Содержание
- Определяем IP устройства по MAC-адресу
- Способ 1: Ручной ввод команд
- Способ 2: Создание и запуск скрипта
- Вопросы и ответы
IP-адрес подключенного сетевого устройства нужен пользователю в той ситуации, когда на него отправляется определенная команда, например, документ для печати на принтер. Помимо этого примеров существует достаточно много, мы не будем перечислять все их. Иногда юзер сталкивается с ситуацией, когда сетевой адрес оборудования для него неизвестен, а на руках имеется лишь физический, то есть MAC-адрес. Тогда нахождение IP осуществляется достаточно просто с помощью стандартных средств операционной системы.
Для выполнения сегодняшней задачи мы воспользуемся только «Командной строкой» Windows и в отдельном случае встроенным приложением «Блокнот». Вам не нужно знать никаких протоколов, параметров или команд, сегодня мы ознакомим вас со всеми ними. От юзера требуется только наличие правильного MAC-адреса подключенного аппарата для произведения дальнейшего поиска.
Приведенные в этой статье инструкции будут максимально полезны только тем, кто ищет IP других устройств, а не своего локального компьютера. Определить MAC родного ПК можно проще. Предлагаем вам ознакомиться с другой статьей по этой теме далее.
Читайте также: Как посмотреть MAC-адрес компьютера
Способ 1: Ручной ввод команд
Есть вариант использования скрипта для проведения необходимых манипуляций, однако максимально полезным он будет только в той ситуации, когда определение IP производится большое количество раз. Для одноразового поиска достаточно будет самостоятельно прописать необходимые команды в консоли.
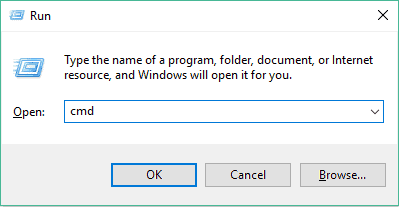
- Откройте приложение «Выполнить», зажав комбинацию клавиш Win + R. Впишите в поле ввода cmd, а затем щелкните на кнопку «ОК».
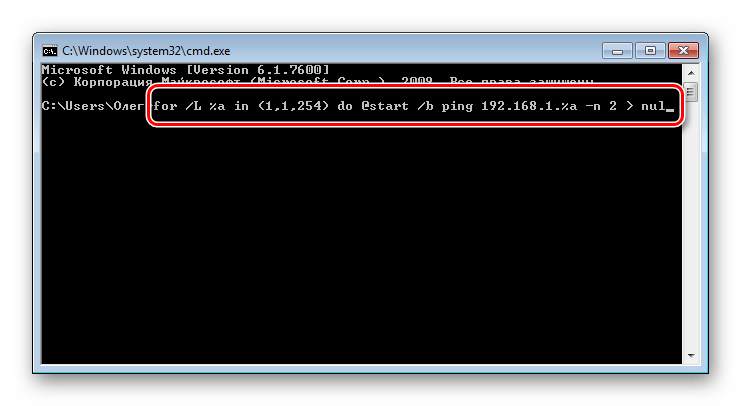
- Считывание IP-адресов будет происходить через кэш, поэтому его сначала нужно наполнить. За это отвечает команда
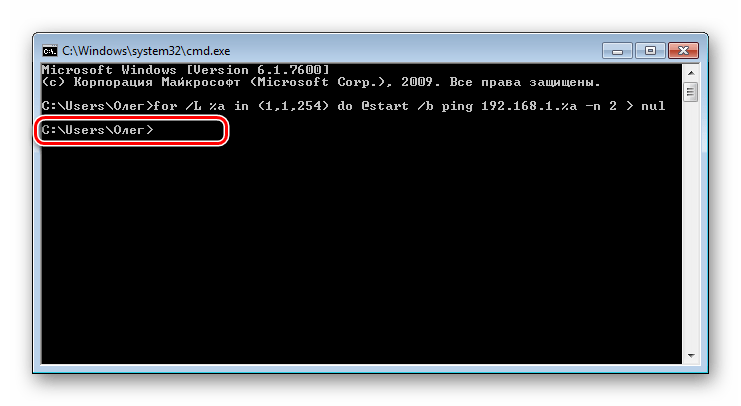
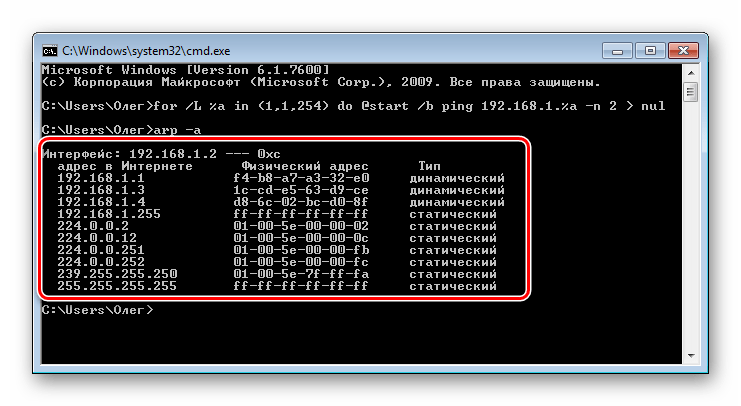
for /L %a in (1,1,254) do @start /b ping 192.168.1.%a -n 2 > nul. Обратите внимание, что сработает она только тогда, когда сетевые настройки являются стандартными, то есть 192.168.1.1 / 255.255.255.0. В противном случае изменению подлежит часть (1,1,254). Вместо 1 и 1 вводятся начальные и конечные значения измененного IP сети, а вместо 254 — установленная маска подсети. Пропечатайте команду, а затем нажмите на клавишу Enter. - Вы запустили скрипт на пропинговку всей сети. За нее отвечает стандартная команда ping, которая сканирует только один указанный адрес. Введенный же скрипт запустит быстрый анализ всех адресов. По завершении сканирования отобразится стандартная строка для дальнейшего ввода.
