Эта статья подходит для:
TL-MR3020 , TL-WA5110G , TL-MR3040 , TL-WA7510N , TL-WR743ND , TL-WA5210G , TL-WR543G , TL-WR702N , TL-WR802N , TL-WR700N
Некоторые устройства TP—LINK обладают множеством рабочих режимов, такими как AP (Точка доступа)/ Wireless Router (Беспроводной маршрутизатор)/ Repeater (Ретранслятор)/ Bridge (Мост)/ Client (Клиент)/ AP Client Router (Точка доступа с клиент-маршрутизатором).
1. Режим точки доступа (для подключения к Интернету в отеле)
Режим точки доступа предназначен для преобразования проводного подключения в беспроводное. В данном случае устройство работает как коммутатор. Обычно он подключается за маршрутизатором.
Если вы находитесь в офисе, отеле или местах, где доступно только проводное подключение, или, к примеру, на вечеринке, где играют в сетевые игры, на небольшом совещании или в прочих условиях, где необходимо временно подключение к беспроводной сети, пожалуйста, используйте режим точки доступа.
2. Режим беспроводного маршрутизатора (для совместного доступа к Интернет дома)
В режиме маршрутизатора устройство может создавать доступ к одному проводному подключению к Интернет для нескольких клиентов. В этом случае будет использоваться один порт WAN. Данный режим поддерживает несколько типов подключения, такие как Dynamic IP/Static IP/PPPoE/L2TP/PPTP (динамический IP/статический IP/PPPoE/L2TP/PPTP). Когда для одного пользователя доступен Интернет от DSL или кабельного модема – используйте режим беспроводного маршрутизатора для обеспечения доступа к Интернет для большего количества пользователей.
3. Режим ретранслятора (для усиления сигнала Wi—fi дома)
Режим ретранслятора используется для увеличения зоны покрытия беспроводного сигнала с использованием одного SSID (имени беспроводной сети) и пароля. Вы можете использовать режим ретранслятора в том случае, если у вас уже имеется беспроводная сеть, и вам необходимо увеличить покрытие в определённой зоне. При использовании режима ретранслятора будет использоваться один SSID, но ваши устройства смогут получить доступ к сети в данной зоне.
4. Режим моста (для сетевого подключения в офисе и дома)
Режим моста использует существующий канал беспроводного Интернета и транслирует его, используя другое имя сети (SSID) и пароль. Данный режим позволяет создавать несколько отдельных сетей для разных групп пользователей , делящих одно подключение к Интернет.
Для небольшого ресторана или бара, офиса или дома, где доступ к Интернет необходимо предоставить гостям не раскрывая пароль от существующей сети – это лучший выбор.
5. Режим клиента (для домашней игровой консоли)
В режиме клиента устройство может подключаться к устройству с проводным доступом и выступать в качестве беспроводного адаптера для подключения к вашей беспроводной сети.
Для Smart TV, проигрывателя медиа или игровой консоли с портом Ethernet. Используйте режим клиента, чтобы предоставить вашим устройствам доступ к беспроводной сети.
6. Точка доступа с клиент-маршрутизатором (для использования в сетях WISP)
В режиме точки доступа с клиент-маршрутизатором устройство может подключаться к беспроводной сети и обеспечивать к ней общий доступ для клиентских устройств. Со стороны WAN используется беспроводное подключение. Устройство также поддерживает Dynamic IP/Static IP/PPPoE/L2TP/PPTP (динамический IP/статический IP/PPPoE/L2TP/PPTP).
Когда станция беспроводного доступа ограничивает количество клиентов или требует имя пользователя и пароль для подключения, точка доступа с клиент-маршрутизатором – это то, что вам нужно.
Был ли этот FAQ полезен?
Ваш отзыв поможет нам улучшить работу сайта.
Что вам не понравилось в этой статье?
- Недоволен продуктом
- Слишком сложно
- Неверный заголовок
- Не относится к моей проблеме
- Слишком туманное объяснение
- Другое
Как мы можем это улучшить?
Спасибо
Спасибо за обращение
Нажмите здесь, чтобы связаться с технической поддержкой TP-Link.
