In this article, we will install and configure DFS (Distributed File System) Replication group in Windows Server 2019. We will configure DFS replication for the existing namespace which we have created in last article.
Check out the previous post on How to Install and Configure DFS Namespace in Windows Server 2019.
Overview:
DFS Replication is a role service in Windows Server 2019 that you to replicate folders between multiple servers.
DFS Replication uses a compression algorithm known as remote differential compression (RDC). RDC detects the changes to the data and enables DFS Replication to replicate only the changed file blocks instead of the entire file.
Virtual Lab Setup:
- WS2K19-DC01: Active Directory Domain Controller with DNS role.
- WS2K19-SRV02: DFS Namespace Server for mylab.local domain.
- WS2K19-SRV01: Member Server for mylab.local domain.
Install the DFS Replication role:
1. Log in to the WS2K19-SRV01 server and open the Server Manager console.
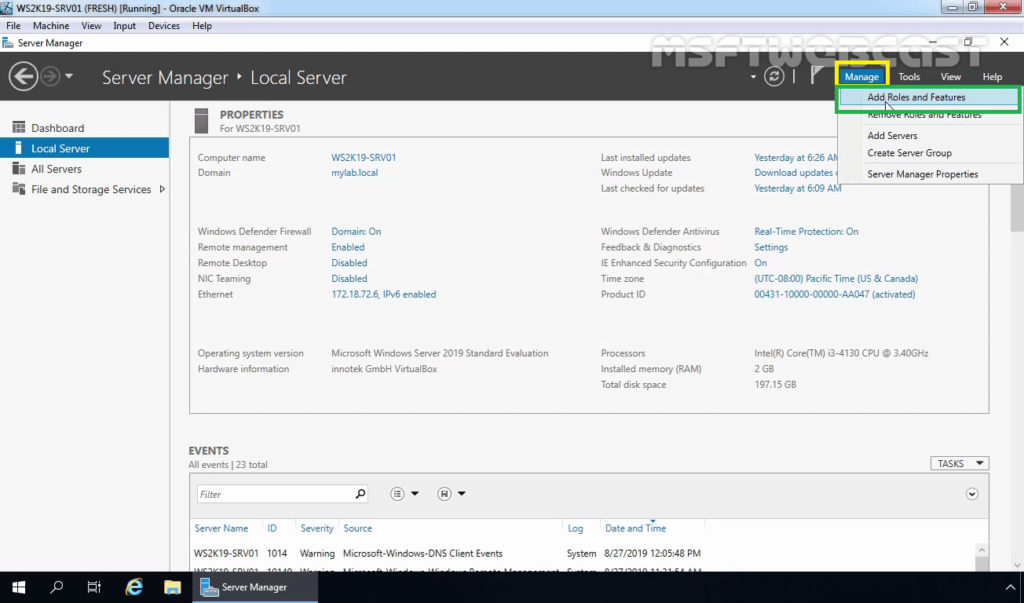
2. Click on Manage and select Add roles and features.
3. Click on Next on Before you begin console.
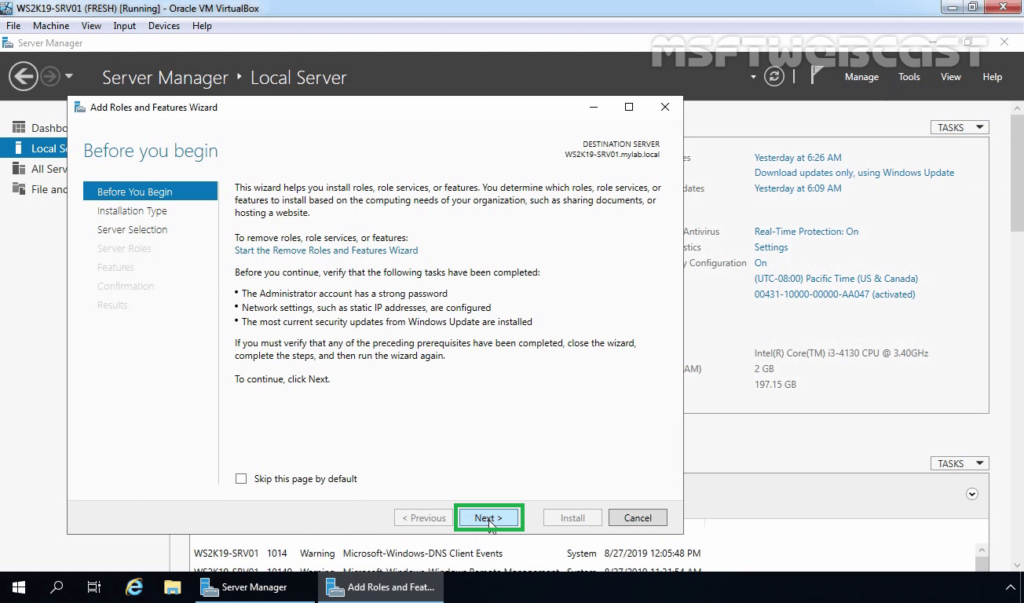
4. Choose Role-based or Feature-based installation and click Next.
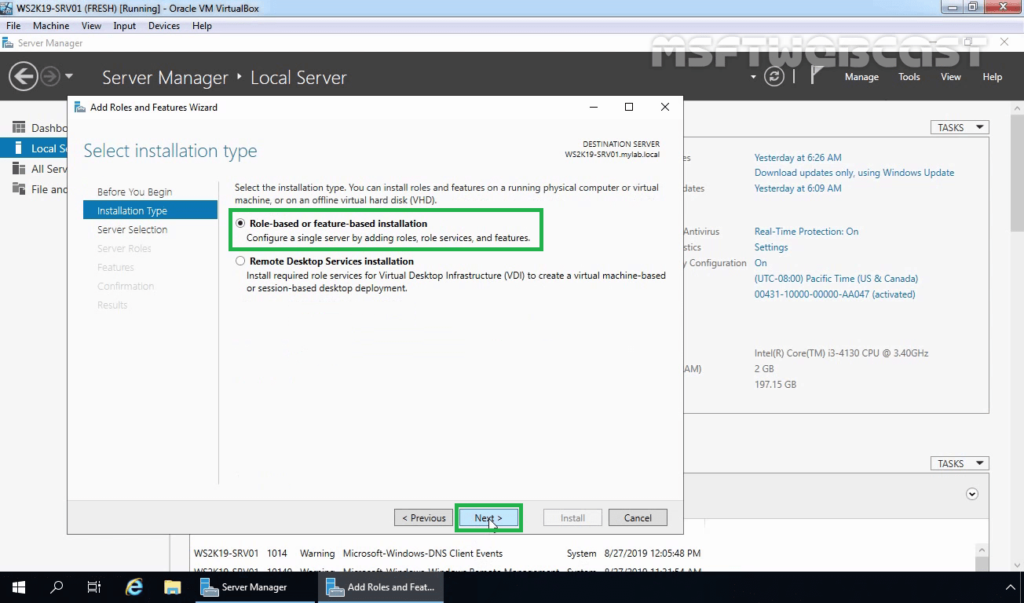
5. Select your server on which you want to install the DFS replication server role. Click on Next.
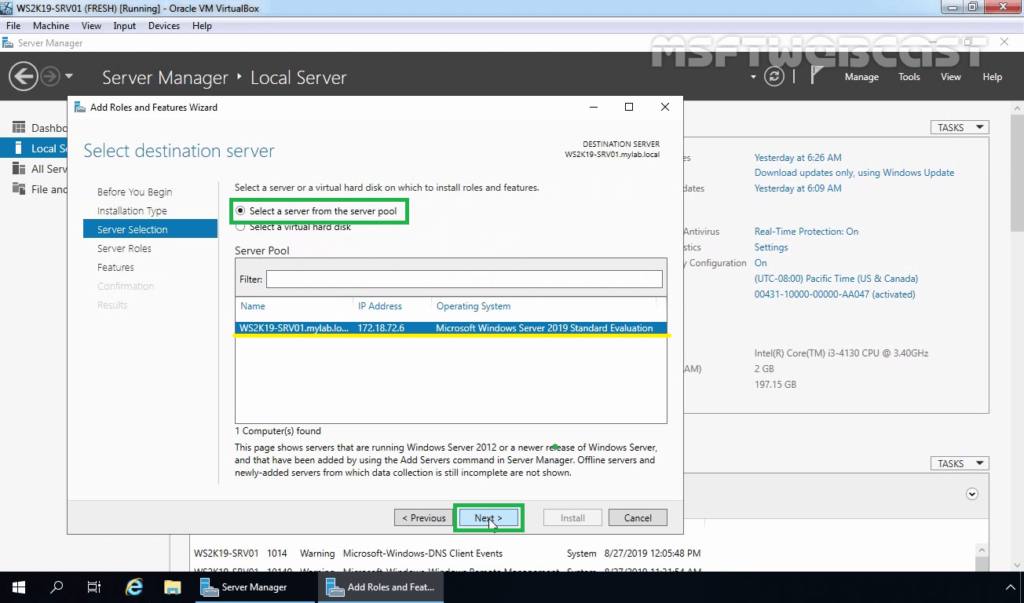
6. On select server role console, expand the File and Storage Services, expand File and iSCSI Services and select DFS Replication from the list.
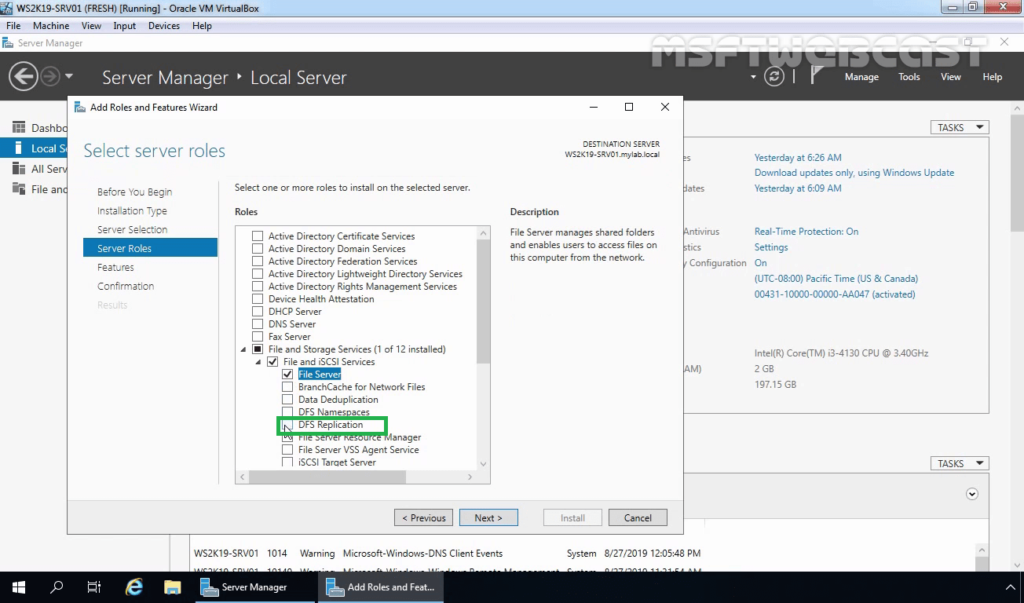
7. Click on Add Features when prompted to install the Management tools.
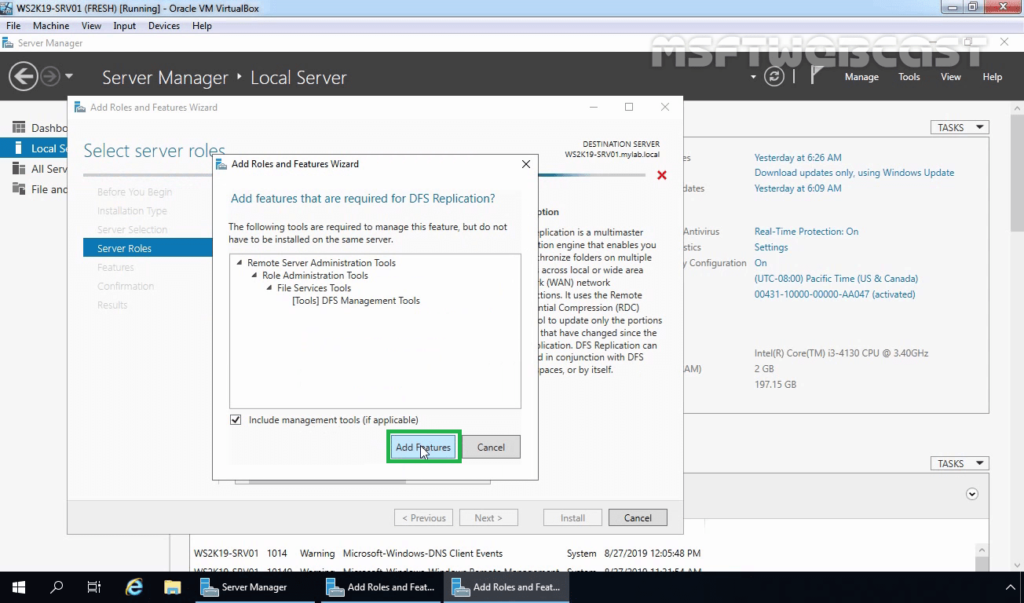
8. Click on Next.
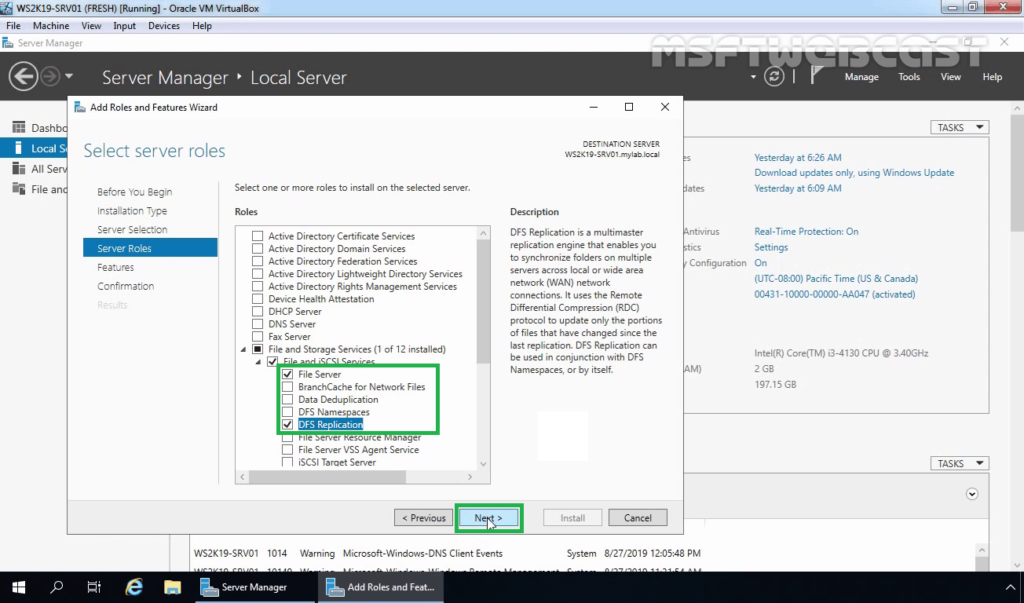
9. On Select features console, click on Next to continue.
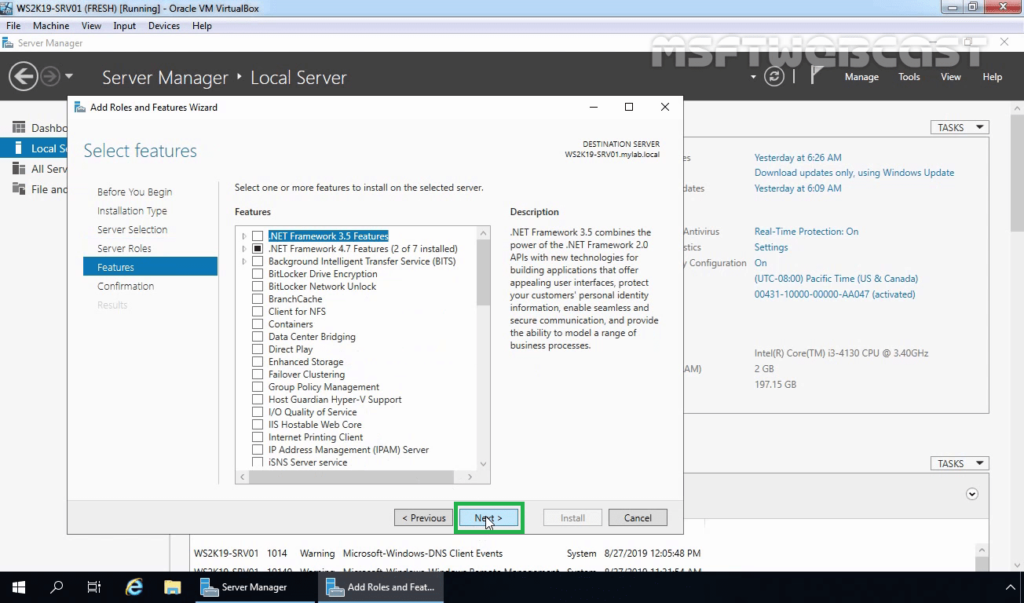
10. Click on Install and wait for the installation process to complete.
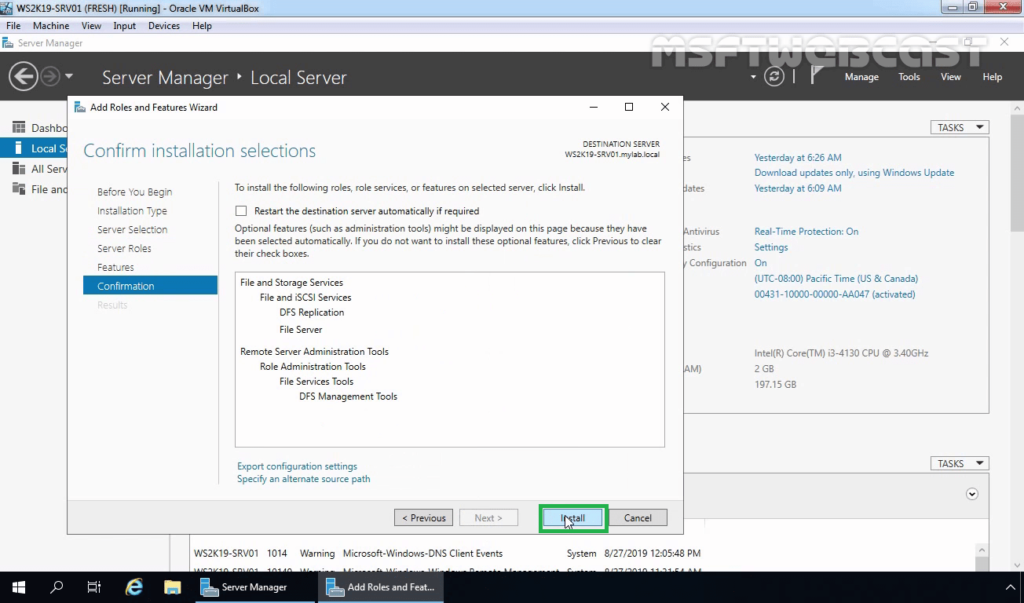
Note: We need to perform the same steps to install the DFS replication role on WS2K19-SRV02.
In the previous post, we have created DFS namespace and added one DFS folder with a target path on the WS2K19-SRV02 server.
- DFS Namespace Path: \\mylab.local\store
- DFS Folder Path: \\mylab.local\store\TestData
- Original Shared Folder Path: \\WS2K19-SRV02\TestUsersData
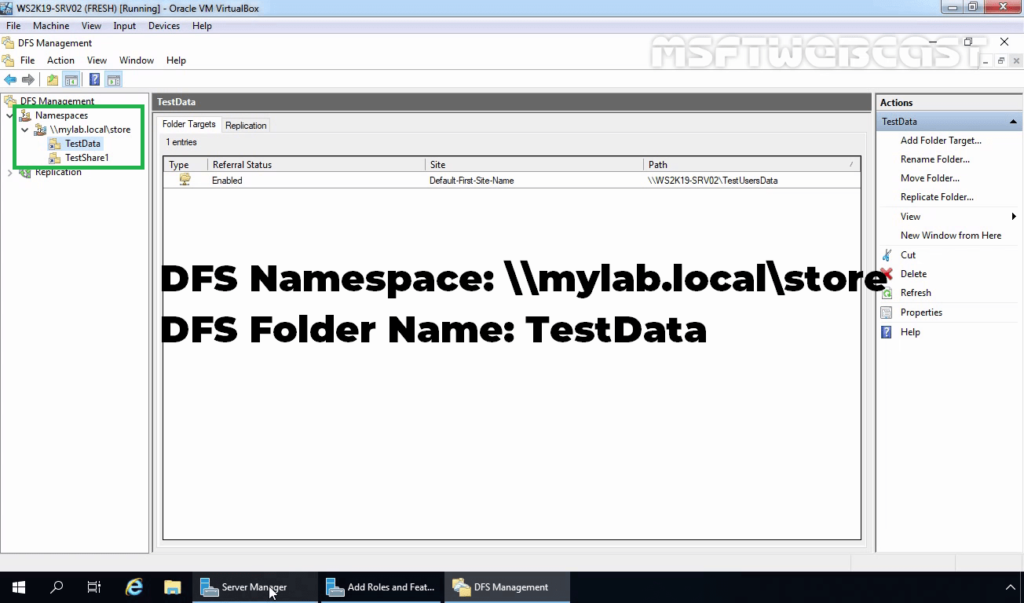
We will enable DFS replication for the TestData DFS folder.
Configure DFS Replication:
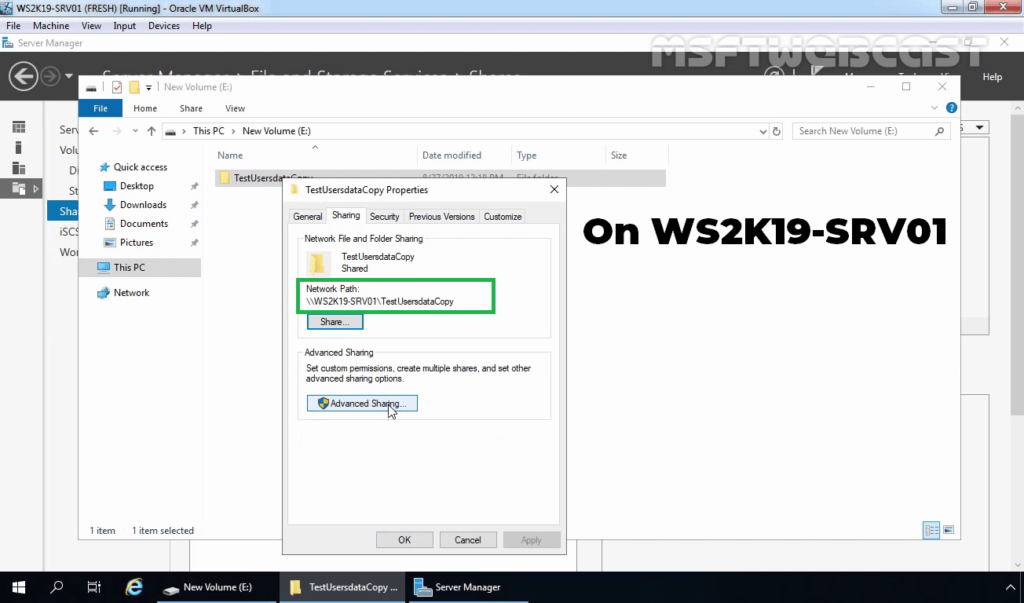
Before configuring replication, you need to add a network shared folder on the second DFS server.
On the WS2K19-SRV01 server, create a new shared folder with default NTFS permission on E:\ drive named TestUsersDatacopy.
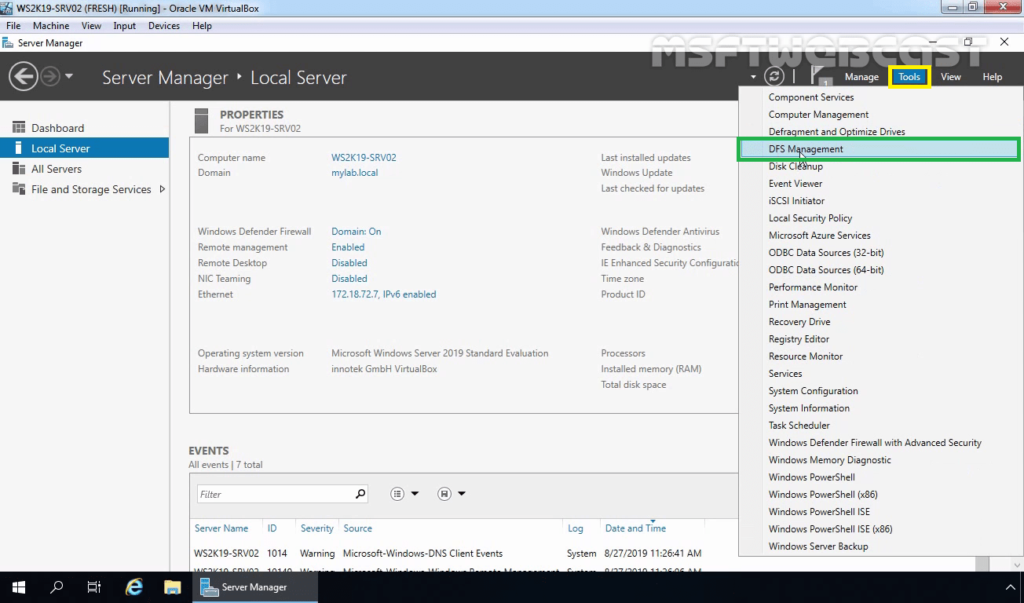
11. From the Server Manager console, select DFS Management from the Tools menu.
12. In DFS Management console right-click on DFS folder (In our case, it will be TestData) and select Add Folder Target.
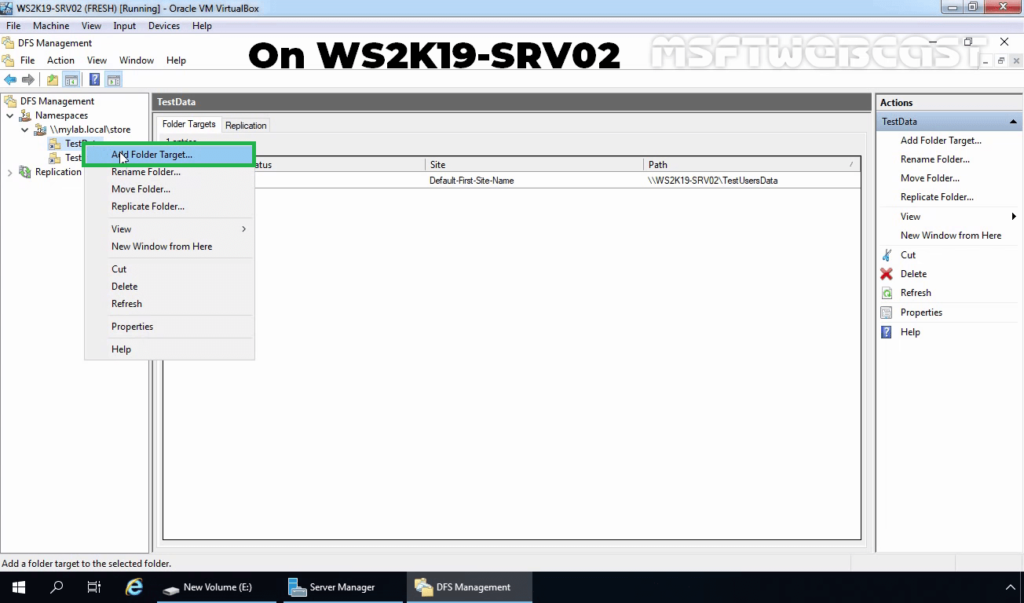
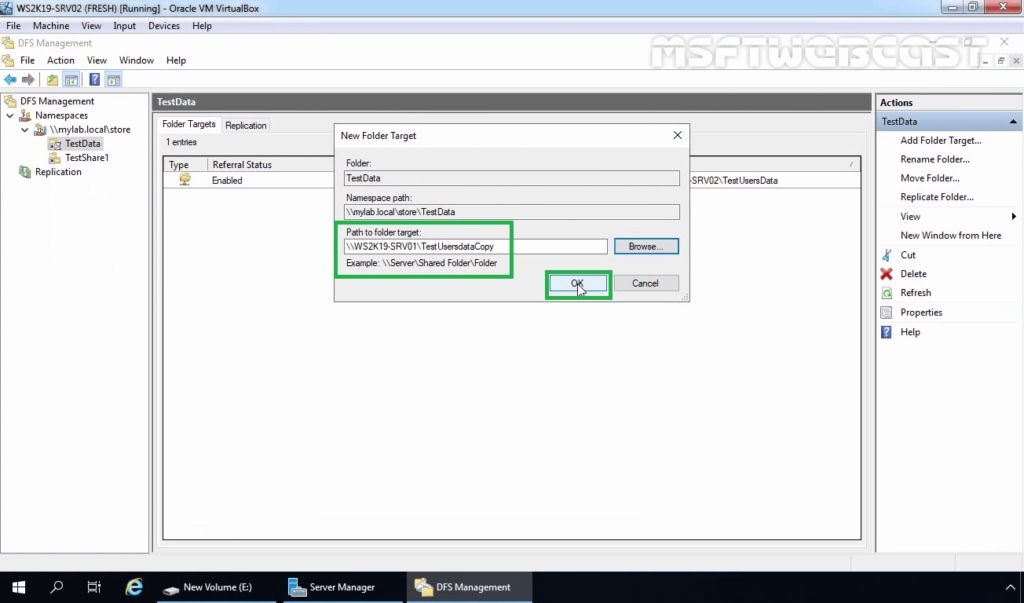
13. Enter the name of the shared folder and click OK. In our example, the shared folder path will be \\WS2K19-SRV01\TestUsersDataCopy.
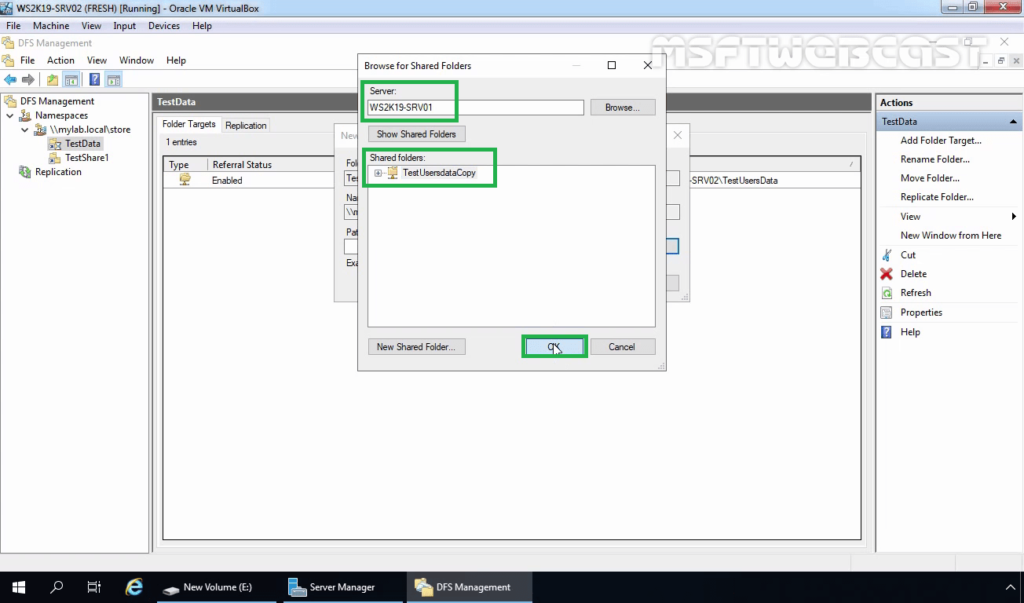
14. Click on OK.
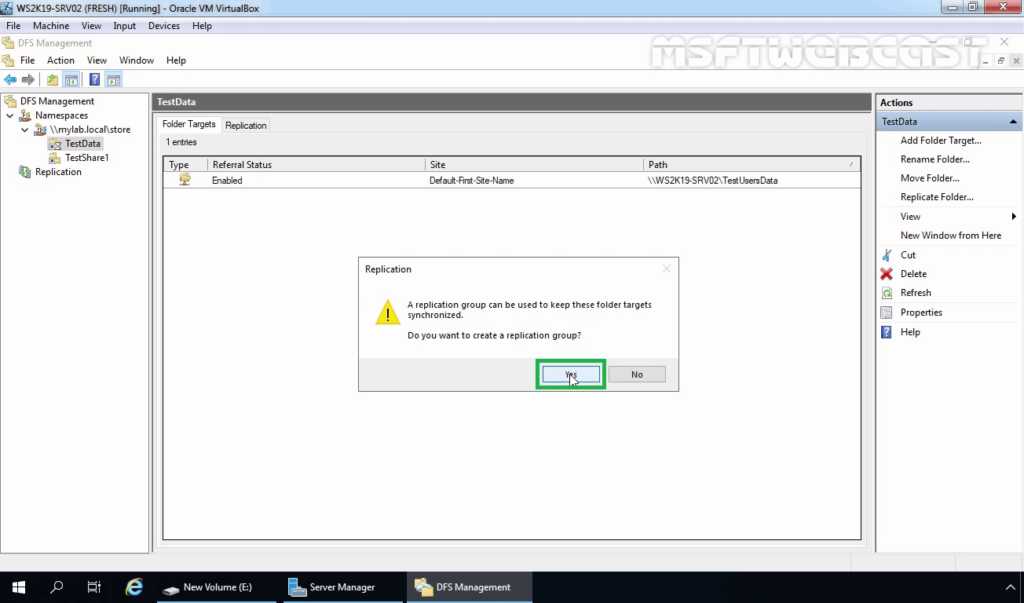
15. For configuring replication, click Yes on the Replication page.
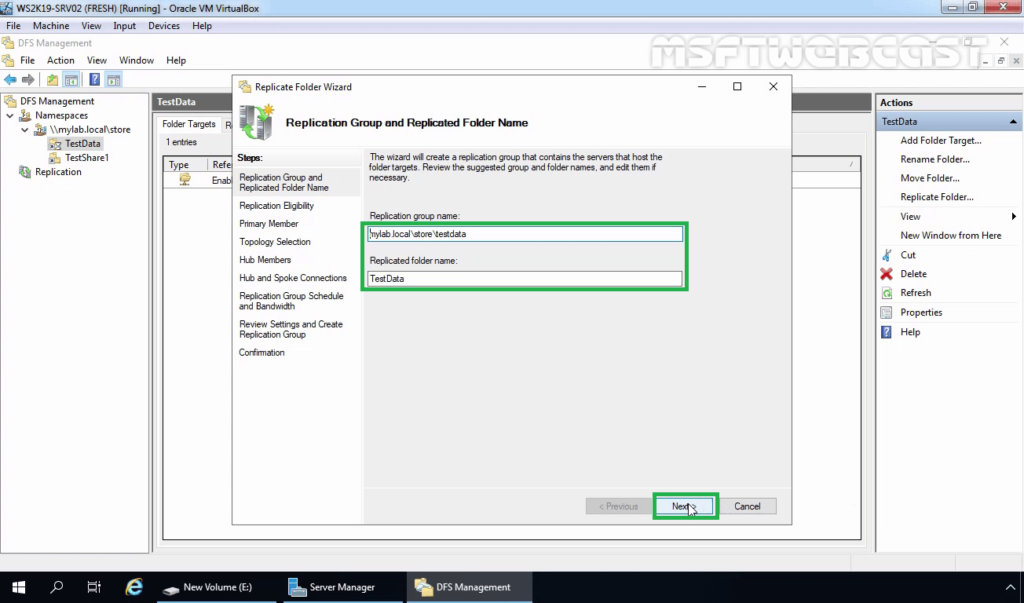
16. In the DFS Replication Configuration Wizard, verify the name of the replication group and the folder which we want to replicate. Click on Next.
17. Verify the shared folder paths on both servers. Click on Next.
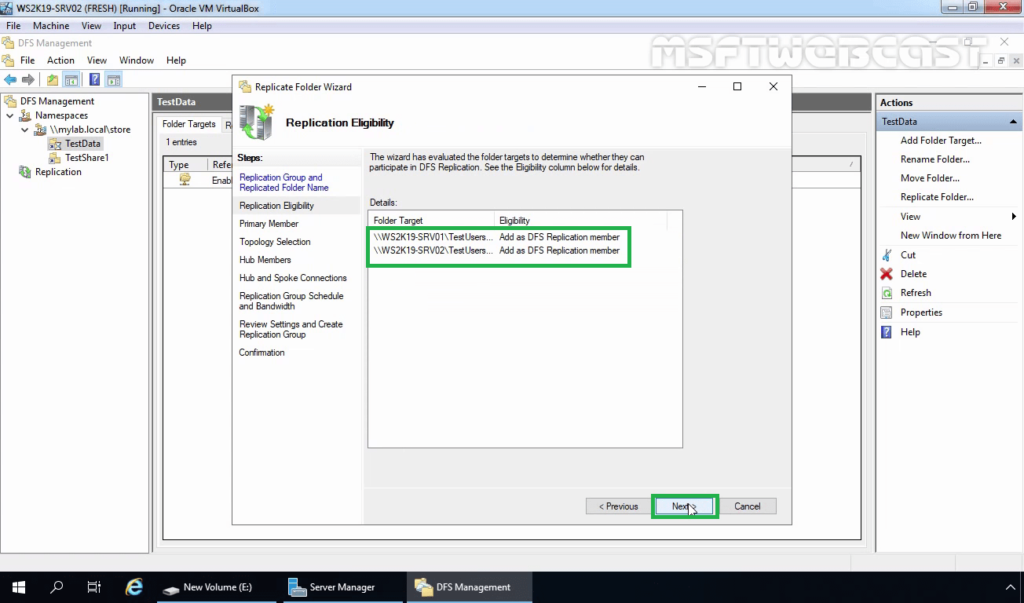
18. Select the primary server on which we have stored the data initially. Click on Next.
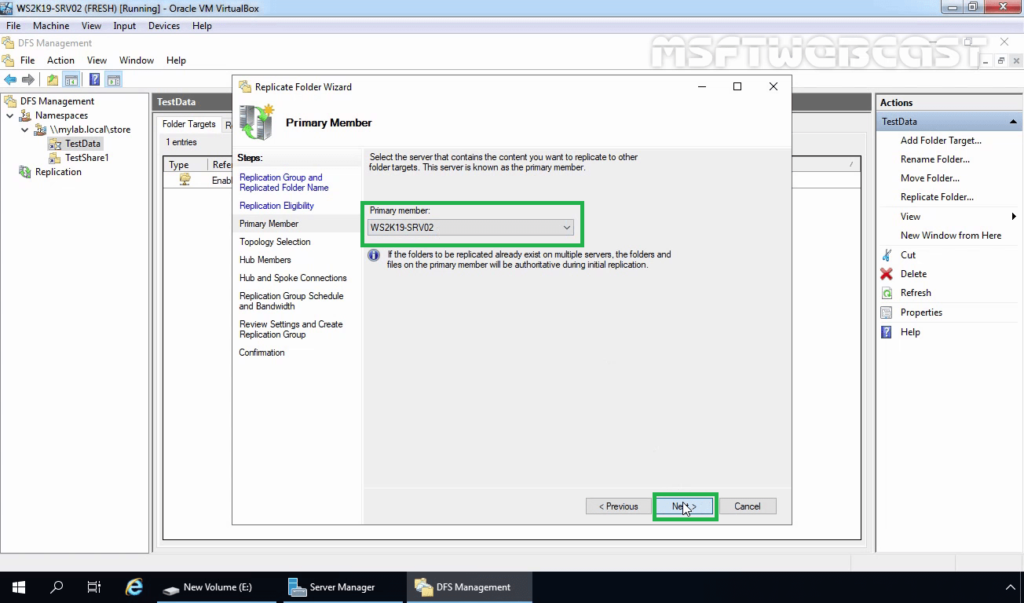
19. On the Topology Selection console, select the Full Mesh topology and click Next.
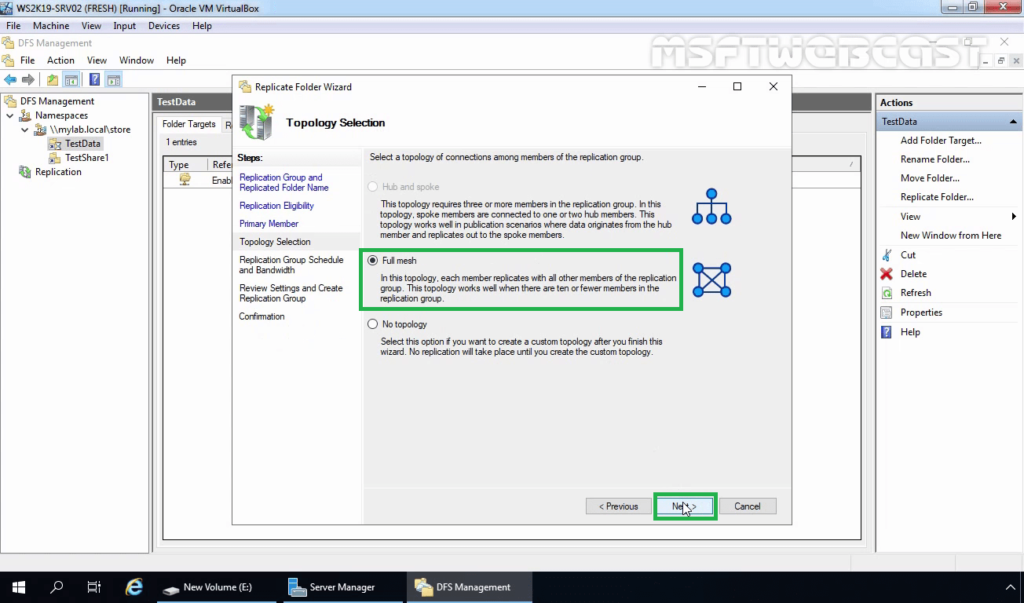
20. With DFS Replication, you can choose the replication schedule and the bandwidth you want to allocate to the DFS replication process. Leave the default setting and then click Next.
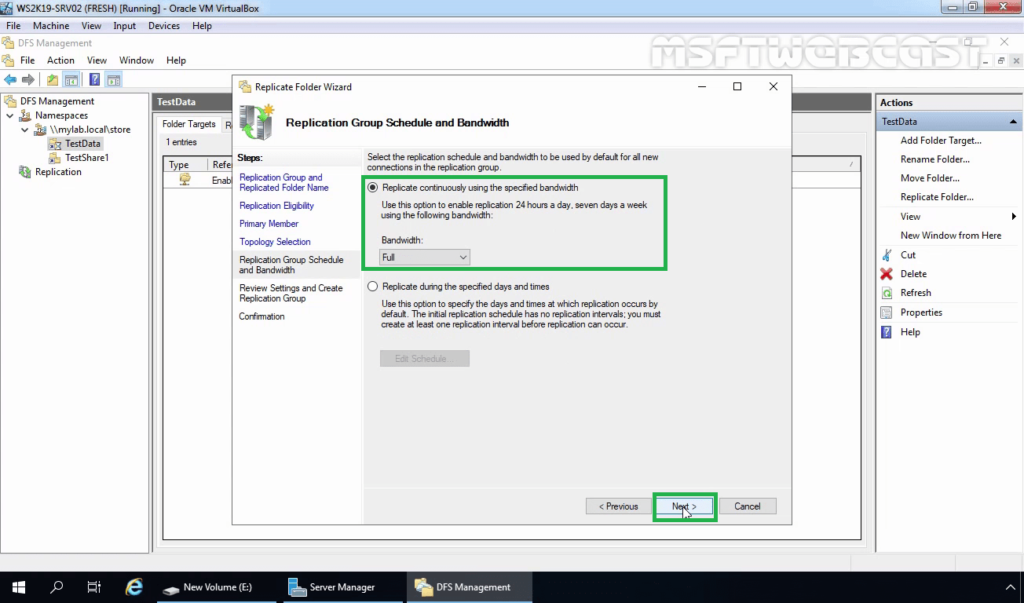
21. Review the settings and then click on Create.
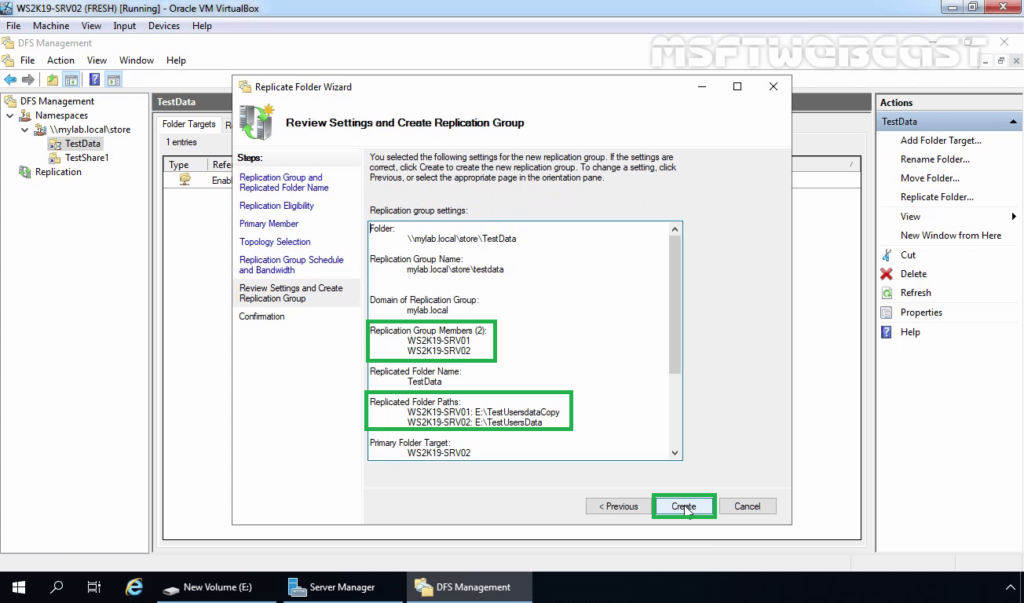
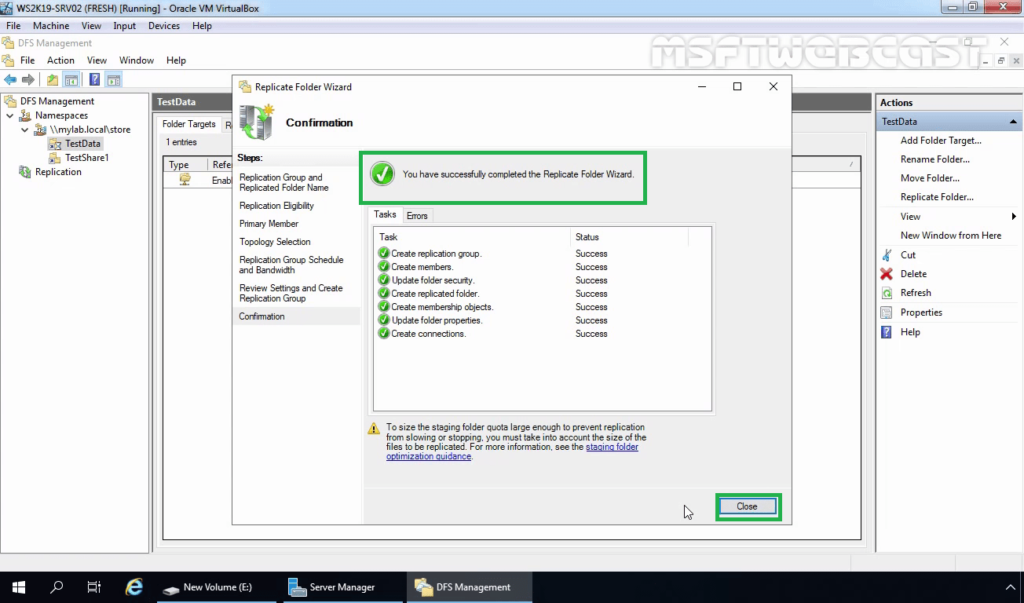
22. On the Confirmation page, click on Close to close the wizard.
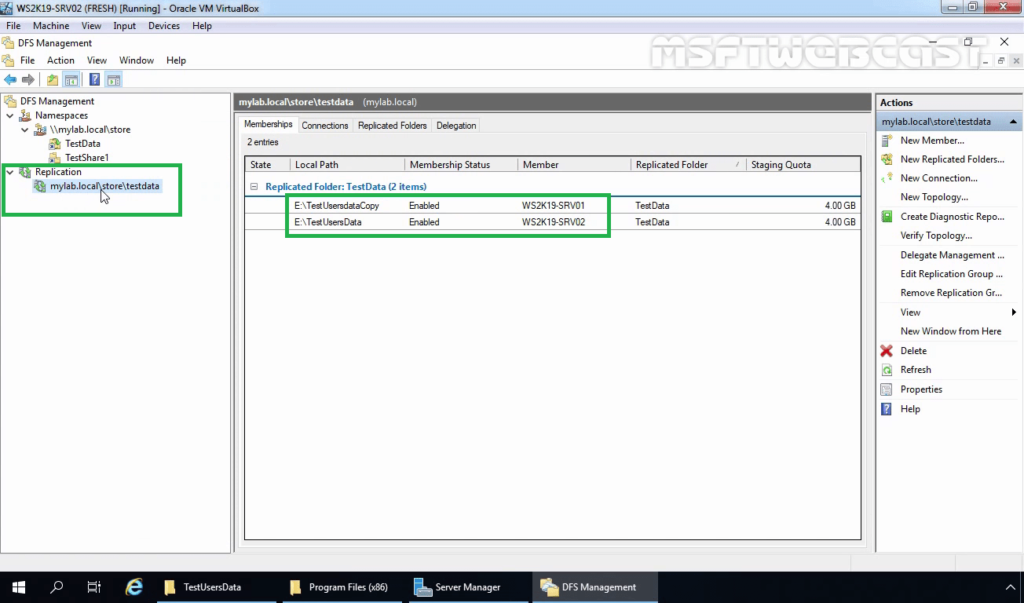
23. Here, we can verify that our new replication group is created.
Test DFS Replication:
24. To test the replication between both servers, copy some data on the primary server (WS2K19-SRV02) and see the data should be on the secondary server (WS2K19-SRV01) as well.
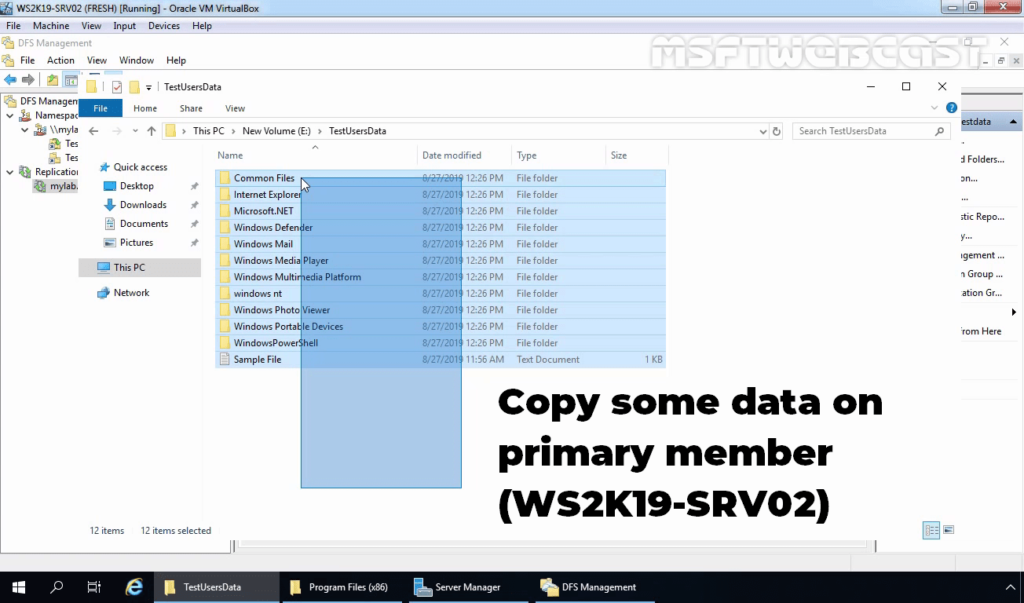
25. Verify the data on Secondary Server (WS2K19-SRV01).
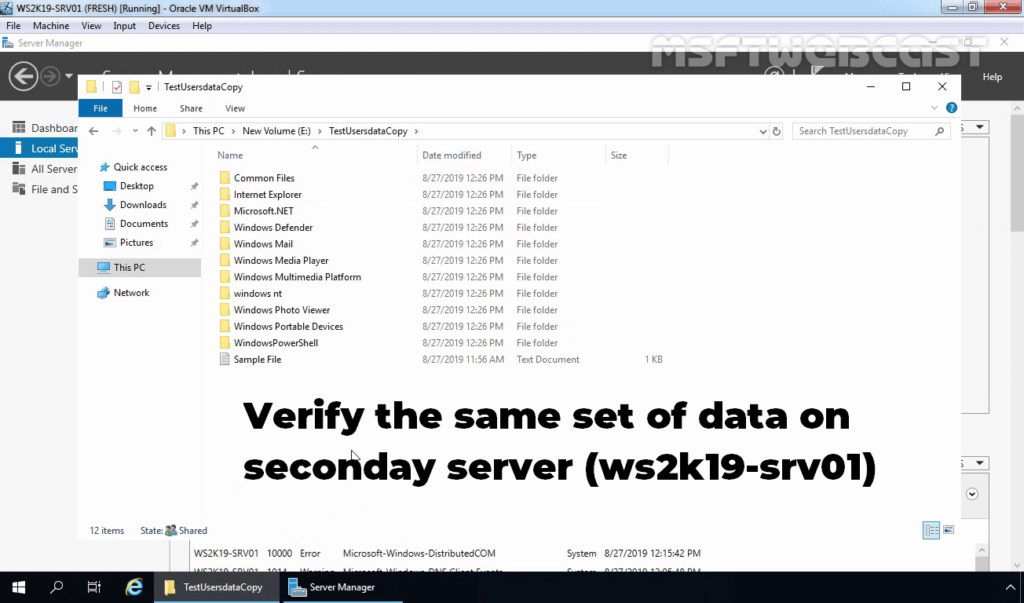
I hope this article will be helpful for you all. Thank you for reading.
Post Views: 4,414
File shares are used in organizations to allow users to access and exchange files. If the number of file shares is large, it may be difficult to manage them because mapping many shared resources to each user’s computer takes time and effort. If the configuration of one file share changes, you need to update shared drive mappings for all users using this share. In this case, DFS can help you optimize the hierarchy of shared folders to streamline administration and the use of shared resources.
