В операционной системе Windows 10 имеются разные редакции (версии) системы для использования на компьютерах, различающиеся по своим функциональным возможностям. В статье мы подробно остановимся на различиях редакций ОС Windows 10.
На большинстве компьютеров, покупаемых в розницу (ноутбуки, нетбуки, моноблоки, гибридные планшеты, системные блоки настольных компьютеров), уже установлена производителем устройства определенная редакция Windows 10. В этом случае, у покупателя нет выбора, приходиться довольствоваться тем, что есть.
Содержание:
- Редакции Windows 10 Home
- Редакции Windows 10 Pro
- Редакции Windows 10 Enterprise
- Другие версии Windows 10
- Различие редакций Windows 10
- Сравнение версий Windows 10 в таблице
- Выводы статьи
Пользователи, покупающие устройство без операционной системы (ноутбук, готовый системный блок, собранный системный блок и т. д.), самостоятельно устанавливают на компьютер какую-либо версию операционной системы Windows. Большинство пользователей выбирают современную операционную систему Windows 10 для установки на компьютер. Перед установкой системы, встает вопрос: какую редакцию Windows 10 выбрать, чем отличаются редакции Windows между собой.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим редакции Windows 10 для ПК и ноутбуков, не затрагивая мобильные и серверные версии Windows. Пользователи, не знающие подробностей о версии Windows 10, установленной на компьютере, могут легко узнать редакцию системы, прочитав эту статью.
Microsoft с момента выхода Windows 10 в июле 2015 года, время от времени, добавляет новые редакции операционной системы. Помимо разделения на версии, каждая редакция имеет номер сборки, номера сборок меняются после установки обновлений системы.
Основные версии Windows 10 разделены на три категории, отличающиеся друг от друга функциональными возможностями:
- Windows 10 Home (Windows 10 Домашняя).
- Windows 10 Pro (Windows 10 Профессиональная).
- Windows 10 Enterprise (Windows 10 Корпоративная).
От основных категорий Windows 10 отделяются производные категории (подвиды основных версий), в которых основная версия имеет несколько вариантов производных редакций системы. Выбор редакции Windows 10, зависит от потребностей конкретного пользователя. Сравнение редакций Windows 10 между собой в виде таблицы, вы увидите в конце статьи.
Существует программа Windows 10 Insider Preview для предварительной оценки новых выпусков Windows 10. Пользователи, выполняющие функции тестирования, бесплатно получают предварительные версии Windows для использования на своих компьютерах. Взамен получает телеметрию об использовании системы, это позволяет проверить работу системы с новыми функциями, выявить неисправности и устранить неполадки в следующих сборках Виндовс 10.
Для продажи в розницу поступают только 3 версии Windows 10 для установки на новые компьютеры:
- Windows 10 Домашняя (Windows 10 Home).
- Windows 10 Профессиональная (Windows 10 Pro).
- Windows 10 S.
Версия Windows 10 Enterprise устанавливается на компьютеры только в качестве обновления с редакции Windows 10 Pro. Остальные версии Microsoft поставляет производителям оборудования (ПК, ноутбуков) для установки на устройства, перед продажей потребителям.
Оригинальную операционную систему Windows 10 можно скачать с официального сайта Майкрософт, способами, описанными в этой статье.
Редакции Windows 10 Home
Для домашних пользователей выпущена редакция Windows 10, в которой присутствуют все базовые основные возможности операционной системы. Дома не нужны функции системы, применяемые на предприятиях, поэтому нет смысла переплачивать за лишнюю функциональность. Данная редакция хорошо подойдет для домашнего использования. В редакции Windows 10 Home применяется автоматическое обновление.
Версии Windows 10 для домашних пользователей подразделяются на следующие редакции:
- Windows 10 Домашняя (Windows 10 Home).
- Windows 10 Домашняя для одного языка (Windows 10 Home Single Language; Windows 10 Home SL; Windows 10 Single Language; Windows 10 SL) — версия аналогичная домашней редакции, отличающаяся лишь тем, что здесь нельзя поменять язык операционной системы. Очень часто данная редакция устанавливается на ноутбуках и нетбуках. Для производителей это более дешевый вариант лицензирования Майкрософт, чем Windows 10 Home.
- Windows 10 Домашняя с Bing — в этой версии нельзя поменять поисковую систему Bing в браузерах Microsoft Edge и Internet Explorer (ничто не мешает использовать другой браузер). Данная редакция устанавливается на некоторых ноутбуках.
Редакции Windows 10 Pro
Для предприятий малого бизнеса и домашних пользователей, которым необходимы расширенные возможности системы, предлагается профессиональная версия Windows 10, которая, в свою очередь, подразделяется на несколько редакций. В этой версии доступен гипервизор (виртуальная машина) Hyper-V, BitLocker и другие функции системы.
Профессиональные версии Windows 10 имеют следующие редакции:
- Windows 10 Профессиональная (Windows 10 Pro).
- Windows 10 Pro для образовательных учреждений (Windows 10 Pro Education).
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations (Windows 10 Pro для рабочих станций) — версия Windows 10 Pro с расширенной поддержкой оборудования для предприятий с высокой вычислительной нагрузкой.
- Windows 10 S — версия со специальной конфигурацией Windows 10 Pro, в которой возможна работа приложений, установленных из Магазина приложений (Microsoft Store). Все другие программы не будут работать в этой версии операционной системы.
Редакции Windows 10 Enterprise
Для предприятий среднего и крупного бизнеса создана корпоративная версия системы. Редакция Windows Enterprise имеет все возможности профессиональной версии, а также дополнительные функции, которые актуальны для применения на предприятиях.
Корпоративная версия Windows 10 имеет следующие редакции:
- Windows 10 Корпоративная (Windows 10 Enterprise).
- Windows 10 Корпоративная с долгосрочным обслуживанием (Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB).
- Windows 10 для образовательных учреждений (Windows 10 Education).
Версия Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB имеет долгосрочный срок поддержки, предназначена для стабильной надежной работы. В системе отсутствуют встроенные приложения, ограничен некоторый функционал, устанавливаются только важные обновления. ОС Windows 10 LTSB можно бесплатно использовать в течение 90 дней (пробный период), система работает на английском языке. О том, как установить русский язык в Windows читайте тут.
Другие версии Windows 10
Также имеются несколько других версий Windows 10, среди них:
- Windows 10 IoT (Windows 10 для «Интернета вещей») — эта версия имеет несколько редакций для установки на промышленное оборудование (терминалы, банкоматы и т. п.).
- Windows 10 Team — данная версия устанавливается на планшеты Surface Hub.
Различие редакций Windows 10
Многие пользователи, наверное, замечали отличия редакций Windows 10 с буквами в конце обозначения версий системы.
Буква «N» добавляется к редакциям Windows 10, выпущенных для стран Европейского Союза. Название редакций имеют такой вид: Windows 10 Home N, Windows 10 Pro N, Windows 10 Enterprise N и т. д. Отличие от стандартных версий в том, что в этих версиях, по требованию ЕС, отсутствуют некоторые приложения (музыка Groove, Windows Media Player, Кино и ТВ), которые можно добавить в ОС самостоятельно.
Буквы «KN» добавляется к версиям системы для Южной Кореи. Здесь отсутствуют те же самые приложения. Обозначение версий выглядит следующим образом: Windows 10 Enterprise KN, Windows 10 Pro KN, Windows 10 Home KN и т. д.
Для Китая выпущена специальная версия Windows 10 China Government Edition для использования в государственных учреждениях.
Буквенные сочетания «VL», «OEM», «COEM», «GGK», «GGWA», «FPP» обозначают типы лицензий для Windows.
Сравнение версий Windows 10 в таблице
Для использования на личных компьютерах оптимально подходят две редакции: Windows 10 Домашняя и Windows 10 Профессиональная. С помощью списка, отображающего возможности разных редакций Виндовс 10, намного легче выбрать лучшую версию системы, подходящую под требования конкретного пользователя.
Для наглядного сравнения версий Windows 10 посмотрите таблицу, в которой отображены основные возможности системы в разных редакциях: Windows 10 Home, Windows 10 Pro, Windows 10 Enterprise, Windows 10 Education.
| Компоненты | Window 10 Home | Window 10 Pro | Window 10 Enterprise | Window 10 Education |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Меню «Пуск» и живые плитки | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Режим планшета | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Голос, перо, сенсорное управление и жесты | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Кортана | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Microsoft Edge | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Windows Ink | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Continuum для телефона | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Windows Hello | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Групповая политика | √ | √ | √ | |
| Управление мобильными устройствами | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Центр обновления Windows | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Центр обновления Windows для бизнеса | √ | √ | √ | |
| Магазин Microsoft для бизнеса | √ | √ | √ | |
| Конфигурация общего ПК | √ | √ | √ | |
| ТесТ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Ограниченный доступ | √ | √ | √ | |
| BitLocker | √ | √ | √ | |
| AppLocker | √ | √ | ||
| Direct Access | √ | √ | ||
| Надежная загрузка | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Служба подтверждения работоспособности устройства Windows | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Шифрование устройства | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Присоединение к домену | √ | √ | √ | |
| Internet Explorer в режиме предприятия (EMIE) | √ | √ | √ | |
| Режим ограниченного доступа (Assigned Access) | √ | √ | √ | |
| Удаленный рабочий стол | √ | √ | √ | |
| Hyper-V | √ | √ | √ | |
| Windows To Go | √ | √ | ||
| BranchCache | √ | √ | ||
| Управление начальным экраном с помощью групповой политики | √ | √ | ||
| Поддержка TPM | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Присоединение к Azure Active Directory с единым входом в облачные приложения | √ | √ | √ | |
| Microsoft Passport | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Защита корпоративных данных (Enterprise Data Protection) | √ | √ | √ | |
| Защита учетных данных (Credential Guard) | √ | √ | ||
| Защита устройств (Device Guard) | √ | √ | ||
| Песочница Windows (Windows Sandbox) | √ | √ | √ |
Выводы статьи
Операционная система Windows 10 выпускается в разных редакциях, которые отличаются функциональными возможностями, в зависимости от потребностей потребителей. Для домашнего использования рекомендованы версии: Windows 10 Домашняя и Windows 10 Профессиональная.
