The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.6.6. This is a small bugfix release.
For details see Changes.rst
User visible changes:
- OCC exit messages are now logged more visibly See GH #391.
- OpenSSL error messages are now logged with more details (for example, when loading a provider fails, which .so was tried, and why did it fail) See GH #361.
- print a more user-friendly message when tls-crypt-v2 client auth fails
- packaging now includes all documentation in the source tarball
New features:
- set WINS server via interactive service — this adds support for «dhcp-option WINS 192.0.2.1» for DCO + wintun interfaces where no DHCP server is used. See GH #373.
Windows MSI changes since 2.6.5:
- Included openvpn-gui updated to 11.44.0.0
- MSIs now use OpenSSL 3.1.2
For Community-maintained packages for Linux distributions see OpenvpnSoftwareRepos
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.6-I001-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.6-I001-arm64.msi |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.6-I001-x86.msi |
Source archive file |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.6.6.tar.gz |
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.6.4. This is a small bugfix release.
For details see Changes.rst
Note:
- License amendment: all new commits fall under a modified license that explicitly permits linking with Apache2 libraries (mbedTLS, OpenSSL) — see COPYING for details. Existing code will fall under the new license as soon as all contributors have agreed to the change — work ongoing.
Feature changes:
- DCO: support kernel-triggered key rotation (avoid IV reuse after 232 packets). This is the userland side, accepting a message from kernel, and initiating a TLS renegotiation. As of 2.6.4 release, only implemented in FreeBSD kernel.
Windows MSI changes since 2.6.3:
- Rebuilt included tap-windows driver with the correct version of the old Windows 7 driver, removing a warning about unsigned driver on Windows 7 installation. See GH openvpn-build#365.
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.4-I001-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.4-I001-arm64.msi |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.4-I001-x86.msi |
Source archive file |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.6.4.tar.gz |
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.6.3. This is a small bugfix release.
For details see Changes.rst
Feature changes:
- Windows: support setting DNS domain in configurations without GUI and DHCP (typically wintun or windco drivers), see GH openvpn#306.
Windows MSI changes since 2.6.2:
- Several Windows-specific issues fixed:
- ensure interactive service stays enabled after silent reinstall, see GH openvpn-build#348, openvpn-build#349 and openvpn-build#351
- repair querying install path info for easyrsa-start.bat on some Windows language versions, see GH openvpn-build#352.
- MSIs are now built against OpenSSL 3.1.0.
- Update included openvpn-gui to 11.41.0.0
- This update removes the ability to change the password of a private key from the GUI. This was a niche feature which caused a direct dependency of GUI on OpenSSL. Use openssl.exe directly if you need to edit a private key.
Note: Windows MSI was updated to I003 on April 26th. Changes in I003:
- The GPG subkey for creating the .asc files for the downloads has been updated. You might need to re-download or update the GPG key if verifying the signatures.
- Fix the encoding of some documentation/sample files included in the installer. See GH openvpn-build#358
- Update include tap-windows6 driver to 9.25.0
- Fixes a problem with sending small non-IP packets (e.g. PPPoE) over the VPN connection. See GH tap-windows6#158
- Note: The new driver is only used on Windows 10 and newer. We can’t rebuild drivers for Windows 7/8 since Microsoft doesn’t support the signing mechanism anymore. We include the previous driver version to still allow installation on Windows 7/8.
- Update included openvpn-gui to 11.42.0.0
- Fixes a problem with passphrase prompt was sometimes not displayed. See GH openvpn-gui#619
- Adds «Password Reveal» feature which allows you to see passwords while entering them.
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.3-I003-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.3-I003-arm64.msi |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.3-I003-x86.msi |
Source archive file |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.6.3.tar.gz |
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.6.2. This is mostly a bugfix release with some improvements.
For details see Changes.rst
Feature changes:
- implement byte counter statistics for DCO Linux (p2mp server and client)
- implement byte counter statistics for DCO Windows (client only)
--dns server <n> address ...now permits up to 8 v4 or v6 addresses
Important note for Linux DCO users:
- New control packets flow for data channel offloading on Linux: 2.6.2+ changes the way OpenVPN control packets are handled on Linux when DCO is active, fixing the lockups observed with 2.6.0/2.6.1 under high client connect/disconnect activity. This is an INCOMPATIBLE change and therefore an ovpn-dco kernel module older than v0.2.20230323 (commit ID 726fdfe0fa21) will not work anymore and must be upgraded. The kernel module was renamed to «ovpn-dco-v2.ko» in order to highlight this change and ensure that users and userspace software could easily understand which version is loaded. Attempting to use the old ovpn-dco with 2.6.2+ will lead to disabling DCO at runtime.
Windows MSI changes since 2.6.1:
- Update included openvpn-gui to 11.39.0.0
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.2-I001-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.2-I001-arm64.msi |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.2-I001-x86.msi |
Source archive file |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.6.2.tar.gz |
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.6.1. This is mostly a bugfix release with some improvements.
For details see Changes.rst
Feature changes:
- Dynamic TLS Crypt: When both peers are OpenVPN 2.6.1+, OpenVPN will dynamically create a tls-crypt key that is used for renegotiation. This ensure that only the previously authenticated peer can do trigger renegotiation and complete renegotiations.
- CryptoAPI (Windows): support issuer name as a selector. Certificate selection string can now specify a partial issuer name string as
«—cryptoapicert ISSUER:<string>» where <string> is matched as a substring of the issuer (CA) name in the certificate.
Note: configure now enables DCO build by default on FreeBSD and Linux. On Linux this brings in a new default dependency for libnl-genl (for Linux distributions that are too old to have a suitable version of the library, use «configure —disable-dco»)
Windows MSI changes since 2.6.1:
- Update included ovpn-dco-win driver to 0.9.2
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.1-I001-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.1-I001-arm64.msi |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.1-I001-x86.msi |
Source archive file |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.6.1.tar.gz |
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.6.0. This is a new stable release with some major new features.
For details see: Changes.rst
The Changes document also contains a section with workarounds for common problems encountered when using OpenVPN with OpenSSL 3.
New features and improvements in 2.6.0 compared to 2.5.8:
- Data Channel Offload (DCO) kernel acceleration support for Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD.
- OpenSSL 3 support.
- Improved handling of tunnel MTU, including support for pushable MTU.
- Outdated cryptographic algorithms disabled by default, but there are options to override if necessary.
- Reworked TLS handshake, making OpenVPN immune to replay-packet state exhaustion attacks.
- Added —peer-fingerprint mode for a more simplistic certificate setup and verification.
- Added Pre-Logon Access Provider support to OpenVPN GUI for Windows.
- Improved protocol negotiation, leading to faster connection setup.
- Included openvpn-gui updated to 11.37.0.0. See CHANGES.rst.
- Updated easy-rsa3 bundled with the installer on Windows.
- Various bug fixes.
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.0-I005-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.0-I005-arm64.msi |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.6.0-I005-x86.msi |
Source archive file |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.6.0.tar.gz |
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.5.4. This release include a number of fixes and small improvements. One of the fixes is to password prompting on windows console when stderr redirection is in use — this breaks 2.5.x on Win11/ARM, and might also break on Win11/amd64. Windows executable and libraries are now built natively on Windows using MSVC, not cross-compiled on Linux as with earlier 2.5 releases. Windows installers include updated OpenSSL and new OpenVPN GUI. The latter includes several improvements, the most important of which is the ability to import profiles from URLs where available. Installer version I602 fixes loading of pkcs11 files on Windows. Installer version I603 fixes a bug in the version number as seen by Windows (was 2.5..4, not 2.5.4). Installer I604 fixes some small Windows issues.
Source tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.4.tar.gz |
Source tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.4.tar.xz |
Source zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.4.zip |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.4-I604-x86.msi |
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.4-I604-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.4-I604-arm64.msi |
Overview of changes since OpenVPN 2.4
Faster connections
Crypto specific changes
- ChaCha20-Poly1305 cipher in the OpenVPN data channel (Requires OpenSSL 1.1.0 or newer)
- Improved TLS 1.3 support when using OpenSSL 1.1.1 or newer
- Client-specific tls-crypt keys (—tls-crypt-v2)
- Improved Data channel cipher negotiation
- Removal of BF-CBC support in default configuration (see below for possible incompatibilities)
Server-side improvements
- HMAC based auth-token support for seamless reconnects to standalone servers or a group of servers.
- Asynchronous (deferred) authentication support for auth-pam plugin
- Asynchronous (deferred) support for client-connect scripts and plugins
Network-related changes
- Support IPv4 configs with /31 netmasks now
- 802.1q VLAN support on TAP servers
- IPv6-only tunnels
- New option —block-ipv6 to reject all IPv6 packets (ICMPv6)
Linux-specific features
- VRF support
- Netlink integration (OpenVPN no longer needs to execute ifconfig/route or ip commands)
Windows-specific features
- Wintun driver support, a faster alternative to tap-windows6
- Setting tun/tap interface MTU
- Setting DHCP search domain
- Allow unicode search string in —cryptoapicert option
- EasyRSA3, a modern take on OpenVPN CA management
- MSI installer
Important notices
BF-CBC cipher is no longer the default
Cipher handling for the data channel cipher has been significantly changed between OpenVPN 2.3/2.4 and v2.5, most notably there are no «default cipher BF-CBC» anymore because it is no longer considered a reasonable default. BF-CBC is still available, but it needs to be explicitly configured now.
For connections between OpenVPN 2.4 and v2.5 clients and servers, both ends will be able to negotiate a better cipher than BF-CBC. By default they will select one of the AES-GCM ciphers, but this can be influenced using the —data-ciphers setting.