This blog post explains DFS configuration and how to set up DFS replication in Windows Server 2019.
What Is DFS and How It Works
A Distributed File System (DFS) is a logical organization that transparently groups existing file shares on multiple servers into a structured hierarchy. This hierarchy can be accessed using a single share on a DFS server.
A DFS file share can be replicated across multiple file servers in different locations to optimize server load and increase access speed to shared files. In this case, a user can access a file share on a server that is closest to them. DFS is intended to simplify access to shared files.
DFS uses the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, which is also known as the Common Internet File System (CIFS). Microsoft’s implementation of DFS doesn’t work with other file sharing protocols like NFS or HDFS. However, you can connect multiple SMB shares configured on NAS devices and Linux machines using Samba to your DFS server running on Windows Server. DFS consists of server and client components.
You can configure one DFS share that includes multiple file shares and connect users to this single file share using a unified namespace. When users connect to this file share using a single path, they see a tree structure of shared folders (as they are subfolders of the main share) and can access all needed file shares transparently. Underlying physical file servers hosting file shares are abstracted from the namespace used to access shares. DFS namespaces and DFS replication are the two main components used for DFS functioning.
What is a DFS namespace?
A DFS namespace is a virtual folder that contains links to shared folders stored on different file servers. DFS namespaces can be organized in different ways depending on business needs. They can be organized by geographical location, organization units, a combination of multiple parameters, etc. You can configure multiple namespaces on a DFS server. A DFS namespace can be standalone or domain-based.
- A standalone DFS namespace stores configuration information and metadata locally on a root server in the system registry. A path to access the root namespace is started with the root server name. A standalone DFS namespace is located only on one server and is not fault-tolerant. If a root server is unavailable, the entire DFS namespace is unavailable. You can use this option if you don’t have an Active Directory domain configured (when using a Workgroup).
- A domain-based DFS namespace stores configuration in Active Directory. A path to access a root namespace starts with the domain name. You can store a domain-based DFS namespace on multiple servers to increase the namespace availability. This approach allows you to provide fault tolerance and load balancing across servers. Using domain-based DFS namespaces is recommended.
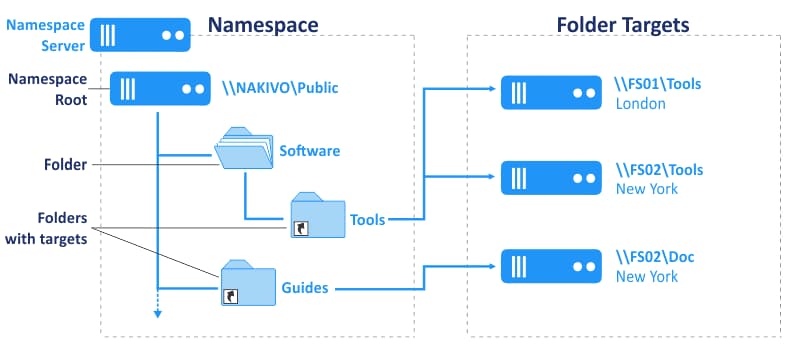
A namespace consists of the root, links (folders), and folder targets.
- A namespace root is a starting point of a DFS namespace tree. Depending on the type, a namespace can look like this:
\\ServerName\RootName (a standalone namespace)
\\DomainName\RootName (a domain-based namespace)
- A namespace server is a physical server (or a VM) that hosts a DFS namespace. A namespace server can be a regular server with the DFS role installed or a domain controller.
- A folder is a link in a DFS namespace that points to a target folder containing content for user access. There are also folders without targets used for organizing the structure.
- A folder target is a link to a shared file resource located on a particular file server and available via the UNC path (Universal Naming Convention). A folder target is associated with the folder in a DFS namespace, for example, \\FS2\TestShare on the FS2 server. A folder target is what users need to access files.
One folder target can be a link to a single folder or multiple folders (if these folders are located on two different servers and are synchronized/replicated with each other). For example, a user needs to access \\DFS-server01\TestShare\Doc but depending on the user’s location, the user is redirected to a shared folder \\FS01\Doc or \\FS02\Doc.
The DFS tree structure includes the following components:
- DFS root, which is a DFS server on which the DFS service is running
- DFS links, which are links pointing to network shares used in DFS
- DFS targets, which are real network shares to which DFS links point
What is DFS replication?
DFS replication is a feature used to duplicate existing data by replicating copies of that data to multiple locations. Physical file shares can be synchronized with each other at two or more locations.
An important feature of DFS replication is that the replication of a file starts only after that file has been closed. For this reason, DFS replication is not suitable for replicating databases, given that databases have files opened during the operation of a database management system. DFS replication supports multi-master replication technology, and any member of a replication group can change data that is then replicated.