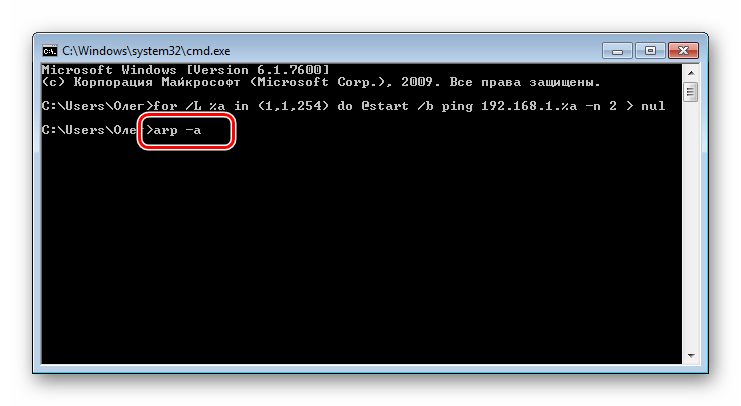
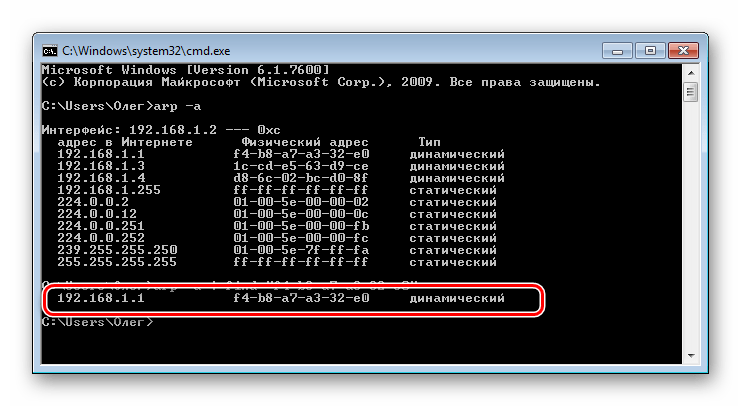
- Теперь следует просмотреть сохраненные в кэше записи с помощью команды arp и аргумента -a. Протокол ARP (Address resolution protocol) показывает соответствие MAC-адресов к IP, выводя все найденные устройства в консоль. Учтите, что после наполнения некоторые записи хранятся не более 15 секунд, поэтому сразу после наполнения кэша запустите сканирование, введя
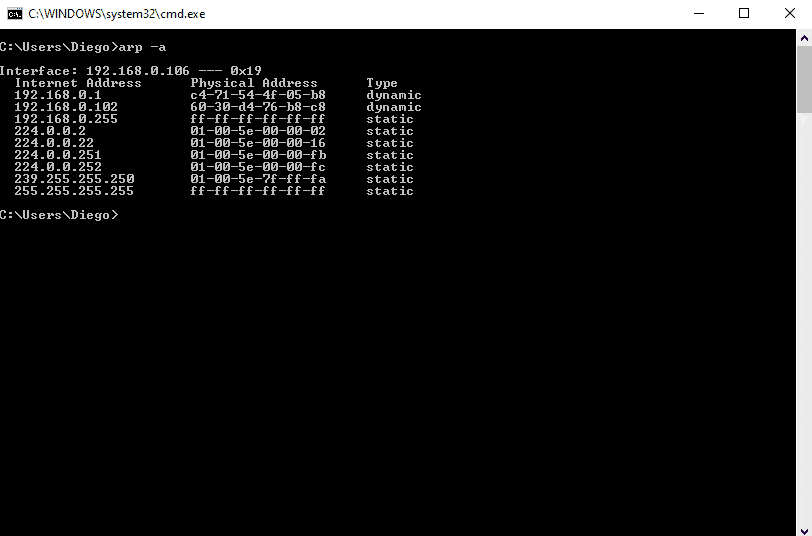
arp -a. - Обычно результаты считывания показываются через несколько секунд после запуска команды. Теперь вы можете сверить имеющийся MAC-адрес с соответствующим ему IP.
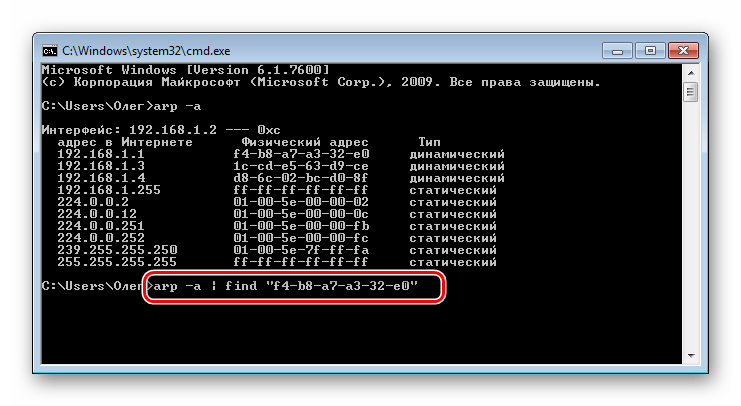
- Если список получился слишком длинный или вы хотите целенаправленно найти только одно совпадение, вместо arp -a после наполнения кэша следует ввести команду
arp -a | find "01-01-01-01-01-01", где 01-01-01-01-01-01 — имеющийся MAC-адрес. - Тогда вы получите только один результат, если совпадение будет найдено.