Connections between OpenVPN 2.3 and v2.5 that have no —cipher setting in the config (= defaulting to BF-CBC and not being negotiation-capable) must be updated. Unless BF-CBC is included in —data-ciphers or there is a «—cipher BF-CBC» in the OpenVPN 2.5 config, a v2.5 client or server will refuse to talk to a v2.3 server or client, because it has no common data channel cipher and negotiating a cipher is not possible. Generally, we recommend upgrading such setups to OpenVPN 2.4 or v2.5. If upgrading is not possible we recommend adding data-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:AES-128-CBC (for v2.5+) or cipher AES-128-CBC (v2.4.x and older) to the configuration of all clients and servers.
If you really need to use an unsupported OpenVPN 2.3 (or even older) release and need to stay on BF-CBC (not recommended), the OpenVPN 2.5 based client will need a config file change to re-enable BF-CBC. But be warned that BF-CBC and other related weak ciphers will be removed in coming OpenVPN major releases.
Connectivity to some VPN service provider may break
Connecting with an OpenVPN 2.5 client to at least one commercial VPN service that
implemented their own cipher negotiation method that always reports back that it is using BF-CBC to the client is broken in v2.5. This has always caused warning about mismatch ciphers. We have been in contact with some service providers and they are looking into it. This is not something the OpenVPN community can fix. If your commercial VPN does not work with a v2.5 client, complain to the VPN service provider.
More details on these new features as well as a list of deprecated features and user-visible changes are available in Changes.rst.
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.5.3. Besides a number of small improvements and bug fixes, this release fixes a possible security issue with OpenSSL config autoloading on Windows (CVE-2021-3606). Updated OpenVPN GUI is also included in Windows installers.
Source tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.3.tar.gz |
Source tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.3.tar.xz |
Source zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.3.zip |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.3-I601-x86.msi |
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.3-I601-amd64.msi |
Windows ARM64 MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.3-I601-arm64.msi |
Overview of changes since OpenVPN 2.4
Faster connections
- Connections setup is now much faster
Crypto specific changes
- ChaCha20-Poly1305 cipher in the OpenVPN data channel (Requires OpenSSL 1.1.0 or newer)
- Improved TLS 1.3 support when using OpenSSL 1.1.1 or newer
- Client-specific tls-crypt keys (—tls-crypt-v2)
- Improved Data channel cipher negotiation
- Removal of BF-CBC support in default configuration (see below for possible incompatibilities)
Server-side improvements
- HMAC based auth-token support for seamless reconnects to standalone servers or a group of servers.
- Asynchronous (deferred) authentication support for auth-pam plugin
- Asynchronous (deferred) support for client-connect scripts and plugins
Network-related changes
- Support IPv4 configs with /31 netmasks now
- 802.1q VLAN support on TAP servers
- IPv6-only tunnels
- New option —block-ipv6 to reject all IPv6 packets (ICMPv6)
Linux-specific features
- VRF support
- Netlink integration (OpenVPN no longer needs to execute ifconfig/route or ip commands)
Windows-specific features
- Wintun driver support, a faster alternative to tap-windows6
- Setting tun/tap interface MTU
- Setting DHCP search domain
- Allow unicode search string in —cryptoapicert option
- EasyRSA3, a modern take on OpenVPN CA management
- MSI installer
Important notices
BF-CBC cipher is no longer the default
Cipher handling for the data channel cipher has been significantly changed between OpenVPN 2.3/2.4 and v2.5, most notably there are no «default cipher BF-CBC» anymore because it is no longer considered a reasonable default. BF-CBC is still available, but it needs to be explicitly configured now.
For connections between OpenVPN 2.4 and v2.5 clients and servers, both ends will be able to negotiate a better cipher than BF-CBC. By default they will select one of the AES-GCM ciphers, but this can be influenced using the —data-ciphers setting.
Connections between OpenVPN 2.3 and v2.5 that have no —cipher setting in the config (= defaulting to BF-CBC and not being negotiation-capable) must be updated. Unless BF-CBC is included in —data-ciphers or there is a «—cipher BF-CBC» in the OpenVPN 2.5 config, a v2.5 client or server will refuse to talk to a v2.3 server or client, because it has no common data channel cipher and negotiating a cipher is not possible. Generally, we recommend upgrading such setups to OpenVPN 2.4 or v2.5. If upgrading is not possible we recommend adding data-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:AES-128-CBC (for v2.5+) or cipher AES-128-CBC (v2.4.x and older) to the configuration of all clients and servers.
If you really need to use an unsupported OpenVPN 2.3 (or even older) release and need to stay on BF-CBC (not recommended), the OpenVPN 2.5 based client will need a config file change to re-enable BF-CBC. But be warned that BF-CBC and other related weak ciphers will be removed in coming OpenVPN major releases.
Connectivity to some VPN service provider may break
Connecting with an OpenVPN 2.5 client to at least one commercial VPN service that
implemented their own cipher negotiation method that always reports back that it is using BF-CBC to the client is broken in v2.5. This has always caused warning about mismatch ciphers. We have been in contact with some service providers and they are looking into it. This is not something the OpenVPN community can fix. If your commercial VPN does not work with a v2.5 client, complain to the VPN service provider.
More details on these new features as well as a list of deprecated features and user-visible changes are available in Changes.rst.
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.5.2. It fixes two related security vulnerabilities (CVE-2020-15078) which under very specific circumstances allow tricking a server using delayed authentication (plugin or management) into returning a PUSH_REPLY before the AUTH_FAILED message, which can possibly be used to gather information about a VPN setup. In combination with «—auth-gen-token» or a user-specific token auth solution it can be possible to get access to a VPN with an otherwise-invalid account. OpenVPN 2.5.2 also includes other bug fixes and improvements. Updated OpenSSL and OpenVPN GUI are included in Windows installers.
Source tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.2.tar.gz |
Source tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.2.tar.xz |
Source zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.2.zip |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.2-I601-x86.msi |
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.2-I601-amd64.msi |
Overview of changes since OpenVPN 2.4
Faster connections
- Connections setup is now much faster
Crypto specific changes
- ChaCha20-Poly1305 cipher in the OpenVPN data channel (Requires OpenSSL 1.1.0 or newer)
- Improved TLS 1.3 support when using OpenSSL 1.1.1 or newer
- Client-specific tls-crypt keys (—tls-crypt-v2)
- Improved Data channel cipher negotiation
- Removal of BF-CBC support in default configuration (see below for possible incompatibilities)
Server-side improvements
- HMAC based auth-token support for seamless reconnects to standalone servers or a group of servers.
- Asynchronous (deferred) authentication support for auth-pam plugin
- Asynchronous (deferred) support for client-connect scripts and plugins
Network-related changes
- Support IPv4 configs with /31 netmasks now
- 802.1q VLAN support on TAP servers
- IPv6-only tunnels
- New option —block-ipv6 to reject all IPv6 packets (ICMPv6)
Linux-specific features
- VRF support
- Netlink integration (OpenVPN no longer needs to execute ifconfig/route or ip commands)
Windows-specific features
- Wintun driver support, a faster alternative to tap-windows6
- Setting tun/tap interface MTU
- Setting DHCP search domain
- Allow unicode search string in —cryptoapicert option
- EasyRSA3, a modern take on OpenVPN CA management
- MSI installer
Important notices
BF-CBC cipher is no longer the default
Cipher handling for the data channel cipher has been significantly changed between OpenVPN 2.3/2.4 and v2.5, most notably there are no «default cipher BF-CBC» anymore because it is no longer considered a reasonable default. BF-CBC is still available, but it needs to be explicitly configured now.
For connections between OpenVPN 2.4 and v2.5 clients and servers, both ends will be able to negotiate a better cipher than BF-CBC. By default they will select one of the AES-GCM ciphers, but this can be influenced using the —data-ciphers setting.
Connections between OpenVPN 2.3 and v2.5 that have no —cipher setting in the config (= defaulting to BF-CBC and not being negotiation-capable) must be updated. Unless BF-CBC is included in —data-ciphers or there is a «—cipher BF-CBC» in the OpenVPN 2.5 config, a v2.5 client or server will refuse to talk to a v2.3 server or client, because it has no common data channel cipher and negotiating a cipher is not possible. Generally, we recommend upgrading such setups to OpenVPN 2.4 or v2.5. If upgrading is not possible we recommend adding data-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:AES-128-CBC (for v2.5+) or cipher AES-128-CBC (v2.4.x and older) to the configuration of all clients and servers.
If you really need to use an unsupported OpenVPN 2.3 (or even older) release and need to stay on BF-CBC (not recommended), the OpenVPN 2.5 based client will need a config file change to re-enable BF-CBC. But be warned that BF-CBC and other related weak ciphers will be removed in coming OpenVPN major releases.
Connectivity to some VPN service provider may break
Connecting with an OpenVPN 2.5 client to at least one commercial VPN service that
implemented their own cipher negotiation method that always reports back that it is using BF-CBC to the client is broken in v2.5. This has always caused warning about mismatch ciphers. We have been in contact with some service providers and they are looking into it. This is not something the OpenVPN community can fix. If your commercial VPN does not work with a v2.5 client, complain to the VPN service provider.
More details on these new features as well as a list of deprecated features and user-visible changes are available in Changes.rst.
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.5.1. It includes several bug fixes and improvements as well as updated OpenSSL and OpenVPN GUI for Windows.