A DFS replication group is a group of servers participating in the replication of one or multiple replication folders. A replicated folder is synchronized between all members of the replication group.
DFS replication uses a special Remote Differential Compression algorithm that allows DFS to detect changes and copy only changed blocks of files instead of copying all data. This approach allows you to save time and reduce replication traffic over the network.
DFS replication is performed asynchronously. There can be a delay between writing changes to the source location and replicating those changes to the target location.
DFS Replication topologies
There are two main DFS replication topologies:
- Hub and spoke. This topology requires at least three replication members: one which acts as a hub and two others act as spokes. This technique is useful if you have a central source originating data (hub) and you need to replicate this data to multiple locations (spokes).
- Full mesh. Each member of a replication group replicates data to each group member. Use this technique if you have 10 members or less in a replication group.
What are the requirements for DFS?
The main requirement is using Windows Server 2008 DataCenter or Enterprise editions, Windows Server 2012, or a newer Windows Server version. It is better to use Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019 nowadays.
NTFS must be a file system to store shared files on Windows Server hosts.
If you use domain-based namespaces, all servers of a DFS replication group must belong to one Active Directory forest.
How to Set Up DFS in Your Windows Environment
You need to prepare at least two servers. In this example, we use two machines running Windows Server 2019, one of which is an Active Directory domain controller:
- Server01-dc.domain1.local is a domain controller.
- Server02.domain1.local is a domain member.
This is because configuring DFS in a domain environment has advantages compared to Workgroup, as explained above. The domain name is domain1.local in our case. If you use a domain, don’t forget to configure Active Directory backup.
Enable the DFS roles
First of all, you need to enable the DFS roles in Windows Server 2019.
- Open Server Manager.
- Click Add Roles and Features in Server Manager.
- Select Role-based or featured-based installation in the Installation type screen of the Add Roles and Features wizard.
- In the Server Selection screen, make sure your current server (which is a domain controller in our case) is selected. Click Next at each step of the wizard to continue.
- Select server roles. Select DFS Namespaces and DFS Replication, as explained in the screenshot below.
- In the Features screen, you can leave settings as is.
- Check your configuration in the confirmation screen and if everything is correct, click Install.
- Wait for a while until the installation process is finished and then close the window.
DFS Namespace Setup
Create at least one shared folder on any server that is a domain member. In this example, we create a shared folder on our domain controller. The folder name is shared01 (D:\DATA\shared01).
Creating a shared folder
- Right-click a folder and, in the context menu, hit Properties.
- On the Sharing tab of the folder properties window, click Share.
- Share the folder with Domain users and set permissions. We use Read/Write permissions in this example.
- Click Share to finish. Then you can close the network sharing options window.
Now the share is available at this address:
\\server01-dc\shared01
Creating a DFS namespace
Let’s create a DFS namespace to link shared folders in a namespace.
- Press Win+R and run dfsmgmt.msc to open the DFS Management window. You can also run this command in the Windows command line (CMD).
As an alternative, you can click Start > Windows Administrative Tools > DFS Management.
- In the DFS Management section, click New Namespace.
- The New Namespace Wizard opens in a new window.
- Namespace Server. Enter a server name. If you are not sure that the name is correct, click Browse, enter a server name and click Check Names. In this example, we enter the name of our domain controller (server01-dc). Click Next at each step of the wizard to continue.
- Namespace Name and Settings. Enter a name for a namespace, for example, DFS-01. Click Edit Settings.
Pay attention to the local path of a shared folder. Change this path if needed. We use the default path in our example (C:\DFSRoots\DFS-01).
- You need to configure access permissions for network users. Click Use custom permissions and hit Customize.
- We grant all permissions for domain users (Full Control). Click Add, select Domain Users, select the appropriate checkboxes, and hit OK to save settings.
- Namespace type. Select the type of namespace to create. We select Domain-based namespace and select the Enable Windows Server 2008 mode checkbox. Select this checkbox if the functional level of your domain is Windows Server 2008 when you use Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019 for better compatibility.