На чтение 6 мин Просмотров 129к. Опубликовано
Обновлено
На повестке дня вопрос — как настроить режим роутера WiFi? Если вы собрались создать беспроводную сеть у себя дома, то я рекомендую выбирать для этой цели именно маршрутизатор, а не точку доступа, модем, репитер или что-то еще. Почему? Потому что это устройство многофункциональное и заменяет собой все эти штучки. В этой статье мы рассмотрим его основные режимы работы и посмотрим, как они настраиваются на примере модели от Asus.
Какие бывают режимы роутера?
Прежде всего нужно разобраться с понятиями. Всего у роутера существует четыре основных режима:
- Точка доступа
- Репитер или Усилитель
- Клиент, Мост или Адаптер
- Модем
Точка доступа (Access Point)
В режиме точки доступа, или как его называют иностранцы «Access Point», роутер работает как устройство, которое превращает кабельный сигнал в беспроводной. Основное отличие маршрутизатора в режиме точки доступа от другого сетевого прибора, который собственно называется «точка доступа», в том, что он не только раздает WiFi, то есть превращает в радиосигнал проводной интернет, но и имеет функционал для раздачи IP адресов и перенаправления портов, в чем и заключается основная функция именно роутера.
Режим модема (ADSL Modem)
В чистом видео модем — это аппарат, который предназначен для работы с провайдерами, предоставляющими доступ во всемирную паутину через телефонный кабель по технологии ADSL. И больше ни для чего другого — сам модем в режиме роутера работать либо просто не может. А вот роутер в режиме модема с поддержкой ADSL способен не только получать интернет по телефонному шнуру, но и ретранслировать его беспроводным способом и назначать IP другим клиентам.
Репитер (Repeater)
Вообще «репитер» — это беспроводной удлинитель или повторитель сигнала, продлевающий его от точки раздачи wifi на некоторое расстояние для присоединения к интернету компьютеров, находящихся в зоне неуверенного приема. Если наш любимый с вами wifi роутер имеет режим репитера, значит умеет делать то же самое — удлинять беспроводной сигнал, тем самым расширяя зону приема. Кроме того, режим повторителя полезен, если необходимо обойти какое-либо препятствие при создании беспроводного моста, когда между двумя точками доступа нет прямой видимости. Тогда помещаем роутер в режиме ретранслятора в прямой видимости от обеих точек и передаем сигнал через него.
Клиент, или Мост (Client, WISP, WDS, Bridge)
У роутера в режиме моста много названий, но суть сводится к одному — он принимает беспроводной сигнал и передает его по кабелю на присоединенное к нему устройство. Режим моста удобно использовать, когда необходимо подключить к wifi «клиента», то есть какой-то девайс, у которого нет встроенного беспроводного модуля, например, телевизор или принтер.
В разных моделях настройка режима роутера происходит по-разному. Нам надо будет подключиться к какому-то уже существующему вайфайю, который раздается каким-то другим роутером, и распространять его уже в нашей квартире. Показываю на примере Asus RT-N10U B в новой прошивке.
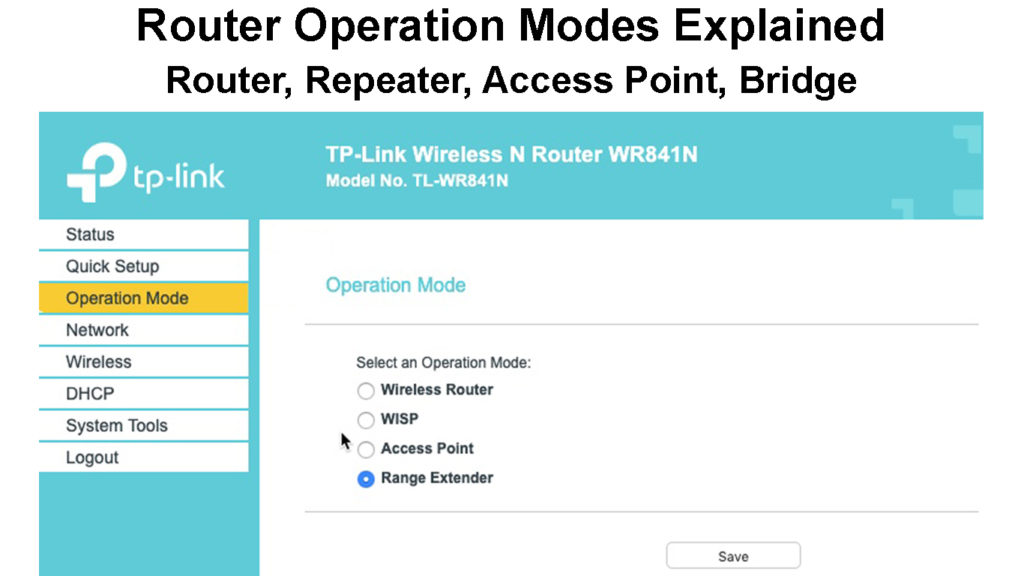
Заходим в админку (http://192.168.1.1), пункт «Администрирование», вкладка «Режим работы» (красным) или сразу кликаем на «Беспроводной роутер» в самом верху страницы настроек (зеленым).