Читайте также: Как запустить «Командную строку» в Windows
Вот такое простое руководство поможет вам определить IP-адрес сетевого устройства с помощью имеющегося MAC. Рассмотренный способ требует от пользователя ручного ввода каждой команды, что не всегда удобно. Поэтому тем, кому нужно часто производить подобные процедуры, мы советуем ознакомиться со следующим методом.
Способ 2: Создание и запуск скрипта
Для упрощения процесса нахождения мы предлагаем воспользоваться специальным скриптом — набором команд, автоматически запускающихся в консоли. Вам потребуется только создать вручную этот скрипт, запустить его и ввести MAC-адрес.
- На рабочем столе щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и создайте новый текстовый документ.
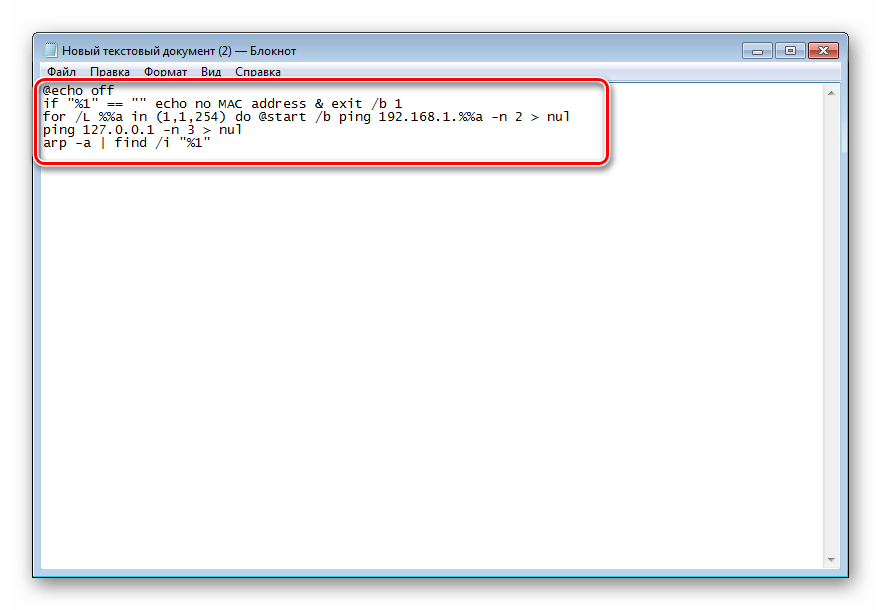
- Откройте его и вставьте туда следующие строки:
@echo off
if "%1" == "" echo no MAC address & exit /b 1
for /L %%a in (1,1,254) do @start /b ping 192.168.1.%%a -n 2 > nul
ping 127.0.0.1 -n 3 > nul
arp -a | find /i "%1" - Мы не будем объяснять значение всех строк, поскольку вы можете ознакомиться с ними в первом способе. Ничего нового здесь не добавлено, только оптимизирован процесс и настроен дальнейший ввод физического адреса. После ввода скрипта через меню «Файл» выберите пункт «Сохранить как».
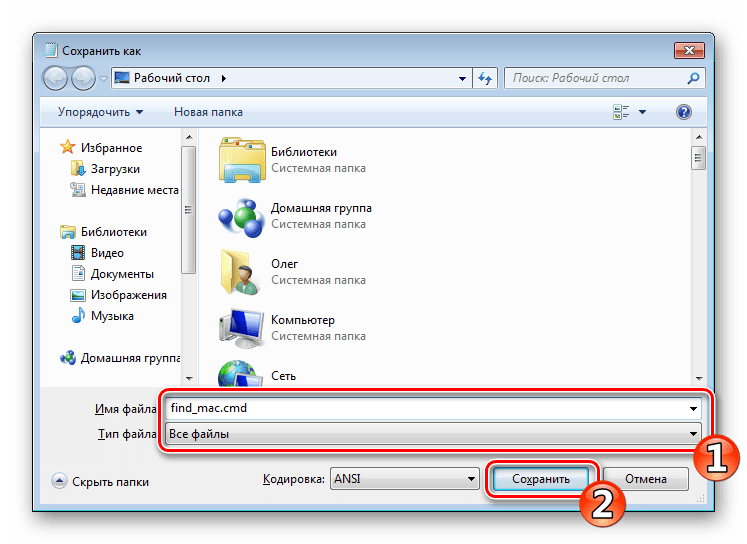
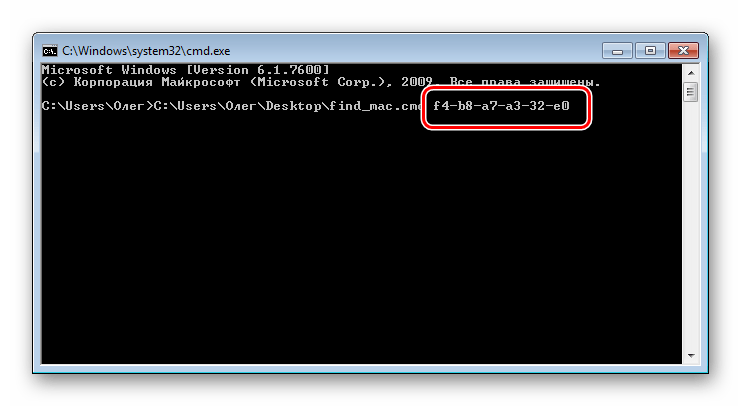
- Задайте файлу произвольное название, например Find_mac, и после названия допишите
.cmd, выбрав в поле ниже тип файла «Все файлы». В итоге должно получитьсяFind_mac.cmd. Сохраните скрипт на рабочем столе. - Сохраненный файл на десктопе будет выглядеть так:
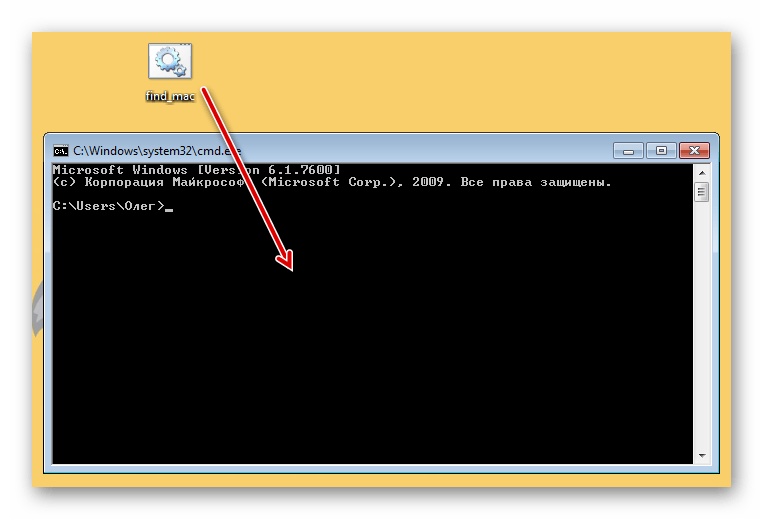
- Запустите «Командную строку» и перетащите туда скрипт.