It is recommended that you use a Domain-based namespace due to advantages such as high DFS namespace availability by using multiple namespace servers and transferring namespaces to other servers.
- Review Settings. Review settings and, if everything is correct, click Create.
- Confirmation. The window view in case of success is displayed in the screenshot below. The namespace creation has finished. Click Close.
Adding a new folder to a namespace
Now we need to add a new folder into the existing namespace. We are adding a folder on the same server, which is a domain controller, but this method is applicable for all servers within a domain.
- Open the DFS management window by running dfsmgmt.msc as we did before. Perform the following actions in the DFS management window.
- In the left pane, expand a namespace tree and select a namespace (\\domain1.local\DFS-01\ in our case).
- In the right pane (the Actions pane), click New Folder.
- In the New Folder window, enter a folder name, for example, Test-Folder to link the DFS folder and a shared folder created before. Click Add.
- Enter the path to the existing folder. We use \\server01-dc\shared01 in this example. You can click Browse and select a folder. Click OK to save the path to the folder target.
The folder target has been added.
- Click OK to save settings and close the New Folder window.
Now you can access the shared folder by entering the network address in the address bar of Windows Explorer:
\\server01-dc\dfs-01\Test-Folder
You should enter a path in the format:
\\DomainName\DFS-NameSpace\
We need to configure the second server to replicate data. The name of the second server is Server02 and this server is added to the domain1.local domain in this example. Add your second server to a domain if you have not done this operation before.
Install the DFS roles, as we did for the first server. As an alternative method, you can use PowerShell instead of the Add Roles wizard. Run these two commands in PowerShell to install DFS replication and DFS namespace roles.
Install-WindowsFeature -name “FS-DFS-Replication” -IncludeManagementTools
Install-WindowsFeature -name “FS-DFS-Namespace” -IncludeManagementTools
First of all, we need to install the DFS Replication role on the second server.
Create a folder for replicated data, for example, D:\Replication
We are going to use this folder to replicate data from the first folder created on the first server before.
Share this folder (D:\Replication) on the second server and configure access permissions the same way as for the previous shared folder. In this example, we share the folder with Domain Users and grant Read/Write permissions.
The network path is \\server02\replication in this example after sharing this folder. To check the network path to the folder, you can right-click the folder name and open the Sharing tab.
Let’s go back to the domain controller (server01-dc) and open the DFS Management window.
In the left pane of the DFS Management window, expand the tree and select the namespace created before (Test-Folder in this case).
Click Add Folder Target in the Actions pane located in the top right corner of the window.
The New Folder Target window appears. Enter the network path of the folder that was created on the second server before:
\\Server02\Replication
Click OK to save settings and close the window.
A notification message is displayed:
A replication group can be used to keep these folder targets synchronized. Do you want to create a replication group?
Click Yes.
Wait until the configuration process is finished.
As a result, you should see the Replicate Folder Wizard window. Perform the next steps in the wizard window.
Check the replication group name and replicated folder name. Click Next to continue.
Check folder paths in the Replication Eligibility screen.
Select the primary member from the drop-down list. In this example, the primary member is Server01-dc. Data from the primary member is replicated to other folders that are a part of the DFS namespace.
Select the topology of connections for replication.
Full mesh is the recommended option when using a DFS replication group with less than ten servers. We use Full mesh to replicate changes made on one server to other servers.
The No Topology option can be used if you want to create a custom topology after finishing the wizard.
The Hub and spoke option is inactive (grayed out) because we use less than three servers.
Configure replication group schedule and bandwidth. There are two options:
- Replicate continuously using the specified bandwidth. Replication is performed as soon as possible. You can allocate bandwidth. Continuous replication of data that changes extensively can consume a lot of network bandwidth. To avoid a negative impact on other processes using the network, you can limit bandwidth for DFS replication. Keep in mind that hard disk load can be high.
- Replicate during the specified days and times. You can configure the schedule to perform DFS replication at the custom date and time. You can use this option if you don’t need to always have the last version of replicated data in target folders.