В данный момент по умолчанию активирован режим «Беспроводной роутер». Его настройки вы найдете в этой статье, а мы поставим флажок на втором по счету — режим повторителя. И нажимаем кнопку «Сохранить».
Откроется страница, на которой отобразятся все беспроводные сети, находящиеся в радиусе приема роутера. Выбираем из них ту, к которой нам надо подключиться и вводи ключ доступа, если она запаролена.
Жмем подключить. После соединения со сторонним роутером, вы сможете сделать еще одну интересную настройку: либо использовать данные для доступа той существующей сети, которую мы удлиняем. Либо задать свои собственные — тогда к нашему мы подключаемся с одними данными (SSID и паролем), а к тому, второму, в который непосредственно вставлен кабель интернета и сигнал которого мы удлиняем, — с другими.
Дальше дело техники — ждем, когда все эти настройки применятся, и вы отключитесь от сети. После чего в списке доступных беспроводных подключений появится то новое, которое только что создали. Подключаемся к нему — и вперед, по просторам рунета!
Маршрутизатор Асус в режиме точки доступа
Режим точки доступа а Асуса заключается в том, что он соединяется кабелем с другим роутером или модемом, который в свою очередь подключен к провайдеру и уже передает дальше сигнал wifi. Его удобно использовать, если у вас интернет работает через ADSL модем, а у самого роутера такой встроенной возможности нет. Либо если ваш маршрутизатор не оснащен беспроводным модулем и не может раздавать сигнал по вайфай. Думаю, разбирать его нет смысла, так как подробно все описано в статье про модем в режиме роутера, ссылку на которую я уже дал выше.
Роутер Asus в режиме моста, или клиента
Клиент — тот, кто что-то получает. Этот режим называется так, потому что при нем роутер работает в обратном направлении — не вещает беспроводной сигнал из подключенного кабеля, а наоборот, получает по wifi интернет от другой точки доступа и распространяет его на другие устройства при помощи кабеля. Этот порядок работы доступен только в некоторых моделях.
Самым ярким примером аппарата, работающего в этом ключе — wifi адаптер. А из роутеров такой способностью обладает Asus EA-N66.
Называется этот режим в данной модели «Беспроводной сетевой адаптер».
Данный тип также позволяет объединить две автономные сети при помощи беспроводного «моста». При создании такого подключения нужно, чтобы оба роутера имели данный режим (Bridge). Либо можно сделать так, чтобы одно устройство было активировано как «точка доступа», транслирующая сигнал, а другое — как «клиент», принимающее его и распространяющее по кабелям на компьютеры своей сети. Из линейки Асуса, коего поклонником я являюсь, для организации такого моста подойдет современная моделька RT-N13U.
В этой заметке я перечислил все основные режимы WiFi роутера и перечислил их самые распространенные названия. Подробнее о настройке каждого из них я описываю в отдельных статьях на блоге. Если вам попадались какие-либо еще и вы не знаете, как они работают, то пишите в комментариях, будем разбираться вместе.
Видео инструкции
Актуальные предложения:

Задать вопрос
- 10 лет занимается подключением и настройкой беспроводных систем
- Выпускник образовательного центра при МГТУ им. Баумана по специальностям «Сетевые операционные системы Wi-Fi», «Техническое обслуживание компьютеров», «IP-видеонаблюдение»
- Автор видеокурса «Все секреты Wi-Fi»
Routers are essential for providing wireless internet in various environments. Most routers require very little configuration during installation to get them going. Once you access the router’s General User Interface and set the SSID and password, your wireless network is ready for use. If curiosity takes over and you navigate the various router settings, you will come across various operation modes that enhance connectivity in different situations.