- Его адрес добавится в строку, а значит объект успешно загружен.
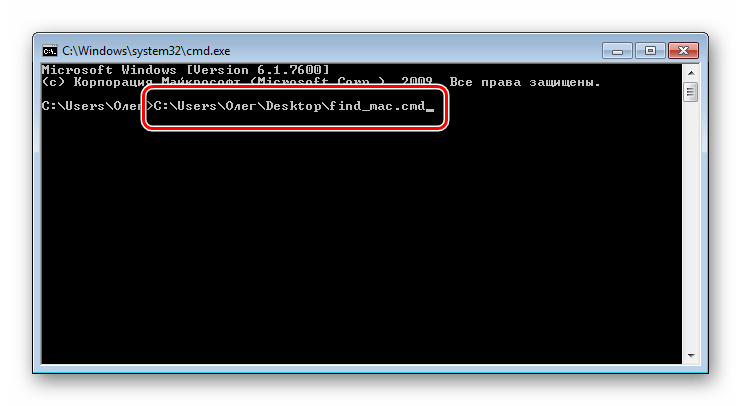
- Нажмите Пробел и впишите MAC-адрес в таком формате, как указано на скриншоте ниже, а затем нажмите на клавишу Enter.
- Пройдет несколько секунд и вы увидите результат.
Предлагаем вам ознакомиться с другими методами поиска IP-адресов различных сетевых устройств в отдельных наших материалах по следующим ссылкам. Там представлены только те способы, которые не требуют знания физического адреса или дополнительной информации.
Читайте также: Как узнать IP-адрес Чужого компьютера / Принтера / Роутера
Если поиск двумя приведенными вариантами не принес никакого результата, внимательно перепроверьте вводимый MAC, а при использовании первого способа не забывайте, что некоторые записи в кэше хранятся не более 15 секунд.
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
Pinging mac address is a great way to troubleshoot network connectivity issues. It’s a simple process that can help you determine whether a device on your network is responding as expected. Here’s a quick tutorial on how to Ping a mac address on a Mac or Windows computer:
-
First, open the Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on a Mac.
-
Next, you’ll need to find the MAC address of the device you want to Ping a mac address. You can usually find this information in the device’s settings, or by looking at the device itself (many devices will have the MAC address printed on a label somewhere).
-
Once you have the MAC address, you’ll need to enter the command to Ping a mac address. On Windows, the command is “ping -a [MAC address]” (without the quotes). On a Mac, it’s “ping -c 3 -s 56 [MAC address]” (without the quotes). The “-c 3” flag tells the ping command to send three packets, and the “-s 56” flag sets the packet size to 56 bytes.
-
Press enter and wait for the results. If the device is online and responding, you should see a response similar to this:
Pinging [MAC address] with 56 bytes of data:
Reply from [MAC address]: bytes=56 time=1ms TTL=128
Reply from [MAC address]: bytes=56 time=2ms TTL=128
Reply from [MAC address]: bytes=56 time=1ms TTL=128If you don’t get a response, it means that the device is not online or is not responding to ping requests. This could be caused by a number of things, like a network configuration issue or a problem with the device itself.
Keep in mind that pinging a MAC address only works on the local network, it won’t work if the device is outside of the network, it would require to ping the IP address instead.
That’s all there is to it! Pinging a MAC address is a quick and easy way to check the connectivity of a device on your network. Give it a try the next time you’re troubleshooting a network issue, and you’ll be able to narrow down the problem in no time.
Tools I use for this site
- I buy all my domain names on Namecheap, as thetrendycoder.com
- The hosting of this website is made on Bluehost.
- The website is created with WordPress.org (and not WordPress.com).
- I use the page builder Elementor because it makes it easy to create modern pages with drag and drop.
- I have multiple websites, and on most of them, I use themes from wpKoi. I love their design, they are very original and work well with Elementor.
- All the designs and images are created using canvas.
- I use Grammarly and languagetool to correct all my spelling and grammar mistakes.
- SEO is a big thing on a website, I use a WordPress plugin called YoastSEO to help me with the basic analysis. I also use a tool called Keysearch for choosing the right keywords.
- To handle affiliate links, I use two platforms: impact and ShareASale.
