Художник думает рисунком (С. Дали).
Когда Microsoft анонсировала свой Windows Server 2019, многие из тех пользователей или компаний, которые в настоящее время пользовались версией 2016 года той же службы, столкнулись с серьезной загадкой, т.е. продолжать ли Windows Server 2016 или перейти на новую версию Windows Server 2019?
Очевидно, что такой значительный сдвиг потребует полного обновления текущих процессов, регулирующих версию 2016 года, и также потребует значительных затрат, поэтому было бы разумно выбрать вариант, если версия 2019 года дала бы какие-либо существенные преимущества, которые может лучше служить бизнес-целям фирмы.
Microsoft предоставила полный список продолженных, снятых с производства и недавно добавленных функций для версии 2019 по сравнению с версией 2016 года, но этот список был довольно сложным и не позволил понять основные различия между двумя версиями.
Вы еще можете купить Windows Server 2016 по относительно невысокой цене в отличие от Windows Server 2019.
Чтобы облегчить эту проблему и все же позволить вам сделать осознанный выбор по этому вопросу, мы прошли через все эти изменения и сосредоточились на четырех различных областях, где были внесены эти существенные изменения.
Вот эти четыре основных области:
Поддержка, предлагаемая для гибридного облака
Самым большим недостатком Windows Server 2016, который постепенно становился очевидным для большинства пользователей, было отсутствие поддержки гибридного подхода в отношении облачной миграции. Microsoft также поняла это и сделала версию 2019 года такой функциональной. Таким образом, вы можете гарантировать, что ваши облачные решения могут работать в тандеме с локальными ресурсами, чтобы обеспечить оптимизированную корпоративную среду, которая в высшей степени дружественна к облакам.
Если вы научились работать в сети с Windows Server 2016, вы были бы хорошо осведомлены о том, что эта версия поддерживает только облако для активного каталога, синхронизирует серверы для файлов и создает хранилища данных. Это ограничение было снято с версии 2019 года, и теперь вы можете легко использовать его для доступа к передовым облачным инструментам и технологиям, таким как ресурсы IoT.
Кроме того, версия 2019 поддерживает Project Honolulu, которая, если поддерживается Microsoft Azure, может обеспечить действительно гибкую и настраиваемую платформу для ваших нужд.
Добавление новых надежных функций безопасности
Server 2016 никогда не поддерживал виртуальные машины Linux, что было проблематично с точки зрения безопасности. Это также ограничивало возможности фирм использовать только экранированные виртуальные машины, что ограничивало их функциональную область. Версия сервера 2019 теперь добавляет поддержку виртуальных машин на основе ОС Linux с открытым исходным кодом.
Windows-сервер 2019 также выпустил новые функции, связанные с безопасностью, которые служат трехстороннему подходу, направленному на защиту и быструю идентификацию угроз для улучшения реагирования.
Защитник Windows Advanced Threat Protection — это также ориентированная на безопасность функция сервера 2019, которая позволяет ему стать гораздо более компетентной платформой, когда речь идет о защите системы от исходящих угроз.
Изменения в положениях на основе приложений
Когда Windows Server 2019 собирался дебютировать, у разработчиков было много ожиданий, связанных с ним, и Microsoft, конечно, не разочаровалась, поскольку одно из ее основных улучшений появилось в области серверов Windows.
Контейнеры Windows Server оказались чрезвычайно эффективными для повышения эффективности процесса разработки, когда они входили в состав Windows Server 2016. Но теперь образ контейнера может вместить базовое ядро сервера гораздо меньшего размера, чем было. Это возможно в Windows 2016, что делает его невероятно гибким и ориентированным на разработку ресурсом для новых групп разработчиков DevOps на предприятиях, которым требуется гибкость в создании приложений.
Обновленная поддержка развертывания HCI
Это немного сложнее, поскольку развертывание Hyper-Converged Infrastructure также поддерживалось сервером Windows 2016, но затем этот сервер позволил малым предприятиям использовать его в доступном диапазоне.
На этот раз функции значительно улучшились, поскольку теперь вы можете повысить гибкость, повысить производительность и получить более надежный ресурс для запуска HCI, но эти функции принесут пользу бизнесу только в том случае, если он работает на более крупной платформе. масштаб, делая эту функцию за пределы для малых и средних корпораций.
Стоит ли принимать обновление Windows Server 2019?
Обновление с Windows до версии 2019, безусловно, принесло в свой основной пакет обновлений некоторые заметно продвинутые и мощные функции. От гораздо лучшей поддержки для развертывания HCI до введения ATP, версия Windows Server 2019, безусловно, намного больше подходит для современных ИТ-потребностей. Если сравнивать его с 2016 годом, он, безусловно, более безопасен и удобен для разработчиков, чем его предшественник.