This article will briefly discuss the various operation modes you might come across and what they do. Additionally, we will identify the appropriate times and situations each mode serves best.
1. Router Mode
Router mode (also Wireless Router Mode) is the default operation mode on many routers. When the router is in this mode, it facilitates a connection for your devices to the internet.
In other terms, it turns a Wide Area Network (WAN) into a Local Area Network (LAN) for all the devices at home.
A WAN is an extensive computer network over long distances, and LAN is a computer network in a localized area, e.g., a home or office.
Therefore, your router can analyze incoming and outgoing data and, with the help of IP addresses, direct it exactly where it should be going.
If you only have one router in your home, this is an ideal mode for it. That way, the router can grant internet access wirelessly or via Ethernet to all devices. Router mode is also ideal if you are a first-time router user.
2. Repeater Mode
In repeater mode, your router only works to extend the range of your wireless signal from another router or Access Point.
When in this mode, the router receives a Wi-Fi signal and retransmits it, thus increasing the range. You would need the MAC address of the primary router so that you can wirelessly link the two and allow the secondary router to extend the signal.
This mode requires you to have an access point or two routers where one will transmit the signal to be repeated.
Repeaters are devices made to perform the extension of the Wi-Fi signal range solely. Most Access points can also act as repeaters.
Note that as much as this mode will allow signal range extension, it will significantly affect the network speed. The more repeaters/routers between the primary wireless signal source, the slower your wireless connection will be.
VIDEO TUTORIAL – Using a Router in Repeater Mode
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EFEZIyQ-eA0
3. Access Point (AP) Mode
Essentially routers provide wired and wireless connections. However, in Access Point mode, also known as wireless client mode, the router only provides a wireless connection.
The mode is meant to enable wireless connectivity on wired connections; therefore, there is usually a router/gateway behind one in AP mode. Both routers connect via Ethernet, and the one in AP mode transmits a wireless signal.
Difference Between a Wi-Fi Router and a Wireless Access Point
When in this mode, the router acts as a switch that enables wireless connectivity on a network that previously had none. The AP mode router simply provides a wireless connection while the router/modem behind it handles all other processes.
An Access Point can also be a gadget built to enable wireless connectivity on a wired network.
Consider getting an actual Access Point since they are made and explicitly configured for enabling wireless connectivity. An AP can also have additional features that a router on AP mode will not.
A router in AP mode can also be used to extend wireless signals or create additional wireless networks.
Recommended reading:
- What is Panoramic Wi-Fi?
- Can’t Connect to McDonald’s Wi-Fi (What to Do?)
- MyFiOSGateway is Not Secure (Should I Be Worried?)
Since APs are fed with an Ethernet connection, a router in AP mode can improve wireless connectivity. If you configure all the wireless access points with the same SSID and password, your devices can connect to the strongest wireless signal, just like in a mesh network (without the AI part).
AP mode can also come in handy if the primary router has problems with wireless connectivity. Simply add a router that supports AP mode and will take over.
Remember to check the manual before enabling AP mode in case there are additional configuration settings that need updating.
AP mode is faster than Repeater mode because AP mode sources its signal using Ethernet, thus reducing signal degradation.
VIDEO TUTORIAL – Turning a Router into an Access Point
4. Bridge Mode
Bridge mode disables the primary router’s Network Address Translation (NAT), so the secondary router can take over. Therefore, in bridge mode, only the secondary router connects to the primary router, and all other devices connect to the secondary router.
NAT is a method of mapping multiple private IP addresses to one public IP address. The feature is necessary for IP conversion, especially on systems that use IPV4.
If both routers were left to conduct NAT, a double NAT issue would arise, resulting in connectivity issues with VoIP services, online games, and port forwarding.
Bridge mode is essential when using two routers on the same network or adding a mesh network to your primary router.
Bridge mode is essential as it allows the secondary router to transfer data to the primary router as the primary router acts as a bridge between the internet and the secondary router.
Bridge mode enables you to use advanced features of a router without having to uninstall the primary router. Some ISPs require you to contact them so that they can enable bridge mode from their end.
Using a Router in a Wireless Bridge Mode
5. WISP Mode
The Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP) mode is also known as the WISP client.
Once activated, WISP mode makes your router’s WAN port a wireless port while still using NAT.
