Время на прочтение
6 мин
Количество просмотров 23K
Пока некоторые читатели (да что уж там, и писатели — например, я) наслаждались в отпуске теплыми летними денечками, известный автор нашего англоязычного блога Адам Бертрам подготовил краткий обзор Windows Storage Spaces. В него он включил, в частности, сведения о настройке Windows Storage Spaces на популярных конфигурациях. Перевод его статьи я и предлагаю вашему вниманию.
Во многих дата-центрах и серверных фермах для хранения данных используются HDD и SSD. Статистика, однако, сообщает о том, что после трёх лет работы 10% дисков становятся негодными.
Конечно, те организации, которые заботятся о целостности и сохранности своих данных, держат руку на пульсе, а также отслеживают и другие факторы риска — будь то человеческий фактор, железо или софт. И тут тем, кто работает с Windows-инфраструктурой, могут помочь Windows Storage Spaces. Ведь их RAID-подобная функциональность (то, что мы видим в File Explorer как виртуальные диски) весьма полезна в деле обеспечения резерва мощностей хранения.
Гибкие возможности масштабирования тоже привлекательны: можно объединить 3 и более драйвов в единый сторадж-пул и затем формировать на его основе “стораджики” нужного размера. А поскольку при работе с пулом формируются и сохраняются дополнительные копии для ваших данных, то проблемы с одним из дисков не приведут к потере всего и вся. А если понадобилось больше места? Просто добавь воды еще дисков в пул.
Storage Spaces для Windows 10
— Он забирается на самую высокую сосну и оттуда планирует.
— Ага, простите, что планирует?
— Он прыгает и планирует.
(“День радио”)
Даже если сценарий развертывания, который вы хотите воплотить, входит в число самых популярных, и инструкция к нему коротка и вроде даже сходу понятна, этап подготовки и планирования все равно никто не отменял. Итак:
Если вы используете дисковые пространства Storage Spaces на машине с Windows 10, то рекомендуется обеспечить наличие минимум 2 дисков помимо системного. Эти диски могут быть как встроенными, так и внешними. Поддерживаются SSD; можно комбинировать SATA, USB и SAS.
Количество дисков рассчитывается исходя из того, какой метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости вы хотите применить. Есть вот такие варианты:
-
Simple (простой) — требует наличия минимум двух дисков. Хоть этот метод и дает хорошую производительность, но ничем вам не поможет в случае отказа. Его можно использовать, например, если вы настраиваете storage space для хранения временных данных (например, файлов видео-рендеринга, файлов-черновиков в графических редакторах, и так далее).
-
Mirror (зеркальный) — позволяет сохранять несколько копий данных на случай отказа. Так, Two-way mirror spaces хранят две копии данных, и с ними вы переживете отказ одного из дисков. Для их организации потребуется минимум два диска. Three-way mirror spaces позволят пережить отказ двух дисков, а для их организации потребуется минимум пять. Зато хранить в таких storage spaces можно самые разнообразные данные.
-
Parity (с контролем четности) — рекомендуется для хранения архивных и стриминговых данных. Хранят несколько копий на случай отказа. Если вы хотите обеспечить отказоустойчивость в случае проблемы с одним диском, то в сценарии с Parity spaces вам понадобится минимум три диска, а на случай проблемы с двумя — минимум семь дисков.
После того, как вы все рассчитали и подготовили, можно организовать собственно Storage Spaces. Для этого в Windows 10 нужно выполнить вот такие шаги:
-
Проверить, что диски, которые вы планируете задействовать, у вас подключены.
Важно! Если вы укажете, что в сторадж-пул хотите включить размеченный диск, имейте в виду, что Windows безвозвратно удалит все разделы и файлы на нём. До начала работы сделайте резервную копию всего, что вам дорого на этом диске!
-
Для простоты в поле поиска в панели задач вводим Storage Spaces и из полученного списка выбираем Storage Spaces.
-
Кликаем Create a new pool and storage space.
-
Выберем нужные нам диски и затем кликнем Сreate new storage pool.
-
Указываем имя, буквенное обозначение и файловую систему для нового сторадж пула.
-
На случай сбоя рекомендуется выбрать метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости (Resiliency) как одну из следующих опций: Two-way mirror, Three-way mirror или Parity.
Важно! Помните про количество дисков, которые потребуются в каждом из указанных вариантов, о чем мы говорили выше. Если, допустим, вы предпочтете Two-way mirror, то для нового storage space будет создаваться две копии данных. Так что для такого сценария понадобится минимум два диска (помимо системного).