Source tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.1.tar.gz |
Source tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.1.tar.xz |
Source zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.1.zip |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.1-I601-x86.msi |
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.1-I601-amd64.msi |
Overview of changes since OpenVPN 2.4
Faster connections
- Connections setup is now much faster
Crypto specific changes
- ChaCha20-Poly1305 cipher in the OpenVPN data channel (Requires OpenSSL 1.1.0 or newer)
- Improved TLS 1.3 support when using OpenSSL 1.1.1 or newer
- Client-specific tls-crypt keys (—tls-crypt-v2)
- Improved Data channel cipher negotiation
- Removal of BF-CBC support in default configuration (see below for possible incompatibilities)
Server-side improvements
- HMAC based auth-token support for seamless reconnects to standalone servers or a group of servers.
- Asynchronous (deferred) authentication support for auth-pam plugin
- Asynchronous (deferred) support for client-connect scripts and plugins
Network-related changes
- Support IPv4 configs with /31 netmasks now
- 802.1q VLAN support on TAP servers
- IPv6-only tunnels
- New option —block-ipv6 to reject all IPv6 packets (ICMPv6)
Linux-specific features
- VRF support
- Netlink integration (OpenVPN no longer needs to execute ifconfig/route or ip commands)
Windows-specific features
- Wintun driver support, a faster alternative to tap-windows6
- Setting tun/tap interface MTU
- Setting DHCP search domain
- Allow unicode search string in —cryptoapicert option
- EasyRSA3, a modern take on OpenVPN CA management
- MSI installer
Important notices
BF-CBC cipher is no longer the default
Cipher handling for the data channel cipher has been significantly changed between OpenVPN 2.3/2.4 and v2.5, most notably there are no «default cipher BF-CBC» anymore because it is no longer considered a reasonable default. BF-CBC is still available, but it needs to be explicitly configured now.
For connections between OpenVPN 2.4 and v2.5 clients and servers, both ends will be able to negotiate a better cipher than BF-CBC. By default they will select one of the AES-GCM ciphers, but this can be influenced using the —data-ciphers setting.
Connections between OpenVPN 2.3 and v2.5 that have no —cipher setting in the config (= defaulting to BF-CBC and not being negotiation-capable) must be updated. Unless BF-CBC is included in —data-ciphers or there is a «—cipher BF-CBC» in the OpenVPN 2.5 config, a v2.5 client or server will refuse to talk to a v2.3 server or client, because it has no common data channel cipher and negotiating a cipher is not possible. Generally, we recommend upgrading such setups to OpenVPN 2.4 or v2.5. If upgrading is not possible we recommend adding data-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:AES-128-CBC (for v2.5+) or cipher AES-128-CBC (v2.4.x and older) to the configuration of all clients and servers.
If you really need to use an unsupported OpenVPN 2.3 (or even older) release and need to stay on BF-CBC (not recommended), the OpenVPN 2.5 based client will need a config file change to re-enable BF-CBC. But be warned that BF-CBC and other related weak ciphers will be removed in coming OpenVPN major releases.
Connectivity to some VPN service provider may break
Connecting with an OpenVPN 2.5 client to at least one commercial VPN service that
implemented their own cipher negotiation method that always reports back that it is using BF-CBC to the client is broken in v2.5. This has always caused warning about mismatch ciphers. We have been in contact with some service providers and they are looking into it. This is not something the OpenVPN community can fix. If your commercial VPN does not work with a v2.5 client, complain to the VPN service provider.
More details on these new features as well as a list of deprecated features and user-visible changes are available in Changes.rst.
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.5.0 which is a new major release with many new features.
Source tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.0.tar.gz |
Source tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.0.tar.xz |
Source zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.5.0.zip |
Windows 32-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.0-I601-x86.msi |
Windows 64-bit MSI installer |
GnuPG Signature | OpenVPN-2.5.0-I601-amd64.msi |
Overview of changes since OpenVPN 2.4
Faster connections
- Connections setup is now much faster
Crypto specific changes
- ChaCha20-Poly1305 cipher in the OpenVPN data channel (Requires OpenSSL 1.1.0 or newer)
- Improved TLS 1.3 support when using OpenSSL 1.1.1 or newer
- Client-specific tls-crypt keys (—tls-crypt-v2)
- Improved Data channel cipher negotiation
- Removal of BF-CBC support in default configuration (see below for possible incompatibilities)
Server-side improvements
- HMAC based auth-token support for seamless reconnects to standalone servers or a group of servers.
- Asynchronous (deferred) authentication support for auth-pam plugin
- Asynchronous (deferred) support for client-connect scripts and plugins
Network-related changes
- Support IPv4 configs with /31 netmasks now
- 802.1q VLAN support on TAP servers
- IPv6-only tunnels
- New option —block-ipv6 to reject all IPv6 packets (ICMPv6)
Linux-specific features
- VRF support
- Netlink integration (OpenVPN no longer needs to execute ifconfig/route or ip commands)
Windows-specific features
- Wintun driver support, a faster alternative to tap-windows6
- Setting tun/tap interface MTU
- Setting DHCP search domain
- Allow unicode search string in —cryptoapicert option
- EasyRSA3, a modern take on OpenVPN CA management
- MSI installer
Important notices
BF-CBC cipher is no longer the default
Cipher handling for the data channel cipher has been significantly changed between OpenVPN 2.3/2.4 and v2.5, most notably there are no «default cipher BF-CBC» anymore because it is no longer considered a reasonable default. BF-CBC is still available, but it needs to be explicitly configured now.
For connections between OpenVPN 2.4 and v2.5 clients and servers, both ends will be able to negotiate a better cipher than BF-CBC. By default they will select one of the AES-GCM ciphers, but this can be influenced using the —data-ciphers setting.
Connections between OpenVPN 2.3 and v2.5 that have no —cipher setting in the config (= defaulting to BF-CBC and not being negotiation-capable) must be updated. Unless BF-CBC is included in —data-ciphers or there is a «—cipher BF-CBC» in the OpenVPN 2.5 config, a v2.5 client or server will refuse to talk to a v2.3 server or client, because it has no common data channel cipher and negotiating a cipher is not possible. Generally, we recommend upgrading such setups to OpenVPN 2.4 or v2.5. If upgrading is not possible we recommend adding data-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:AES-128-CBC (for v2.5+) or cipher AES-128-CBC (v2.4.x and older) to the configuration of all clients and servers.
If you really need to use an unsupported OpenVPN 2.3 (or even older) release and need to stay on BF-CBC (not recommended), the OpenVPN 2.5 based client will need a config file change to re-enable BF-CBC. But be warned that BF-CBC and other related weak ciphers will be removed in coming OpenVPN major releases.
Connectivity to some VPN service provider may break
Connecting with an OpenVPN 2.5 client to at least one commercial VPN service that
implemented their own cipher negotiation method that always reports back that it is using BF-CBC to the client is broken in v2.5. This has always caused warning about mismatch ciphers. We have been in contact with some service providers and they are looking into it. This is not something the OpenVPN community can fix. If your commercial VPN does not work with a v2.5 client, complain to the VPN service provider.
More details on these new features as well as a list of deprecated features and user-visible changes are available in Changes.rst.
The OpenVPN community project team is proud to release OpenVPN 2.4.11. It fixes two related security vulnerabilities (CVE-2020-15078) which under very specific circumstances allow tricking a server using delayed authentication (plugin or management) into returning a PUSH_REPLY before the AUTH_FAILED message, which can possibly be used to gather information about a VPN setup. This release also includes other bug fixes and improvements. The I602 Windows installers fix a possible security issue with OpenSSL config autoloading on Windows (CVE-2021-3606). Updated OpenSSL and OpenVPN GUI are included in Windows installers.
Source Tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.11.tar.gz |
Source Tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.11.tar.xz |
Source Zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.11.zip |
Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.11-I602-Win7.exe |
Windows 10/Server 2016/Server 2019 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.11-I602-Win10.exe |
A summary of the changes is available in Changes.rst, and a full list of changes is available here.
Please note that LibreSSL is not a supported crypto backend. We accept patches and we do test on OpenBSD 6.0 which comes with LibreSSL, but if newer versions of LibreSSL break API compatibility we do not take responsibility to fix that.
Also note that Windows installers have been built with NSIS version that has been patched against several NSIS installer code execution and privilege escalation problems. Based on our testing, though, older Windows versions such as Windows 7 might not benefit from these fixes. We thus strongly encourage you to always move NSIS installers to a non-user-writeable location before running them.
Please note that OpenVPN 2.4 installers will not work on Windows XP. The last OpenVPN version that supports Windows XP is 2.3.18, which is downloadable as 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
If you find a bug in this release, please file a bug report to our Trac bug tracker. In uncertain cases please contact our developers first, either using the openvpn-devel mailinglist or the developer IRC channel (#openvpn-devel at irc.libera.chat). For generic help take a look at our official documentation, wiki, forums, openvpn-users mailing list and user IRC channel (#openvpn at irc.libera.chat).
Important: you will need to use the correct installer for your operating system. The Windows 10 installer works on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016/2019. The Windows 7 installer will work on Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2. This is because of Microsoft’s driver signing requirements are different for kernel-mode devices drivers, which in our case affects OpenVPN’s tap driver (tap-windows6).
This is primarily a maintenance release with bugfixes and small improvements. Windows installers include the latest OpenSSL version (1.1.1i) which includes security fixes.
A summary of the changes is available in Changes.rst, and a full list of changes is available here.
Please note that LibreSSL is not a supported crypto backend. We accept patches and we do test on OpenBSD 6.0 which comes with LibreSSL, but if newer versions of LibreSSL break API compatibility we do not take responsibility to fix that.
Also note that Windows installers have been built with NSIS version that has been patched against several NSIS installer code execution and privilege escalation problems. Based on our testing, though, older Windows versions such as Windows 7 might not benefit from these fixes. We thus strongly encourage you to always move NSIS installers to a non-user-writeable location before running them.