Therefore, once enabled, your router can connect to another wireless network. Once connected, it can provide Ethernet and wireless connections to devices in your home. Hence, WISP mode uses your wireless adapter as a WAN port and a client.
WISP is ideal in rural settings where internet infrastructure is not robust. The mode lets users connect their routers to public hotspots or fixed wireless networks provided by their ISP.
WISP has the downside of increasing network latency; therefore, consider other modes and only use WISP if there is no other option.
Using a Wi-Fi Router in WISP Mode
6. Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
WDS mode enables your router to connect to another router’s Wi-Fi radio wirelessly. Once established, the mode allows file sharing between networks over relatively long distances like between or across floors.
It is convenient for those living in apartment buildings and wishing to wirelessly share the internet while everyone has administrative access to their networks.
In Summary
Router operation modes can be quite challenging, especially if you are new to routers. But once you grasp them, the modes streamline your home network. Some modes like AP, bridge and repeater mode can help you reuse old or idle routers instead of spending on brand new devices that perform the same functions.
If you encounter any challenges while using the router modes above, reset your router and try setting them up again. You can also consult the user manual or manufacturer’s website for help specific to your router model.
Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.
CONTENTS
- 1. Router Mode
- 2. Repeater Mode
- 3. Access Point (AP) Mode
- 4. Bridge Mode
- 5. WISP Mode
- 6. Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
- In Summary
Many of the routers offers different operation modes that you can use. However, some of them do not really tell you the best situations to use specific operation modes. In this guide, we will provide some basic guidelines to help you decide.
Wireless Router Mode
(Default, Home Internet Sharing)
Connection: Internet -> Modem -> Router -> Computer
Related Terms: Gateway, Default Gateway
Official Tooltip Information
In wireless router/ IP sharing mode, the router connects to the Internet via PPPoE, DHCP, PPTP, L2TP, or Static IP and shares the wireless network to LAN clients or devices. In this mode, NAT, firewall, and DHCP server are enabled by default. UPnP and Dynamic DNS are supported for SOHO and home users. Select this mode if you are a first-time user or you are not currently using any wired/wireless routers.
Wireless Router Mode Usage Notes
If you have 1 router, this will almost always be the default router operating mode that you will implement for your basic home use. You connect the modem to the router, and then the router “shares” its internet connection to all the devices.
Repeater Mode
(Home Wi-fi Range Extension)
Connection: Internet -> Modem -> Router ->Wireless Extend to Repeater
Related Terms: Wireless Hub
Official Tooltip Information
In Repeater mode, your router wirelessly connects to an existing wireless network to extend the wireless coverage. In this mode, the firewall, IP sharing, and NAT functions are disabled.
Repeater Mode Usage Notes
You will generally use repeaters or wireless extenders when you have hard to reach places with your home wifi setup. The repeater acts as a “transition” island between your actual client device with the main router.
The repeaters should carry the same SSId.
In general, if you do need to extend your home wifi range. It may be cheaper to purchase a wifi extender instead of using your router in repeater mode because wifi extender is usually cheaper.
Access Point(AP) Mode
(General Internet Extension – Home, Hotel, Etc)
Connection: Internet -> Modem -> Router ->Wired Connection to AP
Related Terms: Wireless Switch
In Access Point (AP) mode, the router connects to a wireless router through an Ethernet cable to extend the wireless signal coverage to other network clients. In this mode, the firewall, IP sharing, and NAT functions are disabled by default.
Access Point Usage Notes
Use Access Point when you cannot alter the main router, but still need a temporary wireless network. This mode is best to be used in an office, hotel, and places where you only have wired network.
Media Bridge
Or known as Client Mode (Generally for home gaming console)
Connection: Internet -> Modem -> Router ->Wireless Connection to Media Bridge -> Wired Connection to end user devices.
Official Description
The Router can be configured in Media Bridge mode.The Media Bridge mode provides the fastest 802.11ac Wi-Fi connection for multiple media devices simultaneously. To set up the Media Bridge mode, you need two routers: one configured as the Media station and the other as a router. Configure one router as a “router” and another router as an 802.11ac Media Bridge to provide a simultaneous 802.11ac Wi-Fi connection for your media devices such as computer, Smart TV, game console, DVR, or media player via Ethernet cable. Change to Media Bridge mode to provide a simultaneous 802.11ac Wi-Fi connection for your media devices.