Тем не менее, стоимость по-прежнему остается основным предметом спора, так как Microsoft недвусмысленно упомянула, что лицензирование клиентского доступа Windows Server теперь будет иметь повышенную цену. Это затрудняет выбор малого бизнеса для принятия решений, что делает область операций сервера Windows 2019 крайне ограничивающей для отраслевых вертикалей.
Кроме того, для запуска версии 2019 важно, чтобы ИТ-группа получила сертификаты относительно версии 2016 года, поскольку большинство предшествующих технологий на сервере 2019 продолжают работать в том же рабочем формате, что и сервер 2019. Если вы выполнили установку для хранилища MS 20740 и рассчитать с сертификацией Windows Server 2016 , вы, вероятно, не столкнетесь с трудностями при запуске установки сервера 2019, так как большинство платформ остаются одинаковыми в обеих версиях.
Завершение дела
Различия между двумя версиями довольно разнообразны, и анализ отдельных элементов остается за рамками этой статьи. Поэтому вместо этого мы решили представить только сравнение основных функций этого обновления.
Но какой из них лучше? Ну, нет однозначного ответа на этот вопрос, так как различные потребности бизнеса могут изменить способ восприятия и оценки новых обновлений для каждой проблемы. Если вы хотите сделать скачок, то ATP, а также предоставление облачной поддержки гибридной модели, являются двумя наиболее важными факторами, которые могут принести большую пользу вашему бизнесу, приняв версию Windows Server 2019.
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
474 просмотров
Windows Server 2016 vs 2019
Windows Server 2019 is the latest version of Microsoft Windows Server. The current version of Windows Server 2019 improves on the previous Windows 2016 version in regards with better performance, improved security, and excellent optimizations for hybrid integration. Apps4Rent compares both the versions – Windows Server 2019 vs 2016 – in a comparison table below:
Need help in migrating Windows Servers?
Over 10,000 migrations performed by Microsoft-certified experts.
- ✓ Free consultation call
- ✓ 24/7 Support by Windows experts
- ✓ Fully managed servers
Windows Server 2016 was, at the time, the fastest and most advanced server that Microsoft ever produced. However, Server 2019 has improved performance over Server 2016 in multiple areas. Quite a few features have been added, a number have been improved upon, and some aspects have been removed. As luck would have it, all the new features are covered in our Windows Server training.
Because the previous version was so solid and the newest version has quite a few improvements and new features, many administrators are asking which is better: Server 2016 or Server 2019?
Windows Server 2016 vs Server 2019: What’s New?
Microsoft focused on a few critical areas in their most recent release. New features in Windows Server 2019 include improved security and better enabled hyper-convergence. Some of the major improvements Server 2019 has over 2016 are facilitating a hybrid platform that can easily work with on-prem resources and the cloud simultaneously, as well as improving the main areas comprising the application platform. These categories are some of the biggest Windows Server 2016 vs. Windows 2019 differences.
Storage Migration Service
One of the challenges Microsoft and consumers alike face is maintaining legacy systems that have far outlived their usefulness. This eats up resources while compromising overall security. However, upgrading to new systems can seem difficult and cost-prohibitive to many users.
Several years ago, administrators were really kicking the tires of Server 2019. A brief glance at IT discussion boards at that time shows the same question that’s being asked today about Server 2019 — is it worth it?
This year, Microsoft introduced Storage Migration Service, a tool that facilitates migration to Server 2019 from every version of Windows Server dating back to 2003. Although mechanisms that allow file copying and transfer have existed for years, administrators have never before had access to a tool that fully automated the process of migrating files, shares, permissions, and the identity of an old server onto a new one.
This corresponds with improvements in Storage Replica, a feature that facilitates replicating a storage logical unit number (LUN) between servers. Windows Server 2019 Standard Edition doesn’t require a Windows Server Datacenter license, allowing you to replicate storage volumes that contain up to 2TB of data at a time.
System Insights
Machine learning and artificial intelligence have come a long way in a short time, and Server 2019 enhances performance over Server 2016 with a System Insights module. It’s easy to review a system log of past events, and administrators have been able to view live occurrences for years. With this module, however, the server also looks to the future, analyzing the platform for issues before they happen. This limits downtime, reduces crashes, and can preclude potential security issues.
Systems Insights builds on the Windows Admin Center, where Server 2019 has improved over Server 2016. With 2019, you can check the status of latency, storage, cluster CPU, and IOPS in real-time, giving unprecedented visibility into your systems’ operating environment and health.
Azure Network Adapter
When the cloud was first introduced, it was met with an odd mixture of responses. Many believed that it would completely replace on-premises data centers, but server technology continued to be geared toward the latter. Over the past few years, the strengths and weaknesses of both cloud and on-prem resources have become more evident. There’s a cornerstone role for both, and neither is going anywhere.