-
Затем задайте максимальный размер стораджа для Storage Spaces.
Примечание: Можно указать значение, превышающее размер сторадж-пула — когда место будет заканчиваться, вы просто добавите еще один диск.
-
Когда с настройками покончено, нажимаем Create storage space.
Оптимизация работы
Рекомендуется своевременно оптимизировать работу с дисками. Вот что советует делать Microsoft:
При добавлении новых дисков в существующий пул рекомендуется оптимизировать использование диска. При этом некоторые данные будут перемещены на новый диск, чтобы оптимизировать использование емкости пула. Это стандартное действие при добавлении нового диска в обновленный пул в Windows 10: флажок Optimize to spread existing data across all drives будет установлен по умолчанию.
Однако если вы сняли этот флажок или добавили диски до обновления пула, вам нужно вручную оптимизировать использование диска. Для этого в поле поиска на панели задач введите Storage Spaces, выберите Storage Spaces из списка результатов поиска, а затем щелкните Optimize drive usage.
Автономный сервер
Если у вас один отдельно взятый сервер, то для настройки на нем дисковых пространств Storage Spaces есть подробная инструкция от Microsoft, на русском языке и даже с картинкой. Storage Spaces поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows Server 2012.
Обратите внимание: до начала настройки нужно обеспечить наличие одного или нескольких пулов, а также проверить конфигурацию на соответствие ряду требований (они перечислены в разделе «Предварительные условия»).
На базе сторадж-пула можно создать несколько виртуальных дисков. (Windows идентифицирует их как обычные диски, которые могут быть отформатированы.)
Для их создания можно использовать File and Storage Services; в настройках можно указать thin provisioning либо fixed provisioning, а также размер. Дополнительные настройки можно задать с помощью команд PowerShell.
Кластеры и Storage Spaces Direct
Если вы работаете с кластером и используете для каждой его ноды СХД с прямым подключением (DAS), то Storage Spaces Direct могут оказаться вполне разумным и эффективным вариантом по сравнению с NAS и SAN. Storage Spaces Direct отличаются хорошей масштабируемостью и возможностями управления. Технология Storage Spaces работает наряду с кэшированием, RDMA и поддержкой СХД для разных уровней (tiers). Помимо этого, поддерживаются диски NVMe.
Storage Spaces Direct поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, 2016 Datacenter и Insider Preview Builds. Можно создать конвергентное или гипер-конвергентное пространство.
Вкратце, основные этапы развертывания Storage Spaces Direct — это:
-
Развертывание Windows Server — установка и настройка ОС, добавление доменных учеток, настройка ролей и необходимых фич.
-
Настройка сети (этот этап не относится к сценарию развертывания Storage Spaces Direct на виртуальных машинах).
-
Конфигурация собственно Storage Spaces Direct — очистка дисков и разделов, настройка кластеров, настройка Storage Spaces Direct, создание томов, развертывание необходимых виртуальных машин.
-
Для конвергентной инфраструктуры — развертывание масштабируемых файловых серверов, настройка ролей, создание шар, настройка ограниченного делегирования Kerberos.
Все эти этапы очень подробно описаны здесь (на русском языке).
Возможен сценарий, при котором все физические диски содержатся в enclosures с общим доступом — это т.н. JBOD enclosure. Такая инфраструктура должна соответствовать требованиям Windows Certification, а также включать в себя идентичные SAS HBA (имеющие сертификацию Storage Spaces). Такие диски в кластере не должны иметь встроенную функциональность RAID.
Storage Spaces vs. RAID
Как водится, у Windows Storage Spaces и RAID есть свои преимущества и свои недостатки. Об этом уже написана не одна сотня строк (например, здесь). Вкратце:
-
У RAID есть два аспекта: аппаратный и программный — а Windows Storage Spaces, так сказать, является software-driven, настраивается целиком через графический интерфейс или командную строку.
-
Для программных RAID, как и для Storage Spaces отсутствуют ограничения по числу сокетов (у традиционных RAID они есть).
-
ОС по-разному “видит” диски в RAID и в Storage Spaces — диски RAID предстают как цельный юнит (даже если у физических дисков разная емкость), что может приводить к неоптимальному использованию свободного пространства. Для Storage Spaces такой проблемы нет, так как есть доступ к отдельным дискам.
