Формулировка вопроса напрашивается на соотвествующий ответ…
Но если по существу — узнать какая программа занимает порт можно
netstat -aon | findstr 8080
потом
tasklist /fi «PID eq 12345»
— вместо 12345 подставить число из вывода первой команды
Что значит «очистить»? Если надо освободить, то просто прибейте процесс, который его занял.
Порт это цифра, номер.
Используется при передаче пакетов по сети. К имени пакета добавляют номер, чтобы получатель знал кому именно передать пакет.
Объясните пожалуйста как номер может «залагать»? Что вы под этим подразумеваете?
Как очистить использующийся порт в windows?
Никак. Они все чистые. И их всего имеется 65536.
Dedar Alam
Posted on
• Updated on
Step 1:
Open up cmd.exe (note: you may need to run it as an administrator, but this isn’t always necessary), then run the below command:
netstat -ano | findstr <Port Number>
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
(Replace with the port number you want, but keep the colon)
The area circled in red shows the PID (process identifier). Locate the PID of the process that’s using the port you want.
Step 2:
Next, run the following command:
taskkill /F /PID <Process Id>
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Example
STEP — 1
netstat -ano | findstr 8080
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
TCP 0.0.0.0:18080 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 19788
TCP [::]:18080 [::]:0 LISTENING 19788
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
STEP — 2
taskkill /F /PID 19788
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
SUCCESS: The process with PID 19788 has been terminated.
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Source
How can I remove the current process/application which is already assigned to a port?
For example: localhost:8080
asked Sep 22, 2016 at 7:19
4
Step 1:
Open up cmd.exe (note: you may need to run it as an administrator, but this isn’t always necessary), then run the below command:
netstat -ano | findstr :<PORT>
(Replace <PORT> with the port number you want, but keep the colon)
The area circled in red shows the PID (process identifier). Locate the PID of the process that’s using the port you want.
Step 2:
Next, run the following command:
taskkill /PID <PID> /F
(No colon this time)
Lastly, you can check whether the operation succeeded or not by re-running the command in «Step 1». If it was successful you shouldn’t see any more search results for that port number.
Mujeeb
1,0551 gold badge9 silver badges18 bronze badges
answered Sep 22, 2016 at 7:59
KavinduWijeKavinduWije
39.8k4 gold badges14 silver badges17 bronze badges
15
I know that is really old question, but found pretty easy to remember, fast command to kill apps that are using port.
Requirements: [email protected]^ version
npx kill-port 8080
You can also read more about kill-port here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/kill-port
answered Jun 16, 2020 at 10:32
Rafał FiguraRafał Figura
5,5461 gold badge15 silver badges20 bronze badges
3
There are two ways to kill the processes
Option 01 — Simplest and easiest
Requirement : [email protected]^ version
Open the Command prompt as Administrator and give the following command with the port (Here the port is 8080)
npx kill-port 8080
Option 02 — Most commonly used
- Step 01
Open Windows command prompt as Administrator
- Step 02
Find the PID of the port you want to kill with the below command: Here port is 8080
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :8080"
TCP 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 18264
- Step 03
Kill the PID you received above with the below command (In my case PID is 18264)
taskkill /PID 18264 /f
answered Jul 21, 2020 at 4:16
1
Step 1 (same is in accepted answer written by KavinduWije):
netstat -ano | findstr :yourPortNumber
Change in Step 2 to:
tskill typeyourPIDhere
Note: taskkill is not working in some git bash terminal
answered Sep 21, 2017 at 11:20
afsarkhan10182afsarkhan10182
2,1721 gold badge13 silver badges17 bronze badges
1
With Windows 10/11 default tools:
✔ Step one:
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator
✔ Step two:
Find the ProcessID for the port you need to kill (e.g. 3000)
netstat -aon | findstr 3000
TCP 0.0.0.0:3000 LISTEN 1234
✔ Step three:
Kill the zombie process:
taskkill /f /pid 1234
where «1234» is your ProcessID (aka PID)
*Extra tip if you use Windows Subsystem for Linux (Ubuntu WSL):
✔ Step one:
sudo lsof -t -i:3000
✔ Step two:
sudo kill -9 1234
answered Mar 18, 2019 at 10:01
Java wanna beeJava wanna bee
2,6021 gold badge12 silver badges25 bronze badges
4
If you are using GitBash
Step one:
netstat -ano | findstr :8080
Step two:
taskkill /PID typeyourPIDhere /F
(/F forcefully terminates the process)
answered Sep 17, 2017 at 19:55
Ara YaghsizianAra Yaghsizian
1,2891 gold badge8 silver badges10 bronze badges
1
The simplest solution — the only one I can ever remember:
In Windows Powershell
Say we want to stop a process on port 8080
- Get the process:
netstat -ano | findstr :8080
- Stop the process
stop-process 82932
answered Sep 3, 2021 at 15:38
Luke GarriganLuke Garrigan
4,6111 gold badge21 silver badges31 bronze badges
2
If you already know the port number, it will probably suffice to send a software termination signal to the process (SIGTERM):
kill $(lsof -t -i :PORT_NUMBER)
answered Dec 19, 2018 at 7:43
Fellow StrangerFellow Stranger
32.3k35 gold badges170 silver badges233 bronze badges
4
For use in command line:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| find ":8080" ^| find "LISTENING"') do taskkill /f /pid %a
For use in bat-file:
for /f "tokens=5" %%a in ('netstat -aon ^| find ":8080" ^| find "LISTENING"') do taskkill /f /pid %%a
answered Jun 29, 2018 at 10:10
4
Simple CMD is working me. Easy to remember
find the port number which you want kill and run the below cmd
npx kill-port 8080
After complete the Port get stopped and getting this message
npx: installed 3 in 13.796s
Process on port 8080 killed
ux.engineer
10.3k14 gold badges67 silver badges112 bronze badges
answered Apr 28, 2021 at 7:45
DeepakDeepak
5717 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
In Windows PowerShell version 1 or later to stop a process on port 3000 type:
Stop-Process (,(netstat -ano | findstr :3000).split() | foreach {$[$.length-1]}) -Force
As suggested by @morganpdx here`s a more PowerShell-ish, better version:
Stop-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 3000).OwningProcess -Force
answered Dec 8, 2017 at 15:54
todormtodorm
4744 silver badges6 bronze badges
3
Open command prompt and issue below command
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :8888"
Output will show the process id occupying the port
Issue below command to kill the PID
taskkill /pid 8912 /f
You will receive the output as below
SUCCESS: The process with PID 8860 has been terminated.
answered Mar 31, 2021 at 13:08
Waqas AhmedWaqas Ahmed
4,8313 gold badges37 silver badges45 bronze badges
1
If you can use PowerShell on Windows you just need :
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort "8080").OwningProcess | Stop-Process
answered Oct 27, 2020 at 10:20
2
For Windows users, you can use the CurrPorts tool to kill ports under usage easily:
answered Oct 3, 2018 at 11:43
Zuhair TahaZuhair Taha
2,8382 gold badges35 silver badges33 bronze badges
1
I was running zookeeper on Windows and wasn’t able to stop ZooKeeper running at 2181 port using zookeeper-stop.sh, so tried this double slash «//» method to taskkill. It worked
1. netstat -ano | findstr :2181
TCP 0.0.0.0:2181 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 8876
TCP [::]:2181 [::]:0 LISTENING 8876
2.taskkill //PID 8876 //F
SUCCESS: The process with PID 8876 has been terminated.
answered Dec 6, 2018 at 4:29
Let’s Automate!
If you fall into this issue much often like me, make an .bat file and run it to end process.
create a bat file «killport.bat»
set /P port="Enter port : "
echo showing process running with port %port%
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :%port%"
set /P pid="Enter PID to kill : "
taskkill /pid %pid% /f
set /P exit="Press any key to exit..."