Please note that OpenVPN 2.4 installers will not work on Windows XP. The last OpenVPN version that supports Windows XP is 2.3.18, which is downloadable as 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
If you find a bug in this release, please file a bug report to our Trac bug tracker. In uncertain cases please contact our developers first, either using the openvpn-devel mailinglist or the developer IRC channel (#openvpn-devel at irc.libera.chat). For generic help take a look at our official documentation, wiki, forums, openvpn-users mailing list and user IRC channel (#openvpn at irc.libera.chat).
Important: you will need to use the correct installer for your operating system. The Windows 10 installer works on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016/2019. The Windows 7 installer will work on Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2. This is because of Microsoft’s driver signing requirements are different for kernel-mode devices drivers, which in our case affects OpenVPN’s tap driver (tap-windows6).
Source Tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.10.tar.gz |
Source Tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.10.tar.xz |
Source Zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.10.zip |
Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.10-I601-Win7.exe |
Windows 10/Server 2016/Server 2019 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.10-I601-Win10.exe |
Instructions for verifying the signatures are available here.
This release is also available in our own software repositories for Debian and Ubuntu, Supported architectures are i386 and amd64. For details. look here.
The Windows installers are bundled with OpenVPN-GUI — its source code is available on its project page and as tarballs on our alternative download server.
This is primarily a maintenance release with bugfixes and improvements. This release also fixes a security issue (CVE-2020-11810, trac #1272) which allows disrupting service of a freshly connected client that has not yet not negotiated session keys. The vulnerability cannot be used to inject or steal VPN traffic.
A summary of the changes is available in Changes.rst, and a full list of changes is available here.
Please note that LibreSSL is not a supported crypto backend. We accept patches and we do test on OpenBSD 6.0 which comes with LibreSSL, but if newer versions of LibreSSL break API compatibility we do not take responsibility to fix that.
Also note that Windows installers have been built with NSIS version that has been patched against several NSIS installer code execution and privilege escalation problems. Based on our testing, though, older Windows versions such as Windows 7 might not benefit from these fixes. We thus strongly encourage you to always move NSIS installers to a non-user-writeable location before running them. We are moving to MSI installers in OpenVPN 2.5, but OpenVPN 2.4.x will remain NSIS-only.
Compared to OpenVPN 2.3 this is a major update with a large number of new features, improvements and fixes. Some of the major features are AEAD (GCM) cipher and Elliptic Curve DH key exchange support, improved IPv4/IPv6 dual stack support and more seamless connection migration when client’s IP address changes (Peer-ID). Also, the new —tls-crypt feature can be used to increase users’ connection privacy.
OpenVPN GUI bundled with the Windows installer has a large number of new features compared to the one bundled with OpenVPN 2.3. One of major features is the ability to run OpenVPN GUI without administrator privileges. For full details, see the changelog. The new OpenVPN GUI features are documented here.
Please note that OpenVPN 2.4 installers will not work on Windows XP. The last OpenVPN version that supports Windows XP is 2.3.18, which is downloadable as 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
If you find a bug in this release, please file a bug report to our Trac bug tracker. In uncertain cases please contact our developers first, either using the openvpn-devel mailinglist or the developer IRC channel (#openvpn-devel at irc.libera.chat). For generic help take a look at our official documentation, wiki, forums, openvpn-users mailing list and user IRC channel (#openvpn at irc.libera.chat).
Important: you will need to use the correct installer for your operating system. The Windows 10 installer works on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016/2019. The Windows 7 installer will work on Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2. This is because of Microsoft’s driver signing requirements are different for kernel-mode devices drivers, which in our case affects OpenVPN’s tap driver (tap-windows6).
Source Tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.9.tar.gz |
Source Tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.9.tar.xz |
Source Zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.9.zip |
Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.9-I601-Win7.exe |
Windows 10/Server 2016/Server 2019 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.9-I601-Win10.exe |
NOTE: the GPG key used to sign the release files has been changed since OpenVPN 2.4.0. Instructions for verifying the signatures, as well as the new GPG public key are available here.
We also provide static URLs pointing to latest releases to ease automation. For a list of files look here.
This release is also available in our own software repositories for Debian and Ubuntu, Supported architectures are i386 and amd64. For details. look here.
You can use EasyRSA 2 or EasyRSA 3 for generating your own certificate authority. The former is bundled with Windows installers. The latter is a more modern alternative for UNIX-like operating systems.
The Windows installers are bundled with OpenVPN-GUI — its source code is available on its project page and as tarballs on our alternative download server.
This is primarily a maintenance release with bugfixes and improvements. The Windows installers (I601) have several improvements compared to the previous release:
- New tap-windows6 driver (9.24.2) which fixes some suspend and resume issues
- Latest OpenVPN-GUI
- Considerable performance boost due to new compiler optimization flags
A summary of the changes is available in Changes.rst, and a full list of changes is available here.
Please note that LibreSSL is not a supported crypto backend. We accept patches and we do test on OpenBSD 6.0 which comes with LibreSSL, but if newer versions of LibreSSL break API compatibility we do not take responsibility to fix that.
Also note that Windows installers have been built with NSIS version that has been patched against several NSIS installer code execution and privilege escalation problems. Based on our testing, though, older Windows versions such as Windows 7 might not benefit from these fixes. We thus strongly encourage you to always move NSIS installers to a non-user-writeable location before running them. We are moving to MSI installers in OpenVPN 2.5, but OpenVPN 2.4.x will remain NSIS-only.
Compared to OpenVPN 2.3 this is a major update with a large number of new features, improvements and fixes. Some of the major features are AEAD (GCM) cipher and Elliptic Curve DH key exchange support, improved IPv4/IPv6 dual stack support and more seamless connection migration when client’s IP address changes (Peer-ID). Also, the new —tls-crypt feature can be used to increase users’ connection privacy.
OpenVPN GUI bundled with the Windows installer has a large number of new features compared to the one bundled with OpenVPN 2.3. One of major features is the ability to run OpenVPN GUI without administrator privileges. For full details, see the changelog. The new OpenVPN GUI features are documented here.
Please note that OpenVPN 2.4 installers will not work on Windows XP. The last OpenVPN version that supports Windows XP is 2.3.18, which is downloadable as 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
If you find a bug in this release, please file a bug report to our Trac bug tracker. In uncertain cases please contact our developers first, either using the openvpn-devel mailinglist or the developer IRC channel (#openvpn-devel at irc.libera.chat). For generic help take a look at our official documentation, wiki, forums, openvpn-users mailing list and user IRC channel (#openvpn at irc.libera.chat).
Important: you will need to use the correct installer for your operating system. The Windows 10 installer works on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016/2019. The Windows 7 installer will work on Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2. This is because of Microsoft’s driver signing requirements are different for kernel-mode devices drivers, which in our case affects OpenVPN’s tap driver (tap-windows6).
Source Tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.8.tar.gz |
Source Tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.8.tar.xz |
Source Zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.8.zip |
Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.8-I602-Win7.exe |
Windows 10/Server 2016/Server 2019 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.8-I602-Win10.exe |
NOTE: the GPG key used to sign the release files has been changed since OpenVPN 2.4.0. Instructions for verifying the signatures, as well as the new GPG public key are available here.
We also provide static URLs pointing to latest releases to ease automation. For a list of files look here.
This release is also available in our own software repositories for Debian and Ubuntu, Supported architectures are i386 and amd64. For details. look here.
You can use EasyRSA 2 or EasyRSA 3 for generating your own certificate authority. The former is bundled with Windows installers. The latter is a more modern alternative for UNIX-like operating systems.
The Windows installers are bundled with OpenVPN-GUI — its source code is available on its project page and as tarballs on our alternative download server.
This is primarily a maintenance release with bugfixes and improvements. One of the big things is enhanced TLS 1.3 support. A summary of the changes is available in Changes.rst, and a full list of changes is available here.
Please note that LibreSSL is not a supported crypto backend. We accept patches and we do test on OpenBSD 6.0 which comes with LibreSSL, but if newer versions of LibreSSL break API compatibility we do not take responsibility to fix that.
Also note that Windows installers have been built with NSIS version that has been patched against several NSIS installer code execution and privilege escalation problems. Based on our testing, though, older Windows versions such as Windows 7 might not benefit from these fixes. We thus strongly encourage you to always move NSIS installers to a non-user-writeable location before running them. We are moving to MSI installers in OpenVPN 2.5, but OpenVPN 2.4.x will remain NSIS-only.
Compared to OpenVPN 2.3 this is a major update with a large number of new features, improvements and fixes. Some of the major features are AEAD (GCM) cipher and Elliptic Curve DH key exchange support, improved IPv4/IPv6 dual stack support and more seamless connection migration when client’s IP address changes (Peer-ID). Also, the new —tls-crypt feature can be used to increase users’ connection privacy.
OpenVPN GUI bundled with the Windows installer has a large number of new features compared to the one bundled with OpenVPN 2.3. One of major features is the ability to run OpenVPN GUI without administrator privileges. For full details, see the changelog. The new OpenVPN GUI features are documented here.
Please note that OpenVPN 2.4 installers will not work on Windows XP. The last OpenVPN version that supports Windows XP is 2.3.18, which is downloadable as 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
If you find a bug in this release, please file a bug report to our Trac bug tracker. In uncertain cases please contact our developers first, either using the openvpn-devel mailinglist or the developer IRC channel (#openvpn-devel at irc.libera.chat). For generic help take a look at our official documentation, wiki, forums, openvpn-users mailing list and user IRC channel (#openvpn at irc.libera.chat).