-
Если говорить о производительности, то RAID 0 превосходит Storage Spaces с режимом simple mode примерно вдвое. Однако на скоростях 4K они уже сравнимы. RAID 1 быстрее выполняет последовательные операции чтения, зато Storage Spaces в режиме two-way mirror mode вдвое быстрее выполняет операции записи, нежели RAID 1. Что касается hardware RAID, то операции чтения и записи для них гораздо быстрее, чем Storage Spaces в режиме parity mode.
Ссылки
Общие сведения о дисковых пространствах Storage Spaces
Развертывание Storage Space Direct
Дисковые пространства в Windows 10
Кейс о развертывании Storage Space Direct компанией-провайдером Veeam
With Windows Server 2019, Server manager includes simple and easy to use, user interface that enables management of Windows
Storage Spaces and other Storage Subsystems such as EMC Clariion VNX and Dell EqualLogic (but not limited to these) storage arrays with supporting SMI-S and SMP based Storage provider respectively.
By using Server Manager’s File and Storage Services Role user interfaces, you can create and manage storage objects such as storage pools and virtual disks.
In the following post, we will cover common storage spaces administrative tasks by using the “File and Storage Services” pages on Server Manager
In Server Manager, select File and Storage Services > Volumes > Storage Pools. Under PHYSICAL DISKS, select New Storage Pool.
Now read the needed information about the storage pool then click Next.
Specify a storage pool name with description and click Next.
Now select the disks you want to create storage pool also you can select a disk as a hot spare which is for failover clustering/ if a disk fails then the Hot spare disk will work and save the files from being deleted.
Confirm all the settings have been done correctly then click Create.
The new storage pool has successfully completed, now click create a virtual disk when this wizard closes to create a virtual disk after this wizard and click Close.
Create a Virtual Disk for Storage Pool
After creating the storage pool now start creating a virtual disk for the pool you had created.
When the storage pool wizard finishes, just mark the create a virtual disk option to create a virtual disk after this wizard.
When the virtual disk wizard opened, read the details about it then click Next.
Specify the virtual disk name and click Next.
At this step, you don’t do anything just click Next.
Select the storage pool to create a virtual disk, if it’s selected automatically just click Next.
Select a storage layout/style you need then click Next. If you don’t know the definition, select the one and read the explanation beside it.
Select a provisioning type then click Next. The thin option uses space from the storage pool as needed, up to volume size and the fixed option uses from the storage pool equal to the volume size.
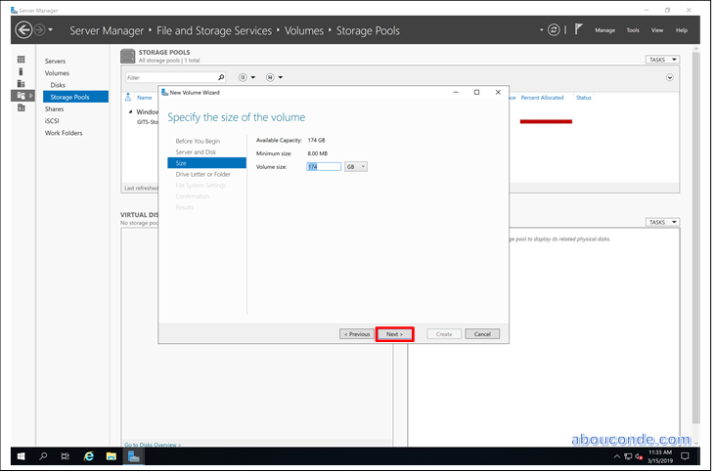
Specify the size of the virtual disk or select maximum size then click Next. If you specify the size the remaining size will be offline and not used and if you select the maximum size it will select all the size of the storage pool.
At this point, check all the configuration you’ve done and click Create to start the process.
Now the wizard has accomplished successfully and the new virtual disk has created, mark the create a volume when this wizard closes and click Close.
Create a Volume for the Virtual Disk
After creating the virtual disk, mark the Create a volume when this wizard closes then click Close.
When the new volume wizard opened, read the required information about it then click Next.
Select the server and disk you want to create volume for, if it’s selected automatically just click Next.
Specify the size of the disk, or let it by default then click Next. If the volume size will be specified, the remaining size will be offline and unused, it can be configured separately from it.
Select a drive letter or folder to assign then click Next.
Select the file system like NTFS then type a volume name or you can let it by default then click Next.
Notice that all the settings have done correctly and click Create.