Run this file by double clicking and
- Enter port number (then it will list process with PID)
- Enter PID to kill
Done
(Optional)
Set to path environment so that you can access this file from anywhere.
Most probably you will know how to add an new path to env. But here’s how if you don’t
Step 1 of 4
Search ENV on start menu
Step 2 of 4
Select Environment Variables
Step 3 of 4
Select ‘path’ and click Edit button
Step 4 of 4
Click ‘New’ add the path where .bat file is stored. Since I saved it on ‘../Documents/bats’ folder I am adding this path. Your path will depend on where you save this file.
Open CMD and test. Remember you filename will the word to run this file. Since I saved the .bat file as ‘killport.bat’ => ‘killport’ is the word to run it.
if do enjoy!
else share how you done it here
Dharman♦
31.1k25 gold badges87 silver badges138 bronze badges
answered May 10, 2021 at 10:46
Run cmd as administrator. Then type this code in there.
netstat -ano | findstr :<8080>
Then you can see the PID run on your port. Then copy that PID number. ( PID is a unique number that helps identify a hardware product or a registered software product.) And type below code line and press enter.
taskkill /PID <Enter the copied PID Number> /F
answered Jun 10, 2021 at 18:13
If you’re using Windows Terminal then the killing process might be little less tedious.
I’ve been using windows terminal and kill PID works fine for me to kill processes on the port as the new Windows Terminal supports certain bash commands. For example: kill 13300
So, the complete process will look like this-
- Open Windows Terminal
- Type the following command to show processes running on the port you’re looking to kill processes.
netstat -ano | findstr :PORT - Type following to kill the process.
kill PID
For Example:
PS C:\Users\username> netstat -ano | findstr :4445
TCP 0.0.0.0:4445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 7368
TCP [::]:4445 [::]:0 LISTENING 7368
PS C:\Users\username> kill 7368
PS C:\Users\username> netstat -ano | findstr :4445
PS C:\Users\username>
See when I typed the first command to list processes on the port it returned empty. That means all processes are killed now.
Update: kill is an alias for Stop-Process. Thanks, @FSCKur for letting us know.
answered May 21, 2020 at 9:55
lazycipherlazycipher
3403 silver badges14 bronze badges
7
If you use powershell 7+ this worked for me. Just add this function in your $PROFILE file.
function killport([parameter(mandatory)] [string] $uport){
if($upid = (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort $uport -ErrorAction Ignore).OwningProcess){kill $upid}
}
then simply use killport 8080
or if you prefer just the command you can try this:
kill $(Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 8761 -ErrorAction Ignore).OwningProcess
answered Feb 1, 2022 at 19:19
Deekshith AnandDeekshith Anand
2,2431 gold badge22 silver badges24 bronze badges
4
You can do by run a bat file:
@ECHO OFF
FOR /F "tokens=5" %%T IN ('netstat -a -n -o ^| findstr "9797" ') DO (
SET /A ProcessId=%%T) &GOTO SkipLine
:SkipLine
echo ProcessId to kill = %ProcessId%
taskkill /f /pid %ProcessId%
PAUSE
answered Dec 5, 2018 at 7:53
flopcoderflopcoder
1,19512 silver badges26 bronze badges
the first step
netstat -vanp tcp | grep 8888
example
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.8888 *.* LISTEN 131072 131072 76061 0
tcp46 0 0 *.8888 *.* LISTEN 131072 131072 50523 0
the second step: find your PIDs and kill them
in my case
sudo kill -9 76061 50523
answered Aug 25, 2020 at 19:35
rusconruscon
772 silver badges9 bronze badges
1
netstat -ano | findstr :PORT
kill PI
answered Oct 30, 2020 at 11:31
harun ugurharun ugur
1,72620 silver badges19 bronze badges
One line solution using GitBash:
tskill `netstat -ano | grep LISTENING | findstr :8080 | sed -r 's/(\s+[^\s]+){4}(.*)/\1/'`
Replace 8080 with the port your server is listening to.
