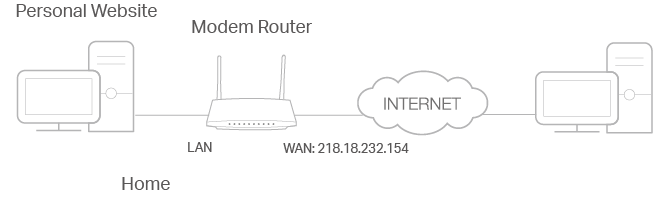
Share my personal website I’ve built in a local network with my friends through the internet.
For example, the personal website has been built on my home PC (192.168.1.100). I hope that my friends can visit my website. The PC is connected to the modem router with the WAN IP address 218.18.232.154.
How can I do that?
1.Assign a static IP address to your PC, for example 192.168.1.100.
2.Visit http://tplinkmodem.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
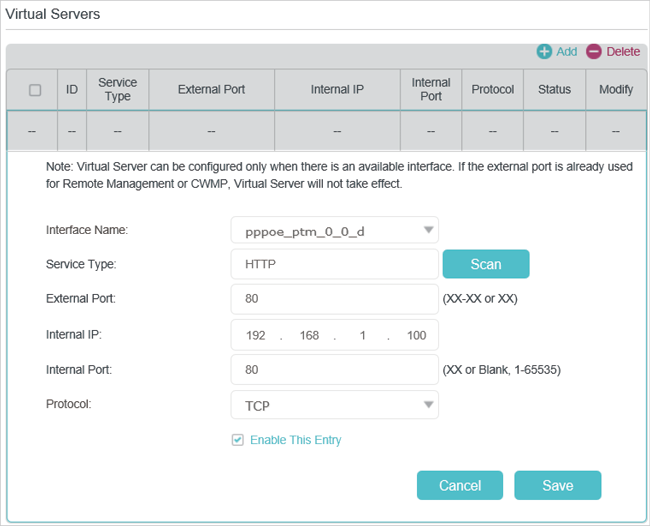
3.Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > Virtual Servers, click Add.
4.Click Scan, and choose HTTP. The external port, internal port and protocol will be automatically filled with contents. Enter the PC’s IP address 192.168.1.100 in the Internal IP field.
5.Click OK to save the settings.
Tips:
1.It is recommended to keep the default settings of Internal Port and Protocol if you are not clear about which port and protocol to use.
2.If the service you want to use is not in the Service Type, you can enter the corresponding parameters manually. You should verify the port number that the service needs.
3.You can add multiple virtual server rules if you want to provide several services from a modem router. Please note that the External Port cannot be overlapped.
Done!
Internet users can enter http://WAN IP (in this example: http://218.18.232.154) to visit your personal website.
Tips:
1.For a WAN IP that is assigned dynamically by ISP, it is recommended to apply and register a domain name for the WAN by DDNS, go to Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account for more information. Then you can use http://domain name to visit the website.
2.If you have changed the default External Port, you should use http://WAN IP: External Port or http://domain name: External Port to visit the website.
3. Open Ports Dynamically by Port Triggering
Port triggering can specify a triggering port and its corresponding external ports. When a host in the local network initiates a connection to the triggering port, all the external ports will be opened for subsequent connections. The modem router can record the IP address of the host. When the data from the internet returns to the external ports, the modem router can forward them to the corresponding host. Port triggering is mainly applied to online games, VoIPs and video players. Common applications include MSN Gaming Zone, Dialpad, Quick Time 4 players, and so on.
Follow the steps below to configure the port triggering rules:
1.Visit http://tplinkmodem.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
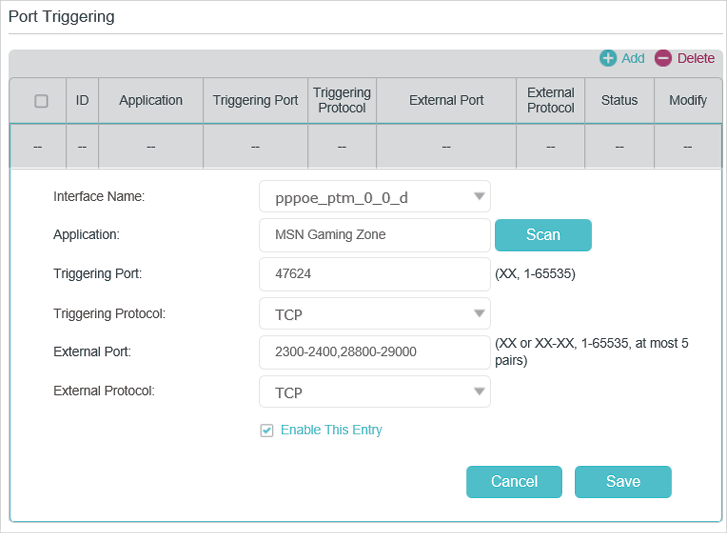
2.Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > Port Triggering and click Add.
3.Click Scan, and select the desired application. The triggering port and protocol, the external port and protocol will be automatically filled with contents. Here we take MSN Gaming Zone as an example.