This required a server designed around facilitating the seamless integration of both technologies, and Server 2019 is able to do that much more efficiently than Server 2016. The Azure Network Adapter automates the creation of a VPN tunnel between an on-prem Windows Server 2019 and a cloud-based Azure environment. Although administrators could do this manually before, it wasn’t the most natural process. Performance and security in Server 2016 were less optimal than what Server 2019 offers. This automated network adapter takes the hassle out of the entire situation, effortlessly incorporating the two for the highest security and performance levels.
Cluster Sets
With the combination of cloud and on-prem technology, drastically increased deployment of virtual machines, and the need to access massive data sets stored across numerous drives, clusters have become more and more critical. While Server 2016 heavily emphasized clusters, Server 2019 introduces the concept of Cluster Sets, which are essentially clusters of clusters.
This large-scale application of the cluster concept improves the availability of applications and data while emphasizing resiliency across the entire system, making Windows Server 2019 a much better choice than 2016. Cluster Sets are geared for high growth, providing an extremely efficient way to scale without compromising performance.
Persistent Memory
Drastically increased data storage is one thing, but the ability to rapidly access that data is another. Persistent Memory, or PMem, is Microsoft’s solution — and it’s impressive. At Microsoft Ignite 2018, the latest version of Windows Server demonstrated an astounding latency of fewer than 40 microseconds, even when performing as many as 13.8 million input/output operations per second (IOPS). Windows Server 2019 vs. 2016 performance is more than double the prior industry benchmark of 6.7 million IOPS, and it required a mere 12 server nodes.
In addition to its speed, one of PMem’s most notable features is its resiliency. This non-volatile RAM maintains its contents through both scheduled and unexpected power cycles, which is why it’s often referenced as «storage-class memory.»
Virtual Network Peering
While the cloud has drastically improved network flexibility and functionality, it has come at a cost. When dealing with a public cloud and multi-cloud world, the devices you’re using can continually shift between any number of racks, cages, or datacenters. You might even have reoccurring migrations between regions and hosting providers, which triggers a tremendous amount of effort by network administrators to address, readdress, and update device tables just to maintain a functioning network.
Depending on your setup, Vnet Peering functionality is somewhat limited to resources in the same cloud region or even datacenter. Even with these constraints, however, the consistency in virtual networks with Server 2019 represents a substantial improvement over Windows Server 2016.
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) with Leap Second
This is a specialized feature that isn’t necessary for the majority of users, but it’s a game changer for those who need it. Some industries and applications require absolute precision timekeeping, down to the microsecond. While Server 2016 was accurate, 2019 is much better. PTP is a protocol that permits network devices to compile the latency added by each network device into timing measurements, resulting in the most accurate time tracking possible.
Another new feature, Leap Second, tracks the rotation of the earth and adds leap seconds to compensate for any resulting changes.
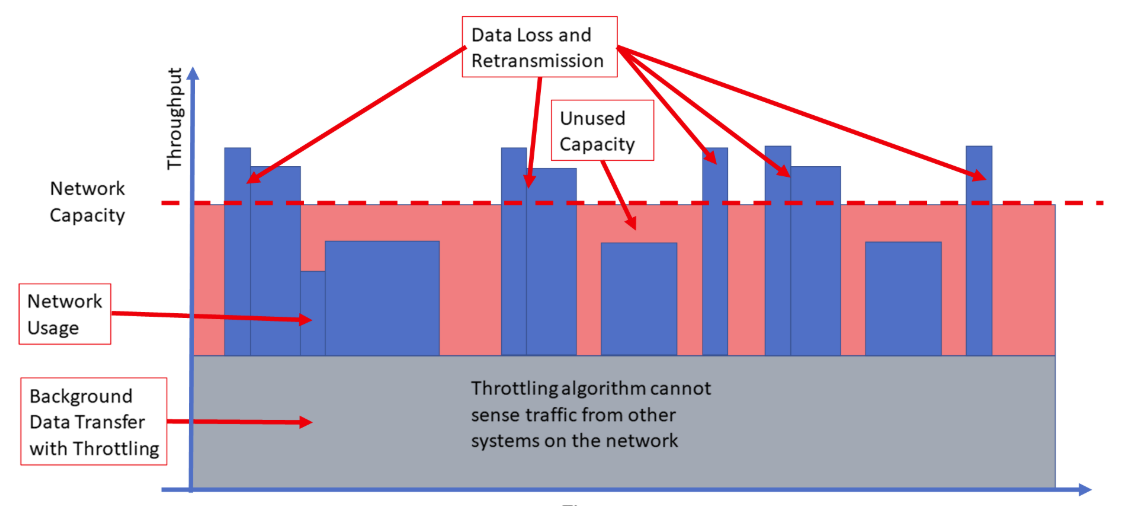
Low Extra Delay Background Transfer (LEDBAT)
Managing bandwidth and minimizing network congestion isn’t a new battle for network administrators, but current tools have substantial limitations. For example, throttling outlines the maximum bandwidth permitted for a specific purpose, and those limits can’t be exceeded even when the entire bandwidth is unused and available. Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) employs Adaptive Bit Rates (ABRs) to decide what level of bandwidth is available to lower priority traffic. Although useful, it can take quite a few adjustments to dial in the settings correctly, and each change introduces a delay.