You want to write on TheTrendyCoder ?
If you are interested in publishing guest articles on this website, sharing your experience or coding tutorials, apply through this form.
NO EXPERIENCE needed!
NO PERFECT English needed!
NO DEGREE needed!
NO AGE limits!
No matter at what stage we are in our tech journey, we all have learned things and experienced things. Sharing them can help others and even help us. So, if you are a student, a professional, or a self-taught coder, feel at home and share some of your knowledge with the community.
Women in tech
More resources
More cheatsheets

Есть набор mac-адресов некоторого количества PC, как под Windows или Linux узнать их IP-адреса, если соединения с этими компьютерами ни разу не происходило и arp пуст?
p.s. Можно предложить вариант как для Linux так и для Windows, под рукой есть обе ОС
-
Вопрос задан
-
193715 просмотров
Можно попробовать вот так (для Windows, в консоли)
Запустите пинг на бродкастовый адрес вашей сети.
Например если у вас сеть 192.168.0.0 с маской 255.255.255.0, ваш адрес тогда будет 192.168.0.1-254, а бродкастовый — самый последний 192.168.0.255. Вот именно его нужно попинговать, потом дать команду
arp -a
Увидите все ip адреса в вашей сети с их маками. Ну а там уже найдете нужный.
Пригласить эксперта
ну и просто что бы было напишу:
В винде (не нужно ставить доп утилиты)
узнать мак по ip: nbtstat -A 172.28.22.190
узнать ip по мак: arp -a | grep 00-11-22-33-44-55 //естественно с ограничением пределами одной сети.
Еще вариант, пропинговать все адреса в сети (что-нибудь типа nmap -sP 192.168.1.1-254), а потом arp -an | grep %MAC%
Если соединения с этими компьютерами ни разу не происходило и arp пуст, то просканируйте Вашу локальную сеть самым простым icmp ping-ом, например nmap-ом; и на 15 минут в Вашей ARP таблице будет весело и жизнерадостно.
Для Windows нужно сделать bat файл назвать как вам нравится. Например ping-by-mac.bat
@echo off
if "%1" == "" echo no MAC address & exit /b 1
for /L %%a in (1,1,254) do @start /b ping 192.168.31.%%a -n 2 > nul
ping 127.0.0.1 -n 3 > nul
arp -a | find /i "%1"Потом запускаете данный bat файл с параметром
ping-by-mac.bat X1-X2-X3-X4-X5-X6
Всё.
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
10 окт. 2023, в 11:58
2000 руб./за проект
10 окт. 2023, в 11:57
300000 руб./за проект
10 окт. 2023, в 11:47
15000 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
- Forums
- Networking
- How To Ping By MAC Address? Ping Command Prompt
this article will demonstrate how you can ping a network device if you only have the MAC address of the hardware you are trying to ping without an IP address on the network using the most common tool in windows the DOS command prompt and in linux shell [3490], Last Updated: Thu Dec 29, 2022
Webune Support
Mon Jan 11, 2010
12 Comments
64961 Visits
Please follow these instructions to successfully ping a network MAC access. MAC Address means Media Access Control Address. The MAC address is an identifier for computer network hardware. It is a unique identifier set by the manufacturer and is permanently set into the hardware equipment. This identifier helps network communicate with each other. You can find MAC address on the following devices:
- Computers
- Smart Phones
- Enterprise Servers
- Industrial Equipment
- Internet Of Things
- WIFI
Today’s questions is regarding networking. the question is:
«is it possible to ping a device using only the mac address of the machine? or what tools I can use to check if a device is connected to the network»
ANSWER: the answer is no. IP Address is layer 3 of the OSI Model, and the MAC Address belongs to Layer 2
However, there is a way for example, if I have a network printer connected to my LAN but I can’t ping it. the printer may be in your network and you probably are just pinging the wrong ip address for that printer. so how do you find the correct ip address? this is what I would do
Go to the printer, usually devices will have the MAC ADDRESS printed on the back, so for example, lets say my printer has this MAC ADDRESS:
01-00-5e-7f-ff-fa
So what I can do is run the arp command. to run the arp utility, open your command terminal. I am using windows 7 for this tutorial, so I will use windows DOS terminal.
ARP COMMAND:
arp -a
It will give you a list of all the devices recorded in your computer:
This is the output on my computer:
C:\Users\MYPC>arp -a Interface: 192.168.0.2 --- 0xe Internet Address Physical Address Type 192.168.0.1 02-00-00-00-00-00 dynamic 192.168.0.255 ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff static 224.0.0.22 01-00-5e-00-00-16 static 224.0.0.252 01-00-5e-00-00-fc static 239.255.255.250 01-00-5e-7f-ff-fa static 255.255.255.255 ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff static Interface: 192.168.56.1 --- 0x12 Internet Address Physical Address Type 192.168.56.255 01-00-5e-7f-ff-fa static 224.0.0.22 01-00-5e-00-00-16 static 224.0.0.252 01-00-5e-00-00-fc static 239.255.255.250 ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff static
As you can see from the list, the device with 01-00-5e-7f-ff-fa is IP ADDRESS 192.168.56.1 so I can ping that device now.
MAC Address Quiz
Now that you know what a MAC address is and how you can ping. Are you ready for a quick quiz?
In this article, we’ll show you how to use a MAC address to locate devices and find IPs.
You might be in a situation where you don’t have the IP address of a device in a local network, but all you have is records of the MAC or hardware address. Or your computer is unable to display its IP due to various reasons, and you are getting a “No Valid IP Address” error.
This guide has three methods for finding IPs on your network; with ARP, with DHCP or by using a packet sniffer like Nmap.