4.Click OK to save the settings.
Tips:
1.You can add multiple port triggering rules according to your network need.
2.If the application you need is not listed in the Existing Applications list, please enter the parameters manually. You should verify the external ports the application uses first and enter them into External Port field according to the format the page displays.
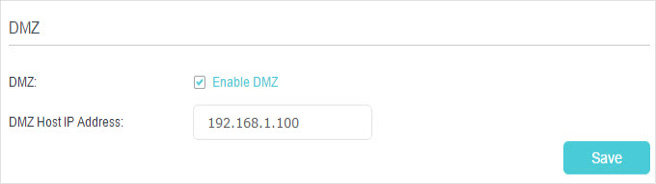
4. Make Applications Free from Port Restriction by DMZ
When a PC is set to be a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) host in the local network, it is totally exposed to the internet, which can realize the unlimited bidirectional communication between internal hosts and external hosts. The DMZ host becomes a virtual server with all ports opened. When you are not clear about which ports to open in some special applications, like IP camera and database software, you can set the PC to be a DMZ host.
Note:
DMZ is most applicable when you don’t know which ports to open. When it is enabled, the DMZ host is totally exposed to the internet, which may bring some potential safety hazard. If DMZ is not in use, please disable it in time.
I want to:
Make the home PC join the internet online game without port restriction.
For example, Due to some port restriction, when playing the online games, you can login normally but cannot join a team with other players. To solve this problem, set your PC as a DMZ with all ports opened.
How can I do that?
1.Assign a static IP address to your PC, for example 192.168.1.100.
2.Visit http://tplinkmodem.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
3.Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > DMZ and select the checkbox to enable DMZ.
4.Enter the IP address 192.168.1.100 in the DMZ Host IP Address filed.
5.Click Save to save the settings.
Done!
The configuration is completed. You’ve set your PC to a DMZ host and now you can make a team to game with other players.
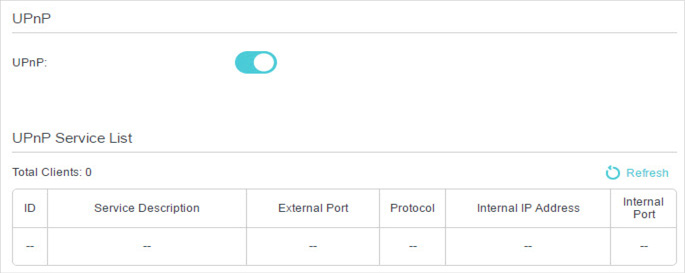
5. Make Xbox Online Games Run Smoothly by UPnP
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) protocol allows the applications or host devices to automatically find the front-end NAT device and send request to it to open the corresponding ports. With UPnP enabled, the applications or host devices in the both sides of NAT device can freely communicate with each other realizing the seamless connection of the network. You may need to enable the UPnP if you want to use applications such as multiplayer gaming, peer-to-peer connections, real-time communication (for example, VoIP or telephone conference), or remote assistance.
Tips:
1.UPnP is enabled by default in this modem router.
2.Only the application supporting UPnP protocol can use this feature.
3.UPnP feature needs the support of operating system (e.g. Windows Vista/ Windows 7/ Windows 8, etc. Some of operating system need to install the UPnP components).
For example, when you connect your Xbox to the modem router which has connected to the internet to play online games, UPnP will send request to the modem router to open the corresponding ports allowing the following data penetrating the NAT to transmit. Therefore, you can play Xbox online games without a hitch.
If necessary, you can follow the steps to change the status of UPnP.
1.Visit http://tplinkmodem.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > UPnP and toggle on or off according to your needs.
Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is an application-level protocol for the transfer of real-time media data. Used for establishing and controlling media sessions between end points, RTSP is a control channel protocol between the media client and the media server. The typical communication is between a client and a streaming media server.
Streaming media from a private network to a public network requires translating IP addresses and port numbers over the network. NetScaler functionality includes an Application Layer Gateway (ALG) for RTSP, which can be used with Large Scale NAT (LSN) to parse the media stream and make any necessary changes to ensure that the protocol continues to work over the network.
How IP address translation is performed depends on the type and direction of the message, and the type of media supported by the client-server deployment. Messages are translated as follows:
- Outbound request—Private IP address to NetScaler owned public IP address called an LSN pool IP address.
- Inbound response—LSN pool IP address to private IP address.
- Inbound request—No translation.
- Outbound response—Private IP address to LSN pool IP address.
Note
RTSP ALG is supported in a NetScaler standalone appliance, in a NetScaler high availability setup, as well as in a NetScaler cluster setup.
Limitations of RTSP ALG
The RTSP ALG does not support the following:
- Multicast RTSP sessions
- RTSP session over UDP
- TD/admin partitioning
- RSTP Authentication
- HTTP tunneling
RTSP and LSN scenario
Typically, a RTSP SETUP request specifies how a single media stream must be transported. The request contains the media stream URL and a transport specifier. This specifier typically includes one local port for receiving RTP data (audio or video), and another for receiving RTCP data (meta information). The server reply usually confirms the chosen parameters and fills in the missing parts, such as the server’s chosen ports. Each media stream must be configured by using the SETUP command before an aggregate play request can be sent.