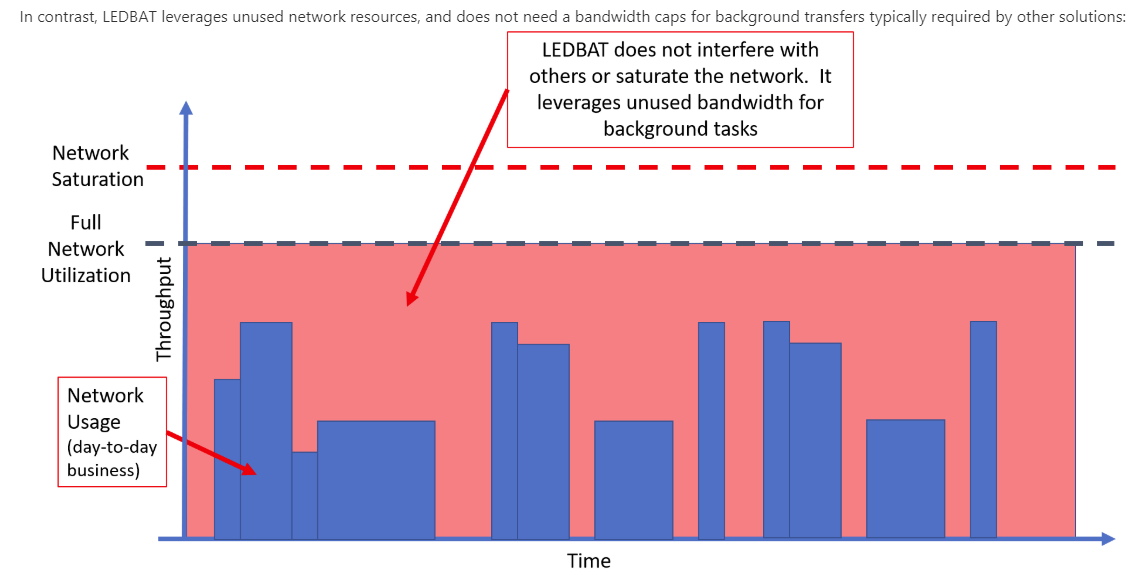
LEDBAT is a network congestion controller that manages available bandwidth for users and applications in real-time, then consumes the entire bandwidth when a network isn’t in use. It’s referred to as a scavenger protocol because it actively searches for any available bandwidth on the network and puts it to use.
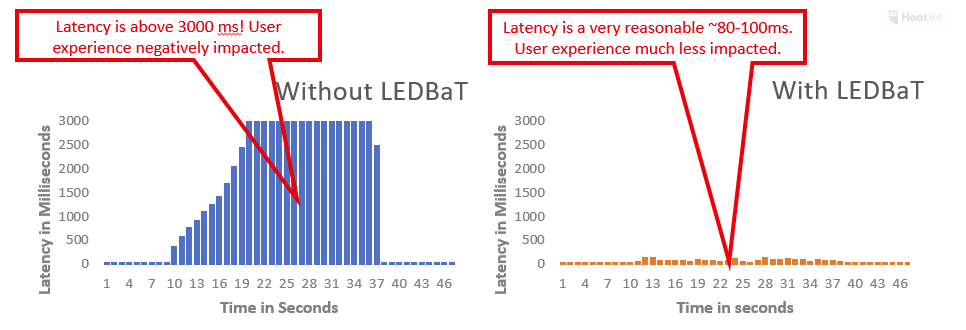
Latency is a critical concept in user satisfaction, and LEDBAT makes a remarkable difference. In the tables below, the same network traffic is shown with and without LEDBAT optimization in place. As you can see, the user experience is night and day.
Shielded Virtual Machines: Linux Expansion and HGS Offline Mode
Until now, shielded VMs were only available for Windows. With Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V technology, expanded support is now available for shielded VMs to Linux. This drastically expands network flexibility if you have Linux VMs, permitting secure data without loss of performance for both operating systems on the same network.