In Media Bridge mode, only wireless devices connect to the P-AP. Client devices need to be connected to the Media Bridge with a network cable.
Media Bridge Usage Notes
With client mode or media bridge, it can connect to a wired device and works as a wireless adapter to receive wireless signal from your wireless network.
For a Smart TV, Media Player, or game console with an Ethernet port. Use the Client Mode to make your devices Wi-Fi enabled, granting them access to your wireless network. So imagine the Media Bridge or client router acts as the end user device’s wireless adapter.
The reason for this mode is that it can increase the speed of your wireless connection so that it matches the speed of the Ethernet connection. AC is a relatively newer wireless technology that has not been widely adapted by the major gaming console. For example: Playstation 4 and Xbox One only support up to 802.11 b/g/n standards. However, with the media bridge setup, you can grant them AC speeds by using two AC rated routers that connect wireless to one another.
Finally, although the tooltip states that you need to use two same routers to achieve Media Bridge or Client Mode. It is not true but recommended. The reason is that your wireless speed is capped and bounded by your slower connections or router.
In general, you should however use the same brands of router for the Media Bridge type connection to ensure compatibility.
Other Network Terms
Hubs are used to connect computers on a network with cables so as to communicate with each other. The hub can send or receive information, but it can’t do both at the same time. So if you have alot of information passed in your network, hubs can flood and have poor performances.
Switchesfunctions the same way as hubs, but they can identify the intended destination of the information that they receive. In general, you should use a switch instead of hub when you have multiple devices.
FAQ
[Wireless Router] Introduction of Operation Mode
ASUS router supports several modes in operation to meet different requirements.(Please refer to the specification of your router on ASUS website to check which operation mode is equipped with.)
1. Wireless router mode (Default) : In wireless router/ IP sharing mode, router connects to the Internet via PPPoE, DHCP, PPTP, L2TP, or Static IP and shares the wireless network to LAN clients or devices. In this mode, NAT, firewall, and DHCP server are enabled by default. UPnP and Dynamic DNS are supported for SOHO and home users. Select this mode if you are a first-time user or you are not currently using any wired/wireless routers. Click here for detailed steps.
2. Access Point mode: In Access Point (AP) mode, router connects to a wireless router through an Ethernet cable to extend the coverage of wireless signal to other network clients. In this mode, the firewall, IP sharing, and NAT functions are disabled by default. Click here for detailed steps.
3. Repeater Mode: In Repeater mode, the router wirelessly connects to an existing wireless networks to extend the wireless coverage. In this mode, the firewall, IP sharing, and NAT functions are disabled. Click here for detailed steps.
4. Media Bridge: Router can be configured in Media Bridge mode. The Media Bridge mode provides the fastest 802.11ac Wi-Fi connection for multiple media devices simultaneously.To set up the Media Bridge mode, you need two Routers: One configured as the Media station and the other as a router. Configure one router as the first router and the second router as an 802.11ac Media Bridge to provide a simultaneous 802.11ac Wi-Fi connection for your media devices such as computer, Smart TV, game console, DVR, or media player via Ethernet cable. Change to Media Bridge mode to provide a simultaneous 802.11ac Wi-Fi connection for your media devices. In Media Bridge mode, only wireless devices connect to the Parent AP. Client devices need to be connected to the Media Bridge with a network cable. Click here for detailed steps.
5. AiMesh Node: You can set this router as an AiMesh node to extend an existing AiMesh routers WiFi coverage.
1. Factory resetting this router will allow it to join an existing AiMesh network.
2. Please go to the AiMesh settings page of your existing router to add an AiMesh node. Click here for detailed steps.
How to get the (Utility / Firmware)?
You can download the latest drivers, software, firmware and user manuals in the ASUS Download Center.
If you need more information about the ASUS Download Center, please refer this link.
Was this information helpful?
Yes
No
- Above information might be partly or entirely quoted from exterior websites or sources. please refer to the information based on the source that we noted. Please directly contact or inquire the sources if there is any further question and note that ASUS is neither relevant nor responsible for its content/service
- This information may not suitable for all the products from the same category/series. Some of the screen shots and operations could be different from the software versions.
- ASUS provides the above information for reference only. If you have any questions about the content, please contact the above product vendor directly. Please note that ASUS is not responsible for the content or service provided by the above product vendor.
- Brand and product names mentioned are trademarks of their respective companies.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)