IP and MAC Address Relationships
The Role of RARP
Finding the IP from a known MAC address should be the task of a ReverseARP application, the counterpart of ARP. However, RARP, due to its many disadvantages, became obsolete and was swiftly replaced by protocols like BOOTP and DHCP that directly interact with IP addresses.
Understanding ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
ARP is responsible for detecting MAC addresses associated with IPs in local network segments. It functions with frames on the data link layer. Notably, devices in this layer rely on MAC addresses for communication, and their frames encase packets rich with IP address data.
The Importance of MAC Addresses in Local Communication For local communication through media types like Ethernet or WiFi, a device needs to be aware of the destination MAC address, specifically in layer 2 of the OSI model. Grasping how ARP operates can streamline the process of identifying IPs and MAC addresses.
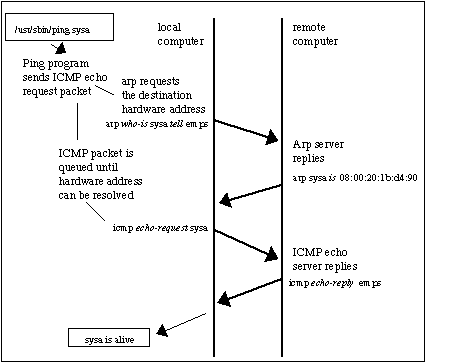
The following message flow diagram can help you understand the concept:
- The local computer sends a ping (ICMP echo request) to a destination IP address (remote computer) within the same segment. Unfortunately, the local computer does not know the MAC address… it only knows the IP address.
- The destination hardware address is unknown, so the ICMP echo request is put on hold. The local computer only knows its source/destination IP and its source MAC addresses. ARP uses two types of messages, ARP Request and Reply.
The local computer sends an ARP REQUEST message to find the owner of the IP address in question.
This message is sent to all devices within the same segment or LAN through a broadcast MAC (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) as the destination.
- Because the remote computer is part of the same network segment, it receives the broadcast message sent by the local computer. All other computers in the LAN also receive the broadcast but they know that the destination IP is not theirs, so they discard the packet. Only the remote computer with destination IP, responds to the ARP REQUEST with an ARP REPLY, which contains the target MAC address.
- The local computer receives the ARP REPLY with the MAC address. It then resumes the ICMP echo request, and finally, the remote computer responds with an ICMP echo reply.
Finding IPs with ARP
You can use ARP to obtain an IP from a known MAC address.
But first, it is important to update your local ARP table in order to get information from all devices in the network.
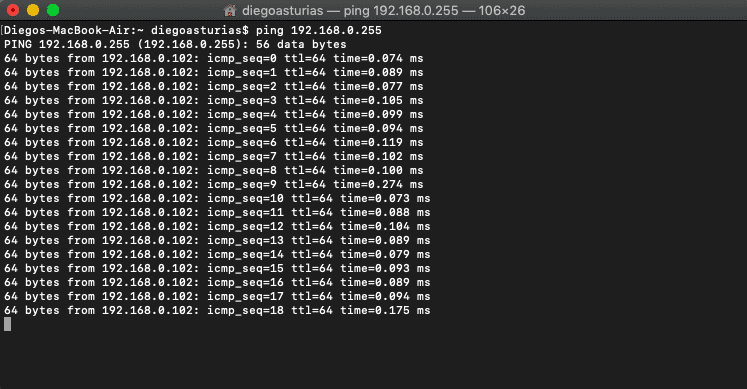
- Send a ping (ICMP echo reply) to the entire LAN, to get all the MAC entries on the table.
- To ping the entire LAN, you can send a broadcast to your network.
- Open the Command Prompt in Windows or terminal in macOS and type.
ping 192.168.0.255
My subnet is 192.168.0.0/24 (mask of 255.255.255.0), so the broadcast address is 192.168.0.255 which can be calculated or found with a “Print Route” command in Windows or a “netstat -nr” in macOS. Alternatively, it can also be obtained with a subnet calculator that you can download for free.
Free Subnet Calculator
100% FREE Calculator
For Windows:
Step 1
- Open the CMD (Command Prompt)
- Go to the “Start” menu and select “Run” or press [Windows-key] + [R] to open the Run application
- In the “Open” textbox type “cmd” and press “OK”.
This will open the command-line interface in Windows.
Step 2
- Enter the “arp” command.
- The arp command without any additional arguments will give you a list of options that you can use.
Step 3
- Use the arp with additional arguments to find the IP within the same network segment.
- With the command “arp -a” you can see the ARP table and its entries recently populated by your computer with the broadcast ping.
Step 4.
- Reading the output.
- The information displayed in the arp-a is basically the ARP table on your computer.
- It shows a list with IP addresses, their corresponding physical address (or MAC), and the type of allocation (dynamic or static).