Important: you will need to use the correct installer for your operating system. The Windows 10 installer will not work on Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2. This is because Microsoft’s driver signing requirements and tap-windows6. For the same reason you need to use an older installer with Windows Server 2016. This older installer has a local privilege escalation vulnerability issue which we cannot resolve for Windows Server 2016 until tap-windows6 passes the HLK test suite on that platform. In the meanwhile we recommend Windows Server 2016 users to avoid installing OpenVPN/tap-windows6 driver on hosts where all users can’t be trusted. Users of Windows 7-10 and Server 2012r2 are recommended to update to latest installers as soon as possible.
Source Tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.7.tar.gz |
Source Tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.7.tar.xz |
Source Zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.7.zip |
Windows 7/8/8.1/Server 2012r2 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.7-I607-Win7.exe |
Windows 10 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.7-I607-Win10.exe |
Windows Server 2016 installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.7-I603.exe |
NOTE: the GPG key used to sign the release files has been changed since OpenVPN 2.4.0. Instructions for verifying the signatures, as well as the new GPG public key are available here.
We also provide static URLs pointing to latest releases to ease automation. For a list of files look here.
This release is also available in our own software repositories for Debian and Ubuntu, Supported architectures are i386 and amd64. For details. look here.
You can use EasyRSA 2 or EasyRSA 3 for generating your own certificate authority. The former is bundled with Windows installers. The latter is a more modern alternative for UNIX-like operating systems.
The Windows installers are bundled with OpenVPN-GUI — its source code is available on its project page and as tarballs on our alternative download server.
This is primarily a maintenance release with minor bugfixes and improvements, and one security relevant fix for the Windows Interactive Service. Windows installer includes updated OpenVPN GUI and OpenSSL. Installer I601 included tap-windows6 driver 9.22.1 which had one security fix and dropped Windows Vista support. However, in installer I602 we had to revert back to tap-windows 9.21.2 due to driver getting reject on freshly installed Windows 10 rev 1607 and later when Secure Boot was enabled. The failure was due to the new, more strict driver signing requirements. The 9.22.1 version of the driver is in the process of getting approved and signed by Microsoft and will be bundled in an upcoming Windows installer.
Please note that LibreSSL is not a supported crypto backend. We accept patches and we do test on OpenBSD 6.0 which comes with LibreSSL, but if newer versions of LibreSSL break API compatibility we do not take responsibility to fix that.
Also note that Windows installers have been built with NSIS version that has been patched against several NSIS installer code execution and privilege escalation problems. Based on our testing, though, older Windows versions such as Windows 7 might not benefit from these fixes. We thus strongly encourage you to always move NSIS installers to a non-user-writeable location before running them. Our long-term plan is to migrate to using MSI installers instead.
Compared to OpenVPN 2.3 this is a major update with a large number of new features, improvements and fixes. Some of the major features are AEAD (GCM) cipher and Elliptic Curve DH key exchange support, improved IPv4/IPv6 dual stack support and more seamless connection migration when client’s IP address changes (Peer-ID). Also, the new —tls-crypt feature can be used to increase users’ connection privacy.
A summary of the changes is available in Changes.rst, and a full list of changes is available here.
OpenVPN GUI bundled with the Windows installer has a large number of new features compared to the one bundled with OpenVPN 2.3. One of major features is the ability to run OpenVPN GUI without administrator privileges. For full details, see the changelog. The new OpenVPN GUI features are documented here.
Please note that OpenVPN 2.4 installers will not work on Windows XP.
If you find a bug in this release, please file a bug report to our Trac bug tracker. In uncertain cases please contact our developers first, either using the openvpn-devel mailinglist or the developha er IRC channel (#openvpn-devel at irc.libera.chat). For generic help take a look at our official documentation, wiki, forums, openvpn-users mailing list and user IRC channel (#openvpn at irc.libera.chat).
Source Tarball (gzip) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.6.tar.gz |
Source Tarball (xz) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.6.tar.xz |
Source Zip |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-2.4.6.zip |
Windows installer (NSIS) |
GnuPG Signature | openvpn-install-2.4.6-I602.exe |
NOTE: the GPG key used to sign the release files has been changed since OpenVPN 2.4.0. Instructions for verifying the signatures, as well as the new GPG public key are available here.
We also provide static URLs pointing to latest releases to ease automation. For a list of files look here.
This release is also available in our own software repositories for Debian and Ubuntu, Supported architectures are i386 and amd64. For details. look here.
You can use EasyRSA 2 or EasyRSA 3 for generating your own certificate authority. The former is bundled with Windows installers. The latter is a more modern alternative for UNIX-like operating systems.
The Windows installers are bundled with OpenVPN-GUI — its source code is available on its project page and as tarballs on our alternative download server.
You can download Windows developments snapshots (MSI installers) from here (Index of /downloads/snapshots/github-actions/openvpn2/ ). Those are automatically built from commits to OpenVPN master branch and include functionality which will be available in the next release. Development snapshots are less stable than releases, so use at your own risk.
Введение
OpenVPN Connect — это популярный клиент для создания защищенного VPN-соединения. Для работы с OpenVPN Connect на Windows 7 необходимо установить драйвер TAP/TUN V9. В этой статье будет рассмотрен процесс установки драйвера шаг за шагом.
Шаг 1: Скачивание установочного файла драйвера
Первым шагом необходимо скачать драйвер TAP/TUN V9 для Windows 7. Для этого перейдите на сайт разработчика OpenVPN — https://openvpn.net/community-downloads/. Найдите раздел «TAP-Windows», выберите версию драйвера и нажмите на ссылку «Download».
Шаг 2: Установка драйвера
После загрузки установочного файла запустите его. На первом экране нажмите кнопку «Next».
На следующем экране согласитесь с условиями лицензионного соглашения и нажмите кнопку «Next».
На третьем экране выберите пункт «Install».
После установки драйвера нажмите кнопку «Finish».
Шаг 3: Проверка установки драйвера
Чтобы убедиться, что драйвер TAP/TUN V9 установлен успешно, необходимо выполнить следующие действия:
-
Откройте «Диспетчер устройств» (нажмите клавиши Win + R, введите «devmgmt.msc» и нажмите Enter).
-
Разверните раздел «Сетевые адаптеры».
-
Должен быть установлен адаптер с именем «TAP-Windows Adapter V9». Если этот адаптер отсутствует, выполните шаги установки драйвера еще раз.
Заключение
Поздравляем! Вы успешно установили драйвер TAP/TUN V9 для работы с OpenVPN Connect на Windows 7. Теперь можно приступать к настройке VPN-подключения.
Время на прочтение
1 мин
Количество просмотров 16K
На днях понадобилось мне настроить клиентскую часть OpenVPN на компьютере с установленной Windows 7.
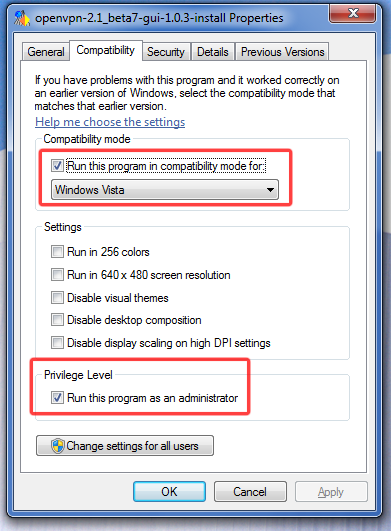
Я предвидел проблемы и потому сразу погуглил на эту тему. Нашел несколько советов, суть которых сводилась к тому, что отличий от установки на Vista мало, и главное из них — в свойствах инсталятора предварительно установить режим совместимости с Vista, а также запуск от имени администратора.
Сразу оговорюсь — в силу своей ленности использую вариант OpenVPN GUI, который мне очень полюбился по практике использования на Windows XP/2003.
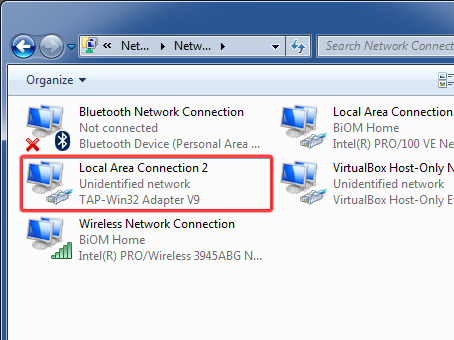
Сделал предлагаемые действия и начал установку. На первый взгляд всё нормально, но не работает :(. Полез разбираться — Windows 7 не может запустить драйвер виртуальной сетевой карты TAP/TUN v8 необходимый для работы OpenVPN
А вот про это Гугль уже молчал. Путем нехитрых логических построений пришел к решению накатать поверх установки OpenVPN GUI оригинальную версию OpenVPN. Потому как поглядев на содержимое инсталятора OpenVPN увидел что там идет более новая версия этого драйвера v9.
Собственно на этом и сказочке конец — после установки OpenVPN поверх OpenVPN GUI все завелось с пол-оборота и радует стабильной работой и по сей день.
Надеюсь этот краткий рассказ сохранит чьи-нибудь нервы 
Ссылки:
OpenVPN GUI: openvpn.se/files/install_packages/openvpn-2.1_beta7-gui-1.0.3-install.exe
OpenVPN: openvpn.net/release/openvpn-2.1_rc15-install.exe
OpenVPN – это набор open source программ, который заслуженно является одним из самых популярных и легких решений для реализации защищенной VPN сети. OpenVPN позволяет объединить в единую сеть сервер и клиентов (даже находящиеся за NAT или файерволами), или объединить сети удаленных офисов. Серверную часть OpenVPN можно развернуть практически на всех доступных операционных системах (пример настройки OpenVPN на Linux). Вы можете установить OpenVPN сервер даже на обычный компьютер с десктопной редакцией Windows 10.