In a typical RTSP communication, the media client in the public network sends a SETUP request to the media server in the private network. RSTP ALG intercepts the request and, in the media stream, replaces the public IP address and port number with the LSN pool IP address and LSN port number.
The media server in the private network uses the LSN pool IP address and LSN port number to send a 200 OK response to the media client in the public network. The NetScaler RTSP ALG intercepts the response and replaces the LSN pool IP address and LSN port number with the public IP address and port number of the media client.
Configuring RTSP ALG
Configure RTSP ALG as part of the LSN configuration. For instructions on configuring LSN, see Configuration Steps for LSN. While configuring LSN, make sure that you:
- Set the NAT Type as DETERMINSTIC or DYNAMIC while adding the LSN pool.
- Set the following parameters while adding the LSN application profile:
- IP Pooling = PAIRED
- Address and Port Mapping = ENDPOINT-INDEPENDENT
- Filtering = ENDPOINT-INDEPENDENT
- Create a RTSP ALG profile and bind the RTSP ALG profile to the LSN group
Sample RTSP ALG Configuration:
The following sample configuration shows how to create a simple LSN configuration with a single subscriber network, single LSN NAT IP address, and RTSP ALG settings:
enable ns feature WL SP LB CS LSN
Done
add lsn pool pool1 -nattype DETERMINISTIC
Done
bind lsn pool pool1 10.102.218.246
Done
add lsn client client1
Done
bind lsn client client1 -network 200.200.200.11 -netmask 255.255.255.0
Done
add lsn appsprofile app1 TCP -ippooling PAIRED -mapping ENDPOINT-INDEPENDENT -filtering ENDPOINT-INDEPENDENT
Done
add lsn appsprofile app2 UDP -ippooling PAIRED -mapping ENDPOINT-INDEPENDENT -filtering ENDPOINT-INDEPENDENT
Done
bind lsn appsprofile app1 1-65535
Done
bind lsn appsprofile app2 1-65535
Done
add lsn rtspalgprofile rtspalgprofiledefault -rtspIdleTimeout 1000 -rtspportrange 554
Done
add lsn group group1 -clientname client1 -nattype DETERMINISTIC -portblocksize 512 -rtspalg ENABLED
Done
bind lsn group group1 -poolname pool1
Done
bind lsn group group1 -appsprofilename app1
Done
bind lsn group group1 -appsprofilename app2
Done
bind lsn group group1 -rtspalgprofilename rtspalgprofiledefault
Done
<!--NeedCopy-->
TL-WR940N/TL-WR941ND
Беспроводной маршрутизатор серии N со
скоростью передачи данных до 300 Мбит/с
Руководство пользователя
— 63 —
VPN — Функция Пропуск трафика VPN должна быть включена, если вы хотите
разрешить создание VPN-туннелей согласно протоколам IPSec, PPTP или L2TP для
прохождения межсетевого экрана маршрутизатора.
Пропуск трафика PPTP — Технология Пропуск трафика PPTP (Туннельный
протокол типа точка-точка) позволяет создавать специальные туннели в IP-сети.
Чтобы разрешить создание таких туннелей, выберите
Включить.
Пропуск трафика L2TP — Протокол L2TP — это метод создания сессий точка-точка
через Интернет на уровне второго слоя. Чтобы разрешить прохождение
L2TP-туннелей через маршрутизатор, выберите
Включить.
Пропуск трафика IPSec — Протокол IPSec — это набор протоколов для обеспечения
защиты данных, передаваемых по сетям на базе протокола IP, посредством
применения алгоритмов шифрования. Чтобы разрешить прохождение
IPSec-туннелей черезмаршрутизатор, выберите
Включить.
ALG — Рекомендуется включить шлюз уровня приложения (ALG), т.к. эта функция
разрешает установку настраиваемых обходных NAT-фильтров в шлюзе с целью
поддержки преобразования адресов и портов для некоторых протоколов уровня
приложения типа «контроль/данные», как например FTP, TFTP, H323 и т.д.
FTP ALG — Чтобы разрешить FTP-клиентам и серверам передавать данные через
NAT, выберите
Включить.
TFTP ALG — Чтобы разрешить TFTP-клиентам и серверам передавать данные
через NAT, выберите
Включить.
H323 ALG — Чтобы разрешить клиентам Microsoft NetMeeting обмениваться
данными через NAT, выберите
Включить.
RTSP ALG — Чтобы позволить клиентам медиа-плеера связываться с некоторыми
серверами потоковых медиа-данных через NAT, нажмите
Включить.
Нажмите кнопку
Сохранить, чтобы сохранить настройки.
4.9.2 Расширенные настройки защиты
Выбрав
Безопасность – Расширенные настройки защиты, вы сможете защитить
маршрутизатор от таких атак, как TCP-SYN Flood, UDP Flood и ICMP-Flood, как показано на
Рис. 4-41.