Похожие публикации:
- 7 способов как узнать ключ продукта Windows
- Как удалить папку Объемные объекты в Windows 10
- Как перенести Документы, Загрузки, Рабочий стол на другой диск — 3 способа
- Автозагрузка Windows 10: как добавить или удалить программу из автозагрузки
- Как отключить обновления в Windows 10 — 5 способов

Можно провести небольшое сравнение и понять основные отличия версий Windows 10. Для настольных компьютеров предлагается четыре основных редакций ОС. Они немного отличаются по функциональности. Например, пользователи встречаются с проблемой, когда не получается внести изменения, поскольку групповые политики отсутствуют в домашней версии.
Эта статья расскажет об основных отличиях версий Windows 10. Сравнение лучше всего представлено в таблице редакций. Лицензионная версия операционной системы может сэкономить не только время, но и нервы пользователя. Вспомните, только постоянные напоминания об активации, ограничения в параметрах и многое другое.
- Windows 10 Home (Домашняя) — предоставляет встроенные средства защиты для безопасной и эффективной работы. Имеет некоторые ограничения в сравнении профессиональной редакцией. Это базовая версия системы на компьютеры и ноутбуки для домашнего использования. Зачастую поставляется в ноутбуках и нетбуках.
- Windows 10 Pro (Профессиональная) — содержит всё, что предлагает домашняя версия, но включает полезные функции для опытных пользователей и бизнеса. Это оптимальный выбор профессионалов. Присутствует поддержка шифрования дисков BitLocker и наличие групповых политик для быстрого изменения настроек системы.
- Windows 10 Enterprise (Корпоративная) — сборка больше ориентирована на использование в больших компаниях. В отличие от вышеперечисленных версий она предназначена преимущественно для работы с бизнес-приложениями. Эта редакция приобретается только в виде обновления на уже ранее приобретённую профессиональную.
- Windows 10 Education (Для образовательных учреждений) — представляет из себя рабочую станцию с уклоном на образовательные учреждения. По сути, функциональность версии для образовательных учреждений аналогична корпоративной версии, за исключением отсутствующей Кортаны (до версии 1703).
| Функциональность | Windows 10 Home | Windows 10 Pro | Windows 10 Enterprise | Windows 10 Education |
| Центр обновления Windows | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Центр обновления Windows для бизнеса | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Отключение Microsoft Store | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Управление мобильными устройствами | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Изменение групповых политик | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Присоединение к домену | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Шифрование BitLocker | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Режим предприятия Internet Explorer 11 | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Режим ограниченного доступа | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Удалённый рабочий стол | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Виртуальная машина Hyper-V | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Компонент Direct Access | ➖ | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Политики AppLocker | ➖ | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Windows To Go Creator | ➖ | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Служба BranchCache | ➖ | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Защита корпоративных данных | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Защита учётных данных | ➖ | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Защита устройств (Device Guard) | ➖ | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ |
| Песочница Windows (Windows Sandbox) | ➖ | ➕ | ➕ | ➕ |
Основные отличия Windows 10 Home от Pro
В первую очередь, основным отличием домашней от профессиональной это максимальный объём поддерживаемой оперативной памяти. Версия Home поддерживает максимум 128 Гб — этого будет более чем достаточно. Уже редакция Pro поддерживает до 2 Тб (может в будущем и увидим необходимость в превышении 128 Гб).
Для обычного пользователя думаю неважно, присутствует ли компонент Direct Access, защита корпоративных данных или режим предприятия Internet Explorer 11. Некоторые компоненты действительно могут быть полезными пользователю, но они отсутствуют в редакции Windows 10 Домашняя.
- Компонент Hyper-V — позволяет настраивать виртуальные машины без необходимости использования стороннего ПО. Смотрите, как правильно настроить виртуализацию Hyper-V.
- Windows Sandbox — встроенная среда для безопасного тестирования ПО. Закрытые окна песочницы удаляет все изменения. Нужно будет только включить песочницу в Windows 10.
- Групповые политики — позволяют настраивать параметры для определённого набора пользователей или компьютеров. Для исправления проблем системы часто его используют.
- Удалённый рабочий стол — удалённое управление может понадобиться, особенно если Вы работаете за компьютером. Как подключиться к удалённому рабочему столу Windows 10.
Более подобные сравнения можете посмотреть в представленной таблице Microsoft. К сожалению, она на английском языке, но там всё более-менее понятно. Основные преимущества описаны в вышеуказанной таблице.
Заключение
Как всегда, таблица помогает пользователю выполнить сравнение и найти отличия версий Windows 10. Можно конкретно узнать, чем Windows 10 Pro отличается от Home. Напомним, в таблице сравнения рассматриваются только десктопные версии операционной системы. Именно их чаще встречает пользователь в процессе работы за компьютером.
Не думаю, что в таблицу стоит добавлять функции, которые присутствуют во всех версиях Windows 10. На сайте Microsoft указывается антивирусная программа Защитник Windows, как функция, которая в домашней и профессиональной редакциях. Все изменения стоит отслеживать непосредственно на официальном ресурсе. Смотрите: Чем Windows 10 лучше Windows 7.
(2 оценок, среднее: 5,00 из 5)
Администратор и основатель проекта Windd.pro. Интересуюсь всеми новыми технологиями. Знаю толк в правильной сборке ПК. Участник программы предварительной оценки Windows Insider Preview. Могу с лёгкостью подобрать комплектующие с учётом соотношения цены — качества. Мой Компьютер: AMD Ryzen 5 3600 | MSI B450 Gaming Plus MAX | ASUS STRIX RX580 8GB GAMING | V-COLOR 16GB Skywalker PRISM RGB (2х8GB).
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Windows 10 has several editions, all with varying feature sets, use cases, or intended devices. Certain editions are distributed only on devices directly from an original equipment manufacturer (OEM), while editions such as Enterprise and Education are only available through volume licensing channels. Microsoft also makes editions of Windows 10 available to device manufacturers for use on specific classes of devices, including IoT devices and previously marketed Windows 10 Mobile for smartphones.
Baseline editions[edit]
Baseline editions are the only editions available as standalone purchases in retail outlets. PCs often come pre-installed with one of these editions.
- Home
- Windows 10 Home is designed for use in PCs, tablets and 2-in-1 PCs. It includes all features directed at consumers.[1][2][3]
- Pro
- Windows 10 Pro includes all features of Windows 10 Home, with additional capabilities that are oriented towards professionals and business environments, such as Active Directory, Remote Desktop, BitLocker, Hyper-V, and Windows Defender Device Guard.[1][2][3]
- Pro for Workstations
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations is designed for high-end hardware for intensive computing tasks and supports Intel Xeon, AMD Opteron and the latest AMD Epyc processors; up to 4 CPUs; up to 256 cores; up to 6 TB RAM; the ReFS file system; Non-Volatile Dual In-line Memory Module (NVDIMM); and remote direct memory access (RDMA).[4][5][6]
Organizational editions[edit]
These editions add features to facilitate centralized control of many installations of the OS within an organization. The main avenue of acquiring them is a volume licensing contract with Microsoft.
- Education
- Windows 10 Education is distributed through Academic Volume Licensing. It was based on Windows 10 Enterprise and initially reported to have the same feature set.[1][2][3] As of version 1709, however, this edition has fewer features. See § Comparison chart for details.
- Pro Education
- This edition was introduced in July 2016 for hardware partners on new devices purchased with the discounted K–12 academic license. It was based on the Pro edition of Windows 10 and contains mostly the same features as Windows 10 Pro with different options disabled by default, and adds options for setup and deployment in an education environment. It also features a «Set Up School PCs» app that allows provisioning of settings using a USB flash drive, and does not include Cortana, Microsoft Store suggestions, Windows Sandbox, or Windows Spotlight.[7][8][9]
- Enterprise
- Windows 10 Enterprise provides all the features of Windows 10 Pro for Workstations, with additional features to assist with IT-based organizations.[1][2][3] Windows 10 Enterprise is configurable on two servicing channels, Semi-Annual Channel and Windows Insider Program.[10]
- Enterprise LTSC
- Enterprise LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel) is a long-term support variant of Windows 10 Enterprise released every 2 to 3 years. Each release is supported with security updates for either 5 or 10 years after its release, and intentionally receive no feature updates.[11] Some features, including the Microsoft Store and bundled apps, are not included in this edition.[12][1][3] This edition was first released as Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB (Long-Term Servicing Branch).[13] There are currently 4 releases of LTSC: one in 2015 (version 1507), one in 2016 (version 1607), one in 2018 (labeled as 2019, version 1809), and one in 2021 (version 21H2).[14][15]
S mode[edit]
Since 2018, OEMs can ship Windows 10 Home and Pro in a feature-limited variation named S mode which evolved from the discontinued Windows 10 S. Organizations employing Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education can make use of S mode too.[16] S mode is a feature-limited edition of Windows 10 designed primarily for low-end devices in the education market. It has a faster initial setup and login process, and allows devices to be provisioned using a USB drive with the «Set Up School PCs» app.