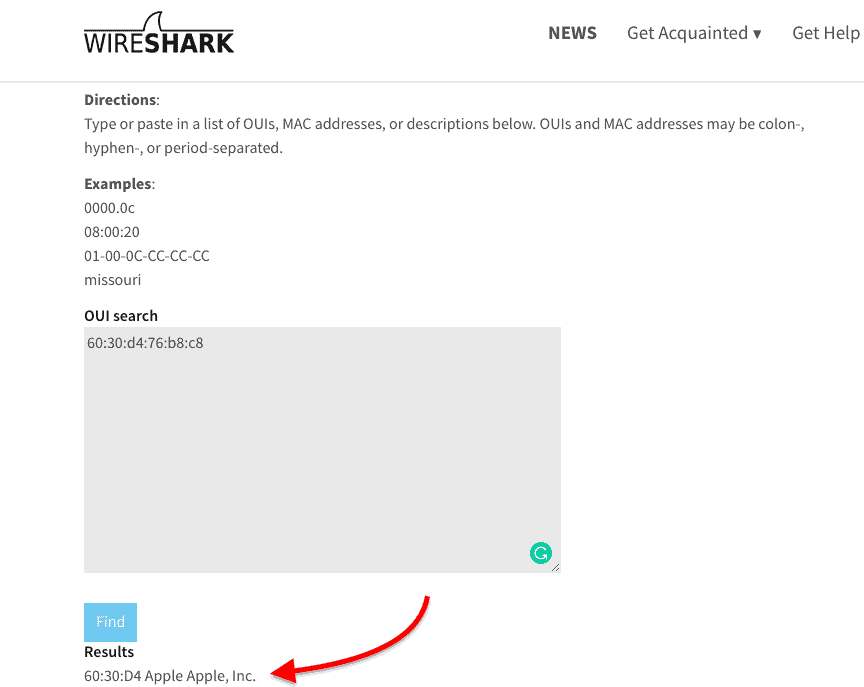
Let’s say you have the MAC address 60-30-d4-76-b8-c8 (which is a macOS device) and you want to know the IP.
From the results shown above, you can map the MAC address to the IP address in the same line.
The IP Address is 192.168.0.102 (which is in the same network segment) belongs to 60-30-d4-76-b8-c8.
You can forget about those 224.0.0.x and 239.0.0.x addresses, as they are multicast IPs.
For macOS:
Step 1
- Open the Terminal App. go to Applications > Utilities > Terminal or Launchpad > Other > Terminal.
Step 2
- Enter the “arp” command with an “-a” flag.
- Once you enter the command “arp -a” you’ll receive a list with all ARP entries to the ARP Table in your computer.
- The output will show a line with the IP address followed by the MAC address, the interface, and the allocation type (dynamic/static).
Finding IPs with the DHCP Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is the network protocol used by TCP/IP to dynamically allocate IP addresses and other characteristics to devices in a network. The DHCP works with a client/server mode.
The DHCP server is the device in charge of assigning IP addresses in a network, and the client is usually your computer.
For home networks or LANs, the DHCP Server is typically a router or gateway.
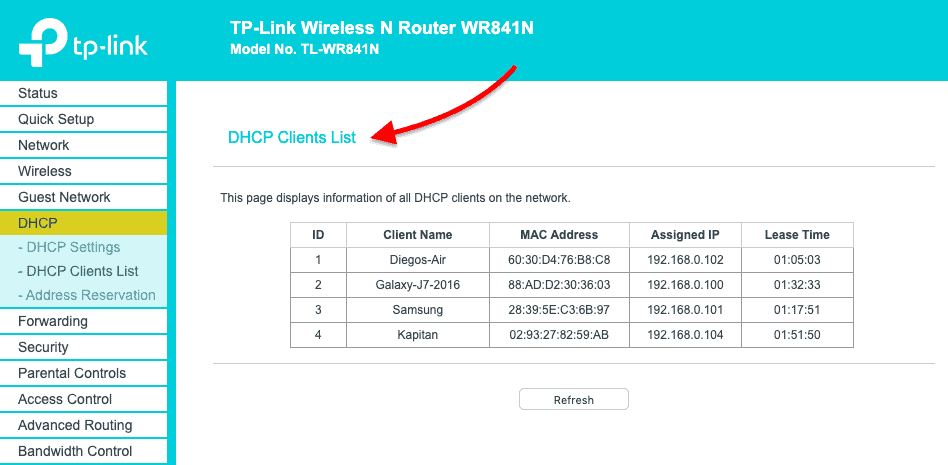
If you have access to the DHCP Server, you can view all relationships with IPs, MACs, interfaces, name of the device, and lease time in your LAN.
Step 1
- Log into the DHCP Server. In this example, the DHCP server is the home gateway.
- If you don’t know the IP address of your DHCP Server/ Gateway, you can run an ipconfig (in Windows) or ifconfig (in macOS/Linux)
- This particular DHCP Server/Gateway has a web interface.
Step 2
- Enter the IP address on the search bar of the web browser, and input the right credentials.
Step 3
- Find the DHCP Clients List.
- In this TP-Link router, the DHCP Server functionality comes as an additional feature.
- Go to DHCP > DHCP Clients List. From this list, you can see the mapping between MAC addresses and their assigned IPs.
Using Sniffers – Nmap
If you couldn’t find the IP in the ARP list or unfortunately don’t have access to the DHCP Server, as a last resort, you can use a sniffer.
Packet sniffers or network analyzers like Nmap (or Zenmap which is the GUI version) are designed for network security.
They can help identify attacks and vulnerabilities in the network.
With Nmap, you can actively scan your entire network and find IPs, ports, protocols, MACs, etc.
If you are trying to find the IP from a known MAC with a sniffer like Nmap, look for the MAC address within the scan results.
How to find the Device and IP with a Sniffer?
Step 1
- Keep records of your network IP address information.
- In this case, my network IP is 192.168.0.0/24. If you don’t know it, a quick “ipconfig” in Windows cmd or an “ifconfig” in macOS or Linux terminal can show you the local IP and mask.
- If you can’t subnet, Download this Free Subnet Calculator tool and find your network IP.
Step 2
- Download and open Nmap.
- Download Nmap from this official link https://nmap.org/download.html and follow its straightforward installation process.