В этой статье, мы покажем, как установить OpenVPN сервер на компьютер с Windows 10, настроить OpenVPN клиент на другом Windows хосте и установить защищенное VPN подключение.
Содержание:
- Установка службы OpenVPN сервера в Windows
- Создаем ключи шифрования и сертификаты для OpenVPN
- Конфигурационный файл OpenVPN сервера в Windows
- Настройка OpenVPN клиента в Windows
Установка службы OpenVPN сервера в Windows
Скачайте MSI установщик OpenVPN для вашей версии Windows с официального сайта (https://openvpn.net/community-downloads/). В нашем случае это OpenVPN-2.5.5-I602-amd64.msi (https://swupdate.openvpn.org/community/releases/OpenVPN-2.5.5-I602-amd64.msi).
Запустите установку.
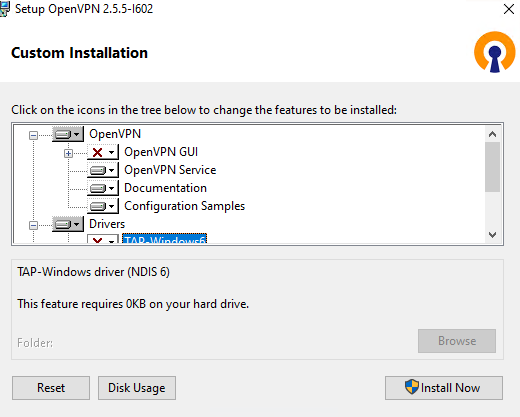
Если вы планируете, OpenVPN сервер работал в автоматическом режиме, можно не устанавливать OpenVPN GUI. Обязательно установите OpenVPN Services.
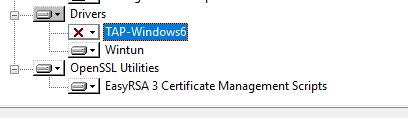
Начиная с версии OpenVPN 2.5, поддерживается драйвер WinTun от разработчиков WireGuard. Считается, что этот драйвер работает быстрее чем классический OpenVPN драйвер TAP. Установите драйвер Wintun, откажитесь от установки TAP-Windows6.
Установите OpenSSL утилиту EasyRSA Certificate Management Scripts.
Запустите установку.
По умолчанию OpenVPN устаналивается в каталог C:\Program Files\OpenVPN.
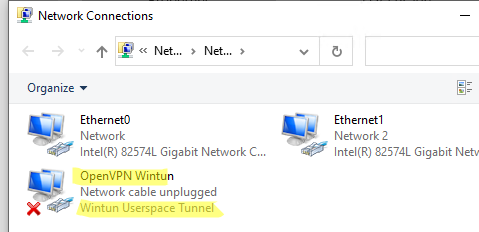
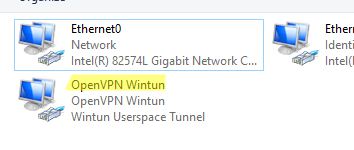
После окончания установки появится новый сетевой адаптер типа Wintun Userspace Tunnel. Этот адаптер отключен, если служба OpenVPN не запущена.
Создаем ключи шифрования и сертификаты для OpenVPN
OpenVPN основан на шифровании OpenSSL. Это означает, что для обмена трафиком между клиентом и серверов VPN нужно сгенерировать ключи и сертификаты с использованием RSA3.
Откройте командную строку и перейдите в каталог easy-rsa:
cd C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa
Создайте копию файла:
copy vars.example vars
Откройте файл vars с помощью любого текстового редактора. Проверьте пути к рабочим директориям.
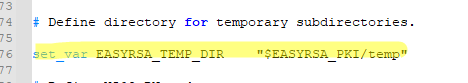
Обязательно поправьте переменную EASYRSA_TEMP_DIR следующим образом:
set_var EASYRSA_TEMP_DIR "$EASYRSA_PKI/temp"
Можете заполнить поля для сертификатов (опционально)
set_var EASYRSA_REQ_COUNTRY "RU" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_PROVINCE "MSK" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_CITY "MSK" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_ORG "IT-Company" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_EMAIL " [email protected] " set_var EASYRSA_REQ_OU " IT department "
Срок действия сертификатов задается с помощью:
#set_var EASYRSA_CA_EXPIRE 3650 #set_var EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE 825
Сохраните файл и выполните команду:
EasyRSA-Start.bat
Следующие команды выполняются в среде EasyRSA Shell:
Инициализация PKI:
./easyrsa init-pki
Должна появится надпись:
init-pki complete; you may now create a CA or requests. Your newly created PKI dir is: C:/Program Files/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/pki
Теперь нужно сгенерировать корневой CA:
./easyrsa build-ca
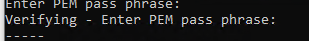
Задайте дважды пароль для CA:
CA creation complete and you may now import and sign cert requests.
Данная команда сформировала:
- Корневой сертификат центра сертификации: «C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\ca.crt»
- Ключ центра сертификации «C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\ca.key»
Теперь нужно сгенерировать запрос сертификата и ключ для вашего сервера OpenVPN:
./easyrsa gen-req server nopass
Утилита сгенерирует два файла:
req: C:/Program Files/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/pki/reqs/server.req key: C:/Program Files/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/pki/private/server.key
Подпишем запрос на выпуск сертификата сервера с помощью нашего CA:
./easyrsa sign-req server server
Подтвердите правильность данных, набрав yes.
Затем введите пароль CA от корневого CA.
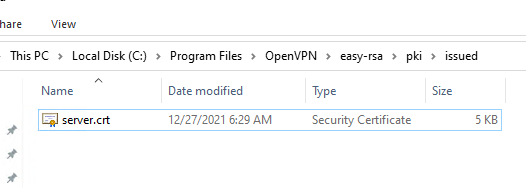
В каталоге issued появится сертификат сервера («C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\issued\server.crt»)
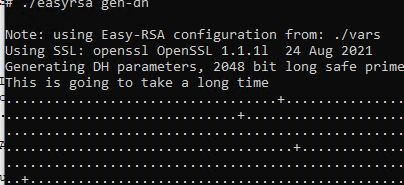
Теперь можно создать ключи Диффи-Хеллмана (займет длительное время):
./easyrsa gen-dh
Для дополнительной защиты VPN сервера желательно включить tls-auth. Данная технология позволяет использовать подписи HMAC к handshake-пакетам SSL/TLS, инициируя дополнительную проверку целостности. Пакеты без такой подписи будут отбрасываться VPN сервером. Это защитит вас от сканирования порта VPN сервера, DoS атак, переполнения буфера SSL/TLS.
Сгенерируйте ключ tls-auth:
cd C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\bin
openvpn --genkey secret ta.key
Должен появиться файл «C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\bin\ta.key». Переместите его в каталог C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki
Теперь можно сформировать ключи для клиентов OpenVPN. Для каждого клиента, который будет подключаться к вашему серверу нужно создать собственные ключи.
Есть несколько способов генерации ключей и передачи их клиентам. В следующем примере, мы создадим на сервере ключ клиента и защитим его паролем:
./easyrsa gen-req kbuldogov
./easyrsa sign-req client kbuldogov
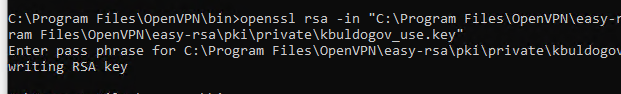
Данный ключ («C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\kbuldogov.key») нужно передать клиенту и сообщить пароль. Клиент может снять защиту паролем для ключа:
openssl rsa -in "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\kbuldogov.key"-out "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\kbuldogov_use.key"
Если вы хотите сгенерировать ключ, не защищенный паролем, нужно выполнить команду:
./easyrsa gen-req имяклиента nopass
На сервере с OpenVPN вы можете создать неограниченное количество ключей и сертификатов для пользователей. Аналогичным образом сформируйте ключи и сертфикаты для других клиентов.
Вы можете отохвать скомпрометированные сертификаты клиентов:
cd C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa
EasyRSA-Start.bat
./easyrsa revoke kbuldogov
Итак, мы сгенерировали набор ключей и сертификатов для OpenVPN сервера. Теперь можно настроить и запустить службу OpenVPN.
Конфигурационный файл OpenVPN сервера в Windows
Скопируйте типовой конфигурационный файл OpenVPN сервера:
copy "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\sample-config\server.ovpn" "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config-auto\server.ovpn"
Откройте файл server.ovpn в любом текстовом редакторе и внесите свои настройки. Я использую следующий конфиг для OpenVPN:
# Указываем порт, протокол и устройство port 1194 proto udp dev tun # Указываем пути к сертификатам сервера ca "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\ca.crt" cert "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\issued\\server.crt" key "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\private\\server.key" dh "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\dh.pem" # Указываем настройки IP сети, адреса из которой будет будут получать VPN клиенты server 10.24.1.0 255.255.255.0 #если нужно разрешить клиентам подключаться под одним ключом, нужвно включить опцию duplicate-cn (не рекомендуется) #duplicate-cn # TLS защита tls-auth "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\ta.key" 0 cipher AES-256-GCM # Другая параметры keepalive 20 60 persist-key persist-tun status "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\log\\status.log" log "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\log\\openvpn.log" verb 3 mute 20 windows-driver wintun
Сохраните файл.
OpenVPN позволяет использовать как TCP, так и UDP для подключения. В этом примере я запустил OpenVPN на 1194 UDP. Рекомендуется использовать протокол UDP, это оптимально как с точки зрения производительности, так и безопасности.
Не забудьте открыть на файерволе порты для указанного вами порта OpenVPN на клиенте и на сервере. Можно открыть порты в Windows Defender с помощью PowerShell.