If you need to use it often, try adding to your ~/.bashrc the function:
function killport() {
tskill `netstat -ano | findstr LISTENING | findstr :$1 | sed -r 's/^(\s+[^\s]+){4}(\d*)$/\1/'`
}
and simply run
killport 8080
answered May 20, 2020 at 21:04
Italo BorssattoItalo Borssatto
15.1k7 gold badges63 silver badges88 bronze badges
2
I wrote a tiny node js script for this. Just run it like this:
node killPort.js 8080 or whatever port you need to kill. Save the following to a killPort.js file:
const { exec } = require('child_process');
const fs = require(`fs`);
const port = process.argv.length > 2 ? process.argv[2] : ``;
if (!port || isNaN(port)) console.log(`port is required as an argument and has to be a number`);
else {
exec(`netstat -ano | findstr :${port}`, (err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (!stdout) console.log(`nobody listens on port ${port}`);
else {
const res = stdout.split(`\n`).map(s => s.trim());
const pid = res.map(s => s.split(` `).pop()).filter(s => s).pop();
console.log(`Listener of ${port} is found, its pid is ${pid}, killing it...`);
exec(`taskkill /PID ${pid} /F`, (err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (!stdout) console.log(`we tried to kill it, but not sure about the result, please run me again`);
else console.log(stdout);
})
}
});
}
answered Aug 31, 2021 at 9:11
shalshal
2,8544 gold badges20 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
I am using GitBash and I error like below when ran
taskkill //PID XXXX
ERROR: The process with PID 7420 could not be terminated. Reason: This
process can only be terminated forcefully (with /F option).
So used //F like below and worked fine
taskkill //F //PID XXXX
answered Dec 25, 2021 at 11:29
Vatsal ShahVatsal Shah
1,33418 silver badges21 bronze badges
Here is a script to do it in WSL2
PIDS=$(cmd.exe /c netstat -ano | cmd.exe /c findstr :$1 | awk '{print $5}')
for pid in $PIDS
do
cmd.exe /c taskkill /PID $pid /F
done
answered Aug 14, 2020 at 9:59
MyrionSC2MyrionSC2
1,2481 gold badge14 silver badges24 bronze badges
We can avoid this by simple restarting IIS, using the below command:
IISRESET
answered Aug 21, 2018 at 12:31
0
Предисловие: При недавнем написании проекта vue мне нужно было использовать локальный порт 8080 для имитации сбора данных, но я обнаружил, что порт 8080 занят, что странно.
Есть так много ям, как их решить?
win + r Откройте быстрое окно программы, введите cmd, войдите в окно командной строки, а затем введите netstat -ano в окне, после чего отобразятся все занятые порты. Обратите внимание, что после netstat есть пробел, вы должны добавить , Однако большая часть данных порта не появилась, и об ошибке было сообщено: netstat -ano Система подсказывает, что это не внутренняя или внешняя команда, потому что Windows не задает инструкцию пути для запуска внешних команд по произвольному пути, как ее добавить:
Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши / Мой компьютер / Дополнительно / Переменные среды, а затем просмотрите одну из следующих системных переменных, где значение PATH равно c: \ windows; c: \ windows \ system32, если эти два в порядке, добавьте их. ,
Если вы действительно не хотите добавлять или беспокоитесь, вы можете напрямую
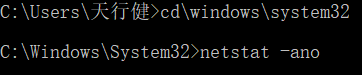
Откройте окно командной строки: Пуск-> Выполнить-> Введите CMD-> ОК. Введите в окне: C: (Enter). Введите: cd \ windows \ system32 (Enter). Затем выполните команду: netstat -ano следующим образом :
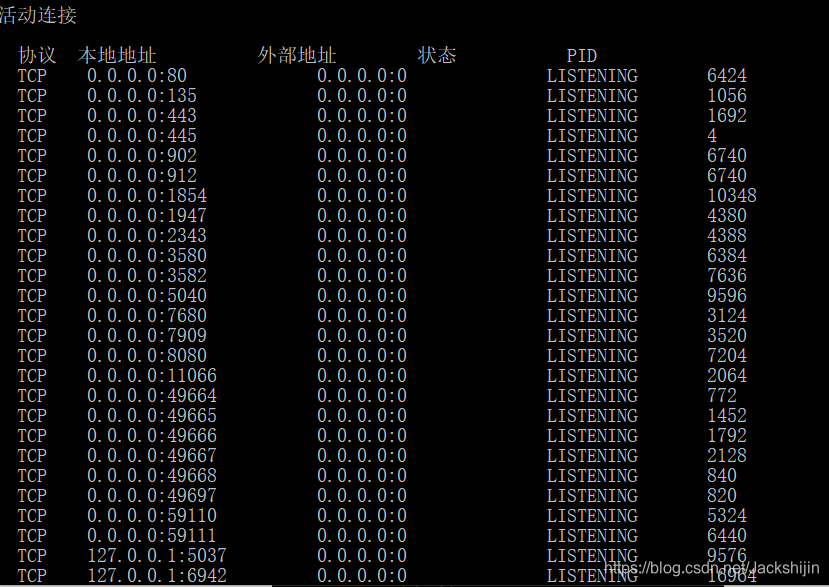
Вы получите много значений занятости порта и PID следующим образом:
Ослепительно, порт занят правым концом PID, это номер порта, который трудно найти. Не паникуйте —-> продолжайте вводить следующую команду:
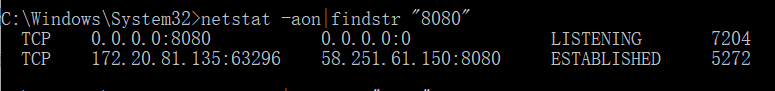
netstat -aon | findstr «8080», после нажатия Enter вы увидите PID порта 8080 в списке (самый правый столбец). Просмотрите соответствующую программу занятия в диспетчере задач компьютера в соответствии с PID, а затем закройте ее.
Видя, что приложения с PID 7204 и 5272 занимают порт 8080, как закрыть программный процесс:
Введите в окне поиска компьютера Диспетчер задач. После входа в диспетчер задач и нажатия на подробности появится следующий интерфейс:
Просто найдите, что процесс с портом 7204 5272 можно закрыть. Вот небольшая хитрость. Нажмите на данные PID там. В верхней части столбца есть небольшая стрелка для сортировки, поэтому вам не нужно ее медленно искать. В то же время вам следует также обратить внимание на то, являются ли занятые программы процессами системы по умолчанию. Сначала вы можете использовать имя процесса Google, чтобы увидеть, что происходит. Но мой взять один
Самозапускающийся процесс предварительной загрузки Tencent остановился решительно, и произошел процесс программного обеспечения Apache, которое использовалось в качестве сервера при создании PHP, и благополучно остановился. Кроме того, многие научные доступ в Интернет также будут занимать порт. Обратите внимание на это тоже.
——— На данный момент, еще одна яма была заполнена.
Un jour… vous décidez d’installer un serveur HTTP en local, afin de pouvoir développer vos applications, sites sans avoir besoin d’un hébergement web… Vous installez le serveur web local (Wamp, Mamp, Xampp, EasyPHP, …).
Jusqu’ici tout va bien !
Ensuite, vous lancez le serveur Apache et là le fameux message d’erreur vous indiquant qu’Apache ne pourra pas se lancer, à cause du port HTTP 80 bloqué !
Après plusieurs heures de recherche (et un peu d’aide) sur internet, j’ai pu débloquer le port 80 et le service Apache marche de nouveau.