Changes[edit]
With the exception of the Microsoft Teams desktop client which was made available for S mode in April 2019,[citation needed] the installation of software (both Universal Windows Platform (UWP) and Windows API apps) is only possible through the Microsoft Store, and built-in and Microsoft Store-obtained command line programs or shells cannot be run in this mode.[17][18][19][20] System settings are locked to allow only Microsoft Edge as the default web browser with Bing as its search engine.[21] The operating system may be switched out of S mode using the Microsoft Store for free. However, once S Mode is turned off, it cannot be re-enabled.[22][23] All Windows 10 devices in S mode include a free one-year subscription to Minecraft: Education Edition.[citation needed] Critics have compared the edition to Windows RT, and have considered it to be an alternative to ChromeOS.[22][24][25][26][27]
Device-specific editions[edit]
These editions are licensed to OEMs only, and are primarily obtained via the purchase of hardware that includes it:
- Holographic
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s HoloLens mixed reality smartglasses.[28][29]
- IoT Enterprise
- A rebranded variant of Microsoft’s earlier embedded operating systems, Windows Embedded. Designed specifically for use in small footprint, low-cost devices and IoT scenarios.[30][31] IoT Core was discontinued on 10 November 2020,[32][33] while IoT Core LTSC is supported up through 9 January 2029.[34]
- Team
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s Surface Hub interactive whiteboard.[35]
Discontinued editions[edit]
The following editions of Windows 10 were discontinued (as of Windows 10 version 21H2). For both Mobile and Mobile Enterprise, Microsoft confirmed it was exiting the consumer mobile devices market, so no successor product is available.[36]
- Mobile
- Windows 10 Mobile was designed for smartphones and small tablets. It included all basic consumer features, including Continuum capability. It was the de facto successor of Windows Phone 8.1 and Windows RT.[1][2]
- Mobile Enterprise
- Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise provided all of the features in Windows 10 Mobile, with additional features to assist IT-based organizations, in a manner similar to Windows 10 Enterprise, but optimized for mobile devices.[1][2]
- IoT Mobile
- A binary equivalent of Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise licensed for IoT applications. Also known as IoT Mobile Enterprise.[37][38]
- S
- Windows 10 S was an edition released in 2017 which ultimately evolved into the so-called S mode of Windows 10. In March 2018, Microsoft announced that it would be phasing out Windows 10 S, citing confusion among manufacturers and end-users.[39][40]
- 10X
- Originally announced for use on dual-screen devices such as the Surface Neo and other potential form factors, 10X featured a modified user interface designed around context specific interactions or «postures» on such devices, including a redesigned Start menu with no tiles, and use of container technology to run Win32 software.[41][42] The platform was described as a more direct competitor to ChromeOS.[43][44] On May 4, 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would first be used on single-screen devices, and that they would «continue to look for the right moment, in conjunction with our OEM partners, to bring dual-screen devices to market».[45] Microsoft also added anti-theft protection to Windows 10X, just like how Apple’s Activation Lock and anti-theft protection on Android devices and Chromebooks work.[46] On May 18, 2021, Head of Windows Servicing and Delivery John Cable stated that Windows 10X had been cancelled, and that its foundational technologies would be leveraged for future Microsoft products.[47] Several design changes in 10X, notably the centered taskbar and redesigned start menu, would be later introduced in Windows 11.[48]
Regional variations[edit]
- N/KN
- As with previous versions of Windows since Windows XP, all Windows 10 editions for PC hardware have «N» and «KN» variations in Europe and South Korea that exclude multimedia functionality, in compliance with antitrust rulings.[49] According to details that Microsoft has published, any app that relies on Microsoft multimedia technologies experiences impaired functionality on these editions, unable to even play audio notification tones.[50] Restoring the missing functionality to these editions entails installing the «Media Feature Pack», followed by Skype, Movies & TV, Windows Media Player, Xbox Game Bar, Windows Voice Recorder, and four codecs.[50] The variation cannot be changed without a clean install, and keys for one variation will not work on other variations.
- Home with Bing
- As with Windows 8.1, a reduced-price «Windows 10 with Bing» SKU is available to OEMs; it is subsidized by having Microsoft’s Bing search engine set as default, which cannot be changed to a different search engine by OEMs. It is intended primarily for low-cost devices, and is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home.[51]
- Home Single Language
- In some emerging markets,[citation needed] OEMs preinstall a variation of Windows 10 Home called Single Language without the ability to switch the display language. It is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home. To change display language, the user will need to upgrade to Windows 10 Home or Windows 10 Pro.
- China Government Edition
- In May 2017, it was reported that Microsoft, as part of its partnership with China Electronics Technology Group, created a specially-modified variant of Windows 10 Enterprise («G») designed for use within branches of the Chinese government. This variant is pre-configured to «remove features that are not needed by Chinese government employees», and allow the use of its internal encryption algorithms.[52][53]
Comparison chart[edit]
| Item | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Yes | Feature is present in the given edition |
| Yes, since [update] | Feature is present in the given edition after installing a certain update |
| No | Feature is absent from the given edition |
| No, since [update] | Feature is absent from the given edition after installing a certain update (It might have been fully or partly present prior to that update) |
| [Explanation] | Feature is partly present in the given edition |
| [Explanation], since [update] | Feature is partly present in the given edition, after installing a certain update (It might have been fully present prior to that update, or not present at all) |
Microsoft OEM licensing formula takes display size, RAM capacity and storage capacity into account. In mid-2015, devices with 4 GB RAM were expected to be $20 more expensive than devices with 2 GB RAM.[75]
Upgrade path[edit]
Free upgrade[edit]
At the time of launch, Microsoft deemed Windows 7 (with Service Pack 1) and Windows 8.1 users eligible to upgrade to Windows 10 free of charge, so long as the upgrade took place within one year of Windows 10’s initial release date. Windows RT and the respective Enterprise editions of Windows 7, 8, and 8.1 were excluded from this offer.[76]
| Windows version and edition | Windows 10 edition |
|---|---|
| Windows 7 Starter SP1 | Home |
| Windows 7 Home Basic SP1 | |
| Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 with Bing | |
| Windows 8.1 | |
| Windows 7 Professional SP1 | Pro |
| Windows 7 Ultimate SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 Pro | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Mobile |
Transition paths[edit]
The following table summarizes possible transition paths (upgrade, downgrade, or migration) that can be taken, provided that proper licenses are purchased.
Windows RT does not appear in this table because it cannot be upgraded to Windows 10.
On September 28, 2023, Microsoft disabled the free upgrade path to Windows 10 from Windows 7 or 8.x, although upgrades from Windows 10 to 11 are still supported.[77][78]
| Transition path | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Upgrade | Constitutes replacing the OS while preserving apps, their settings, and user data |
| Repair | Constitutes fixing a damaged OS by «upgrading» from one edition to the same |
| Downgrade | Similar to upgrade, but deliberately removes some features |
| Migration | Constitutes replacing the operating system, reinstalling the apps, restoring their settings via backup, and safeguarding user data against accidental deletion. |
| None | It is impossible to replace the OS with the intended target because of platform incompatibility |
| Windows version |
Windows edition |
Transition target | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Home |
Windows 10 Pro |
Windows 10 Pro for Workstations |
Windows 10 Pro (Education) |
Windows 10 Education |
Windows 10 Enterprise |
Windows 10 Mobile |
||
| Windows 7 | Starter | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None |
| Home Basic | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Home Premium | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Professional | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Ultimate | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | Migration | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Windows 8.1 | (Core) | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None |
| with Bing | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Pro | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro for Students | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro with Media Center | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Embedded Industry | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | None | |
| Phone 8.1 | None | None | None | None | None | None | Upgrade | |
| Windows 10 | Home | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None |
| Pro | Downgrade | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro for Workstations | Downgrade | Downgrade | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro Education | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Repair | Migration | Migration | None | |
| Education | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Repair | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Downgrade | Repair | None | |
| Mobile | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
Release channels[edit]
Microsoft releases minor versions of Windows 10 through the free feature updates.[12] Originally, Microsoft released feature updates semiannually. They contained new features as well as changes.[80] With the release of Windows 11, however, Microsoft has changed the release schedule to annual. These feature updates do not contain any noticeable changes.
The pace at which a system receives feature updates depends on the «release channel» (originally, «release branch») from which the system downloads its updates.[12]
Insider Channel[edit]
Windows Insider is a beta testing program that allows access to pre-release builds of Windows 10, enabling power users, developers, and vendors to test and provide feedback on future feature updates to Windows 10 as they are developed. Windows Insider itself consists of four «rings.»