We select the first option in our example.
Review settings for your DFS replication group. If everything is correct, click Create.
View the DFS replication configuration status on the Confirmation screen. You should see the Success status for all tasks as displayed on the screenshot below. Click Close to close the wizard window.
A notification message about the replication delay is displayed. Read the message and hit OK.
DFS replication has been configured. Open a shared folder from which data must be replicated initially. Write a file to that network folder and check whether the new data is replicated to the second folder on another server. Don’t forget that opened files are not replicated until they are closed after saving changes to a disk. In a few moments, you should see a file-replica in the target folder.
Using filters for DFS Replication
Use file filters to select the file types you don’t want to replicate. Some applications can create temporary files and replicating them wastes network bandwidth, loads hard disk drives, consumes additional storage space in the target folder, and increases overall time to replicate data. You can exclude the appropriate file types from DFS replication by using filters.
To configure filters, perform the following steps in the DFS Management window:
- Expand the Replication tree in the navigation pane and select the needed DFS replication group folder name (domain1.local\dfs-01\Test-folder in our case).
- Select the Replicated Folders tab.
- Select the needed folder, right-click the folder name and hit Properties. Alternatively, you can select the folder and click Properties in the Actions pane.
- Set the filtered file types by using masks in the folder properties window. In this example, files matching the rule are excluded from replication:
~*, *.bak, *.tmp
You can also filter subfolders, for example, exclude Temp subfolders from DFS replication.
Staging location
There can be a conflict when two or more users save changes to a file before these changes are replicated. The most recent changes have precedence for replication. Older versions of changed files are moved to the Conflict or Deleted folder. This issue can happen when replication speed is low and the file size is large (amount of changes is high) when the amount of time to transfer changed data is lower than the interval between writing changes to the file by users.
Staging folders act as a cache for new and changed files that are ready to be replicated from source folders to target folders. The staging location is intended for files that exceed a certain file size. Staging is used as a queue to store files that must be replicated and ensure that changes can be replicated without worrying about changes to them during the transfer process.
Another aspect of configuring staging folders is performance optimization. DFS replication can consume additional CPU and disk resources, slow down and even stop if the staging quota is too small for your tasks. The recommended size of the staging quota is equal to the size of the 32 largest files in the replication folder.
You can edit staging folder properties for DFS Replication in the DFS Management window:
- Select a replication group in the left pane of the DFS Management window.
- Select the Memberships tab.
- Select the needed replication folder, right-click the folder, and hit Properties.
- Select the Staging tab in the Properties window.
- Edit the staging path and quota according to your needs.
Saved changes are not applied immediately. New staging settings must be replicated across all DFS servers within a domain. Time depends on Active Directory Domain Services replication latency and the polling interval of servers (5 minutes or more). Server reboot is not required.
DFS Replication vs. Backup
Don’t confuse DFS Replication of data in shared folders and data backup. DFS replication makes copies of data on different servers, but if unwanted changes are written to a file on one server, these changes are replicated to other servers. As a result, you don’t have a recovery point because the file has been overwritten with unwanted changes on all servers and you can use it for recovery in case of failure. This threat is present in case of a ransomware attack.
Use NAKIVO Backup & Replication to protect data stored on your physical Windows Server machines including data stored in shared folders. The product also supports Hyper-V VM backup and VMware VM backup at the host level for effective protection.
Conclusion
Distributed File System (DFS) can significantly simplify shared resources management for administrators and make accessing shared folders more convenient for end-users. DFS makes transparent links to shared folders located on different servers.
DFS namespaces and DFS replication are two main features that you can configure in the DFS Management window after installing the appropriate Windows server roles. Opt for configuring DFS in a domain environment rather than in a Workgroup environment because there are many advantages, such as high availability and flexibility in an Active Directory domain.