The volume has created successfully click Close and start using the storage pool.
The storage pool and the disks have now been successfully created and ready to use, like the screenshot.


Software defined storage today is one of the hottest and most desired technology solutions in the enterprise datacenter. Most organizations are looking very seriously at software defined storage solutions as opposed to refreshing SAN storage devices in the next refresh cycle. Why is this? Software defined storage provides exceptional features and functionality that generally allow businesses today to not be tied to a specific hardware vendor for features and functionality as has traditionally been the case. With the release of Windows Server 2019 (in a state of non release due to retraction from Microsoft with reported issues), the latest version of Storage Spaces Direct is now available. Storage Spaces Direct or S2D is Microsoft’s software-defined stoage solution that allows using commodity directly attached storage to be used as production storage for Hyper-V and other infrastructure technologies. In this post, we will take a look at Configuring Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct S2D in VMware vSphere to see how S2D is configured and how this can be done inside of VMware virtual machines for lab purposes.
To begin with, let me give you an overview of the VMware vSphere lab itself that is being used as well as the Windows Server 2019 variant used in testing. In the home lab, I am running VMware vSphere 6.7 (waiting on U1). Windows Server 2019 has been installed in three VMware virtual machines each with (3) 10 gig disks for provisioning to use in the S2D configuration. Prior to the recall of sorts on the current Windows Server 2019 binaries, I had downloaded the ISO and had built a 3-node Hyper-V cluster using the GA release. However, I received the following error when attempting to enable S2D on the cluster.
Microsoft supposedly has a registry key that will allow storage spaces direct to be installed regardless of the compatibility with the product. At the time of this writing however, I do not have my hands on the registry key to allow the installation to move forward. Microsoft however, plainly states the Insider versions of the Server OS do allow installing S2D on non-supported hardware. I did find this to be true as backing back down to the 17744 build release on each of the three cluster nodes of the Insider preview did allow me to run the Enable-Clusters2d command.
Highlights:

- vSphere 6.7 virtual machines
- 80 GB OS drive, (3) 50 GB drives for use with S2D
- Windows Server 2019 – Version 1809, Build 17744
Configuring Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct S2D in VMware vSphere
Below, I will run through the steps to get Storage Spaces Direct up and running and in a configured state so you are ready to begin carving out storage for your virtual machines running on top of your S2D cluster. As a disclaimer here, I closely followed the steps found on Virtualtothecore blog with a few little changes for my environment. I am continuing to play with the commands to see what is needed in Windows Server 2019 and what may not be needed for this to work in a VMware virtual machine.
The first thing we need to do is install the Windows features needed for Failover Clustering and Hyper-V, since our cluster will be intended for use as a Hyper-V cluster running on top of Storage Spaces Direct.
After rebooting the hosts after installing the Windows features/roles we need, we can now create the cluster itself. From PowerShell, this is as simple as running the New-Cluster command, naming the cluster, and then providing the hosts that will be members. Also, we provide the IP address assigned to the Cluster name.
New-Cluster -Name S2Dcluster -Node hyper19-01.cloud.local, hyper19-02.cloud.local, hyper19-03.cloud.local -NoStorage -StaticAddress 10.1.149.190
To check and see whether the disks we have provisioned to the servers are available to pool, we can run the Get-Physicaldisk cmdlet to check the status of the disks.
To actually enable the Storage Spaces Direct functionality on the cluster, we run the following command:
Enable-Clusters2d -cachestate disabled -autoconfig:0 -skipeligibilitychecks
The configuration process begins on the cluster.
You should see the command finish without error. There is a log file that gets created covering the process found at C:WindowsClusterReportsEnableClusterS2D.
The next step is to create the Storage Pool. The Storage Pool is the raw storage that we can create virtual disks from.
New-StoragePool -StorageSubSystemFriendlyName *Cluster* -FriendlyName S2D -ProvisioningTypeDefault Fixed -PhysicalDisk (Get-PhysicalDisk | ? CanPool -eq $true)
To visually manage the new Storage Pool, you can launch Server Manager, click the Cluster name, navigate to Storage Pools and you should see the Storage Pool created in the step above.