One of the most noticeable Server 2016 vs. 2019 differences is that Server 2019 introduces the capability to host virtual machines offline, allowing you to shield them as long as the Hyper-V host’s security hasn’t changed.
Enhanced Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection
When it comes to security, Server 2019 vs. 2016 isn’t even a contest. The newest security set included with Windows Server 2019 provides an array of intrusion prevention capabilities, such as attack detection, zero-day exploits, and preventative protection. Expect Breach is one feature that constantly monitors areas that have been identified as vulnerable to detect a breach instantly if one occurs.
Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK)
The demand for increased media resolution has driven the evolution from high-definition to 4K, and the industry is already preparing for the next leap into 8K resolution. Real-time multiplayer gaming and augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) will only drive the demand for resolution higher. Cisco estimates that IP video traffic will comprise an astounding 82 percent of all consumer internet traffic by 2021.
Facilitating this while maintaining an operational network requires high bandwidth and low latency, necessitating a modified approach to network architecture. This need is met by mating DPDK libraries with Windows Server, which bypasses the host networking stack and emphasizes fast packet processing capabilities by user-mode applications. Until now, DPDK was exclusively available on Linux, but Windows 2019 vs. 2016 Server provides a tremendous boost in flexibility.
Server 2019 Improvements Over Server 2016
When you’re looking at Windows Server 2016 vs. 2019 differences, the benefits aren’t limited to new features. Although Server 2019 introduces an impressive array of new capabilities, the improvements on existing functionalities is equally remarkable.
Container Networking with Kubernetes
In recent years, application modernization using containers has become increasingly popular. As applications are moved from virtual machines to containers, being able to exercise network management agility takes on critical importance. Windows Server utilizes Kubernetes to orchestrate this via an open-source, standardized framework, and Server 2019 noticeably increases usability over Server 2016 in two ways.
First, enhanced platform network resiliency is a cornerstone concept in 2019 and positively impacts container employment. Second, the support of container networking plugins has been increased, providing greater flexibility than 2016 had across a variety of user requirements.
Improved Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
Virtual machines have continued to grow in popularity and utility, requiring servers to evolve in ways that continue to support this technology. S2D is the primary software-defined solution Microsoft uses for hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) deployments. It sets aside local storage space in each individual server, then aggregates that space in a distributed storage system to facilitate the employment of virtual machines.
Critical upgrades for Server 2019 include 64TB of space per volume and an astounding 4PB of space per storage pool. Microsoft has also streamlined the ability to monitor and manage S2D through the Windows Admin Center, enabling the functionality to increase simultaneously with storage upgrades.
Resilient File System (ReFS)
The amount of data we digitize and constantly reference has increased exponentially, and so has the way we handle it. Limited storage space on single drives has evolved into massive storage distributed among sizeable arrays of disks. Microsoft previously utilized NTFS to manage files, but by Server 2012, this system had become outdated, leading to the inaugural version of the Resilient File System.
ReFS was designed to be self-repairing and facilitate virtualization between physical disks and logical volumes. The earliest versions offered some improvement over NTFS but were slower in many respects. Server 2016 addressed these issues, implementing ReFS in a highly improved and fully functional approach to file storage. Server 2019 built on that foundation to emphasize two crucial improvements: deduplication and compression. Although Server 2016 was functional, Server 2019 fully supports both processes and eliminates a few persistent bugs 2016 had.
Cloud Witness
This high availability feature employs failover clusters stored in the Azure cloud platform to ensure continued operation if a site outage occurs. In Server 2016, Cloud Witness required a cluster name object (CNO) with an Active Directory account to access this feature. Server 2019 is an improvement over 2016 Cloud Witness functionality, eliminating this requirement and permitting a local user account on the Windows Server to employ failover clusters.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Gateways
Although SDN has been around for a while, its importance is only increasing. Software-defined networking frees a network from its physical constraints by abstracting it, overlaying an SDN on top of the underlying physical cable, VLANs, and gateway addresses. This allows for rapid design, deployment, and adjustment of the network without requiring any material change, drastically improving network deployment speed, security features, and various automation capabilities.
Server 2019’s gateways boast substantial speed improvements over Windows Server 2016 that can be as much as three times faster, depending on your application. Microsoft’s most recent release also supports IPv6 and dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 addressing, permitting encryption for all traffic on your virtual network.
Virtual Network (Vnet) Encryption
Traffic encryption has typically been done at the application layer, but Server 2019 expands 2016’s ability to encrypt traffic between virtual machines. It’s now built into the operating system as a foundation of server, application, and hypervisor communications. Network administrators can protect all subnet communications between host servers, automatically encrypting all network traffic that occurs under that umbrella.
This provides increased efficiency and performance when more web frontend and backend databases need to be added because they join the same encrypted communication stream that’s already been established. Securing comms at the network level rather than the application level is a substantial improvement in encrypted network performance.