- The «Fast» ring distributes new builds as they are released
- The «Slow» ring distributes new builds with a delay following their availability on the Fast ring
- The «Release Preview» ring distributes release candidate
- The «Skip Ahead» ring distributes builds of the next feature update while a current release is being finished
General Availability Channel[edit]
Since 2022, the General Availability Channel (GAC) distributes feature updates annually. To receive these updates, users must either request them manually or wait for their version of Windows 10 to go out of support.
Originally, however, Microsoft distributed feature updates through two distinct channels, the «Current Branch» (CB) an the «Current Branch for Business» (CBB).
- The «Current Branch» (CB) distributed all feature updates as they graduated from the Windows Insider program. Microsoft only supported the latest build. Windows would automatically install the latest feature update from CB. Users could defer the CB feature update for up to 365 days.[81][82][83][84] Microsoft renamed CB to «Semi-Annual Channel (Targeted)» in version 1709.
- The «Current Branch for Business» (CBB), which was not available in the Home edition, distributed feature updates with a four-month delay. This allowed customers and vendors to evaluate and perform additional testing on new builds before broader deployments. Devices could be switched back to the Current Branch at any time.[12][85] Microsoft renamed CBB to «Semi-Annual Channel» in version 1709.
Since version 1903, Microsoft dismantled the two-channel scheme in favor of a unified «Semi-Annual Channel» (SAC). Microsoft supports each SAC version of Windows for 30 months. Windows no longer installs new feature updates automatically before the expiry of the 30-months support period. With the release of Windows 11, Microsoft changed the release schedule to annual, and change the channel’s name to «General Availability Channel» (GAC).
Long-Term Servicing Channel[edit]
LTSC exclusively distributes the «Enterprise LTSC», «IoT Core», and «IoT Enterprise LTSC» editions of Windows 10. Microsoft releases a new minor version of these editions every 2–3 years. LTSC builds adhere to Microsoft’s traditional support policy which was in effect before Windows 10, including:
- Five years of mainstream support
- Critical and security updates for ten years after their release
- No feature updates from Windows Update
Microsoft discourages the use of LTSC editions outside of «special-purpose devices» that perform a fixed function and thus do not require new user experience features. As a result, these editions do not come with Microsoft Store, most Cortana features, and most bundled apps.[12][1][3] LTSC was originally called the «Long-Term Servicing Branch» (LTSB) until 2016.[13]
See also[edit]
- Windows Server 2016, based on Windows 10 version 1607[86]
- Windows Server 2019, based on Windows 10 version 1809
- Xbox system software, an operating system now based on the Windows 10 core, designed to run on consoles
- Windows 10 version history
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b c 32-bit architectures like IA-32 and ARM32 have a memory addressing limitation of four gigabytes. In practice, less than 4 GB of memory is addressable as the 4 GB space also includes the memory mapped peripherals.
- ^ Windows 10 utilises processor groups on x86-64 to manage processor affinity and scheduling. The Windows 10 kernel has a hard-coded limit of 20 processor groups, and each processor group can contain up to 64 logical processors. A logical processor is either a physical or SMT core. Processor groups are allocated based on the NUMA topology of the system. One processor group cannot span multiple sockets or NUMA nodes. Processor groups are not available on IA-32; 32-bit builds instead use an older affinity mask implementation with a limit of 32 logical processors. The limit of 20 processor groups does not change between Windows 10 editions. There is no specific limit on the number of physical cores that can be used on Windows 10, unlike Windows Server where physical cores must be additionally licensed.[58][60][61][62]
- ^ There are three (previously four) telemetry levels, in the order of magnitude: Diagnostic data off (Security), Required (Basic), and Optional (Full). The higher the level, the more information that is sent to Microsoft. Previous Windows 10 versions had a level between Required and Optional, and the older names for the levels are shown in the parenthesis.
- ^ Cortana is available only in certain markets. Experience may vary by region and device.
- ^ a b This feature was missing from Windows 10 version 1803, but not the prior or next versions.
- ^ Windows Hello requires specialized hardware, such as a fingerprint reader, illuminated IR sensor or other biometric sensor.
- ^ On Windows 10 Pro, a Control Panel applet corresponding to this feature appears, but a Windows 10 Enterprise or Education image is still needed.[73][74]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Prophet, Tony (May 13, 2015). «Introducing Windows 10 Editions». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ a b c d e f Bott, Ed (May 14, 2015). «Windows 10 editions: Everything you need to know». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b c d e f Foley, Mary Jo (July 2, 2015). «Which Windows 10 editions get which features?». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Diaconu, Klaus (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft announces Windows 10 Pro for Workstations». Windows For Your Business. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft confirms new Windows 10 Pro for Workstations edition». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Warren, Tom (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft reveals new Windows 10 Workstations edition for power users». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 27, 2016). «Microsoft to add new Windows 10 Pro Education edition to its line-up». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 editions for education customers». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ a b «Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, «fun facts», and suggestions». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ DaniHalfin. «Assign devices to servicing branches for Windows 10 updates (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ «The next Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) release». Microsoft. February 18, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Overview of Windows as a service». Microsoft. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ a b Brinkmann, Martin (July 28, 2017). «Windows 10 LTSB becomes Windows 10 LTSC». gHacks Technology News.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg. «FAQ: Windows 10 LTSB explained». Computerworld. Retrieved October 3, 2018.
- ^ greg-lindsay. «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021 — What’s new in Windows». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved November 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 in S mode FAQ». Windows.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Turner, Rich (May 18, 2017). «Will Linux distros run on Windows 10 S?». Microsoft. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Gartenberg, Chaim (May 19, 2017). «Linux distros won’t run on Windows 10 S after all». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Smith, Sharon. «Get clients for Microsoft Teams — Microsoft Teams». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ «Update get-clients.md · MicrosoftDocs/OfficeDocs-SkypeForBusiness@5c2ca5a». GitHub. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 2, 2017). «Windows 10 S won’t let you change the default browser or switch to Google search». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ a b Chacos, Brad. «Meet Windows 10 S, a streamlined, simplified, Microsoft Store-only OS for schools». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Warren, Tom (June 19, 2017). «Microsoft now lets Surface Laptop owners revert back to Windows 10 S». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «Windows 10 S is Microsoft’s answer to Chrome OS». The Verge. Vox Media. May 2, 2017. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (September 14, 2016). «Desktop apps make their way into the Microsoft Store». Ars Technica. Condé Nast.
- ^ «Windows 10 Cloud looks just like Windows 10 in leaked screenshots». The Verge. Vox Media. February 3, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ «Leaked Microsoft document confirms Windows 10 Cloud and a Chromebook competitor». PC World. IDG. Retrieved April 23, 2017.
- ^ «Unlock Windows Holographic for Business features». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft pushes Windows 10 Holographic as the one-stop option for VR and AR». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT for your business». Windows for Business. Microsoft. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise». MS Embedded. Silica. August 14, 2015. Archived from the original on May 8, 2017. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft to combine Windows 10 IoT Core and IoT Enterprise in 2021». ZDNet. Mary Jo Foley. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ «Windows 10 Team Anniversary Update now available for Microsoft Surface Hub». Neowin. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ Patrizio, Andy (September 29, 2016). «Microsoft is leaving the consumer mobile market». Network World. IDG Publishing. Retrieved August 30, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 on Thin Clients: Deliver Best Results with Scout Agents (Part 1 of 2)». Fujitsu. Archived from the original on January 23, 2021. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Supported operating systems and browsers in Intune». Microsoft. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft admits Windows 10 S was confusing, new ‘S Mode’ upgrades will be free». The Verge. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Tung, Liam. «Windows 10 to permit block on apps installing if they’re not from Microsoft Store». ZDNet. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 2, 2019). «Microsoft Surface Neo first look: the future of Windows 10X is dual-screen». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Hollister, Sean (October 2, 2019). «Windows 10X is Microsoft’s latest stab at a ‘Lite’ operating system, exclusively for dual-screens». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft reportedly shelves Windows 10X, its Chrome OS competitor». The Verge. May 7, 2021. Retrieved May 7, 2021.
- ^ Salter, Jim (May 13, 2021). «Microsoft puts Windows 10X variant on the back burner». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 4, 2020). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is coming to laptops amid big jump in Windows usage». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Ballard, Barclay (January 25, 2021). «This clever Windows 10X feature will prevent thieves from resetting stolen devices». TechRadar. Retrieved January 21, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 11 Leaks Indicate a Dramatic New Look Is Coming Soon». Gizmodo. Archived from the original on June 16, 2021. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ Ron (August 2, 2015). «Grab the Media Feature Pack for Windows 10 N and Windows 10 KN editions». OnMSFT.com. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ a b «Media Feature Pack for Windows 10/11 N (February 2023)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ^ Slater-Robins, Max. «Microsoft is helping manufacturers make cheap tablets that can run Windows as well as Android». Business Insider UK. Retrieved April 23, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft made a version of Windows 10 for the Chinese government». Engadget. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Myerson, Terry (May 23, 2017). «Announcing Windows 10 China Government Edition and the new Surface Pro». Windows Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ Dudau, Vlad (June 10, 2015). «Microsoft shows OEMs how to market Windows 10; talks features and SKUs». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved June 19, 2015.