Dans ce tutoriel vous allez découvrir les différentes causes de ce problème et pourquoi — parfois — le système (kernel) peut lui-même réserver le port 80.
Vous allez aussi découvrir comment libérer le port 80 de A à Z
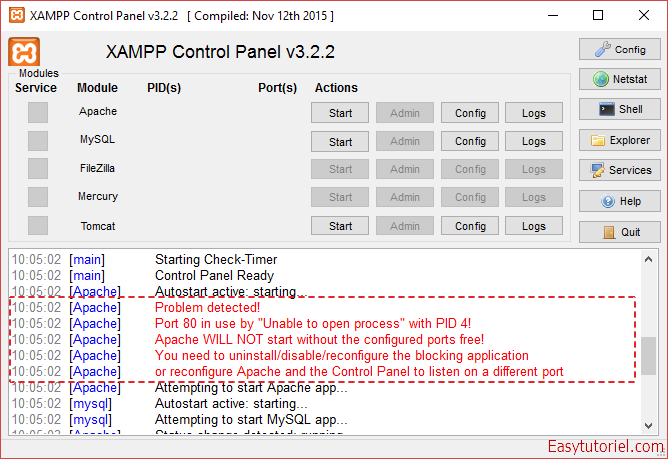
Voici un aperçu de l’erreur (port 80 occupé par le PID 4) sur Xampp (site officiel) lors du lancement d’Apache :
Sur d’autres serveurs locaux (EasyPHP par exemple) on ne vous affiche pas le PID du processus / service qui bloque le port HTTP 80.
1. Savoir la cause du blocage du port HTTP
Analyser les processus utilisant le port 80.
Pour chercher le processus ou service occupant le port 80, ouvrez la fenêtre Exécuter ( Win+R) puis mettez CMD.
Recopiez cette commande et exécutez-la sur l’invite de commandes.
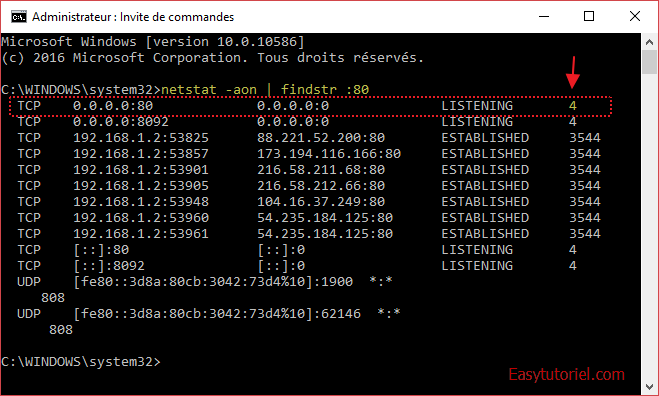
netstat -aon | findstr :80
Comme vous pouvez le voir dans la première ligne, le processus avec le PID = 4 (le numéro dans la dernière colonne) réserve le port 80.
Savoir le nom du processus.
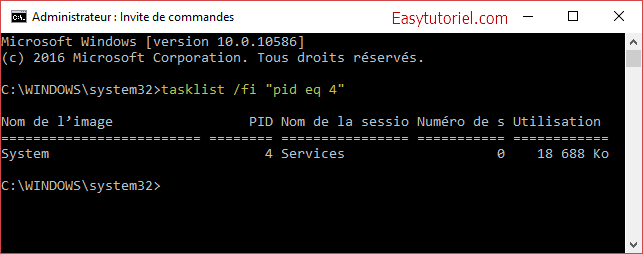
Pour identifier le processus exécutez la commande suivante sans oublier de changer le «4» dans pid eq 4 par le PID du processus identifié dans la première partie.
tasklist /fi "pid eq 4"
Le nom du processus est System, cela veut dire que c’est le système Windows qui occupe le port 80 !!
2. Désactiver les services utilisant le port 80
Il se peut que votre système utilise lui-même le port 80 à travers ses propres services.