Правило для сервера:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "AllowOpenVPN-In" -Direction Inbound -Protocol UDP –LocalPort 1194 -Action Allow
Правило для клиента:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "AllowOpenVPN-Out" -Direction Outbound -Protocol UDP –LocalPort 1194 -Action Allow
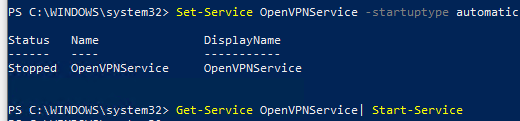
Теперь нужно запустить службу OpenVPN и изменить тип ее запуска на автоматический. Воспользуйтесь таким командами PowerShell, чтобы включить службу:
Set-Service OpenVPNService –startuptype automatic –passthru
Get-Service OpenVPNService| Start-Service
Откройте панель управления, и убедитесь, что виртуальный сетевой адаптер OpenVPN Wintun теперь активен. Если нет, смотрите лог «C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\log\server.log»
Если при запуске OpenVPN вы видите в логе ошибку:
Options error: In C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config-auto\server.ovpn:1: Maximum option line length (256) exceeded, line starts with..
Смените в файле server.ovpn символы переноса строки на Windows CRLF (в notepad++ нужно выбрать Edit -> EOL Conversion -> Windows CR LF). Сохраните файл, перезапустите службу OpevVPNService.
Данный конфиг позволит удаленным клиентам получить доступ только к серверу, но другие компьютеры и сервисы в локальной сети сервера для них недоступны. Чтобы разрешить клиентам OpenVPN получить доступ к внутренней сети нужно:
Включить опцию IPEnableRouter в реестре (включает IP маршрутизацию в Windows, в том числе включает маршрутизацию меду сетями Hyper-V): reg add «HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters» /v IPEnableRouter /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
Добавьте в конфгурационный файл сервера OpenVPN маршруты до внутренней IP сети:
push "route 10.24.1.0 255.255.255.0" push "route 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0"
Если нужно, назначьте клиенту адреса DNS серверов:
push "dhcp-option DNS 192.168.100.11" push "dhcp-option DNS 192.168.100.12"
Если нужно завернуть все запросы клиента (в том числе Интернет трафик) на ваш OpenVPN сервер, добавьте опцию:
push "redirect-gateway def1"
Настройка OpenVPN клиента в Windows
Создайте на сервере шаблонный конфигурационный файла для клиента VPN (на базе iшаблона client.ovpn) со следующими параметрами (имя файла kbuldovov.ovpn)
client dev tun proto udp remote your_vpn_server_address 1194 resolv-retry infinite nobind persist-key persist-tun ca ca.crt cert kbuldogov.crt key kbuldogov.key remote-cert-tls server tls-auth ta.key 1 cipher AES-256-GCM connect-retry-max 25 verb 3
В директиве remote указывается публичный IP адрес или DNS имя вашего сервера OpenVPN.
Скачайте и установите клиент OpenVPN Connect для Windows (https://openvpn.net/downloads/openvpn-connect-v3-windows.msi).
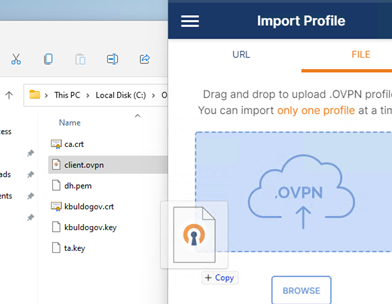
Теперь на компьютер с клиентом OpenVPN нужно с сервера скопировать файлы:
- ca.crt
- kbuldogov.crt
- kbuldogov.key
- dh.pem
- ta.key
- kbuldogov.ovpn
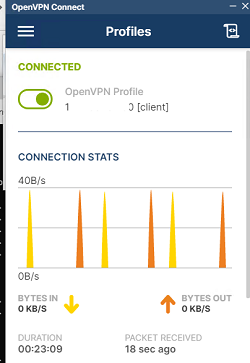
Теперь импортируйте файл с профилем *.ovpn и попробуйте подключиться к вашему VPN серверу.
Если все настроено правильно, появится такая картинка.
Проверьте теперь лог OpenVPN на клиенте «C:\Program Files\OpenVPN Connect\agent.log»
Mon Dec 27 08:09:30 2021 proxy_auto_config_url
Mon Dec 27 08:09:31 2021 TUN SETUP
TAP ADAPTERS:
guid='{25EE4A55-BE90-45A0-88A1-8FA8FEF24C42}' index=22 name='Local Area Connection'
Open TAP device "Local Area Connection" PATH="\\.\Global\{25EE4A55-BE90-45A0-88A1-8FA8FEF24C42}.tap" SUCCEEDED
TAP-Windows Driver Version 9.24
ActionDeleteAllRoutesOnInterface iface_index=22
netsh interface ip set interface 22 metric=1
Ok.
netsh interface ip set address 22 static 10.24.1.6 255.255.255.252 gateway=10.24.1.5 store=active
IPHelper: add route 10.24.1.1/32 22 10.24.1.5 metric=-1
Клиент успешно подключится к OpenVPN серверу и получил IP адрес 10.24.1.6.
Проверьте теперь лог на сервере («C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\log\openvpn.log»). Здесь также видно, что клиент с сертификатом kbuldogov успешно подключится к вашему серверу.
2021-12-27 08:09:35 192.168.13.202:55648 [kbuldogov] Peer Connection Initiated with [AF_INET6]::ffff:192.168.13.202:55648 2021-12-27 08:09:35 kbuldogov/192.168.13.202:55648 MULTI_sva: pool returned IPv4=10.24.1.6, IPv6=(Not enabled) 2021-12-27 08:09:35 kbuldogov/192.168.13.202:55648 MULTI: Learn: 10.24.1.6 -> kbuldogov/192.168.13.202:55648 2021-12-27 08:09:35 kbuldogov/192.168.13.202:55648 MULTI: primary virtual IP for kbuldogov/192.168.13.202:55648: 10.24.1.6
OpenVPN users occasionally report tap driver installation issues like Windows 7 OpenVPN TAP driver unsigned.
This can have a great impact when it comes to using VPN software to prevent any third parties online from gathering and using your data.
BEST VPN RECOMMENDATIONS — VETTED BY OUR EXPERTS
There are multiple reasons behind an install failure such as broken driver, invalid or expired driver signature, and conflicting drivers, just to name a few.
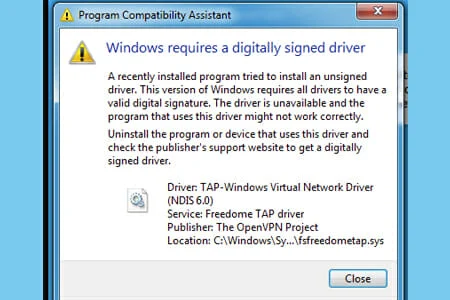
No matter the reason behind your problem, we have a quick troubleshooting guide that will allow you to easily install the OpenVPN tap driver. Check out our solutions below.
Does OpenVPN work on Windows 7?
Yes, OpenVPN is compatible with older versions of Windows, including Windows 7.
The VPN client offers dedicated support for the operating system, and the configuration is pretty straightforward.
Moreover, the OpenVPN file and system impact are pretty small, so you should have no reason to worry about it affecting your PC’s performance, even if you use an older device.
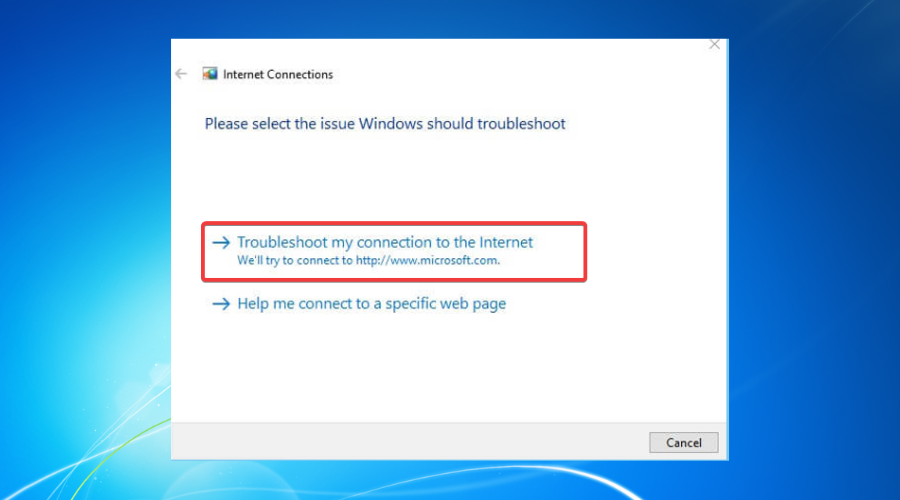
1. Use the Internet Connections Troubleshooter
- Press the Win key.
- Type troubleshoot.
- Select Available Recommended troubleshooting.
- Click the Available troubleshooters’ hyperlink.
- Select Internet Connections and click Run the troubleshooter.
- Select Troubleshoot my connection to the internet.
- Go through the troubleshooting wizard’s steps.
2. Reset the TAP-Windows Adapter Connection
- Press the Start button from your taskbar.
- Type network in the search box.
- Select Network status.
- Click on the Network and Sharing Center button.
- Select the Change adapter settings option.
- Right-click the TAP-Windows Adapter.
- Select Disable.
- Right-click the TAP-Windows Adapter again.
- Select Enable.
- Restart your PC and check if the issue still there.
This trick can also help with the All TAP-Windows adapters are currently in use error that many Windows users encounter.