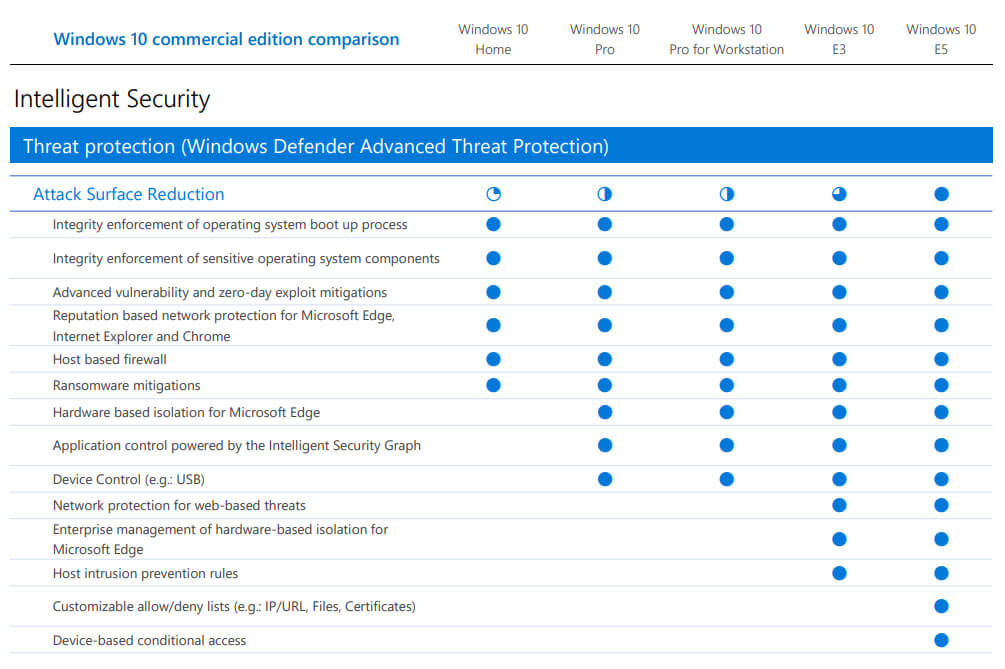
- ^ «Compare Windows 10 Pro & Enterprise (E3 & E5) Commercial Editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2015.
- ^ «Compare Windows 10 Editions & Versions | Home & Pro». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ^ Howse, Brett (July 2, 2015). «Windows 10 Editions Compared». AnandTech. Purch.
- ^ a b Graham Sutherland (April 7, 2022). «CPU Socket and Core Count Limits in Windows 10 (And How To Remove Them)». Codeinsecurity. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Andre Da Costa (September 15, 2015). «Understanding Windows 10 Editions, Architectures and Builds». groovyPost. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- ^ «Processor Groups — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. December 30, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «NUMA Support — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. August 19, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Geoff Chappell (December 17, 2019). «KAFFINITY_EX». Geoff Chappell, Software Analyst. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «Configure Windows telemetry in your organization». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. August 10, 2020.
- ^ «Continuum on Windows 10». July 27, 2015.
- ^ Confirmed by @MicrosoftHelps (Verified) on Twitter
- ^ «Features that are removed or deprecated in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update». Support (28 ed.). Microsoft. October 17, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ shortpatti. «DirectAccess». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ «DirectAccess and Windows 10 in Education». August 4, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 10, 2017). «Ask Paul: Is Windows To Go Coming to Windows 10 Pro?». thurrott.com. BWW Media Group.
- ^ Niehaus, Michael; Lich, Brian. «Windows To Go frequently asked questions (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 30, 2017.
How can Windows To Go be deployed in an organization? [~snip~] A Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education image
- ^ «TrendForce Adjusts Notebooks’ Unit Memory Capacity for 2015 Down by 3~5% due to Microsoft’s New License Fee Arrangement for Windows 10». DRAMeXchange. TrendForce Corp. July 27, 2015. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ Trent, Rod (June 9, 2015). «Windows 10 Upgrade Paths». SuperSite for Windows. Penton.
- ^ «Windows Ends Installation Path for Free Windows 7/8 Upgrade». Microsoft. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Tyson, Mark (September 29, 2023). «Microsoft Says the Days of Free Windows 7 to 10 or 11 Updates Are Over». Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Lindsay, Greg; Lich, Brian (April 5, 2017). «Windows 10 upgrade paths». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 20, 2017). «Microsoft will now release major Windows 10 updates every March and September». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «How to Pause Windows 10 Automatic Updates To Avoid Critical Bugs». www.bleepingcomputer.com. Retrieved September 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 : the case of the missing update deferral options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. May 28, 2019. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (March 1, 2017). «Put Windows 10 updates on hold—now available in Creators Update build 15046». Computerworld. IDG. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ Paul, Ian (April 18, 2017). «How to defer future updates in the Windows 10 Creators Update». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (November 17, 2015). «How to defer upgrades and updates in Windows 10 Pro». Computerworld. IDG.
- ^ Woods, Rich (September 24, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809 will be generally available in October». Neowin.
В операционной системе Windows 10 имеются разные редакции (версии) системы для использования на компьютерах, различающиеся по своим функциональным возможностям. В статье мы подробно остановимся на различиях редакций ОС Windows 10.
На большинстве компьютеров, покупаемых в розницу (ноутбуки, нетбуки, моноблоки, гибридные планшеты, системные блоки настольных компьютеров), уже установлена производителем устройства определенная редакция Windows 10. В этом случае, у покупателя нет выбора, приходиться довольствоваться тем, что есть.
Пользователи, покупающие устройство без операционной системы (ноутбук, готовый системный блок, собранный системный блок и т. д.), самостоятельно устанавливают на компьютер какую-либо версию операционной системы Windows. Большинство пользователей выбирают современную операционную систему Windows 10 для установки на компьютер. Перед установкой системы, встает вопрос: какую редакцию Windows 10 выбрать, чем отличаются редакции Windows между собой.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим редакции Windows 10 для ПК и ноутбуков, не затрагивая мобильные и серверные версии Windows. Пользователи, не знающие подробностей о версии Windows 10, установленной на компьютере, могут легко узнать редакцию системы, прочитав эту статью.
Microsoft с момента выхода Windows 10 в июле 2015 года, время от времени, добавляет новые редакции операционной системы. Помимо разделения на версии, каждая редакция имеет номер сборки, номера сборок меняются после установки обновлений системы.
Основные версии Windows 10 разделены на три категории, отличающиеся друг от друга функциональными возможностями:
- Windows 10 Home (Windows 10 Домашняя)
- Windows 10 Pro (Windows 10 Профессиональная)
- Windows 10 Enterprise (Windows 10 Корпоративная)
От основных категорий Windows 10 отделяются производные категории (подвиды основных версий), в которых основная версия имеет несколько вариантов производных редакций системы. Выбор редакции Windows 10, зависит от потребностей конкретного пользователя. Сравнение редакций Windows 10 между собой в виде таблицы, вы увидите в конце статьи.
Существует программа Windows 10 Insider Preview для предварительной оценки новых выпусков Windows 10. Пользователи, выполняющие функции тестирования, бесплатно получают предварительные версии Windows для использования на своих компьютерах. Взамен Майкрософт получает телеметрию об использовании системы, это позволяет проверить работу системы с новыми функциями, выявить неисправности и устранить неполадки в следующих сборках Виндовс 10.
Для продажи в розницу поступают только 3 версии Windows 10 для установки на новые компьютеры:
- Windows 10 Домашняя (Windows 10 Home)
- Windows 10 Профессиональная (Windows 10 Pro)
- Windows 10 S
Версия Windows 10 Enterprise устанавливается на компьютеры только в качестве обновления с редакции Windows 10 Pro. Остальные версии Microsoft поставляет производителям оборудования (ПК, ноутбуков) для установки на устройства, перед продажей потребителям.
Оригинальную операционную систему Windows 10 можно скачать с официального сайта Майкрософт, способами, описанными в этой статье.
Редакции Windows 10 Home
Для домашних пользователей выпущена редакция Windows 10, в которой присутствуют все базовые основные возможности операционной системы. Дома не нужны функции системы, применяемые на предприятиях, поэтому нет смысла переплачивать за лишнюю функциональность. Данная редакция хорошо подойдет для домашнего использования. В редакции Windows 10 Home применяется автоматическое обновление.
Версии Windows 10 для домашних пользователей подразделяются на следующие редакции:
- Windows 10 Домашняя (Windows 10 Home)
- Windows 10 Домашняя для одного языка (Windows 10 Home Single Language; Windows 10 Home SL; Windows 10 Single Language; Windows 10 SL) — версия аналогичная домашней редакции, отличающаяся лишь тем, что здесь нельзя поменять язык операционной системы. Очень часто данная редакция устанавливается на ноутбуках и нетбуках. Для производителей это более дешевый вариант лицензирования Майкрософт, чем Windows 10 Home.
- Windows 10 Домашняя с Bing — в этой версии нельзя поменять поисковую систему Bing в браузерах Microsoft Edge и Internet Explorer (ничто не мешает использовать другой браузер). Данная редакция устанавливается на некоторых ноутбуках.
Редакции Windows 10 Pro
Для предприятий малого бизнеса и домашних пользователей, которым необходимы расширенные возможности системы, предлагается профессиональная версия Windows 10, которая, в свою очередь, подразделяется на несколько редакций. В этой версии доступен гипервизор (виртуальная машина) Hyper-V, BitLocker и другие функции системы.