Ouvrez la fenêtre «Exécuter» ( Win+R) puis exécutez la commande : services.msc
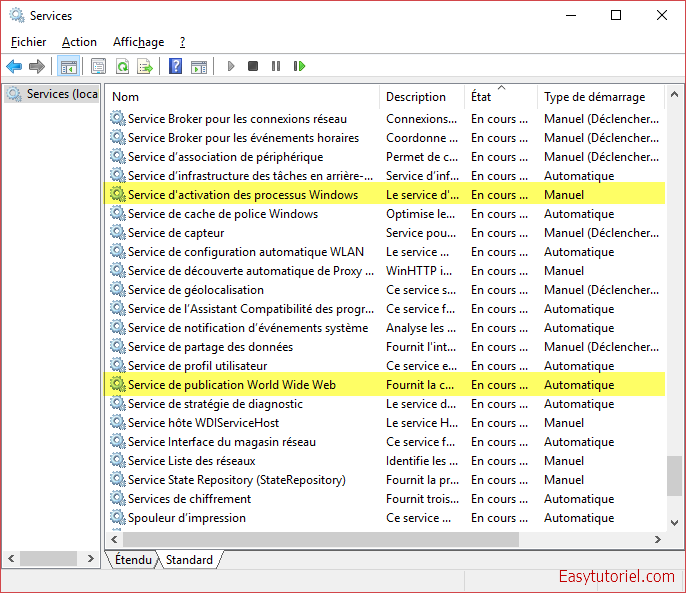
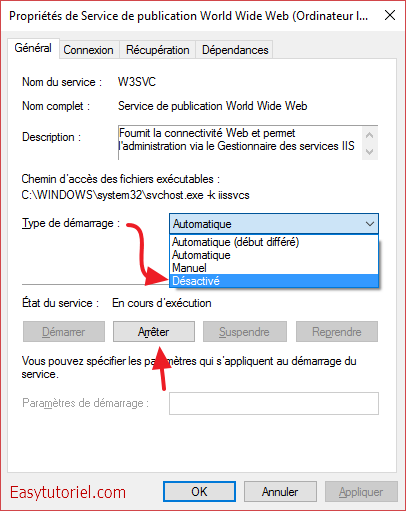
Puis arrêtez et désactivez les services suivants un par un :
- Service de publication World Wide Web (W3SVC)
- Service d’activation des processus Windows (WAS)
- SQL Server Reporting Services (ReportServer)
- BranchCache (PeerDistSvc)
- Service Broker pour les connexions réseau (NcbService)
L’arrêt et désactivation est facile ; vous n’avez qu’à ouvrir les «Propriétés» du service puis faire «Arrêter» et mettre «Désactivé» dans «Type de démarrage :«.
Vérifiez maintenant si le serveur Apache peut se lancer, s’il ne se lance pas continuez la lecture ; si ça a marché mettez un commentaire
Si par exemple votre serveur Apache marche lorsque vous avez désactivé W3SVC, faites un clic droit pour le désactiver une fois pour toute.
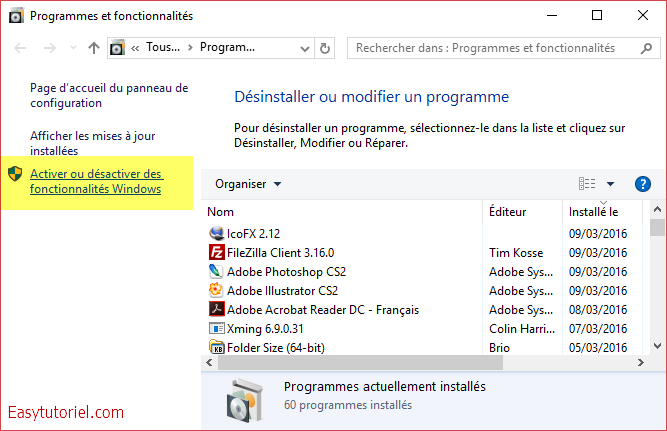
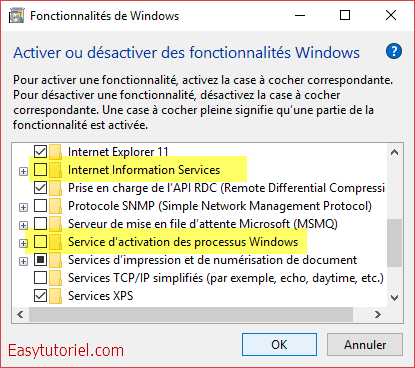
Désinstaller les services depuis les fonctionnalités Windows.