Takeaways
The process of Configuring Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct S2D in VMware vSphere was simpler that I thought it would be as I expected to see errors or other unexplained behavior. I had tried this once before in Windows Server 2016 cluster hosts and ran into a few odditites that I was never able to get around with the time I had to play around with it. It looks like however, in Windows Server 2019, these issues are no longer present. One thing to emphasize again, this is the Insiders Preview release build 17744 that was used in the post. Hopefully the registry key that will allow using the GA release will be published so we can hack away with the GA release, once it is re-released. Stay tuned for more Storage Spaces Direct information, configuration, and labbing.
Skip to content
Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Best Practices
Windows Server 2019 brings about significant improvements across the platform when it comes to software-defined solutions. Software-defined storage is garnering a lot of attention from customers as most are looking outside of traditional storage with upcoming refreshes for storage infrastructure. With Storage Spaces Direct being introduced in Windows Server 2016, the technology from a Windows perspective is relatively new. However, with Windows Server 2019, Storage Spaces Direct has matured from a new technology to a tried and proven platform for running production workloads.
Table of Contents
- Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Best Practices
- Use RDMA
- Use Switch Embedded Teaming
- Resiliency Considerations
- Storage Devices
- Sizing Best Practices
- Buy WSSD Solutions
- Manage Storage Spaces Direct with Windows Admin Center
- Concluding Thoughts
While Windows Server 2019 has only been released for a few days now, there are Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Best Practices to note for running S2D on Microsoft’s newest server operating system platform. Many of these best practices carry over from Windows Server 2016 and are worth noting for Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct.
Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Best Practices
When thinking about the various best practices with Storage Spaces Direct in Windows Server 2019, there are several areas we want to consider when thinking about an S2D design. Recently, at Microsoft Ignite, (7) Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct best practices were considered.
- Using RDMA
- Switch Embedded Teaming
- Resiliency
- Use Storage devices with high endurance
- Size the environment correctly
- Buy WSSD Solutions
- Manage S2D with Windows Admin Center
Let’s take a look at each of these areas and how each contributes to running a Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct environment that is resilient, stable and performs extremely well.
Use RDMA
RDMA is a core technology to having a Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct infrastructure that performs really well.

What is RDMA?
RDMA or remote direct memory access allows devices to access memory without having to interact with the operating system. This allows a great deal more performance that devices do have to interact with host operating systems. With RDMA applications have direct access to the network which reduces latency and CPU overhead.
There are basically two methods for implemented RDMA network technology. This can be done using either RoCE or iWarp technology.
RoCE is the most difficult out of the two to configure correctly. However, either can be used to provide a stable and high-performance RDMA network fabric for Storage Spaces Direct.
A few things to consider with RoCE implementations:
- Do not route RoCE traffic
- Do not neglect the switch configuration
With iWarp, the implementation is generally easier than with RoCE. However, there are still things to consider when implementing it with S2D.
- Do not route iWarp traffic
- With high bandwidth implementations, use priority flow control or PFC
Use Switch Embedded Teaming
What is Switch Embedded Teaming or SET?
SET is an alternative NIC teaming solution that can be used in Hyper-V environments with both Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019 that integrates some of the NIC teaming functionality into the Hyper-V virtual switch. This allows grouping between one and eight physical Ethernet network adapters into one or more software-based virtual network adapters.
You can still use the LBFO NIC teaming in the traditional sense, however, using SET allows you to benefit from new switch features such as vRSS, vRDMA, DVMMQ, and RSC. When configuring the network for SMB traffic, use separate subnets for each SMB network. This helps with clear network design and congestion control.
Resiliency Considerations
With Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct, you have access to many different resiliency options. You can use the following:
- 3-way mirror – three copies of the same block on three different servers. Two servers can fail if you have 4 or more nodes and you will have great performance across the board
- Mirror Accelerated Parity – Mirror accelerated parity is a great compromise of resiliency and capacity. Part of the volume is a three-way mirror, and the other part is double parity so you get the best of both worlds
- Double Parity – This is not recommended and is recommended to use mirror accelerated parity
- 2-way mirror – This is not a recommended configuration unless you are running a two-node cluster
Storage Devices
When sourcing and provisioning cache devices pay attention to the endurance of the cache device. Steer towards cache devices only that have at least 3 DWPD or disk writes per day. With Capacity devices, use devices that have a rating of 1-3 DWPD. With Storage Spaces Direct, you want to have a minimum of (2) cache devices and pay attention to the 4K random I/O numbers of the device in particular.
When considering hardware for caching devices, choose NVMe when possible. NVMe devices are only 30% more expensive but perform 300% faster than comparable SSDs.