Dynamic Virtual Machine Multi-Queue (d.VMMQ)
VMs need the highest level of throughput possible. As network interface cards have gotten faster, the level of processing required to facilitate low-latency network traffic began to exceed what a single CPU could facilitate. Server 2019 introduces Virtual Machine Multi-Queue, which is an improvement over Server 2016’s Virtual Machine Queue, so traffic can be processed by multiple processors.
Although the capability for this technically existed previously, it was a labor-intensive manual effort that required quite a bit of planning, monitoring, establishing baselines, and constant tuning to achieve the optimal effect. With d.VMMQ, that entire process is automated and is designed to autotune to the existing workload. After a supporting driver has been installed, no further setup is required.
What’s Gone with Windows Server 2019?
Along with the tremendous number of new and improved features, Server 2019 has removed several aspects of Server 2016. Although these are reasonable adjustments, if you’re migrating from Server 2016 and your infrastructure employs any of the below features, it’s good to know they won’t be available before you begin updating your server.
Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS)
Interaction between iSNS servers and clients has traditionally used this feature, but Server Message Block has replaced it. SMB was initially introduced in Server 2012, and its functionality has increased to the point where it can do everything iSNS could and more.
Print Components for Server Core
In nearly all previous versions of Windows Server, these print components were disabled by default. In Server 2016, Microsoft changed the default settings to enabled. This didn’t prove to be useful, so one of Server 2019’s differences over 2016 was reverting to a default disablement. If you need these components, however, you can run a commandlet to enable them.
Business Scanning/Distributed Scan Management
This feature was introduced in Server 2012 and required that scanners support it. The tech is now outdated, and no scanners currently support it, so it has been removed.
Remote Desktop Connection Broker and Virtualization Host in Server Core Installation
Microsoft found that these features weren’t useful in most server configurations. As a result, they’re not included by default in any version except Windows Server with Desktop Experience, but can be installed if you need them for your Remote Desktop infrastructure.
Which is Better: Server 2016 or Server 2019?
Windows Server 2019 has been widely praised within the IT community as a substantial improvement over Server 2016. Increased security, decreased latency, and a vastly improved suite of tools to facilitate hybrid platforms are phenomenally useful assets. All in all, this is definitely a win for information technology.
have already written new features of Windows Server 2019 on my previous article which detailed the list of features available on Windows Server 2019, now want to compare the difference between Windows server 2016 and 2019, will list difference
Also Read: Windows Server 2019 Features
Comparison of Windows server 2016 vs 2019
Below features are only available on Windows server 2019 compared to Windows server 2016
Also Read: Windows server 2016 co-existence and migrate/upgrade scenarios with Windows server 2012 R2/2008/2003
Azure hybrid capabilities
System Insights – the built-in tool which pre-actively analysis the system data and alert the findings
Azure network adaptor – Used to connects to Azure virtual networks
Nested Mirror Accelerated parity – Two-node clusters which provide fault tolerance
USB thumb drive as cluster witness – USB drive can be used as a cluster witness which allows true two node HCI deployments
Deduplication for ReFS – This will save 90% disk space using de-duplication
Also Read: Nano Server Features and Benefits
Cluster-wide monitoring – Monitor real time system performance related to Cluster
Cluster sets – Now we can create large scale Cluster
Persistent memory – PM provides byte level access to non-volatile memory to improve performance
Virtual network peering – Now we can connect two virtual networks with High speed connectivity
Improved SDN gateway – Improved site to site VPN connectivity
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) – Replacement for NTP (Network Time Protocol)
Leap Second support – Now Windows support the leap second changes
Latency Optimised Background Transport (LEDBAT) – LEDBAT network bandwidth management
Also Read: Difference between windows server 2008 and 2012
Security Capabilities
Enhanced Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) – ATP now uses preventative protection, attack detection, and zero-day exploits
Shielded VMs for Linux – More secure VMs
HGS offline mode for shielded VMs – shielded VMs are more secure event HGS cannot be reached
VM Connect for shielded VMs – Easy to manage shielded VMs
Cluster hardening – Now Cluster works without NTLM
SDN encrypted subnet – secure encrypted communication between VMs that communicate with each other within subnets
Also Read: Windows Server Containers Features on Windows Server 2016
Container Capabilities
Linux containers – Now we can manage Windows and Linux applications on the same environment
Server Core base container image – Reduced container image size
Server Core Features on Demand (FoD) – Improved application compatibility
Kubernetes platform support – Improves computing, storage, and networking components
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) – Use Windows tools like Command Prompt and PowerShell from Linux
And Storage Migration Service – migrate the existing server to new hardware or new Operating system version
Also Read: Virtualized Active Directory without Physical Domain Controller
Also Read: Active Directory (AD) Real Time Interview Questions and Answers
With the introduction of Windows Server 2016 and now 2019, many businesses are looking at upgrading their infrastructure to use the latest versions of Windows Server operating systems.