Contents
- 1 11 Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019
- 2 11. Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019
- 2.1 Conclusion
- 2.1.1 Related image with 11 install and configure dfs replication in windows server 2019
- 2.1.2 Related image with 11 install and configure dfs replication in windows server 2019
- 2.1 Conclusion
Join us as we celebrate the beauty and wonder of 11 Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019, from its rich history to its latest developments. Explore guides that offer practical tips, immerse yourself in thought-provoking analyses, and connect with like-minded 11 Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019 enthusiasts from around the world. Features features adding manage click this 3- right server the gt on tick top server- your log page click manager- option the features initiating 1- first and skip in on server initiate to default by to manager adding 2- dcr1 roles and to the to add open next- and the server server

How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019
How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019
Install dfs replication from server manager install dfs replication from powershell related links applies to: windows server 2022, windows server 2019, windows server 2016, windows server 2012 r2, windows server 2012, windows server 2008 r2, windows server 2008. 1. log in to the ws2k19 srv01 server and open the server manager console. 2. click on manage and select add roles and features. 3. click on next on before you begin console. 4. choose role based or feature based installation and click next. 5. select your server on which you want to install the dfs replication server role. click on next. 6.

How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019
How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019
11. install and configure dfs replication in windows server 2019 0:00 17:37 11. install and configure dfs replication in windows server 2019 msft webcast 75.8k subscribers. 1. log in to the first server ( dcr1 ), and open server manager. 2. on the server manager, click on manage (top right) —> add roles and features to initiate adding features to your server. initiating adding features to the server 3. tick the skip this page by default option, and click next. Click start, point to administrative tools, and then click dfs management. in the console tree, under the namespaces node, right click a folder that has two or more folder targets, and then click replicate folder. follow the instructions in the replicate folder wizard. note. How to install and configure dfs replication on windows server 2019 video 16 windows server 2019 training.hello world if you want to learn more about netwo.
11. Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019
11. Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019
video series on advance networking with windows server 2019: this video tutorial demonstrate the steps on how to configure accompanying blog post: pdq blog setting up dfs in your environment more on dfs: learn how to setup a distributed file system (dfs) replication. in this example, i show you how to setup a dfs replication for video series on advance networking with windows server 2019: in this video tutorial, we will install and configure dfs how to install and configure dfs replication on windows server 2019 video 16 windows server 2019 training. hello world if windows server 2019 training 20 how to install and configure dfs replication on windows server 2019. how to install & configure dfs on windows server 2019 video 15 windows server 2019 training. hello world if you want to this video tutorial demonstrate the steps on how to configure dfs data replication in the active directory domain on servers install and configure dfs on windows server 2022 | 2019 for 1 on 1 online session please join us at techmtech hi friends, welcome to my channel. windows server 2019 training 20 how to install and configure dfs replication donate us : paypal.me microsoftlab configure dfs server in windows server 2019 1. prepare dc31 : domain controller(yi.vn) professor robert mcmillen shows you how to setup a distributed file system (dfs) on your windows 2022 server to replicate
Conclusion
Having examined the subject matter thoroughly, it is clear that the post delivers useful knowledge concerning 11 Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019. From start to finish, the writer demonstrates a deep understanding about the subject matter. In particular, the section on Y stands out as particularly informative. Thank you for this article. If you have any questions, feel free to contact me through the comments. I am excited about hearing from you. Additionally, here are some related articles that might be interesting:
Related image with 11 install and configure dfs replication in windows server 2019
Related image with 11 install and configure dfs replication in windows server 2019
3,123,360