Sizing Best Practices
When thinking about the sizing best practices for Storage Spaces Direct, to enable the parallel rebuild feature you need at least one HDD worth of space free in your S2D pool. With the parallel rebuild, the Storage Pool will repair itself even if the failed drive isn’t replaced. Parallel rebuild is much faster than rebuilding the failed drive itself since parallel rebuild is using multiple drives to repair the storage pool instead of rebuilding the single failed drive which can take some time depending on the size and type of the drive.
Be sure to size storage tiers correctly. Set aside at least 10% of your storage pool for caching devices. Provision 20% for the performance tier and the rest for capacity. This will provide a great mix of cache, performance, and capacity for production workloads.
Buy WSSD Solutions
Microsoft has introduced a program called the WSSD Solutions program which stands for “Windows Server Software Defined”. This is essentially a Microsoft certificate for hardware that verifies the hardware is tested and certified to run Storage Spaces Direct. Microsoft sends vendors a rigorous testing program that simulates S2D traffic for a year in the span of a week or so. If the vendor hardware passes the simulated checks, they can become WSSD certified.
Buying these solutions means that you are buying hardware that is certified to run Storage Spaces Direct. This is extremely important from a support perspective and from a stability and reliability perspective for running production workloads.
Manage Storage Spaces Direct with Windows Admin Center
Windows Admin Center is the centerpiece to managing Windows Server 2019. It provides the way forward for managing software defined infrastructure with Windows Server 2019. The Windows Admin Center is a free download from Microsoft if you have a valid Windows operating system license. New dashboards have been designed with Windows Admin Center that allow a high level of visibility into the S2D infrastructure, including historical performance metrics and even health of the infrastructure down to the drive level. Windows Admin Center provides all tools in a single interface instead of having to switch between various tools to manage hosts, clusters, and HCI environments. It is also web based which allows accessing it from any client or server if configured in the gateway mode.
Concluding Thoughts
Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct provides a powerful platform for running production workloads on top of a software defined infrastructure based on Windows Server Failover Cluster technology. By following best practices with the solution, customers can expect to have the best experience with the platform including stability, performance, and reliability. Many of the recommended best practices carry over from Windows Server 2016 S2D and equally apply with Windows Server 2019. The Windows Sever 2019 S2D best practices cover all areas of the components, including network, virtual switch, sizing, resiliency, certified hardware and others. When provisioning a new Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct cluster, be sure to follow Microsoft’s recommended best practices for S2D which will ensure the best experience with the latest S2D release.
Related Posts:
Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V SAN vs Storage Spaces Direct
Configuring Storage Spaces Direct and Resilient File System (ReFS)
Managing Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct with Windows Admin Center
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.
Windows Server 2019 storage pool configuration
tags: Computer network application server
Intelligent Recommendation
windows server 2019 server build
1. Windows server 2019 installation Install Windows Server 2019 under Vmware. Second, the server configuration 1. Enable the remote function first Right click on «This Computer»-«Proper…
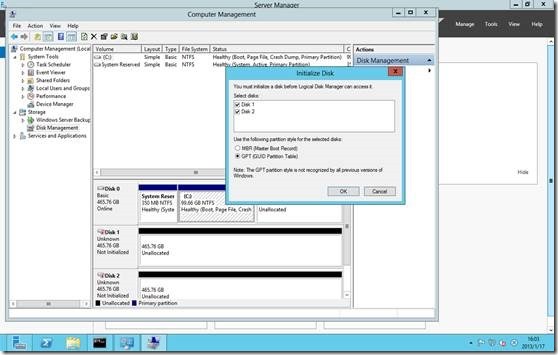
On the Windows Server 2012 storage
Physical disk initialization Add File and storage services You may need to create a failover cluster according to Start New Storage Pool Wizard Define the storage pool name Selecting a physical disk s…
Sentry storage connection pool configuration
As a data rights management system, sentry does not introduce this article. For details, please refer to the official documentation:http://sentry.apache.org/ In practical applications, you are likely …
More Recommendation
Windows Server 2016 upgrade to Windows server 2019
Ready to work Prepare the image file of Windows server 2019 (similar to this file 17763.107.101029-1455.rs5_release_svc_refresh_SERVER_VOL_x64FRE_en-us.iso) step Copy the iso file to Windows server 20…
windows configuration iscsi storage
By default, the Windows built-in iscsi component is not started. The specific start and configuration methods are as follows: 1. Open Control Panel\All Control Panel Items\Administrative Tools\iSCSI I…