If you are running a legacy version of Microsoft Windows Server like Windows Server 2008, it is imperative that you upgrade now to avoid being in an unsupported state. Either Windows Server 2016 or 2019 would be a major step up in terms of features, functionality, supportability, and many other facets.
However, the question remains – Windows Server 2019 vs 2016, how to choose? It can depend on what you want and expect from Windows Server. However, let’s take a look at Windows Server 2019 vs 2016 and see what features might help make the difference in your decision.
Windows Server 2019 vs 2016 – Feature Comparison
When it comes down to Windows Server 2019 vs 2016, it becomes a comparison of features that makes the difference between the two. Generally speaking, with each new version of Windows Server, it contains all the features and capabilities of the previous version while extending and adding to these.

Windows Server 2019 is certainly the most fully-featured Windows Server operating system to date and provides the best Windows Server operating system for cloud solutions and provides the best integration with Azure when compared to Windows Server 2016.
Let’s look at the following features of Windows Server 2019 that may make the difference in choosing it over Windows Server 2016.
- Storage Migration Service
- System Insights
- Azure Network Adapter
- Better Storage Spaces Direct
- Better Storage Replica
- Deduplication for ReFS
- Enhanced Cloud Witness
- Cluster-wide Monitoring
- Cluster sets
- Persistent Memory
- Virtual Network Peering
- Improved SDN gateway
- Precision Time Protocol including Leap Second
- Latency Optimized Background Transport (LEDBAT)
- Improved SDN
- Shielded VMs for Linux
- HGS Offline Mode for Shielded VMs
- HGS Secure Connect
- Enhanced Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP)
1. Storage Migration Service
The Storage Migration Service is one of the best tools moving forward for those who are looking to migrate off their current legacy server platform to a newer Windows Server. Microsoft is serious about helping customers get to a supported version of Windows as this new tool supports Windows Server all the way back to Windows Server 2003. Read more in our walk through of Storage Migration Service.
2. System Insights
Microsoft is also serious about introducing predictive analysis to Windows Server in Windows Server 2019. With the new System Insights module in Windows Admin Center, you can view predictive analysis of the health of your Windows Server 2019 platform. Powered by machine learning, it intelligently analyzes the platform for issues before they happen.

3. Azure Network Adapter
Creating a VPN connection between your on-premises environment and your Azure environment can be difficult when left to be configured manually.
With Azure Network Adapter inside of Windows Server 2019 and powered by Windows Admin Center, it allows easily creating a VPN tunnel between your Windows Server 2019 installation and your Azure environment.
This highly software-defined solution allows network connectivity to Azure to seamlessly be an extension of your on-premises network without the hassle of fancy networking configurations needed. Take a further look at how to Install and Configure Azure Network Adapter here.
4. Better Storage Spaces Direct
Storage Spaces Direct is Microsoft’s software defined solution for HCI deployments. It allows making use of local storage in each Windows Server and aggregating the storage together for a distributed storage system that can be used for virtual machines.
Windows Server 2019 contains the latest version of S2D that provides many additional benefits. This includes a 4PB per storage pool and 64TB per volume in Windows Server 2019.
Additionally, with Windows Admin Center, the functionality to manage and monitor S2D in Windows Server 2019 is much better. Take a look at how to Create Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Volumes in Windows Admin Center.
5. Better Storage Replica
Storage Replica is a feature that allows replicating an entire storage LUN from one server to another server. This is at the block-level and does not depend on a particular storage vendor to implement. You can replicat your data either asynchronously or synchronously.
With Windows Server 2019, you no longer need the Windows Server Datacenter license. You can replicate one storage volume with up to 2 TB of data in Windows Server 2019 Standard Edition. Look at Storage Replica in Windows Server 2019 Features and Configuration.
6. Deduplication for ReFS
ReFS for Windows Server 2016 introduced an entirely new level of ReFS that had even more powerful features. However, one of the hindrances to ReFS adoption with Windows Server 2016 was the lack of deduplication.
However, Microsoft has now solved this issue with ReFS in Windows Server 2019 ReFS. Now, deduplication and compression are both supported. This latest version takes virtual machine storage possibilities to new heights. Take a look at When to use Windows Server 2016 ReFS.
7. Enhanced Cloud Witness
Cloud Witness enables Azure blob storage as a witness in a Windows Server Failover Cluster for quorum for a stretched cluster. Windows Server 2019 extends the cloud witness functionality in that you can now create a file share witness not requiring the Cluster Name Object (CNO), but rather using a local user account on the Windows Server the file share witness is connected to.