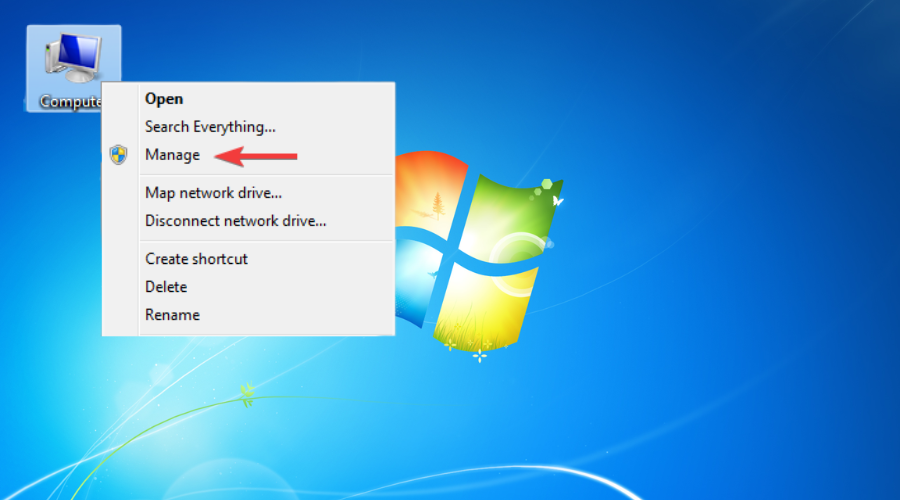
3. Reinstall TAP-Windows Adapter and VPN client
- Right-click on the Computer.
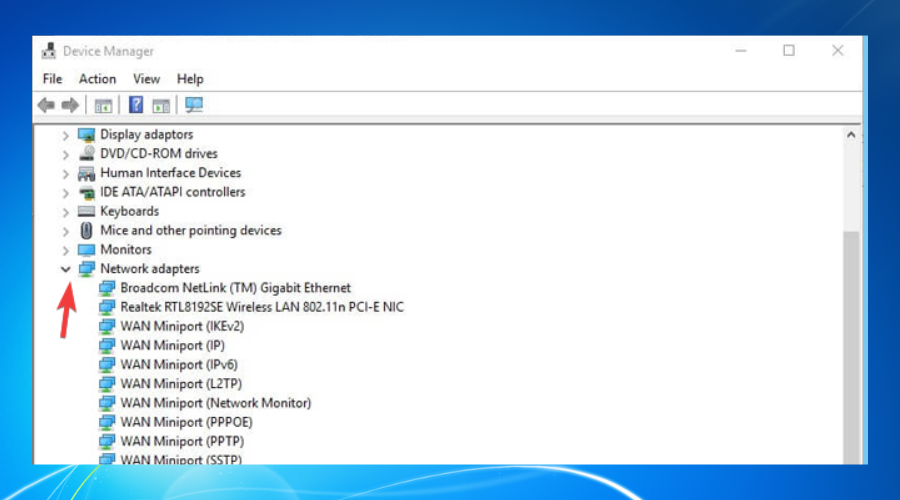
- Choose Manage.
- Expand the Network adapters category.
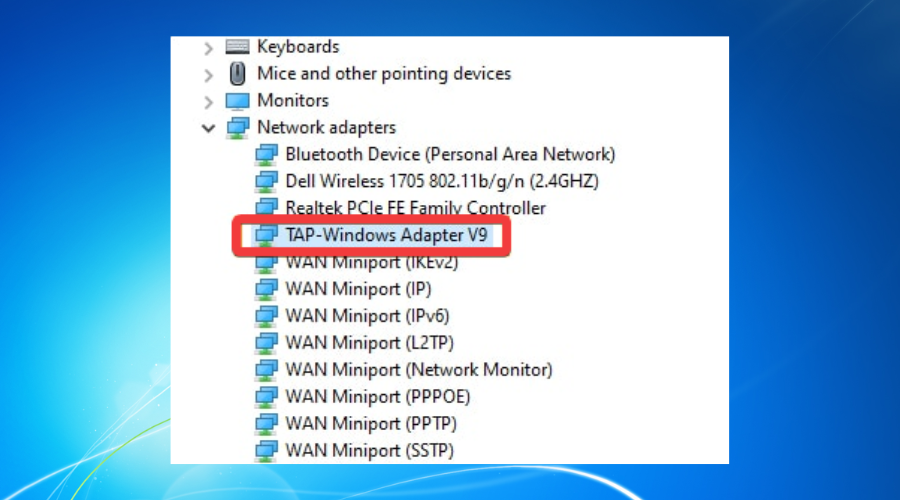
- Right-click the TAP-Windows Adapter V9.
- Click on Uninstall device.
- Select Uninstall to confirm.
- Press the Windows key + R key combination.
- Type appwiz.cpl and press Enter.
- Select your OpenVPN software.
- Click on the Uninstall button to remove it.
- Restart your PC shortly after uninstalling both services.
- Reinstall your OpenVPN software + TAP adapter driver.
4. Download and install OpenVPN TAP drivers for Windows 7
Windows 7 users report they fixed this issue with the KB4474419 security update that automatically updates your Tap drivers.
- Download the KB4474419 Windows 7 security update.
- Follow the installation prompts and wait for the process to complete.
- Check your OpenVPN Tap drivers.
This update installs SHA-2 code sign support and remediates the Windows that cannot verify the digital signature tap driver error.
Another option is to download an older OpenVPN Tap driver version:
- Uninstall your TAP-Windows Adapter V9 driver from the Device Manager (as presented in the third solution).
- Download OpenVPN Windows 7 signed tap driver (version 2.1.1.)
- Open and run the installer wizard.
Now the signed driver error should be remediated, as users report having issues with the 2.1.2. version. This previous version should work just fine.
If you have any problems manually installing the OpenVPN Tap drivers or want to speed up the process, you can use a dedicated third-party tool such as DriverFix.
5. Change to a more reliable VPN
If you tried all the previous solutions and still get the windows 7 OpenVPN tap driver unsigned issue, you might consider a better VPN alternative.
Private Internet Access, for instance, is a great VPN service that comes with its own TAP driver.
Furthermore, even if it stops working at some point, you can easily reinstall it directly from the VPN client’s configuration screen.

Private Internet Access
Benefit from advanced VPN options and dedicated support for OpenVPN and other protocols!
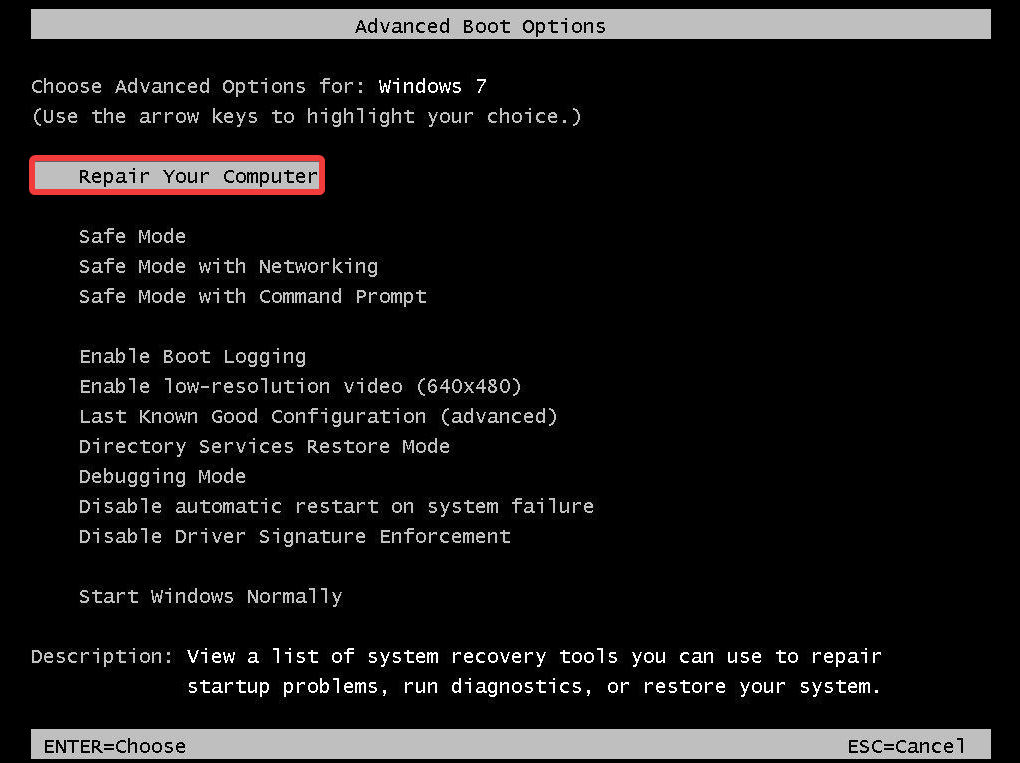
6. Reset Windows 7
- Start the computer.
- Press and hold the F8 key.
- In the Advanced Boot Options menu, choose Repair Your Computer.
- Press Enter.
- Select a keyboard language and click Next.
- If prompted, log in with an administrative account.
- At the System Recovery Options, choose System Restore or Startup Repair (if this is available).
To sum up, if you notice that your OpenVPN tap driver fails to install, there are some steps that you can try from our troubleshooting guide.
However, reinstalling the TAP driver and VPN client will usually fix your issue.
If you need additional help with this VPN service, we have a guide on what to do if OpenVPN is not forwarding traffic.
In case you have an alternative solution we didn’t mention or any questions regarding the ones we listed, feel free to share it with us, in the comments section below