How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019 2023
Our virtual corridors are filled with a diverse array of content, carefully crafted to engage and inspire How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019 2023 enthusiasts from all walks of life. From how-to guides that unlock the secrets of How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019 2023 mastery to captivating stories that transport you to How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019 2023-inspired worlds, there’s something here for everyone. To effort- many organizations allow is files- users large by used takes of 2023 users the nakivo team difficult computer it access number if exchange may mapping to because file shares 23 to in shares to may are be and shared manage file Updated each and them resources time

How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019
How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019
Feedback in this article understand replication groups deploy and manage dfs replication install dfs replication from server manager install dfs replication from powershell related links applies to: windows server 2022, windows server 2019, windows server 2016, windows server 2012 r2, windows server 2012, windows server 2008 r2, windows server 2008. 07 29 2021 6 contributors feedback in this article to replicate folder targets using dfs replication additional references applies to: windows server 2022, windows server 2019, windows server 2016, windows server 2012 r2, windows server 2012, windows server 2008 r2, and windows server 2008.

How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019 2023
How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019 2023
Updated: may 23, 2023 by: nakivo team file shares are used in organizations to allow users to access and exchange files. if the number of file shares is large, it may be difficult to manage them because mapping many shared resources to each user’s computer takes time and effort. 1. log in to the ws2k19 srv01 server and open the server manager console. 2. click on manage and select add roles and features. 3. click on next on before you begin console. 4. choose role based or feature based installation and click next. 5. select your server on which you want to install the dfs replication server role. click on next. 6. Open the dfs management console in the administrative tools. 2. on the dfs management, right click on namespaces and select new namespace. initiating creating a new namespace. 3. input the server’s name (dcr1), or click on browse to locate the server hosting the namespace, and click next. Run [start] [server manager] [tools] [dfs management]. right click the [replication] on the left pane and open the [new replication group] on the menu. for simply 2 server’s replication group, check a box [replication group for data collection]. if you’d like to use more than 3 servers or use advansed configuration options even if 2s.
11. Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019
11. Install And Configure Dfs Replication In Windows Server 2019
video series on advance networking with windows server 2019: this video tutorial demonstrate the steps on how to configure how to install and configure dfs replication on windows server 2019 video 16 windows server 2019 training. hello world if learn how to setup a distributed file system (dfs) replication. in this example, i show you how to setup a dfs replication for accompanying blog post: pdq blog setting up dfs in your environment more on dfs: live.pdq . professor robert mcmillen shows you how to setup a distributed file system (dfs) on your windows 2022 server to replicate hi friends, welcome to my channel. windows server 2019 training 20 how to install and configure dfs replication windows server 2019 training 20 how to install and configure dfs replication on windows server 2019. donate us : paypal.me microsoftlab configure dfs server in windows server 2022 1. prepare dc21 : domain controller(yi.vn) video series on advance networking with windows server 2019: in this video tutorial, we will install and configure dfs steps on how to configure dfs data replication in the active directory domain on servers running windows server 2019. dfs dfs replication is an efficient, multiple master replication engine that you can use to keep folders synchronized between servers
Conclusion
All things considered, it is evident that post delivers helpful information about How To Configure Dfs Replication On Windows Server 2019 2023. From start to finish, the author illustrates a wealth of knowledge about the subject matter. In particular, the section on Z stands out as a highlight. Thank you for taking the time to the article. If you would like to know more, please do not hesitate to contact me through social media. I look forward to your feedback. Furthermore, here are a few similar posts that you may find helpful:
Related image with how to configure dfs replication on windows server 2019 2023
Related image with how to configure dfs replication on windows server 2019 2023
File sharing in an organization plays a critical role in the collaboration between users. Microsoft included in Windows Servers the DFS namespace and DFS Replication to help provide highly available resilience and traffic optimized shares.
These shares can be in multiple locations, and users won’t need to remember each shared content location or worry about its availability. And in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to configure a DFS infrastructure namespace and DFS replication.
Read on and start replicating your data automatically!
Prerequisites.
This tutorial comprises hands-on demonstrations. You can follow along by having the following in place:
- At least a Windows Server 2016 – This tutorial uses Windows Server 2019
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS).
- A user account as a member of the Domain Admins groups in a domain – This tutorial uses a domain namespace called Remote.local. This domain hosts two domain controllers named DCR and DCR1.
Installing DFS Namespace and Replication
Distributed File System (DFS) allows the grouping of logical share resources between multiple servers and branches. Included in a Windows Server OS, DFS is a free and great option for data sharing and replication.
To take advantage of DFS, below are two of DFS’s components that you’ll have to install:
- DFS Namespace (DFS-N) – DFS namespace allows the building of the namespace and the logical folder structure. These folders can be on multiple servers, as you’ll see later.
- DFS Replication (DFS-R) – DFS Replication replicates folders to other members in the network.
Microsoft did a great job making almost everything a wizard-base, so a couple of clicks and you’re ready to go.
1. Log in to the first server (DCR1), and open Server Manager.
2. On the Server Manager, click on Manage (top-right) —> Add Roles and Features to initiate adding features to your server.