Vous pouvez aussi désinstaller les services Web à partie des «fonctionnalités Windows» sur la fenêtre «Programmes et fonctionnalités«.
Décochez «Internet Information Services» et «Service d’activation des processus Windows«.
Cliquez sur «OK«.
On va vous demander de redémarrer votre PC ; faites-le puis testez si «Apache» démarre à nouveau, sinon continuez la lecture.
3. Désactiver le service caché HTTP.SYS
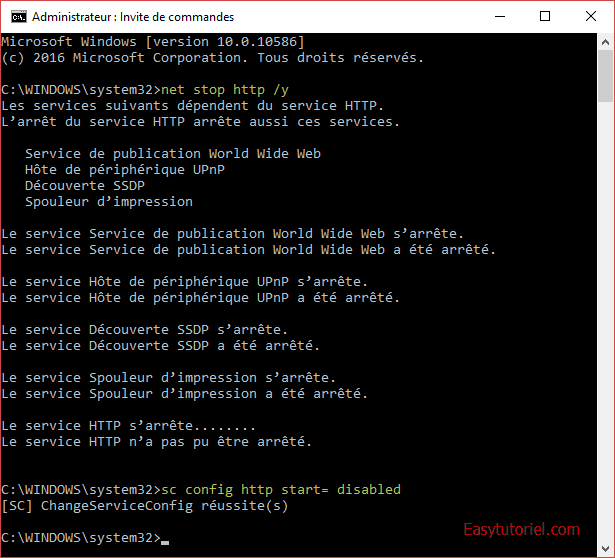
Pour la plupart des cas, la cause du port 80 occupé est le service HTTP.SYS sur Windows.
Pour l’arrêter et arrêter tous les services utilisant le port HTTP utilisez cette commande sur l’invite de commande (exécutée en tant qu’administrateur).
net stop http /y
Pour désactiver le service HTTP.SYS utilisez cette commande :
sc config http start= disabled
Voici ce que cela donne :
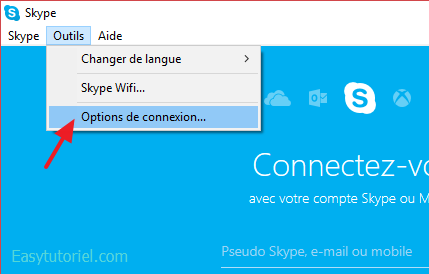
4. Changez le port de Skype
Si Skype est le programme causant le problème, allez sur «Outils» > «Options de connexion…«
Décochez «Utiliser les ports 80 et 443 pour les connexions entrantes supplémentaires«.
Mettez un port au hasard supérieur à 1024 dans la case en haut.
Cliquez sur «Enregistrer» puis redémarrez Skype.
Changer le port d’Apache.
Si aucune des solutions en haut n’a marché, ouvrez le fichier httpd.conf de votre serveur web local.
Changez le port par défaut 80 en 8080 ou 8000
Et puis vous n’avez qu’à profiter de votre serveur Apache local à nouveau
Si ce tutoriel vous a aidé n’hésitez pas à laisser un commentaire de remerciement.
Une question ? Je suis là pour vous aider !
Par