Профессиональные версии Windows 10 имеют следующие редакции:
- Windows 10 Профессиональная (Windows 10 Pro)
- Windows 10 Pro для образовательных учреждений (Windows 10 Pro Education)
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations (Windows 10 Pro для рабочих станций) — версия Windows 10 Pro с расширенной поддержкой оборудования для предприятий с высокой вычислительной нагрузкой
- Windows 10 S — версия со специальной конфигурацией Windows 10 Pro, в которой возможна работа приложений, установленных из Магазина приложений Майкрософт (Microsoft Store). Все другие программы не будут работать в этой версии операционной системы.
Редакции Windows 10 Enterprise
Для предприятий среднего и крупного бизнеса создана корпоративная версия системы. Редакция Windows Enterprise имеет все возможности профессиональной версии, а также дополнительные функции, которые актуальны для применения на предприятиях.
Корпоративная версия Windows 10 имеет следующие редакции:
- Windows 10 Корпоративная (Windows 10 Enterprise)
- Windows 10 Корпоративная с долгосрочным обслуживанием (Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB)
- Windows 10 для образовательных учреждений (Windows 10 Education)
Версия Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB имеет долгосрочный срок поддержки, предназначена для стабильной надежной работы. В системе отсутствуют встроенные приложения, ограничен некоторый функционал, устанавливаются только важные обновления. ОС Windows 10 LTSB можно бесплатно использовать в течение 90 дней (пробный период), система работает на английском языке. О том, как установить русский язык в Windows читайте тут.
Другие версии Windows 10
Также имеются несколько других версий Windows 10, среди них:
- Windows 10 IoT (Windows 10 для «Интернета вещей») — эта версия имеет несколько редакций для установки на промышленное оборудование (терминалы, банкоматы и т. п.).
- Windows 10 Team – данная версия устанавливается на планшеты Surface Hub
Различие редакций Windows 10
Многие пользователи, наверное, замечали отличия редакций Windows 10 с буквами в конце обозначения версий системы.
Буква «N» добавляется к редакциям Windows 10, выпущенных для стран Европейского Союза. Название редакций имеют такой вид: Windows 10 Home N, Windows 10 Pro N, Windows 10 Enterprise N и т. д. Отличие от стандартных версий в том, что в этих версиях, по требованию ЕС, отсутствуют некоторые приложения (музыка Groove, Windows Media Player, Кино и ТВ), которые можно добавить в ОС самостоятельно.
Буквы «KN» добавляется к версиям системы для Южной Кореи. Здесь отсутствуют те же самые приложения. Обозначение версий выглядит следующим образом: Windows 10 Enterprise KN, Windows 10 Pro KN, Windows 10 Home KN и т. д.
Для Китая выпущена специальная версия Windows 10 China Government Edition для использования в государственных учреждениях.
Буквенные сочетания «VL», «OEM», «COEM», «GGK», «GGWA», «FPP» обозначают типы лицензий для Windows.
Сравнение версий Windows 10 в таблице
Для использования на личных компьютерах оптимально подходят две редакции: Windows 10 Домашняя и Windows 10 Профессиональная. С помощью списка, отображающего возможности разных редакций Виндовс 10, намного легче выбрать лучшую версию системы, подходящую под требования конкретного пользователя.
Для наглядного сравнения версий Windows 10 посмотрите таблицу, в которой отображены основные возможности системы в разных редакциях: Windows 10 Home, Windows 10 Pro, Windows 10 Enterprise, Windows 10 Education.
Заключение
Операционная система Windows 10 выпускается в разных редакциях, которые отличаются функциональными возможностями, в зависимости от потребностей потребителей. Для домашнего использования рекомендованы версии Windows 10 Домашняя и Профессиональная.
Windows 10 has several editions, all with varying feature sets, use cases, or intended devices. Certain editions are distributed only on devices directly from an original equipment manufacturer (OEM), while editions such as Enterprise and Education are only available through volume licensing channels. Microsoft also makes editions of Windows 10 available to device manufacturers for use on specific classes of devices, including IoT devices and previously marketed Windows 10 Mobile for smartphones.
Baseline editions
Edit
Baseline editions are the only editions available as standalone purchases in retail outlets. PCs often come pre-installed with one of these editions.
- Home
- Windows 10 Home is designed for use in PCs, tablets and 2-in-1 PCs. It includes all features directed at consumers.[1][2][3]
- Pro
- Windows 10 Pro includes all features of Windows 10 Home, with additional capabilities that are oriented towards professionals and business environments, such as Active Directory, Remote Desktop, BitLocker, Hyper-V, and Windows Defender Device Guard.[1][2][3]
- Pro for Workstations
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations is designed for high-end hardware for intensive computing tasks and supports Intel Xeon, AMD Opteron and the latest AMD Epyc processors; up to 4 CPUs; up to 256 cores; up to 6 TB RAM; the ReFS file system; Non-Volatile Dual In-line Memory Module (NVDIMM); and remote direct memory access (RDMA).[4][5][6]
Organizational editions
Edit
These editions add features to facilitate centralized control of many installations of the OS within an organization. The main avenue of acquiring them is a volume licensing contract with Microsoft.
- Education
- Windows 10 Education is distributed through Academic Volume Licensing. It was based on Windows 10 Enterprise and initially reported to have the same feature set.[1][2][3] As of version 1709, however, this edition has fewer features. See § Comparison chart for details.
- Pro Education
- This edition was introduced in July 2016 for hardware partners on new devices purchased with the discounted K–12 academic license. It was based on the Pro edition of Windows 10 and contains mostly the same features as Windows 10 Pro with different options disabled by default, and adds options for setup and deployment in an education environment. It also features a «Set Up School PCs» app that allows provisioning of settings using a USB flash drive, and does not include Cortana, Microsoft Store suggestions, Windows Sandbox, or Windows Spotlight.[7][8][9]
- Enterprise
- Windows 10 Enterprise provides all the features of Windows 10 Pro for Workstations, with additional features to assist with IT-based organizations.[1][2][3] Windows 10 Enterprise is configurable on two servicing channels, Semi-Annual Channel and Windows Insider Program.[10]
- Enterprise LTSC
- Enterprise LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel) is a long-term support variant of Windows 10 Enterprise released every 2 to 3 years. Each release is supported with security updates for either 5 or 10 years after its release, and intentionally receive no feature updates.[11] Some features, including the Microsoft Store and bundled apps, are not included in this edition.[12][1][3] This edition was first released as Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB (Long-Term Servicing Branch).[13] There are currently 4 releases of LTSC: one in 2015 (version 1507), one in 2016 (version 1607), one in 2018 (labeled as 2019, version 1809), and one in 2021 (version 21H2).[14][15]
S mode
Edit
Since 2018, OEMs can ship Windows 10 Home and Pro in a feature-limited variation named S mode which evolved from the discontinued Windows 10 S. Organizations employing Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education can make use of S mode too.[16] S mode is a feature-limited edition of Windows 10 designed primarily for low-end devices in the education market. It has a faster initial setup and login process, and allows devices to be provisioned using a USB drive with the «Set Up School PCs» app.
Changes
Edit
With the exception of the Microsoft Teams desktop client which was made available for S mode in April 2019,[citation needed] the installation of software (both Universal Windows Platform (UWP) and Windows API apps) is only possible through the Microsoft Store, and built-in and Microsoft Store-obtained command line programs or shells cannot be run in this mode.[17][18][19][20] System settings are locked to allow only Microsoft Edge as the default web browser with Bing as its search engine.[21] The operating system may be switched out of S mode using the Microsoft Store for free. However, once S Mode is turned off, it cannot be re-enabled.[22][23] All Windows 10 devices in S mode include a free one-year subscription to Minecraft: Education Edition.[citation needed] Critics have compared the edition to Windows RT, and have considered it to be an alternative to ChromeOS.[22][24][25][26][27]
Device-specific editions
Edit
These editions are licensed to OEMs only, and are primarily obtained via the purchase of hardware that includes it:
- Holographic
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s HoloLens mixed reality smartglasses.[28][29]
- IoT Enterprise
- A rebranded variant of Microsoft’s earlier embedded operating systems, Windows Embedded. Designed specifically for use in small footprint, low-cost devices and IoT scenarios.[30][31] IoT Core was discontinued on 10 November 2020,[32][33] while IoT Core LTSC is supported up through 9 January 2029.[34]
- Team
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s Surface Hub interactive whiteboard.[35]
Discontinued editions
Edit
The following editions of Windows 10 were discontinued (as of Windows 10 version 21H2). For both Mobile and Mobile Enterprise, Microsoft confirmed it was exiting the consumer mobile devices market, so no successor product is available.[36]
- Mobile
- Windows 10 Mobile was designed for smartphones and small tablets. It included all basic consumer features, including Continuum capability. It was the de facto successor of Windows Phone 8.1 and Windows RT.[1][2]
- Mobile Enterprise
- Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise provided all of the features in Windows 10 Mobile, with additional features to assist IT-based organizations, in a manner similar to Windows 10 Enterprise, but optimized for mobile devices.[1][2]
- IoT Mobile
- A binary equivalent of Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise licensed for IoT applications. Also known as IoT Mobile Enterprise.[37][38]
- S
- Windows 10 S was an edition released in 2017 which ultimately evolved into the so-called S mode of Windows 10. In March 2018, Microsoft announced that it would be phasing out Windows 10 S, citing confusion among manufacturers and end-users.[39][40]
- 10X
- Originally announced for use on dual-screen devices such as the Surface Neo and other potential form factors, 10X featured a modified user interface designed around context specific interactions or «postures» on such devices, including a redesigned Start menu with no tiles, and use of container technology to run Win32 software.[41][42] The platform was described as a more direct competitor to ChromeOS.[43][44] On May 4, 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would first be used on single-screen devices, and that they would «continue to look for the right moment, in conjunction with our OEM partners, to bring dual-screen devices to market».[45] Microsoft also added anti-theft protection to Windows 10X, just like how Apple’s Activation Lock and anti-theft protection on Android devices and Chromebooks work.[46] On May 18, 2021, Head of Windows Servicing and Delivery John Cable stated that Windows 10X had been cancelled, and that its foundational technologies would be leveraged for future Microsoft products.[47] Several design changes in 10X, notably the centered taskbar and redesigned start menu, would be later introduced in Windows 11.[48]
Regional variations
Edit
- N/KN
- As with previous versions of Windows since Windows XP, all Windows 10 editions for PC hardware have «N» and «KN» variations in Europe and South Korea that exclude multimedia functionality, in compliance with antitrust rulings.[49] According to details that Microsoft has published, any app that relies on Microsoft multimedia technologies experiences impaired functionality on these editions, unable to even play audio notification tones.[50] Restoring the missing functionality to these editions entails installing the «Media Feature Pack», followed by Skype, Movies & TV, Windows Media Player, Xbox Game Bar, Windows Voice Recorder, and four codecs.[50] The variation cannot be changed without a clean install, and keys for one variation will not work on other variations.