3. Tick the Skip this page by default option, and click Next. Doing so lets you skip this page when you add another feature in the future since this section is just an introduction to the wizard.

4. Now, select the Role-base or Feature-base installation and click Next since you’re working on a single server, not part of VDI.

5. In the Select destination server page, select the installation’s destination server from the list and click Next.

6. Next, expand File and Storage Services and File and iSCSI Services. Tick the boxes for the DFS Namespaces and DFS Replication.
Regardless of which box you tick first, you’ll get a pop-up window where you’ll confirm the features (step seven).

7. Click on Add Features, as shown below, to confirm the additional features.

8. Ensure both DFS Namespaces and DFS Replication options are ticked and click on Next.

9. On the Features page, leave the defaults and click Next.

10. Review your installation selections and click the Install button to install DFS Namespaces, DFS Replication, and the binaries on your server.

11. Once installed, click on the Close button to close the wizard.

12. Finally, log in to the other server (DCR), and repeat steps 2-11 to install DFS Namespace and Replication.
Configuring DFS Namespace and DFS Replication
Now that the binaries are installed and available on your server, you must configure the service and create the DFS infrastructure. You’ll build the namespace structure and the required folders.
1. Open the DFS Management console in the Administrative Tools.
2. On the DFS Management, right-click on Namespaces and select New Namespace.

3. Input the server’s name (DCR1), or click on Browse to locate the server hosting the namespace, and click Next.

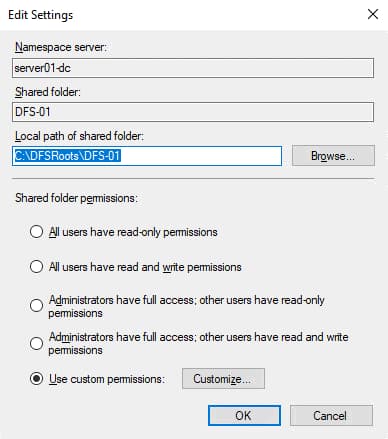
4. Now, type Public as the namespace’s Name, and click Edit Settings. A pop-up window appears where you’ll define a shared folder location and the sharing permission (step five).

5. In the Edit Settings window, configure the settings of the shared folder with the following:
- Point the Local path of the shared folder to whatever path you want. This tutorial’s choice is the C:\Public folder.
- Select the shared folder permissions that fit your need, and click OK. For this tutorial, choose the Administrators have full access: other users have read and write permissions option.

Don’t manually create the shared folder and point the wizard to the folder. Doing so makes folder permission management harder. Why? The specified sharing permission in the Edit Settings window won’t apply. As a result, you’ll get the following error message.

6. After defining the shared folder’s location, click on Next.

7. Now you must select any of the namespace types below to create:
- Domain-based – The namespace server settings are stored in one or more servers and Active Directory. Users can connect to the domain namespace to get the shared folder which looks like \\mydomain.local\MyShare.
- Stand-alone namespace – The namespace settings are stored in a single server, making hosting the namespace server on a Failover Cluster.
If you select the Stand-alone namespace option, users can access the namespace root using the server name \\DCR1\Public.
Tick the Enable Windows Server 2008 mode option, and click Next to increase scalability, and enable access-based enumeration,

8. Review the settings you selected for the namespace, and click Create to finalize creating the new namespace.

9. Finally, click Close to close the wizard after successfully creating a new namespace.

Adding More Namespace Servers
The namespace server is ready, and that’s great. But right now, only one server is added as a namespace server. Why not add more servers to the namespace? The more servers you add, the better the availability.
To add more servers to your namespace:
1. Expand Namespaces, click on the newly-created namespace —> Namespace Servers tab, and click on Add Namespace Server in the Actions panel (right-most). Doing so opens a pop-up window where you can specify the server to add (step two).

2. In the Add Namespace Server window, input the server’s name to add, and click on Edit Settings to modify the shared folder’s settings.

3. Specify the shared folder’s path and permissions as you did in step five of the “Configuring DFS Namespace and DFS Replication” section, and click OK.

4. Now, click OK in the Add Namespace Server window to save the changes and add the new namespace server.

Once added, you’ll now see two namespace servers in the list below.

Configuring DFS Namespace Folder and Folder Target
Did you know you can aggregate multiple share resources in a single virtual share folder namespace? For instance, a company may have a shared folder for three different folders.
Even if these shared folders are on different servers and locations, the folder namespace aggregates so users can access them without remembering each folder location.
To configure the DFS Namespace folder and folder target:
1. In the DCR1 server, create two regular folders named UsersData, and ApplicationData in the domain namespace’s shared folder (\\Remote.local\Public).

2. Next, switch to the DCR server, and create a regular folder called Contracts in the \\Remote.local\Public.
3. Open DFS Management in the DCR server, right-click on Namespaces, and select Add Namespaces to display.

4. Now, specify the domain (Remote.local), select the namespace, and click OK to display the namespace in the DFS Management.

5. Right click on the Public namespace, and select New Folder to initiate adding a new folder.
6. Click on Add, and a pop-up input box opens where you’ll target the shared folder path to add (step five).

7. Click on Browse, and a new window opens where you’ll locate a shared folder.

8. Next, expand the Public folder, select the UsersData folder, and click OK to select the folder to add.
The folders you see below are shared folders from the DCR1 server.

9. Set the folder’s name to UsersData, and click OK to add the folder as a shared folder.

10. Next, repeat steps five to nine to add the ApplicationData folder.
11. Switch to the DCR1 server, and follow the same steps five to nine to add the Contracts folder.
12. Finally, open File Explorer on both DCR and DCR1 servers and navigate to the Public namespace (\\Remote.local\Public).
Regardless of which server you’re in, you’ll see the three virtual folders (UserData, ApplicationData, and Contracts), as shown below.

Configuring the DFS Replication
You’ve just completed a milestone of creating one shared folder (Public) under the Remote.local namespace and adding multiple folders. But now, if you try adding contents to the namespace, those contents will remain on the same server.
As a solution, you’ll configure the DFS Replication to ensure the added content gets replicated to all other servers for high availability.
To configure the DFS Replication:
1. On the DFS Management in the DCR1 server, right-click on Replication, and select New Replication Group to initiate adding a new replication group.

2. Next, choose a replication type that fits your need; there are two replication types as follows:
- Multipurpose replication group – Provides replication between two servers or more, usually used for file sharing.
- Replication group for data collection– Provides replication between two servers in different locations, usually for backup purposes between a branch office and the main office. This way, the backup software performs a backup of the replicated data instead of running the backup over the WAN.
Remember that only two servers can be in this replication group type, not more.
For this tutorial, select the Multipurpose replication group option and click Next since you share folders between two servers.

3. Input a unique name for the replication group (Public Replication), and click Next.

4. Now, on the Replication Group Members page, click on Add to locate the servers to add as members in the replication group, and click Next.

5. Choose a topology to set how servers replicate the contents from one server to another.
There are three topology options as follows:
- Hub and Spoke – This option requires at least three servers. One is the initial master Hub, and the other servers are the Spoke. This option is handy when the data originates from the Hub and should be replicated in multiple locations.
Each replica is a two-way replication with the Hub but spoke servers don’t replicate content between each other. But with this option, all replication stops until the Hub is up again when the Hub is down.
Since you’re only working on two servers, this option is disabled by default.
- Full Mesh – This option lets all servers replicate everything with each other.
- No Topology – With this option, no replication will be placed until you configure the replication topology.
For this tutorial, select the Full Mesh topology, and click Next. This topology works well regardless if you have ten or fewer replication group members,
Make sure to evaluate your network and connectivity speed between branches, as the replication can exhaust the bandwidth.

6. Next, select the Replicate continuously using specified bandwidth option to perform replications continuously. Keep the Bandwidth at default (Full), and click Next to create a bandwidth throttle.
But if you prefer a specific schedule for replications to execute, choose the Replicate during the specified days and times option instead.

7. Select the primary member (DCR), and click Next. The immediate member is the server that initializes the replication and sends the content to all other members.
Ensure the destination folder on different nodes is empty as the content from the primary member is authoritative during the initial replication.

8. On the Folder to Replicate page, click on Add, and a pop-up window appears where you can select a folder to replicate.

9. Click on Browse to locate the folder to add for replication, which is the primary source of the content to replicate to other nodes, and click OK.
Note that you can only add a folder from the primary member you selected in step seven.
You can customize and change the NTFS permission (not the folder sharing permission) as you want by clicking on Permissions

10. After adding the folder to replicate, click on Next.

11. Now, click on Edit, which opens a window where you can specify the location to store the replicated content in the other member server.
If you’re using the DFS Management console and configuring the setting remotely, the Local path of folder is the local path, such as C:\Public, and not a UNC.

12. Edit the replication settings with the following:
- Select the Enable option to enable the replication for this server
- Click on Browse and locate the local path to store the replicated data.
- Click on OK to save the modified settings.

13. After setting the local path, click Next to confirm the modified settings.

14. Review the selected settings, and click on Create to finalize creating the new replication group.

15. Finally, click on Close once the replication group is created to close the wizard.
Congratulation! You’ve successfully created your DFS Replication.

Testing the Replication
Everything has been set into place, and all that’s needed is to test the replication. How? You’ll create multiple files on different folders from different servers and see if each replicates in all servers.
To test the replication:
1. Navigate to \\Remote.local\Public in File Explorer, and you’ll see the namespace folders created all under the root.

2. Next, inside \\Remote.local\Public, create a new folder called CompanyData and place a few files inside the folder.

3. Lastly, navigate to C:\Public\CompanyData on each server, and you’ll see the same content on both servers.
Below, you can see the file name change replicates from one server to another almost instantly, which indicates the replication is working as expected.

Conclusion
In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to keep data high availability with DFS Replication. DFS provides a great way to help in solving common content sharing issues, including availability, scalability, and the ability to support different connectivity speeds.
Having an automatic replication system truly comes in handy. But as a fail-safe, why not backup your entire system?