8. Cluster-wide Monitoring
With Windows Server 2019, you can now in real-time check the status of cluster CPU, IOPS, latency, storage, and other metrics with real-time alerting, etc. In conjunction with Windows Admin Center, the monitoring and statistics available to you gives extreme visibility to the environment.
9. Cluster Sets
Cluster sets are a new technology introduced with Windows Server 2019 that allows you to have large scale-out sets of clusters. Think of cluster sets as a cluster of clusters.
Cluster sets allow you to exponentially increase your resiliency and availability of your applications and data. If you are looking to have the most effective way to scale out, cluster sets are a really powerful new architecture.
10. Persistent Memory
Windows Server 2019 provides support for persistent memory (PM) technology. Persistent memory provides increased storage speeds in orders of magnitude over current storage technologies.
When thinking about the fastest access to data for applications that are data base driven as an example, persistent memory provides very exciting capabilities.
11. Virtual Network Peering
Windows Server 2019 virtual network peering provides high speed connectivity between two virtual networks. With this new technology, traffic between the virtual networks does not need to traverse a gateway, but instead simply is communicated between the underlying fabric. The two virtual networks need to be part of the same datacenter stamp.
12. Improved SDN gateway
If you are using SDN gateways in your environment, Windows Server 2019 provides leaps and bounds better performance. It boasts improvements up to 3x for GRE tunnels and IPSec site-to-site VPN.
This will definitely be a selling point for deploying Windows Server 2019 instead of 2016 in your environment.
13. Precision Time Protocol including Leap Second
Are you in an industry where seconds and even fractions of a second count? Windows Server 2019 offers a tremendous step up in terms of accurate time keeping.
It introduces what is known as Precision Time Protocol (PTP). This new time keeping protocol enables network devices to add the latency introduced by each network device into the timing measurements. This produces a far more accurate measure of time when compared to the standard NTP protocol.
Windows Server 2019 even introduces what is know as Leap Second support. As the earth’s rotation slows, leap seconds may need to be added to compensate. Windows Server 2019 supports this additional time accuracy provision.
14. Latency Optimized Background Transport LEDBAT
Latency Optimized Background Transport – LEDBAT is a new network congestion control provider. Low Extra Delay Background Transfer (LEDBAT). It automatically provides bandwidth to users and applications, while consuming the entire bandwidth available when the network is not in use.
15. Improved SDN and Encrypted Networks
Software defined networking in Windows Server has had a long way to come. However, Windows Server 2019 has made great improvements in the SDN features provided with Windows Server.
Windows Server 2019 now supports IPv6 and dual stack IPv4/IPv6 addressing as well. Additionally with Windows Server 2019, you have the capability to do encrypted networks. This allows easily encrypting all traffic traversing your virtual network subnets.
Couple this with the new Cluster Creation features found in Windows Admin Center 1910 that helps to do much of the heavy lifting with HCI clusters including provisioning virtual SDN, Windows Server 2019 provides many nice improvements over Windows Server 2016.
16. Shielded VMs for Linux
Up until Windows Server 2019, you could only make use of shielded vms for Windows with Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V. However, with Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V technology, you now have support for shielded VMs for Linux as well.
If you have a large number of Linux VMs in your environment and want to have the most secure data possible with Hyper-V, Windows Server 2019 is the way to go.
17. HGS Offline Mode for Shielded VMs
Another new feature with Windows Server 2019 is the ability to have offline mode for shielded VMs. With this new mode, you can start VMs that are shielded if the security of the Hyper-V host has not changed.
18. HGS Secure Connect
Secure Connect provides a secure console connection to the Windows or Linux shielded VMs in your environment protected with encryption.
19. Enhanced Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP)
Enhanced Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) is a new set of security contained in Windows Server 2019. It includes a new set of host intrusion prevention capabilities such as preventative protection, attack detection, and zero-day exploits.
If you want the latest and greatest set of features in the realm of security, Windows Server 2019 provides the ultimate set of security tools and solutions to secure your environment.
As you can see there are many reasons that you would opt to choose Windows Server 2019 vs 2016. While it certainly would not be a bad move to upgrade to Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019 makes a lot of sense as a target since the effort is relatively the same and it gets you a lot of new features as well as improved features that are found in Windows Server 2016.
Additionally, when you think about support, Windows Server 2019 vs 2016 gets you a lot further down the road of support timeframe. The end of life on 2019 is going to be much further down the road when compared to 2016.
Also, when you consider the fact that the Storage Migration Service supports migrating data all the way from Windows Server 2003 all the way to Windows Server 2019. This really makes it a no brainer to upgrade to Windows Server 2019 vs 2016.