Step 3
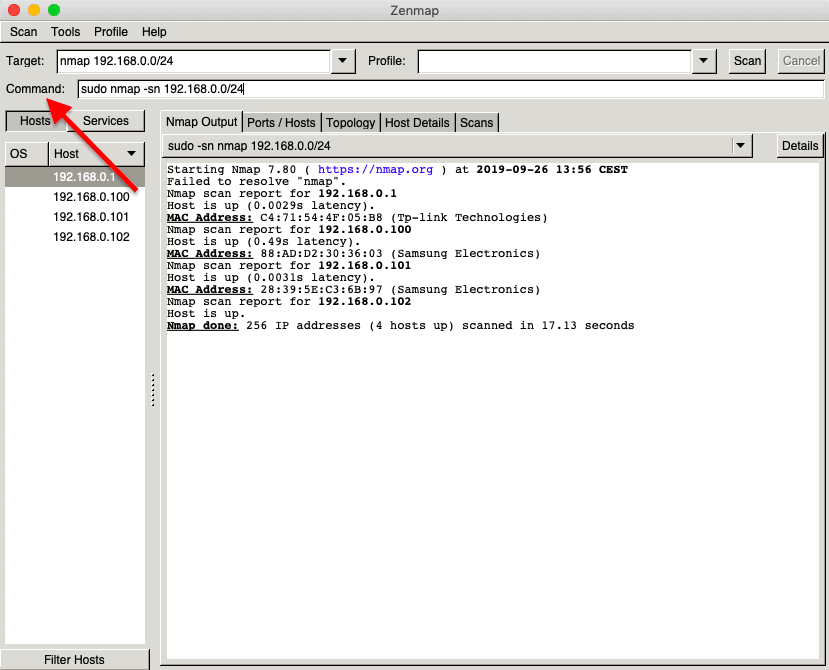
- Open Nmap (or Zenmap) and use the command “sudo nmap -sn (network IP)” to scan the entire network (without port scan).
- The command will list machines that respond to the Ping and will include their MAC address along with the vendor.
- Don’t forget the “sudo” command.
- Without it, you will not see MAC addresses.
Finding out the device vendor from a MAC address
Ok, so now you were able to find out the IP address using “arp -a” command or through the DHCP Server.
But what if you want to know more details about that particular device?
What vendor is it?
Your network segment or LAN might be full of different devices, from computers, firewalls, routers, mobiles, printers, TVs, etc.
And MAC addresses contain key information for knowing more details about each network device.
First, it is essential to understand the format of the MAC address.
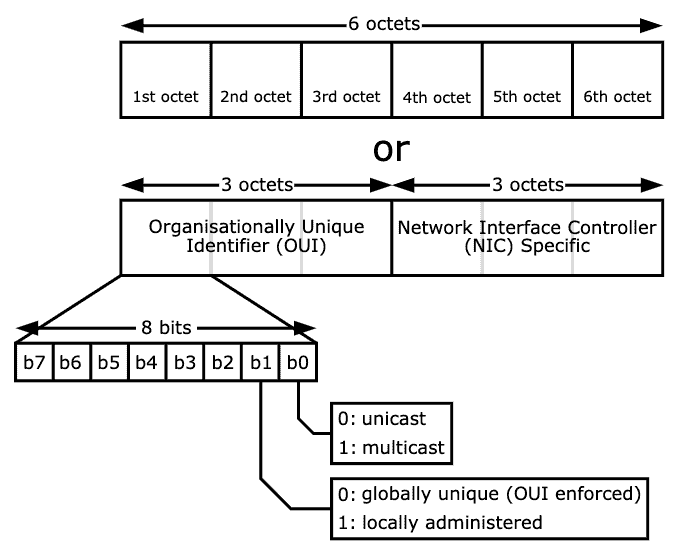
Traditional MAC addresses are 48 bits represented in 12-digit hexadecimal numbers (or six octets).
The first half of the six octets represent the Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI) and the other half is the Network Interface Controller (NIC) which is unique for every device in the world.
There is not much we can do about the NIC, other than communicating with it.
But the OUI can give us useful information about the vendor if you didn’t use Nmap, which can also give you the hardware vendor.
Using Wireshark OUI Lookup
A free online OUI lookup tool like Wireshark OUI Lookup can help you with this.
Just enter the MAC address on the OUI search, and the tool will look at the first three octets and correlate with its manufacturing database.
Using DHCP to view IP info
Although the RARP (the counterpart of ARP) was specifically designed to find IPs from MAC addresses, it was quickly discontinued because it had many drawbacks.
RARP was quickly replaced by DHCP and BOOTP. But ARP is still one of the core functions of the IP layer in the TCP/IP protocol stack. It finds MAC addresses from known IPs, which is most common in today’s communications. ARP works under the hood to keep a frequently used list of MACs and IPs.
But you can also use it to see the current mappings with the command arp -a.
Aside from ARP, you can also use DHCP to view IP information. DHCP Servers are usually in charge of IP assignments. If you have access to the DHCP server, go into the DHCP Client list and identify the IP with the MAC address. Finally, you can use a network sniffer like Nmap, scan your entire network, and find IPs, and MACs.
If you only want to know the vendor, an online OUI lookup like Wireshark can help you find it quickly.
Can you find an IP address from a MAC address?
Yes. Open a Command Prompt window and enter the command arp -a. The output shows all of the IP addresses that are active on your network. The next column in the output is headed Physical Address. This is the MAC address. Look for the line in the output that has the MAC address that you know and note down the IP address on that line.
How can I access a device by MAC address?
The easiest way to access a device, knowing the MAC address is to use the arp -a command to find the related IP address. With this address, you can access the device using Remote Desktop Management, a Telnet program, or some other connection facility.
How can I find a device by IP address? (cmd instructions)
You can follow a path to a device if you know its IP address by using the tracert command at the command prompt (cmd). Open a Command Prompt window and type in tracert followed by the IP address that you know. The output will show each router that has a connection to that device will pass through.