- Home with Bing
- As with Windows 8.1, a reduced-price «Windows 10 with Bing» SKU is available to OEMs; it is subsidized by having Microsoft’s Bing search engine set as default, which cannot be changed to a different search engine by OEMs. It is intended primarily for low-cost devices, and is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home.[51]
- Home Single Language
- In some emerging markets,[citation needed] OEMs preinstall a variation of Windows 10 Home called Single Language without the ability to switch the display language. It is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home. To change display language, the user will need to upgrade to Windows 10 Home or Windows 10 Pro.
- China Government Edition
- In May 2017, it was reported that Microsoft, as part of its partnership with China Electronics Technology Group, created a specially-modified variant of Windows 10 Enterprise («G») designed for use within branches of the Chinese government. This variant is pre-configured to «remove features that are not needed by Chinese government employees», and allow the use of its internal encryption algorithms.[52][53]
Comparison chart
Edit
| Item | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Yes | Feature is present in the given edition |
| Yes, since [update] | Feature is present in the given edition after installing a certain update |
| No | Feature is absent from the given edition |
| No, since [update] | Feature is absent from the given edition after installing a certain update (It might have been fully or partly present prior to that update) |
| [Explanation] | Feature is partly present in the given edition |
| [Explanation], since [update] | Feature is partly present in the given edition, after installing a certain update (It might have been fully present prior to that update, or not present at all) |
Microsoft OEM licensing formula takes display size, RAM capacity and storage capacity into account. In mid-2015, devices with 4 GB RAM were expected to be $20 more expensive than devices with 2 GB RAM.[75]
Upgrade path
Edit
Free upgrade
Edit
At the time of launch, Microsoft deemed Windows 7 (with Service Pack 1) and Windows 8.1 users eligible to upgrade to Windows 10 free of charge, so long as the upgrade took place within one year of Windows 10’s initial release date. Windows RT and the respective Enterprise editions of Windows 7, 8, and 8.1 were excluded from this offer.[76]
| Windows version and edition | Windows 10 edition |
|---|---|
| Windows 7 Starter SP1 | Home |
| Windows 7 Home Basic SP1 | |
| Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 with Bing | |
| Windows 8.1 | |
| Windows 7 Professional SP1 | Pro |
| Windows 7 Ultimate SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 Pro | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Mobile |
Transition paths
Edit
The following table summarizes possible transition paths (upgrade, downgrade, or migration) that can be taken, provided that proper licenses are purchased.
Windows RT does not appear in this table because it cannot be upgraded to Windows 10.
On September 28, 2023, Microsoft disabled the free upgrade path to Windows 10 from Windows 7 or 8.x, although upgrades from Windows 10 to 11 are still supported.[77][78]
| Transition path | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Upgrade | Constitutes replacing the OS while preserving apps, their settings, and user data |
| Repair | Constitutes fixing a damaged OS by «upgrading» from one edition to the same |
| Downgrade | Similar to upgrade, but deliberately removes some features |
| Migration | Constitutes replacing the operating system, reinstalling the apps, restoring their settings via backup, and safeguarding user data against accidental deletion. |
| None | It is impossible to replace the OS with the intended target because of platform incompatibility |
| Windows version |
Windows edition |
Transition target | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Home |
Windows 10 Pro |
Windows 10 Pro for Workstations |
Windows 10 Pro (Education) |
Windows 10 Education |
Windows 10 Enterprise |
Windows 10 Mobile |
||
| Windows 7 | Starter | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None |
| Home Basic | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Home Premium | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Professional | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Ultimate | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | Migration | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Windows 8.1 | (Core) | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None |
| with Bing | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Migration | None | |
| Pro | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro for Students | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro with Media Center | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Embedded Industry | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Upgrade | None | |
| Phone 8.1 | None | None | None | None | None | None | Upgrade | |
| Windows 10 | Home | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None |
| Pro | Downgrade | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro for Workstations | Downgrade | Downgrade | Repair | Upgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | None | |
| Pro Education | Downgrade | Upgrade | Upgrade | Repair | Migration | Migration | None | |
| Education | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Repair | Upgrade | None | |
| Enterprise | Migration | Migration | Migration | Migration | Downgrade | Repair | None | |
| Mobile | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
Release channels
Edit
Microsoft releases minor versions of Windows 10 through the free feature updates.[12] Originally, Microsoft released feature updates semiannually. They contained new features as well as changes.[80] With the release of Windows 11, however, Microsoft has changed the release schedule to annual. These feature updates do not contain any noticeable changes.
The pace at which a system receives feature updates depends on the «release channel» (originally, «release branch») from which the system downloads its updates.[12]
Insider Channel
Edit
Windows Insider is a beta testing program that allows access to pre-release builds of Windows 10, enabling power users, developers, and vendors to test and provide feedback on future feature updates to Windows 10 as they are developed. Windows Insider itself consists of four «rings.»
- The «Fast» ring distributes new builds as they are released
- The «Slow» ring distributes new builds with a delay following their availability on the Fast ring
- The «Release Preview» ring distributes release candidate
- The «Skip Ahead» ring distributes builds of the next feature update while a current release is being finished
General Availability Channel
Edit
Since 2022, the General Availability Channel (GAC) distributes feature updates annually. To receive these updates, users must either request them manually or wait for their version of Windows 10 to go out of support.
Originally, however, Microsoft distributed feature updates through two distinct channels, the «Current Branch» (CB) an the «Current Branch for Business» (CBB).
- The «Current Branch» (CB) distributed all feature updates as they graduated from the Windows Insider program. Microsoft only supported the latest build. Windows would automatically install the latest feature update from CB. Users could defer the CB feature update for up to 365 days.[81][82][83][84] Microsoft renamed CB to «Semi-Annual Channel (Targeted)» in version 1709.
- The «Current Branch for Business» (CBB), which was not available in the Home edition, distributed feature updates with a four-month delay. This allowed customers and vendors to evaluate and perform additional testing on new builds before broader deployments. Devices could be switched back to the Current Branch at any time.[12][85] Microsoft renamed CBB to «Semi-Annual Channel» in version 1709.
Since version 1903, Microsoft dismantled the two-channel scheme in favor of a unified «Semi-Annual Channel» (SAC). Microsoft supports each SAC version of Windows for 30 months. Windows no longer installs new feature updates automatically before the expiry of the 30-months support period. With the release of Windows 11, Microsoft changed the release schedule to annual, and change the channel’s name to «General Availability Channel» (GAC).
Long-Term Servicing Channel
Edit
LTSC exclusively distributes the «Enterprise LTSC», «IoT Core», and «IoT Enterprise LTSC» editions of Windows 10. Microsoft releases a new minor version of these editions every 2–3 years. LTSC builds adhere to Microsoft’s traditional support policy which was in effect before Windows 10, including:
- Five years of mainstream support
- Critical and security updates for ten years after their release
- No feature updates from Windows Update
Microsoft discourages the use of LTSC editions outside of «special-purpose devices» that perform a fixed function and thus do not require new user experience features. As a result, these editions do not come with Microsoft Store, most Cortana features, and most bundled apps.[12][1][3] LTSC was originally called the «Long-Term Servicing Branch» (LTSB) until 2016.[13]
See also
Edit
- Windows Server 2016, based on Windows 10 version 1607[86]
- Windows Server 2019, based on Windows 10 version 1809
- Xbox system software, an operating system now based on the Windows 10 core, designed to run on consoles
- Windows 10 version history
Notes
Edit
- ^ a b c 32-bit architectures like IA-32 and ARM32 have a memory addressing limitation of four gigabytes. In practice, less than 4 GB of memory is addressable as the 4 GB space also includes the memory mapped peripherals.
- ^ Windows 10 utilises processor groups on x86-64 to manage processor affinity and scheduling. The Windows 10 kernel has a hard-coded limit of 20 processor groups, and each processor group can contain up to 64 logical processors. A logical processor is either a physical or SMT core. Processor groups are allocated based on the NUMA topology of the system. One processor group cannot span multiple sockets or NUMA nodes. Processor groups are not available on IA-32; 32-bit builds instead use an older affinity mask implementation with a limit of 32 logical processors. The limit of 20 processor groups does not change between Windows 10 editions. There is no specific limit on the number of physical cores that can be used on Windows 10, unlike Windows Server where physical cores must be additionally licensed.[58][60][61][62]
- ^ There are three (previously four) telemetry levels, in the order of magnitude: Diagnostic data off (Security), Required (Basic), and Optional (Full). The higher the level, the more information that is sent to Microsoft. Previous Windows 10 versions had a level between Required and Optional, and the older names for the levels are shown in the parenthesis.
- ^ Cortana is available only in certain markets. Experience may vary by region and device.
- ^ a b This feature was missing from Windows 10 version 1803, but not the prior or next versions.
- ^ Windows Hello requires specialized hardware, such as a fingerprint reader, illuminated IR sensor or other biometric sensor.
- ^ On Windows 10 Pro, a Control Panel applet corresponding to this feature appears, but a Windows 10 Enterprise or Education image is still needed.[73][74]
References
Edit
- ^ a b c d e f g h Prophet, Tony (May 13, 2015). «Introducing Windows 10 Editions». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ a b c d e f Bott, Ed (May 14, 2015). «Windows 10 editions: Everything you need to know». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b c d e f Foley, Mary Jo (July 2, 2015). «Which Windows 10 editions get which features?». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Diaconu, Klaus (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft announces Windows 10 Pro for Workstations». Windows For Your Business. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft confirms new Windows 10 Pro for Workstations edition». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Warren, Tom (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft reveals new Windows 10 Workstations edition for power users». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 27, 2016). «Microsoft to add new Windows 10 Pro Education edition to its line-up». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 editions for education customers». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ a b «Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, «fun facts», and suggestions». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ DaniHalfin. «Assign devices to servicing branches for Windows 10 updates (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ «The next Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) release». Microsoft. February 18, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Overview of Windows as a service». Microsoft. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ a b Brinkmann, Martin (July 28, 2017). «Windows 10 LTSB becomes Windows 10 LTSC». gHacks Technology News.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg. «FAQ: Windows 10 LTSB explained». Computerworld. Retrieved October 3, 2018.
- ^ greg-lindsay. «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021 — What’s new in Windows». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved November 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 in S mode FAQ». Windows.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Turner, Rich (May 18, 2017). «Will Linux distros run on Windows 10 S?». Microsoft. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Gartenberg, Chaim (May 19, 2017). «Linux distros won’t run on Windows 10 S after all». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Smith, Sharon. «Get clients for Microsoft Teams — Microsoft Teams». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ «Update get-clients.md · MicrosoftDocs/OfficeDocs-SkypeForBusiness@5c2ca5a». GitHub. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 2, 2017). «Windows 10 S won’t let you change the default browser or switch to Google search». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ a b Chacos, Brad. «Meet Windows 10 S, a streamlined, simplified, Microsoft Store-only OS for schools». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Warren, Tom (June 19, 2017). «Microsoft now lets Surface Laptop owners revert back to Windows 10 S». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «Windows 10 S is Microsoft’s answer to Chrome OS». The Verge. Vox Media. May 2, 2017. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (September 14, 2016). «Desktop apps make their way into the Microsoft Store». Ars Technica. Condé Nast.
- ^ «Windows 10 Cloud looks just like Windows 10 in leaked screenshots». The Verge. Vox Media. February 3, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ «Leaked Microsoft document confirms Windows 10 Cloud and a Chromebook competitor». PC World. IDG. Retrieved April 23, 2017.
- ^ «Unlock Windows Holographic for Business features». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft pushes Windows 10 Holographic as the one-stop option for VR and AR». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT for your business». Windows for Business. Microsoft. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise». MS Embedded. Silica. August 14, 2015. Archived from the original on May 8, 2017. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft to combine Windows 10 IoT Core and IoT Enterprise in 2021». ZDNet. Mary Jo Foley. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ «Windows 10 Team Anniversary Update now available for Microsoft Surface Hub». Neowin. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ Patrizio, Andy (September 29, 2016). «Microsoft is leaving the consumer mobile market». Network World. IDG Publishing. Retrieved August 30, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 on Thin Clients: Deliver Best Results with Scout Agents (Part 1 of 2)». Fujitsu. Archived from the original on January 23, 2021. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Supported operating systems and browsers in Intune». Microsoft. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft admits Windows 10 S was confusing, new ‘S Mode’ upgrades will be free». The Verge. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Tung, Liam. «Windows 10 to permit block on apps installing if they’re not from Microsoft Store». ZDNet. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 2, 2019). «Microsoft Surface Neo first look: the future of Windows 10X is dual-screen». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Hollister, Sean (October 2, 2019). «Windows 10X is Microsoft’s latest stab at a ‘Lite’ operating system, exclusively for dual-screens». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft reportedly shelves Windows 10X, its Chrome OS competitor». The Verge. May 7, 2021. Retrieved May 7, 2021.
- ^ Salter, Jim (May 13, 2021). «Microsoft puts Windows 10X variant on the back burner». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 4, 2020). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is coming to laptops amid big jump in Windows usage». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Ballard, Barclay (January 25, 2021). «This clever Windows 10X feature will prevent thieves from resetting stolen devices». TechRadar. Retrieved January 21, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 11 Leaks Indicate a Dramatic New Look Is Coming Soon». Gizmodo. Archived from the original on June 16, 2021. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ Ron (August 2, 2015). «Grab the Media Feature Pack for Windows 10 N and Windows 10 KN editions». OnMSFT.com. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ a b «Media Feature Pack for Windows 10/11 N (February 2023)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ^ Slater-Robins, Max. «Microsoft is helping manufacturers make cheap tablets that can run Windows as well as Android». Business Insider UK. Retrieved April 23, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft made a version of Windows 10 for the Chinese government». Engadget. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Myerson, Terry (May 23, 2017). «Announcing Windows 10 China Government Edition and the new Surface Pro». Windows Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ Dudau, Vlad (June 10, 2015). «Microsoft shows OEMs how to market Windows 10; talks features and SKUs». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved June 19, 2015.
- ^ «Compare Windows 10 Pro & Enterprise (E3 & E5) Commercial Editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2015.
- ^ «Compare Windows 10 Editions & Versions | Home & Pro». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ^ Howse, Brett (July 2, 2015). «Windows 10 Editions Compared». AnandTech. Purch.
- ^ a b Graham Sutherland (April 7, 2022). «CPU Socket and Core Count Limits in Windows 10 (And How To Remove Them)». Codeinsecurity. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Andre Da Costa (September 15, 2015). «Understanding Windows 10 Editions, Architectures and Builds». groovyPost. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- ^ «Processor Groups — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. December 30, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «NUMA Support — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. August 19, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Geoff Chappell (December 17, 2019). «KAFFINITY_EX». Geoff Chappell, Software Analyst. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «Configure Windows telemetry in your organization». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. August 10, 2020.
- ^ «Continuum on Windows 10». July 27, 2015.
- ^ Confirmed by @MicrosoftHelps (Verified) on Twitter
- ^ «Features that are removed or deprecated in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update». Support (28 ed.). Microsoft. October 17, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ shortpatti. «DirectAccess». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ «DirectAccess and Windows 10 in Education». August 4, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 10, 2017). «Ask Paul: Is Windows To Go Coming to Windows 10 Pro?». thurrott.com. BWW Media Group.
- ^ Niehaus, Michael; Lich, Brian. «Windows To Go frequently asked questions (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 30, 2017.
How can Windows To Go be deployed in an organization? [~snip~] A Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education image
- ^ «TrendForce Adjusts Notebooks’ Unit Memory Capacity for 2015 Down by 3~5% due to Microsoft’s New License Fee Arrangement for Windows 10». DRAMeXchange. TrendForce Corp. July 27, 2015. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ Trent, Rod (June 9, 2015). «Windows 10 Upgrade Paths». SuperSite for Windows. Penton.
- ^ «Windows Ends Installation Path for Free Windows 7/8 Upgrade». Microsoft. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Tyson, Mark (September 29, 2023). «Microsoft Says the Days of Free Windows 7 to 10 or 11 Updates Are Over». Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Lindsay, Greg; Lich, Brian (April 5, 2017). «Windows 10 upgrade paths». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 20, 2017). «Microsoft will now release major Windows 10 updates every March and September». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «How to Pause Windows 10 Automatic Updates To Avoid Critical Bugs». www.bleepingcomputer.com. Retrieved September 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 : the case of the missing update deferral options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. May 28, 2019. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (March 1, 2017). «Put Windows 10 updates on hold—now available in Creators Update build 15046». Computerworld. IDG. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ Paul, Ian (April 18, 2017). «How to defer future updates in the Windows 10 Creators Update». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (November 17, 2015). «How to defer upgrades and updates in Windows 10 Pro». Computerworld. IDG.
- ^ Woods, Rich (September 24, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809 will be generally available in October». Neowin.